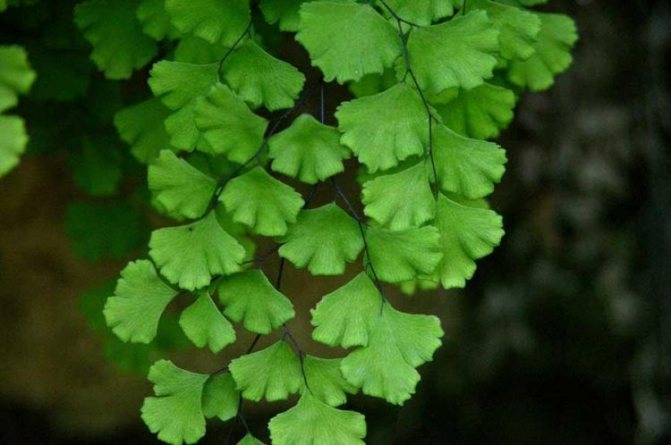
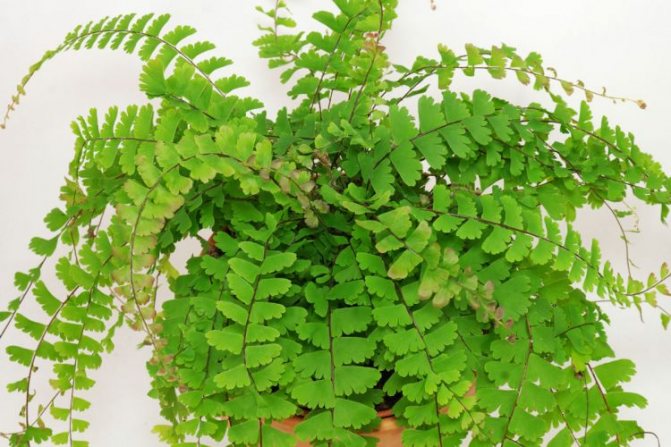
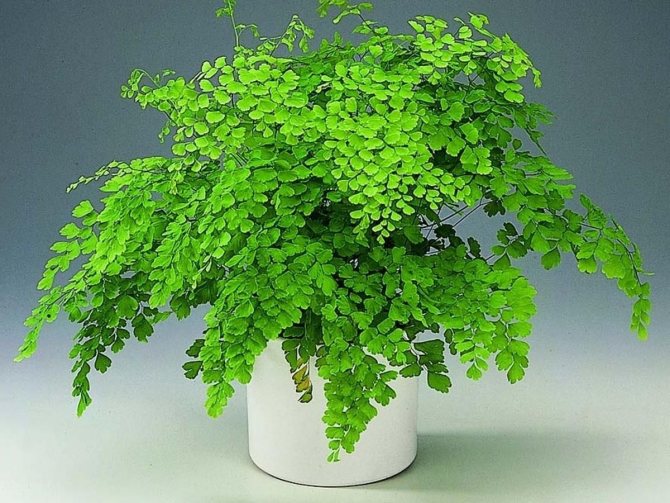
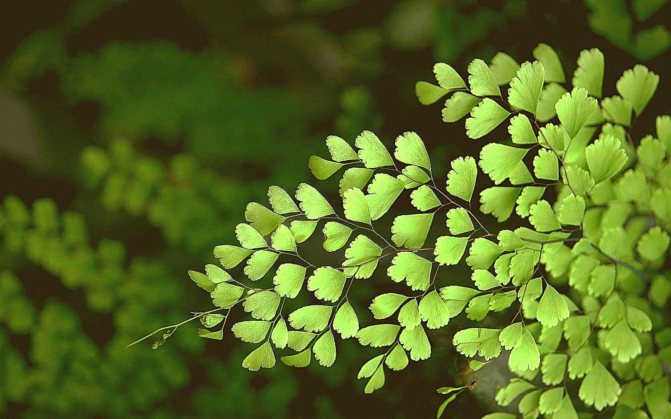
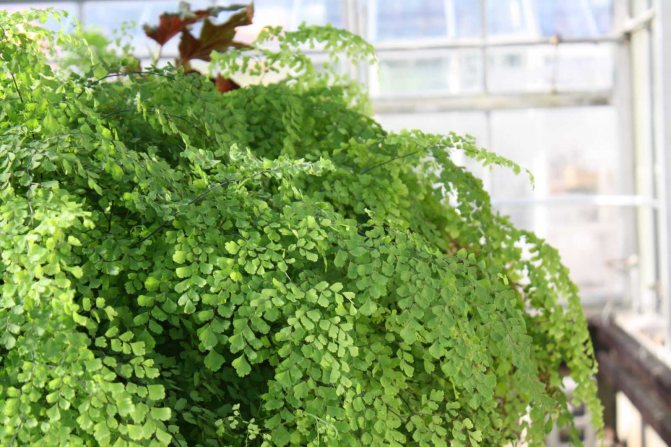
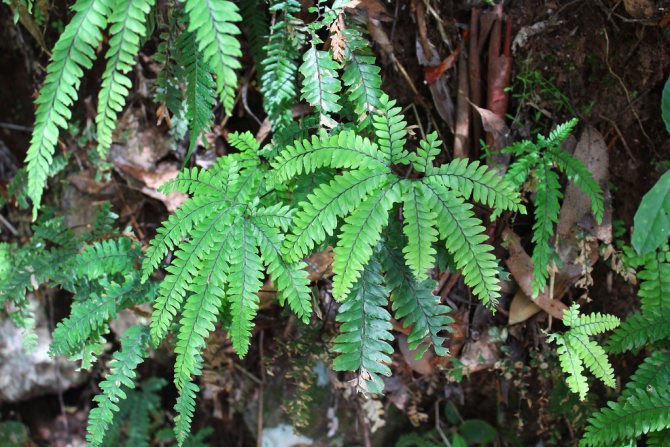
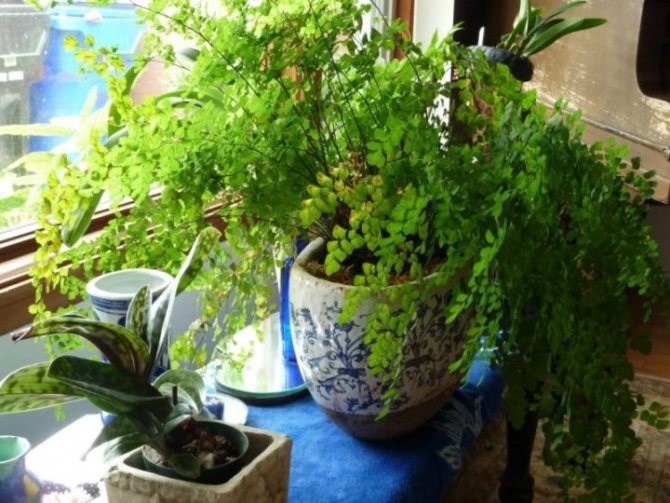
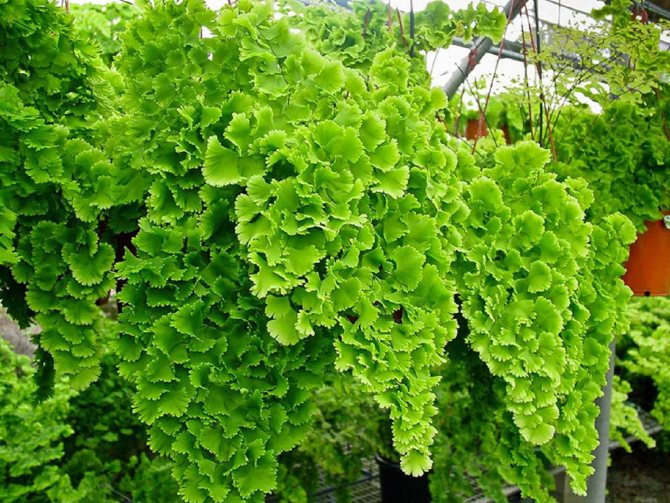
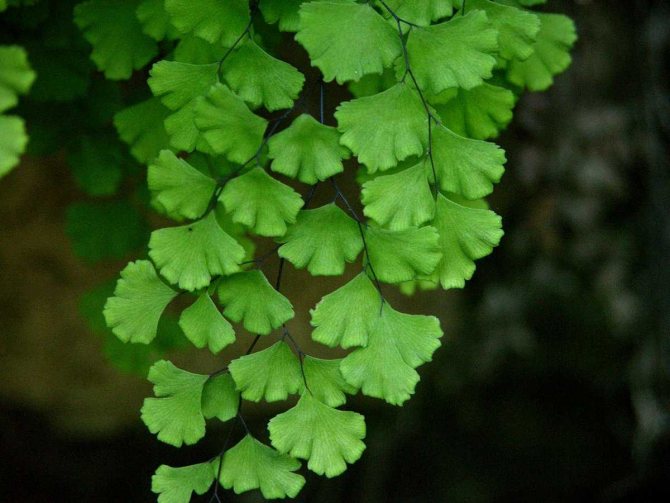
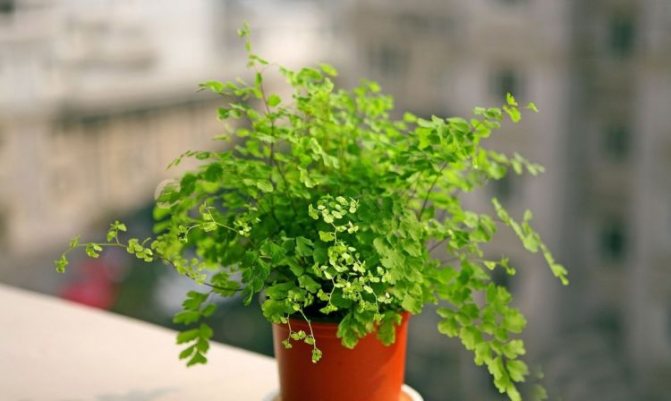
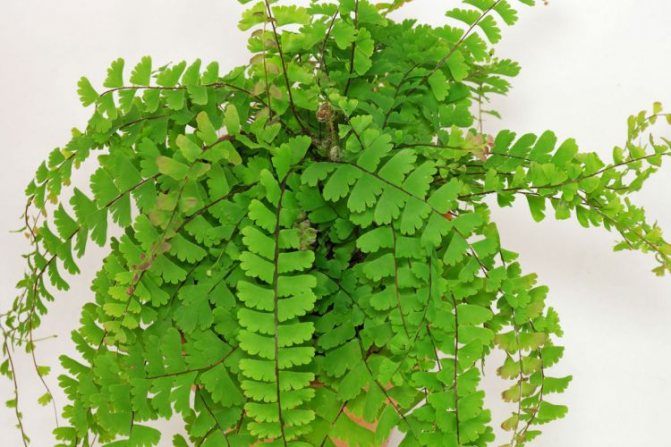
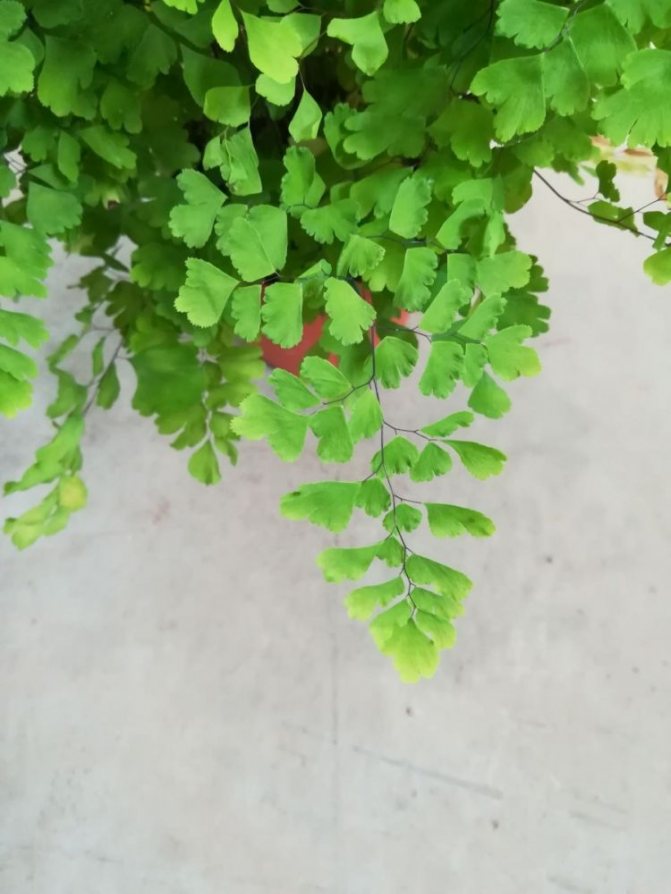
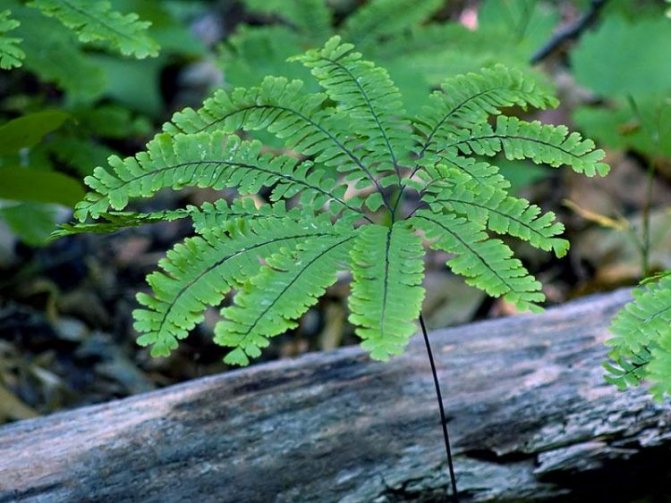
The adiantum plant, which is also called adiant, belongs to the genus of ferns of the monotypic Pteris family. This genus unites about 200 species. The name of such a plant consists of the prefix "a", which translates as "no-, no-", and the second part of the name from Greek translates as "moisten", or "moisten". As a result, the name of such a flower is translated as "non-wetting plant", this is due to the fact that its foliage has the property of repelling water, so that it does not get wet. Such a plant is most often found in the tropical regions of the South American Andes and East Asia. Maidenhair prefers to grow on fertile moist soil, which is typical for rocks in places located near waterfalls and springs. The maidenhair was already known to man at the time of Pliny the Elder, who was the author of Natural History, he wrote about it in his writings. Among flower growers, maidenhair is the most popular among all decorative ferns. It can be grown both at home and in a greenhouse. In addition to the fact that this plant has a spectacular appearance, it is also healing.
Array
Four-leafed maidenhair (A. Tetraphyllum)

