While we were on vacation, the mother-in-law tried so hard to care for the flowers that she completely flooded the orchid. As a result, the plant was left without a root system. Of course, at first I was very scared that the orchid would die, but after looking for all the information, I found a way to revive and revive it. I want to share my experience with all flower lovers, how to revive an orchid without roots and save a flower.
Possible reasons
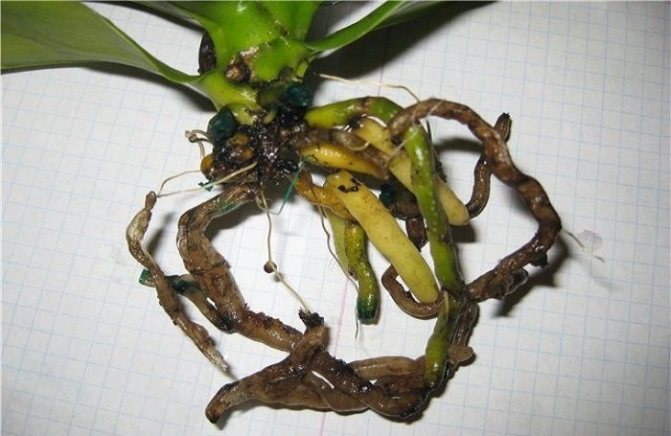

The structure of the Phalaenopsis root system is inherent in all epiphytes. This group of plants does not have small and thin roots, which, like other crops, absorb nutrients. This role is assigned to the ribbed surface of the large roots. It consists of dead hollow cells, it is they who absorb moisture and nourish the culture.
If the absorption process is disturbed, the plant begins to hurt and, if no action is taken, dies. There are many reasons that the roots of an orchid rot, yellowed leaves are formed.
- The substrate in the pot gradually compresses, becomes compacted and heavy. This leads to accumulation of moisture and a lack of oxygen supply. It is important to change the substrate and prevent the formation of small particles.
- With a lack of light, some of the moisture remains on the roots. Too wet soil contributes to the onset of decay processes. Lack of light and moisture is detrimental to the orchid.
- Incorrect fertilization. The roots are very thin and delicate. If you use the wrong ratio of potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen components when feeding, then there is a high probability that the roots will suffer from chemical burns.
- Damage can be easily caused during transplantation. An infection can get into any untreated cut, which leads to decay, the plant dies.
- Damage by pests (for example, click beetles) and fungal diseases.
Most of the reasons are due to improper care, namely nutrition, hydration and watering.
On a note!
Problems often appear in the fall or winter when Phalaenopsis is at rest. During this period, it is required to reduce watering.
Why do roots die off in an orchid?
The main reason for orchid decay is waterlogging during watering or planting in a too dense substrate. In the natural environment, the roots are on bark or stones and independently regulate the amount of absorbed moisture. At home, a constantly moist and dense substrate interferes with air circulation in the roots. Unable to cope with an excess of water, they begin to rot.
The reasons for the violation of metabolic processes in the roots and their withering away can also be as follows:
- Lack of moisture or overdrying of the substrate.
- Infection with fungi or bacteria.
- Watering with hard and saline water;
- Burns from improper fertilization or overfeeding. Thin orchid roots suffer from high content of macronutrients in top dressing and begin to "burn".
- Lack of lighting. With a lack of sunlight, the roots stop developing, the processes of photosynthesis are disrupted in them.
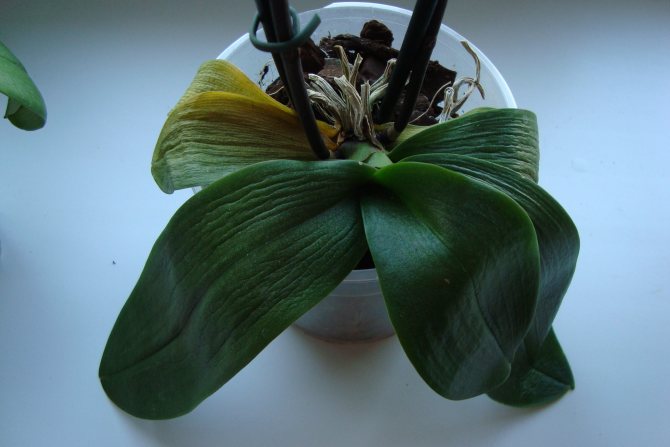
Signs of decay appear on the leaves of the orchid and are reflected in its general condition:
- the leaves lose their green color, become lethargic, the tips dry out;
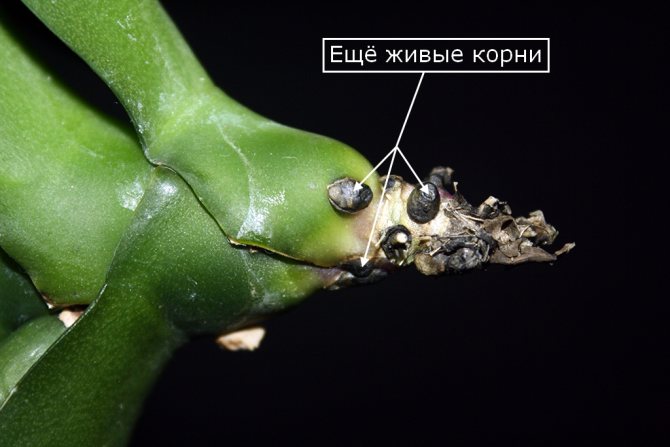
- the roots soften, darken, become covered with necrotic spots;
- the orchid does not release a flower arrow, does not form new shoots.


Symptoms of the disease
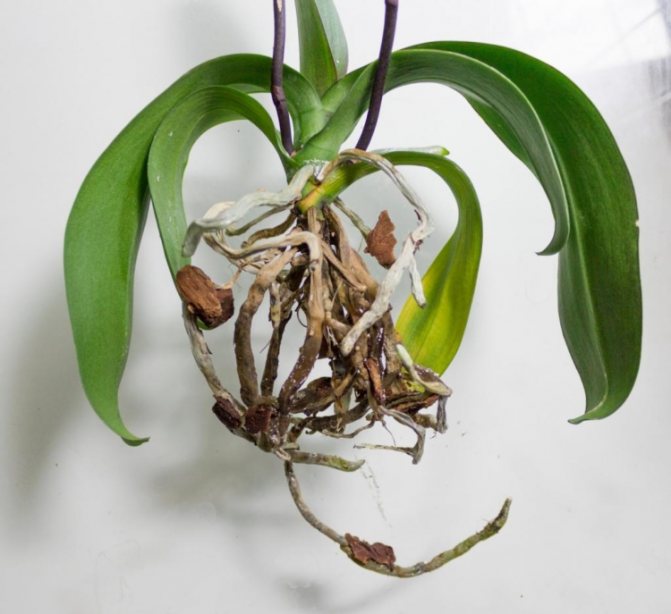
One of the reasons to use transparent containers for planting orchids is the ability to monitor the health of the root system. With a regular examination of the condition of the roots, it will be possible to cope with the problem in time. Healthy roots have a gray-green color, they are firm, firm, with a smooth surface. If they turn pink, brown, yellow, this is a sign that the plant is gradually disappearing.
Signs of culture malaise:
- a greenish bloom begins to appear on the walls of the pot, consisting of spores and algae;
- diseased roots do not hold in the substrate, the flower moves;
- the root system does not seem airy and light, it has become shrunken, darkened;
- leaves wither and turn yellow.
If even one of the signs is present, then the plant is pulled out of the pot and each root is carefully examined.
Confirm that the roots have rotted, the following points:
- slimy and wet areas are observed;
- root tissues fall apart into separate threads;
- when pressed, the roots secrete liquid;
- the root system has become dark in color.
Root decay is irreparable, so it will not be possible to restore these areas, but it is real to save the intact parts. You will need to gradually grow new roots in the orchid.
Additional resuscitation measures
It is advisable to strengthen a reanimated plant in a greenhouse or flowerpot without a substrate using the following manipulations:
- daily soaking of the neck with the remnants of the rhizome in a nutrient solution for 2-3 hours (in a greenhouse - once every 10-12 days);
- rubbing the root collar and remaining leaves with a cotton pad or sponge dipped in a stimulating solution;
- bathing in warm water with dissolved vitamins, fertilizers, glucose.
Orchids planted in a substrate are fed by irrigating the surface of the soil or by foliar method, wiping the base of the stem and the remaining leaves with a weak solution of fertilizers or growth regulators.
How to save a flower with rotten roots


