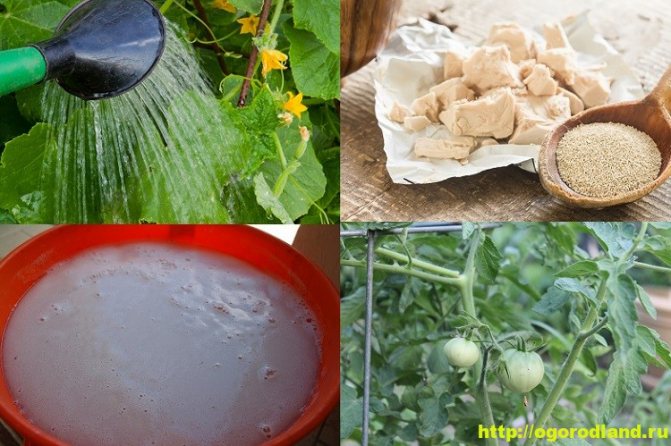
Most people know about the capabilities of yeast only that they are capable of causing fermentation. Due to this property, they are an irreplaceable component of various baked goods and beer drinks. But few people know that this type of fungus is a rich source of proteins, carbohydrates, iron and various trace elements. That is why summer residents consider it an excellent fertilizer that can significantly improve the growth of many plants.
Substance from microscopic fungi
Lovers of home flowers have the same opinion about this method of feeding. Many of them try to use fertilizers without chemical components for the good development of their pets, preferring various kinds of natural products. They have already been convinced more than once that their application helps to achieve an effective and long-awaited result.
Useful properties of yeast feeding
Make-up based on biological baking powder is distinguished by useful properties, including:
- protection of plants from diseases;
- supplying them with the necessary food;
- general strengthening of the landing.
The product is rich in protein (up to 65%), minerals, amino acids, vitamins. He is a storehouse of elements necessary for the growth of cultures. We are talking about copper, iron, phosphorus, iodine, calcium.
The use of this folk remedy provides:
- acceleration of planting growth;
- better rooting of cuttings and shoots;
- overgrowth of roots;
- normal development of vegetable crops growing in conditions of lack of sunlight;
- abundant ovary;
- improving the quality of fruits;
- acceleration of their maturation.
The use of a biological baking powder as a top dressing (root and foliar) gives especially good results when growing cucumbers and tomatoes, melons, peppers, carrots and radishes. The product is not suitable for fertilizing the planting of potatoes, garlic and onions.

Methods for feeding plants with yeast
Feeding plants with yeast is divided into 2 types: root and root. Let's consider in more detail how each type of fertilization is carried out and their frequency.
Root dressing
The introduction of yeast root dressings is carried out in the following sequence:
- When the first leaf appears on the plant.
- After the second dive of seedlings.
- After transplanting the plants to a permanent place in outdoor conditions.
- During the appearance of inflorescences and their subsequent flowering;
It is important to remember that for seedlings planted in a new place, no more than ½ l of the prepared substance is required per bush. An adult mature plant should increase the dose to 2 liters.
Foliar dressing
Foliar dressing is carried out at a time when the root can not be carried out. This applies to weak, only planted in the ground (in an open or in a greenhouse) seedlings. Thanks to such feeding, the plant grows foliage more quickly, becomes strong and hardy. In addition, the spray applied is more quickly absorbed.
Top dressing of the foliar type is recommended at the beginning of the growing season.
It is important to remember that the yeast solution should be less concentrated than in the case of root dressing.
For open ground conditions, top dressing is carried out in the evening or in non-sunny weather.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the benefits of a fertilizer made from a bakery product, you can see:
- Possibility of using for vegetable and horticultural crops, indoor plants, berries, ornamental shrubs.
- Acceleration of the decomposition processes of organic feeds introduced earlier. At the same time, the soil is enriched with nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Low cost of the product.
This folk remedy has practically no drawbacks. One of the few is the depletion of the soil due to the absence of such an element as potassium in the composition of the yeast solution. The solution is to enrich it with ash.
It is advisable to prepare a feed based on a biological baking powder using additives in the form of herbs, milk and other components.