A South American fern, the four-leafed maidenhair, found in the wild on the mountainous plateaus in Brazil, is one of the most interesting and ornamental plants of the genus. Unlike many varieties of maidenhair, which have pinnately complex foliage, here the frond plants are pointed and finger-like.
The leaf stalks are painted in green-brown tones and rise almost half a meter above the ground. The leaves are somewhat drooping, with lobes alternately collected on the rods. The lobes themselves are asymmetric trapezoidal, medium-sized, glossy on the outside. Densely set sori are located along the edge on the back side.


Four-leafed maidenhair perfectly tolerates life in indoor conditions. Propagated by dividing the rhizome, which is thick in the fern and extending shallowly under the surface of the substrate.
Requirements
- Loves the shadow. Direct sunlight can cause burns. Leaves turn yellow and dry. It will be optimal to keep the flower in the shade of other plants or on a windowsill on the north or east side. Or close to the window on a stand.
- Dislikes frequent transplants and movements.
- The optimum temperature is 15-20 C. Loves coolness at night. Poor heat tolerance.
- The pot is selected wide, spacious.
- Good soil drainage is required.
- Does not like the proximity of heating radiators. You can neutralize the harm by hanging a damp cloth on them.
- It is negatively affected by tobacco smoke, dust, drafts.
- It is undesirable to place it in the kitchen, near the gas stove.
- Poorly tolerates chemical treatment.
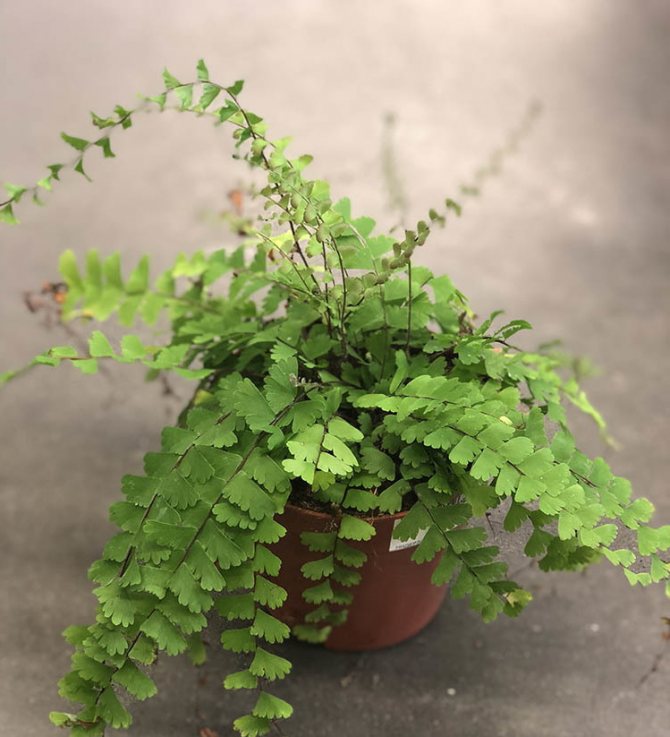


Tailed maidenhair (A. caudatum)


The homeland of this type of maidenhair, which prefers to settle not only on stones, but also on the trunks of large representatives of the flora, is South America. The tailed maidenhair is distinguished by the presence of long leaves, up to 40 cm.
Leaves of the first order on the petioles are arranged alternately, tightly to each other. They have a trapezoidal, strongly dissected shape. The teeth are blunt or rounded along the edge. Spores are located on the outer side of leaf segments, in dense sporangia notches formed along the cut.


As a room culture, the tailed maidenhair is more capricious than other types of maidenhair. The plant requires more frequent watering, since dry soil for fern rhizomes is destructive. It is equally important to maintain high humidity in the room where the maidenhair species shown in the photo is contained.
Care
Caring for the maidenhair plant at home is simple.


From October to March, the plant has a dormant period. Watering is required once a week, it can be a little more often if the ground dries up quickly. The rest of the time, watering is needed 2-3 times a week. But at the same time, it is important that the roots are not flooded, otherwise they may begin to rot.


Maidenhair loves humid air, at least 50%. You can install a humidifier next to it or occasionally spray it with water from a spray bottle. A pallet with damp pebbles will also help.


From March to August, you need to feed the plant every 2 weeks, alternating organic fertilizers with mineral fertilizers.


Periodic showers are well tolerated. In this case, the soil should be covered.


Without moisture, the fern can last a week. For a while, you can put the pot on wet expanded clay.


Types of maidenhair with photos and names
Adiantum capillus-veneris
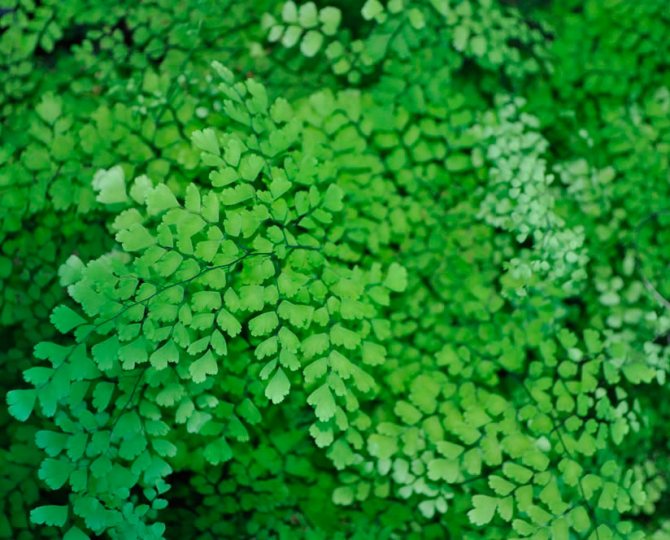


Under natural conditions, the species can be found in the mountains of the Crimea and the Caucasus, as well as in Central Asia. It prefers to grow on moist limestone stones near water sources. Its thin rhizomes are colored black. The species got this name due to the fact that delicate and light fan-shaped leaf plates of a greenish color grow on long petioles (about 25 centimeters). As a rule, the species is cultivated at home.
Adiantum pedatum
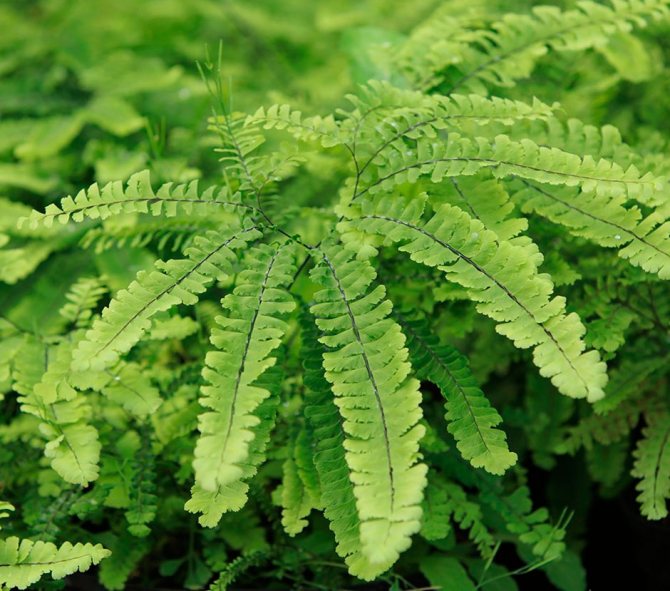


