Green spaces for landscaping cities, recreation areas, parks and squares, industrial areas play an important role in improving the environmental conditions of the environment. For landscaping, shrubs and woody plants are selected that do not lose their decorative appeal for a long time.
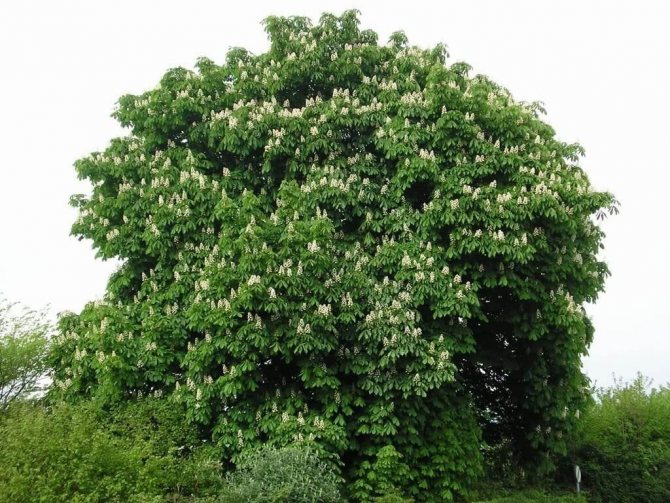
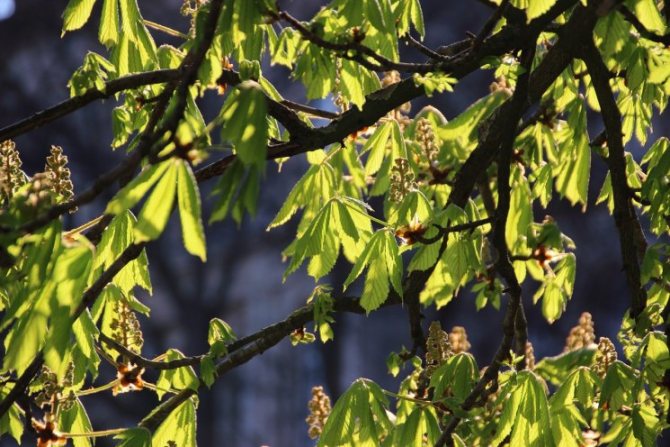
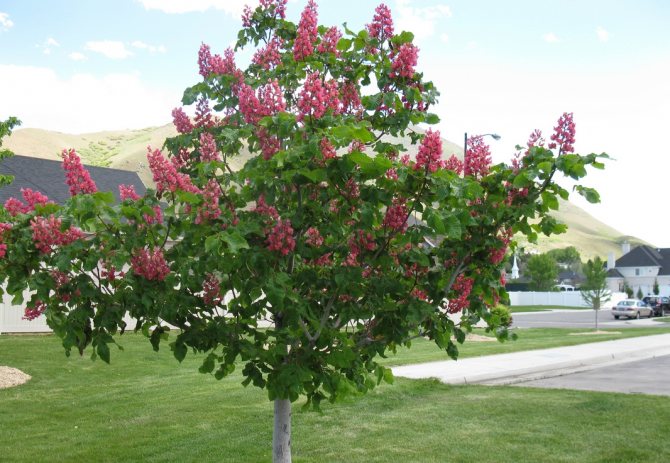
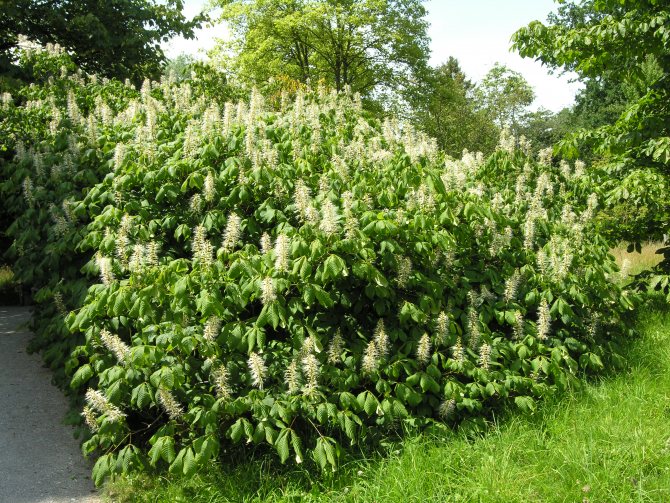
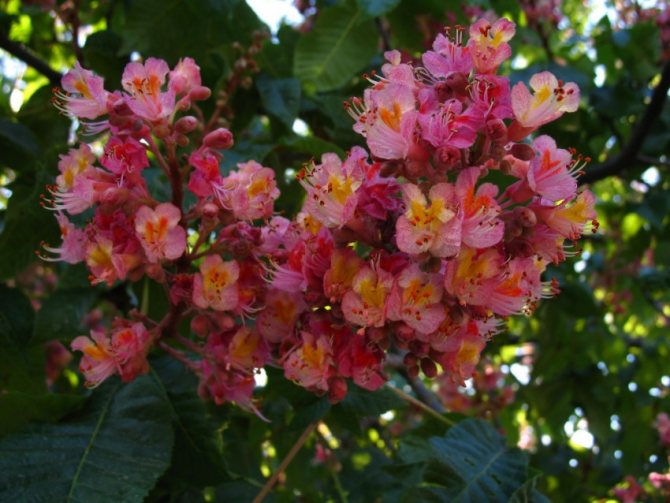
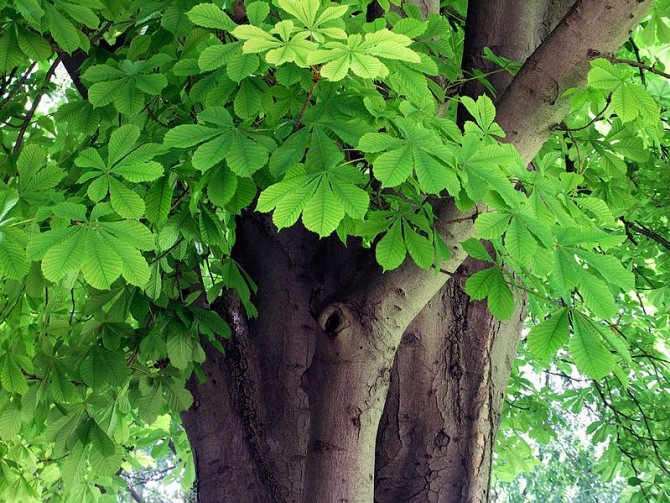
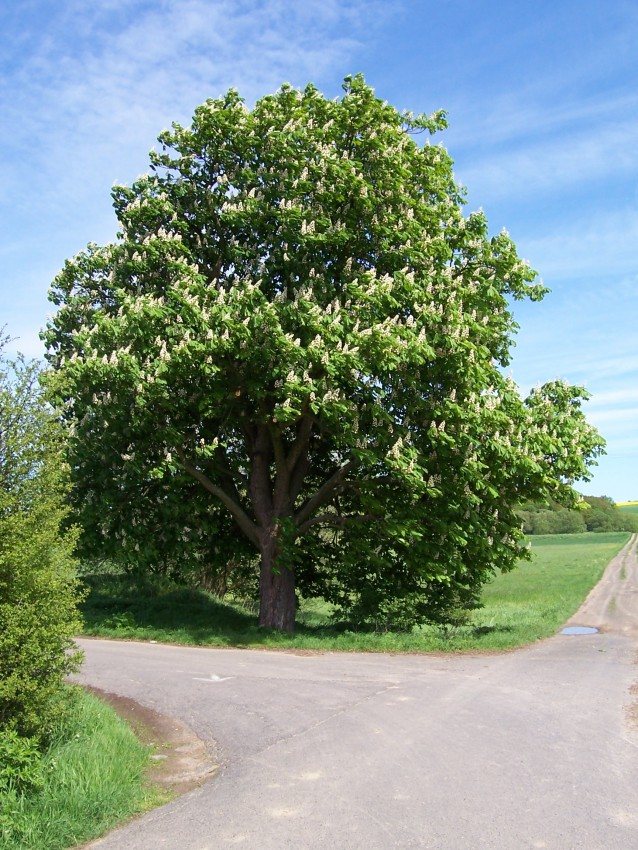
Thus, the common horse chestnut forms a spectacular, dense crown with large foliage, which in autumn is painted in a variety of colors of purple, crimson, yellow and brown shades. Powerful plants with original inflorescences and capsule fruits are amazingly beautiful! In addition, they are perfectly adapted to urban living conditions. Chestnuts can thrive and thrive even in a polluted atmosphere.
general information
When growing all varieties of chestnuts, you need to be patient because they don't grow very quickly. But with careful and proper care of it after about 10 years, overtaking the growth of neighboring garden trees, it can become an excellent protection from the sweltering heat in the summer thanks to its dense and delicate foliage. And if necessary, it can be used as a healer for many ailments.
Umbrella high chestnut crown gives good shade, and surprisingly delicate flower chestnut candles every spring for a couple of weeks delight with their beauty and freshness. In the wild, this plant grows in many southern countries, but they can often be found as an ornamental culture in the middle lane. Planting and grooming procedures are not as complicated and costly as newbies might think. The main thing is to be patient and do everything right.
There are about 15 species of this plant around the world. The flowering period also depends on the type of plant. The most common species in Russia are noble and horse chestnut, which bloom in early May. Chestnut is an excellent honey plant.

