Chestnuts are often perceived as uninteresting woody ones, which are used only in urban landscaping. And if they are grown in gardens, it is more likely for the sake of the harvest of edible or medicinal chestnuts and only in really large areas. But this delightfully hardy plant with extraordinarily beautiful leaves and candlesticks deserves a very different reputation. Chestnuts cannot be called small, but among them there are true beauties. One of the most decorative species is the pavia horse chestnut, a graceful, ornate plant that can make the perfect giant even for a small garden.
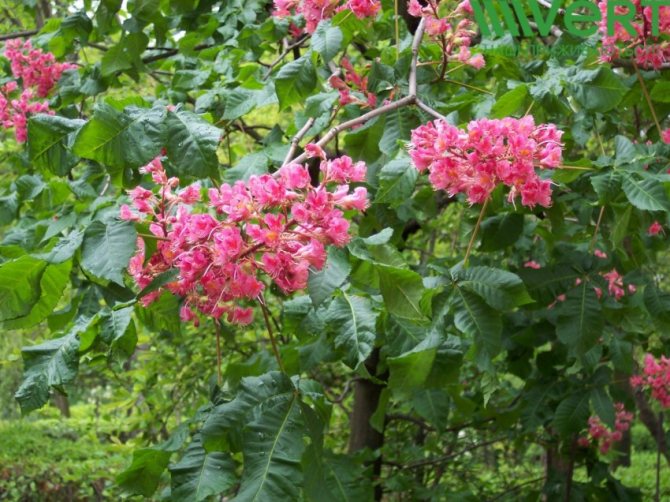
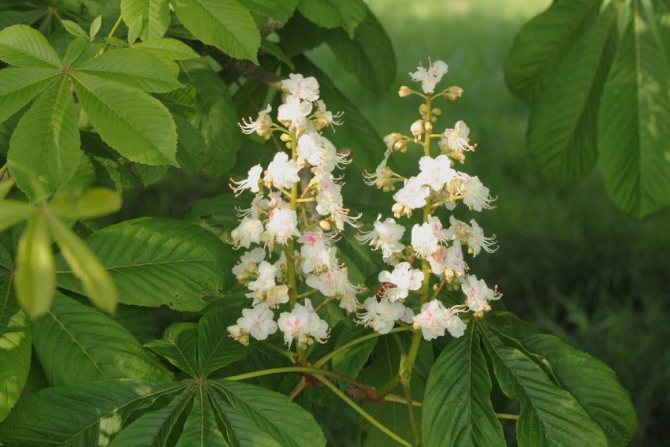
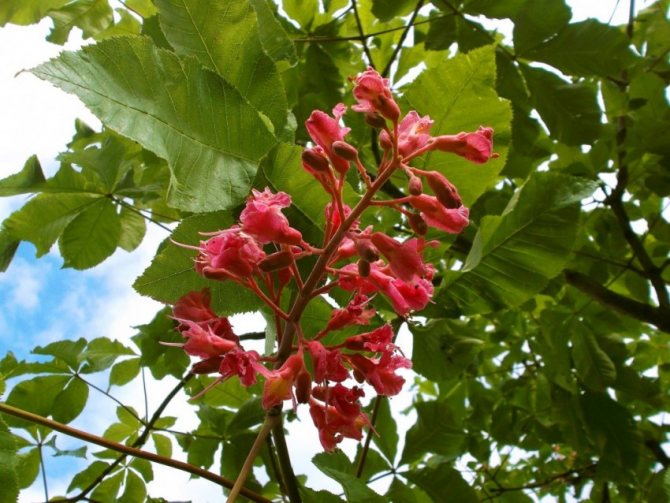
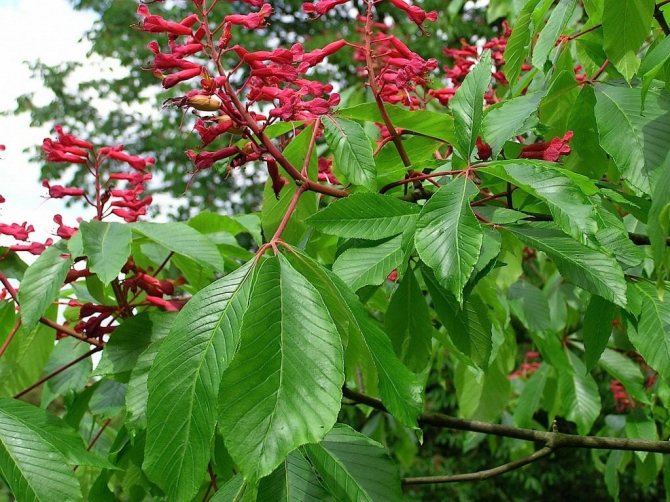
Red horse chestnut, or dark red pavia horse chestnut (Aesculus pavia atrosanguinea). <>
Favorite among favorites
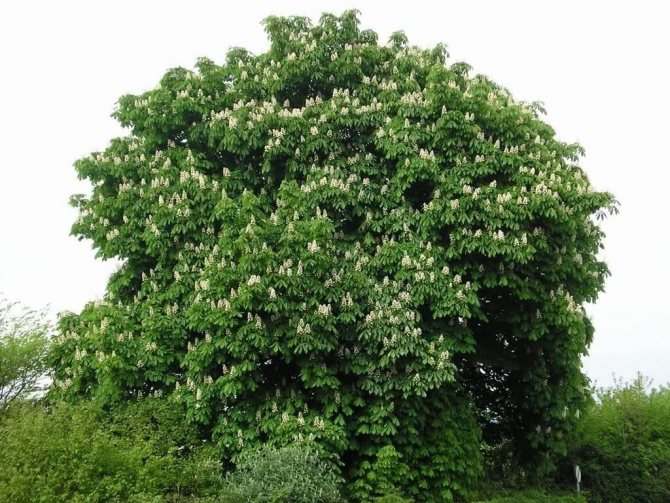
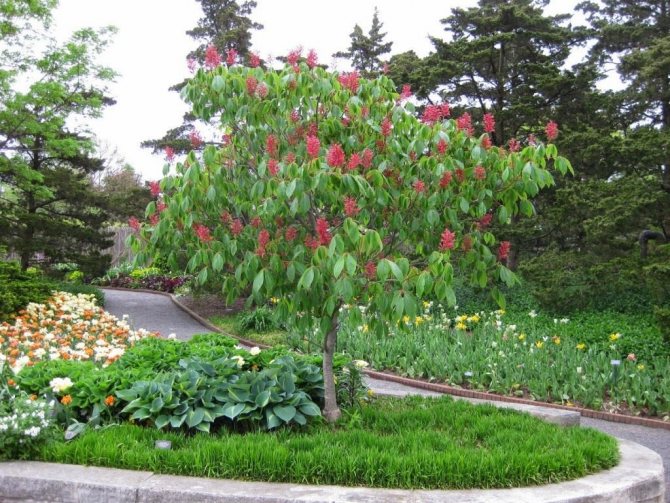
It is no coincidence that horse chestnuts are called the most decorative among the huge family of these giants. Fast-growing, but at the same time very "obedient", allowing to successfully carry out the formation at any age, they differ in a neat, rounded crown from nature. The tallest species of horse chestnuts will not exceed 20-25 meters in height, the best decorative ones are limited to 3-10 meters. Half the usual in all parameters - from overall growth to leaf size, but the pavia horse chestnut is several times more effective. This is one of the best species with beautiful flowering and high decorativeness that persists throughout the year.
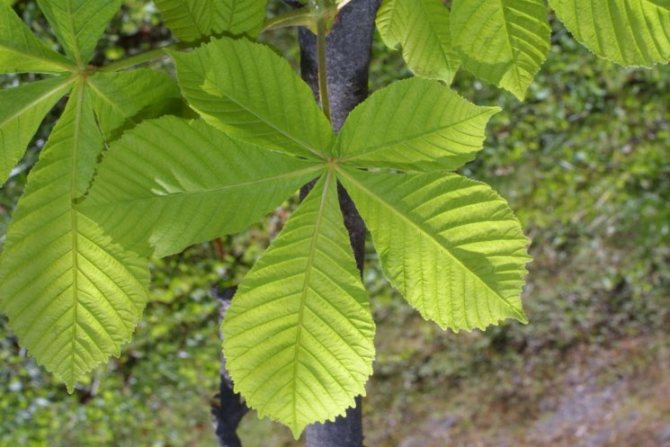
Horse chestnut pavia (Aesculus pavia) - large ornamental shrubs and trees with a maximum height of 12 m (shrubs - 3-6 m). In regions with severe winters, pavia is most often limited to 3-4 meters in height. We have this woody also known as "red horse chestnut". The bark is quite light, grayish, the trunk is slender, and growth is slow (it reaches full height not earlier than 10 years). The crown is dense, lush and ornamental. The twigs are reddish, sagging a little. The leaves of this horse chestnut are two times smaller than those of the common horse chestnut. They consist of 5 narrowly elliptical lobes, with a serrate-serrate edge and prominent veins. In length, the individual lobes do not exceed 10-14 cm. The light edge of the bottom and light cuttings emphasize the rich green color, bright and fresh even during the heat.
Horse chestnut red, or horse chestnut pavia (Aesculus pavia) is a horse chestnut tree from the horse chestnut family.
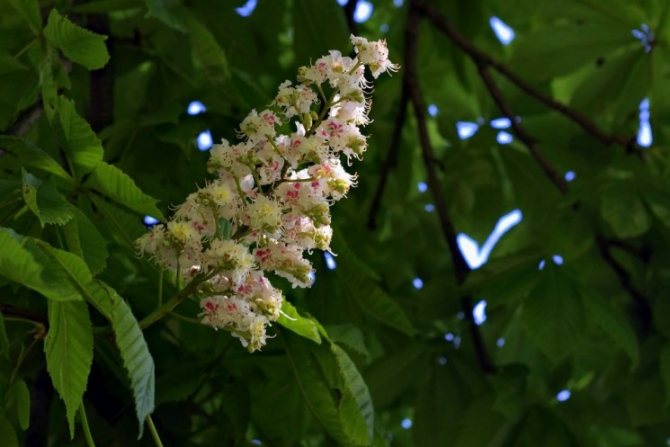
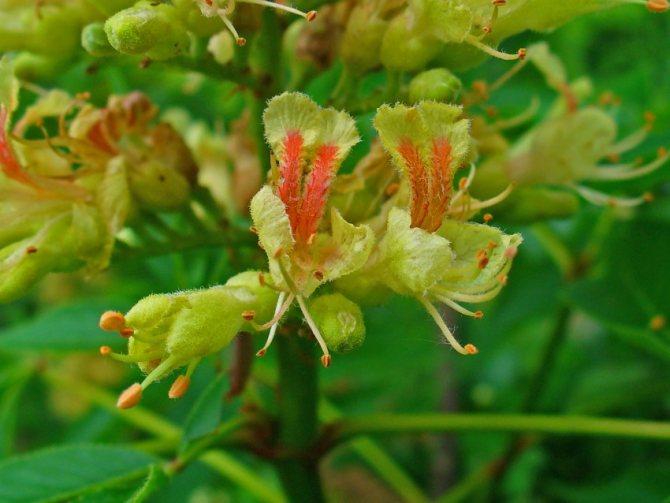
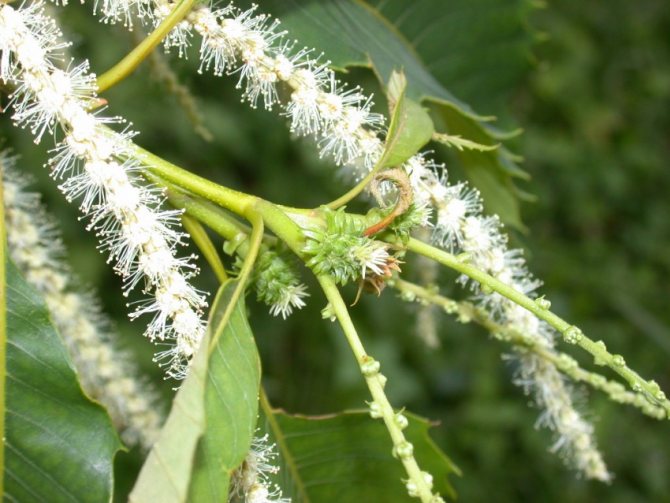
The greatest pride of the pavia horse chestnut is its panicle inflorescence. They appear looser, more lush and less pyramid-like than the inflorescences of common horse chestnuts. Reaching a length of 15-18 cm, they conquer with their bright color, unusual transitions of tones and the effect of exoticism. The inflorescences are densely tubular, with a bell-shaped pharynx and asymmetric petals, which, despite the difference in size, still form a funnel-shaped corolla. The stamens of the red horse chestnut always exceed the length of the petals.
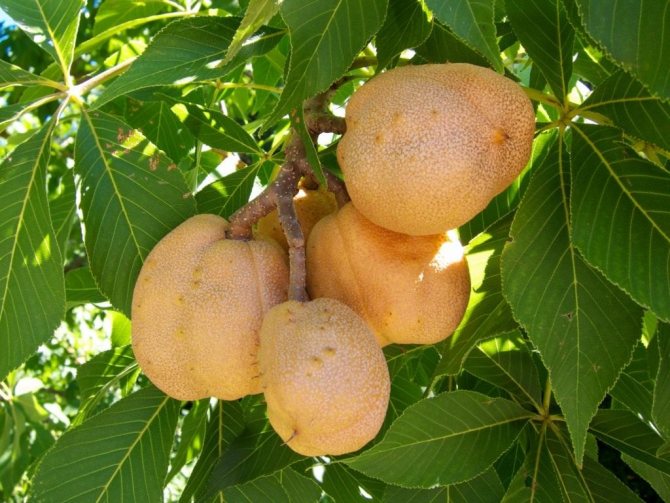

