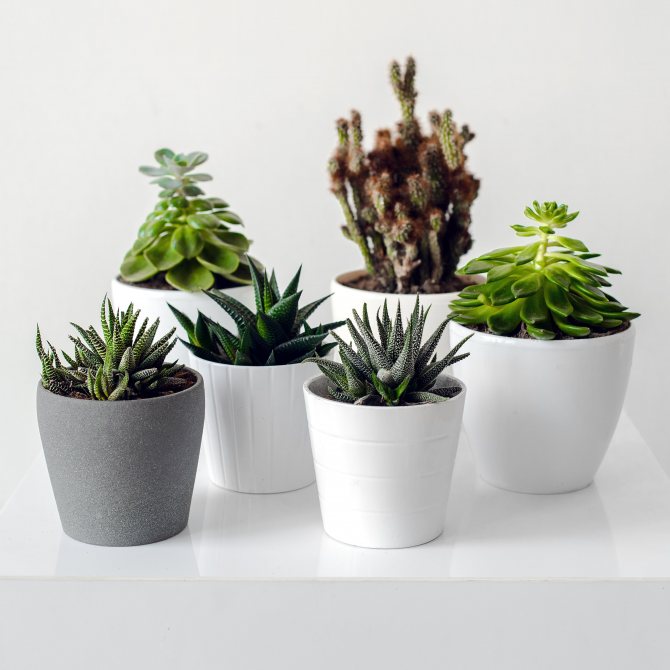
The name succulent - translated from Latin "juicy", refers to a group of plants whose homeland is the arid territories of the tropical belt: South American and African continents, islands located at the latitude of Madagascar. Indoor cultivation is available to novice growers. A common property of unpretentious plants is the ability to store moisture in fleshy leaves or stems for a long period. Conventionally, succulents are divided into stem (cacti, milkweed) and leafy ones:
- aloe, known as the agave;
- kolanchoe, or "doctor";
- crassula ("money tree", fat woman);
- other bastards - echeveria, otherwise referred to as "stone rose"; rejuvenated, sedum (sedum), beard, doodle;
- Haworthia;
- "Living stones" - double-leaved lithops and lapidarium;
- unpretentious agave from the asparagus family;
- zamioculcas, or "dollar tree";
- wild aloe;
- gasteria;
- a relative of the grape cissus quadrangular, called "chiropractor".
From the names themselves, accepted by the people, it follows that indoor plants of this group have an original appearance, and many have medicinal properties.
The main methods of breeding
Such unpretentious plants can be propagated in many simple ways. Breeding of succulents is carried out:
- By cuttings - separating the cutting from the mother plant and transplanting it into a separate container with soil.
- Leaf propagation - when the succulent has leaves and can be separated, they are placed in a container of water before the roots appear, and then they are planted.
- Seed reproduction. If a succulent gives birth to seeds, planting them in a separate pot is the least stressful way to propagate it.
The third method of plant breeding is widely used by gardeners and simply exotic lovers. Succulents from seeds grow quickly and in large numbers, but for this they need to create the right conditions and do not forget about regular care.
Soil preparation
As soon as the seeds have arrived and you have prepared everything you need for planting, need to find clean sand... The sand that is sold in garden shops may contain fungicides or herbicides. That is why it is best to use construction sand, which is mixed with cement.
Small pieces of rock create small air pockets and ensure good root development.
The best advice we can give, is that you need to wet the sand well before sowing the seeds. Succulent seeds are tiny in size and therefore rinse off easily when watering. But if the soil is wet, they will stick to it and stay in place until they have roots.

Preparatory work
The first step towards breeding these exotic plants is selecting and sourcing seeds. Experienced gardeners buy an already adult plant and extract them themselves, but for beginners it is better to purchase ready-made sachets. They are sold both in Chinese online stores and in some specialized outlets in the CIS countries.
Growing succulents from seeds at home requires thorough preparation. It is not difficult in essence, but it must be done efficiently so that further breeding does not cause additional difficulties.
Selecting a container for sowing
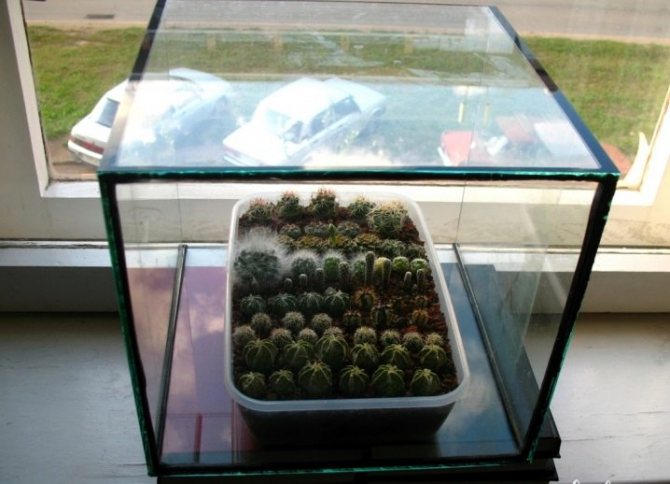
The unpretentiousness of succulents is visible even in where the seeds are planted for germination. These plants do not need special pots made of heat-resistant materials. For proper cultivation, you will need not too deep (side height approximately 5 cm) plastic containers. At the bottom, you need holes for excess moisture so that the seeds do not rot. If the manufacturer did not provide them, make the holes yourself. The hole diameter should be between 3 and 5 mm.
Since succulents are exotic plants that love warmth, the container must be covered with a transparent lid on top to create a humid and hot atmosphere inside. As a last resort, you can also use plastic wrap.
You can also plant succulents in ready-made mini-greenhouses, which are sold in special stores, including those brought from China.
Selection and preparation of soil
No less important in breeding is the soil in which the seeds will germinate. Land for succulents does not need to be ordered from abroad. Ready-made mixtures are sold in stores, you just have to pay attention to a few nuances:
- Succulents grow in difficult conditions, so for the plant to adapt to the new environment more quickly, it is better to use coarse soil, such as a mixture of soil with sand or fine gravel. Some gardeners recommend adding crushed coal to this composition.
- It is imperative to take a ready-made substrate for planting plants. The soil and sand from under the entrance are not suitable for breeding succulents. In special stores, the soil is not just poured into bags, it is also treated and disinfected before that.
- If there is no special store nearby, then you can purchase a regular peat filler, and add sand and other minerals to it yourself.
Seed preparation
Preparation for sowing is the most difficult and painstaking stage in the breeding of succulents. Small seeds are very similar to each other, so it is easy to confuse them, and different types of plants require different soil and.
Preparation for germination begins with selection. It is necessary to spread the seeds on a white sheet of paper and select dried or rotten ones. After that, all the seeds are divided into groups and tags are created for them, which will be attached to the pot after sowing.
It is absolutely impossible to disinfect seeds. This will kill the protective layer.
Close to natural soil for succulent crops
Under natural conditions, the soil of deserts is depleted, stony, loose, and poor in nitrogen. Fat soil, peaty soil retains water, which leads to root rot, even with dosed watering. The same negative effect is caused by an excess of nitrogen in the soil.
When transplanting, a three-layer mixture is prepared:
- In the lower part - drainage to a depth of 1/6 of the pot (can take up to 1/3)
- With two parts of coarse sand with a stony fraction, dilute one part of the garden soil and one part of humus. The soil is loosened with pebbles, coconut fiber, sphagnum moss, 0.5 part of crushed hardwood coal is added to adsorb impurities from water.
- The upper drainage layer 1–1.5 cm thick, removed before watering - expanded clay, perlite, crushed brick or small stones.


When self-preparation of soil taken "from the street", all ingredients must undergo long-term heat treatment to destroy pests and pathogens. For some epiphytic crops related to succulents, only soil made up for orchids is suitable.
Sowing technology and care of seedlings
Growing a variety of succulents from seeds at the sowing stage follows the same rules, regardless of the type of plant. These rules are not complicated and may differ slightly in different textbooks, but the essence of the described procedures is always the same.
At home, sowing seeds in the ground is easiest to do with a regular A4 sheet. It needs to be folded into a small envelope with a free edge, from which the seed will fall into the moistened soil. From above, the seeds are covered with a thin layer (the thickness should not exceed the size of the seed) of sand or a mixture of sand and earth.
After the first planting, the ground is watered from a spray bottle with water at room temperature. Very little water is needed, just to create a greenhouse effect. The home greenhouse can be closed afterwards. Growing in a greenhouse allows you to save much more seeds than in the open air, so you need to remove the cover only when the sprouts are clearly visible from the ground (at least 1-2 cm).
Succulents will begin to sprout after several months of abundant watering, so the gardener needs to be patient if he wants to decorate his windowsill with these exotic plants.
- Maintain the optimal temperature in the greenhouse - from 20 to 30 degrees during the day and 18-20 degrees at night.
- Succulents cannot stand drafts.
- Young sprouts should not be exposed to direct sunlight, but at the same time they need abundant lighting, so you cannot keep the greenhouse on the windowsill, but you can do it on a table in a well-lit room.
- Succulents need to be watered regularly so that the soil does not dry out. At the same time, for succulents, stagnation of water is just as harmful as drought, therefore, the moisture of the soil must be monitored extremely carefully.
Features of sowing certain species
Not all plants in the same family can be grown under the same conditions. Planting succulents of different types requires observance of certain nuances, otherwise the seeds will die before the sprouts appear.
- Some plants are not as thermophilic as their counterparts. For example, Dioscorea grows best in temperatures between 18 and 20 degrees, so it is best to plant its seeds in winter rather than summer.
- Certain types of succulents need to be planted in specially prepared soil. For example, more thermophilic members of the family prefer soil with sand, and those that like lower temperatures are better planted in the ground with fine gravel.
- The amount of watering also varies from species to species. Leafy succulents are watered more often than their other cousins.
To sow seeds correctly, you need to study the plant that will be grown, its requirements for lighting, watering and soil composition. Only then will the emerging succulent be healthy and beautiful.
The emergence of sprouts
After the sprouts have grown to the amount necessary to remove the cap from the greenhouse, gardeners have new problems with their breeding. The main ones are diseases and the need to fertilize the sprouts that have appeared.
Planting is impossible without the enrichment of the soil with useful minerals. Since fertilizers are practically not mixed when planting in the ground, after the sprouts appear, the soil must be watered with liquid fertilizers. Succulent nutrient bottles available from flower shops are suitable for this purpose.
Taking care of plants after the appearance of fungi or bacteria is extremely difficult, so you need to work ahead of schedule. Fungicides can be used to prevent diseases. For the best effect, you must strictly follow the manufacturer's instructions, which are indicated on the packaging.
Succulents are ideal for those who want to beautifully decorate their windowsill, but do not want to buy too "capricious" plants. You can easily choose a species to your liking: leafy or more similar to a cactus, thermophilic or accustomed to cooler temperatures. Succulents grown from seeds will immediately tune in to the conditions of the house in which they were "born" and will not cause the owners almost any trouble.
Succulents have been very popular lately. These plants look unusual, moreover, they are extremely easy to care for.Most succulents are resistant to any adversity, including sudden changes in temperature and lack of moisture, besides, they are unpretentious to the amount of sunlight. In this article, we will talk about some curious ways to grow succulents and how to create stylish interior compositions out of them.
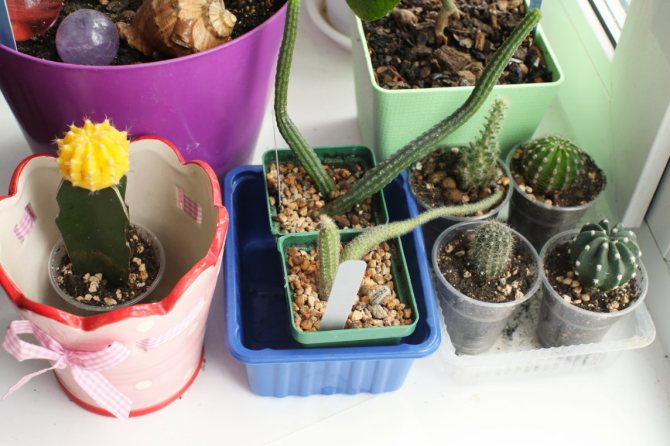
Since succulents are small in size, it is not necessary to use full-size flower pots to grow them. They can be replaced with conventional cylinders, which are obtained by sawing PVC pipes. These cylinders are placed in a pebble tray. Soil is poured into the tubes, and plants are planted.
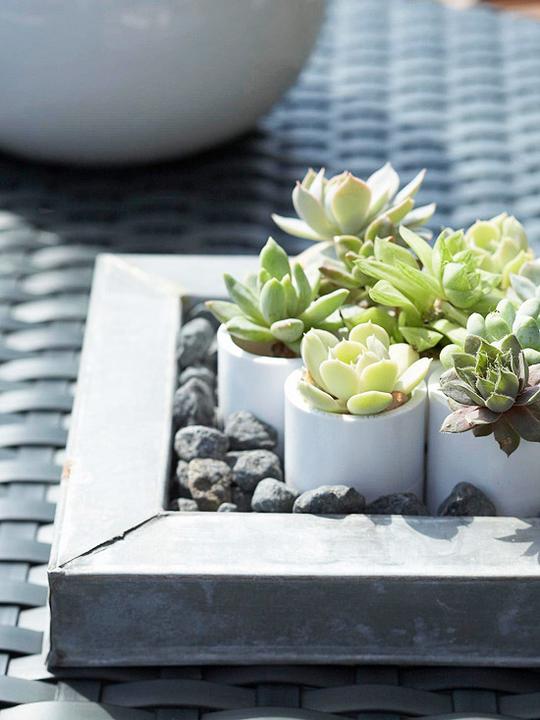