Why is yeast good for plants?
Yeast is incredibly helpful for many plants. The reasons for their use may be different, because for some, the quantity of the crop plays the main role, while others simply take care of its purity in an ecological sense.
Let's take a closer look at the benefits of such plant nutrition:
- Help in the formation and development of the root system.
- Accelerated growth of the entire culture.
- Creation of a favorable microflora, which has an overwhelming effect on pathogenic organisms.
- The restructuring of the soil composition and the accelerated processing of organic components, and as a result of this, a greater amount of nitrogen (N) and potassium (K) appears here.
- The culture is able to develop even under unfavorable factors such as insufficient lighting.
- The likelihood of manifestations of diseases and infections decreases.
- The endurance of culture increases significantly.
- Seedlings do not stretch upwards and tolerate the picking process better.
Due to the accelerated growth of the plant, more shoots are formed, which as a result leads to an increase in yield.
Composition and action of yeast
Yeast contains the following useful components:
- Phosphorus (P);
- Potassium (K);
- Sodium (Na);
- Calcium (Ca);
- Cagnium (Mg);
- Iron (Fe);
- Vitamins: B, C, PP, K, Choline;
- Carbohydrates and Proteins.
In order for yeast feeding to bring only benefits, it is worth remembering that everything should be in moderation. Be sure to first familiarize yourself with the rules of conduct and important norms for crops.
What crops can be fertilized with yeast?
Yeast feeding has a beneficial effect on almost all plants. This also applies to indoor crops, and garden, and horticultural. Fertilizers of this type even benefit trees.
Yeast is used especially often for fertilization:
- strawberries and strawberries;
- peppers;
- carrot;
- cucumbers;
- tomatoes;
- radish;
- indoor geranium;
- petunia is garden.
But it is also worth remembering that some plants cannot be fertilized with yeast, these include:
- onion;
- potatoes;
- garlic.
This is due to the fact that the resulting crop will turn out to be loose and in a short time will become unusable.
How to use it correctly
The preparation and use of yeast fertilizer formulations must be competent. You can not overdo it, feeding vegetable beds with this folk remedy. There is a risk of soil impoverishment.
Timing and frequency
It is optimal to use a bakery product for fertilizing a garden or garden planting no more than 3 times during 1 season:
- for the first time - for better rooting of seedlings;
- the second top dressing - after rooting of seedlings (increasing the consumption of the solution to 1 liter);
- the third time is used on the eve of flowering (using 2 liters per bush).
Useful Tips
Fertilizers for indoor flowers are fertilized with dry or compressed yeast and sourdoughs obtained by fermentation.
Tips from an experienced gardener:
- yeast fertilizers work well when applied to heated soil, if it is cold in the room, top dressing will not work;
- an expired product will not give the desired effect;
- during the fermentation process, potassium and calcium are consumed, which are present in the soil, together with yeast fertilizer, grated eggshell or wood ash is added.
You can understand that it's time to feed the flowers with useful substances by the following signs:
- slower growth, thinning of the stem;
- weak, small, yellowish leaves;
- cessation of flowering for a long time;
- shedding foliage;
- defeat by diseases.
Houseplant nutrients usually last for about 60 days. Fertilizers from yeast fungi are applied no more than three times a season. By reducing the concentration of the composition, you can fertilize the soil a little more often.
Features of application for plants in the open field
Professionals are sure that in order to prepare a life-giving and beneficial yeast fertilizing for plants, it is necessary to take into account the particular culture for which the substrate will be used. Each vegetable has its own proportions and ingredients used.
Feeding cucumbers
It is necessary to start fertilizing cucumber bushes when transplanting seedlings to a permanent place. This will reduce the number of barren flowers, improve the taste of cucumbers. The first feeding of this vegetable crop is carried out with yeast hydrate on herbs.
The second is brought in at the time of flowering. Ash hydrate is suitable for this purpose. 40 liters will require 400 g of yeast, 300 g of ash, 2 kg of manure, 1 bucket of chopped nettle. The components are thoroughly mixed and leave the slurry warm for 2 weeks. The concentrate is diluted 1:10 before use.


