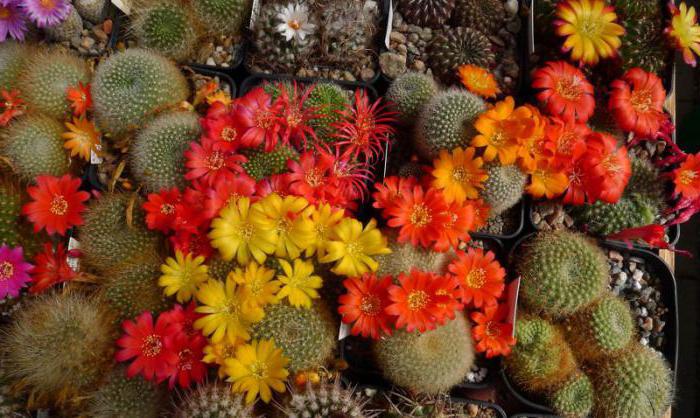
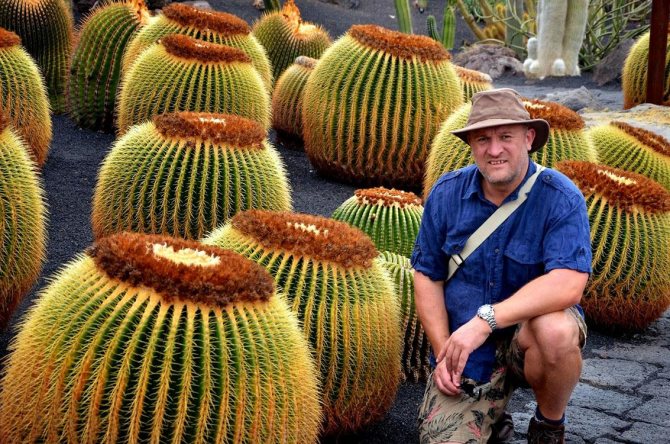
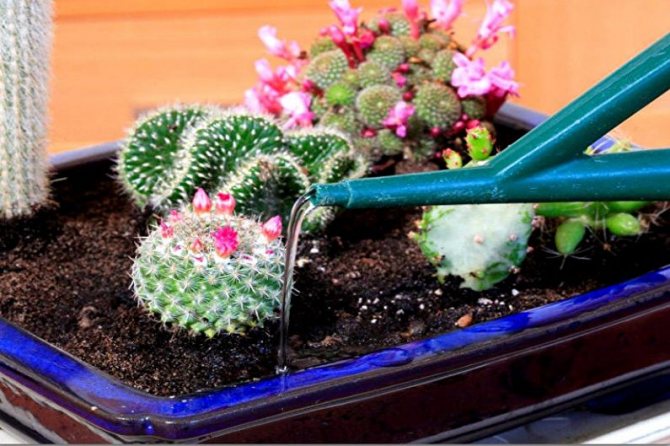
Types of cacti
Cacti are one of the most ancient plants on the planet. They come from North and South America. Depending on the habitat, desert and tropical (forest) cacti are distinguished. Most species, with the exception of perxia, lack true leaves. Instead of leaves, there are hairs or thorns on the stems of cacti. In extreme conditions, this helps them economically use scarce moisture.
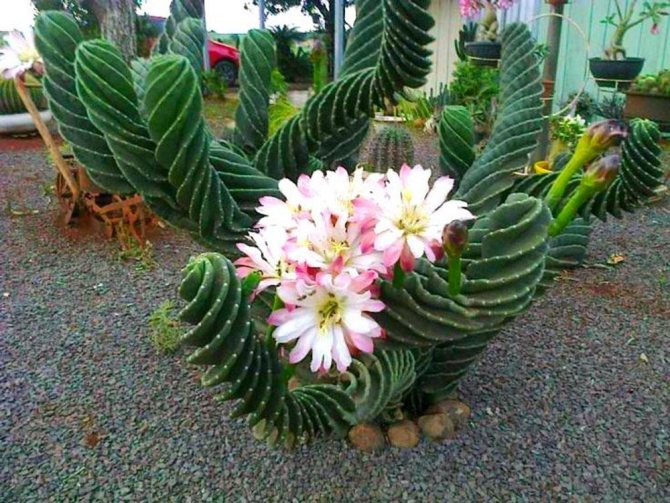
Astrophytum
The name of this type of cactus is taken from the Greek language and in translation means "plant-star", because, if you look at it from above, this cactus looks like a star with rays.
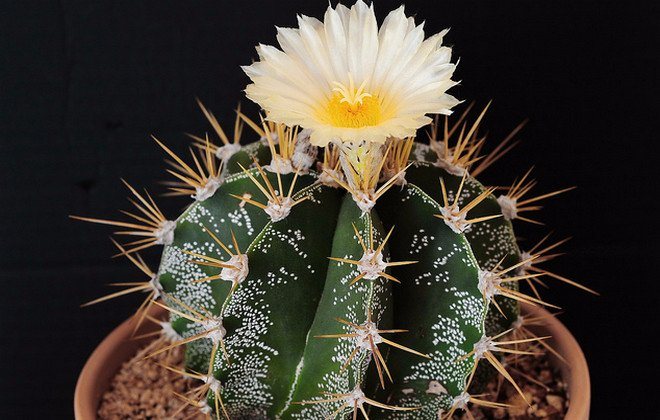


This species is distinguished by a variety of subspecies: some of them are without needles, and some boast rather long curly needles; some grow quite quickly, while others need a long time to grow even a couple of centimeters.
Stem: strong, spherical, elongated.
Flowers: wide opening, white or yellowish in color. They bloom at a young age.
Flowering period: 2-3 days in spring-summer.
Maintenance and care: require good lighting, tolerate direct sunlight, but prefer diffused light. They are tolerant in hot weather, they feel comfortable in rooms where the temperature does not exceed +28 ° С.
During dormancy, it is better to keep such cacti at a temperature of + 10 ... + 12 ° C. They do not need additional manipulations to humidify the air. During the growing season, astrophytums should be watered rarely (after the earth is completely dry) and so that the soil is completely saturated with water.
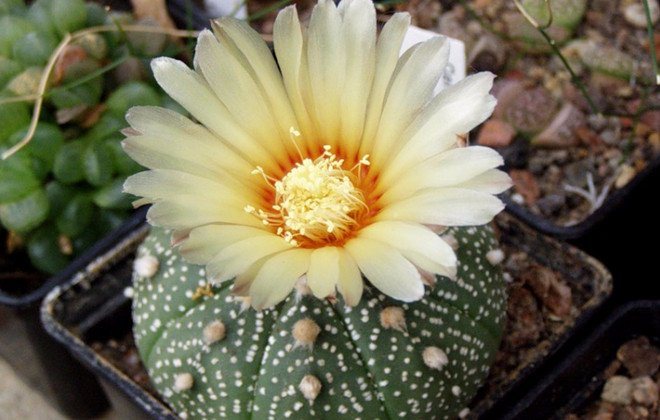