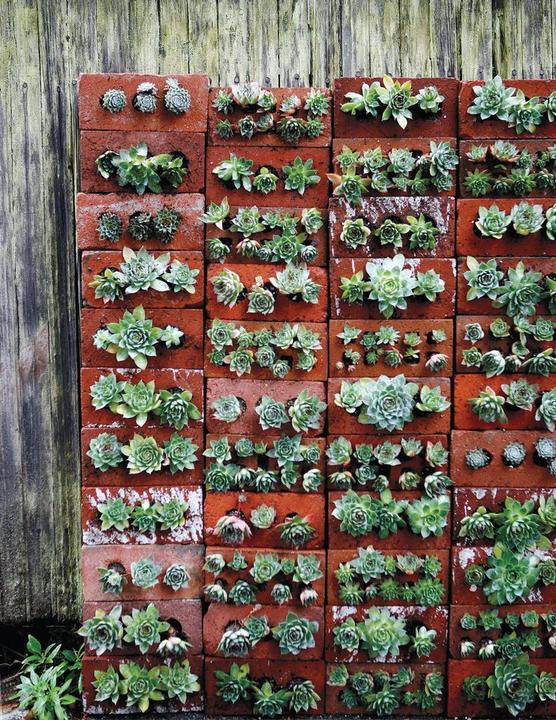
For growing succulents, you can use a vertical flower bed, which is a regular wall built of red brick. A little soil is compacted into each of the three holes in the brick, since succulents do not need more.


A wide variety of containers can be used to grow succulents. For example, succulents are tightly planted in an ordinary metal box.


Note:
remember that succulents need good drainage, so a layer of pebbles should be placed on the bottom of the container or pot. It is better to mix the soil for succulents with sand.
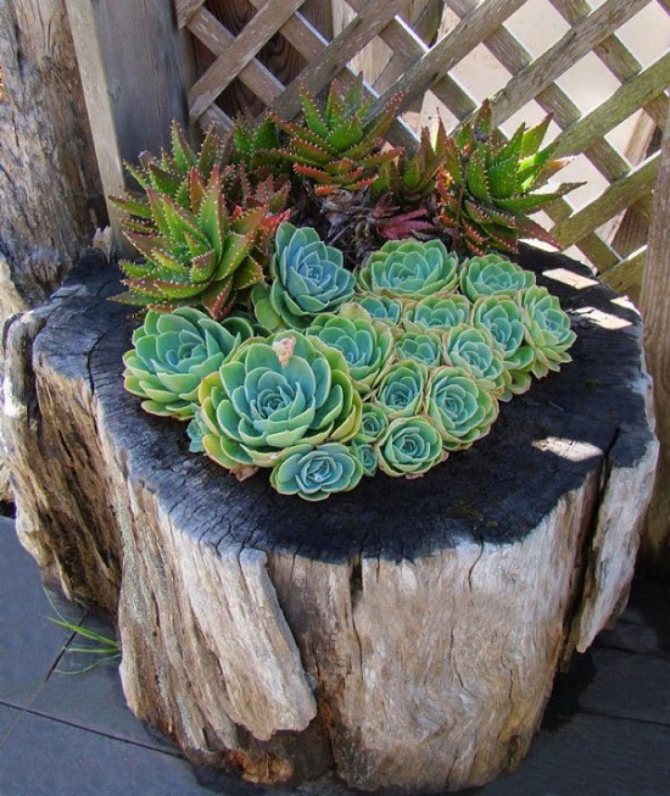
And here is an example of a succulent pot made from a fragment of a regular log. It looks incredibly organic and stylish. In the case of using natural materials, drainage problems should not arise.


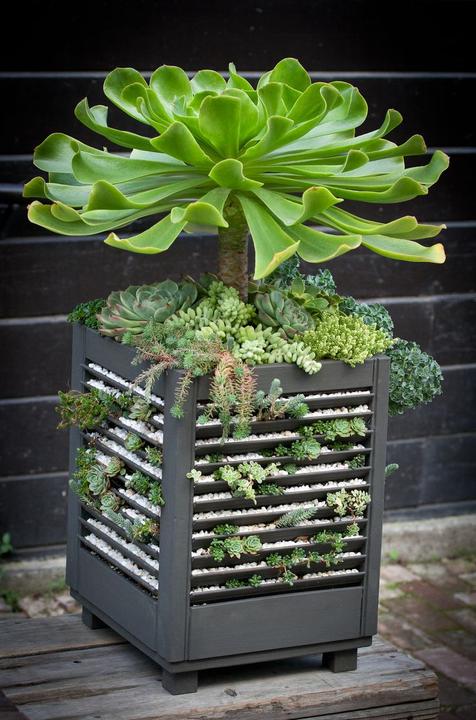
Here's another great example. In such a pot made of wooden blinds, you can grow several large plants, and plant many smaller succulents in the slots on the walls. Such a pot is also suitable for germinating young plants, which can later be transplanted into larger containers or pots.


Note:
succulents are easily propagated by leaves, you can learn about plant propagation methods from.
Whole pictures can be made from succulents. To do this, the soil is compacted tightly into a container with low sides, and a fine mesh is laid on top. When the plants take root, this picture can be hung on the wall.
Succulents can be used to create decorative flower beds that combine plants with rocks, shells, and other materials.


Another very interesting idea is to plant succulents in the bowl of the fountain. It looks just great. It feels like you are in an abandoned temple deep in the jungle.


And here are the succulents planted in an old chicken feeder. Instead of a feeder, you can use a lamp housing for fluorescent lamps.
Succulents look quite interesting inside concrete flower pots.
And here is a whole wall planted with succulents. Just look at the variety of shapes, sizes and colors. Looks awesome. To create such a wall, panels with small cells are used.
Succulents are different types of plants, often not even similar to each other. But they have one thing in common - they are all able to survive drought, storing moisture in leaves, thorns and other types of plant tissue. Cacti, aloe, euphorbia, lithops and many others - they are all united under a common concept.
How to grow succulents at home, this article will tell you.
As a rule, such plants require a place with good lighting, but some species are intolerant of direct sunlight and may be in a darkened room. It should be well ventilated, but at the same time, you need to take care of the absence of drafts.
In the summer, it is useful to take these plants outside, avoiding direct sunlight. In winter, succulents thrive at temperatures between 5 and 15 degrees.
Fertilizer selection and feeding regime
An excess of nutrients and trace elements leads to artificial sublimation of plants, usually growing by no more than 1 cm per year. Organic matter is especially harmful in this respect - manure, bird droppings. Top dressing is inappropriate in winter, it will lead to stretching, disproportionate development of the plant. Fertilizers are applied in the spring, at intervals of 4 weeks or more, after a preliminary abundant watering - this will protect the root system from chemical burns. Mineral formulations are the same as those sold in flower shops, but the nutrient mixture is diluted in a lower concentration than for other plant species.
Compositions with a large amount of nitrogen should be avoided, its excess causes rotting. The main ingredients for the nutrition of succulents are potassium and phosphorus... The selection of related components depends on the development problems noticed by the florist:
- Calcium strengthens weak rhizomes, activates photosynthesis in case of chlorosis symptoms.
- Iron will prevent drying and falling of buds, fading of growth points.
- Magnesium revives the faded color of leaves, activates flowering.
- Zinc will stop the excessive reproduction of children by the plant.
- Nitrogen in additional quantities is necessary if the succulent has stopped growing (provided there is sufficient illumination and a comfortable temperature).
Fertilizers should not be applied if the succulent has just been transplanted into a new pot. Root survival occurs in two to three weeks. You should not feed plants with obvious signs of a parasitic disease - in this case, the flower is first of all transplanted, the whole plant, especially the root system, is disinfected, and dead and diseased parts are removed. The immunity of succulents is strong enough, they can be damaged by a relatively small number of pests, however, a weakened specimen, especially in the hands of an inexperienced grower, is often affected by this or that disease.
Soil and transplant
Succulents are transplanted in the spring. The need for this procedure is due to several factors, for example, depletion of the land, a cramped pot, growth disorders, or the replacement of store soil. The reasons may vary.
The transplant is carried out as follows. To begin with, you must not water the plant for several days so that the earth easily crumbles from the roots. Drainage is laid at the bottom of the new pot and the required amount of dry earth is poured. It is categorically impossible to water succulents after transplanting, this is a common mistake of many home garden lovers. Without watering, the plant must be kept for about a week to avoid contamination of the soil and give it time to recover and get used to the new place.
Many growers believe that the transplant should be carried out in the spring season. However, the main thing here is to observe the rule so that the plant is not in the stage of active growth and flowering. Of course, in 90% of cases, the right time falls just after wintering - at the beginning of spring.
Depending on the type of succulents, you can buy ready-made soil in the store or compose it yourself. Do not forget about feeding, which is also carried out no more than once a month after winter dormancy. Here it is important to pay attention to the fact that succulents require a much lower concentration of it than other indoor plants. It is quite easy to care for them, so even a beginner will not have much difficulty in growing succulents.
The emergence of sprouts
Depending on the type of plant, germination time can vary from a few days to a couple of weeks. As you can see below, the sprouts are as small as the seeds, so it will take another week or so of stable moisture before you can let the substrate dry.
Do not forget to remove the plastic that you covered the tray with after the sprouts have emerged. Too much moisture will cause them to rot.