This species is one of the most beautiful ferns. The delicate openwork plant can be found in the deciduous forests of North America and East Asia. The height of the bush is about 0.6 m. Its foliage is glossy one-sided flat greenish color, it is pinnately dissected and incised along the edge. The leaf plates are arranged horizontally on thin glossy petioles. The species has a very high frost resistance, it is able to withstand a temperature drop down to minus 35 degrees. The most popular varieties:
- Compactum - the height of the bush is about 0.35 m;
- Imbricatum - such a dwarf variety in height reaches only about 15 centimeters;
- Aleutikum - This variety has a height of only about 10-12 centimeters, but it can reach a width of 15 to 20 centimeters, most often it is grown in a pot, since it tolerates bright sunlight better than other ferns;
- Japonikum - the young bush has shoots of a copper-pink hue, but over time they turn green, the height of the bush is up to 0.45 m, and in diameter it reaches about 0.3 m.
Tenerum adiantum (Adiantum tenerum)
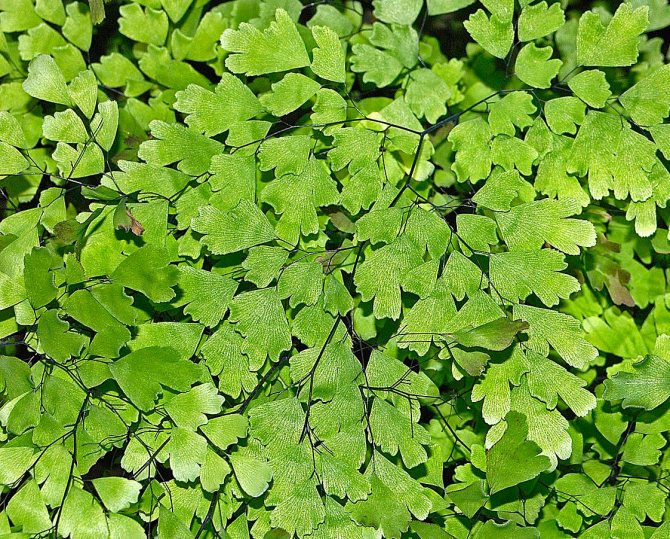


Under natural conditions, the species can be found in the tropical regions of America and in the Greater and Lesser Antilles. The creeping rhizome of the bush is rather short. The triple-pinnate leaf plates at the base have a wedge-shaped shape, and along the upper edge they are broadly serrate. The foliage is about half a meter wide and up to 0.7 m long; it grows on long petioles (about 0.3 m). The best varieties:
- Farleyens - the foliage of the bush is very effectively twisted;
- Scutum Roseum - young foliage can reach 0.3 m in height, it has a variable color from green to pinkish.
Small-haired maidenhair (Adiantum hispidulum)
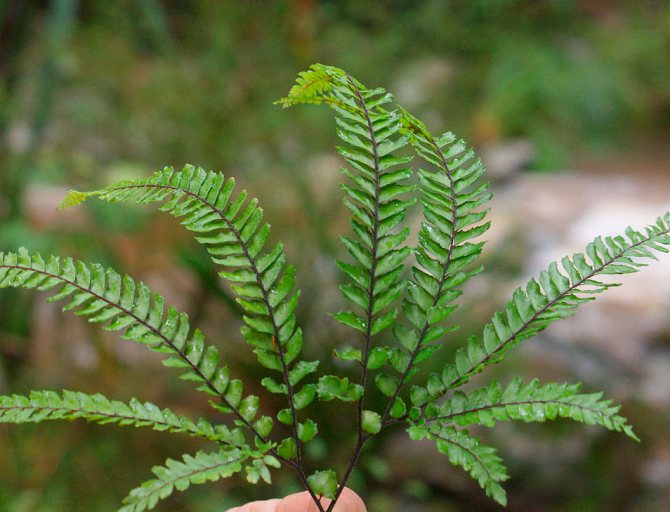


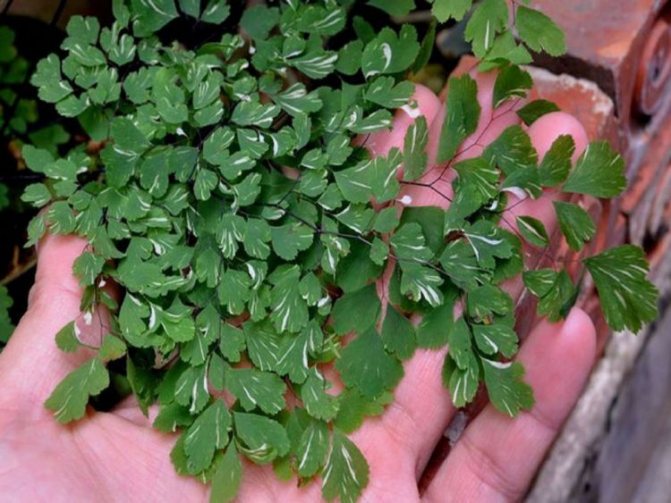
In nature, the species prefers to grow along the snow line of the African mountains, and it is also found in Australia, Madagascar, India and New Zealand. The rhizome of the bush is creeping, the shape of the leaves is hand-cut, they are covered with small bristles, and their length varies from 15 to 25 centimeters. Foliage is located on petioles about 0.35 m long.Diamond-shaped leaves of the second order are about 5 mm wide and up to 20 mm long, both of their surfaces are covered with small bristles. In indoor conditions, the view looks very impressive.
Adiantum raddianum
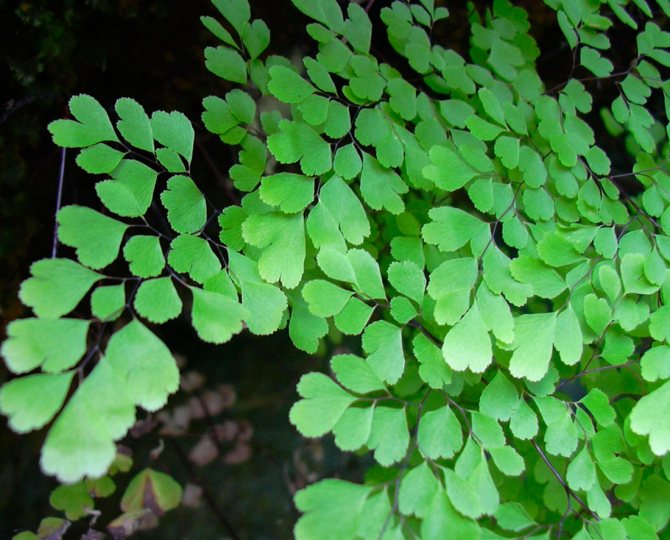


Or wedge-shaped (Adiantum cuneatum). The homeland of this epiphyte is the subtropical Brazilian forests. The length of the gracefully curved leaf plates is about 0.45 m, and their width is up to 0.25 m. The foliage is dissected into numerous rich green leaves, which are located on glossy black petioles. Popular varieties:
- Grasillium and Micropinnulum - these varieties have finely dissected foliage and are distinguished by a high demand for high humidity, therefore it is recommended to cultivate them in florariums;
- Fritz Luth and Festum - these varieties are more resistant to adverse conditions, and therefore they can be cultivated at home.
Adiantum caudatum
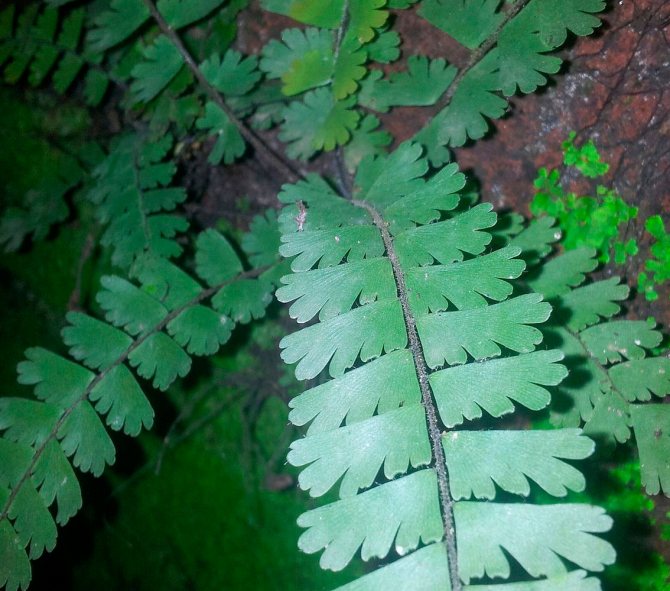