Pharmacy preparations with horse chestnut
At the pharmacy, you can buy horse chestnut medications:
- Aescusan - horse chestnut liquid extract, used for chronic venous insufficiency. Helps with hemorrhoids, muscle pains, cramps, swelling, ulcers, thrombophlebitis. In addition to the liquid extract, Aescusan is produced in the form of an ointment and gel. Read about horse chestnut ointment in this article.
- Esflazid - a domestic drug - venotonic, has pronounced angioprotective and tonic properties.
- Venitan - gel, has a venotonic, anti-inflammatory, anti-edema effect.
You can also buy 911 horse chestnut gel-balm at the pharmacy. It is an adjunct for the treatment of varicose veins and thrombophlebitis.
Types and varieties of chestnut
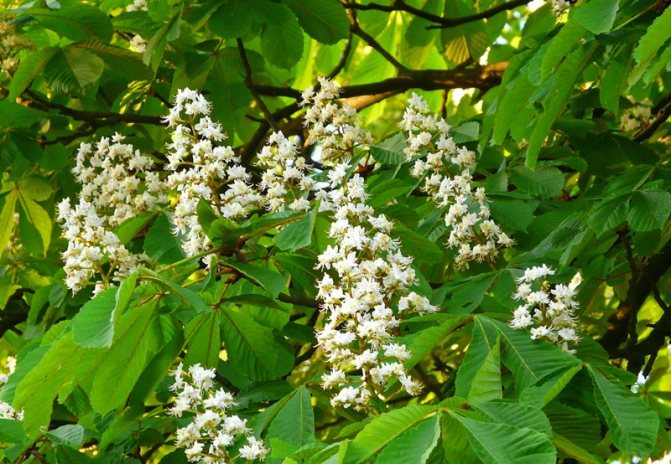
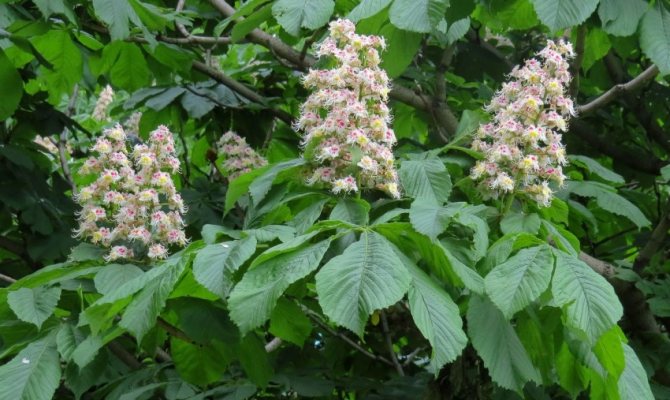
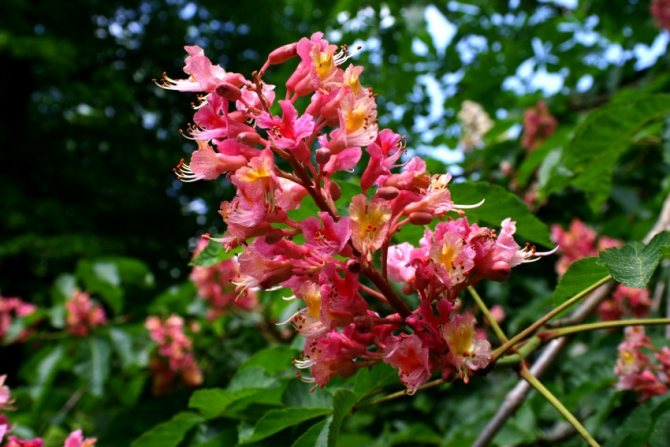
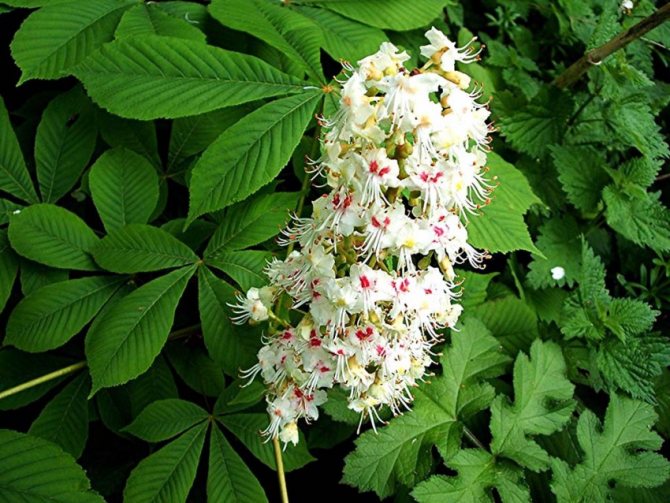
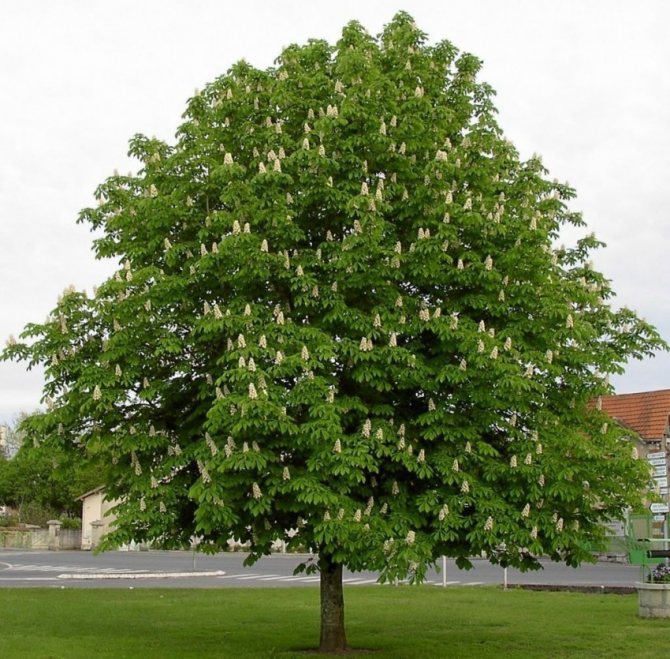
The most popular and widespread representative of the plant in Russia is the horse chestnut. An adult chestnut tree of this variety grows up to 30 meters in height. It has large, finger-like compound leaves with well-defined veins. Inflorescences racemose with double white, pink and yellow flowers appear in May. There are red spots in the very center.
There are other types of chestnuts:
- Californian, which grows in the western United States and has a height of up to 10 meters, as well as white-pink flowers.
- Red is a Crimean variety that grows up to 30 meters in height and has large racemose inflorescences of a dark red hue.
- Yellow - A tree with a pyramidal crown, jagged golden leaves and yellow inflorescences, which is an Eastern American variety.
- Small-flowered chestnut, which is a shrub form (height up to 5 meters) with small complex leaves, painted on the lower side in a grayish color.
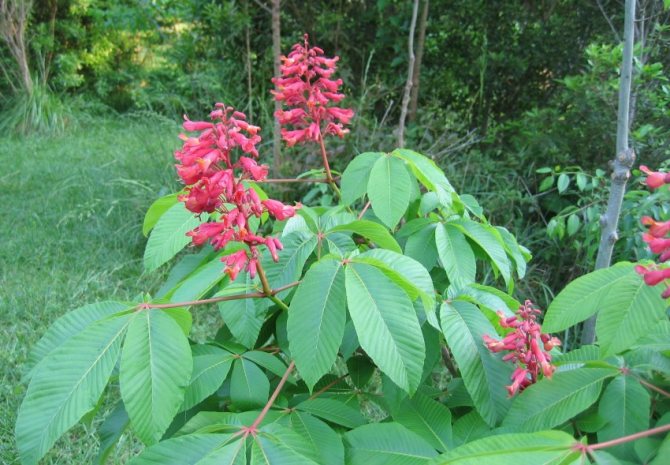
- Red chestnut, or pavia, is a tree or shrub (up to 10 meters high) with bright red flowers, growing in the eastern United States.
- Japanese is an erect tree with large leaves, yellow-white flowers and pear-shaped fruits.