If the leaves look lethargic, lifeless, and watering is not conducive to recovery, you should be on your guard. If you detect rotting at an early stage, then it will be faster to reanimate the orchid at home. With the right approach, you can reanimate an orchid even without leaves.
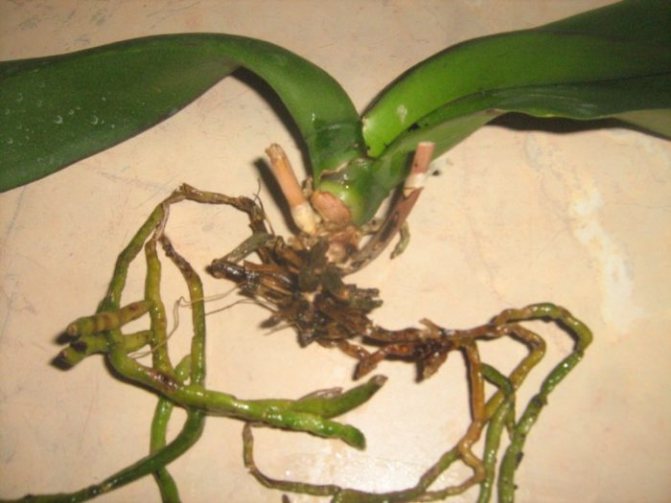
First, the condition inside the pot is examined. If the roots of the orchid are yellow, they do not think about what to do, but remove it. This is the first sign of the onset of rot. All rotten and dry roots are cut off.
On a note!
If only 2-3 roots have been removed, then nothing else will be required besides transplanting into fresh soil and competent care. The plant will recover quickly.
But if the entire root system or most of it is removed, then they begin emergency recovery.
Rescue methods
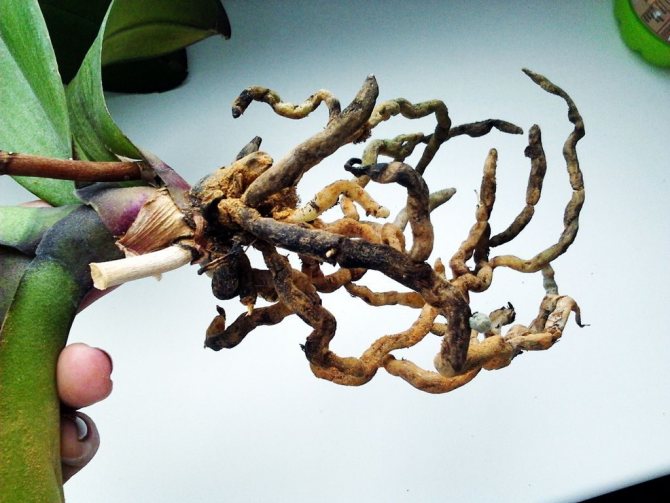


Reanimate the orchid if all the roots have rotted. They do not throw it away, but try to save it by growing new ones. They use one of three resuscitation methods to help grow roots in an orchid:
- we restore using a window-type greenhouse;
- by transplanting into a traditional substrate;
- resuscitation with alternating placement in water and drying.
Before the start of recovery, the condition of the flower and the degree of root infection are assessed. If a flower has lost about 60% of its roots, then it is really possible to save it in 1-2 months. In the absence of roots at all, recovery can take about a year.
The choice of recovery method depends on:
- from the general state of culture;
- from the volume of the roots located at the base of the outlet;
- from the state of the leaves.
Also, the choice of the recovery method is influenced by the conditions organized by the owner. Reanimate if all the roots of an orchid have rotted, it is more expedient in a greenhouse.
How to restore correctly in greenhouse conditions
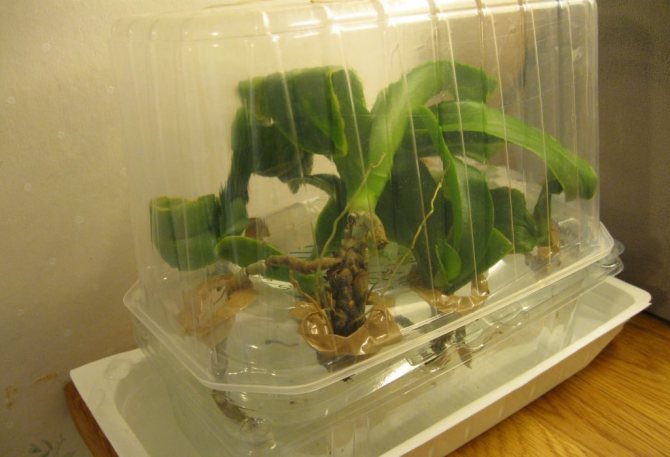


It will be faster to save an orchid at home if there is a greenhouse for a window, where a specially high humidity (70-100%) and temperature (22-28 degrees) are created. At the same time, light is provided with a duration of 12-14 hours. At rates lower or higher, the roots will not develop, but pathogenic bacteria and fungal spores will actively multiply.
Resuscitation of an orchid without roots is carried out as follows.
- The first layer is drainage (expanded clay).
- Sphagnum is distributed from above. It is pre-cleaned and steamed.
- The substrate is slightly moistened and a flower is set in it.
The flower will have to be in the shelter until the roots of the orchid grow up to 3-5 cm.To speed up, they regularly stimulate growth. The substrate is moistened on demand, the greenhouse is ventilated.
On a note!
It is more advisable to leave it at night, so that the soil and air inside are saturated with carbon dioxide. It is this component that contributes to the fastest formation of growing roots, it will turn out to grow them faster.
How to save without a greenhouse