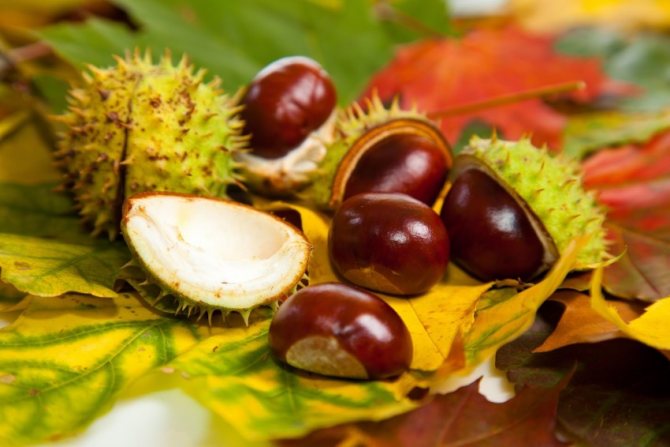
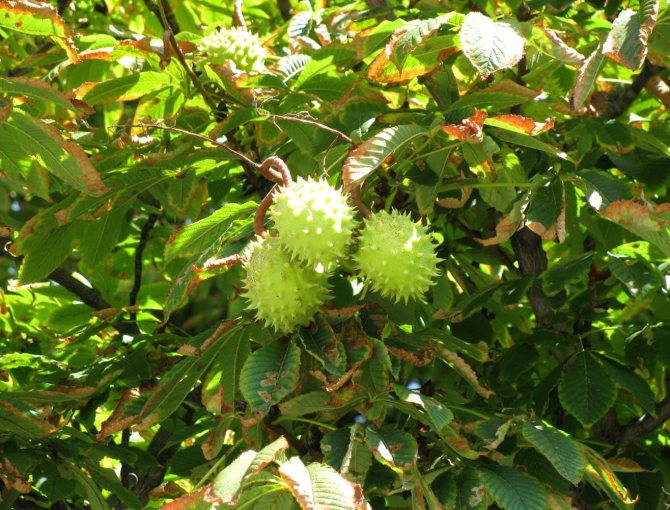
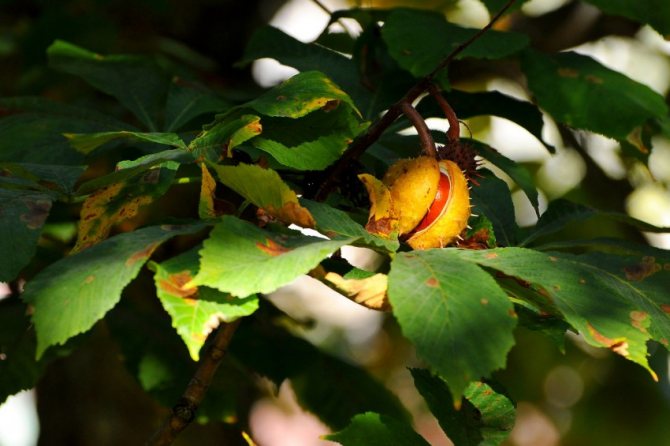
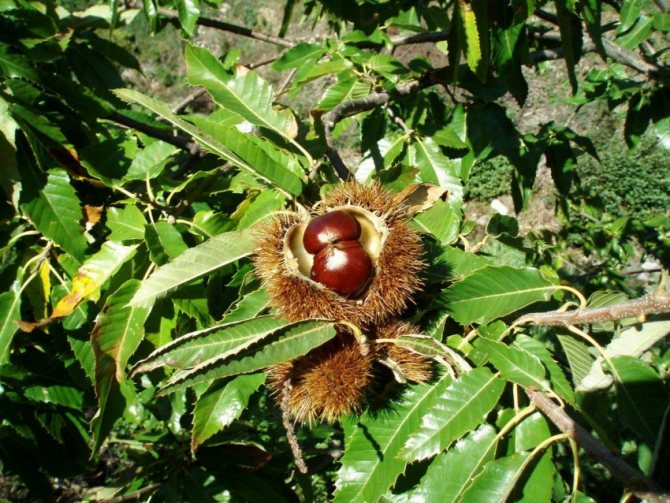
Red horse chestnut fruit. <>
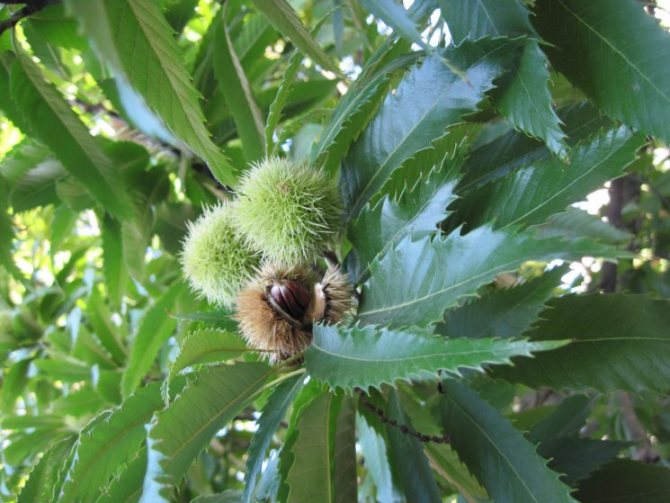
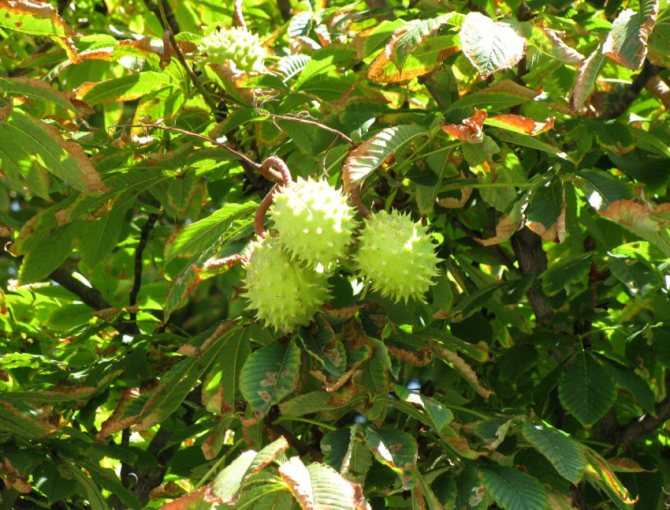
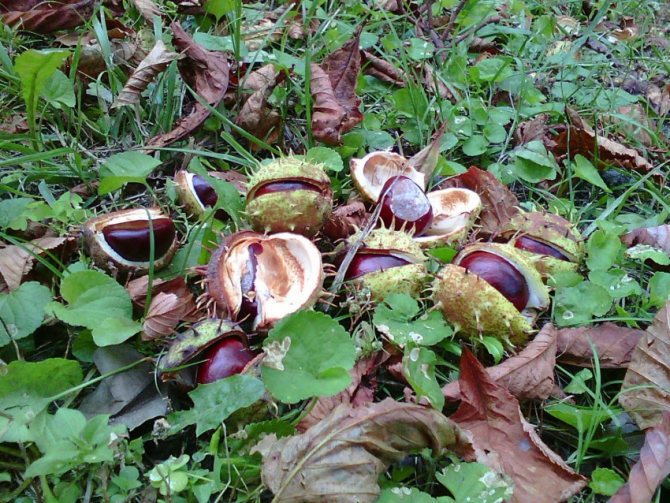
The fruits of the red horse chestnut are easy to recognize: despite the shape similar to other horse chestnuts, their surface is absolutely smooth, without bristles.And the fruits themselves are quite peculiar: lumpy or smooth, with an elliptical-ovoid shape, tricuspid, they often contain not one "chestnut", but several seeds. In length, the fruits reach from 3 to 6 cm. This chestnut bears fruit in September.
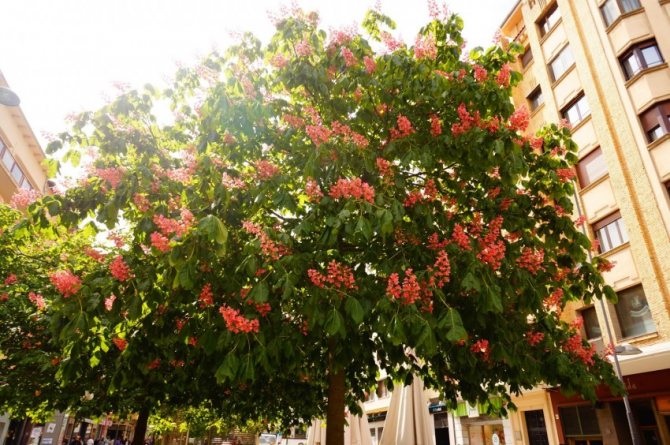
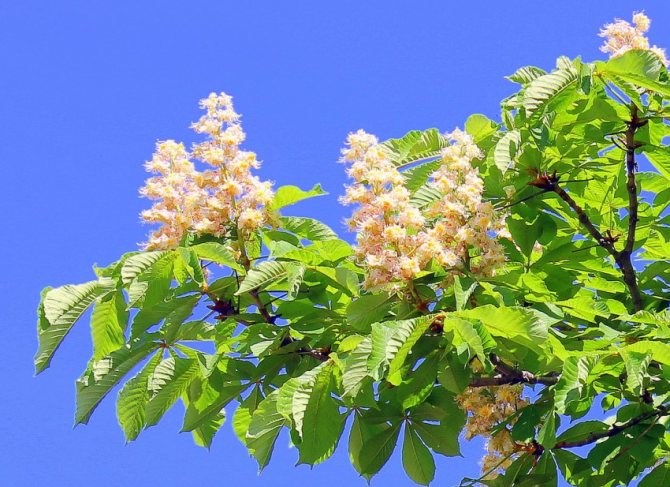
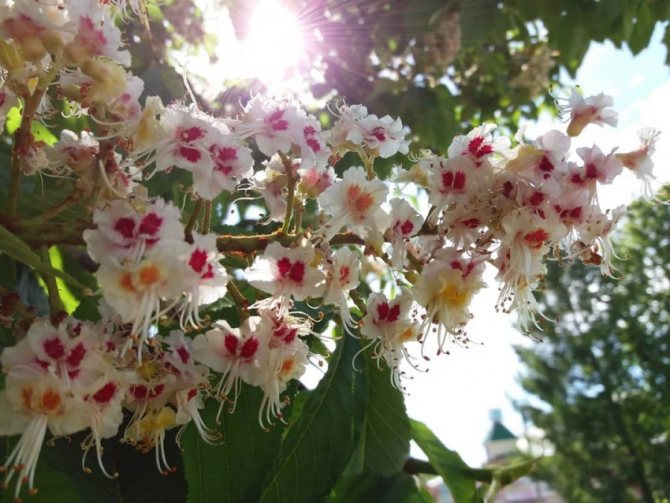
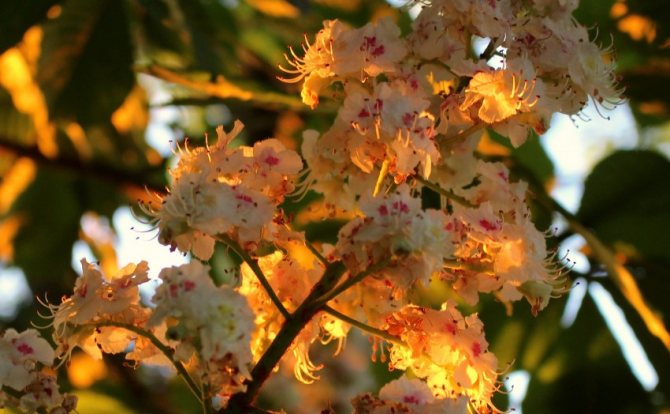
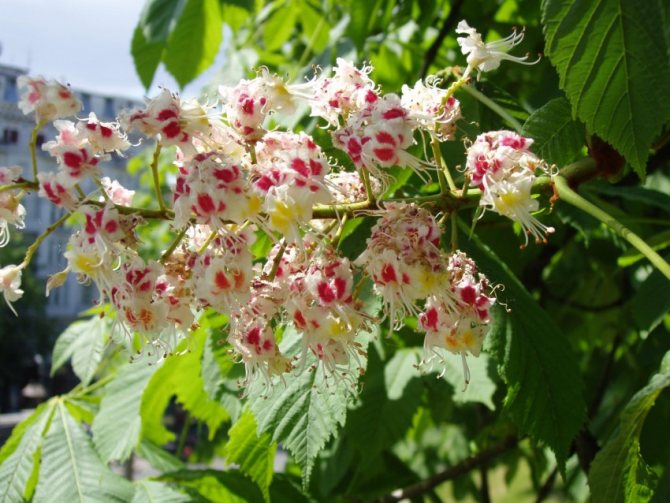
Pavia bloom at the end of May and delight with beautiful and bright candles at the very beginning of summer. The color palette of red horse chestnut is more than interesting. In the base plant, the flowers are bright red, while the upper side of the corolla is usually lighter. In addition to carmine flowers, there are also yellow flowers, and a combination of rich red with yellow spots and specks. Regardless of the variety and shape, in the red horse chestnut, when flowering, the inflorescences always turn yellow.
Varieties
There are 10 species of this plant in total. In Central Russia, chestnuts are used for planting, which are distinguished by good resistance to subzero temperatures. Severe frosts (up to -30 ° C) can withstand such species as European (sowing, noble), American (toothed). It should be remembered that they all belong to the beech family.
The bark of the American chestnut is brown, the shoots are yellow and bare, the foliage is dark green. Chestnut flowers sit in spike-shaped inflorescences (length - 20 centimeters). Covered with bright green fluff, the fruits are edible.
European chestnut is distinguished by the presence of a ribbed surface of shoots of olive and red shades. Crescent-shaped teeth appear along the edges of the oblong leaves. The underside of the foliage is covered with a bluish fluff. The inflorescences are spike-shaped, up to 35 centimeters long. Quite large fruits are edible.
Decorative forms and varieties of pavia horse chestnut
The basic plant of the horse chestnut pavia today is significantly inferior in popularity to decorative forms. And this is not surprising: the natural North American species is less winter-hardy than the common horse chestnut, and its considerable height limits the possibilities of use. But selectively bred hybrid forms adorn with more interesting forms of growth, and compact size, and more saturated tones of colors.