Differences between edible fruits and poisonous


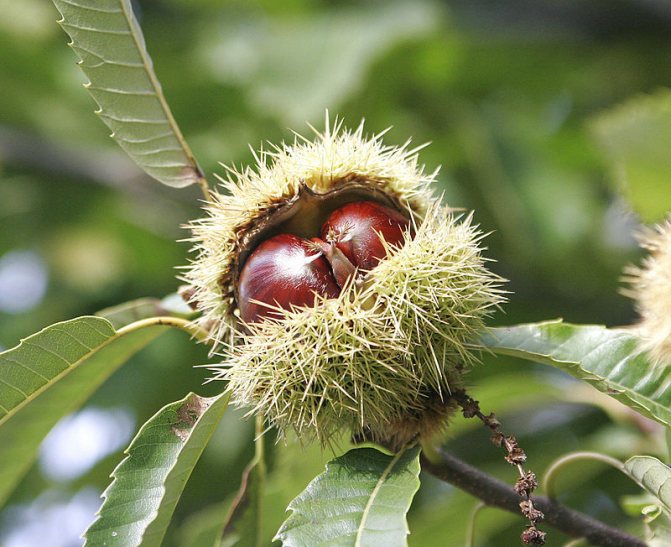
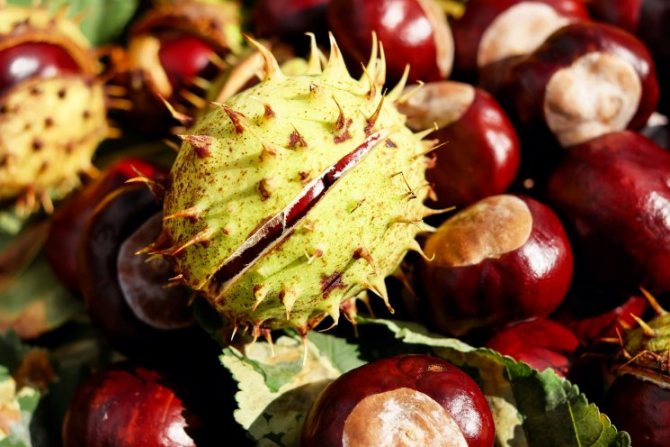
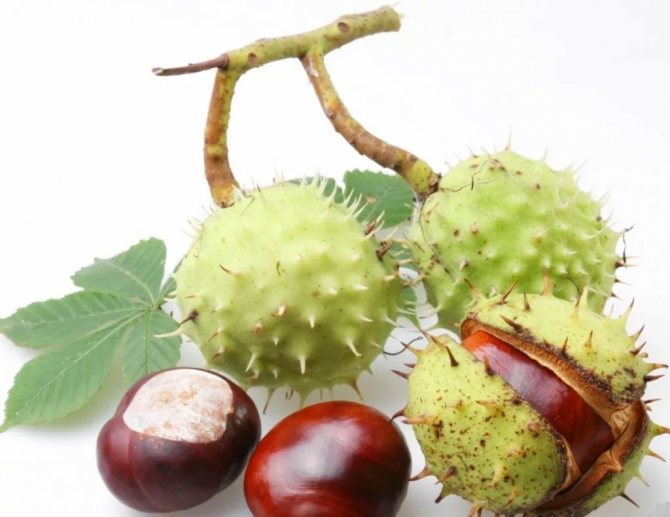
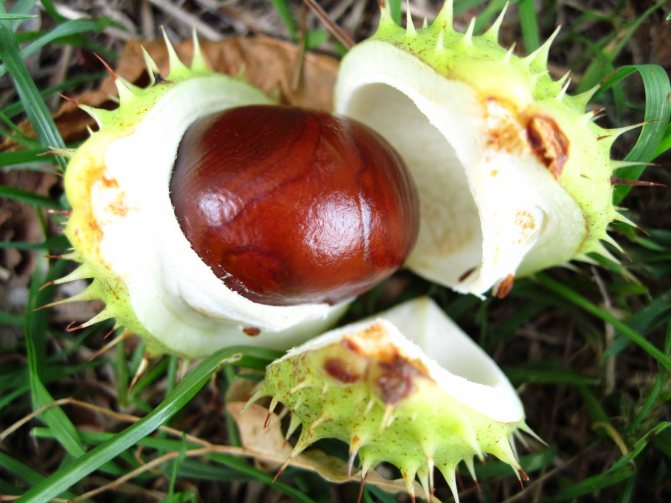
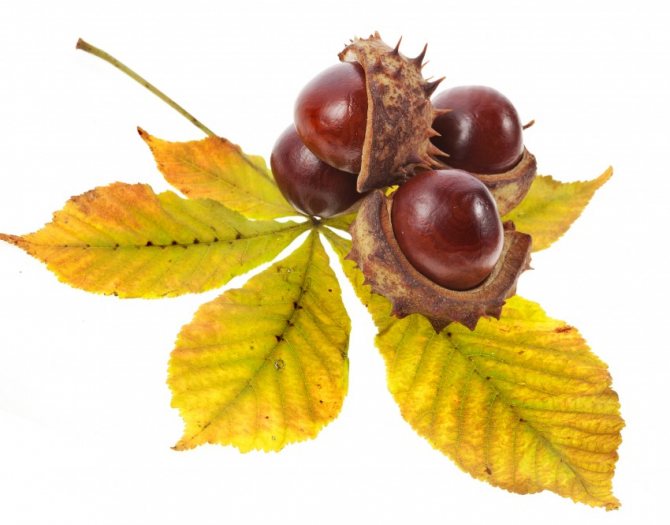
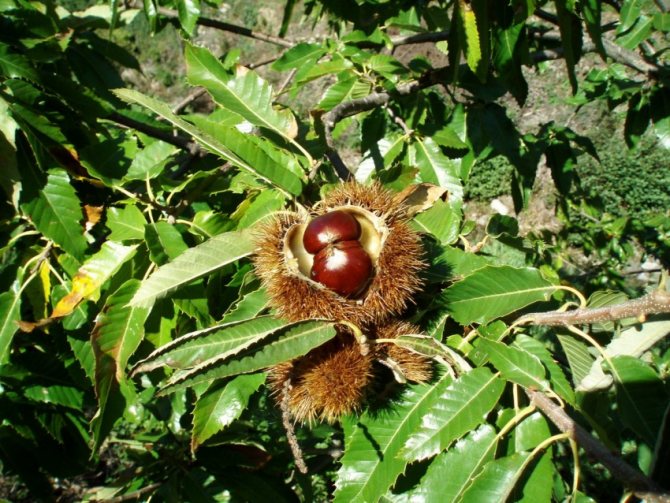
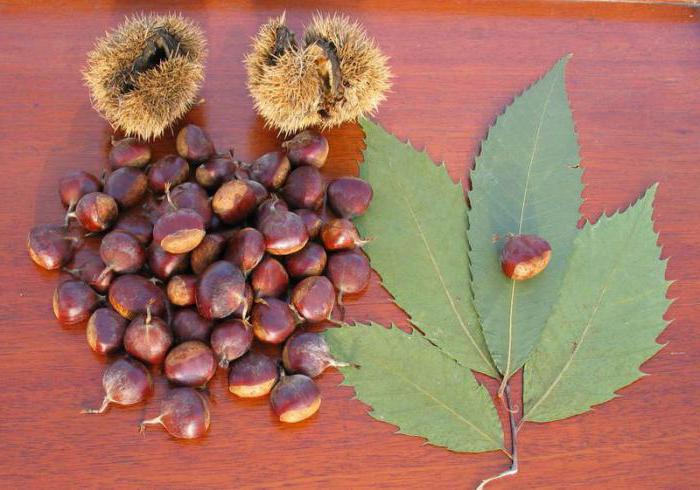
A peeled edible chestnut looks like a yellowish fleshy nut. In wild edible fruits, one box contains several medium-sized nuts, and in cultivated garden fruits, only one, but large.
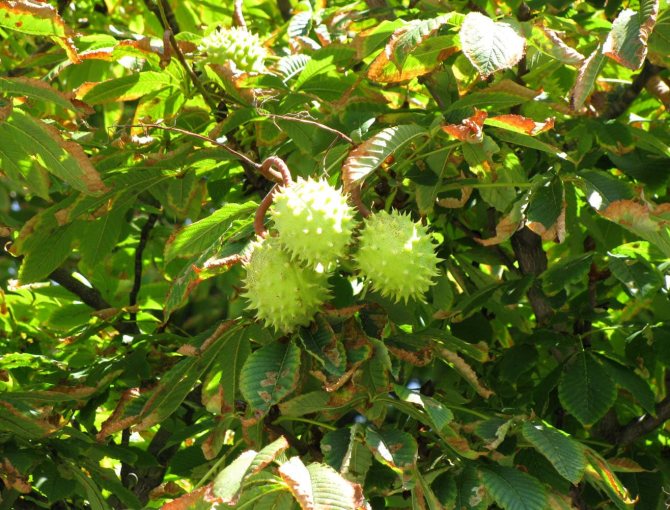
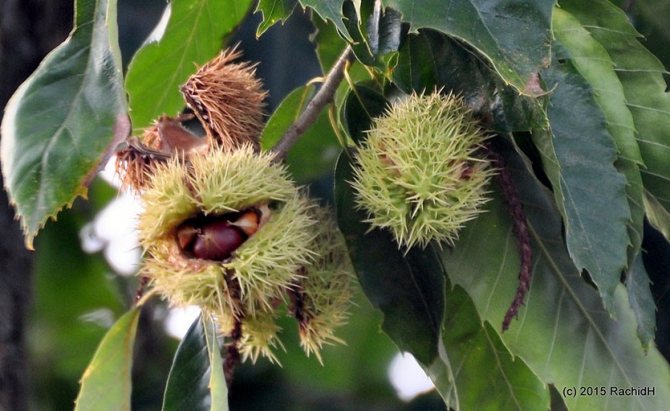
Chestnuts are fast growing deciduous trees and shrubs. They grow in height from 2 to 40 meters. They bear fruit towards the end of September. The fruits are shaped like thorny balls. In the summer months, they acquire a light green color. When ripe, they turn brown. These balls contain seeds with a golden brown smooth and thin shell. They are somewhat larger than hazelnuts. Seeds contain large amounts of starch and protein.
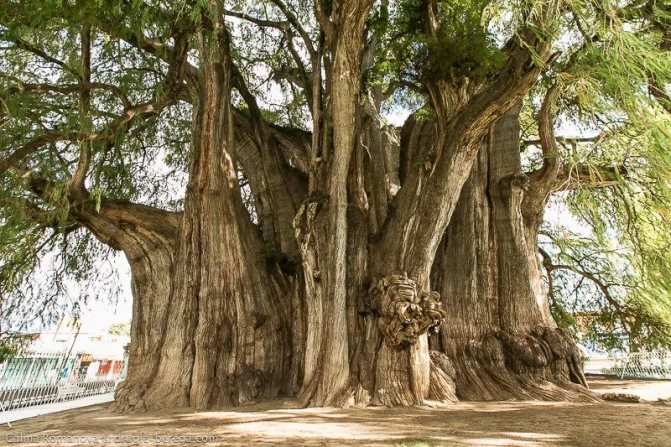
Trees grow from hundreds of years and longer. There are natural monuments over two thousand years old in the world. While the inedible horse chestnut withstands almost any climate, the noble loves warm and humid living conditions. The equine variety can grow in many parks, while the edible variety still needs to be looked for. It is noteworthy that these trees are representatives of completely different species.
Horse has its own name "chestnut", because outwardly it is very similar to the noble one. And he was nicknamed "horse" due to the similarity of the color of the fruit with the color of the coat of a chestnut horse, the same brown, smooth and shiny. But you cannot eat this type of chestnut. In addition, due to the external similarity of nuts, poisoning often occurs.
Here the question arises, what are the differences between fruits of different varieties. To do this, you need to take a closer look at the trees themselves. The horse has a more luxurious crown, reminiscent of a pyramid, and he himself is taller. It begins to bloom with white-pink buds, and the leaves are collected in fives. The noble chestnut is covered with dense, glossy leaves growing separately on a branch. The needles on the fruit of the trees are also different. The edible should look like hedgehogs, and the horse should look rare. The main difference between the edible chestnut fruit and the horse chestnut is a small sharpening at the end of the seed capsule.
Description
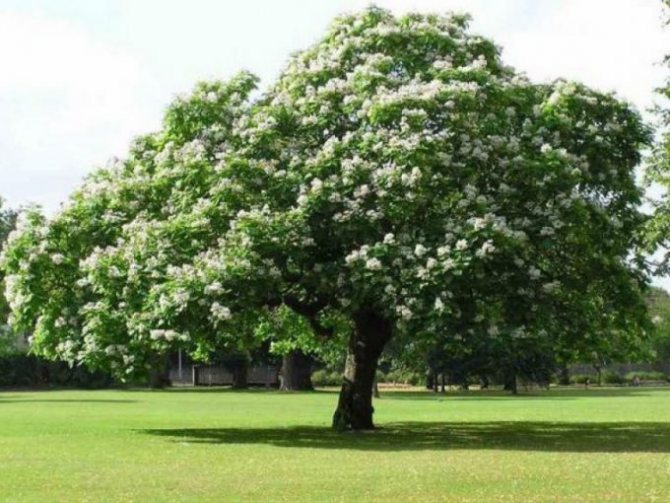
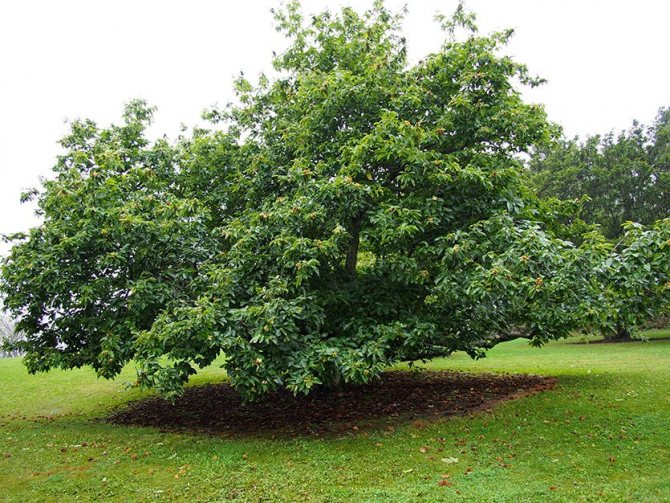
The chestnut tree is able to decorate any suburban and garden plot. It is a large deciduous plant belonging to the Beech family. Its height can reach 25 meters.
The straight, slender trunk, which has a brown-gray color, can be up to one meter in diameter. The fairly strong root system of the chestnut with the main taproot has very branched lateral roots, making the tree resistant to gusts of wind.
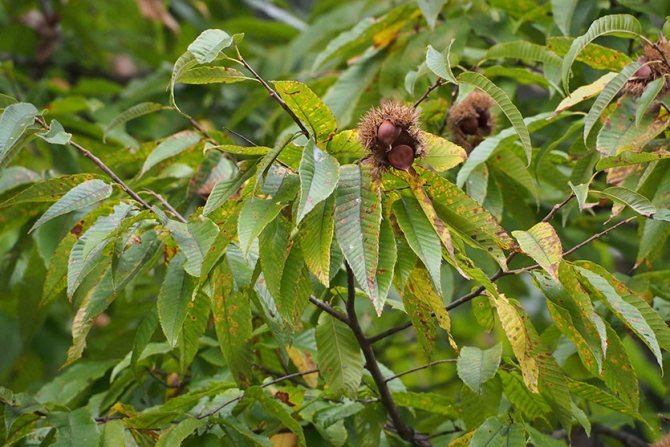
Chestnut leaves are large and complex, five- or seven-fingered, with a long root. In the summer, the leaves are green, and in the fall they acquire yellowish, brown, purple and crimson hues. Chestnut greens contain tannins, vitamin K and pectin. It is often used in the preparation of decoctions and tinctures used for various ailments.
The crown of the tree, thanks to its large openwork leaves, is wide and very dense. It has a rounded shape.