Reproduction using leaves
There are two ways to grow succulents at home. The first is vegetative. It is used when the trunk of the plant is already strong. For divorce, choose the lower healthy leaves. Do not try to get a new plant from a weak, dried out or damaged plant.
When a suitable leaf is found, it is necessary to carefully grasp its base with your fingers and separate it from the stem with smooth swaying movements. It is best to prepare a few pieces, since not everyone will be able to take root. After that, you should spread the leaves in a well-lit place to dry and leave them for about a week. This period may vary depending on how quickly the junction with the stem is tightened.
When everything is ready, you can practically understand how to grow a succulent from a leaf:
- First you need to prepare a suitable place for the formation of the root system. For this, a small pallet is suitable, which should be filled with special soil for succulents or wet sand.
- Then the leaves prepared for reproduction are laid out on it with a tear-off point upward and provide good lighting (without direct sunlight).
- Watering is best done by spraying to avoid rotting.
- After about a month, small pink roots will begin to form on the leaf, which need to be sprinkled with a small amount of soil.
- When the new plant has formed and has its own leaves, you should carefully separate the mother leaf, and then transplant the succulents into a separate pot, matched to the size.
Most popular succulents
The types of these indoor flowers, which are most often bred by plant lovers, can be listed for a long time, because there are more than eight hundred of them. You can select it in size, color, and shape. Most often, flora lovers prefer:
- cacti;
- crassul;
- echeveria;
- aloe;
- Kalanchoe;
- sedum;
- doodles;
- beard;
- lapidaries;
- agave, etc.
How to grow succulents from seeds
This method is more painstaking than the one described above:
- Before planting succulent seeds, you must first prepare the ground. It should not contain microflora, therefore, before sowing, it is necessary to calcine the soil in the oven or microwave, and also add a little charcoal.
- The landing site must be sealed with a transparent cover. You can also cover the seed containers with polyethylene. The room should be well and evenly lit.
- Seed germination occurs at a temperature of 25 degrees.
- Before planting, you need to leave the seeds for a day in a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Due to their small size, when planting, the seeds are left on the surface and lightly sprinkled with soil on top so that they can be seen.
- You need to distribute the seeds at a short distance from each other.
- Germination should take place within two weeks. As soon as the first shoots appear, the lid or plastic must be removed.
- Watering should be done as soon as the soil is completely dry. To avoid decay, a good drainage system must be provided. Pour water in the corners so as not to damage the tiny roots of the succulents.
- After 3 months, the plants will be 1 to 3 centimeters in size.
- Six months after planting, succulents can be transplanted into a separate pot.
That's all. If you follow all the steps on how to grow succulents, you can get a large number of beautiful and healthy plants.
Adenium
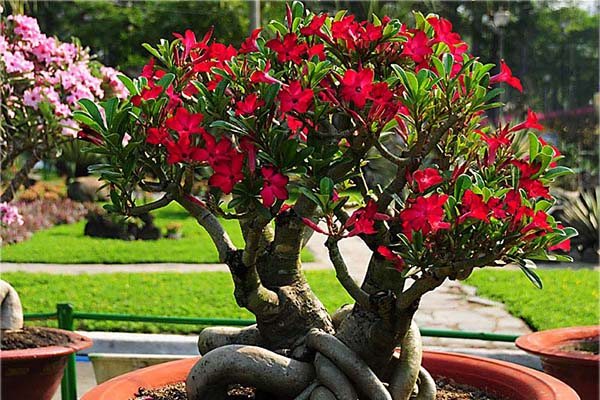


Adenium - flowering indoor succulent
Adenium is a compact, flowering tree. An unusually thickened stem, thick twisted roots immediately attract the eye and give this succulent an original and rather interesting appearance. These plants are in great demand among florists due to their predisposition to the Japanese art of bonsai.
Growing rules
Lighting
This succulent plant is photophilous, so the window sill on the south side will be the best place for it. During extreme heat, it will not be superfluous to darken the lighting a little, since the sun's rays can burn the trunk of this plant.
Temperature
For adenium, whose natural habitat is hot deserts, temperatures of 24-26 degrees are perfect in spring and summer. In winter, the temperature regime should not fall below 10 degrees, otherwise the succulent will die. The optimum temperature will be 14-16 degrees.
Watering
When watering, you should use water at room temperature, and the procedure itself should be repeated only after the soil is completely dry. Adenium, like any other succulent, is afraid of excess moisture.
For more information read Adenium - care and cultivation from seeds
Transfer
It should be taken into account that the root system of these succulents increases in width, so the capacity should be wide. Based on this feature, it is better to choose a container for a plant in light colors so that the soil, and with it the root system, does not overheat. In the process of transplanting with seeds, they should be kept in an epine solution for 6-8 hours, and then planted in a mixture of vermiculite and sand. The first shoots will appear in about 7-10 days. When propagating these succulents using cuttings, one should take seriously the concentration of moisture in the soil, because with an excess of water, the cuttings will simply rot.
How to water?
Home Care and Watering Succulents: Cacti and other succulents need very little watering. They have severely limited water evaporation due to the transformation of leaves into thorns. The fabric accumulates moisture and allows them to survive the absence of water. Therefore, the golden rule applies here: less is better than more. "
Crops and young plants should always be kept moist, even in winter. However, then they need a warm and bright place. Small-rooted species of succulents growing on humus also need to be moistened to prevent drying out. Those succulents that need a dormant period should stand in a cooler place during this time than during growth.
Watering domestic succulents depends on the wintering location. During warm wintering, they are watered only once every two weeks, during cold wintering, not more often than once a month, and some species are not watered at all. During winter dormancy, plants should not be sprayed. If many plants in pots were placed in a barrel filled with plant substrate, then only the substrate needs to be moistened to care for succulents. Depending on the type, cacti are watered little until about the end of March, even if the plant is very embarrassed at the same time. When the first flowers are formed, the growth period begins. Watering is increased, and succulents are again put in a warm place. In the summer, they are sometimes fed with fertilizer for cacti, for example, N. P. K = 4 8. 6.
Pot selection


To plant a succulent, you need to take a pot that is 2-3 centimeters wider than the previous one. You should not use flowerpots "for growth", as cacti grow very slowly. In addition, the transplanted flower will not build up green mass until it fills the entire earthy ball with roots.
For spherical cacti species, the flowerpot should exceed the flower diameter by 2-3 centimeters. When planting columnar cacti, the volume of the pot should be no more than 3 times the volume of the roots.
Which pot to choose: ceramic or plastic? In ceramic dishes, it is easier to maintain a constant temperature, the earth dries out faster, which prevents it from stagnating. But the roots often stick to the wall, which is why they are injured during transplantation. A plastic container will not protect against temperature changes, it can crack from pressing roots, but it is easy to wash and can be cut during transplantation, which will ensure the safety of the root system.
Succulents are planted in low, wide pots. But if the bush is too large, then they take an ordinary flowerpot.If another plant has previously grown in it, then the pot should be disinfected to prevent infection.
Transfer
Home care for succulents is not complete without a transplant. However, succulent plants are transplanted only when the pot becomes small or when the substrate deteriorates (about once every 2 to 4 years). Spring (the end of the dormant period) is more suitable for transplanting domestic succulents. Let the earth dry out a little. Put on sturdy work gloves, turn the plant over and remove the pot. Now gently shake the waste soil, remove the dead roots and inspect them, there are no pests or diseases. The pot should be one or two sizes larger, depending on the plant. First pour a drainage layer into it, and then fill it with a moist plant substrate up to the root collar. After that, pause watering for several days. Plants that form flowers are transplanted only after flowering. Mineralized soil is used as a substrate, in which there is a lot of potassium, relatively little phosphorus and very little nitrogen. Stores sell ready-made soil for cacti, which is not suitable for all epiphytic succulents. They need an epiphytic substrate (soil for orchids).
Succulent roots are divided into two groups:
It is not difficult to make cacti bloom at home if they winter properly: in a cool place with lots of light and almost no watering
The nesting torch cactus (Trichocereus spachiamus) reaches two meters in height. The minimum temperature for it is 8 ° C
Planting seeds
To give a complete picture of growing succulents from seeds at home, we must show you what seeds look like. They are really tiny... Any gust of wind can blow them away, so it is very important to land in a protected location. The easiest way to plant seeds is to place them in the palm of your hand and gently pour the seeds into the tray.


Most importantly, make sure there is a small space between the seeds. Then lightly tap the bottom of the tray on a flat surface. By doing this, you can ensure that any seeds that have not adhered to the sand have found their place. Cover the tray with plastic wrap or a bag... This is very important as most seeds will not germinate if there is not enough moisture in the air.


Reproduction
For reproduction, cacti and other succulent plants produce very beautiful and varied flowers. In milkweed, the petals are reduced. Nectariums produce a lot of nectar by luring insects. The Senecio and Othonna species belong to the Asteraceae family, and they even have tubular and ligulate flowers.
After pollination, fruits and seeds are formed (sometimes even under indoor conditions). The seeds are spread in a variety of ways. Some seeds are equipped with flight devices so that they can fly with the wind. For seeds, the characteristic waterproof shell and lightweight fabric spread along with the streams of water, which allows them to float on the surface. Small hooks on the seeds allow them to cling to birds and animals. Some fruits (for example, in Cereus, Mammillaria and Opuntia) serve as animal food. Undigested seeds enter the soil with animal droppings. Euphorbia catapults its seeds when their fruits burst.
Foreword
As a living organism, a person represents a single ecosystem with the world of animals and plants, constantly draws vital energy from it, satisfies various needs and aesthetic hunger. It is in this indissoluble unity that the community of all living and nonliving that is on Earth is contained. The world of plants is large and extremely diverse, for each person there will be found something in it that will find a response precisely in his heart. And it doesn't matter what kind of plant it is - an exquisitely blooming orchid or a succulent like a thorny ball.The main thing is the feelings that a person will experience while nursing him: satisfaction that the plant is healthy, joy when new leaves and shoots appear, delight and pride at the thought that you have grown a small but living flower.
This book is for those who are partial to plants that amaze the imagination with their diversity and ability to survive in the most difficult conditions. This book is about succulents.
Diseases
If home care with succulents is violated, then they become susceptible to diseases and pests.
The most common harmful insects are mealybugs and root aphids. Wax threads or grains in worms look like small cotton swabs. They sit between the veins and in other dry places. If insects attack, try knocking them off the plant with a jet of water. If it does not help, then you will have to resort to insecticides. Root aphids attack the roots and can kill the plant. Here you will have to renew the land and treat the roots with chemistry.
For prophylaxis, before the scale insects, scale insects revive in spring, or red mites multiply quickly, you need to inspect the plants and immediately destroy the pests. As a prophylaxis against mold fungi, at home you need to create optimal conditions for plants to grow. To care for succulents, diseased plants are isolated, exposed to the sun and monitored for dryness and sufficient fresh air. Plants with viral or bacterial diseases should be removed as soon as possible so that they do not infect other flowers. The light yellow color of young shoots is often the result of too dark a place. Intense sun exposure results in a red coloration. Loss of roots in succulents indicates too much watering.
hint: more capricious plants for the captured grower: Gasteria armstrongii, Haworthia maughanii, Haworthia truncata and Haworthia setata.
Why do they die with you?
Do not plant succulents in purchased peat-based soil and water often.
The main enemies of succulents are dampness and darkness.
... They cannot grow on shady windows or away from windows and the sun. More precisely, they can, but they will be elongated, weak, frail plants.
Succulents die when they are planted in purchased land for cacti (unfortunately, the soil for cacti in the store is also based on peat, which succulents do not like), watered abundantly, put in the shade, watered regularly in winter when kept on cold windows (forgetting about wintering and decay of roots in damp cold soil). In such conditions, they do not survive.
Plant families with succulents
Cactus (Cactaceae, about 2000 species) are mostly devoid of leaves, stems of succulent plants. Their characteristic spiny areoles (modified short growths).
Euphorbiaceae (Euphorbiaceae, about 8000 species) contain milky juice. Stem succulence is found in relatively few species of American cacti from arid regions.
Tolstyankovs (Crassulaceae, about 1400 species) are a purely succulent family, mainly of succulent letters and less often with a succulent trunk. Distributed mainly in South Africa, Mexico and the Mediterranean. A typical feature of most species is a clogged shoot.
Agave (Agavaceae, about 400 species) are recognized by the typical rosette arrangement of succulent leaves and inflorescences in the form of a panicle or brushes. Several years and even decades pass before flowering in agave. After that, the mother plant dies off.
Liliaceae (Ltiiaceae) genera (sometimes an independent family) with succulent leaves - aloe, Haworthia and Gasteria. They are originally from Africa.
Succulent orchids (Orchidaceae) with fleshy false bulbs and thick leaves living in epiphytic, low-water places.
An important feature of cacti and other succulents is their drought-tolerant leaves and stems.Stem succulent plants have a thickened shoot axis with a specialized tissue that accumulates water (cacti, milkweed). Their leaves are often reduced or completely absent. Sometimes they turn into thorns (for example, in cacti, not into thorns, as they are mistakenly called). These leafy thorns are actually sharp, reshaped leaves that serve to ward off moisture evaporation and herbivores.
Leafy succulent plants, on the other hand, strengthen their leaves as an organ that stores vital moisture. Their leaves are thick and succulent (eg in agave, aloe, live stones).
Eonium disc (Aeomum tabuliforme) needs sun and fresh air all year round. Plate-like rosettes are made up of 200 individual leaves. Propagated by seeds.
Watering
To highlight how tiny they are, see the sprout and finger photo. That is why be careful - do not wet the soil too much... The best way to grow a healthy plant is to wait until all the sand is dry and then water it abundantly. Make sure the soil is completely dry between waterings.