It is better to carry out bottom watering so that water does not fall on the plant itself. In autumn and winter, if you keep such cacti at low temperatures, you do not need to water them.
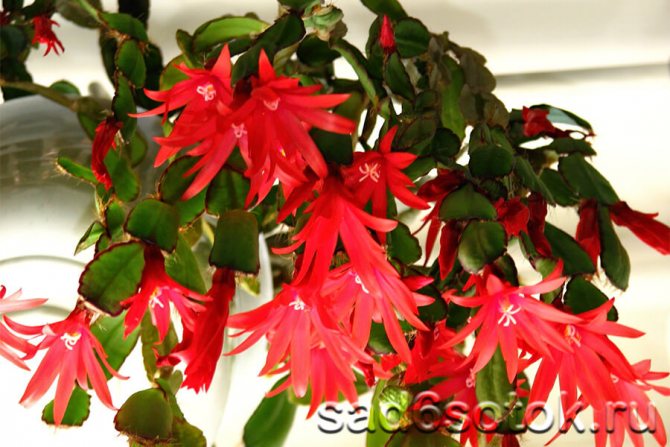
Cacti also include hatiora, epiphyllum, ripsalis, echinocactus Gruzoni, hymnocalycium, Decembrist flower, prickly pear.
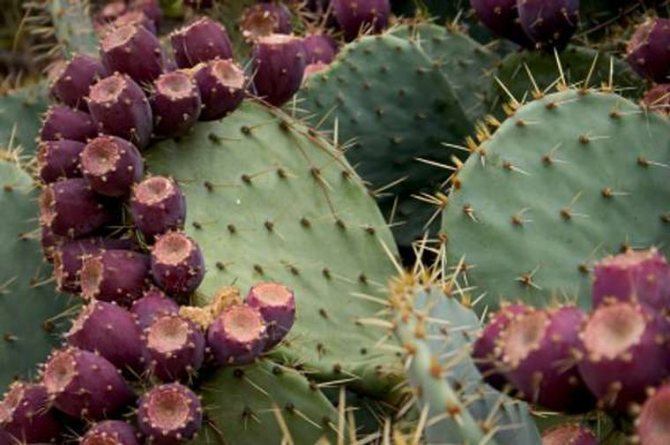
Cactus - a symbol of Mexico
In 1325, the great Aztec priest saw a cactus (Opuntia), on which an eagle was sitting and holding a snake in its claws.


According to legend, this omen determined the place of foundation of the capital of the Aztec empire - Tenochtitlan. Now the cactus is a symbol of Mexico. This cactus is widely used in Mexican cuisine: it is fried, boiled and made marmalade and jam. This plant is rich in iron, vitamins and calcium.
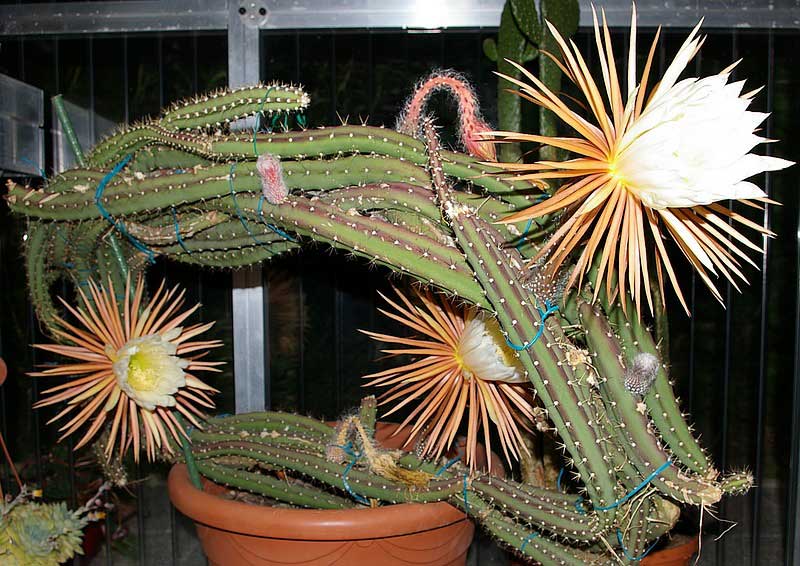
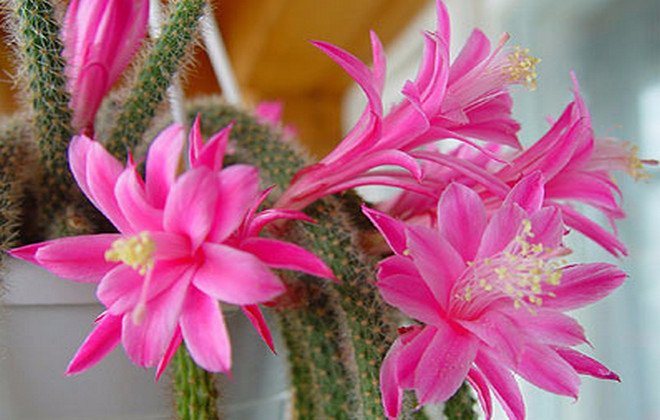
Aporocactus
These unusual cacti were brought to us from Mexico and from the mighty thickets on the mountain slopes have successfully turned into popular houseplants.
Stem: branched into many thin stems, the length of which can reach one meter. The ribs on such stems are not very pronounced, the spines are bristly. At first, the stems grow upward, then downward.
Flowers: tubular, their length is about 10 cm, color - pink, crimson, orange, red (depending on the specific species).
Flowering period: can bloom throughout the spring.
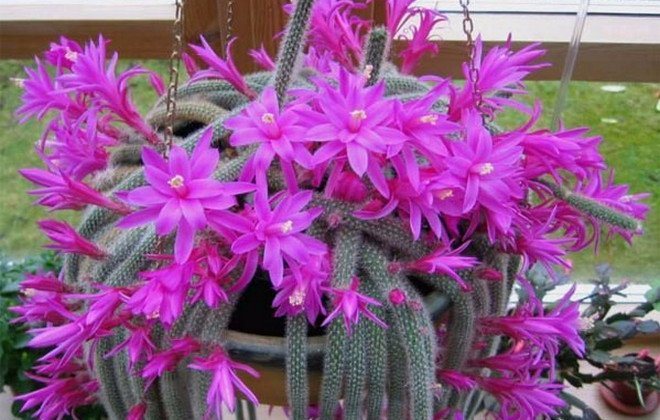


Maintenance and care: for aporocactus, the best option is bright light without direct rays (it can get burned). Good lighting is especially important during the dormant period, since the setting of buds and abundant flowering in the future depend on the light.
In spring and summer, such a plant can be placed on a terrace where there is open air, but no direct sunlight. At such a time, the optimum temperature for aporocactus is + 20 ... + 25 ° С. In winter, a bright, cool room is a suitable place for the plant.
Aporocactuses tolerate drought well, but in the summer it is better to spray them with warm water. Watering such a flowerpot in the warm season is necessary regularly, not allowing the soil to dry out completely. Watering should be bottom, do not let the water in the pan to stagnate.
In winter, it is necessary to water less often, waiting until the soil is completely dry.