The species is grown as an ampelous plant, since its foliage reaches a length of about 0.6 m. The leaf petioles are brown in color, and there are offspring on the tops of the leaves. This species reacts extremely negatively to drying out a clod of earth in a pot.
Beautiful maidenhair (Adiantum formosum)
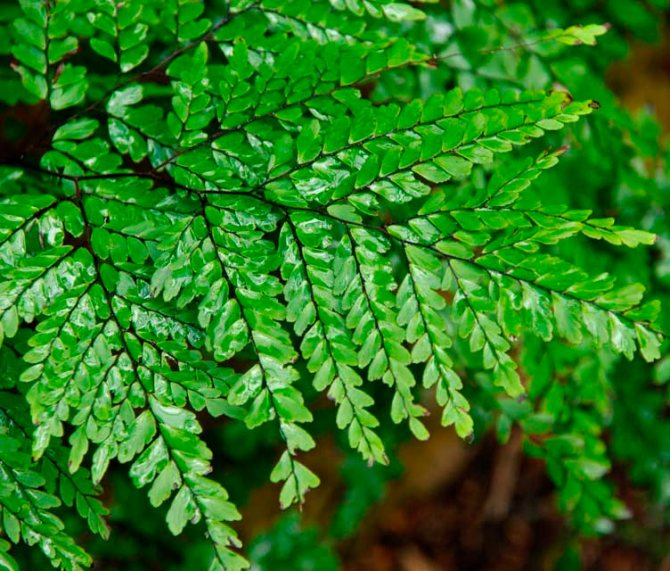


The height of the bush of this species is about 100 cm, its rhizome is very fragile. The multi-pinnate leaves are located on the petioles of a black-purple hue. The dark green segments of the leaf blades are triangular-obovate.
Adorable adiantum (Adiantum venustum)
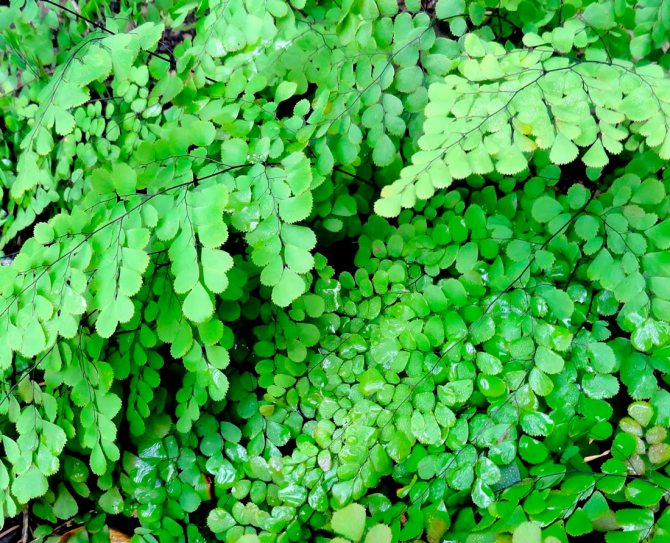


In nature, the species can be found in Kashmir and Nepal. The narrow greenish leaf plates reach about 20 centimeters in length, and they are located on purple-black petioles. Foliage segments are slightly pointed. If the bush is exposed to low temperatures, then its foliage will turn pale brown.
Wedge-shaped maidenhair (Adiantum cuneatum)
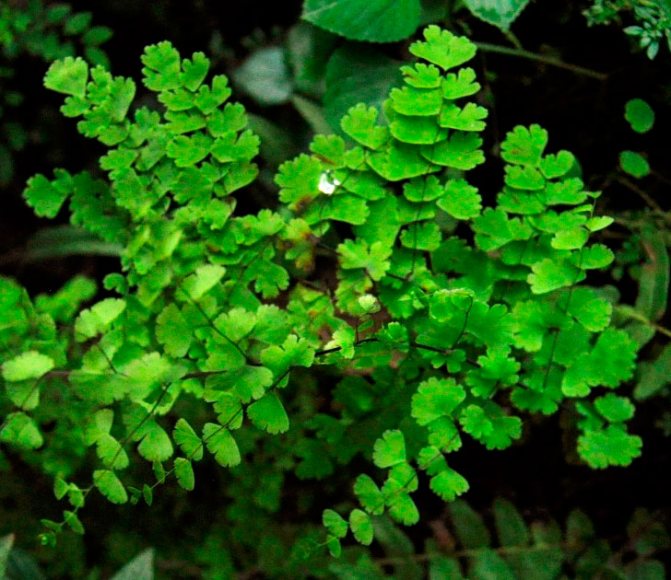


The view is similar to the beautiful maidenhair, but its soruses are shaped like a horseshoe. He comes from the South of Brazil.
Transparent adiantum (Adiantum diaphanum)
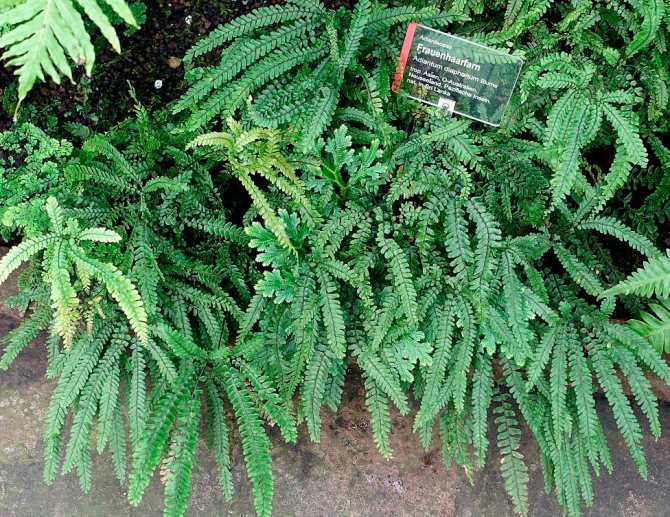


The height of the bush varies from 0.25 to 0.4 m. The pinnate leaf plates are double-pinnate at the base. The length of wai is about 20 centimeters, and the width is up to 3 centimeters, they are located on thin long (about 20 centimeters) petioles. The greenish segments of the leaf blades are glabrous and broadly oval.
Adiantum Fragrans
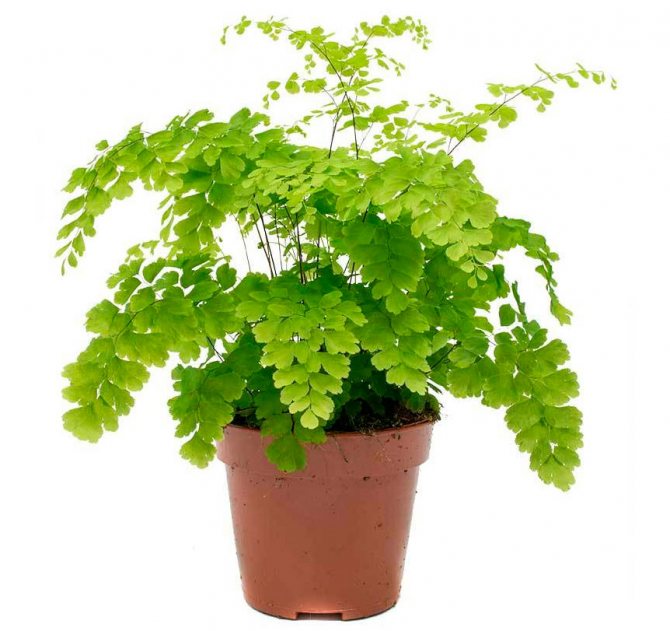


This type is very popular with flower growers. Under natural conditions, it is found in southern Asia and the South American Andes, where it forms dense bushes. This delicate fern is fast growing and reaches a height of about half a meter. The length of the greenish oval-shaped leaf plates is about 30 mm, and the width is up to 15 mm, they are located on very long petioles (from 10 to 15 centimeters).
Transfer
The transplant should be done as needed, but not more often than once a year. The pot is chosen with a small margin. The earth is suitable for breathable, loose, slightly acidic, enriched with humus.