To water the flowers without damaging them, you need to pour water into the corners of the tray. Check that the water drains from the drainage holes: the sand should be wet, but the plants should not sit in the water. You can move the tray to the sink so that all excess moisture is immediately drained.
Sand must dry between waterings... This will simulate the conditions of their natural habitat - the desert. After a few weeks, the sprouts develop into small plants. But if you are tempted to transplant them into another container, it is better to wait and let them grow even more.


If you manage to keep them for three months, you will have a whole group of small Succulents. Please be aware that these are desert flowers... Therefore, they do not grow as fast as other plants.


You can grow a whole family of plants. Perhaps it makes sense to start breeding them? People will be happy to buy them, because many believe that succulents cannot be grown from seeds. In three months, flowers can reach sizes from 1 to 2.5 centimeters.
It may sound slow, but there is an explanation for this. In the area where these plants grow, there is low humidity and a harsh climate, as well as, in most cases, a small amount of nutrients. They had to adapt and use limited resources to grow.
They have adapted by developing thick leaves and stems that withstand harsh climates and maintain a slow but steady growth rate. There are also positive aspects to this: they do not need frequent transplants... Therefore, an adult plant can grow in one pot for decades (if you care for it, of course).
For more information on planting various groups of succulents, see the video below:
Varieties and types
Bromelієvі see sukulentnih ROSSLYN
There are Bromeliad species that have become succulent due to their dry habitat. We present three such rare succulent species:
Abromeitiella brevifolia comes from southern Bolivia and northern Argentina and grows on rocks there. Special parenchymal tissue is used to store water. Thus, the plant overcomes the drought period. During the dormant period, it does not need watering at all.
Hechtia argentea from the Mexican mountains appears silvery white due to the suction scales. It feeds on a humid atmosphere through them.
Dyckia fosteriana is native to Brazil and grows on rocky ground. The plant needs a lot of light and high humidity.
Succulents often fail to boast spectacular blooms. But the incredible variety of their forms makes collectors sigh that the window sill is not limitless.
Species with an unusual color of the stem and leaves - various shades of gray and blue, and sometimes almost white - are especially attractive. Difficult growing conditions in their homeland forced them to "protect" in this way from too bright aggressive sun and excessive evaporation of moisture.
Mealy and felted blue succulents
This group of succulents can be roughly divided into "mealy" and "felt". The former are distinguished by a delicate coating on the epidermis.You need to handle it very carefully - it is erased from the slightest touch, and the decorativeness of the plant inevitably suffers from the imprints that have appeared. These succulents are never sprayed, in no case wiped, and the dust is simply blown off gently. When transplanting, try to hold the plant by the trunk in the area of the root collar. Typical representatives of "mealy" succulents are wavy cotyledon (Cotyledon undulata) and oviferous pachyphytum (Pachyphytum oviferum).
Felt protection is more stable. A kind of cotton-fibrous coating of the epidermis does not suffer so much from getting wet and touching (but it is better not to abuse it), therefore, plants can be handled more boldly and placed in accessible places without fear of accidental damage to fragile beauty. Examples of "felt" succulents are the Addoensis lancet (Senecio scaposus v. Addoensis) and the haworthii (Senecio haworthii).
Succulents are those wonderful plants that are interesting to look at in winter, and for which you need minimal maintenance in the summer when you go to the country or on vacation. These are plants in arid places, they are unpretentious and always have an unusual appearance. Succulents include those plants in which the leaves and stems are dense, fleshy, "juicy". The most common representatives of the middle lane are cacti, agave, fat women, aloe. Plants with delicate, fragile, soft shoots are not succulents.
The main advantage of succulents over other flowers is the ability to grow in the poorest soils in the absence of moisture. Such conditions can be compared to a desert. Why is this happening? Due to the ability to accumulate moisture in leaves and shoots, these plants draw out the smallest drops of water from the soil and slowly consume them in unfavorable dry times. The root system is located close to the surface, after the soil dries out, the roots die off, and the rudiments of young roots immediately start growing when watering. A thick layer of epidermis in the stems and leaves serves as protection from the sun, which evaporates moisture from the plants.
Conditions for growing succulents and caring for them
Home-grown succulents require almost the same care conditions.
1. The soil in which succulents thrive should be light and infertile. The ideal composition would be a mixture of sand, turf and leafy soil, taken in equal proportions, or a mixture of garden soil with sand. When planting, be sure to drain with crushed coal, pebbles or expanded clay. Use a ready-made substrate only one that is intended for growing succulents, but without peat, as it retains moisture inside, which is detrimental to any succulent. Use coarse sand, do not ignite or process with potassium permanganate. If you plant succulents in pots, then in clay or plastic of a small diameter with holes in the bottom.


2. Succulents - lovers of bright light, from this they grow well. If there is little natural light, then install additional lighting. Succulents, in which the color of shoots and leaves is dark green, are highly resistant to a lack of light, but even they will eventually start to wither and hurt. They also do not accept sudden changes from the shadow to the bright sun, burns of the leaves are possible.
3. Watering. Here, everything is extremely simple; a lack of moisture is better than an excess of it. Such plants are watered in the summer 2-3 times a week as the soil dries up, and in winter no more than 2 times per season. Pay attention when watering how the water flows through the soil, it should saturate it completely, and not go through the passages to the drainage holes. Water the succulents with soft room temperature water. Do not spray.
4. Succulents are fertilized with phosphorus-potassium fertilizer. It is better not to use nitrogen. Top dressing should be weakly concentrated and no more than 2 times a month.
five.In summer, succulents grow actively at high air temperatures, they make beautiful ones. In winter, it is better to lower it to 8-10 ° C, so that the plants in the warmth do not stretch out from lack of light, but stay at rest from November to March. In winter, plants are usually placed on a balcony or veranda, away from radiators.
6. How to transplant succulents. Many plants have a thorny trunk, so when transplanting it, you need to wrap it with paper, and holding on to the ends, pull the plant out, transplant it into a new pot and cover it with new earth. Do not water immediately to prevent the roots from rotting. Young specimens are transplanted every year, changing the pots to a larger size. For adult plants, once every 3 years is enough.
7. Diseases. Rot is a serious problem for succulents. When the plants are cold, the rot is fungal, and when it is warm, it is bacterial. They appear as mold or stains. Treatment consists of a surgical method, remove all damaged areas to healthy tissue and treatment with Vitaros, Fundazol, Topaz. Fitosporin as a treatment for developing rot can not cope. As a preventive measure, avoid dampness in the substrate, let it dry out to the end, so that there is no room for bacteria to develop. - this is a good way to grow a new healthy plant than to have an ugly succulent shape after an illness. But there are others.
Succulents are installed in rooms to humidify and absorb harmful carbon dioxide. They become the center of bonsai and mini-gardens using driftwood, pebbles, wood.


Succulents at home
Succulents are easy to keep at home, they are quite unpretentious in care. Without exception, all succulents require a lot of light, so it is better for them to choose the sunniest southern window.
Succulent care in winter
In winter, when there is little light, succulents are watered very rarely, and only so that they do not stretch too much. In winter, it is advisable to place them closer to the glass. And not only because it is so brighter for them. It's just that near the glass itself, the air temperature is slightly lower than in the room. You can even shield the plants from the warm air. Winter maintenance temperature for succulents should be low, about +10 +12 ° C. Such a low temperature of keeping is a condition under which some plants, such as cacti, will bloom.
Summer care for succulents
In early March, some succulents are transplanted or trans-shipped into new soil. The earthen mixture for succulents should be water and air permeable, moderately nutritious, because in nature they grow in sandy soil. Therefore, at home, a mixture of equal parts of leafy earth, humus of their bark and sand is suitable for succulents.
From spring to autumn, succulents need regular watering and feeding.
Reproduction of succulents
Succulents reproduce easily, many of them even by leaf cuttings. These are sedums, Kalanchoe, echeveria, pachyphytums. Even a small leaf that has fallen from a plant into the ground in a pot has every chance to take root and give new shoots. Stem cuttings can propagate all kinds of sedums, for example, Morgan's sedum, fat woman, aloe, slipway.
Some succulents produce side shoots that must be carefully separated and planted in the sand for rooting. But you don't need to put the cuttings of succulents in water, they can quickly rot. Among succulents, viviparous plants are also found, for example, bryophillums.
Which succulent plant to choose for growing?
There can be no recommendations here - a matter of taste. You can choose a slender spurge, very reminiscent of an old candelabrum. Or euphorbia brilliant, which was nicknamed "the crown of thorns." All summer it blooms, and in winter it will attract your attention with spreading thorny branches covered with light green leaves at the ends. Spurge brilliant is a fairly large plant and will require a lot of space, but you can also look for compact varieties.
How do you like succulent sansevier? She has gorgeous cylindrical leaves. A blooming epiphyllum cactus with wide leaf-like shoots will also look very impressive in the room. You can also pick up ampelous succulent, for example, Morgan's sedum, which looks very beautiful in hanging vases or on high shelves.
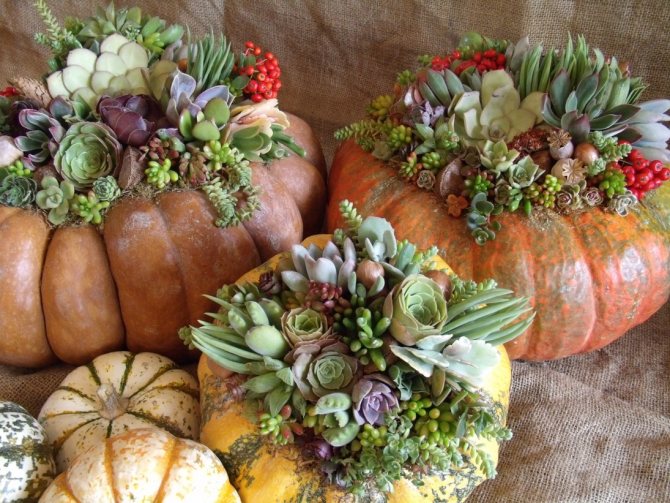
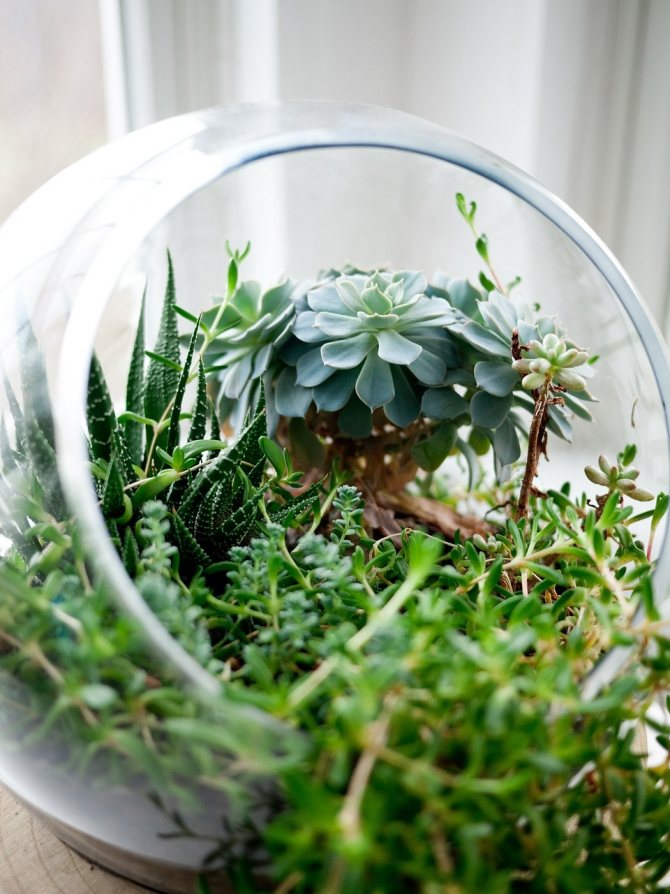
Compositions of succulents
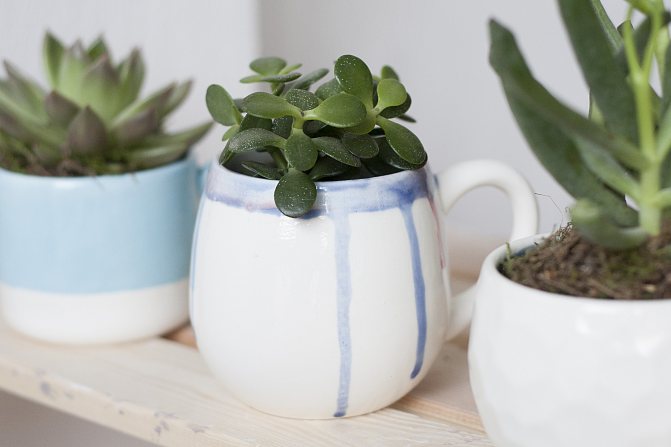
Succulents in a room can be grown in different ways: you can plant each plant in a separate pot. In this case, you can use square pots to save space.
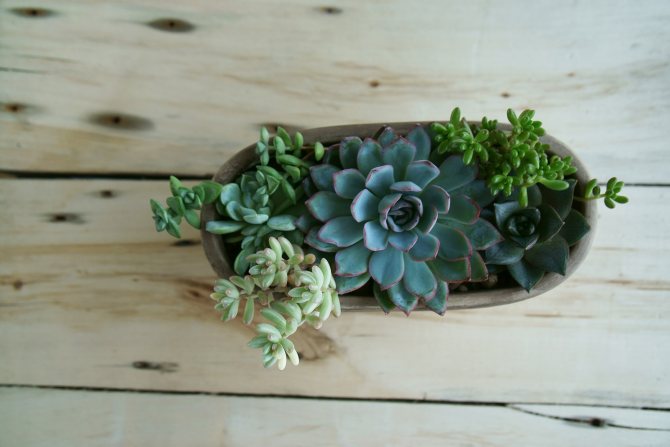
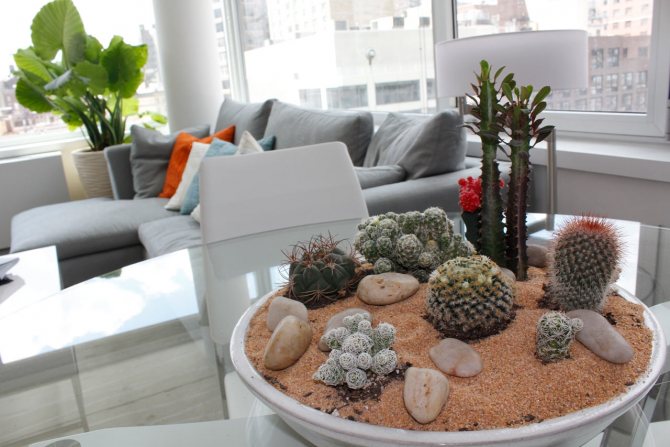
But, if we are to breed succulents, it’s better with a whole group. It is in the composition of different and such dissimilar species that all the originality of these plants, unusual for us, is manifested. For this, miniature succulents are taken; quite a few, up to 60-70 species can be placed on one windowsill.
It is very interesting to create a kind of "desert corners" by planting several plants of various configurations and colors together in ceramic or plastic dishes, complementing them with one or more uneven stones.
It is advisable to sprinkle the surface of the earth in the dishes with sand or fine gravel. The height of the bowl should not exceed 1/3 or 1/4 of the height of the tallest plant.
To compose a composition in a flat ceramic dish, you can take a large rounded cactus, several lithops, echeveria. Plant next to Gasteria or Hawortia with a beautiful rosette. In such a composition, pachyphytum with thick, rounded bluish leaves resembling grapes, as well as low plants with creeping stems - sedums, monantes, lymphatic fatty, - which hang their shoots from the edge of the bowl, will be appropriate. Such a composition of succulents will be the envy of all your friends!
Description
Sedum is a short, herbaceous succulent with a life cycle of several years or one to two years. Stonecrop varieties can be divided into two categories: winter-hardy, ground cover and tropical, thermophilic, grown in our area as a houseplant.
The stems are dense, up to 20 cm in length. Round or oval leaves are attached to them in a non-petiole way. The foliage can be either completely flat (disc-shaped) or swollen, resembling small cylinders. The leaves are arranged in whorls or opposite to each other. Their color can be either pinkish or green with a grayish or bluish tint. The color of the foliage depends not only on the variety and variety, but also on the natural conditions in which the plant grows: shade or direct sunlight, the wind blowing over the place, the composition of the soil.
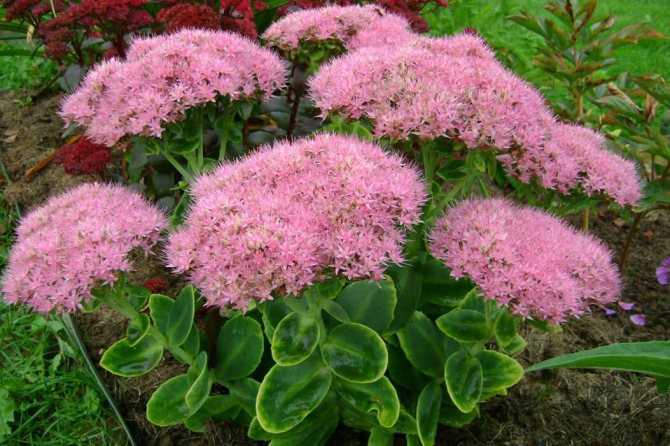