You may be interested in: How to care for orchids in a pot after purchase Why orchid leaves wither and how to save it Features for the care and reproduction of Dendrobium Nobile orchids
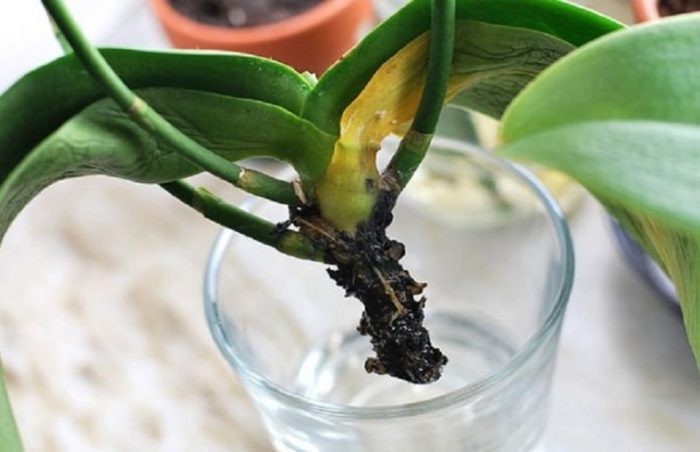
If there is no greenhouse at home, it is still possible to save an orchid without roots. The orchid is reanimated in water. The diseased flower is processed and placed in a glass container. Every morning it is partially filled with water. The water used is pre-filtered or boiled. Water is poured so much that only the lower part of the roots comes into contact with it. The leaves should not get wet. The plant is in the water for 6 hours. The flower is left until morning, during which time it will dry out.
To make the revitalization process go faster, use a little trick. For each liter add 1 tsp. honey or sugar syrup. With regular moistening of the substrate, you can additionally add:
- iron-based products;
- monthly growth stimulant;
- complex fertilizer solution for orchids.
If part of the roots has died, then they are saved by transferring to fresh soil. Rotten roots are removed, the sections are disinfected with chalk or activated carbon. For planting, a pot with a diameter of 6-8 cm is taken. The orchid is provided with a temperature regime of 20-25 degrees with a duration of illumination of 12 hours.
On a note!
It is important not to lower the temperature at night. Instead of traditional irrigation, the option of irrigation over the soil surface is used. You can set the pot in a container of liquid for 30 minutes, then drain the excess and send the orchid to a permanent place.


Condition assessment
Before proceeding with resuscitation, it is necessary to assess the degree of damage caused to the orchid..
Procedure:
- Gently remove the plant from the container.
- Free the roots from the remnants of the old substrate.
- Rinse the rhizome with warm running water.
- Put on a napkin and let dry in the open air at room temperature.
- Sterilize tools (knife, scissors, pruning shears, tweezers, etc.) in boiling water or over a fire. Can be processed in peroxide or potassium permanganate solution.
- Trim and sand off all dead areas to healthy tissue.
- Treat the cut sites with carbon powder (grind a tablet of activated carbon into dust) or cinnamon powder.
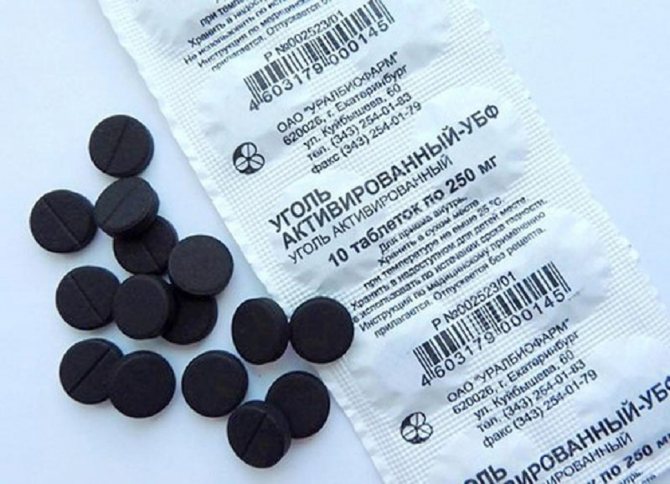

Activated carbon is the best antiseptic agent for treating plant wounds.
You should not get rid of yellowed, partially dried, withering leaves... In the absence of roots, they serve as an alternative food source. For the same reason, it is not recommended to remove shriveled, shriveled pseudobulbs.
How to reanimate at home
If the orchid is sick: the leaves are withering, the roots of the orchid have disappeared or rotted, do not be upset. In most cases, the situation is fixable.The basic rule of recovery: to provide proper care, care.
What to do when there are no roots and leaves
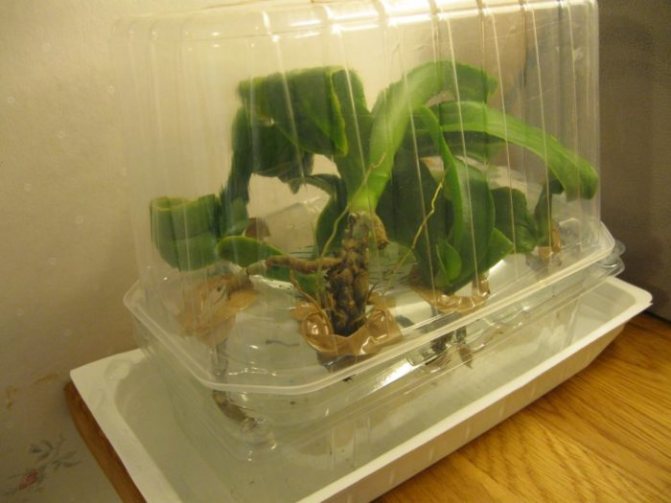
If all the roots have disappeared and the leaves have begun to fall off, then only urgent resuscitation measures can save the orchid. The probability of her death is high. Use a greenhouse. You can buy it at a specialty store or make your own from a plastic bottle. Expanded clay is laid at the bottom, then moss.
An important condition for restoration is high-quality lighting, sometimes it is advisable to buy a phytolamp. In such a substrate, you need to root an orchid without roots.
To restore, the orchid is periodically soaked in an aqueous solution or nutrient composition. The base where new leaves will form is regularly wiped with a growth stimulant.


When bathing orchids, special substances are introduced into the water.
- B vitamins. They stimulate the formation of new roots. Vitamins are stirred in water, feeding is performed once a month, and growing roots are treated with it once a week.
- Growth stimulant. It contains many phytohormones that help restore the structure of the roots. When soaking, add to water monthly.
- Fertilizer with iron chelate. Accelerates the growth of all parts of Phalaenopsis.
- Glucose. In healthy orchids, this substance is created in the required volume as a result of photosynthesis. Glucose is necessary for the creation of new cells, therefore, for diseased flowers, regular feeding is performed based on this substance.
- Complex fertilizer with potassium and phosphorus. Feeding frequency: 1 time in 2 months.
Restoring a diseased orchid without roots or leaves at home takes a long period. Sometimes it takes a year to return a favorite plant to a healthy state.
There is no growth point
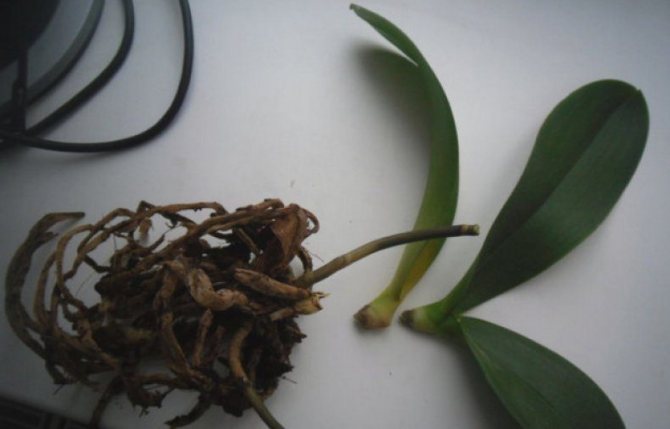