Optimal ready mix for ferns. The composition of the soil mixture is as follows: sand, peat, humus earth and leaf earth in equal proportions.


It does not hurt to add a little moss, crushed charcoal, bark. Be sure to make sure that part of the root is above the ground.
Transparent maidenhair (A. diaphanum)
For this maidenhair, as in the photo, the formation of double-pinnate leaves, excised along one edge, is characteristic. Segments of a leaf do not exceed three centimeters in length, while the total length of a narrow pointed leaf can be up to 25 centimeters.
The lobes are wide, obovate or oval, green. The petioles are dark, with a green or brown tint. Convex sporangia are located along the outer edge of the leaf.
The total height of the decorative species reaches 35–40 cm, while the fern, native to Indochina, Australia or Polynesia, grows well in an apartment.
Reproduction methods
It is much easier to propagate the maidenhair plant by division. You need to take a small part of the root with two buds. The optimal breeding season is early spring and early August.


The maidenhair spores multiply in greenhouses when small sprouts appear next to it. Spores need 3-5 weeks to germinate. You can germinate spores in mini greenhouses in moist soil.


Hibiscus - seedling selection, care, reproduction and advice on watering the plant. 110 photos and video review of the flower

Geranium - secrets of growing, options for use and features of use in decor (95 photos and videos)
- Ahimenes: types, planting, care, reproduction and secrets of use in the garden and in the interior (115 photos)
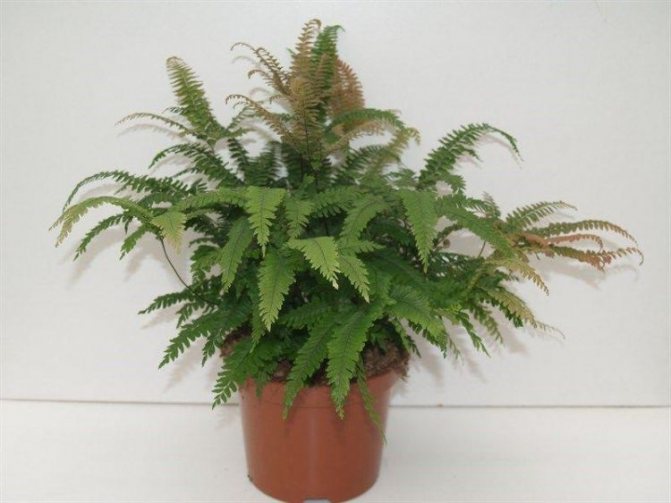


Wedge-shaped maidenhair (A. cuneatum)


The fern comes from the South American rainforests in appearance and structure of the crown and leaves resembles other varieties of maidenhair, already loved by flower growers. The fundamental difference between the wedge-shaped maidenhair is in the shape and location of the sori. In this case, the spores mature in the grooves located along the edge of the first-order leaves. The shape of the sporangia resembles a kidney or a horseshoe.
Possible problems
- The shoots dry out, the tips of the leaves dry out - there is not enough moisture in the air, high temperature.
- The leaves turned pale and wilted - the soil is oversaturated with moisture, more often at low air temperatures. This is fraught with the appearance of rot in the roots.
- The leaves turn pale, turn yellow, dry - signs of sunburn. It is necessary to remove the plant in the shade
- The whole flower turned yellow - lack of moisture or feeding.
- If all the foliage has dried up in winter, it means that the air temperature is increased. The flower can still be saved - dry foliage must be completely cut off, rearranged to cool and regularly moistened the soil.
- Slow growth indicates insufficient soil nutrition.


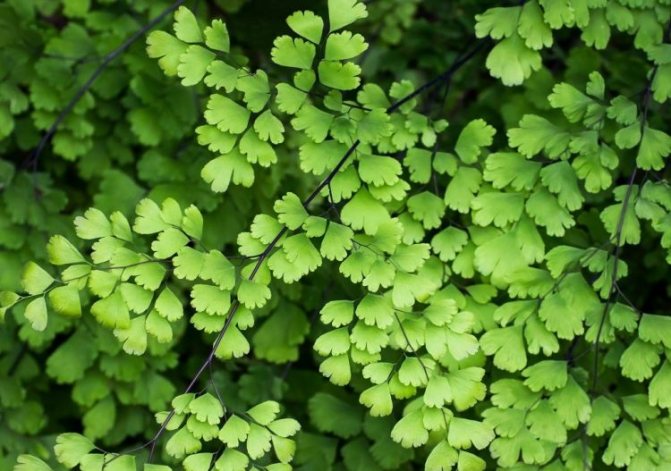
Maidenhair finely pubescent or fine-haired (A. hispidulum)


In nature, the small-haired maidenhair is found in the mountainous regions of Africa, where the plant can be seen in the foothills, overgrown with dense forests, almost on the line of snow. Representatives of this type of maidenhair can be found in other parts of the world, for example, in Australia, New Zealand and India.
The adiantum hispidilum forms palm-shaped dissected leaves with diamond-shaped segments. The length of such a sheet can reach 45 cm.


Sporangia in the small pubescent maidenhair are located along the cut line of the leaf segment almost closely to each other. The petioles, like many varieties of maidenhair, are dark, thin, rather strong.
The view is of interest both for lovers of home floriculture and those who are fond of growing ferns in the winter garden.
Pests
Pests of this plant are rarely affected, due to the essential oils in the leaves. But sometimes mealbugs, whiteflies, aphids, spider mites can start.


It is desirable to treat it with folk remedies, in extreme cases - carefully treat it with a well-diluted chemical composition.
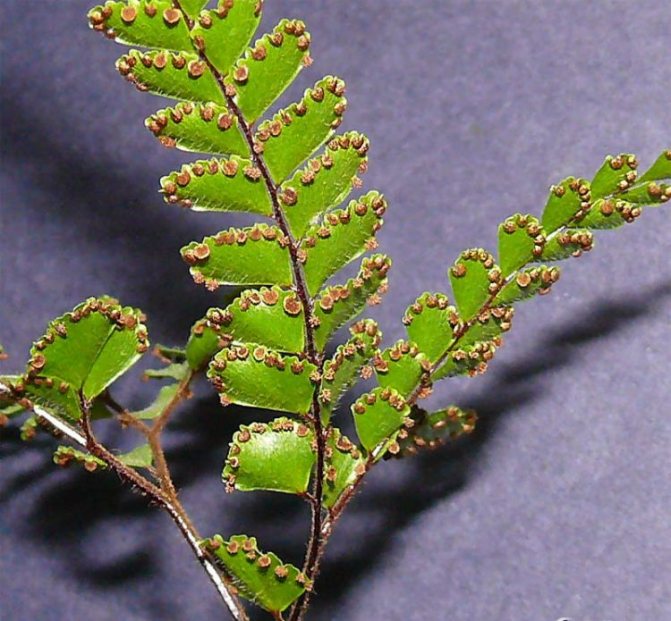


A severe defeat is incurable. Here it is recommended to cut off all the leaves and let the roots germinate again.