In the summer or autumn period, the sedum blooms with dense inflorescences, resembling small umbrellas, which include star-shaped bisexual small flowers. They are painted white, blue, red or yellow. The bent petals closer to the center form a narrow tube, in the center of which there is a bundle of thin and long stamens, as well as an ovary column. The flowers emanate a pleasant, delicate aroma that attracts pollinating insects. This succulent is an excellent honey plant.
The photo shows how sedum goes well with many other garden plants, for example, with juniper, petunia, alissum, cornflower, sanvitalia, platicodon. These plants look most advantageous in one composition with rocky hills. The main advantage of sedum is its ease of care and cultivation. It also attracts and captivates children very quickly, for this reason a group of succulents is often used for landscaping schools and kindergartens.


Temperature


How to care for succulents at home? At what temperature will they grow better? They tolerate changes well. This is especially true for changes in the daytime and at night. In the daytime, the optimum air temperature will be +25. 30 degrees, +15 at night. 18. In the warm season, the plant can be moved to a terrace or balcony.In winter, you can keep the culture at a temperature of 15-18 degrees. At night, in the cold season, a decrease to 13-15 degrees is permissible.


Succulents rarely suffer from pests. However, with improper care, nematodes and thrips can start in the roots of plants. Similar problems arise in cases where the soil or filler was taken from the summer cottage and did not undergo the heat treatment procedure. There are two ways to correct the situation: to propagate the plant with the tip or to transplant the plant with complete cleansing of the roots from the previous soil and their disinfection.
Let's take a closer look at this aspect. How to care for succulents at home? What problems can arise when growing? Novice growers are often faced with root rot. This disease can destroy the entire plant. In order to prevent the formation of rot, it is recommended to observe the watering regime. Also, when transplanting into the soil for a plant, it is imperative to add charcoal.
Often, the fungus Botrytis forms on succulents. A clear sign is the appearance of brown spots on the leaves and shoots. In this case, to get rid of the problem, it is necessary to cut off the affected leaves. It is also recommended to leave the soil dry for a couple of days and reduce watering. After that, the plant should be treated with a fungicide solution.
The defeat of the ervinium bacterium cannot be confused with anything. In addition to brown spots on the leaves, it also causes an unpleasant odor. In order to cure the plant, you will have to completely cut off the affected parts. It is also recommended to reduce watering and treat the flower with potassium permanganate solution. For the prevention of succulents, it is recommended to periodically check for brown spots and rot.
A greenish or reddish bloom may indicate the appearance of a fungus of penigillosis on the plant. To combat it, it is recommended to treat the affected parts of the plant with an alkaline solution or potassium permanganate.
If the plant died without any external signs of disease, then the reason most likely lies in the infection of the root system by nematosis pests. If at the same time the culture has healthy leaves, then you can try to multiply them. The dead flower should be thrown out along with the ground. The pot should then be thoroughly disinfected. The next time you plant a succulent, be sure to add charcoal to the soil. You also need to pay attention to the watering regime.
Burns can sometimes be seen on a newly acquired flower. They appear due to non-compliance with growing conditions. Most likely, the flower in the store stood in the open sun or, after hibernation, was immediately exposed to the window. In this case, it is necessary to limit the effect of sunlight on the plant and gradually accustom it to it.
What is succulent
general characteristics
Succulents (from lat. succulentus
- succulent) - perennial plants with fleshy juicy leaves or stems. This group includes representatives of different families, similar in appearance and biological characteristics. Their common features were developed as a result of adaptation to certain natural conditions. And these conditions are as follows: low precipitation and uneven distribution (periods of rains and droughts), bright sun and strong solar radiation, high dry air, no shade, poor sandy, clayey and stony soils, a large difference between day and night temperatures - in average 30 ° C. Dry periods can last for a long time, and then the plants are in a state of inhibited growth. Then comes the rainy season, with more than a third of the annual rainfall during a rainstorm alone. Evaporating quickly from the hardened soil surface, water penetrates only a few centimeters deep. Due to the special structure of the root system, succulents make the most of this moisture.During the rainy season, they begin to grow and bloom rapidly in order to have time to pollinate flowers and set seeds before a new drought begins. Individual caudexform plants increase their weight up to several kilograms during this period. One of the main features that allows succulents to exist under conditions of moisture deficiency in soil and air is a powerfully developed aquiferous tissue. Large cells of aquiferous tissue store a supply of water that the plant has accumulated during rains, fogs and dew. Evaporation of accumulated moisture occurs very slowly, since plants have protective devices for its preservation: cell sap contains mucous substances with water-retaining properties; the surface layer is covered with a thick wax-like cuticle film and a waxy bloom; the stomata, through which evaporation occurs, are deeply immersed in the tissue of the leaf or stem and are open only at night, etc. Due to these features, succulents consume water very slowly and remain viable for a long time. Having a supply of water in the body and spending it as needed, succulents seem to switch to an autonomous water supply, which allows them to exist in a hot, dry climate. The lignification of the stems is so insignificant that some succulents have received the name "oil tree"
(Cotyledonpaniculata),
"Greasy tree"
(Portulacaria afra),
because their thick "trunks" are easy to cut with a knife - like butter.


Wilcoxia schmolli
It is interesting!
There is a known case when a cactus - a giant carnegia - was not watered for 6 years, during which time the plant lost only 11% of its mass and survived.
Depending on the type of water-storing organ, succulents can be conditionally divided into three groups:
Leafy succulents
(agave, aloe, echeveria, crassula) - plants in which the main water-storing organ is thickened succulent leaves. Their typical shape is a rosette of thick leaves (lithops, conophytums). If the plant receives enough moisture, its leaves unfold in a horizontal plane, and if it tolerates drought, the leaves curl up so that they adhere to the stem and overlap each other. This reduces the evaporation of water.
Lithops
Rhipsalis
Stem succulents
(cacti, milkweed, stocks) - plants with a juicy stem. Their tissues contain chlorophyll, which allows the process of photosynthesis and evaporation. Many stem succulents also have succulent leaves, but they grow only during the rainy season, and fall off under unfavorable conditions. Often they are reduced or modified (into thorns, thorns). And in many stem succulents, the surface area of the stem is increased due to ribs, tubercles, or papillae.
Sometimes the stems and leaves serve as reservoirs for water at the same time, like in wild plants and in some begonias.
Borzikactus


