Gardening »Pear
0
989
Article rating
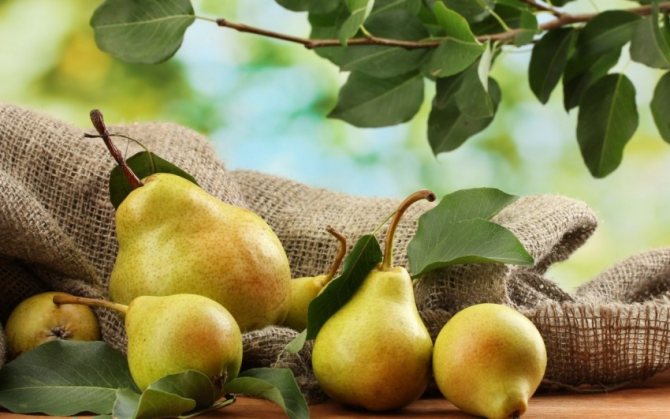
Pear is a fruit tree from the rose family. In the wild, it does not grow in Europe and Asia. For several millennia, it has been grown in gardens. The fruits of this tree are tasty and healthy, easy care for them. Hundreds of varieties have been developed that can be grown in a wide variety of latitudes. Breeding work is still in progress.
Full pear characteristic
Distribution and ecology
In the wild in Europe, the pear is widespread up to about 60 ° C. sh. On the northern border of the range, it is rare.
By 2006, as a result of successful selection of frost-resistant varieties, pears are effectively grown in garden plots located in the Urals and Western Siberia up to 55 ° N. sh.
It is believed that the origin of cultivated pear varieties is associated with the hybridization of a number of species, in particular, Pyrus achras Gärtn., Pyrus persica Pers., Pyrus cordata Desv., Pyrus elaeagnifolia Pall .. Pears were cultivated in ancient Persia, Greece and the Roman Empire.
Currently, there are thousands of varieties of pears.
Further care
They take care of the standard way: pruning, watering, feeding, loosening.
Ornamental pears are very fond of sprinkling, especially the willow pear. Fertilizer is applied every 3 years, but if the soil is too poor, then feeding is done annually.
The formation of the crown in trees is natural, but if desired, you can give the shape corresponding to the design. Sanitary pruning is done at the beginning and end of the season.
Pests and diseases
Ornamental pear is almost a wild plant, therefore it has good immunity to diseases. However, systematic chemical treatment is still needed. Of all the diseases, the tree can sometimes be threatened by black spot, leaf curl and fire blight.
Bacterial burn
Because of this disease, the beautiful leaves of an ornamental pear look like after a fire. The disease is caused by microorganisms of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
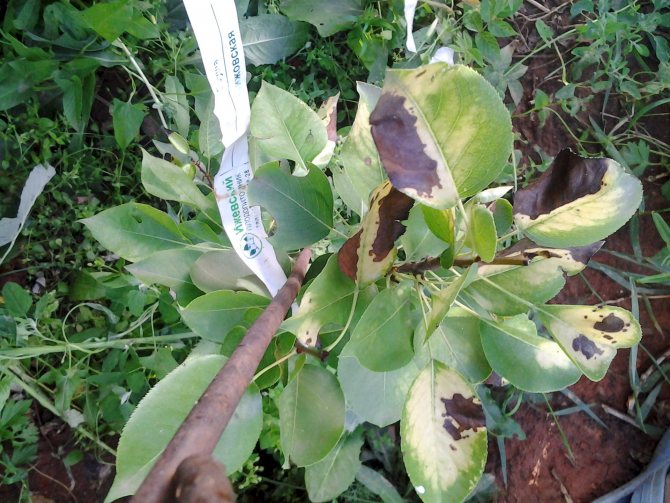

Bacterial burn
Bacterial burns are treated with copper-containing preparations; removal of all affected parts of the tree is also required.
Brown spot
The Entomosporium fungus is active in spring and autumn. The first sign of its presence on the plant is the presence of red spots on young leaves. Over time, they turn gray, then blacken and spread throughout the green mass.
Get rid of the fungus with topaz, phytosporin-M.
Curly leaves
Such a disease is extremely rare, but the harm it causes is enormous. The tree can lose all its green mass.