Watering cucumbers
For leaf dressing, water the planting with the following hydrate. The yeast is dissolved in warm water (1: 5). Before irrigating the foliage, the concentrate is diluted with 5 liters of water.
The solution can be applied not only to cucumber bushes, but also to other garden crops. The product protects plants from pests, improves immunity.
Fertilizing tomatoes
We will feed tomatoes 1-2 times per season. More yeast supplements can be harmful to vegetables.
The first time they feed the tomatoes on the 10th day after transplanting the seedlings to the garden bed (1/2 liter of substrate per bush). The second time is carried out before flowering (1.5 liters under a bush). To prepare a fertilizing solution, you will need to stock up on:
- fresh yeast (30 g);
- manure extract (500 ml);
- wood ash (2 glasses);
- sugar (10 teaspoons);
- water (10 l).
How to feed peppers
To irrigate the seedling bushes of pepper, you will need to prepare a standard brew. Yeast or bread leaven is taken as a basis. For adult plants, an ash mixture with nettles is applicable. To cook it take:
- 1 cup of sugar;
- 4 glasses of ash;
- 60 g yeast.
Nettle is crushed, poured with a liter of water. Then it is mixed with the rest of the ingredients. The hydrate is kept warm for 5 days. Then another 10 liters of water is poured in and insisted during the day. The concentrate is diluted before irrigation (1:10).
Preparation of solutions from raw and dry concentrate
Pour 1 liter of warm water into a container, dissolve 10 g of "raw" yeast in it. Then put a spoonful of granulated sugar into the thoroughly mixed mixture and leave to ferment. You should not add a lot of sugar, because what does not absorb the fungus will get to other bacteria, in particular, mold, and its reproduction in a flower pot is highly undesirable. The resulting extract is watered with home plants, after diluting it 5 times with water.


Homemade Greens Nutrient Blend
A powder product is also suitable for preparing a nutritional formula. In this case, you need to pour 1 liter of warm water into the container, add 8 g of dry product with 1 spoonful of sugar to it. Such a "hoppy" drink, prepared for home flowers, is placed in the heat for fermentation. The fermented saturated mixture should be diluted with water 5 times and used for watering.
When yeast is bad
Illiterate use of yeast feed is harmful to plants. Overfeeding threatens them with wilting.
There is a lot of nitrogen with phosphorus in a solution of biological baking powder. It reduces the potassium content in the soil. The plant may die from a deficiency of this element.
You cannot fertilize the planting of garlic and onions with yeast. Crops do not respond well to this feeding.