Horse chestnut red, or half-cut pavia horse chestnut (Aesculus pavia sublaciniata).
The best decorative forms of the pavia horse chestnut include:
- semi-cut (sublaciniata) - a shrub with a spreading crown, very beautiful narrow leaf lobes with deep, original teeth, which will surprise you with its rich dark red color during flowering, surprisingly elegantly contrasting with the cool shade of the leaves;
- dark red form (atrosanguinea) with wine-scarlet color;
- undersized form (humilis) with uniquely open shoots, forming a beautiful low bush with a reduced size of inflorescences with a light red color.
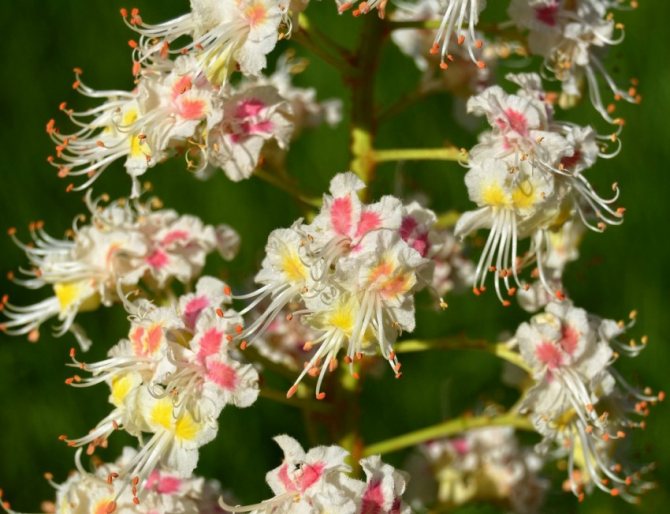
Certain varieties of pavia horse chestnut are also noteworthy. For example, the variety "Koehnei" with loose, as if prickly inflorescences, an elongated tube at the flowers and a play of external orange color and bright pink-red inside the corolla of the flower.
Often on the Russian-speaking Internet, this variety can be found under the name Koebnei, which is not correct.
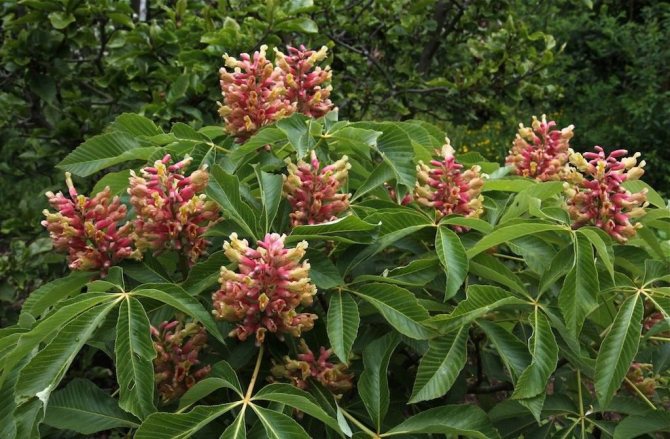