The leaves begin to thicken, acquire curliness, turn red-yellow. To protect the ornamental pear, immediate pruning of diseased areas is required, followed by burning.
To prevent disease, before bud break, plants are treated with copper sulfate.
If you take into account all the nuances of growing a crop, and also choose a suitable variety, as a result, an unusual plant will grow to the envy of all neighbors in the area!
Botanical description
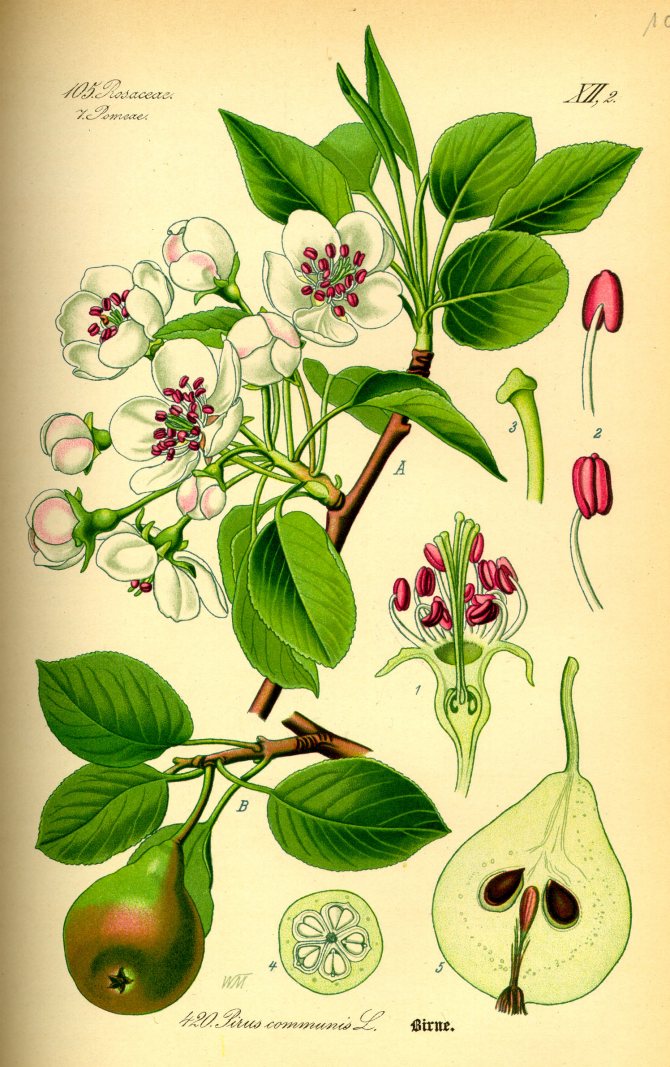

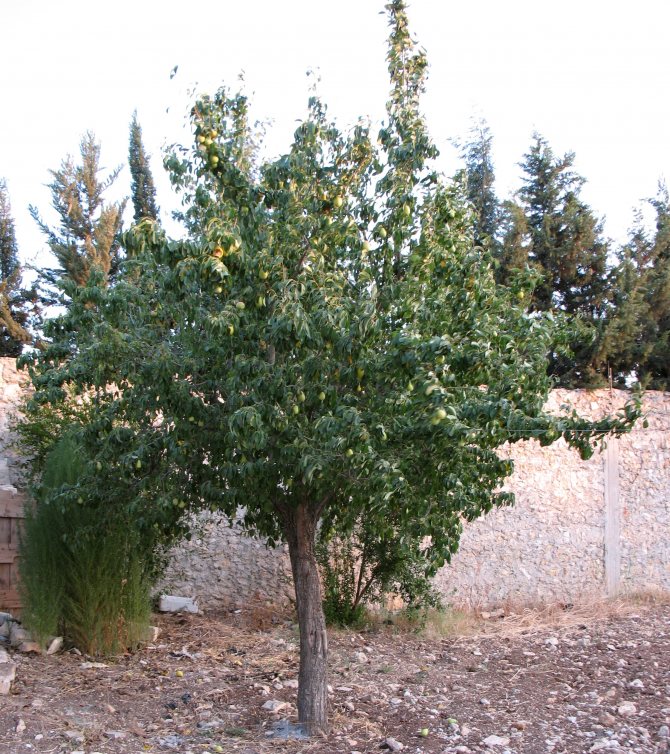
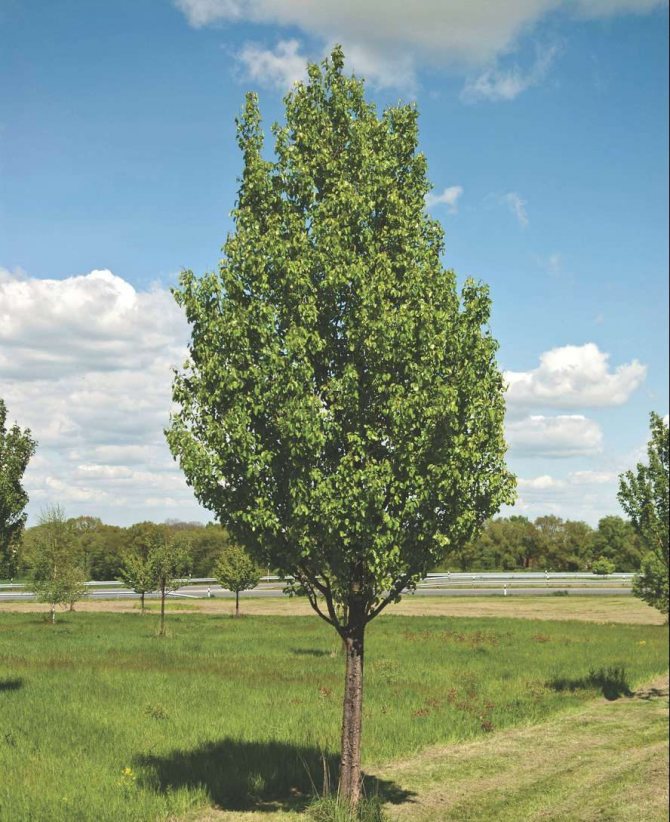