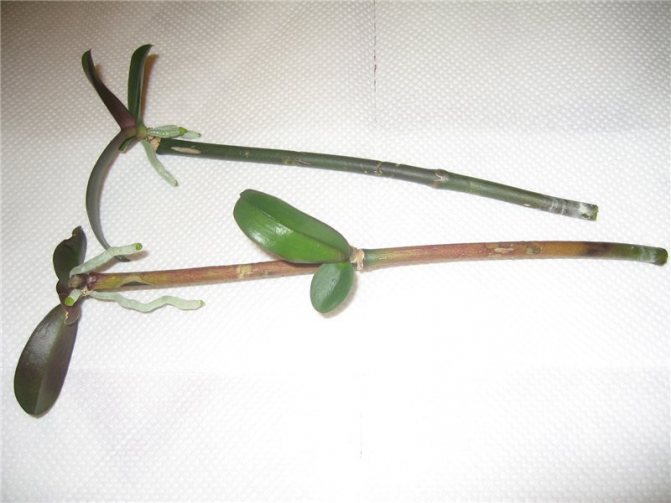
Choose the water rooting option. You must first remove the roots with scissors (they are previously disinfected). Now place the orchid without a growing point in the water. The top of the orchid should be above it.
The orchid is placed on a lighted windowsill. After a while, new roots will begin to form.
How to save an orchid without leaves
Sometimes the leaves dry and rot. It is easiest to save an orchid without leaves, but with roots. They can be restored with simple measures.
- They do not wait until all the leaves fall off, take the flower out of the pot and carefully examine the root system.
- If there is no damage, then you can not transplant.
- Regulate watering.
- If not only the leaves have fallen off, but the roots are also damaged, then a greenhouse is used.
- The system of concentration of dressings and other strengthening agents is clearly monitored.
On a note!
It is important to understand correctly whether a natural change of leaves occurs with a flower or this is a pathological condition. In a natural process, they do not perform any actions other than care, but if an orchid without leaves is damaged by pests, urgent resuscitation is required.
How to root and transplant Phalaenopsis?
Practice shows that the method of growing roots in a greenhouse or substrate is not suitable for the Phalaenopsis orchid. The plant reacts sharply to waterlogging of the substrate, which often occurs in the greenhouse. High humidity created in closed conditions is also harmful. The best option is rooting in sphagnum. This loose material, which retains moisture well, creates the necessary conditions for the plant.
Rooting order:
- A transparent pot with holes in the bottom and walls is filled with a layer of drainage, and then sphagnum is laid. Sprinkle moss from a spray bottle.
- The orchid outlet is kept for 5-10 minutes in a stimulant solution: Radifarm (1 drop per liter), Zircon (4 drops per liter).
- In the center of the sphagnum, a recess is made and a Phalaenopsis rosette is placed in it.
- The plant is kept at a temperature of 21-25 degrees in a well-lit place. In the warm season, the best place is the east window, in winter - a backlit shelving unit.It is not worth installing the plant on the window in winter, because the glass is cold.
After about 2 months, roots begin to grow in Phalaenopsis, and after 4-5 a young leaf is formed. The plant can then be transplanted into an orchid substrate.
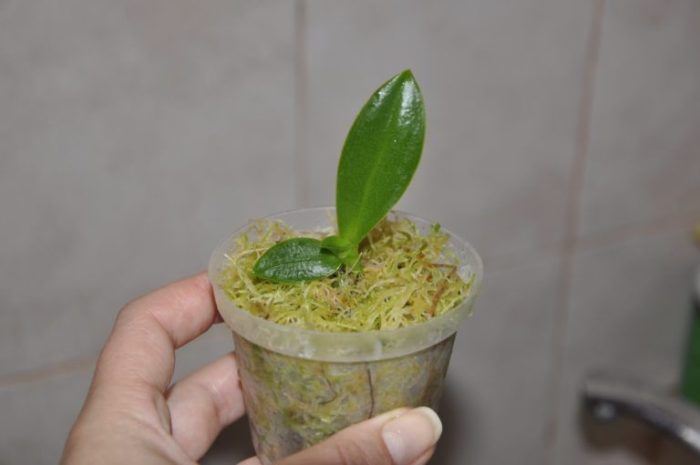


When there is no point in reanimating


If the flower is completely left without roots and leaves, then most likely it will not work to save the dried orchid. All efforts will be in vain. If at least part of the root system is preserved or the roots have dried up and the leaves turn yellow, then it makes sense to try.
The first step is to remove all diseased leaves and roots. Then the flower is dried. The sections on which the cut was performed are thoroughly disinfected. You can treat the roots of the orchid with crushed activated carbon.
The part of the root system, where the formation of new roots will take place, is treated with nutritious vitamin solutions. In order for the plant to recover, thorough care is organized for it.
On a note!
A lot of time can be spent on orchid resuscitation measures: from 1 to 12 months. Therefore, they do not expect a quick effect.
Answers to current questions
Question number 1. What is a closed rooting system?
As practice shows, a damaged orchid recovers faster in a closed system than in the usual "leaky" containers. A closed container is prepared as follows:
- Select a vessel of a suitable size without drainage holes. For a plant without a root system, a glass jar, mug, disposable cup, glass are suitable.
- A layer of expanded clay is poured up to 1/3 of the height of the vessel, which is filled with water.
- Sphagnum is spread on expanded clay with a layer of 2-3 cm.
- The remaining volume up to ¾ of the height is filled with pieces of bark.
- The reanimated plant with the remnants of the rhizome is fixed vertically on the surface of the substrate, without deepening the neck.
Expanded clay at the base of the pot must be constantly covered with water, which evaporates and moistens the upper layers of the substrate. The required level of liquid is maintained by pouring water along the wall of the vessel, being careful not to wet the bark.
Withering plant care


An orchid after resuscitation and in a sluggish state requires careful care. We must not forget that the flower tolerates a slight drought better than overflow. Another important point is quality light (12-14 hours). They make him absent-minded.
In order for the rooted roots to recover faster, the pot is chosen transparent with holes for air intake.


Common mistakes
A typical mistake of novice florists when resuscitating an orchid is to speed up the recovery process by any means. Everything is used at once and in huge quantities. Meanwhile, such unjustified fanaticism, instead of benefit, causes even greater harm to the flawed plant, which is left without the main part of the rhizome and almost without leaves. In this situation, it is much more important to think over a treatment plan, scrupulously implement it, making adjustments depending on what effect this or that procedure gives, how the next drug affects the state of the plant. This process is lengthy and should not be forced.
Preventive measures
In order not to meet with decay of the roots of the orchid, they carefully monitor their condition, strictly observe all recommendations for the care of the crop. These are preventive measures.
An important prerequisite is a correctly chosen pot. It should be transparent, have holes, and a drainage layer. It is impossible to bring the substrate to a state of strong compaction, when there are disturbances in the flow of air, as well as stagnation of moisture.
After watering, excess moisture is allowed to drain, and only then the pot is rearranged to its old place. During the rest period, additional artificial lighting is organized if the daylight hours are less than 12 hours.
Resuscitation in greenhouse conditions
For an orchid during resuscitation, it is desirable to create comfortable conditions close to their natural habitat. For this, the plant, or what is left of it, is placed in a greenhouse, where a constant temperature regime of + 24-28 ° C is maintained and the corresponding humidity level is at least 80-90%. The bottom of the container is laid out with expanded clay, moss or a substrate usual for a particular type of orchid. To avoid the greenhouse effect, the greenhouse is regularly ventilated. In the dark, 10-12-hour daylight hours are organized by means of artificial illumination.
Tip # 1... A greenhouse for resuscitation can be any transparent container that is suitable in size: an empty aquarium, covered with plastic on top, a large plastic bag, an inverted plastic container, a large cut-off water bottle, etc.
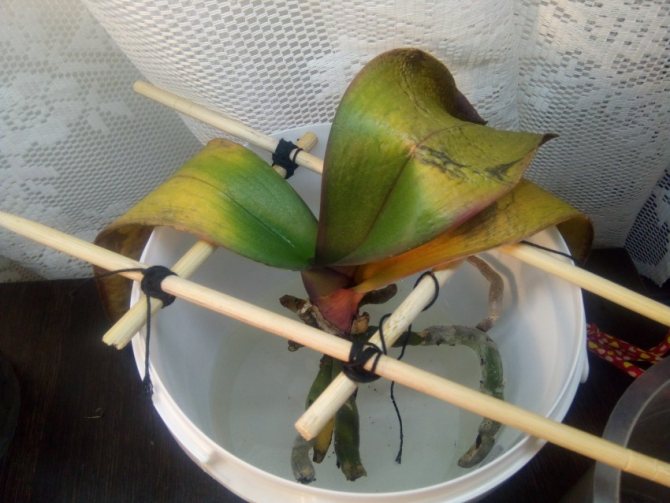