Using yeast as fertilizer
Yeast top dressing is actively used in crop production as an effective way of influencing the soil for the intensive development of green pets. Among the features and advantages of feeding plantings with a fungal composition, the following points are noted:
- yeast as a fertilizer is relevant in all phases of development of flora representatives, including the periods of vegetation, budding and flowering, fruiting. Introductions at the stage of preparing green pets for winter are also effective;
- yeast infusions contain a large amount of vitamins, phytohormones, auxins and help to improve the physical and decorative characteristics of plants;
- yeast feeding has a beneficial effect on the immune system of the seedlings. At the same time, resistance to diseases is ensured, endurance to unfavorable environmental conditions is determined in the form of a lack of light, temperature drops, drafts and excessive humidity of the air and soil;
- the use of fungal applications promotes high-quality rooting of cuttings, thanks to the yeast, the root system of the seedlings grows better.
Fungal nutrient helps to activate the activity of microorganisms in the soil. Thus, biological processes are accelerated, the intensity of decomposition of organic matter improves. As a result, a sufficient amount of nutrients is formed in the substrate, including nitrogen and phosphorus, which stimulate the development of the root system.
Common mistakes
Some common mistakes regarding the use of yeast feeds include:
- their use at the stage of fruiting, threatening a deterioration in the taste of fruits, inhibition of plant growth;
- the use of this fertilizing composition for crops growing in a greenhouse (there is a risk of getting the roots of burns from the substance that has begun to ferment under the influence of high temperature);
- too frequent use of the product (it is not recommended to apply it more often 2-3 times per season).
What conditions are necessary for fungi
Those with even a little culinary experience know three things are needed to induce fermentation:
- Sugar. The sweetness encourages fermentation.
- Heat. Fungi become active when the temperature rises above 15 degrees, therefore, in order for such feeding to be effective, it is necessary to preheat the substrate in flower pots by placing them in the sun.
- Time. If the prepared extract does not have time for fermentation, the mechanism for the release of nutrients into the water will not have time to start.
Another important point is that expired yeast (whether dry or live) is not suitable for feeding. Many people think that these fungi are very hardy and not whimsical. And it is true that they just don't do it with them: they dry, and press, and freeze, and crush. But they cannot be in the neighborhood with other most aggressive bacteria and often simply die. Therefore, you cannot make a nutritious extract from moldy bread or from a product that has expired. The effect of their use, at best, will be zero. Bread slices can be soft or slightly dry, but always clean.
Additional tips and tricks
Experienced gardeners are advised to monitor the condition of plants growing in open ground or in a greenhouse in order to calculate whether the use of yeast supplements is advisable. It is used if:
- the plant has symptoms of morbidity;
- foliage falls;
- there is no flowering;
- weak development of stems and leaves is observed;
- the stem is thinned.
Feed the planting with a solution on a biological baking powder, you should follow the rules:
- water with recharge only if the soil is warmed up enough;
- they are fed no more than 2-3 times during the season and when symptoms of morbidity in plants appear, when they need urgent resuscitation;
- after the application of the yeast substance, they provide additional nutrition with minerals.
Yeast solution is an effective folk remedy for feeding garden and horticultural crops, indoor flowers.
It is an effective plant growth stimulant that allows you to get a more bountiful harvest, in particular for cucumbers and tomatoes.
What can be fertilized with yeast
They are effective for almost all crops: both growing in the room (geranium) and garden flowers (petunia), bushes, trees, vegetables. It turns out to be useful feeding from yeast for peppers, tomatoes, cucumbers. Used as a fertilizer in the cultivation of strawberries and strawberries.


Fundamentals of Plant Fertilizers
Plants need nutrition, like any living organism. They draw useful elements from water, soil and air. If the growing environment is not rich in micronutrients, fertilizers are used.
Top dressing is classified according to their composition:
- Potash. Potassium retains fluid in the stems and increases disease resistance.
- Nitrogen. Promotes active plant growth.
- Phosphoric. The processes of photosynthesis and fruiting depend on the presence of this substance.
- Complex. Contain several of the listed items. They are divided into double, nitrogen-phosphorus, for example, or triple - nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium.

One bag of baker's yeast contains up to 1 billion yeast cells
However, within the framework of the main differentiation, feeding is divided into inorganic and organic. Division by the prevailing element is more typical for mineral fertilizers. They are all present in organic mixtures in varying quantities.
Table 1. Types of dressings
| View | Characteristic |
| Organic | When creating them, exclusively natural materials are used. The main advantage of this type of fertilizer is its non-aggressive effect. Among the disadvantages, an unpleasant odor is noted. This category includes manure, compost, bird droppings, green manure, rotted sawdust, peat, silt, yeast. One of the best is animal feces, especially horses. |
| Mineral | Chemical fertilizing of artificial origin. They have a quick effect, but overdose can lead to plant death. Available in the form of tablets, liquids, suppositories, soluble powders or granules. |
The preferred type of feeding depends on the type of plant, the characteristics of the growing cycle and the problem present. For example, nitrogen-containing substances are used during the formation of buds, and phosphorus ones are relevant during flowering. Recently, the attention of gardeners is directed towards organics.