Chestnut meaning. Chestnut
chestnut
Chestnut Chestnut is a small genus of trees in the family. In addition to the species of the genus Chestnut, other plants from other families can also be called "chestnuts", for example: Chestnut is found in the northern hemisphere between the Tropic of Cancer and 45 ° N.Wikipedia
chestnut
1 Calendar - from the point of view of druids - the period of the zone of influence of one of the sacred stars, a certain deity and a given tree. re. One who was born in such a time period (May 15 - 24 and November 12 - 21).The Comprehensive Modern Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language
chestnut
m 1. A tree of the beech family with brown fruits in the form of a large nut. 2. The fruit of such a tree. 3. The wood of such a tree.The Comprehensive Modern Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language
chestnut
(lat. castanea) genus of trees this. ... beech, common in North. America, Japan, China, the Mediterranean, the Caucasus and Transcaucasia; the fruits are edible.New Dictionary of Foreign Words
chestnut
1) A tree of the beech family with brown fruits in the form of a large nut. 2) The fruit of such a tree. 3) The wood of such a tree.New explanatory and derivational dictionary of the Russian language by Efremova
chestnut
husband. Fagus castanea tree and fruit. (See also cat.). - wild, tree stomach, Aesculus hippocastanum. - pork, mice or ground nuts, Bunium bulbocastanum plant. Chestnut husband. chestnut tree; collect. chestnut grove. | Chestnut lover. -nice wives. lover or saleswoman of chestnuts. Kashtanka for women insect Hispa, on chestnut. Chestnut, related to chestnuts. Chestnut color, reddish brown, bright. CHESTNUT myrrh-eater, see cat.Dahl's Dictionary
chestnut
genus of trees this. beech, common in sowing. America, Japan, China, the Mediterranean, in the USSR - in the Caucasus and Transcaucasia; the fruits are edible.Dictionary of Foreign Expressions
chestnut
chestnut, -aDictionary of the Russian language Lopatin
chestnut
tree of this. beech with brown fruits (nuts), as well as the very fruit of Roasted chestnuts. Carrying chestnuts out of the fire for smb. (trans.: to do a difficult, unpleasant business, the results of which will be used by another). chestnut! a tree of the beech family with brown fruits (nuts) Roasted chestnuts. Carrying chestnuts out of the fire for smb. (trans.: to do a difficult, unpleasant business, the results of which will be used by another).Dictionary of the Russian language Ozhegov
chestnut
a genus of trees of the beech family. OK. 10 species, in the North. America, Japan, China, Mediterranean; sowing chestnut - on the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus and in the Transcaucasus. In culture, this and 3 more species as ornamental plants; fruits are used for food, wood - in construction, furniture production.Modern Explanatory Dictionary, TSB
chestnut
chestnut m. 1) A tree of the beech family with brown fruits in the form of a large nut. 2) The fruit of such a tree. 3) The wood of such a tree.Efremova's Explanatory Dictionary
chestnut
chestnut, m. (Latin castanea). 1. A genus of trees from the beech family. 2. Shelly light brown fruit of this tree species, uptr. for food. Roasted about chestnuts. Pull chestnuts. To drag chestnuts out of the fire for someone (translation from French tirer les marrons du feu - from La Fontaine's fable) (proverb) - to do something. difficult, risky business, the fruits of which are used by another.
Fruit
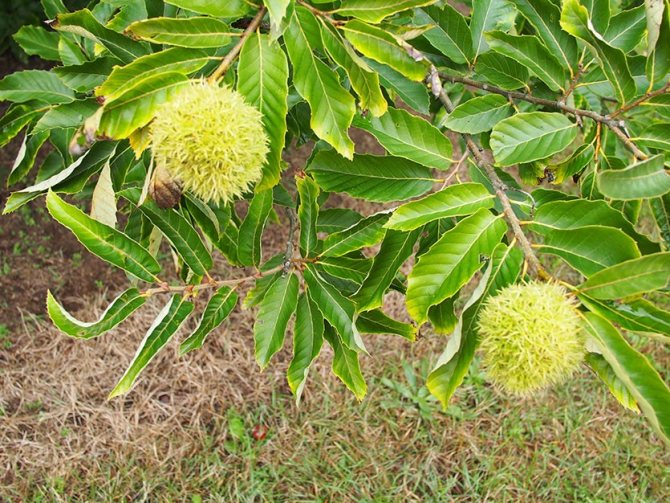
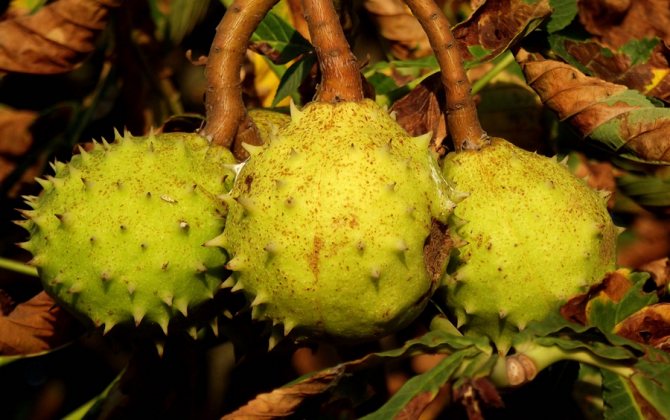
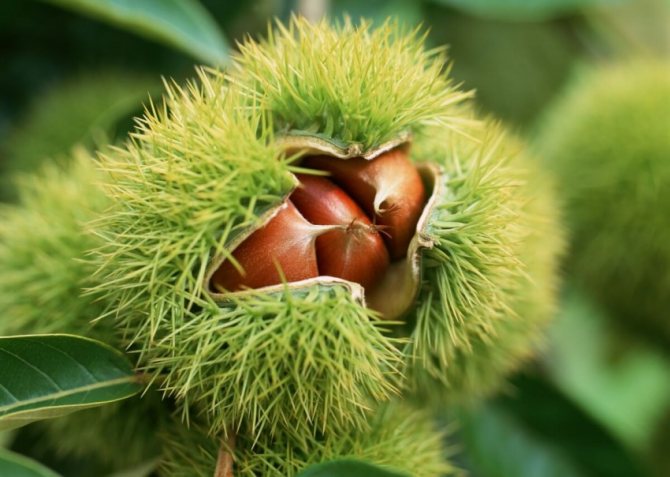
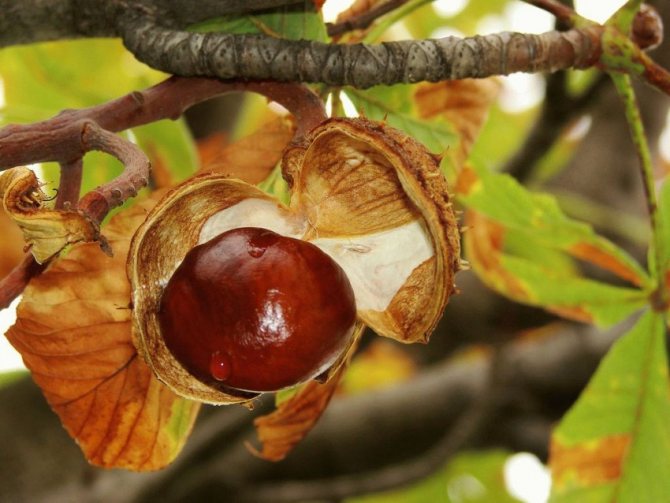
The fruits of the chestnut tree are round capsules (nuts) of green color with opening valves, which are covered with sharp thorns. Each nut contains one to four seeds. The plant begins to bear fruit only from the age of 15-25.
Real (noble) chestnut nuts can be used in cooking. Horse chestnut is mainly used in landscaping. The latter is quite winter-hardy, but it does not tolerate long periods of drought.