Instead of a greenhouse, you can secure the plant in a vessel using a lattice of sticks or wire so that the roots remain above the surface of the water.
Testimonials
Natalia, Novosibirsk
“I bought a flower in a store and gradually began to fade. I looked closely, the roots became smaller. Cut off all rotten roots. In addition to all the measures described, I periodically wiped the roots with succinic acid (1 tablet per 0.5 liter).
Svetlana, Omsk
“I bought a flower, but it turned out to be infected with pests (thrips). I didn't see it right away. The leaves are gone. I thought the orchid was dying. But I read that there is a chance to save, if there is a green root system. I treated them from pests and began to look after. The flower gradually recovers. "
It is difficult to care for a sick and lethargic orchid, but it is quite possible. If you correct your mistakes in care and make a lot of effort, then you can really revive the orchid. Recovery time can be long.
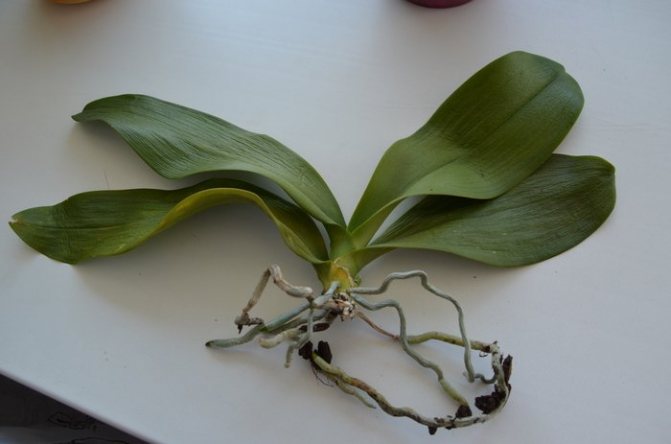
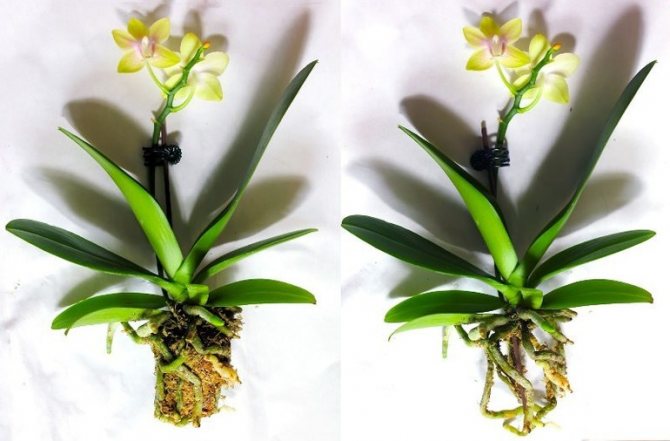
If roots and sluggish leaves rot
Since the orchid is a resident of the tropics, many people mistakenly believe that it needs intense watering and bright sun. This is totally wrong. In the first case, root rot will begin, and the flower will not receive enough nutrients. In the second, burning the orchid with the sun will damage the leaves and cause serious stress for the flower, which can also result in death.


Figure 2. Root decay can be triggered by over-watering
To prevent your orchid from turning yellow and dry, you need to work out a proper care schedule. This primarily concerns watering. To prevent the roots of the orchid from rotting, you do not need to fill it with water. It should be remembered that in the natural environment, this culture parasitizes on trees and absorbs moisture from natural precipitation, so it does not need to be watered too often (Figure 2).
Note: Watering time can be determined visually and by touch. In the first case, the walls of the pot are carefully examined. If condensation has accumulated on them, the plant still has enough moisture. If you are not sure, touch the soil: its top layer should be completely dry. Only then can you start watering.
If the roots of the orchid still rot, remove it from the old pot, carefully trim the damaged parts of the roots and transplant the flower into a new container. In the next few days, you will have to refrain from watering.
Lack or excess of moisture is far from the only reason why an orchid withers. The slow death of a plant can also be provoked by an incorrect location. It should be remembered that in nature the flower illuminates the scattered sun, so you should not put the pot on the southern windowsill.
Leaf problems
The plant often suffers from foliar problems. Orchid greens can:
- turn yellow, and completely;
- wither, sink;
- "Decorate" with spots and holes, other suspicious artifacts.
The likely cause of foliar ailments is overheating of the plant. An orchid can suffer from heat only when it is located near the radiators, but also when it is in direct sunlight.
The first step is to eliminate the likely cause of the problem and wait a few hours. During the waiting period, do not water the plant, only spraying is permissible not earlier than after three hours.
Quickly, however, after overheating, it is unlikely that the orchid can be restored. With the most favorable development of events, the first positive changes should be expected no earlier than in 4 days.
Natural aging
Inexperienced growers often mistake the natural dying off of orchid leaves for a plant disease. You should know that the leaves tend to grow old and sooner or later, but wither, die off and give place to young growth.
In the case of this completely natural process, the foliage will wilt slightly, and only in the lower part of the stem. You should not try to speed up the process by cutting off the withering leaves - such an intervention will negatively affect the well-being of the orchid. The leaves should die off on their own.
How to care after resuscitation procedures


Consider the main nuances of caring for an orchid after the flower has been revived.
Top dressing
Be careful with this procedure after resuscitation. While the orchid has not yet fully recovered, it should not be fed: the plant may react poorly to additional nutrition.
After a month has passed after resuscitation, you can start feeding, but carefully, in moderation. An excess of nutrients leads to darkening of the roots of the plant, tarnishing of its leaves, and wilting of flowers. A banal root burn with a large amount of fertilizers provokes these negative changes.
Watering
The procedure should also be carried out with caution. It is recommended to use the method of spraying or pouring water into the pan.
Protection against parasites and fungi
When only the orchid was brought into the house from the store, it is necessary to immediately check for the presence of pests on the plant. Finding out about the presence of parasites is simple: you need to put a pot with a plant in water. If there are pests, they will begin to crawl up the flower from the water. If insects are found, you need to change the soil in the pot, washing and treating the roots of the orchid with a fungicide.
To prevent the appearance and spread of the fungus, you should be careful about watering the plant, avoiding waterlogging of the soil. A regular examination of the roots will also help in order to have time to stop the onset of the disease at an early stage.
Fertilizing