Each of the varieties of dressings has its own adherents.
Let's summarize
Yeast solutions have a positive effect on plant development and prolong the flowering period. Almost all varieties of both gardening and indoor ornamental plants can be fed with infusion. Results are visible a few days after application to the soil.
Experienced gardeners know that diseases and pests of garden trees not only significantly reduce the yield, but can also cause the death of trees. The pests spread quickly and can damage the entire garden in one season. Only competent and timely measures of control and prevention can ensure the effectiveness of protection. More details about them in a special article.
Video - Yeast-based root dressing
Composition and nutritional value
These indicators are due to the quality of the nutrient medium, cultivation conditions and the state of the cell.
Yeast is rich in potassium, iron, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamins B, H, P, para-aminobenzoic and folic acid, as well as meso-inositol.


Yeast activity is checked by the formation of bubbles or foam after contact with water and sugar
Dry yeast
Powdery free-flowing cream-colored product with a specific aroma. The shelf life of the product is 12 to 24 months. It is not necessary to use a refrigerator.
Caloric content - from 325 to 385 kcal per 100 g. Energy value (g per 100 g):
- proteins - 40.4;
- fats - 7.6;
- carbohydrates - 14.3.
The share of water is no more than 9%.


Dry - the result of drying common yeast cultures
Compressed yeast
In shape, these are small blocks of 50, 100 or 1,000 g, wrapped in wrapping paper. The briquettes are cream colored. They break when pressed. In cold conditions, they are stored for up to 12 days, in a room - up to 24 hours.
Caloric content - 109 kcal per 100 g. Energy value (g per 100 g):
- carbohydrates - 8.5;
- proteins - 12.7;
- fats - 2.7.
The pressed product contains up to 75% water.


Compressed yeast is often referred to as confectionery.
Beneficial features
They have been used as natural bait for a long time. They were especially in demand during the development of the dacha movement. With the advent of a wide range of inorganic fertilizers, the popularity of this product has declined. Nowadays, gardeners prefer ready-made solutions based on NPK-complex.
Yeast is a natural biologically active concentrate. It can be used as a remedy for plant health. They help the crop to use resources that inorganic fertilizers cannot influence.


The peak of the popularity of yeast fertilizers came in the 70s of the last century.
Basic properties:
- Instilling resistance to pests and diseases.
- Boost resilient in low light or low humidity.
- Better rooting and active growth of the root system.
- Strengthening the endurance of seedlings.
- Increase in the quality and volume of vegetative mass.
- Longer flowering.
- Improving the soil structure and enhancing its fertility.


Yeast Fungus Promotes Green Growth
Yeast is an excellent growth stimulant and has a positive effect on the immune system.
Upon contact with the soil, the fungus changes its composition. Dormant microorganisms wake up and recycle the organic matter present in the earth. This process is accompanied by the release of large volumes of potassium and nitrogen, which are necessary for the normal functioning of crops.
Plant growth stimulation
The main role of yeast in growing crops is not feeding, but stimulating. Therefore, it would be most logical to use them in growing seedlings. Including - in greenhouse conditions.
But there are a number of rules, breaking which means only slowing down the development of plants:
- Do not use yeast for growing potatoes - tubers lose their ability to be stored for a long time, already in the middle of winter, their massive rotting is possible. The same goes for onions and garlic.
- You need to do yeast feeding no more than two times - at the beginning of the growing season and after 14-15 days (usually before flowering).
- Apply infusions in accordance with the season, only for soil sufficiently warmed up by spring warmth, because yeast will die in cold soil.
- Do not introduce yeast into the soil in the absence of organic fertilizing in it, such an introduction will not do anything, the mushrooms will have nothing to eat.
If these rules are followed, positive changes will be visible already at the end of the second week.
