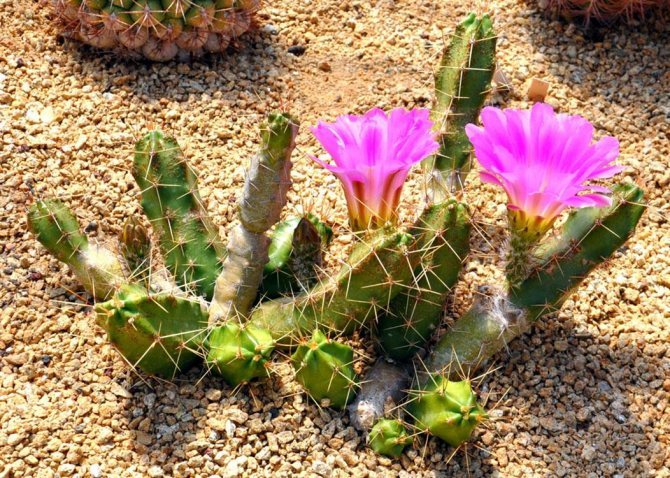
Fraileys
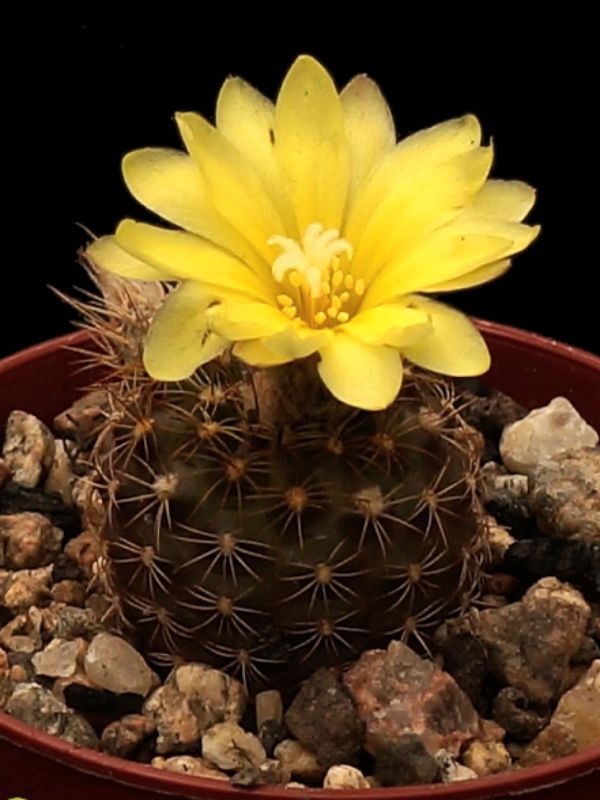


Succulent plant. The body of a cactus is spherical, flattened. An adult plant can reach no more than 15 centimeters in height and 4-10 centimeters in diameter. The body of the cactus is colored gray-green. The spines are up to 1.5 centimeters long, collected in bunches and symmetrically arranged. Flowers are yellow, zygomorphic, single, up to 10 centimeters in diameter. Flowers are located at the top of the body of the cactus.
to the table of contents ^
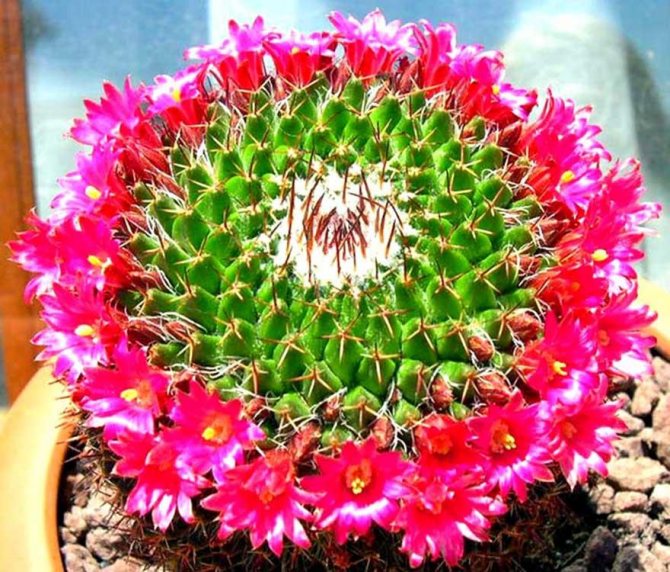
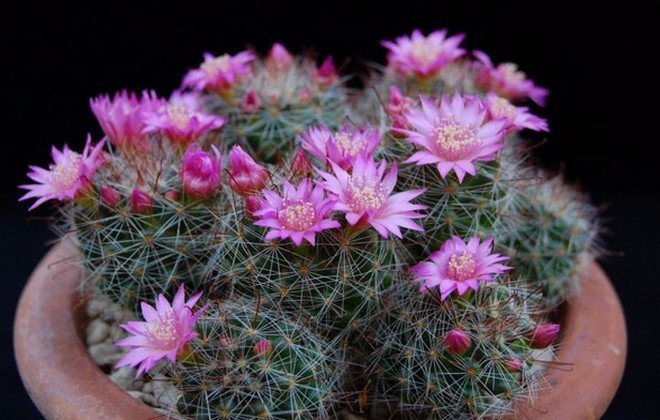
Mammillaria
This type of cactus boasts a huge number of varieties and variations. Plants of the genus Mammillaria are small, can take on different shapes and colors. This genus is the most numerous in the cactus family.
Stem: spherical or cylindrical. Conical soft papillae are located on the stem in even rows. Spines are bristly, soft, thin.
Did you know? The largest home collection of cacti in the CIS countries was collected by a Ukrainian on the roof of his mansion. It has over 20 thousand plants. The total cost of the collection exceeds several tens of thousands of dollars.
Flowers: small (up to 2 cm in diameter), daytime. Color - pink, yellow, white, cream, pink-white. When such a cactus blooms, a "crown" of flowers forms on top of the stem.


Flowering period: the genus of mammillaria is considered to be rarely flowering. As a rule, flowers appear in early spring.
Maintenance and care: these cacti are very fond of light, but which one depends on how pubescent the plant is. Unlike non-pubescent ones, which do not tolerate direct sunlight, pubescent cacti need to receive a large amount of direct light.
Well-lit areas also like begonia, syngonium, daylily, sedum, alstroemeria, pedilanthus, streptocarpus, leucanthemum nivyanik, cordilina, caladium, fuchsia.
In summer, a suitable temperature is about +25 ° С, in winter - + 10 ... + 12 ° С for green species and +15 ° С for pubescent ones. In very hot weather, the plant can be sprayed. Like other cactus plants, mammillaria do not like it when the soil is waterlogged, so watering such a flowerpot should be infrequent.
In winter, when the plant is kept in a cool room, there is no need to water at all.


Adaptive traits of a cactus and adaptation to habitat conditions
The high adaptability of cacti to the environment, to life in adverse conditions is also due to the structure of their roots. Many species have a well-developed superficial root system. This makes it possible to effectively use even a small amount of precipitation. Some types of cacti (for example, the genus Ariocarpus) have a very thickened root, in which a large amount of nutrients are concentrated. This helps the cactus to adapt to its habitat, allows the plant to survive adverse conditions. In some large species, these roots can reach a weight of several kilograms.
For a number of species of the genus Echinopsis, Submatucana and others are characterized by lateral processes growing on the main stem, capable of giving roots themselves. Having broken off from the stem, they quickly take root. On the roots of other cacti, buds are formed, giving life to new plants (root suckers).In epiphytic cacti, aerial adventitious roots grow on the stems, giving the plant additional moisture and attachment to the substrate.
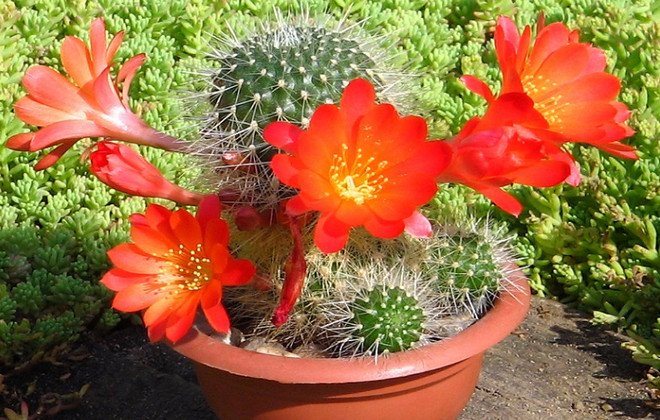
Rebutia
This cactus is one of the most widespread plants in the world and a very popular houseplant that attracts more and more flower growers every year.
Stem: These flowering indoor cacti have a rounded fleshy stem with a depression at the top, covered with spiral ribs and short, hard spines of a silvery or yellowish color.
Flowers: diurnal, have elongated tubes of glossy petals that have grown together, and a diameter of about 2.5 cm. Flowers can be cream, pink, purple or scarlet.
Flowering period: about two days in April-June.
Maintenance and care: they are not afraid of direct sunlight, when the room where the cactus is located is well ventilated, they feel comfortable at temperatures from +5 ° С to +25 ° С and are well adapted to sudden temperature changes. Watering is necessary rarely, waiting for the soil to dry well.