Top dressing is carried out as follows:
- Dilute the fertilizer purchased from the flower shop with water.
- Pour the agent into a spray bottle and spray the orchid, especially the leaves on both sides, excluding getting into the point of their growth.
- It is also allowed to wipe the leaves on both sides with a sponge soaked in fertilizer. This procedure is best done in the morning.
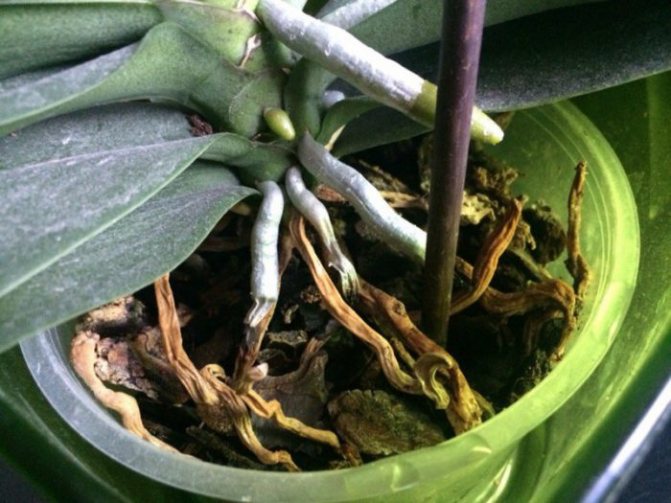
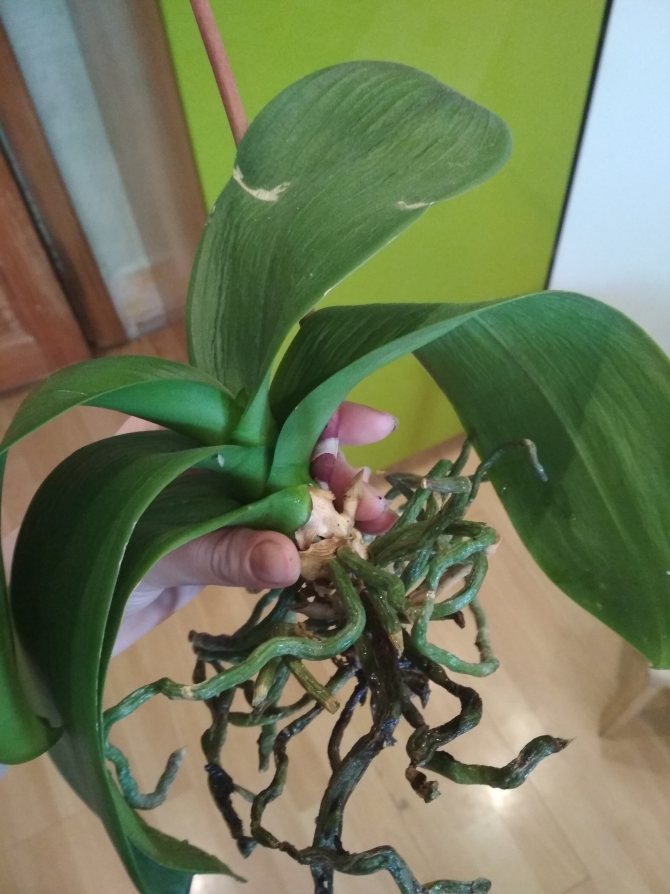
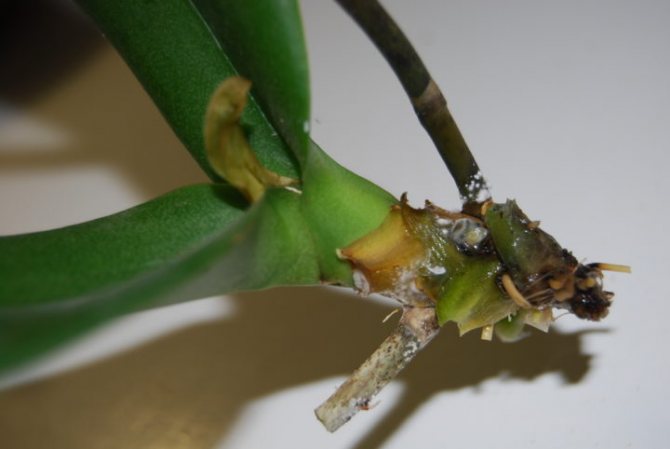
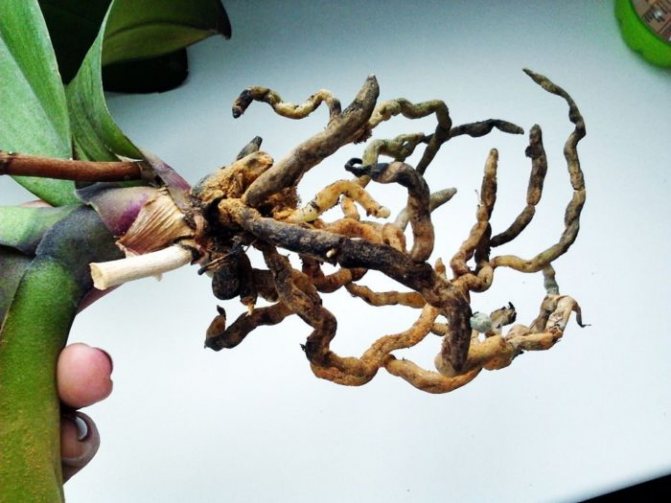
Appearance of healthy and rotten roots
Since the roots are a key part of any plant, if damaged, it will slowly wither or even die. However, if the right measures are taken in time and the culture is properly cared for, it will begin to renew itself and create new roots.
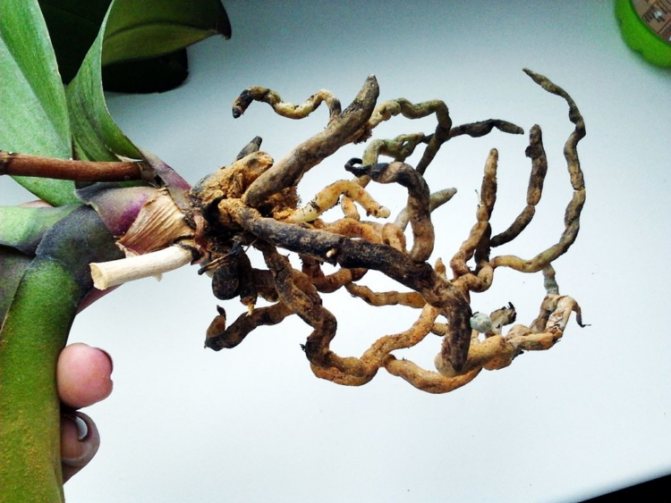
A healthy root system is characterized by a green tint, which is due to the receipt of sufficient nutrient moisture. Dry scions become silvery or white.
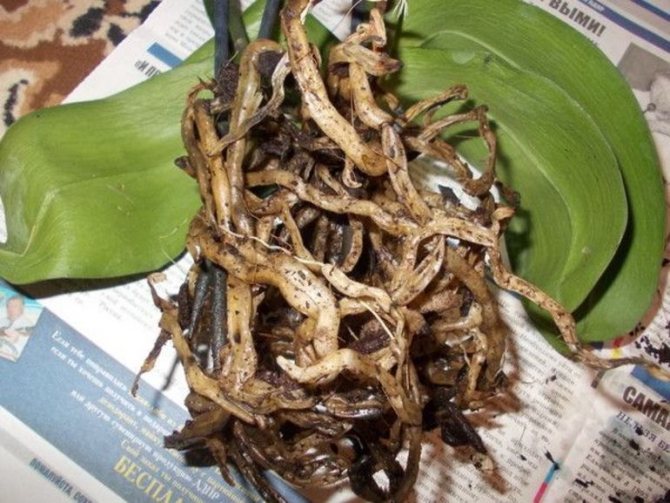