Horse chestnut pavia grade "Koehnei". <>
Today, red horse chestnut is often used for breeding boles. Its rounded crown, thanks to its haircut and shaping, seems especially graceful, and its thin trunk only emphasizes the delicate beauty.
The effect of the drugs used
All products have been tested over the years, their history dates back to our great-grandmothers. With their help:
- The tone of the blood vessel walls will improve.
- The blood will become thinner, and its permeability through the veins will increase.
- Blood clots and blood clots will dissolve.
- The pain and swelling of the legs will disappear.
- The outflow of blood will increase.
- Stagnation in the blood will pass.
If you combine folk remedies with medications prescribed by a phlebologist, the effect will increase.In the event that it is not possible to prepare a drug at home, the following drugs have been developed, which can be purchased at a pharmacy, these are:
- Venitan gel;
- drops of Escuzan;
- Herbion Aesculus.
It is not difficult to apply them, since each package contains instructions for use, with which you can easily calculate the dose and determine the contraindications.
Today in pharmacies you can find Shark Fat with Horse Chestnut cream. Such a remedy has a strengthening effect, relieves fatigue, pain cramps, cramps and swelling of the legs. After a long stay on his feet, he will become a lifesaver. It is very convenient to use. You can take it with you on a trip, carry it to work and, if there is heaviness in your legs, lubricate them. Upon returning home, you need to thoroughly wash your feet, rub them with a terry towel and rub the cream into them.
Chestnut for the treatment of varicose veins is not equally useful for everyone. The same spectrum of active substances that make up the plant, which is used specifically for the treatment of blood vessels, can have a negative effect on patients who have contraindications to their use.
- Chestnut-based medicines should not be used by women during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- patients suffering from reduced blood clotting;
- people with low blood pressure;
- patients with impaired renal function;
- in the presence of internal bleeding;
- with acute and chronic manifestations of disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.
With all the "arsenal" of classical methods of treating vascular diseases, a variety of medicines, traditional medicine, despite the negative attitude towards itself on the part of official medicine, still sometimes remains the only hope for a cure for varicose veins for many people.
And, nevertheless, any treatment, including the treatment of varicose veins with horse chestnut, must, first of all, be agreed with a specialist.
The use of pavia chestnut in ornamental gardening
It is believed that the pavia horse chestnut is best suited for solo parties. It is really planted mainly as a solo soloist on a lawn or a meadow of ground cover. But unlike other horse chestnuts, it provides much more opportunities. Due to the superficial root system of too close proximity, the chestnut still does not like, but it can also be used in groups:
- as a high accent for the front garden, ceremonial decorative compositions;
- as a large tree in small gardens, a source of shade for a recreation area in a small area;
- as a basic unpretentious woody for decorative groups with woody and shrubs;
- in alleys and their imitations;
- in groups of continuous flowering;
- in landscape multi-row hedges.
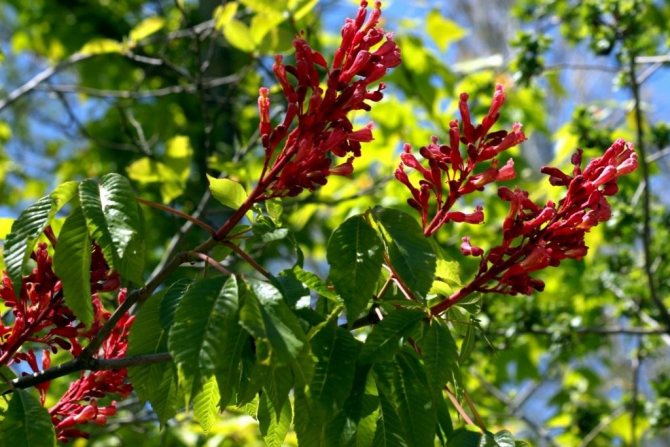