Morphological features and parts of a cactus plant: features of the stem
The stems of cacti, as already noted, have a different shape. They usually have ribs, most often divided into papillae, which are modified leaf bases. Most often, the ribs are straight, descending from the top of the stem to the base, but they can be spiral and wavy curved. Some cacti have flat ribs and barely rise above the stem. From above, the stems are covered with a skin (cuticle) made of a wax-like substance, which protects them from external influences, including moisture evaporation. The cuticle is derived from a deeper layer - the epidermis. From the cells of the epidermis, bundles of elongated capillaries develop, ending on the surface with pubescence, which is able to capture moisture from the air and conduct it to the inner cells of the stem.
An important morphological feature of a cactus is the presence of thorns. These parts of the cactus plant can also capture moisture from the air and conduct it to the inner cells of the stem. This allows plants to efficiently use the moisture that condenses from the air during temperature changes.
The main difference between the structure of the cactus plant and other succulents is the presence of areoles, which are modified axillary buds. From the areoles located on the ribs of the stem, flowers and fruits develop, as from ordinary buds, and in some species, even leaves. In the vast majority of cacti, areoles have spines and, in addition, may have pubescence of fine hairs. In mammillaria and some other cacti, the areola is divided into two parts. One part is in the sinus (axilla) and the other is at the end of the papilla. Flowers and processes in such cacti grow from the axilla, and spines develop at the end of the papilla. If necessary, the areola with a piece of tissue can be rooted and grafted to create a new plant.
One of the characteristics of the cactus stem is that it grows from the top, where the so-called growing point is located. Due to cell division at the point of growth, the cactus grows in diameter and height. Most cacti grow throughout their lives. Some of the cacti have a finite stem growth. In such cacti, division at the point of growth periodically stops, and new shoots appear from the areoles. That is, the cactus stem has a jointed structure. Violation of the growth point stops the growth of the stem and promotes the appearance of lateral shoots. This feature of the structure of a cactus is sometimes used for vegetative propagation of plants by cutting or drilling a growth point. The stem of cacti contains up to 96% water. A large amount of water, features of the structure of the stem (the presence of ribs, thorns, hairs) and features of the physiology of cacti help them survive in the harsh growing conditions.
In addition to the usual forms of stems, in nature and in collections there are two forms of cacti with an ugly growing stem: crested and monstrous. Normally, the growth point of a cactus is at the top of the stem. Annual growth of cells in this area increases the height and diameter of the stem. Substances secreted by cells inhibit the growth of the same cells scattered throughout the stem. If this mechanism is violated, cells begin to divide vigorously in different parts of the stem. At the same time, in crested forms, the apical point of growth stretches into a line, and the cactus takes on a comb-like shape, and in monstrous forms, cells begin to grow throughout the stem. As a result, the crested form takes on the appearance of ridges growing in different planes, and the monstrous form has a stem with separate randomly growing, asymmetric areas. These forms are very decorative and are often found in collections. The reason for such deviations is, most likely, a combination of several factors that has not been clarified so far. It is believed that deviations can occur in virtually any type of cacti. Similar phenomena are known among other plants. In addition to the named forms, the collections also contain chlorophyll-free plant forms (variegates) of red, yellow and other colors. Since the photosynthetic apparatus in such plants is absent, they cannot independently assimilate carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and are able to grow only in a grafted state. To maintain the shape of some species of cristates, they are also grafted.
The characterization of the cactus plant would be incomplete without a description of the thorns. Cactus spines are modified kidney scales. They are subdivided into central and radial spines. The central spine (s) is found in the center of the areola. It is usually larger, rounded or flattened, and quite often bears a hook at the end. More numerous and thinner radial spines are located along the periphery of the areola. The tissue of the thorns is saturated with calcium and some other substances that give it hardness. The number of radial spines in one areola can reach ten or more. Areoles of some species, in addition to spines, can bear hairs. Cacti of the subfamily Pereskievs and Opuntsevs bear small and easily breaking off spines on their stems - glochidia. There are types of cacti with flat and thin “papery” spines, for example, some types of tephrocactus. Of all the cacti, only peresky have well-developed leaves.
Cereus
The name of this variety of cacti in Latin sounds like "Cereus", and in translation means "wax candle". Such cacti are long-lived in the plant world. Under natural conditions, cereus is a giant plant that can grow up to 20 meters in height. For home cultivation, more compact subspecies of cereus are chosen.
Stem: rough with pronounced ribs. Depending on the subspecies, it can be smooth or covered with sharp long needles.
Flowers: large white, lateral. Some subspecies boast a pleasant vanilla aroma.
Important! "Pampering" a cactus (too large a pot, too frequent watering and fertilization) can cause a lack of flowering.
Flowering period: end of spring - beginning of summer, at night. Bloom 24 hours after erection.


Maintenance and care: in order for such a flowerpot to feel comfortable at home and to bloom, it needs good light and long daylight hours. These plants love direct sunlight, but in summer they must be protected from burns.
So that direct light does not harm the plant in spring or summer, it is necessary to accustom the cereus to it immediately after the end of winter. As for the temperature, in winter, when the cactus has a dormant period, the optimum temperature for it is + 8 ... + 12 ° С.
At any other time, Cereus is unpretentious, calmly tolerates heat and sudden changes in temperature.
It is necessary to water it with warm water, in summer - more often, then reduce the frequency of watering.You can not overmoisten the plant: it can get sick and rot.