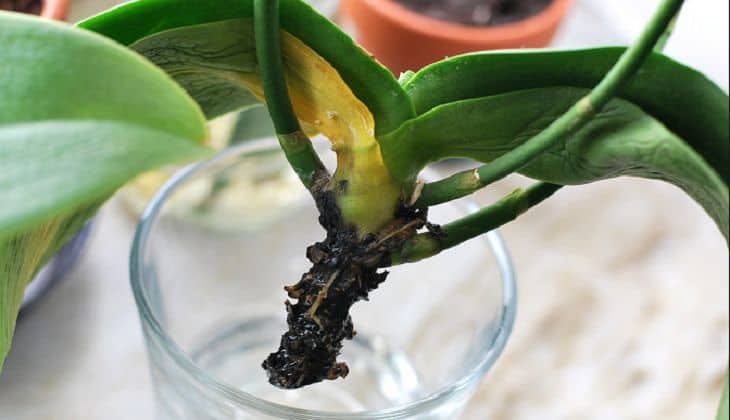
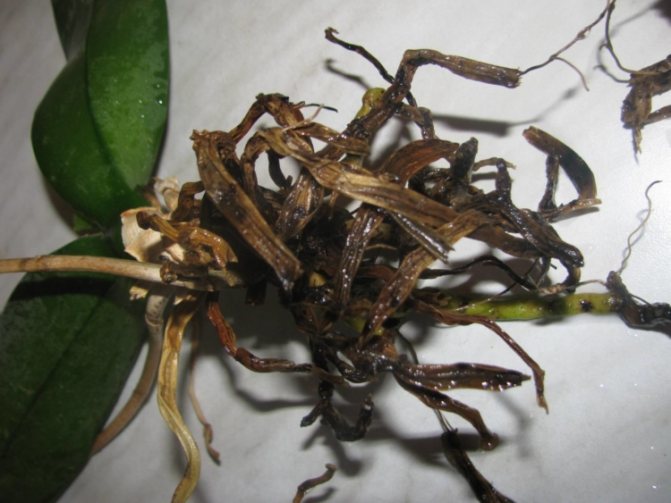
As the roots rot, they lose their normal density.break down and turn brown. Over time, they begin to disintegrate, leading to an unpleasant odor and mucus. In order not to lose an exotic plant, it is worthwhile to start resuscitation as soon as possible.
After purchasing a flower from a store, it is important to do a thorough inspection of its roots and get rid of damaged elements with a cleaned garden tool.Further, the sections of the cuts should be treated with charcoal or activated carbon-based powder. Root decay increases the likelihood of mold growth, which quickly spreads to other crops and causes the death of the orchid.
To obtain accurate information about the condition of the roots, you need to get rid of the substrate and rinse the underground part of the culture.
Among the key signs of putrefactive or infectious processes are:


- The appearance of a dark shade on the root system.
- Formation of areas with mucus and wet surfaces.
- Leakage of fluid when pressing on the root.
- The appearance of a filamentous appearance of deformed roots.
If the roots of an orchid have rotted, how to save them will depend on several factors. If there is a large dark area, it will need to be trimmed to the healthy area.
Do the same with dried rhizomes. If 2-3 roots are lost, the culture will need to provide increased care in order to restore its vitality. However, if the Phalaenopsis or Pachyphytum orchid has lost most of its full-fledged tissues, the likelihood of its death will become extremely high.
Root rot
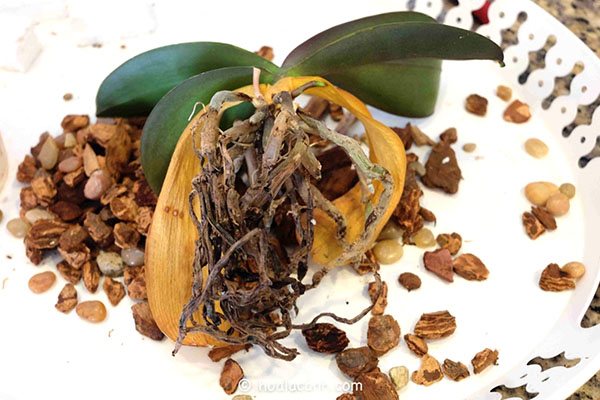


A very dangerous condition that can lead to the death of a flower. Most often, three reasons lead to root decay:
- fine, crumbling substrate;
- lack of light;
- high humidity.
Let's consider all the above reasons in more detail.
Substrate
All growers know that orchid substrate has a special composition: it is fibrous, consists of separate fragments. Therefore, it is important to choose a high-quality soil, with elastic particles that do not lose their shape.
Fragments should not quickly disintegrate into fibers, crumble strongly. When this happens, small particles of the substrate begin to rot, decompose, and mold: as a result, instead of a soil that absorbs moisture well, a mushy substance is formed in the pot. The roots of the orchid, being in such a substrate, rot. Soon the flower may remain without roots at all.
To cope with the problem, you need to fill the container with a fresh substrate, consisting of whole fragments that have not lost their elasticity. It is important that the substrate is well permeable to both moisture and air.
Lighting
Keeping an orchid warm requires a lot of light. Moreover, the higher the air temperature, the more lighting the flower needs. For wintering, choose the lightest window sills in the house, since when the batteries are running, the plant's need for light is especially great.
If the orchid is kept warm, but in partial shade, this will inhibit the development of its root system, lead to decay, yellowing of the leaves.
Humidity
The orchid should be grown in a very high humidity environment - as much as possible. It is clear that in an apartment it is not always possible to provide tropical conditions, but whenever possible, at least carry out regular spraying. The spray should be fine, better dispersed. It is important to take care during the procedure so that water does not enter the deciduous sinuses. Otherwise, decay is also possible on the leaves of the plant.
Keep a distance between waterings: it is important to avoid stagnation of moisture in the soil. Between moisturizing procedures, the substrate should have time to dry well and ventilate. Moisture stagnation can be identified by the musty smell coming from the pot.
Use of growth regulators in orchid nursing
Experienced growers recommend using growth regulators that help strengthen the plant's immune system. The most commonly used are "Epin" (or otherwise - "Epin-Extra"), as well as "Zircon". These drugs help the orchid to regain strength. Dilute "Epin" should be in a dosage of 1 liter - 1 drop. In such a solution, you can soak the plant from 20 minutes to 2 hours. But remember that growth regulators by themselves are not a magic panacea for all orchid diseases.For the plant to feel good, it is necessary to create favorable growing conditions for it, including maintaining high humidity and sufficient lighting in the room. We hope you now know how to revive the phalaenopsis orchid. Care for the plant wisely, observing all agrotechnical rules of cultivation, avoiding overflow, hypothermia or overheating.
What is root decay and what does it look like?
Root decay is a common disease which, as a rule, is caused by improper flower care or the attack of harmful microorganisms. Rot occurs mainly in the cold season, when the daylight hours decrease, the air temperature decreases. Rot, if the process is not too started, is treatable. And throwing out a sick flower is only as a last resort.
Healthy roots are light green or pale gray. When moistened with water, the color acquires a rich, dark shade. Diseased roots are dark brown, pale yellow with white bloom.
How to identify the disease at an early stage?
If you regularly inspect the orchid, then at the next check the following symptoms may alert:
- leaves began to turn yellow and massively fall;
- buds, flowers are crumbling;
- the appearance of dark spots on the foliage;
- the orchid bent to its side;
- the flower is unstable in a pot;
- black or dark brown areas of the roots are visible;
- liquid seeps out of the rhizome;
- the presence of a mucous membrane is possible;
- the roots are moist to the touch;
- there is a clear putrid odor.
Influence on the whole plant
The root is an organ in orchids that is responsible for vital processes. First, the flower is attached by its roots to the substrate, thereby maintaining an upright position. Secondly, the roots absorb moisture and micronutrients from the soil. Thirdly, they, together with leaves, participate in the process of photosynthesis. One can only imagine what will happen to a flower without a root system.
Decay is best cured when the disease is at an early stage. Recognizing the symptoms later, it is unlikely that it will be possible to save the exotic from death.
Important. Use a transparent pot for planting your orchids so that you can regularly check the condition of the root system.
How to understand that the roots of a plant are rotting
In general, inspection of the roots of an orchid is not difficult, since the flower grows in a transparent pot. External roots can be seen, as well as aerial ones, if any.
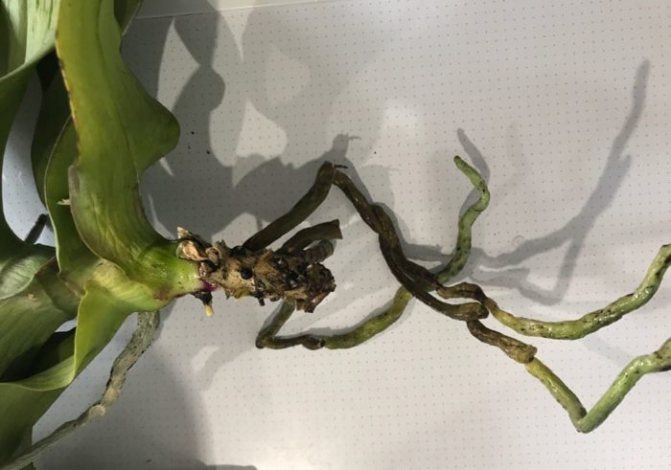
Outwardly, bad roots are easy to distinguish from healthy ones. Good roots have a fresh, green tint. Their surface is smooth, they themselves are fleshy and resilient.
If the spine looks different, for example, is dark, wrinkled, or dry, then there is a problem.
Secondary signs of root rot are when the leaves have dried or turn yellow, and the characteristic bloom on the walls of the pot. It happens that the orchid is already without leaves, the roots turn black or become brownish. Then measures must be taken this minute, without delay.
It should also alert if the leaves become yellowish, yellow roots, or if the greens have lost their elasticity, turgor.
Photo
Below you can see what rotting roots look like:
Freezing and sunburn