Horse chestnut red dark red shape. <>
Red horse chestnut, like other types of horse chestnuts, helps to purify the air, is not afraid of the polluted environment and the neighborhood with the roadway. Moreover, it can be viewed as a culture that promotes air purification.
Useful qualities
The medicinal properties of the tree are widely used in medicine. Nuts are saturated with active biological substances. They contain pectins, oils and flavonoids, which are used to reduce capillary fragility and prevent blood stagnation.
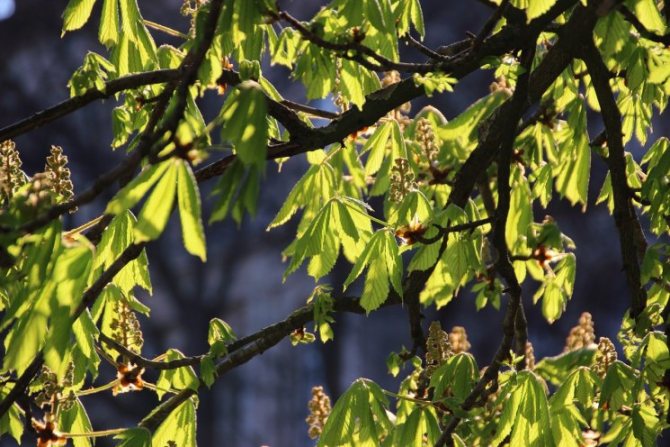


The seeds resist varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, ulcers, contributing to venous tone. They are able to relieve pain and relieve inflammation.