Harvest storage
Ripe fruits contain a lot of moisture. If you leave the harvested crop stored at room temperature, it will disappear after a few days - it will become covered with mold and rot even in the shell.
To keep the nuts fresh for as long as possible, they need to be placed in a refrigerator or in a dry cellar. ... Recommended air temperature: no more than +3 ° C. You can put nuts in boxes and cover with dry sand, like potatoes or carrots. Air-permeable paper or linen bags will do. Cellophane must not be used.Pre-roasted or boiled nuts can be frozen. If all requirements are met, chestnuts will last up to 6-7 months.
Flowering features
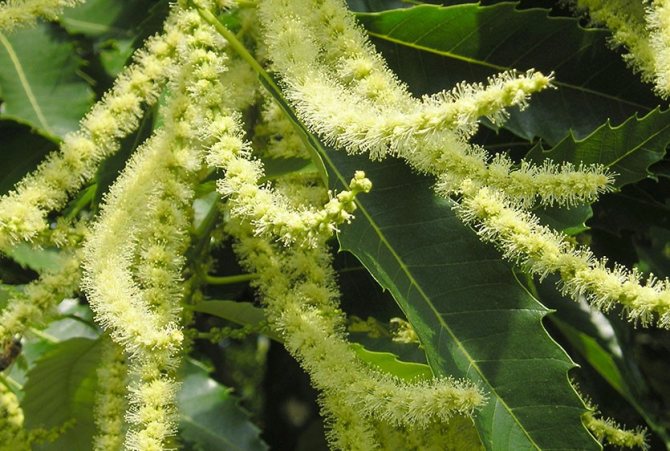
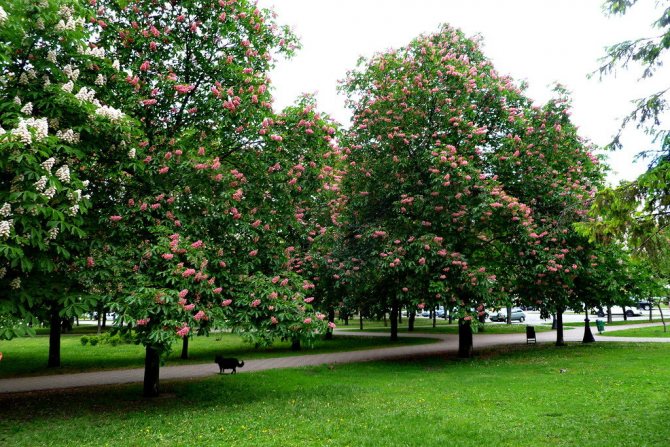
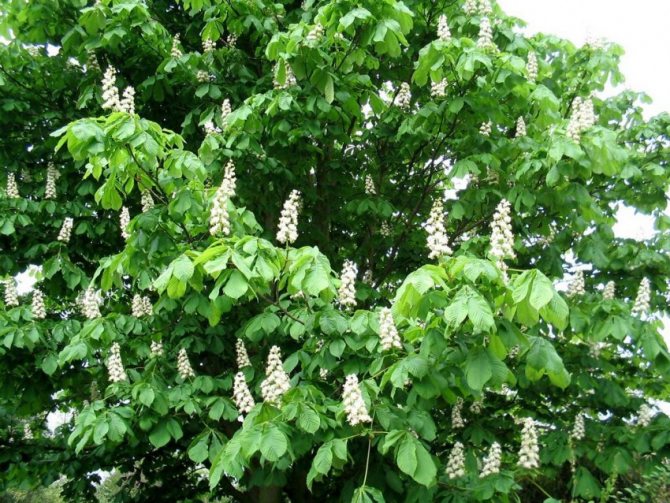
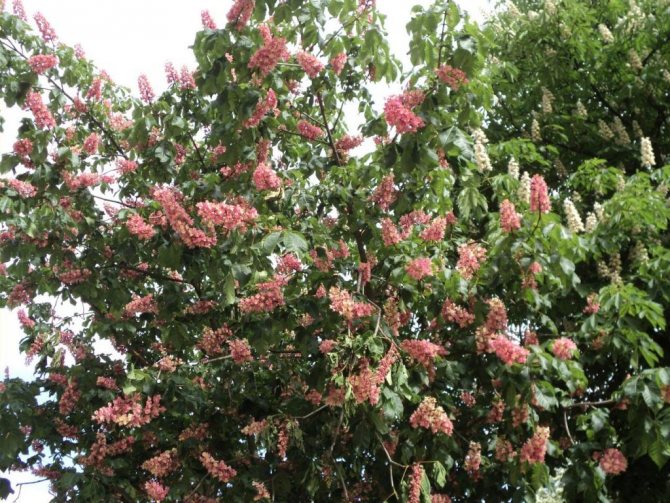
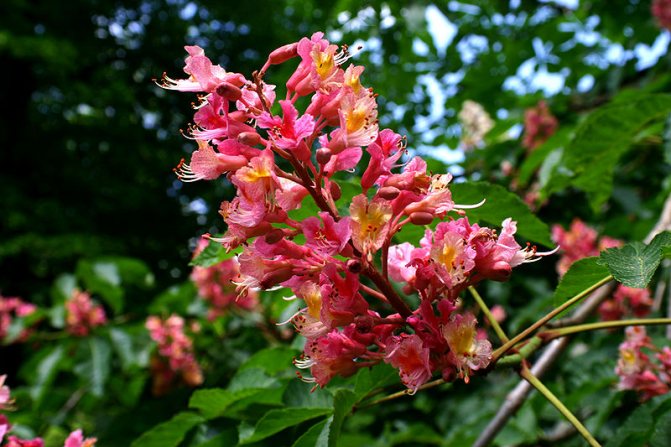
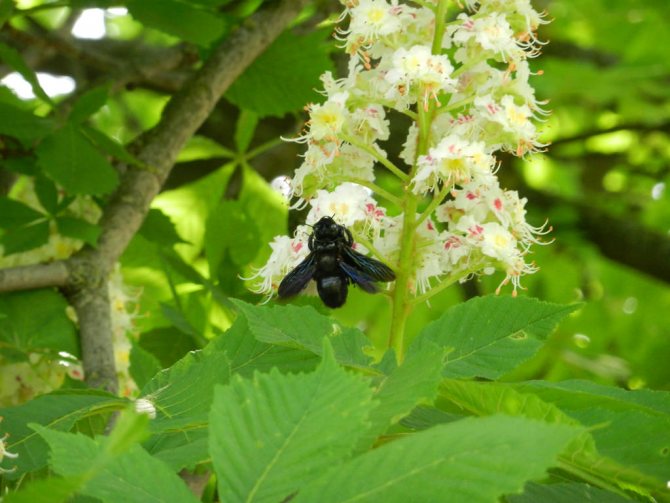
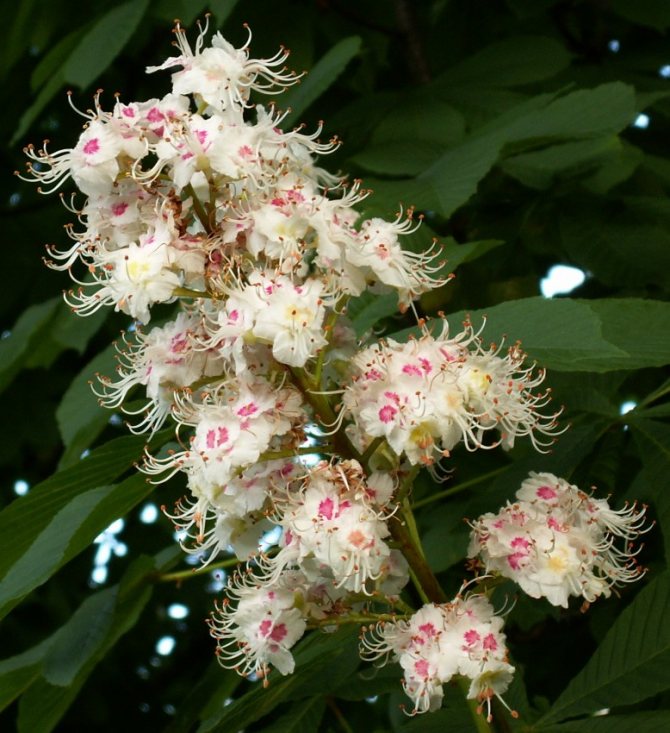
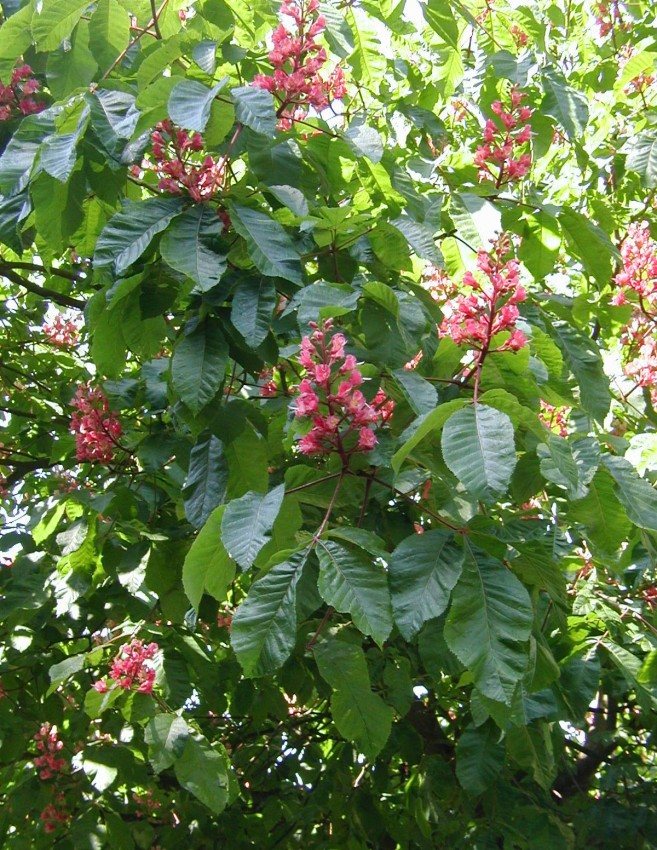
During flowering, chestnuts look very beautiful. Large fragrant inflorescences look like candles, evenly scattered throughout the crown. Spike-shaped, pyramidal inflorescences (length - 10-35 centimeters) are located vertically on the tree. Their lower part is female flowers, the upper part is male.
Each flower has a 5-8-membered perianth. The flowers, depending on the type of chestnut, can be white, pink or red.