Gymnocalycium
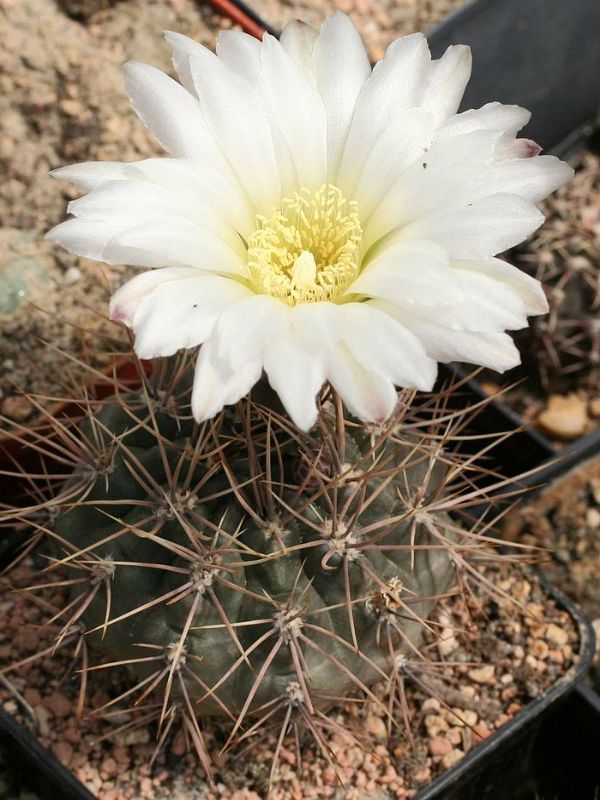


Succulent plant. The body of a cactus is spherical, flattened. An adult plant can reach no more than 15 centimeters in height and 4-10 centimeters in diameter. The body of the cactus is colored gray-green. The spines are up to 3 centimeters long, collected in bunches and symmetrically arranged. The flowers are white, zygomorphic, up to 10 centimeters in diameter.
to the table of contents ^
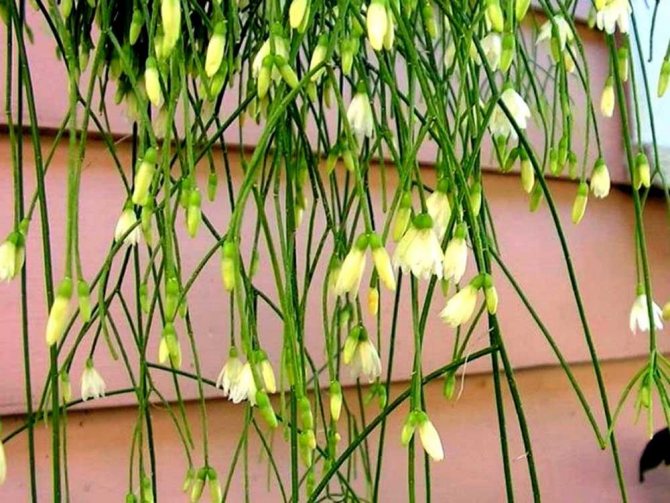
Rhipsalis
“Rhips” is the word from which the name of this species comes from, translated from Greek it means “braid”, which very accurately characterizes the appearance of this plant.
Stem: can be different: ribbed, rounded, flattened. As a rule, the stem is not one, but from one pot many curly hanging stems without thorns grow, which is the main difference between this species from others.
Flowers: small, delicate, like bells of pink, white, yellow or bright red.
Flowering period: several days in spring and summer.
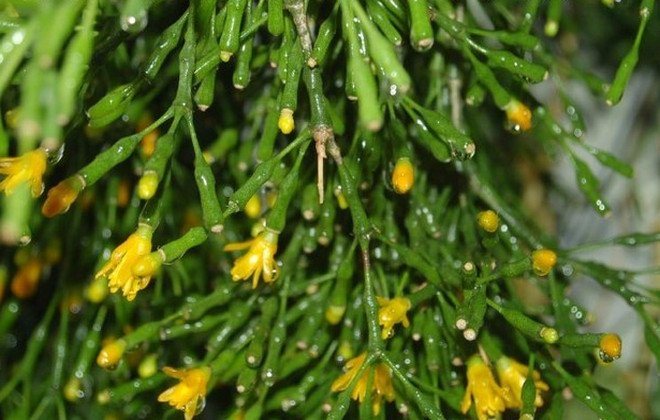


Maintenance and care: representatives of this type of cactus prefer bright diffused light and can grow in the shade. In the summer, you can place a pot with a plant on the veranda or in the yard, but so that direct rays do not fall on it.
For this type of cactus, the comfortable temperature in spring and summer is + 18 ... + 20 ° С, in winter - + 12 ... + 16 ° С. Such cacti are not sensitive to air humidity, but in summer they need to be sprayed with warm infused water.
During the growing season, the plant should be watered regularly, when the topsoil dries up, in the fall watering should be reduced, and in winter it is very rare to water.
Chamecereus
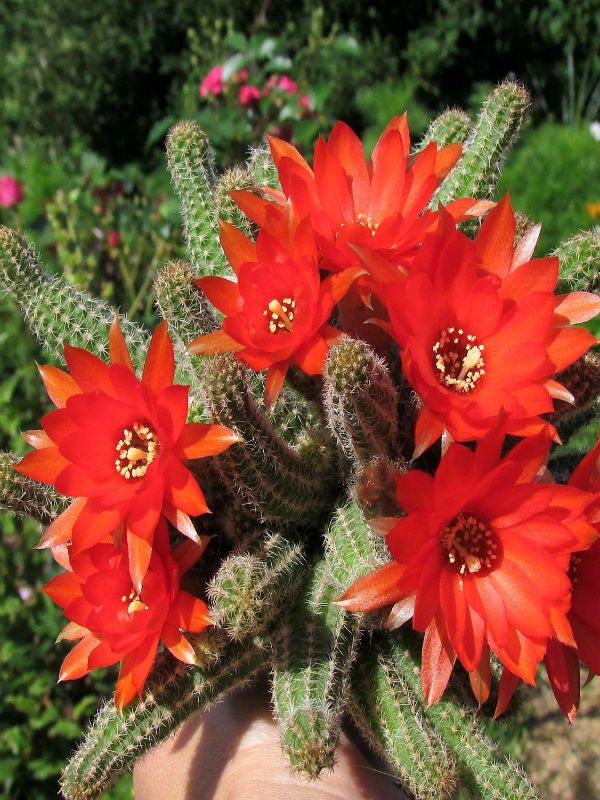


Epiphytic cactus. Stems are thin, erect, short, no more than 20 centimeters in height, weaving. A cactus grows with a bush. The body of the cactus is gray-green, densely covered with small spines. The flowers are zygomorphic, regular, red, pink, white or yellow. Flowers on small pubescent legs, can reach 3-5 centimeters in diameter. Blooms densely.
to the table of contents ^
Echinopsis
Echinopsis does not differ from most types of flowering cacti, which got their names due to external signs. "Echinos" in translation from Greek means "hedgehog", and this name is perfect for all representatives of this species.
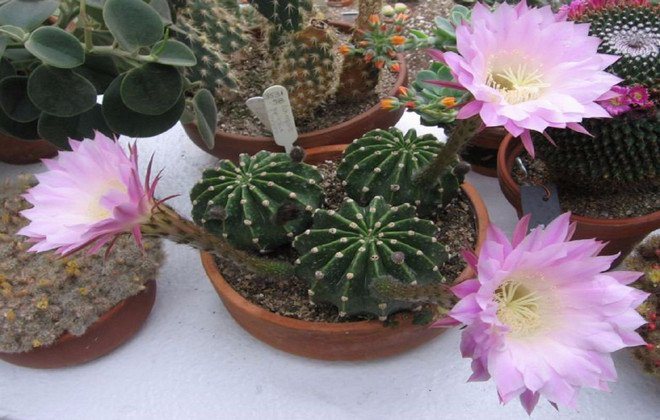


Stem: at first it has a spherical shape, then it stretches and takes the shape of a cylinder. The color can be either bright green or dark. Ribs are even, pronounced. The size and density of the spines differs depending on the specific subspecies.
Flowers: large (diameter - about 14 cm) funnel-shaped pink, white, yellow or orange, grow on a pubescent tube, the length of which can reach 20 cm.
Flowering period: 1-3 days in spring.
Maintenance and care: love bright light, tolerate direct sunlight. Comfortable temperature in summer - from +22 ° С to +27 ° С, in winter - from +6 ° С to +12 ° С. In spring and summer, water should be done a few days after the soil under the plant is completely dry. During the dormant period (in winter), you can not water it at all or do it very rarely. Do not need spraying even in summer.