Planting pavia chestnut
Red horse chestnut, due to its more compact size, allows it to be placed closer to buildings and other plants than other types of horse chestnuts.Shrub pavia horse chestnuts can be planted 1-2 meters from buildings or other trees, woody ones - at a distance of 2 to 6 meters (it is better to check the optimal distance when buying decorative forms and varieties).
It is advisable to improve the soil before planting at least a month before planting the plant. Mature compost, humus, sand, and deep digging will help make the soil ideal for this ornamental woody. On acidic soils, liming is mandatory.
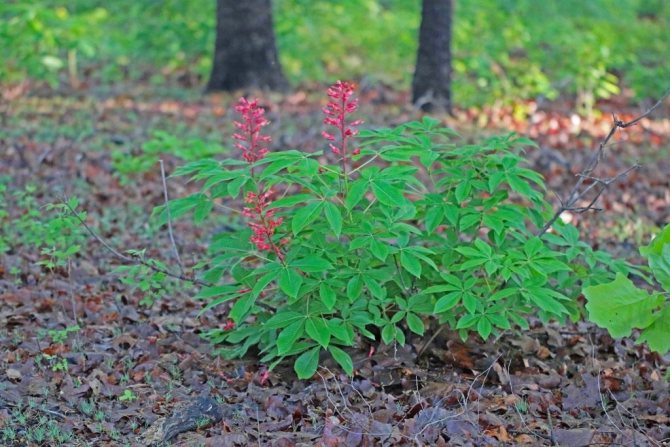


Red horse chestnut, or pavia horse chestnut (Aesculus pavia).
Planting is identical to other chestnuts. Pavia is placed in planting holes with a diameter and depth of about half a meter, on a cushion of rubble and sand. The root collar of the red horse chestnut should be at ground level. After filling the planting hole with soil (it can be additionally mixed with a portion of compost or manure), be sure to install a support to support the thin trunk and provide very abundant watering. The support is removed only after the chestnut gets stronger. Complete drought should not be allowed for the first two weeks after planting.
Leaves
The large and complex leaves of the chestnut are five- or seven-fingered, with a long root. In summer, their color is green, and by autumn they acquire yellow-brown, crimson, brown and purple hues. Chestnut greens contain vitamin K, tannins and pectin. In folk medicine, foliage is used in the preparation of decoctions and infusions used for a variety of diseases.
The chestnut crown, thanks to its openwork large leaves, is very wide and dense, having a rounded shape.
Caring for an unpretentious pavia
Horse chestnut red is a hardy plant. And taking care of him is quite simple, in fact it comes down to just a few procedures per year:
- watering in extreme drought (like all horse chestnuts with a superficial root system, pavia is sensitive to a lack of moisture in the soil);
- loosening the soil, weeding or mulching (for a pavia, it is better to choose sawdust, peat or chips, chopped bark);
- annual removal of damaged and dry shoots (and in chestnuts formed on a trunk or with a strict crown shape - also formative pruning) in early spring;
- top dressing: starting from the third year of cultivation, they are carried out in early spring, using organic fertilizers and half the share of nitrogen fertilizers (urea, ammonium nitrate in the amount of 15 g per tree and a bucket of water) and in the fall, using full mineral fertilizers (15 g of an independently created mixture or nitroammophoska is enough).


Horse chestnut pavia grade "Rosea nana". <>
Flowers
What month do chestnuts bloom? The flowering period depends on the type of tree and where it grows. The most common species in Russia is the sowing chestnut, which is an excellent honey plant that blooms in early May.
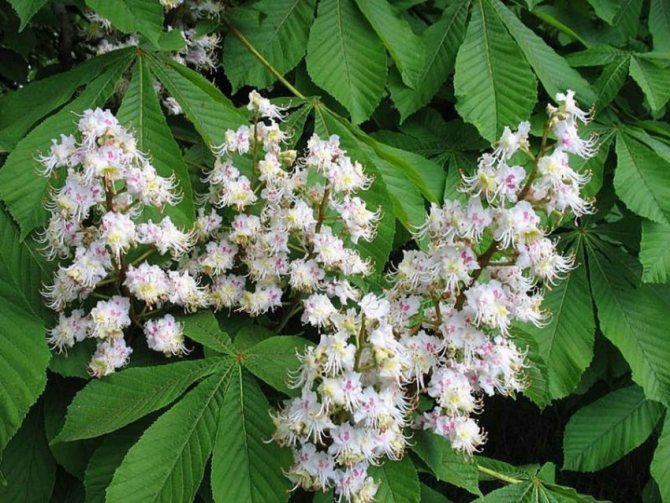
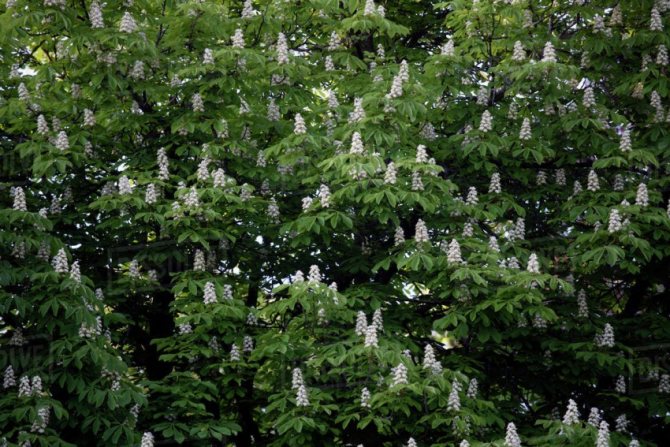
The tree looks great during the flowering period. Fragrant large inflorescences resemble candles, placed vertically and scattered throughout the crown. The length of the spike-shaped, pyramidal inflorescences is 10-35 cm. The lower part is represented by female flowers, the upper part is male.
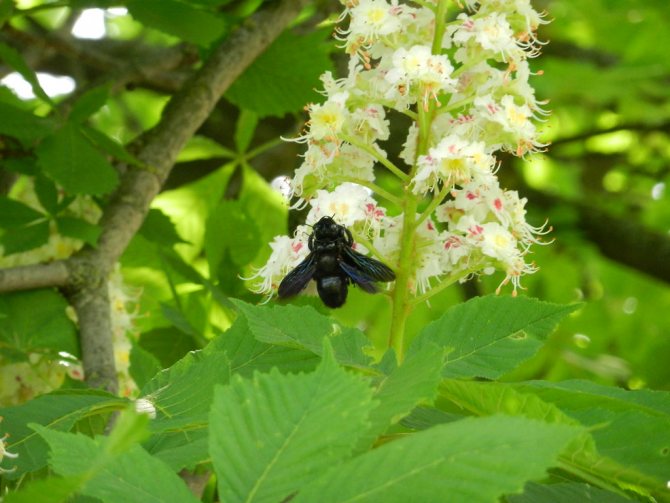


Chestnut flowers are peculiar in their structure, each of which has a five- or eight-membered perianth. Flowers, depending on the species and variety, can be pink, white and red.
Wintering pavia horse chestnut
Despite its shallow root system, the pavia horse chestnut is quite frost-hardy and, with light cover, tolerates even the most snowless and harsh winters. Moreover, pavia recovers well after freezing. In the conditions of the northern strip, it is recommended annually to carry out additional pre-winter mulching of the soil with a layer of dry leaves. For young plants it is better to carry out hilling. The older the tree becomes, the higher its frost resistance.
Horse chestnut red is prone to frostbite, especially at a young age. In February, it is better to wrap the trunks of the plant in several layers of burlap, and during the winter, carefully examine the plants for traces of bark injuries and immediately take action if ruptures appear. Burlap protects all standard baboons for the winter.