The shape of the crown of a freely growing tree is pyramidal or round, prone to thickening. The annual growth is 30-40 cm. Under favorable conditions, the pear reaches large sizes - up to 5-25 meters in height and 5 meters in diameter of the crown.
Leaves are usually falling off. The leaf arrangement is spiral in 5 rows.The leaf is broadly ovate, 2.5-10 cm long, short-pointed; color - dark green, shiny, the underside of the leaf is bluish green, golden orange in autumn.
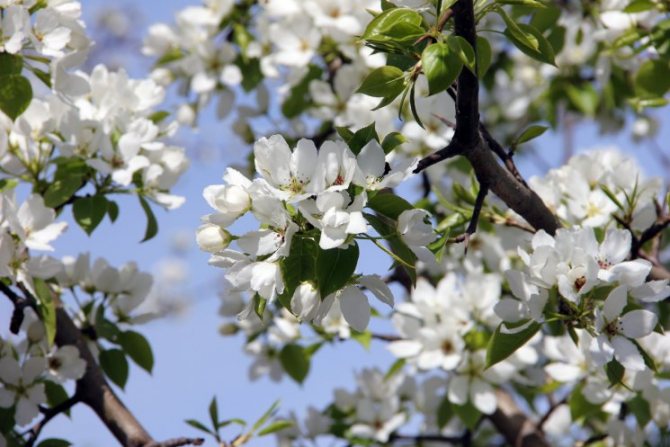
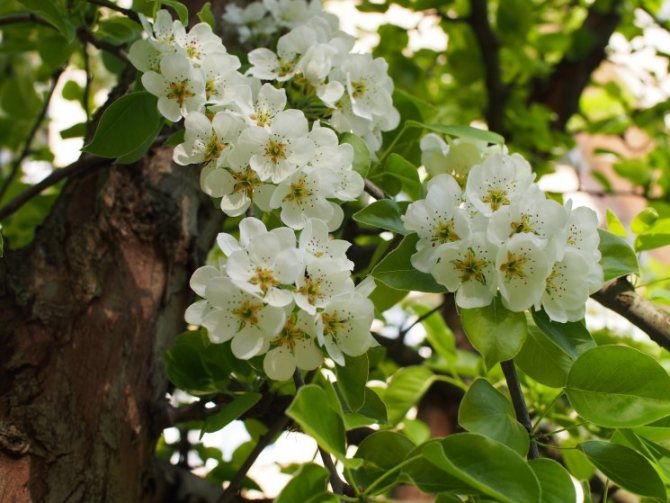
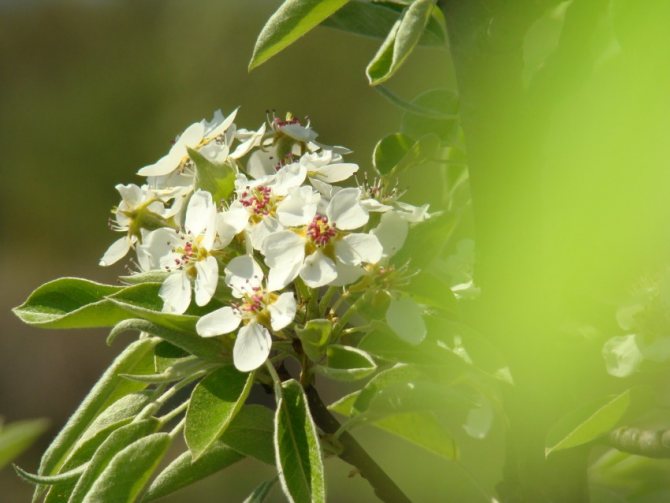
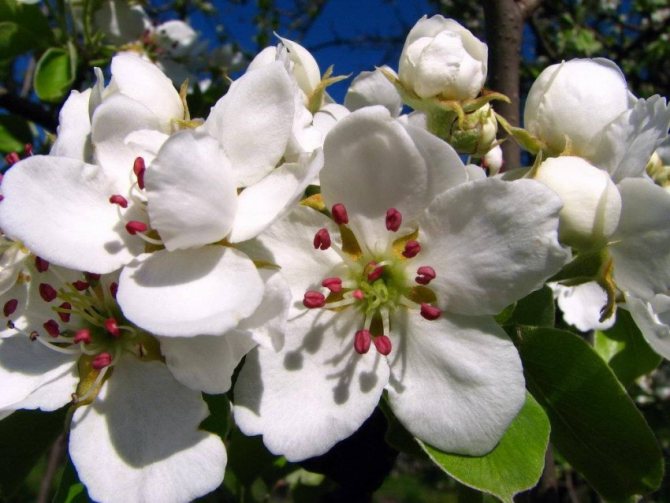
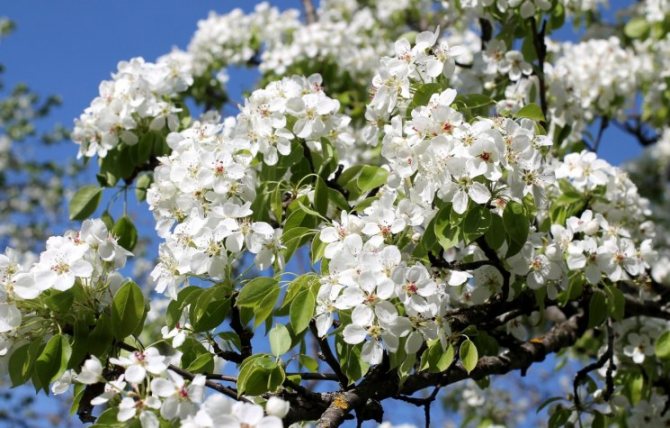