Chestnut leaves in folk medicine: a pantry of health for humans


The plant has received widespread appreciation for its taste and healing power. The medicinal properties of parts of the tree are used by folk Aesculapians all over the world. Chestnut fruits and leaves have the following properties:
- antitussive;
- astringent;
- diuretic;
- anti-inflammatory;
- wound healing;
- antipyretic.
Such an extensive list of beneficial effects is due to the presence of a vitamin and mineral complex. Official pharmaceuticals have recognized that the plant is able to heal from a number of diseases. In pharmacy chains, you can find a lot of preparations based on chestnut leaves. Extracts and decoctions effectively relieve puffiness, stabilize blood pressure.
These drugs have analgesic effects. Infusions normalize the state of the intestinal tract. They also thin the blood, make the walls of blood vessels more elastic, increase their permeability. Prevents the formation of cholesterol plaques. Herbal raw materials are used to combat respiratory pathologies: it suppresses the cough reflex, improves the viscosity of sputum. The funds help stop uterine bleeding.
Growing conditions
How to grow a chestnut and what conditions does it need for this? Having decided to plant this plant in the garden, you should take into account that space is needed for its normal development. It should be planted so that there are no buildings or plantings within a radius of 5 meters from it. Even grass cannot grow under its dense canopy.
Despite the fact that the chestnut is of southern origin, it is quite winter-hardy. Some specimens live for more than a hundred years under the most favorable growing conditions. Due to the presence of a sufficiently powerful and branched root system, the tree can grow in harsh climates, while needing shelter for the winter period only at a young age. In summer, this plant can withstand a heat of 30 degrees, but the best temperature for it is + 20 ... 25 ⁰C. With thick snow cover in winter, the chestnut tree can withstand frosts of twenty degrees, but suffers from piercing and cold winds.
Poorly tolerates chestnut and gas-polluted atmosphere. Therefore, on the streets of cities with a large number of industrial enterprises, one can often observe the withering foliage of these trees in hot summers.


Rules for planting and caring for a plant.
To grow a truly stunning tree in your own backyard, you need to know the basic rules:
- chestnuts are planted at a distance of at least five meters from other trees or building objects, structures;
- the plant needs spring and autumn feeding;
- clay soil when planting is fertilized with superphosphate;
- the tree is protected from pests, in particular - from tree mites.
Many people ask the question chestnut - is it a shrub or a tree? We are happy to answer - this is a tree of the Bukovy family, which prefers a warm, temperate climate. Some types of chestnut are stunted and rather diminutive compared to popular varieties, which makes it similar to a shrub.
Preparing for landing
Planting this plant is not difficult, but the condition of the soil must always be taken into account.The planting site should be prepared in advance if the composition of the soil is unfavorable for this tree. You need to dig a hole, fill it up with a mixture of turf soil (three parts), humus (two parts) and sand (one part).
The best period for planting chestnuts is autumn or early spring. These dates should not be shifted, as there is a possibility that the seedling will not have enough time to take root.
An excellent planting material is three-year-old and older specimens.
What do chestnut leaves look like and when to pick them?
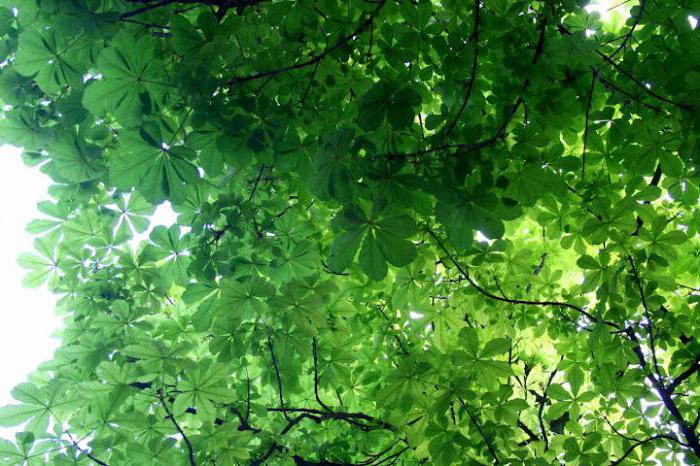


Biologists know over 30 varieties of chestnut tree populations. The most popular is sowing, suitable for consumption. Each subspecies differs in fruiting, trunk height. Healers often use sowing chestnut for medicinal needs. It can be distinguished by its oblong, slightly pointed leaves 25 cm long.
During blooming, they become deep red. The chestnut leaves take on a bright yellow hue in the fall. From August to September, experienced healers begin to harvest. The raw materials are spread in an even layer on a fabric surface, the first few days are periodically turned over to dry evenly. Then they are transferred to containers and stored for 12 months.
The order of work
- Dig a hole more than 0.5 meters wide and deep.
- Add humus and one glass of superphosphate to the soil (add dolomite flour to neutralize excessive acidity).
- For drainage, cover the bottom of the pit with a layer (15 cm) of sand with fine gravel.
- The root collar should remain at ground level when planting a plant.
- Make a small mound around the trunk to prevent subsidence of the root collar.
- Watering should be done with about three to four buckets of warm water, and then, after planting, watering should be done daily.
- For better rooting, the seedling should be tied to a support, which can be removed after the chestnut is completely rooted.