A delicate tropical orchid may well be overcooled - in our climate, this is not surprising. If only leaves and peduncles were frozen, then, without any doubt, the plant will survive and recover, although not quickly.
If the roots have suffered, resuscitation will be more protracted, but, however, in most cases, it will also be successful. However, if the growth point is caught by frost, and the latter has become watery, translucent, unfortunately, the orchid cannot be restored.
In the event of a sunburn, the affected leaves and flowers should be torn off, since it is no longer possible to restore their beauty. Then, be sure to move the orchid to a shaded area.
Outcome
In this article, we looked at a number of ways to save an orchid without roots. Summing up a little, we can conclude the following:
- The orchid disappears mainly due to improper care: due to extreme cultivation methods, violation of the watering regime. The plant also dries up with prolonged drying.
- There are several methods of resuscitation: in a greenhouse, over water and leaves in water. Determining the optimal way to restore the root system can only be based on the state of the plant itself.
- Thanks to proper care after resuscitation, orchids can be blooming after 2 years.
Have you faced the need to revive your phalaenopsis? Share your successes in the comments.
The timing of the revitalization of the orchid and actions after resuscitation
The recovery period of a plant can last from a month to a year, even if everything is done correctly.
The best time for flower resuscitation is spring or autumn. In winter, the chances of salvation are much less.


With the improvement of the external data of the orchid, when the leaves turn green and new aerial roots begin to grow, fertilization is stopped, watering is reduced.
Compliance with the rules of care is not a very laborious process, especially if it is an unpretentious Phalaenopsis orchid, you just need to more closely monitor the plant in order to make corrective actions in time.
The most common causes of death of phalaenopsis
In the wild, Phalaenopsis orchids grow in warm, humid places, holding strong roots to the bark of trees. In the bark, they find a nutritious microflora that allows them to grow and develop. Tropical showers fill the plant with moisture, and the warm sun penetrating the foliage of the trees starts the process of photosynthesis.


Since in our latitudes the air temperature can have very large fluctuations, and humidity and lighting are not always ideal for orchids, phalaenopsis cannot grow in natural conditions, but they have perfectly learned to adapt to domestic ones. Even if the orchid is frozen, the innate immunity will help it to get out or continue its kind in children.
Let's list the most unfavorable conditions for keeping phalaenopsis:
- lack of regular watering;
- high humidity at low air temperatures;
- increased dryness at high temperatures;
- lack of air flows;
- drafts.
Important! Orchids do not respond well to any extreme conditions and do not tolerate extremes in care. The easiest way to speed up the death of a plant is to dry it for too long, and then water it abundantly.
The result of this treatment is often the need to reanimate an orchid without leaves or without roots.
You can understand that the orchid is disappearing by the following symptoms:
- The roots in the pot are gray-brown or black in color - this means that they are rotten and need to be urgently removed from the pot.
- The roots in the pot are not visible.
- Black spots appeared on the neck.
- Leaves lose turgor, become lethargic.
- The leaves dry up or turn yellow from the trunk of the bush.
Many resources write that a long absence of flowering or growth is also a bad sign and requires intervention - transplanting or checking the root system. However, we do not recommend disturbing the plant without a good reason. If the turgor of the leaves is normal, there are no dark spots on the neck, and the roots are green and are normally visible in the pot, no action should be taken.


The orchid can also die due to overprotection: frequent transplants, the search for diseases and the constant pruning of slightly dried-up root areas causes stress and, as a result, real diseases in phalaenopsis.
There are a number of ways to save a dying orchid, but there is not one universal one that suits absolutely everyone. Let's consider them further.
Germination of roots
As mentioned, the roots take about a month to sprout.Then, after another 1-1.5 months, the leaves will begin to grow and, ideally, after 8-9 months, the plant will bloom again. If the old peduncle was not damaged and destroyed during the resuscitation of the plant, then it will bloom even earlier. The success of resuscitation measures directly depends on the following factors:
- From the state of the plant - the degree of damage and its immunity.
- From the time of the year. The best time to revive orchids is spring.
- In winter, the success of resuscitation is directly dependent on the creation of lighting and constant heat.
The fact that new roots have sprouted does not mean the end of the resuscitation of the plant.
The importance of these parts in the life of a flower
The roots and leaves are very important for an orchid.
Roots:
- Collect moisture.
- They accumulate nutrients.
- Photosynthesis is carried out.
Attention! In natural conditions, orchids are never completely submerged in soil or water, some of the horses are on the surface. Therefore, if the soil has dried out, you should not flood the plant with water. It is better to hold the root for 10 minutes in water, and then spray the foliage.
We talked in detail about what to do if a flower bay happened in a separate article.
Leaves:
- The condition of the leaves can indicate how much the plant has adapted to the external environment.
- Dense and taut leaves indicate that the flower has developed in drought conditions.
- Slightly compacted leaves are found in species that grow in open spaces with good lighting.
- Shade-loving orchids have soft and light leaves that burn quickly in the sun.
What are the consequences of their absence?


The consequences of this circumstance will be obvious. A flower cannot grow without these essential elements. Its gradual death will take place.
To determine how serious everything is, it is necessary to examine the roots for damage.
The following signs will indicate the death of the root system:
- Color change (you can find out what the normal color of a healthy root system should be and why it changes here).
- Slick and wet areas.
- If you press on the roots, water will flow out.
- The presence of decayed filamentous roots.





