Peperumia
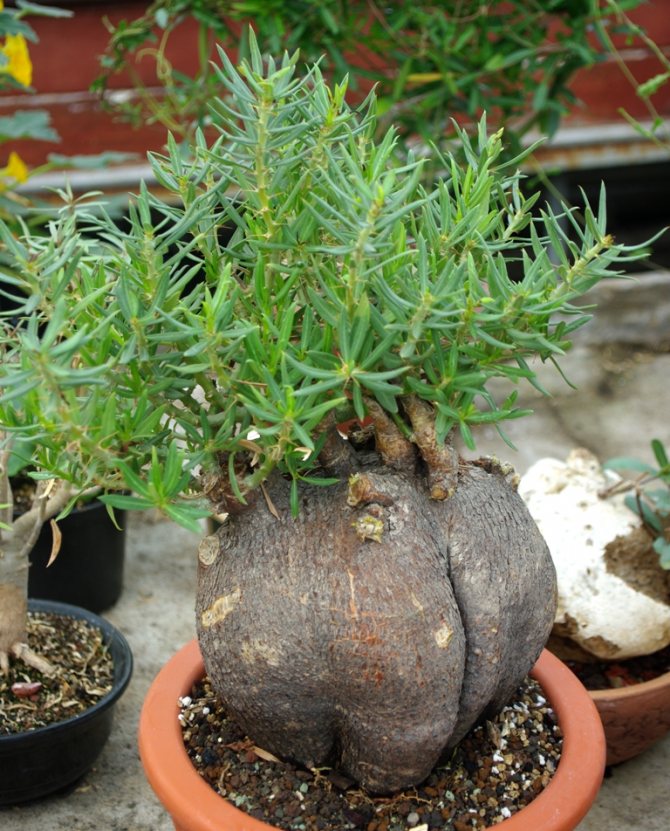
Root or caudexform succulents
(adenia, cyphostema, adenium) - plants that form caudex - a thickened part of the stem or root. Caudex (lat.
caudex
- trunk) is a water-storing organ, during the growing season it significantly increases in volume (while reaching from several centimeters to several meters in diameter). Such succulents often look like a liana or a vine, the leaves are not juicy, they fall off during the drought period, and then the plant can only be found by dry branches sticking out of the ground. Caudex can also appear as a very thick stem of a treelike succulent, reaching several meters in height.
Jatropha
In most foreign sources, all stem succulents are called "caudexform", or "caudex". However, some authors distinguish between caudexform (forming a turnip root) and pachycal, that is, "thick-stemmed" plants. It is sometimes difficult to determine where the underground section ends and the wellbore begins.
Geography of distribution
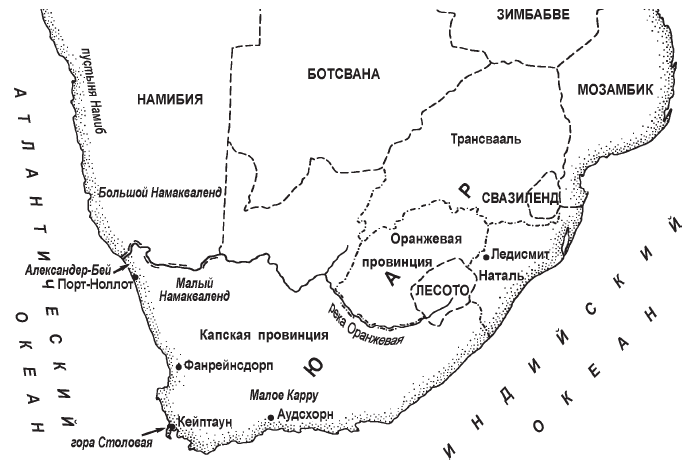
If America is primarily the homeland of cacti, then Africa ranks first in the variety of succulents belonging to different families. Plants grow in South African deserts and semi-deserts, from 18 to 30 ° S latitude.

South Africa is home to numerous succulent plants


Overgrown stocks. Uganda
So, widespread cotyledons, bastards, otona, mesembryanthemums, many species from the Grimaceae family, succulent milkweed make up the flora of the Namaland Desert and the Namib Uplands. The Karoo semi-desert is rich in mesembryanthemums, staples, milkweed, wildflowers and other succulents growing between stones. Of the 100 species of aloe, more than 70 are found in South Africa, mainly in the steppe and desert regions of Natal and Transvaal. Here, in terms of the number of species, the second place among succulents is occupied by fat women, represented by forms amazing in their adaptability to growing conditions in a rocky desert. Many of them are no more than 3-10 cm in size with leaves so tightly pressed against each other that the whole plant seems to be a solid mass. Fat women are able to remain without water for several months. Some euphorbia have acquired the shape of a ball, others have tuberous stems, almost entirely immersed in the sand (euphorbia is edible). There are about 80 types of stocks growing in South Africa. The Cape is an extension of the vast Karoo and Kalahari deserts to the north of it. Annual precipitation here is 60–70 cm. Most of it falls in winter: May - September. Summer - from November to March - is almost devoid of moisture. A characteristic feature of the Cape flora is the abundance of bulbous and tuberous plants from the families of liliaceae, amaryllis, mesembriantemic, etc. There are cactus-like milkweed, aloe, and stapelia.


Landscape in South Africa
Many beautiful and amazing succulents have come to us from the Canary Islands - from the families of Fat, Liliaceae, Compositae, etc. Numerous agaves, echeveria, sedums grow in the stony deserts of Central America. Succulents found their second home in the Mediterranean countries - in Spain, Italy - to the Balkans. Agaves, aloe, milkweed and other succulents can be found here not only in the gardens but also in the wild. They were brought here hundreds of years ago.


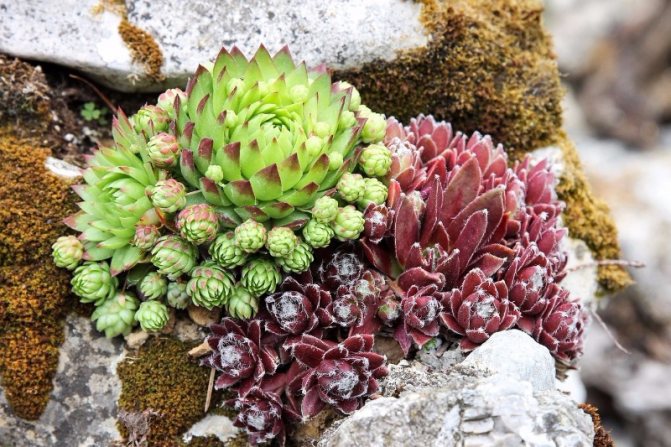
Rejuvenated
The northernmost representative of succulent plants, Rhodiola rosea, is found on the islands of Greenland and Svalbard. And on Tierra del Fuego Darwin's tephrocactus grows.
In our latitudes, there are very few succulents - mainly small herbaceous plants from the genera sedum, rejuvenated, as well as from the family of Euphorbia and Tolstyanka.


Rocky slides
Succulents are cultivated here as special deciduous and ornamental plants for cool and warm rooms, verandas and balconies. In summer, they are planted with rocky gardens and hills.
Using
At home, succulents grow in large quantities and give a unique originality to the landscape. Many are widely used by humans as fodder, technical, medicinal and food. For example, in South Africa, the leaves of many species of mesembriantemum quench thirst. Euphorbia edible, or curved, serves as a good feed for livestock. Caralum and Indian ceropegia are consumed as vegetables. Fokkia is edible onions. Testudinaria from South Africa - a plant with a flat massive aerial tuber - is called Hottentot bread. The natives eat the sweet fruit of carpobrotus, known as figs of the Hottentots. And if you cut out a flower bud from an agave, then sweet juice will begin to flow into the formed hole, which should have gone to the formation of a peduncle, flowers and fruits. The Spaniards call this juice honey water (aquamiel), as it contains up to 10% sugar. It is released over a period of eight to ten months until the leaves dry out. During this time, up to a thousand liters of juice is collected from each plant.It is fermented and intoxicated drink - "pulque" is obtained. In modern Mexico, agave stalks and sour leaf flesh are harvested and eaten. And alcohol is distilled from the roots and stems. In East Africa and on the islands of the Philippines and Java, a special hemp is obtained from sisalan agave fibers - sisal, from which very strong twine, ropes, ropes, nets, shoes, bags are woven. The best Indian lassos are also made from the elastic and gliding fiber of agave. The Aztecs made paper from the skin of the leaves, covered the roofs of huts with dried leaves, and used thorns instead of awls. Dregean spurge from South Africa contains 17.6% rubber, which is used in industry. Some especially thorny euphorbia is planted for the purpose of creating impenetrable thorn hedges.
It is interesting!
Euphorbia curved is even called "Beeskraag", which means "bull strength". Tired bulls, having eaten this plant, can move quickly again.


Collection of milkweed
Typical landscape with agave
Succulents also have medicinal properties, which leads to their widespread use in medicine. Aloe tree
(agave) is one of the most common indoor plants. Its medicinal properties have been known since ancient times (over 3 thousand years). Sabur is made from aloe - a condensed juice obtained by evaporation. It contains organic acids (succinic, acetic, coffee), pectin, phenols, anthraglycosides, resinous substances, essential oils, enzymes, vitamins, phytoncides. It also contains 20-25% aloin glucoside. Aloe-based preparations are officially registered. According to the method of Academician Filatov, an aqueous extract from the leaves is used in ophthalmology. In official medicine, juice from aloe leaves, aged under special conditions, is used to prevent and treat skin lesions during radiation therapy, oily seborrhea.
It is important!
Aloe is a reliable assistant. If we are in the same room with this plant, then we feel freshness and do not succumb to nervousness. This plant also stimulates the human immune system.


Agave fiber braids
Aloe juice is widely used in folk medicine: externally - as a healing agent in the treatment of trophic ulcers, abscesses, burns, phlegmon, eczema, lupus; inside - in the treatment of stomach ulcers, pulmonary tuberculosis, as a laxative for constipation. It should be noted that aloin does not destroy tubercle bacilli, but it helps to increase the overall resistance of the body. In China, it is used in the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases.
Aloe juice is also widely used in the cosmetic industry - it is part of shampoos, creams, gels, etc.
Most often grown aloe tree (Aloe arborescens).
But A.
vera, A. ferox,
A.
succotrina,
A.
saponaria,
A.
obscura,
A.
barbadensis
and some more types.
It is interesting!
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration in the United States (NASA) found that aloe is a plant that is highly effective air purifiers.
Aloe cream
Aloe vera
American agave
(Agave americana)
in its pharmacological properties it is close to aloe tree. It is used as a disinfectant, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic and expectorant. Whole leaves, previously peeled from the skin, are applied to wounds and abscesses, used for sciatica, rheumatism and other joint diseases. Fresh juice, infusion or powder is recommended for diseases of the lungs, stomach and liver.
Tincture of American agave leaves is used to treat rheumatism by rubbing, while there is a rush of blood to the affected area.
On our windowsills you can often see Kalanchoe daigremontiana (Kalanchoe daigremontiana).
However, the most pronounced medicinal properties are possessed by
Kalanchoe pinnate (Kalanchoepinnata),
which is also used in official medicine - the preparation "Kalanchoe Juice" is prepared from it. Preparations based on it have a hemostatic, bactericidal, anti-inflammatory effect, contribute to the rapid cleansing of wounds from necrotic tissues. In official medicine, juice is used to treat trophic ulcers, non-healing wounds, burns, bedsores.
Agave
In folk medicine, the juice of fresh Kalanchoe leaves is widely used to treat abscesses, skin diseases, burns and fistulas. The juice is effective for tonsillitis, periodontal disease and stomatitis.
It was found that Kalanchoe juice not only destroys bacterial infection, but also exhibits antiviral activity. It is used for a cold and for the prevention of influenza (two drops of juice are instilled into each nostril twice a day).
Deciduous is a medicinal species milkweed (Euphorbia lophogona)
and some others. In folk medicine, it is used to treat skin diseases and as an antiseptic. The plant sap removes warts and calluses. Also, these plants are used to treat snakebite wounds, to fight intestinal parasites.


Kalanchoe
Warm juice from the leaves sansevieria
buried in the ears to eliminate pain. A decoction of the plant is used against itching and scabies. In Africa, the roots and leaves of certain species are considered an abortifacient. They are also used for sexually transmitted diseases, convulsions, general weakness and impotence. Rubbed leaves and juice from them help with ulcers. The smoke from burning leaves relieves headaches. The underground parts are considered stimulant and tonic.
Hoya
And the leaves hoya
used to accelerate the maturation of boils and carbuncles.
Sedum
used in medicine for the treatment of epilepsy, for the treatment of abscesses and wounds. Sedum caustic
(Sedum acre)
It is used to treat tumors, burns, open wounds, heart pain, hemorrhoids, hypotension, malaria, and to remove warts.
As raw materials for traditional and official medicine, two types of stonecrops are used - caustic and large (Sedum acre, Sedum maximum).
From the latter, in official medicine, an aqueous extract is produced under the name "Biosed". This drug belongs to biogenic stimulants. It is used as an additional agent that stimulates the processes of metabolism and tissue regeneration in ophthalmology, therapy, surgery and dentistry. Fresh detailed leaves are applied to calluses, burns and purulent wounds. Fresh or dry herb poultices soothe joint pain in rheumatism and colds.
It is interesting!
A plant like the bastard has a mild invigorating effect. It dispels depression and apathy. Under the influence of this plant, partners who have cooled to each other can, for example, revive their feelings.
Sedum
Fat woman
And in the plants of the family tolstyankovy
discovered flanoids, helping in diseases associated with violations of the strength of the walls of blood capillaries. There is also information about the bactericidal and antiviral effects of fatty juice. For example, the leaves of the fatty purslane
(Crassulaportulacea,
"Money tree") is recommended to chew for sore throat, sore throat, and apply gruel from leaves or a cut leaf to wounds and cuts.
A bit of history
The first succulents were brought to Europe by the Spanish and Portuguese at the end of the 15th century. These were such plants as prickly pear, cereus, aloe, agave. They quickly gained popularity, striking with their unusual exotic appearance and a variety of bizarre shapes. They were grown in monastery gardens and in the gardens of large nobles. Interest in them has been preserved to this day and is growing from year to year. Amateur flower growers grow individual plants that they especially love or enthusiastically collect collections of tens and hundreds of species.Professionals pay great attention to succulents: in the greenhouses of botanical gardens there are always collections that are used for scientific and scientific and educational work.