Horse chestnut red, or pavia horse chestnut.
About the origin of the plant
According to scientists, the chestnut existed even in the days of the first monkey-men (Tertiary period). The distribution area in those days was much wider than it is now. It is known that the plant grew in North America, Greenland, Sakhalin and the Mediterranean (subtropical shores). The Caucasus, Asia Minor and the Balkan Peninsula are considered the homeland of the walnut.
For the first time this ornamental plant was brought to Europe in the 15th century from Istanbul by the famous botanist Lukluz, who from the brought chestnuts began to grow it in Vienna. Over time, this attractive tree has become ubiquitous in urban landscaping and private gardens. The fruits were used as livestock feed. The healing properties of chestnut were discovered by scientists only in the XX century.
Breeding horse chestnut pavia
Red horse chestnuts differ little from horse chestnuts in general in terms of their reproductive capabilities. The optimal method for woody plants is considered to be obtaining new plants from seeds.
Chestnut fruits need preliminary stratification. To do this, the collected freshly fallen seeds need to be soaked in warm water for several days, changing it regularly to maintain the temperature. After soaking, the chestnuts are buried in wet sand and sent for stratification at a temperature of about 3-5 degrees Celsius. Stratification should take about 3-4 months. Sowing for germination is carried out in open soil, on a seedling bed, only after the threat of repeated frosts has passed. Traditionally, pavia horse chestnuts are sown in May. For the plant, you need to prepare high-quality nutrient soil. The fruits are buried 10 cm at a sufficient distance for growing for 2 years. Before moving to a permanent place, two-year-old seedlings are carefully dug, partially removed the soil and shortened the taproot by a third of the length for active branching of the rhizome and a lush spreading crown.
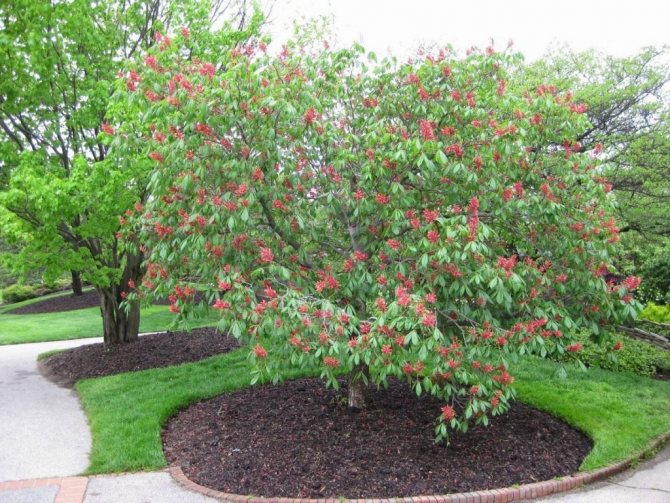


Red horse chestnut, or pavia horse chestnut (Aesculus pavia).
What to do before planting walnut chestnuts
The right place to grow the tree also plays an important role. You need to figure out how to plant chestnuts, because unfavorable conditions tend to create unnecessary problems for crops. There are several rules for how to germinate a chestnut:
- keeping seeds in a cold room for several weeks;
- planting in moist soil to avoid various diseases;
- you need to plant at least 5-6 nuts, which are placed in the dug holes of the earth, since not all will be accepted. The planting depth of the nut is about 5 cm, and the distance between them is 15-20 cm;
- the holes are covered with the same earth, but with the addition of a small amount of river sand.
Some awesome ideas
In addition to traditional medicine, the fruits of this tree are used for other purposes - in gardening, cosmetology, and households.
From aphids
Every gardener knows how threatened plants are aphids. It is very easy to get rid of it, it is enough to prepare a decoction of chestnuts:
- The fruits are boiled under a lid (in a saucepan that is not used for cooking!) For 15 minutes.
- After this time, the fruits are discarded.
- The resulting liquid is cooled, poured into spray bottles.
The broth is sprayed on plants attacked by pests.
Watering flowers
Chestnut broth is sometimes worth adding to the water that is poured over the flowers. Plants watered with decoction will grow beautiful and healthy.
Spider Repeller
It turns out that the smell of chestnuts repels spiders.If their presence in the house is annoying, spread the chestnuts on the windowsills, in all corners between the walls. This effective way to scare away arachnids will become a beautiful autumn decor for your apartment.


For washing
Ecological washing nuts are very popular among the advocates of living in harmony with nature. However, few people know that chestnuts can be used in this way. You just need to prepare them correctly:
- The collected fruits are peeled from the brown shell, cut into quarters.
- The fruits are placed in a linen or cotton bag or sock.
- The bags are placed with the dirty clothes in the drum of the washing machine.
- Select the standard wash program without adding powder or fabric softener.
Soap
You can make chestnut soap:
- Peel 20 chestnuts from brown shells;
- grate the peeled fruits (the one that is no longer used in cooking!);
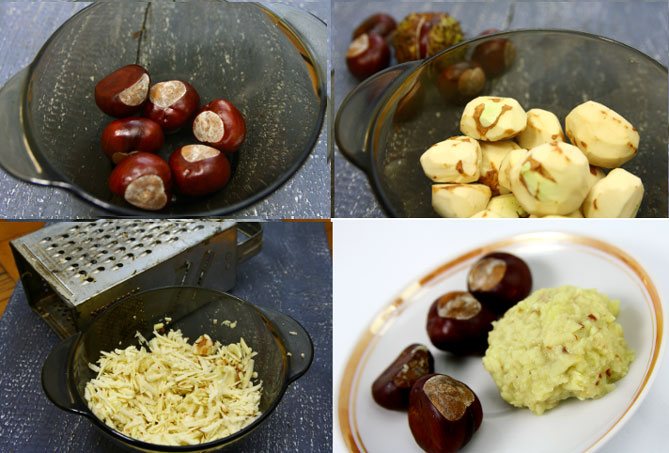


- transfer the resulting pulp to a saucepan, add water and cook for 15 minutes;
- cool and squeeze through a clean cloth, gauze;
- form any shape from the dried mass;
- leave the soap in a dry place to dry;
- after a few hours the soap is ready for use.


Mask for the face
A mask of crushed chestnuts and 1 tablespoon of coconut oil can work wonders. The product makes the skin smooth, elastic and well-hydrated.
Chestnut water for hair
Chestnuts are very beneficial for hair and scalp care. Chestnut water (formed after cooking the fruit) is regularly rubbed into the scalp. The decoction strengthens the hair follicles, preventing hair loss.
Significance and Application [edit | edit code]
Chestnut wood is very similar in appearance and properties to oak wood and differs only in the absence of "mirrors". It is of the ring-pore type with characteristic sinuous stripes and narrow medullary rays. The growth rings are clearly visible. The sapwood is whitish or light brown; the core is dark brown. The wood is used as timber, is used for plywood, parquet riveting, and is used in furniture production. Barrels and casks made of chestnut wood are used for infusion and storage of wines, cognac, whiskey, rum and brandy.
Wood, bark and leaves contain 6 to 14% tannins; they are used to obtain an extract for tanning leather.
Chestnut has been used as a fruit tree for a long time, and Sowing Chestnut ( Castanea sativa
), American Chestnut (
Castanea dentata
) and Chestnut crenate (
Castanea crenata
) gave numerous valuable varieties; The softest chestnut (
Castanea mollissima
) and Chestnut undersized (
Castanea pumila
) were used in hybridization.
Chestnut fruits are rich in carbohydrates and proteins, they are fried and baked, from which they receive high-quality additives in flour and confectionery.
As a tree of powerful growth with a tent-like crown, interesting in all seasons, the chestnut is of great value in gardens and parks. Sensitive to drought, as the roots are close to the surface of the earth (because of this, chestnuts are sometimes planted above wine and beer cellars).
Chestnut is a plant that is actively used not only to decorate parks and recreation areas, but also as a medicine and cosmetics. The tree has a very unusual and beautiful flowering. Therefore, it is fashionable for him to meet on the streets in different countries of the world. Apart from this, the fruits of some types of chestnuts are edible. They make delicious and aromatic dishes that have won the hearts of even the most fastidious people.