Component components


Chestnut leaves are endowed with amazing substances that improve human health. Experts have identified triterpene compositions that play a key role in metabolic processes, tanning compounds that the body needs to fight free radicals. Discovered pectin substances that contribute to the elimination of toxins, heavy metals. It is impossible not to mention flavonoids: they have a positive effect on the enzyme system. They abound in plant glucose, organic acids, lecithin, a wide range of vitamins and minerals.
Care
Chestnut tree care is simple. You should constantly take care of a young tree, and a mature plant practically does not need care.
It is undesirable to leave a young tree in direct sunlight, as it can get quite severe burns from overheating. In the first year of plant growth, it should be watered vigorously and protected from hot sunlight.
Agrotechnical measures after planting:
- Watering. It should be constant for young specimens, and mature ones should be watered as needed. It is better to use settled water for this. Water the plant either early in the morning or before sunset.
- Weeding. It should be done only at the first time, since later on, the dense, overgrown crown of the tree does not provide an opportunity for extraneous vegetation to grow in the near-trunk area.
- Mulching. To maintain looseness around the chestnut, it is necessary to mulch the soil with a 10 cm layer of peat or wood chips with the addition of compost.
- Top dressing. This is an indispensable ritual for good plant growth. After wintering, you can feed with manure and urea, ammonium nitrate and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. In autumn, chestnut can be fertilized with nitroammophos.
- Preparing for the winter period. It is needed only in the first years after planting. To do this, the tree trunk should be wrapped in several layers of burlap, and the trunk circle should be mulched.These measures help to prevent cracking of the bark in frost.
- Pruning. This is necessary for the formation of a lush beautiful crown. During spring pruning, overgrown shoots of young trees should be cut in half. Thin twigs should be harvested in summer to avoid overgrowth. In this case, it is imperative to leave about five strong side shoots intact. The cuts must be covered with garden pitch.
Chestnut leaf in folk medicine


Chestnut foliage has a number of beneficial properties. It relieves coughs and is an excellent diuretic. It is used for various types of inflammation, including for the purpose of wound healing. They help with many conditions:
- high blood pressure;
- infectious diseases accompanied by intense fever;
- swelling;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- lobe of the respiratory system;
- pathologies of the hematopoietic system.
The wide spectrum of action of chestnut leaves is due to the fact that it contains many vitamins and minerals.
Healthy tea for varicose veins


Chestnut leaf tea can help reduce the signs of varicose veins. Crushed raw materials are poured with boiling water in a ratio of 1:15. Tea is infused in a thermos for 4 to 5 hours. To achieve a therapeutic effect, drink 400 ml of tea 2-3 times a day.
With bleeding from the uterus
Dry chestnut foliage will help women with uterine bleeding. A handful of raw materials are stirred in a glass filled with hot water, then boiled in a saucepan for 10-15 minutes. The broth is cooled to room temperature, then filtered through a sieve. You need to drink a little: 10 ml of liquid from 5 to 6 times a day.
Infusion for lipoma ("wen")
It is necessary to prepare an infusion for taking a bath. You will need a large 10 liter bucket. Dry foliage is placed in it, poured with boiled water and insisted for a day. After insisting, the solution is filtered and poured into the bath. You need to take a bath for 15 minutes, with a repetition of the procedure after 2 days. The course of treatment is two weeks.
Cough remedy


To get rid of a cough, you need to take 10 g of dry chestnut leaves and crush them finely. The foliage is poured with a glass of hot water, brought to a boil and insisted for 60 minutes. After infusion, the liquid is filtered and drunk a little during the day. You can also take this infusion one tablespoon three times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days.
The fruits and foliage of the autumn chestnut have long been used in folk medicine and cooking. If you know the rules for using such raw materials, it will always bring health benefits.
People have known about the healing effect of chestnuts since ancient times. It is a small genus of spreading trees native to the southern regions. The fruits of the plant are endowed with a colossal list of useful compounds and elements that few people know about. People are used to eating them, making sweet desserts from nutritious nuts, without even knowing about the healing power. Scientists thoroughly know that all parts of an amazing tree are endowed with a huge bouquet of useful ingredients.
In alternative medicine, the fruits, flowers, seeds, bark and leaves of the edible chestnut are widely used. Official science has proven the therapeutic value of all ingredients. In this material, a place is reserved for green leaves bordering the crown of the tree. You will gain useful information for yourself about the properties, application, and also learn how to prepare healing decoctions.
Diseases and pests
The chestnut tree sometimes suffers from certain diseases (fungi), beetles and other pests. A damaged tree with rusty leaves must be urgently sprayed with Bordeaux liquid or Fundazol.
A tick is also dangerous for chestnut. To prevent its appearance 2 times a month you need to treat the tree with Fitoverm or Karbofos.The most effective folk remedies are broths of dissected hogweed and black henbane.
In recent years, previously unknown Balkan or chestnut moths have begun to attack chestnut trees. From them in the summer the leaves of the chestnut fall off after drying, and by autumn they bloom again. Further, late flowering occurs, and therefore the plant meets the winter unprepared. The latter leads to freezing and even death of the plant. It is difficult to deal with these pests. An effective measure is timely cleaning of damaged fallen leaves, among which numerous pupae of this moth winter.


What is rich in the autumn chestnut leaf


Chestnut leaves contain vitamins B and C, but these are far from all the substances that they contain. Scientists have identified several complex triterpene compounds that help improve metabolism. The tannins contained in the chestnut foliage have a tonic and antiseptic effect. Pectins remove toxins and other decay products from the body. Also, the autumn chestnut leaf contains flavonoids. Flavonoids are substances that stimulate the synthesis of natural enzymes. In addition, foliage contains glucose, lecithin, organic matter, trace elements and vitamins.
Other foliage varieties may not be suitable for medicinal use. Sowing chestnut is common in many regions of Russia. It is distinguished by the appearance of its foliage. It has an oblong shape and is slightly pointed at the ends. The foliage length of the sowing chestnut is about 25 cm.
The collection of chestnut leaves for medicinal use begins in August and ends at the end of September. The material must be evenly laid out on a cloth to dry. In the first days of drying, the leaves need to be turned over so that they dry out evenly. Dried foliage is placed in dry containers and used throughout the year.
Distribution and ecology [edit | edit code]
The horse chestnut grows in a small area in the mountains of the Balkans (in the north of Greece, Albania, the Republic of Macedonia, Serbia and Bulgaria) [7] in deciduous forests along with alder, ash, maple, hornbeam, linden, beech and other tree species, rising in the mountains up to an altitude of 1,000-1,200 m above sea level. Found in the mountainous regions of Iran and in the foothills of the Himalayas. It is widely cultivated in the temperate zone, widespread in plantings in many regions of the European part of Russia.
It is durable (under favorable conditions it reaches the age of 200-300 years). Almost not damaged by insects. It tolerates transplantation well in adulthood.
Shade-tolerant, grows well on deep loose soils - clay or sandy loam, sufficiently moist, but without excessive moisture. It tolerates rather dry chernozem soils in the steppe zone; it does not tolerate saline soils. Sensitive to dry winds, which is why the leaves often burn badly in summer and fall prematurely.
Winter-hardy in culture in the middle zone of the European part of Russia (up to Moscow). At the latitude of Moscow, it freezes under very severe winters; young trees also freeze in St. Petersburg, but in sheltered places they grow into large, abundantly flowering trees.
Diseases [edit | edit code]
Among horse chestnut diseases, fungal diseases are the most common.
Beneficial features
Chestnut-based medicines can cope with an increase in body temperature, inflammation, edema, and tumors. Horse chestnut is also an excellent pain reliever and bactericidal agent, heals abrasions and cuts. The substances in the composition have a beneficial effect on the walls of veins and blood vessels, have a venotonic, antithrombotic effect.
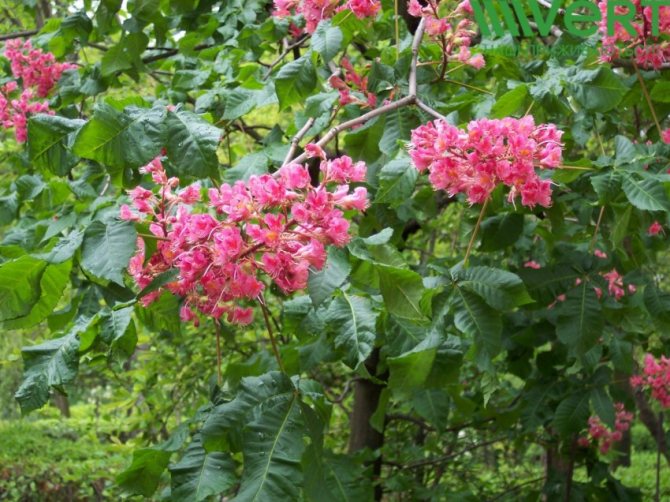


The medicinal properties of horse chestnut help slow down the aging process of the body and help prevent multiple sclerosis.