Acanthokalycium
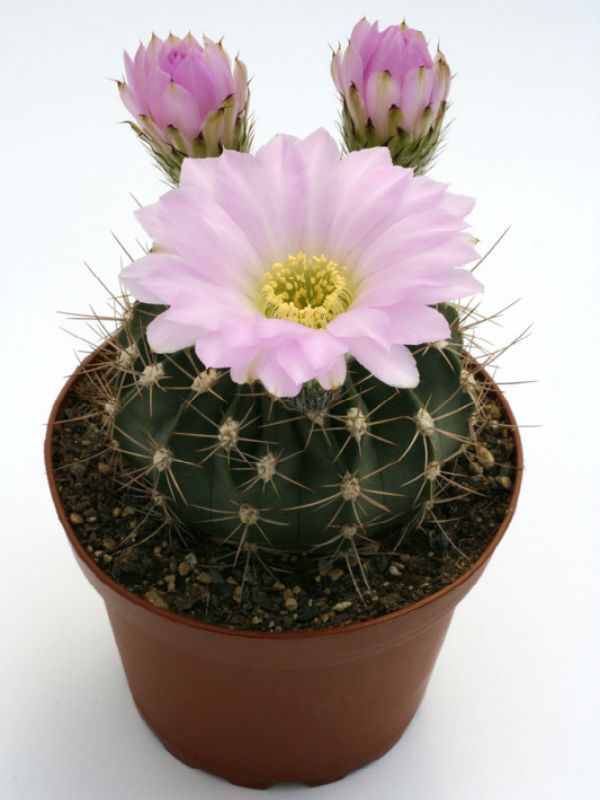


The body of a cactus is most often a dull, dark green color. It is spherical or cylindrical, ribbed with frequent small bushy spines. The height of a cactus can be 10-60 centimeters. The flowers are white, pink, light purple, funnel-shaped, wide open, 3-6 centimeters long. Flowers on short pubescent legs, located in the upper body of the cactus.
to the table of contents ^
Epiphyllum
Epiphyllums are cacti with shrubby growth and woody base.
Wisteria, spiraea, aichrizona, cercis, mountain pine, dieffenbachia, bladderwort, aster, and cinquefoil can also boast of a shrub growth.
The name of the species consists of two Greek words: "epi" - "above" and "phyllum" - "leaf".This plant was unofficially nicknamed "orchid cactus" for its extraordinary beauty.
Stem: leafy, fleshy, serrated.
Flowers: appear on modified stems - cactus leaves. Funnel-shaped, rather large, have a long tube and a pleasant aroma. Color: white, cream, yellow, pink, red.
Flowering period: spring, the flower disappears 5 days after it has blossomed.
Important! You can not change the location of the plant when the buds begin to appear, since they may fall off, and the flowerpot will not bloom.
Maintenance and care: it is useful for the epiphyllum to receive a large amount of scattered light. In the summer, you can take the flower outside, but place it where direct sunlight will not fall on it.


The optimum temperature in spring and summer can range from +20 ° C to +26 ° C. When the plant has a dormant period, a comfortable temperature is from + 10 ° С to + 15 ° С. On hot summer days, it is recommended to spray it with warm water.
Since the epiphyllum is a species of rainforest cacti, it needs water much more often than those cacti that come from arid regions.
To water it, you do not have to wait until the soil in the pot is completely dry, it is necessary that it is always moist, and only the top layer dries out. While the cactus is in bloom, it can be fertilized.
How a cactus blooms: signs, a description of the structure of a flower and a fruit
Cactus flowers are solitary, in most cases located at the top of the stem, one at a time in the areola. They have a variety of colors, with the exception of blue. The structure of a cactus flower includes numerous stamens and a stigma of the pistil. In some species, they can differ in color, for example, yellow stamens and green stigma of the pistil in Echinocereus. Flowers appear on both old and young areoles.
There are types of cacti in which flowers develop on a special organ - cephalia (genus Melocactus, Discocactus), which forms at the top of the stem. The cephalic is an accumulation in the flowering zone of a large amount of fluff, hairs and bristles. It increases annually, reaching a height of 1 m in some species. Flowers can also develop on lateral pseudocephaly, for example, in cacti of the genus Cephalocereus, Pilosocereus, etc. The size of cactus flowers varies from small to huge, 25-30 cm long and in diameter (genus Selenicereus ). Flowers of some species have a scent (genus Echinopsis, some species of the genus Dolichothele, etc.). Flowering occurs during the day and night. Most cacti bloom during the daytime in the morning or afternoon. Most often, cactus flowers are bisexual and cross-pollinated. In the homeland of cacti, in addition to the wind, insects and birds, including hummingbirds, participate in pollination.
After flowering, berry-like juicy, less often dry fruits are tied. In many species, they are edible. Fruit sizes vary from 2-3 mm to 10 cm. The largest fruits are found in prickly pears. The fruits can ripen in the current season or next year (genus Mammillaria). A ripe berry can contain from several pieces to hundreds or more seeds. One of the smallest seeds in bloosfeldia, strombocactus and parodies. The large prickly pear seeds have a hard and durable shell. The rest of the cacti have a thin, fragile seed coat. Seed germination of most species lasts up to a year or more, in Cereus and Mammillaria up to 7-9 years. Roseocactus fissuratus has a known case of seed germination after 30 years.
Notocactus
The name of this type of cactus in translation from Greek means "southern cactus", since it was in this part of the world that they appeared.


Stem: spherical or wedge-shaped with well-defined ribs and a large number of spines.
Flowers: can be of different sizes, depending on the type. The color is usually yellow or yellow-violet.
Flowering period: spring or summer, depending on the subspecies, the flower can stay open for more than 5 days.
Maintenance and care: needs bright diffused lighting. The temperature during the growing season is up to +26 ° С, in winter - not lower than +10 ° С. Water the plant abundantly from March to September and moderately from October to March. The soil must not be allowed to completely dry out. At the same time, it is not good if it is waterlogged.