Distribution and ecology [edit | edit code]
Chestnut is found in the northern hemisphere between the Tropic of Cancer and 45 ° N. sh. in three separate areas from each other - in the Mediterranean, in East Asia and on the Atlantic coast of the United States.
Chestnut is a tree of a warm temperate climate.It grows on mountain slopes, as a rule, on shaded slopes with brown, moderately moist soils, overlying calcareous rocks; does not tolerate dry and waterlogged soils.
The chestnut grows relatively quickly, has a large growth capacity from the stump, which it retains until old age. The largest known specimen is the Chestnut of hundreds of horses, 2-4 thousand years old, with a trunk circumference of 57 m.
Chestnut appears in the Cretaceous deposits and is widespread in all Tertiary deposits [3]:
- Castanea kabinyi Kov. - found in the Sarmatian sediments of the Black Sea region (Orekhov, Krynka) and the Volga-Kama basin (Sterlitamak region) in the lower Tertiary sediments of the Amur region (Novokievsk), Ussuri region (Fatashi, De-Friz, Cape Rechnoy) and Sakhalin (near the city of Alexandrovsk);
- Castanea atavica Ung. - in the Sarmatian deposits of the Western Transcaucasia (Khvteeba).
- Castanea ungeri Heer - in the Lower Tertiary deposits of Primorsky Krai (Cape Rechnoy, De-Friz) and Sakhalin (Mgach).
- Castanea sp. - was indicated without specific identification in the Lower Tertiary sediments of the Balkhash region (Ashutas) and Sakhalin (the Agnevo river).
When to transplant outdoors
If the chestnut is transplanted from a pot into open ground, then you also need to know some rules:
- seedlings will take root better if they are kept indoors for up to 1-2 years, by which time the root system will be well formed;
- for planting, leached loamy black soil is needed;
- for each seedling in the garden, you will have to allocate at least 3 m in diameter if you plan to make a chestnut alley;
- the depth and width of the planting holes - not less than 0.5 m;
- it is better to mix the earth from the deepening with humus and sand, add a little nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium fertilizer to the composition of dolomite flour and slaked lime;
- drainage is laid out at the bottom of the planting pits, it can be a mixture of crushed stone (pebbles) and sand;
- the hole is well moistened with water, then a seedling is placed in it;
- the landing mound should rise about 20 cm above the ground, because gradually the soil will shrink under the influence of precipitation.
On a note. If a large chestnut variety is planted, the planting neck should rise 8 cm above the mound.When planting a low-growing crop, it is not necessary to overestimate the seedling.
Botanical description [edit | edit code]
Monoecious, deciduous trees, up to 50 m [4], or shrubs. The trunk has a deeply grooved, brownish-brown, thick bark.
The buds are rounded-conical, with four outer, leathery, brown scales. Leaves are spirally two-row, simple, relatively short-petiolate, oblong-oval to broadly lanceolate, 6-25 cm long, pointed at the apex and from wedge-shaped to cordate at the base, roughly toothed along the edge, dark green, rather leathery, with pinnate venation ... Stipules are lingual, about 1.5 cm long, pinkish-whitish, early falling.
The flowers are collected in pyramidal erect spike-shaped inflorescences, reaching a length of 5-15 cm; most flowers are staminate, pistillate, located separately at the base of the inflorescence. Stamen flowers, 3-7 in glomeruli (dichasia) in the axils of small covering leaves; perianth simple, bell-shaped, with 5-6 oval-rounded, slightly pubescent lobes; 10-20 stamens attached around the glandular disc, with thin long filaments and two-celled, almost spherical anthers; staminate flowers often contain a rudimentary ovary. Pistillate - one at a time, often three (rarely up to seven) in dichasia in the middle of a four-incised envelope or plyus, covered with scales and branched spines on the outside; perianth 5-8-incised, fused at the bottom with the lower bottle-shaped ovary, having 6-9 nests with two ovules in each; columns 6-9, narrow-ribbon-like, erect, with stigmas at the apex; sometimes there are 6-8 rudimentary stamens.During flowering, the stigma and part of the perianth protrude from the plyus.
By the time the fruits ripen, the plyus is spherical, pubescent inside, outside with hard, branched spines, cracking into 4 (less often 2) segments and containing 1-3 (rarely up to 7) nuts (chestnuts) inside. Nuts are ovoid-spherical, flat on the sides adjoining each other, tapering upwards and bearing the remains of the perianth and columns here. The nut shell is thin, woody-leathery, shiny, glabrous or pubescent, brown in color, with a wide grayish heel at the base. Seeds are triangular-spherical, in a light brown shell, with a large yellowish-white embryo; the embryo has fleshy, wavy cotyledons on the outer surface, containing a large amount of starch.
Pollinated by insects that collect pollen and nectar.
When the fruit germinates, the cotyledons remain in the ground. The first leaves are similar to adults, but below them there are one or two sickle-shaped leaves, 1 cm long and 0.5 cm wide, low-lying formation, quickly falling off. A chestnut seedling develops a long taproot, which in the first year deepens into the soil by 25–40 cm; the stem at the same time reaches a height of 10-25 cm. Later, the chestnut forms a deep root system with several roots that run obliquely into the soil and without a distinct tap root. The breed is not windblown.
Important ingredients
Chestnut is used for the treatment and prevention of various abnormalities of the musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular system, muscle tissue, gastrointestinal tract. The prepared means relieve pain, are able to relieve inflammation, relieve the unpleasant symptoms that appear during serious diseases (arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, gout), improve the state of blood vessels and the brain. Chestnut contains:
- vitamins - A, E, P, C,
- potassium and calcium,
- magnesium and manganese,
- selenium and phosphorus,
- iron,
- organic substances - saponins, glycosides, bioflavonoids, escin, esculinfraxin,
- pectins,
- escin.
Tinctures and rubbing from chestnuts for joints are used in the treatment of various diseases, but self-medication can be harmful. Therefore, be sure to contact your doctor to exclude side and allergic reactions.
The benefits of chestnut
Healing medicines for joints are prepared from all parts of the tree: bark, leaves, seeds, flowers, fruits. In the composition of many pharmacy ointments and creams there is a horse chestnut extract - escin. The advantage of the treatment and prevention of joint diseases with chestnut tinctures is in the provision of a powerful anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, regenerating effect. Such medicines quickly relieve swelling, redness, pain and heal existing wounds. It is important to understand that chestnuts for joints are not a panacea for joint pathologies and pains, so you need to combine alternative treatment with conservative methods.