Botanical Garden. Germany


Nikitsky Botanical Garden
Thus, the collection of cacti and other succulents of the State Nikitsky Botanical Garden, founded in 1812, has many unique specimens. The cactus greenhouse of the botanical garden is a permanent exhibition of cacti and other succulents in open and closed ground. The collection of cacti contains 600 species, varieties and forms. The succulent collection is represented by about 400 taxa. Various types of yuccas, agaves, various cacti are planted in the open field: prickly pears, mammillaria, echinocereus, echinocactus, acanthocaliciums, echinopsis, hymnocalycium, tephro-cacti.
In Russia, one of the oldest and largest is the collection of the Botanical Garden in St. Petersburg. Already in the middle of the 19th century, the collection of plants from arid regions consisted of 550 items, including 40 species of aloe, 23 species of agave, 15 species of hoya, 12 species of Gasteria. And by the end of the 19th century, it already numbered 1,700 taxa (species, varieties and cultivars). The collection was preserved during the years of the revolution, the Civil War and the devastation in the country. During the Great Patriotic War, the efforts of gardeners who worked in besieged Leningrad managed to preserve a large number of large specimens of succulents - about 300 species in total. Now the collection contains more than 1500 systematic units of succulents, including 1000 cacti. Among them there are specimens that are more than 100 years old. One of the “patriarchs” of the collection is the selenicereus cactus, or “queen of the night”, which has been growing in the greenhouse since 1857. This large plant with thin creeping shoots completely braids one of the walls of the greenhouse and blooms annually, forming up to 100 buds. The flowers of the "queen of the night" are luxurious: very large (up to 35 cm in diameter), with golden yellow sepals, snow-white petals and a delicate aroma of vanilla. But the life of these beautiful flowers is short - they open at night and wither by morning. During the flowering selenicereus, the greenhouses are open for night excursions, and on the white nights of May, visitors can admire the beauty of this amazing plant.
What is the peculiarity of succulents


a group of plants that can store water reserves in stem cells (milkweed, cactus) or leaves (aloe, haworthia). Thanks to this ability, they are able to survive in extreme heat.
Also, plants have qualities that help to retain and reduce the evaporation of liquid:
- Gas exchange in plants occurs at night, when the air humidity is higher, and the temperature, on the contrary, decreases.
- Often, the leaves have either a thick layer of fluff or a waxy coating.
- The round shape of the leaves of some representatives helps to reduce the evaporation area.
Bulbine
The genus Bulbin belongs to the Liliaceae family and has about 30 different species. Homeland is South America. Some species have bulbs, others have a lobular or tuberous root system. The genus unites plants that are very different in appearance. Bulbins can grow both outdoors (as annuals) and indoors.
- Plants of this genus love good lighting. In the apartment, their medium-sized views can be located on the windows of the south, south-west and south-east directions. In winter, when the plant is dormant, it can be moved to a darker and cooler room.
- The soil should be loose and neutral in acidity. It can be made up of equal parts of peat, leaf and soil. To prevent root decay, crushed charcoal can be added.
- Water the plant sparingly as the substrate dries. During the rest period, watering is completely reduced. Fertilizers are given only during the growing season.Complex mineral fertilizers are applied twice a month, excluding the winter dormant period.


Of the many types of Bulbina, several of the most interesting can be distinguished: One-year Bulbina, Shrub Bulbina, Half-bearded Bulbina.
Carpobrotus
Groundcover succulent belongs to the Aizoon family. It grows in the territories of Africa, South America and Australia. Leaves are fleshy, pointed, retaining moisture. The color of the leaves ranges from green to burgundy. It blooms very beautifully. Quite large flowers (up to 5 cm in diameter) can have yellow, pink, white shades.
- It prefers well-lit places, it is better to place it on the southern windows, shading from the direct rays of the sun. On warm summer days, it is good to take the plant out into fresh air.
- Acceptable air temperature is about 25 degrees Celsius. By winter, Carpobrotus enters the resting stage and the temperature is reduced to 10 degrees.
- In spring and summer, water is often watered, but not much. It is enough to moisten the topsoil. In winter, watering is sparse and small.
- Indoors, you cannot do without top dressing with complex fertilizer for succulents and cacti. They are applied once a month together with watering.
- The transplant soil consists of 1 part of sheet earth, 1 part of sand, a little clay and crushed coal. You can buy a ready-made mixture for succulents and cacti at the store, adding a little sand to it.


For amateur flower growers, two popular types are interesting: Ross's Krapobrotus and Carpobrotus are edible and Carpobrotus is delicious.
Tylecodon
A genus of succulent plants from the Tolstyankov family, a native of the countries of Namibia, South Africa, Namaqualand. The leaves are simple, oval, can be covered with fine villi or, like in common succulents, smooth. Stems are thick, covered with light brown bark. Bell-shaped flowers, collected in paniculate inflorescences. They have a red-brown or yellow-brown tint.
A big problem in growing is the fact that the period of active growth occurs in the winter. Since Tilekodon is a lover of good lighting, it is impossible to do without artificial lighting llamas, since the winter sun will not be enough.
- Also, this plant requires a special mineral soil, which you will have to make yourself from sand, granulate for drainage of the fine fraction, zeolite of charcoal.
- This succulent cannot do without fresh air in winter, but it cannot be left in a cold draft. The temperature of our apartments is perfect for Tilekodon, as is the dry air.
- He does not like transplants, it is very difficult to go through them. Watering is very moderate at any time of the year. During the growing season (in winter!), Watering can be increased and the introduction of complex mineral fertilizers can be added.
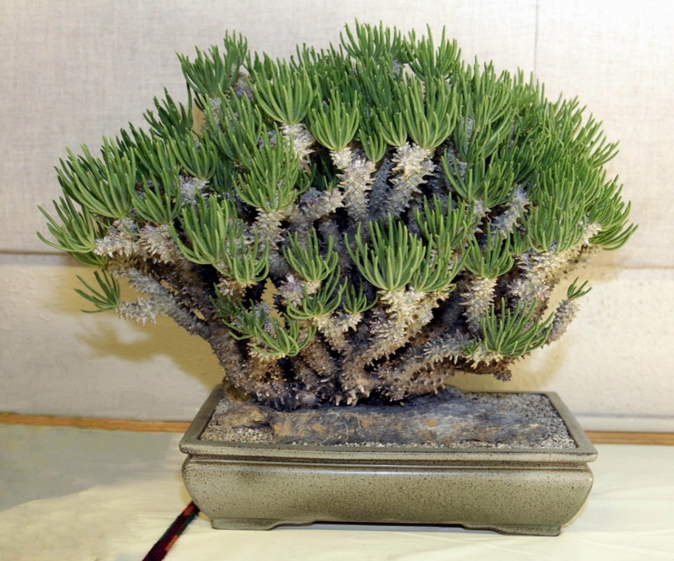


Tilecodon is most often grown as a bonsai, the following types are suitable for this: Panicled, Wallichi, Pearson, Ventricosus.
Greenovia
Evergreen succulent of the Tolstyankov family. A miniature succulent native to the Canary Islands. Forms a lush rosette of round leaves, which dies off after flowering. The flowers are bright yellow in color, collected in racemose inflorescences.
- Greenovia is grown on east and west windows, as it loves diffused sunlight.
- In the warm season, the succulent is suitable for the usual room temperature. In winter, to ensure a full dormant period, the air temperature should be no higher than 10 degrees.
- In the spring and summer, Greenovia is watered with moderately purified water. Do not spray the plant. In winter, watering is completely stopped, only occasionally the topsoil is moistened.
- The plant is fed once a month with liquid fertilizer for succulents and cacti. The soil is selected loose and light, well-conducting water. A substrate made up of 1 part sand, 1 part humus, and ½ part leafy soil works well. Particular attention should be paid to the presence of drainage.
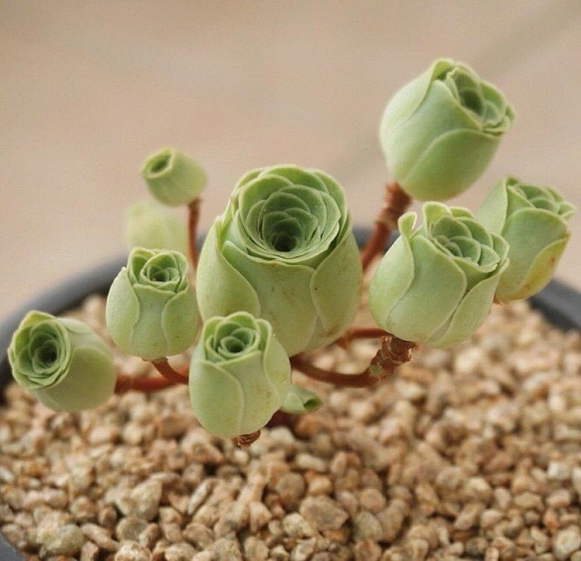


The most common are two types of Greenovia: golden and double.
Fenestraria
Succulent plant from the Aizoon family. The whole genus consists of one plant Fenestraria golden. Naturally, it grows in Namibia, Africa, and the Karoo Desert. Fenestraria has adapted in a special way to the sweltering desert heat. Its leaves are equipped with specific windows through which light enters. It is located at the very top of the leaf, separated by a membrane. It contains a clear liquid. This cunning natural adaptation saves the succulent plant from overheating and drying out.
Fenestraria forms dense rosettes of cylindrical leaves narrowed towards the base. The rosette grows in height only up to 3 cm. In the summer it produces a peduncle with a small flower of white or yellow color. They open in the morning and close in the evening. It blooms for about a week in total.
- This succulent requires a lot of light, but it needs to be protected from the midday sun. If it is not possible to provide natural good lighting, you need to supplement the plant with special lamps.
- Fenestraria spends the winter dormant period at temperatures from +12 to +10 degrees. The rest of the time, room temperature is appropriate. Does not require additional air humidification.
- Fenestria is watered in the summer 2 times a month in a tray. Therefore, the pallet must be high enough. In winter, watering is not required, but if the plant is very dry, you can moisten the soil with a spoonful of soft water.
- The soil should be special for succulents and cacti. After purchase from the store, the plant must be transplanted.
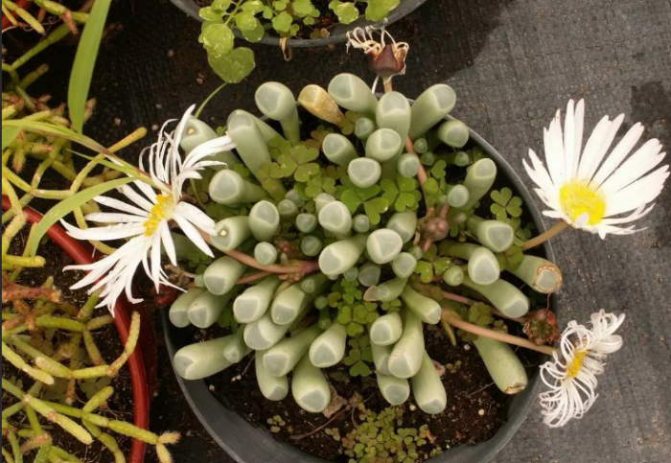
Only one species is cultivated: Fenestraria golden.