Properties of the maidenhair


The adiantum foliage contains triterpenoids, flavonoids, lipids, steroids, phenolcarboxylic acids and their derivatives, as well as essential oil. On the territory of Western Europe, infusions, medicinal powders and syrups, preparation of such a plant from leaf plates are widely used. Syrups and infusions are used as a remedy with antipyretic and expectorant effects, and the aqueous extract has antimicrobial properties.
Means made on the basis of maidenhair are used for diseases of the liver, respiratory tract, bladder and spleen. The juice obtained from the foliage is used to make compresses and lotions against the bites of rabid animals for detoxification purposes, and also in the treatment of malignant ulcers.In Chinese medicine, a decoction is prepared from the leaves of the maidenhair, which helps in the treatment of alcohol addiction.
To reduce the amount of dandruff, it is recommended to rinse your hair with a decoction of maidenhair leaves, or you can add the juice of this plant to the water. In the treatment of psoriasis, an alcoholic tincture of maidenhair is used.
Mr. Summer resident advises: Maidenhair is a useful plant
Maidenhair is not only a beautiful plant, but also a useful one, exhibits medicinal properties. In Europe, for a long time, with powders and infusions from its leaves, diseases of the throat, liver and bladder, coughs of various origins were treated. Its ingredients help reduce fever and kill bacteria. In China, for many years, with the help of adiantum decoctions, alcoholism has been successfully treated.
In some cultures, the leaves are used for food, as a side dish. They are also used to prepare sweet drinks.
In the Caucasus, decoctions are used to rinse hair. It is believed to give hair strength and shine. Feng Shui fans believe that maidenhair brings a special energy to the house and is great for the bedroom. It gives calmness and sound sleep.
Description
Maidenhair is a shrub about a meter high. Sprawling branches with dense foliage resemble voluminous curly hair, where the plant's nickname came from.
Leaves on petioles are located opposite each other. The edges are often dissected, and the surface with a glossy sheen is due to the water-repellent layer. The size of the branches depends on the variety and can reach half a meter in length and width.
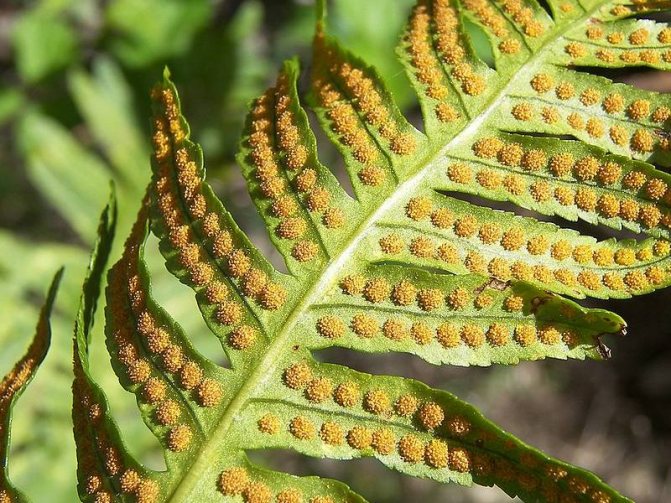
The lower surface of the leaf plate is darker than the upper one. On it, along the veins, small spores are located, covered with a thin film with a rough surface. The root system consists of very thin roots growing almost parallel to the ground.


Reproduction of the maidenhair by dividing the bush
Splitting a bush when replanting is the easiest way to reproduce a fern. The plant is neatly separated: first the foliage, then the roots. The latter are very fragile, so you need to act slowly. When planting, the root collar is not deepened in order to avoid rotting.
Reproduction by spores
Like all ferns, maidenhair is able to reproduce with the help of spores, but this process is rather long and complex. Spores form on the underside of the leaves of mature plants. They are collected in paper bags and dried a little. After that, the spores are spread in a thin layer on the surface of the peat, which is placed in a shallow container.
The pot is placed in the shade, covered with glass, the surface of the soil is constantly sprayed with water. A month later, moss will appear on the ground, which indicates an intermediate stage in the development of the fern. At this time, the formation of male and female germ cells occurs. After their fusion, young plants appear. When their height reaches 4 cm, they are transplanted into separate pots. Young maidenhair is placed under glass.
Although this method of reproduction is considered the most difficult, plants grown from spores will be the strongest and most resistant to external factors.
Care errors, pests, diseases and methods of elimination
Maidenhair produces special substances that scare away insects in nature. However, in modern cities, pests have adapted to chemistry, and sometimes infect the plant.
| External signs | Cause | Elimination method |
| Leaves dry, lose their shine. | Greenhouse whitefly. | Destroyed by special preparations (sold in flower shops): Zeta, Rovikurt. |
| Leaves have white tangles. | Scratch. | Remove carefully with a brush, using denatured alcohol, without wetting the leaves. |
| Small oval growths. | Californian scale shield. | Remove with a cotton swab moistened with alcohol. In case of severe damage, chemistry is used (Actellik). |
| The leaves dry, the leaves turn brown at the edges. | Lack of watering or plant smoke. | Increase watering.If it is not possible to protect the fern from accidental smoke in this place, it is better to rearrange it to another. |
| The foliage is falling. | Insufficiently humid air. | Regular spraying. |
| Leaves turn pale. | Wrong place, too much light. | Move the pot to the shade. |
| Leaves curl but don't dry. | Low air temperature. | Move to a warmer place or maintain the desired temperature. |
| Leaves at the cutting turn yellow, brown spots appear. | High air temperature. | Reposition (if the problem is in the heaters) or install a protective screen. |
| Leaves wither in wet soil. | Decay of the root system. | Remove the plant from the pot, remove the damaged parts of the rhizome, change the substrate. |
| Darkened foliage, brown lines. | Accumulation of salts in the ground. | Soil replacement. |
The most common questions about growing the Maidenhair