Chestnut medications can be used in the treatment of radiation sickness, vein thrombosis, exacerbation of hemorrhoids, rhinitis, throat diseases.


How to grow a peach from a stone - care, maintenance and technology for growing a peach at home (95 photos)

Why plum does not bear fruit - 10 main reasons and tips for choosing a method of treating plums and restoring crops


How to propagate a plum: the best DIY ways to grow, care and plant. Video instruction and 120 photos
Economic value and application [edit | edit code]
The common horse chestnut, which retains its decorative effect throughout the growing season, is a first-class tree for planting on streets, boulevards, alleys of gardens and parks. Its plantings create monumental groves in large parks and forest parks. It is notable for its beautiful shady crown and ornamental large leaves. It is especially beautiful during flowering, when its crown is decorated from top to bottom with large "candles" of erect inflorescences. It blooms profusely, however, only with a free, single planting on the lawn or forest edge. In Russia, it successfully bred in temperate climates with not too hot summers: at the latitude of St. Petersburg [11] and Moscow (in sheltered places), in the Caucasus and the Far East. Abroad, Russia is cultivated in many countries, including even the north of Canada (Alberta [12], Ontario), the Faroe Islands [13] and Norway. In more southern regions it grows best in areas with cool mountain climates.
The fruits are used for the production of women's jewelry (beads) [ source not specified 83 days
] .
Chestnut seed (lat. Semen Hippocastani) is used as a medicinal raw material. The main active ingredients are triterpene saponins of the p-amyrin group, of which the main one is escin, a derivative of escigenin; coumarins of the group of oxy- and methoxycoumarins (esculin [14], fracsin); flavonoids, derivatives of quercetin and kaempferol. The preparations "Eskuzan" (aqueous-alcoholic extract of seeds) and "Esflazid", containing escin and the sum of flavonoids from the leaves, are used as venotonic and antithrombotic agents for venous congestion and varicose veins of the lower extremities [15]. Esculin can be used in the treatment of diseases such as edema, distortion, and in nutritional supplements (the same applies to esculin) [16].
Fruits, which are bitter in taste, especially when unripe, are slightly poisonous. Poisoning is possible when eaten. Some mammals, in particular deer, are able to eat them safely. Sometimes the fruits are used for livestock feed.
In the past, horse chestnut seeds, containing a soapy liquid (due to the presence of saponins), were used in France and Switzerland to bleach hemp, flax, silk and wool. Flax, washed in this liquid, and then washed in running water, acquired a sky-blue color.
Horse chestnut wood has no commercial value, although it has a sufficiently high strength, it dries easily, with minimal loss of quality. Suitable for making small household items and crafts, box containers [17].
The bark contains tannins, and the leaves contain vitamin C (about 56 mg%) [19].
It gives honey bees a lot of nectar (with sugar content from 65 to 75%) and pollen, and in the spring - glue (propolis). The honey collected from the horse chestnut quickly crystallizes in the combs, so it cannot be used for winter feeding of bees [20].
During the last two world wars, the horse chestnut fruit was used as a source of starch, which, in turn, can be used to produce acetone using the method developed by Chaim Weizmann, through fermentation with Clostridium acetobutylicum. Acetone, as a solvent, facilitated the extrusion process of ballistite to cordite in ammunition production.
Horse chestnut in heraldry [edit | edit code]
Horse chestnut inflorescence is a natural symbol of Kiev, the capital of Ukraine [21].
Botanical name: Horse chestnut (Aesculus), also called aesculus or acorn, is a genus of trees or shrubs from the Sapindaceae family, many of which are widely used in culture for landscaping cities and parks.
- Homeland of the horse chestnut: Europe, Asia, North America.
- Lighting: relatively shade-tolerant.
- The soil: loose, sandy loam or loamy.
- Watering: the plant is moisture-loving.
- Maximum tree height: up to 30 m.
- Average tree lifespan: 200-300 years old.
- Landing: propagates by root shoots, seeds, less often by cuttings or layering.
Contraindications and precautions
Forms of medication for oral administration are contraindicated:
- hypotensive: the medicine will further lower the pressure, and this can provoke fainting and a deterioration in well-being.
- with hemophilia.
- with gastritis with low acidity: chestnut has the ability to lower the acidity of the stomach, so the remedy will not work.
- girls and women whose menstrual cycle is characterized by deviations from the norm - a change in the volume of blood loss, delay or absence of menstruation.
- children under 14 years old.


It is not used during pregnancy and while breastfeeding.


Before starting treatment, you should discuss the dosage regimen with your doctor.


Side effects include heartburn and nausea. Allergies are possible, so horse chestnut flowers are contraindicated in hay fever.
In case of overdose, finger cramps occur.


At what distance to plant grapes from each other: tips and advice from professionals for planting grapes in a personal plot (125 photos and videos)

Gooseberry health benefits and harm: beneficial properties for the body and a description of the contents of the berry (115 photos + video)


Red currant care and cultivation: varieties, pruning, planting and breeding rules at home (115 photos)


Application in cosmetology
Due to its anti-inflammatory and restorative effect, flowers can be used in cosmetology. The prepared floral ointment takes care of the face and décolleté area. Also, the ointment is able to whiten the skin.


It is prepared like this: 2.5 tbsp. l. mix dried chestnut flowers with 100 ml. vegetable oil and boil for half an hour in a water bath. After straining, the ointment can be used.
Collection recommendations
In order for the horse chestnut to retain all its useful properties, you need to properly collect and prepare it. Different parts have their own harvesting rules, but it is important to remember that only trees with white flowers are suitable for this purpose.


The bark becomes suitable for harvesting in early spring. Young bark is suitable for collection, it is best to cut it from the branches. Pieces of bark are cut into small pieces and sent to dry in a dark, ventilated place.
The bark retains its medicinal properties for two years when stored in bags made of natural fabric or in rolls of thick paper.


The beginning of flowering is the time to collect flowers. It is not necessary to pluck the entire inflorescence from the branch: it is enough to cut off individual flowers. They are laid out one at a time and then placed in a place with constant air humidity to prevent decay. The beneficial properties of chestnut flowers last up to two years.
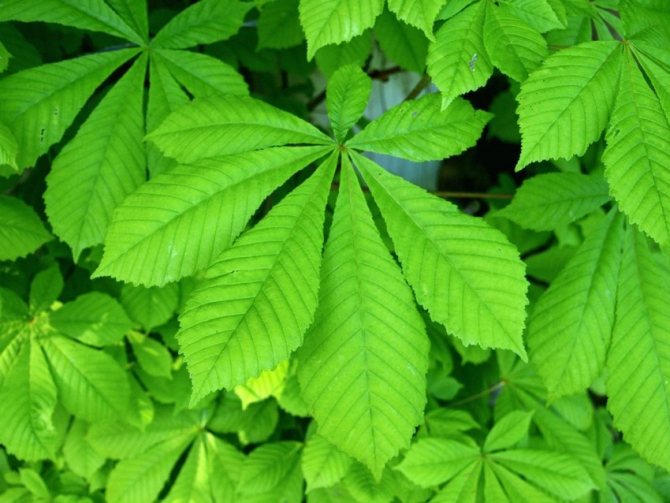


Leaves are harvested in May, while only individual leaves need to be plucked, petioles are not needed. For drying, chestnut leaves are carefully laid out in a ventilated dark place, and after drying, they are stored in tightly closed glass containers.


Black elderberry: planting, watering, pruning and reproduction. Contraindications, medicinal properties and recipes for feeding elderberry (110 photos)

Blackberry-like berry: an overview of black berries growing on bushes and trees. 95 photos and videos of fruit and ornamental plants


Gooseberry care - instructions for beginners, useful tips for care and tips for planting (120 photos and videos)
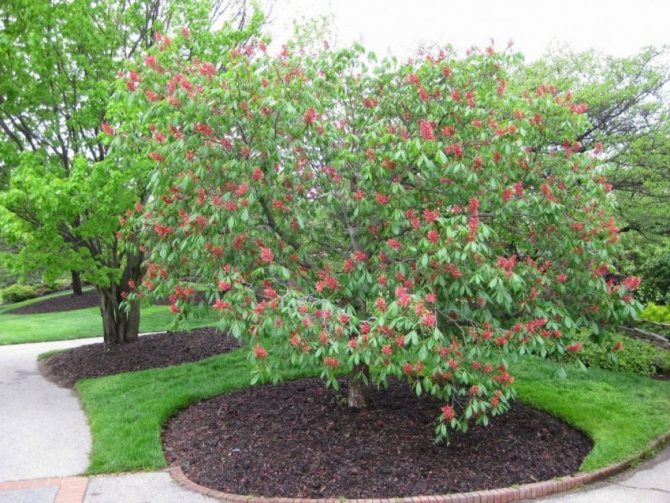


The fruits are harvested in early autumn when they are fully ripe. Already fallen seeds with an opened and darkened capsule are of great value. They are dried and stored in a closed container.