Parody
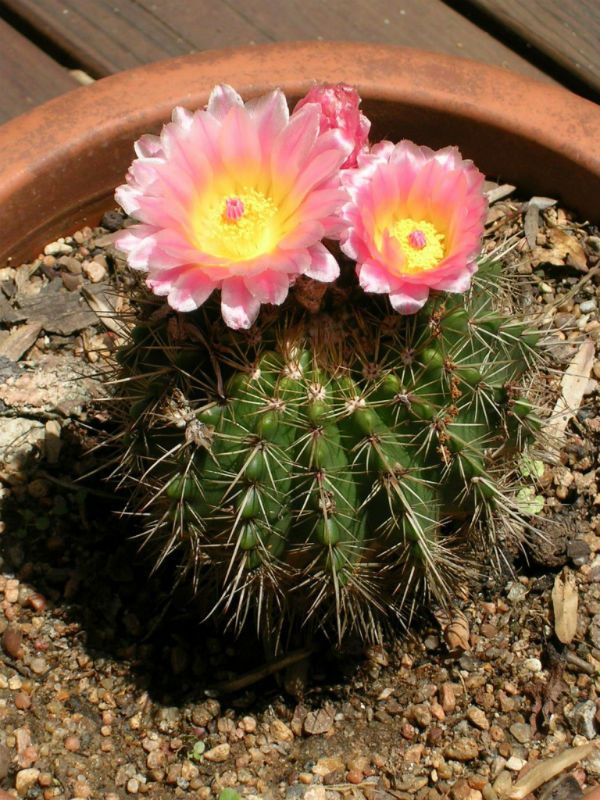


The body of the cactus is a shiny dark green color. The body of a cactus is spherical or cylindrical, ribbed with frequent small bushy spines. The height of a cactus can be 10-60 centimeters. The flowers are white, pink, light purple, funnel-shaped, wide open, 3-6 centimeters in diameter. Flowers on short pubescent legs. Flowers are located in the upper body of the cactus.
to the table of contents ^
Mammillaria
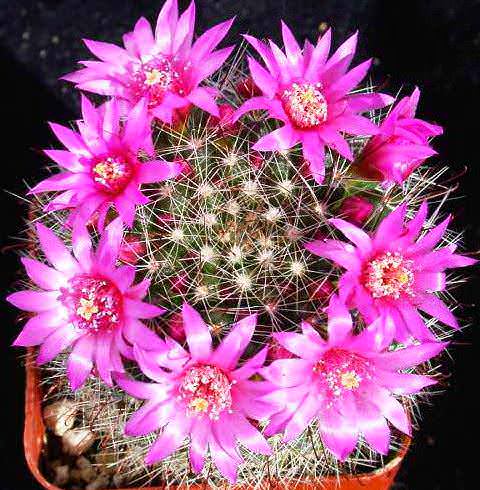


Small cacti with clavate shoots, which have a characteristic feature in the structure in the form of numerous papillae or tubercles. They can grow, forming colonies, so Mammillaria thrives in wide flat pots.
They are distinguished by an amazing variety of stem shapes and flower colors, which bloom in early spring. They form a kind of wreath or crown around the top of the stem.
Diseases and pests
Pests such as spider mites, mealybugs, scale insects, whiteflies are considered dangerous. They are sucking insects. To destroy them, the plant must be sprayed with special preparations, for example, Actellik, Bankol or Decis. In this case, do not allow the treatment solution to get on the soil. Re-processing is recommended after 6-10 days.
If the roots are damaged, the plant must be dug up, cleaned of soil and the damaged areas removed from the root system. Treat the cut sites with crushed activated carbon. After that, the roots must be rinsed in hot water, the temperature of which is within 50 °. In this case, the root collar should not be immersed in water. The cactus can then be planted in sterilized soil.
If we talk about diseases, succulents are threatened by such as root, wet, gray rot, late blight. The reason for their development is stagnation of the soil, which leads to the appearance of fungi. If they are found, it is necessary to dig up the plant, clear it from the ground, and remove the damaged areas. After transplanting, the plant is treated with fungicides.
History
The first documented evidence of cacti dates back to the 16th century, when news of discoveries in the New World reached Europe.
According to scientists, it is believed that this biological kingdom evolved about 30-35 million years ago. Archaic historical descriptions include data on "melon-like blooms" and in no way associated with the common plants at the time.
It was the specific visual features of cacti and their exoticism that made an incredible stir among Europeans. It is believed that the first in the Northern Hemisphere of the Earth were melocactuses, which grew in abundance on the seashores of America.


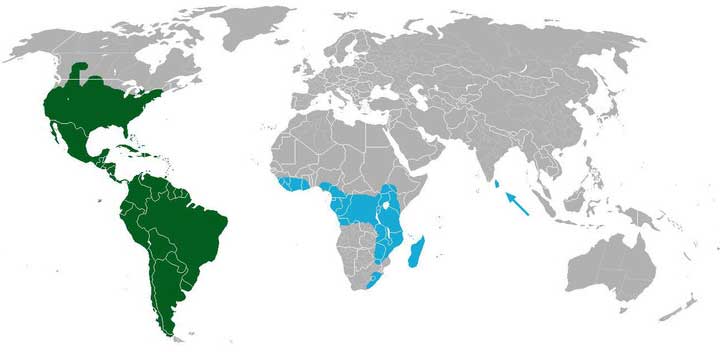
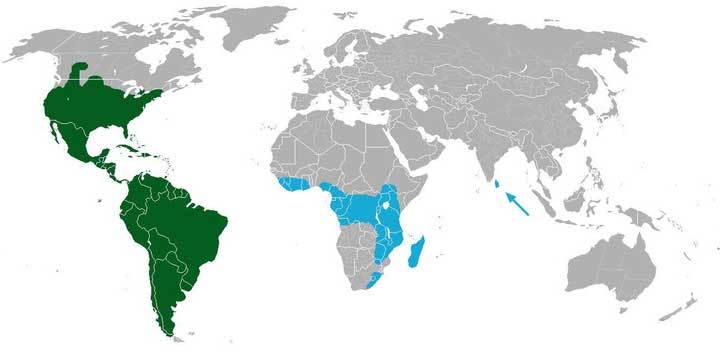
In the wild, cacti are distributed mainly on the continents of America.
One should take into account the fact that in the 16th-18th centuries, exclusively wealthy citizens were able to afford to acquire these inflorescences for collections. The need to own extravagant plants turned into a kind of mania, and prices rose to unimaginable numbers.
By the second quarter of the 19th century, a certain list of specialized associations was formed, engaged in the cultivation of cactus crops and their import from the countries of growth. This made plants more accessible. By the beginning of the 20th century, many botanical collections already existed, numbering hundreds and even thousands of species.
According to the current botanical taxonomy, the Cactaceae family contains approximately 350 genera, including about 3 thousand subspecies of cacti. It is worth noting that the cultivation and collecting of these inflorescences is one of the fascinating and massive, at the same time difficult areas of modern floriculture.
Every person who is first interested in breeding mysterious thorns is likely to face two difficulties: a rather difficult agricultural technique and an extremely confusing naming system compared to other plants.
The distribution area of cacti is very wide. Despite this, they are considered typical desert dwellers of the American regions.
- In the South of America, thorny plants are located along the perimeter of the geological mountain formations of the Pacific coast.
- The main areas of distribution of cacti in North America are parts of the United States such as Arizona, Texas and California.
- The greatest species diversity is typical for Mexico, mountain deserts of Peru, Chile, Argentina and Bolivia. There are cacti of all known forms - both dwarf and giant specimens.
- In the Soviet Union, prickly pears were successfully adapted to grow on the Crimean peninsula and in the Astrakhan region, as well as in Turkmenistan.
- Some varieties of epiphytic cacti are found in the thickets of the African continent, on the island territories of Madagascar, in Sri Lanka and on the Indian Ocean peninsulas. However, it is believed that they were brought to these places by man.