Florists who have just started breeding ferns may have the following questions:
- Why did the Maidenhair leaves darken and brown dots appear on them? This is a signal to check the acidity of the soil. To do this, you need to use a litmus test. The plant thrives only in slightly acidic soil, the acidity index of which is in the range from 5.5 to 6.5. If the normal acidity is disturbed, this indicates a large accumulation of salts. You can try to flush the land with water, but transplanting the plant into new soil will be a more painless way.
- Why do leaves dry? The delicate foliage of Venus hair can react by drying to various negative factors. This can also happen due to the air temperature unsuitable for the plant, or from cigarette smoke and a rarely ventilated room. Drafts or hot dry air rising from radiators can have a negative impact. In order for the leaves to stop drying, you need to try to eliminate all these factors.
- What if all negative factors are eliminated, but the plant dries up anyway? Take a magnifying glass and examine the Maidenhair for harmful insects. Aphids or spider mites can grow on the fern. To get rid of them, the plant can be treated with a tobacco-soap solution. To prepare it, you need to purchase tobacco dust, which is a harmless and environmentally friendly product with insecticidal properties. Tobacco dust must be poured with water in a ratio of 1:10, boiled for 30 minutes and insisted for a day. After that, the broth must be filtered, diluted with water 1: 3, and add soap to it (20 g per 5 liters).
- Why do the leaves turn yellow? The yellowness of the foliage indicates a lack of nitrogen in the soil. In this case, fertilizing can be done with nitrogen fertilizer.
The problems considered in the process of growing the Adiantum are most common. In general, the plant will not bother you too much. Ferns are very tenacious, and if the minimum conditions for the normal growth of indoor plants are met, they will literally grow on their own.
Legends
There are several legends about the origin of the plant. One of them says that at the place where a young beautiful girl fell from a cliff, a waterfall broke through. Her hair turned into a fern.
According to another legend, the goddess of love Venus, cutting off her hair, dropped a small strand from which the maidenhair grew. Hence its name.
There are many different beliefs about fern flowering. Our ancestors believed that the fern blooms magically: on the eve of the summer solstice (the holiday of Ivan Kupala), a fiery flower sprouts, so bright that it is impossible to even look at it. And it blooms for only a few seconds. Then the fiery flower is plucked by an invisible force. But a person who ripped it off earlier can acquire power over everything. The ancestors could not understand how this plant reproduces. Therefore, similar legends about a fern with mysterious power were born then.
However, science has been able to debunk the mysteries of the fern. Absolutely all adiantums never bloom. Nature for them has provided a mechanism for reproduction by spores. They form in this plant from spring to autumn (along the edge of the leaves or at their tips, in sori). They acquire a brownish color as they mature. The spores are very fine, dust-like.
Interesting Facts
There is a mention of this flower in the writings of Pliny the Elder (ancient Roman writer). It says that the healers of those times, noticing the similarity of the foliage of the plant with curls, began to recommend it as a remedy for hair.
In the Caucasus, even today, some peoples rinse their hair with infusions of the hair veneer plant. They believe that thanks to him, their hair shines. A decoction from the leaves of this flower is used in China in the treatment of tobacco and alcohol addiction.
The maidenhair itself, as noted above, does not tolerate tobacco or any other smoke.
Rules for growing Adiantum Venus hair at home
In nature, Adiantum is most often found among stony placers, growing in the ground, which is clogged between the ledges in the rocks. Such plants are called lithophytes, and in order for them to grow well at home, they need to provide the most familiar conditions - a similar soil composition and a suitable pot.
The container for the Venus hair should be shallow, because the fern has a shallow root system. For him, the width of the pot will be more important. Good drainage will also be a prerequisite, which must be placed at the bottom of the container. Pour soil on top. It should have a slightly acidic reaction, absorb moisture well, but not retain it for a long time.
Tip: To keep the substrate nutritious and light enough, add a mixture of humus, perlite, peat bog and sand to it. It will also be useful to add bark and charcoal to the soil.
During the planting process, place the plant in such a way that the root collar remains above the substrate, because it will begin to rot under the ground.
Important find the right place for the plant... Hair Venus develops best in partial shade. The plant will grow well on a windowsill that faces east or northwest. If in summer direct sunlight falls on the Maidenhair, it is better to remove it from the window, or cover it with a translucent screen. From intense sun exposure, the plant can fade and even wilt. But you shouldn't put him in full shade either, he will survive there, but he will not be able to boast of emerald greenery. Venus hair will not grow well even in the presence of drafts and smoke from cigarettes.
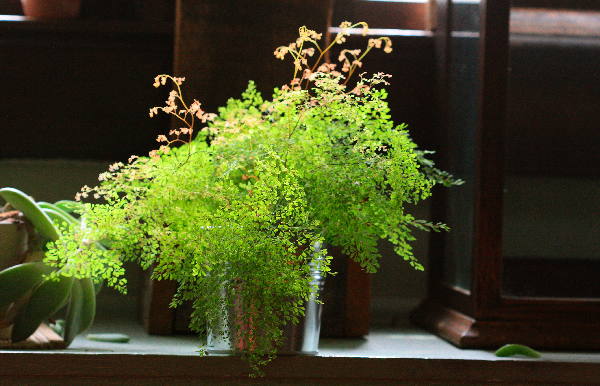
Fern care includes the following activities:
- Watering. Maidenhair does not tolerate both dry soil and excessively moist soil. Therefore, watering should be regular and moderate. The chlorine content in the water will be detrimental to it; for irrigation, use only settled or filtered water. The intensity of watering differs by seasons - in late spring and summer, the plant is watered more often and more abundantly, at this time new leaves are formed, and in the cold period, watering once a week will be enough.
- Top dressing. They can only be carried out during the active growth of the plant, that is, from May to September. To do this, once every 3 weeks, you need to use liquid fertilizers. Only the dosage indicated in the instructions must be halved, because for the Maidenhair a large amount of fertilizers will do more harm than good.
- Maintaining the temperature within acceptable limits. During growth it is 20-25 degrees, and during hibernation - 15 degrees. In such conditions, the fern will not disturb you with yellowed leaves or the appearance of dark spots on them. If signs of wilting or hypothermia have already appeared, it is necessary to timely prune the damaged leaves, and create suitable conditions for the Maidenhair.
- Maintaining the required humidity level. If the leaves of Venus's hair began to dry out, you need to make the air in the room more humid. You can use both household humidifiers and improvised means, such as a container of water or a wet towel on batteries. Frequent spraying of the leaves with water also helps.
Tip: To ensure optimal humidity in the summer, Venus hair can be placed on a closed terrace or in the garden.
Observing all the rules for caring for the Maidenhair, you can easily grow a beautiful, voluminous plant. And then you can learn how to reproduce the fern yourself.


Beautiful maidenhair (A. venustum)


This neat and very elegant plant is barely 20 centimeters tall. The homeland of the beautiful maidenhair is the subtropical regions of Indochina, where the species, as in the photo, settles on stone placers under the canopy of the forest.
According to the photo and description of the maidenhair, it has complex-pinnate openwork leaves with segments of an ovoid-shaped form. The outer edge, where spores mature, is finely toothed. The color of the leaves is light green.
Use in traditional medicine
The benefits of maidenhair were described in antiquity. The then scientists had a theory about the treatment of these ferns hair loss in humans... And even today, in certain regions of Transcaucasia, maidenhair is used in collecting herbs, as a means of activating the growth of hair.
In the modern world, the maidenhair flower has been included in the list of various medicinal preparations due to the official confirmation of its beneficial properties... It helps with the following problems:
- in the treatment of inflammation of the respiratory system;
- with infections parasitic;
- decreased fever;
- for mild soothing of nervous manifestations.


The roots and green part of the stem, when used correctly, can help relieve the symptoms of alcoholic or chemical poisoning... In some countries, ointments were made from a fresh leaf, ground to a homogeneous mass. They were applied to tumors. A decoction from the leaf part helps relieve stomach pain and intestines.
Reproduction and feeding of the plant
Indoor types of Venus hair are planted in small bowls or containers with a drainage system. The substrate is prepared on the basis of deciduous humus. The soil for cultivation can consist of peat, deciduous humus, sand and pieces of wood coal (2: 1: 1: 1). Fern mix should be slightly acidic. It is better to choose breathable containers for maidenhair, such as clay pots.
The plant is propagated vegetatively - by dividing a bush or rhizome in the spring months. It is much more difficult to grow with spores. In humid conditions, a gametophyte is born from spores - a miniature plant on which gamete cells are located.
The plant tolerates transplanting well, and the best time for this will be spring, when the roots will be visible from the drainage hole. Venus hair is transplanted annually into forest, deciduous soil, fertilized with peat. In too large a container, it will not take root, but in a cramped pot it can grow and please the eye with its delicate foliage for a very long time. Only in case of obvious crampedness, when the maidenhair stops its growth and the roots entwine the entire earthen lump, a transplant is needed. The soil should be loose and good air permeability, since stagnant water is unacceptable for hair venus.
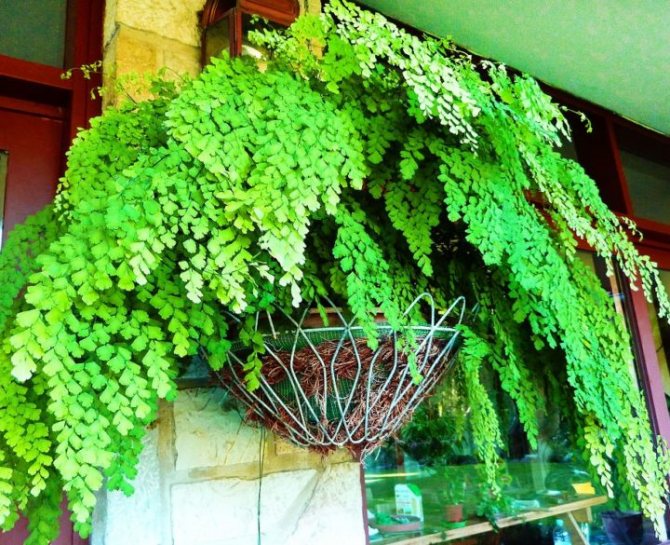


Maidenhair with good feeding
Venus hair is fed during the period of active growth once every 30 days in the spring-summer months with a solution of mineral fertilizers in a half dose. Maidenhair do not react well to high doses of fertilizers.




