Possible problems
In both leaf and cuttings propagation, it is important to keep track of some points that can lead to problems and even death of the succulent. Wrinkles on the planting material are considered the norm, but if the fragments change their color to brown or soften, then it is not recommended to use them further. The humidity level must be monitored. At the stage of root emergence and germination, excess liquid can lead to mold and further decay. You can prevent this situation with the help of good drainage and the initial purchase of a pot with a sufficient number of holes.
Dinteranthus
Dinteranthus is a very small genus in the Aizov family. The genus unites from 4 to 6 species (according to various sources) and grows in the Cape province in the Orange River valley. This perennial is related to the Lithops and also has a popular name - "living stones".
Dinteratus has powerful roots, the stem is short and underground. The ground part has a rounded shape and is very similar to real river stones. The leaves of the succulent are paired, separated by a hollow, but even with flowering they retain their rounded shape. The color of the leaves can be gray, greenish, even creamy. The upper part is often decorated with spotted ornaments.
It blooms with a pretty beautiful flower that resembles a chamomile. The relatively large inflorescence is white, yellow and orange. The fruit is a pod with very small seeds. Dinteranthus grows very slowly.
- When caring for him, it is very important to alternate periods of winter dormancy and the active phase of the growing season. Any window will do for him, except for the north one.
- The temperature in the spring-summer period is from 18 to 25 degrees Celsius. In autumn, the temperature is gradually reduced to 8-10 degrees, which is optimal for winter recreation.
- "Living stones" should not be sprayed, they do not tolerate high humidity, they start to get sick with various diseases. It is also impossible to overmoisten the roots when watering. One spoonful of water is enough for one Dinterantus in warm weather. In winter, they do not water at all.
- Complex fertilizer for succulents and cacti is applied after changing leaves (molting) once a month, in half the dose specified in the instructions.
- For planting, shallow pots are used, with a good drainage layer and a filled substrate for industrial succulents and cacti. The top layer is covered with drainage material, which helps to avoid decay.
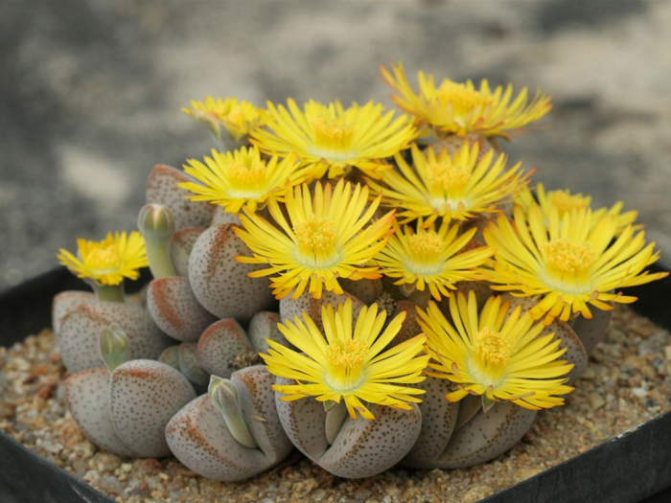


In indoor floriculture, two types of Dinteranthus are popular: Dinterantus Paul Evans Dinterantus Van Zil.
Bearded (Jovibarba)
This succulent plant resembles a rose flower in its appearance. Belongs to the large Tolstyankov family. A close relative of the succulent Younger, but isolated as a separate subspecies. In natural conditions, it grows in the Balkans and in the Eastern Alps.
- The beard loves sunlight, so indoors it is placed on the southern, southwestern and southeastern windows. If this succulent is grown indoors, in a greenhouse, on a terrace, then frequent ventilation is necessary.
- It is necessary to ensure differences in day and night temperatures. When growing in open ground, you need to choose the most illuminated place.
- A beard growing in the open air is not afraid of heat, withstands slight frosts, especially under cover. Indoors in summer, the plant feels comfortable at room temperature in summer, in winter it is necessary to adhere to a temperature of 10 degrees.
- For Borodnik, drought is not terrible, both in the apartment and in the air, much more dangerous is excess moisture, which can lead to decay of the plant. Therefore, the substrate in which the Beardnik grows must be air and moisture permeable. The container should not be deep, have a hole for draining excess water.
- It blooms and sometimes gives seeds only once in a lifetime. After that, the rosette splits into several young plants, which can be transplanted into suitable soil.
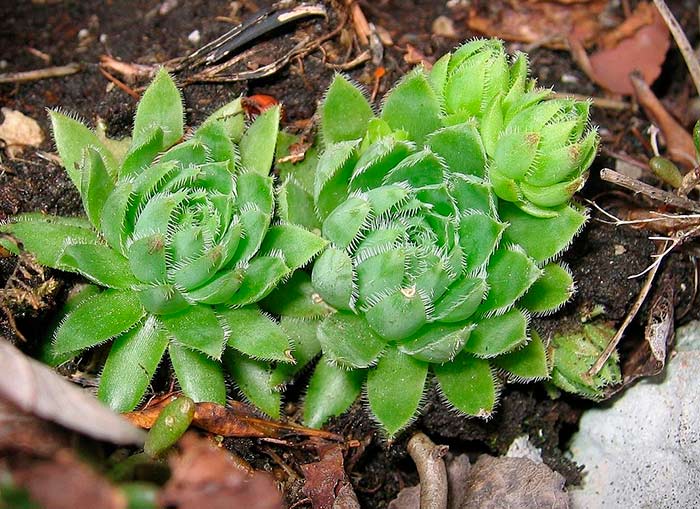


The most famous varieties are: Allion's beard, Hairy beard, Birch beard, Heuffel's beard, Offspring beard.
Monanthes
Perennial succulent from the Tolstyankov family. Very short shoots can be creeping or erect. At the tops of the shoots are leaf rosettes. Small thick leaves are sometimes located opposite, but more often alternately. They are ovoid. The inflorescences are either umbellate or racemose have 6-8-membered flowers, colored green, light pink or brownish.
- It develops and grows well only with sufficient lighting. South windows should be preferred for placement. In low light, the outlets become loose and untidy in appearance. In winter, Monantes also needs light.
- In spring and summer, the plant feels quite comfortable at room temperature, calmly withstands the hottest days. In winter, you need to transfer the succulent to a cool room, where the temperature is about 10-12 degrees.
- Air humidity should be the same as in an ordinary apartment. Additional moistening (spraying) is not required. In the spring and summer, watering should be moderate. The interval between waterings should be such that the soil in the pot dries out completely.
- In winter, watering is scarce, but the leaves should not be allowed to dry. Fertilizer is rarely applied: once every 1-2 years.


The main species cultivated in indoor conditions: Wall Monantes, Thickened Monantes, Amidrian Monantes.
And a little about secrets ...
Have you ever experienced unbearable joint pain? And you know firsthand what it is:
- inability to move easily and comfortably;
- discomfort when going up and down stairs;
- unpleasant crunching, clicking not on their own;
- pain during or after exercise;
- joint inflammation and swelling;
- unreasonable and sometimes unbearable aching pain in the joints ...
Now answer the question: does this suit you? How can you endure such pain? And how much money have you already "poured" on ineffective treatment? That's right - it's time to end it! Do you agree? That is why we decided to publish an exclusive
Bowiea or Bowiea
Belongs to the Hyacinth family.The bulbous plant is found naturally in the desert regions of Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa and Zimbabwe. The plant belongs to the species of herbaceous succulents. In adulthood, the bulb reaches a diameter of 30 cm and is covered with protective scales. The root system is powerful, branched.
Creeping stems can hang like ampelous plants. The leaves are small, branched, but grow only on young shoots. At the end of the growing season, the leaves are replaced by peduncles. They reach a length of 3 meters and have small white flowers. Since the aboveground part is quite voluminous, the plant needs supports for the green mass.
- During the dormant period, which lasts about 6 months, all shoots and flower stalks dry out. In Bovea, periods of dormancy and vegetation can change under the influence of external conditions.
- During the waking period, the plant needs bright, but diffused sunlight. In direct sunlight, the plant can get severe burns.
- The temperature during rest should not be higher than 15 degrees and below 8 degrees. If the temperature is higher than it should be, then Bovea will not shed the foliage, and new shoots will not appear. During the growing season, high temperatures provoke drying of the bulb. Room temperature is suitable during the growing season.
- Watering in the summer is carried out only when the soil ball is completely dry. In winter, the plant is not watered at all. The air humidity should be as low as the normal temperature in the apartment.
- The soil can be made by yourself from 2 parts of leafy soil, 1 part of turf and 1 part of sand. When planting the bulb, it is buried one third. Fertilize once every two to three years with a complex mineral fertilizer.


This plant is presented in a single form in home floriculture.
Temperature and humidity conditions for keeping succulents
In their homeland, unpretentious plants not only can do without water for a long time, but are accustomed to sudden daily temperature changes with a difference of up to 25 ° C. At the same time, the temperature does not fall below 5 ° C, otherwise the plants are threatened with freezing. It is possible to create conditions close to natural by regularly ventilating the room, taking flower pots to the open air in the summer, while the plants must be protected from drafts. The atmosphere should be moderately humid or dry, you should not spray water on the leaves from a spray bottle - its excess can trigger putrefactive processes.
Caralluma
A perennial plant belongs to the Lastovnev family. The succulent plant has fleshy, faceted stems covered with denticles. In the natural environment, Karallum lives in the desert areas of Africa, Arabia and India.
The flowers of the plant have graceful shapes, variegated colors and are quite beautiful, but they exude a very unpleasant smell of rotten meat, which attracts natural pollinators - flies. But in the room content, the smell is weak.
- For Caralluma, windows facing east or west are ideal. Here she feels great and blooms regularly.
- The temperature regime in spring and summer corresponds to room temperature, about 20-25 degrees. In winter, the plant can be moved to a cooler room, where the temperature does not drop below 10-12 degrees.
- The air must be dry, like all succulents, Caralluma does not like damp rooms. No spraying is required either.
- In the warm season, water is rarely watered, but abundantly. After watering, wait until the soil is completely dry before watering again. In autumn and winter, it is enough to slightly moisten the soil.
- Complex fertilizer is applied once a month only during the growing season. Caralluma grows quickly, wide and shallow pots with a sufficient drainage layer are suitable for it.
- The soil can be composed independently of equal parts of coarse sand, leaf and sod land, peat with the addition of crushed charcoal. You can use ready-made soil from the store for succulents and cacti.


Three types of Caralluma are most interesting for lovers of indoor floriculture and rare plants: Socotranskaya, Hesperidum, European.
Cutting succulents
Another way of propagation of these exotic plants is no less popular and simple - cuttings.
The stalk is also cut with a sharpened knife and left to dry for a couple of days. Be sure to pay attention to the plant that gave the cutting. The resulting cut must be sprinkled with coal, which was previously crushed. In this case, before processing, you need to inspect the cut. If the plant belongs to those species that secrete milky juice, then the cut is first washed and then treated with charcoal.
Reproduction by cuttings is a longer process. It is possible to plant a stalk in the ground only after the roots appear in it.
About rooting cuttings - in more detail
To root a succulent stalk, you can place it in a year or in a sand mixture. This method is the most suitable for grafting different types of milkweed and fat women.
Rooting in water
A stalk is placed in a container with clean, settled water (you can take boiled or distilled water), making sure that it does not touch the bottom with its lower part with a cut. At room temperature, the cutting takes root within 2-3 weeks. To create more favorable conditions, you can create greenhouse conditions for the plant. To do this, simply cover it with a clean and transparent plastic bag.
Subtleties of rooting in water:
- Treating the cuttings with a growth stimulator before immersion in the liquid will make the process more efficient.
- The container with the handle should be kept in a well-lit place at room temperature, adding water as needed.
- In case of decay of the cut, the cutting should be cut off and placed back in a container with clean water, after having dried it and treated with a growth stimulator.
Rooting in the sand
The sand mixture is usually used for rooting sansevieria. In prepared (sifted and fried in the oven or in a pan) sand is placed treated with a strengthening compound ("Epin", "Kornevin") a cutting, then watered with warm water.
It is not necessary to deepen the cutting too deep. 1.5 - 2.5 cm deep are ideal for the plant.
In the process of rooting in the sand, the cutting is also kept in a warm and bright place.
Video "Propagation of succulents by cuttings"
















