Cacti are able to survive in extreme wildlife conditions
Cacti are unique examples of survival in all climatic zones. Due to their vegetative system, they are able to accumulate moisture and tolerate adverse weather conditions.
It is important to note that cacti thrive not only in the wild, but also when grown at home. Beautiful compositions are made with this plant and impressive exhibitions are held. In terms of their visual presentation, they are in no way inferior to the best flower collections.
In what year of life does this period begin?
All of the above types of cacti become capable of flowering only after reaching a certain age and a certain size.
- Some Rebucias, Aylostera bloom already in the first - second year of life.
- Mammillaria, Astrophytums, Echinopsis and Gymnocalcium - in the third - fourth years.
- But Ferocactus or Trichocereus bloom for the first time only after 10 - 15 years from the moment of sowing.
It should be noted that the bulk of thorny pets will expel buds in the fifth year of life.
How to choose the right one in the store
When buying prickly pear, be guided by the following rules so as not to acquire a non-viable plant:
- The plant should not wobble in the pot.
- In a healthy prickly pear, all segments of the stem have a dense structure and are covered with thorns or glochidia - softened tissues or spots indicate the presence of a fungal disease.
- You can buy cacti mechanically damaged during transportation, but it should be borne in mind that they will need more delicate care.
- It is better to purchase young plants - adult cacti take a long time to adapt to the new environment and may die.
Important! FROMjust a month after buying a cactus, it needs to be transplanted, but not earlier. Plants take time to get used to a new place.
Useful properties of prickly pear
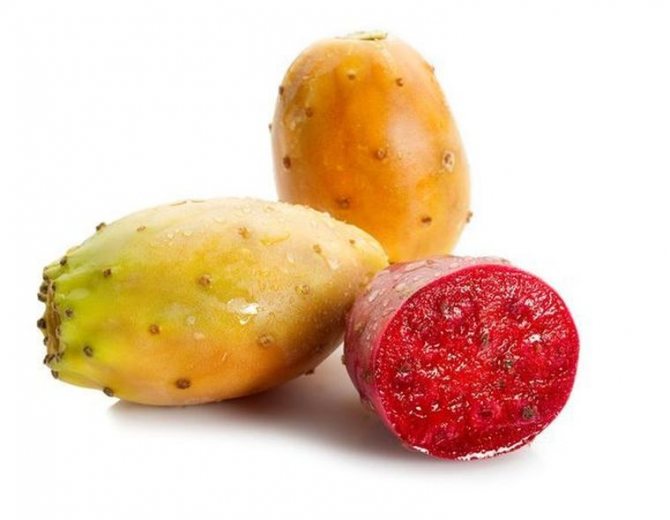
Many types of prickly pear, in particular, Indian or fig (O. ficus-indica), gosselin (O. gosseliniana), cylindrical (O. Cylindrica), monacanth (O. Monacantha) have medicinal properties. For medicinal purposes, different parts (berries, fruits or pulp) can be used.
Butter
Oil can be obtained from cactus flowers by maceration. It includes organic acids, tocopherols, fatty acids. Thanks to this, the oil is used to strengthen the hair follicles.
The oil of the prickly pear cactus will also help to increase the elasticity of the breast, remove fine wrinkles from the face.
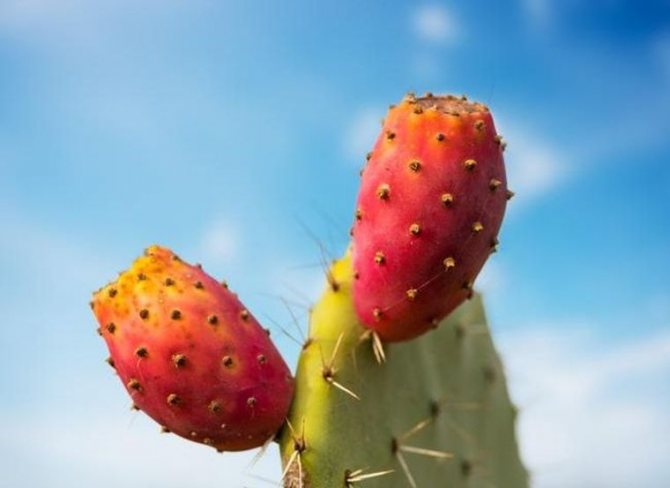
Fruit
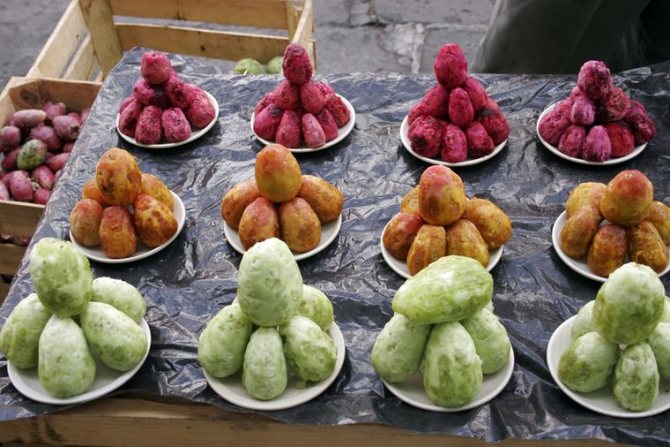
After flowering, fruits or berries are formed. They can be used to prepare various dishes, both raw and after preliminary heat treatment.
Often, prickly pear berries are transported to other countries and regions. This became possible due to the good keeping quality and transportability of the fruits. In composition, they are similar to currant or cherry berries.
Fruits in pictures:
Vinegar
For the manufacture of the product, species that grow in Tunisia or Mexico are used. Vinegar is used in cooking as a condiment, imparting exotic flavors and aromas to dishes.
It is also possible to achieve good results as a result of using prickly pear vinegar in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disorders, as well as for weight loss.
Extract
For the manufacture of prickly pear extract, pulp is used. With its help, you can relieve hangover, get rid of nausea or dry mouth. The extract helps to relieve symptoms resulting from liver disease.
Where can one buy
You can buy fruits in large supermarkets. You can also get them in your own garden or in the garden when growing a desert cactus. The possibility of buying fruits in online stores is also not excluded. Here they offer not only fresh fruits, but also dried ones.
Several online stores where you can buy prickly pear for cultivation:
- Tropics Seeds;
Reproduction
There are several known methods through which you can carry out the propagation of prickly pears:
- Cuttings... Performed in late spring or early summer. After cutting, the cutting should dry out for 3-4 weeks. Its lower end is sharpened in the shape of a pencil. After that, the cutting is planted in moistened sand. It is important not to deepen the stalk, but to fix it to the surface with a support. The handle is covered with a glass cover. The room temperature should be within 20 °. Until the root system is formed, the sand and the cutting are periodically sprayed. The glass cover must be lifted daily for ventilation and fresh air. After rooting, the cutting is transplanted into the soil mixture. For 2 years, a young plant needs shading.
- Seeds... This method is quite complex and painstaking. Previously, the seeds must be soaked for 10 minutes in a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Using a file or sandpaper, erase the top layer of the peel. Place a drainage layer on the bottom of the container, and then a previously prepared soil mixture. Sow the seeds, and cover the container with foil.
Before the first shoots appear, the container should be indoors at a temperature of 20 °. Periodically remove the shelter for ventilation, during which to spray the soil. After the emergence of seedlings, the shelter can be removed, and young plants can be dived into separate pots. Carry out a transplant in a year.
Application, recipes
The beneficial properties of prickly pear make it possible to use it for the following purposes:
- To eliminate rheumatic pains crush the cactus pulp into a gruel and apply it to the inflamed area in the form of a compress. After 10 courses, you can forget about pain.
- Get Rid of Pain During Arthritis also possible when using cactus tincture. To prepare it, you need to chop the pulp and fill it with vodka. Let the mixture brew for 15 days. It is recommended to take the tincture 16 drops half an hour before meals 1 time per day.
- An effective mask can be made from prickly pear oil mixed with pomegranate seed concentrate. 20 minutes after application face masks it must be washed off with warm water. During the week, you can do this mask no more than 1 time. Thanks to this, the skin becomes elastic and fine wrinkles disappear.
- Slimming vinegar or prickly pear extract is used.Products are added to clean water in 10-16 drops. It is recommended to take a drink before meals, 100–150 grams three times a day. You can also reduce appetite and improve metabolic processes when using vinegar for salad dressing.