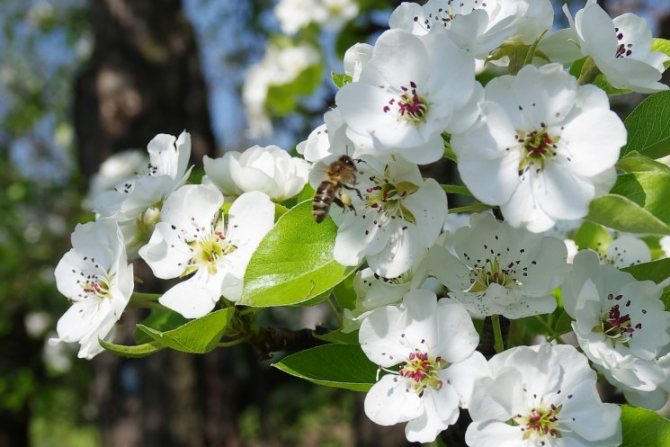
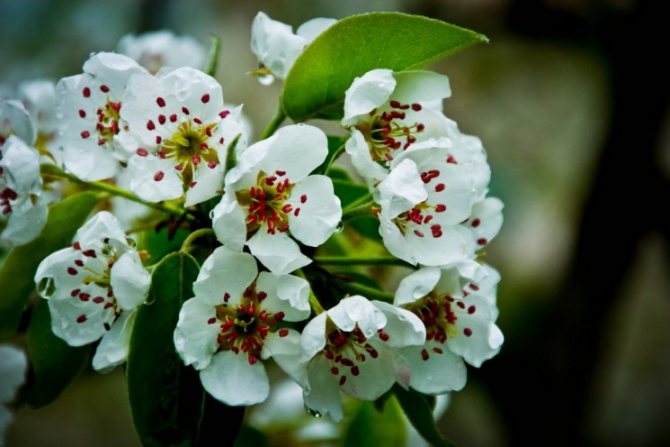
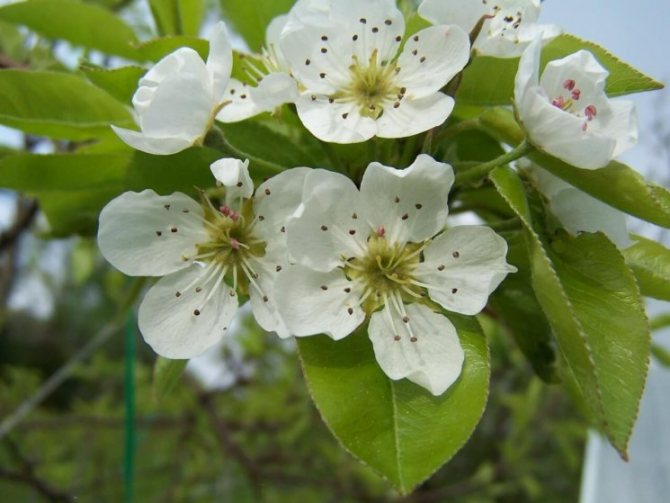
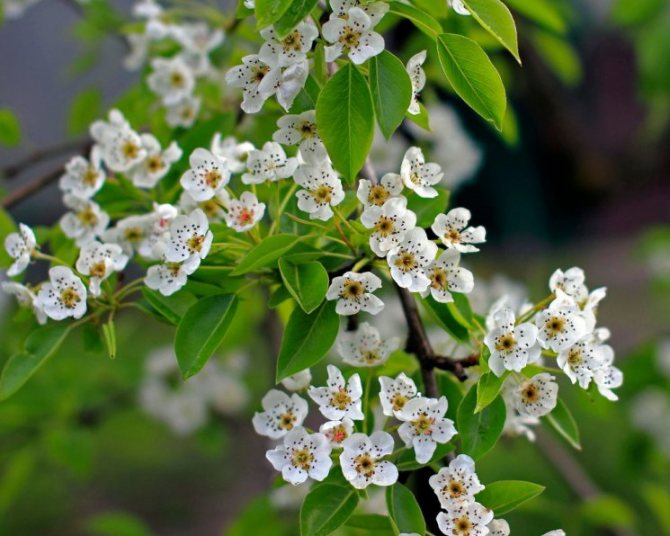
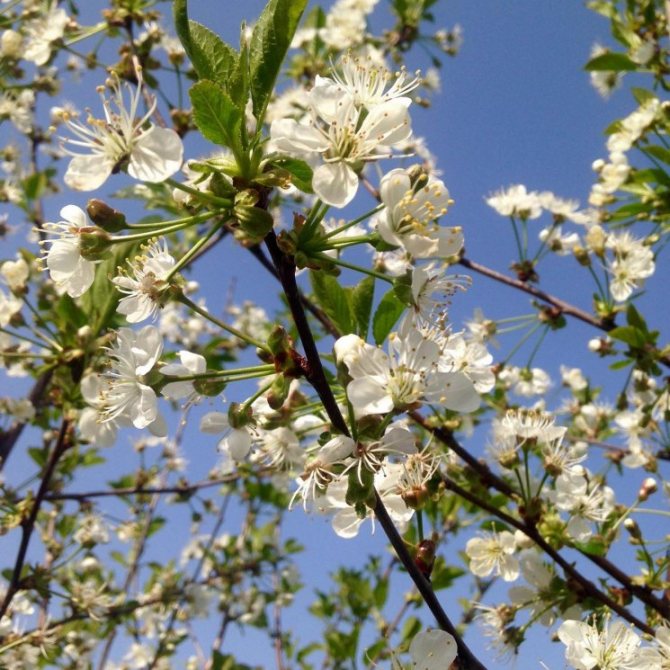
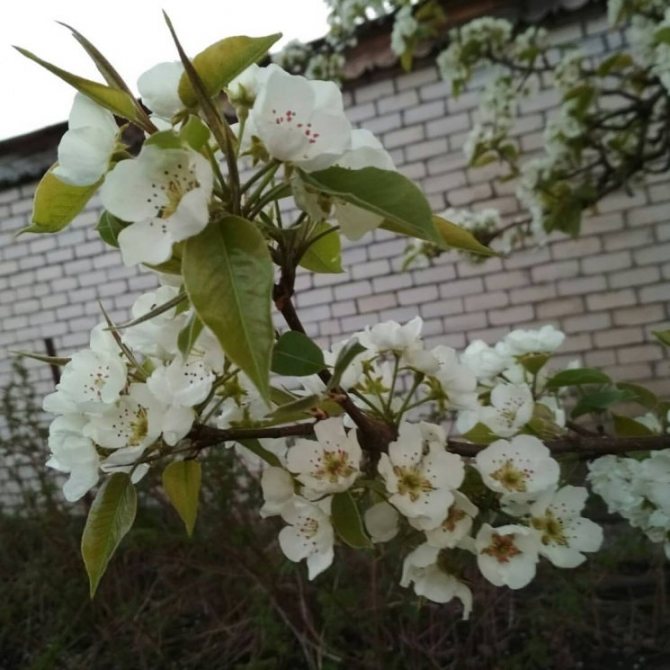
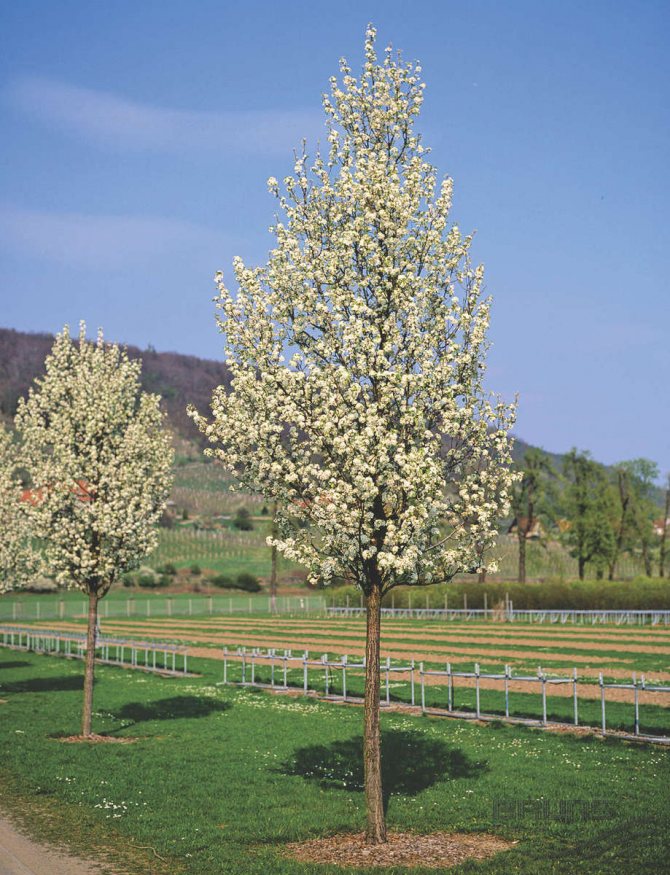
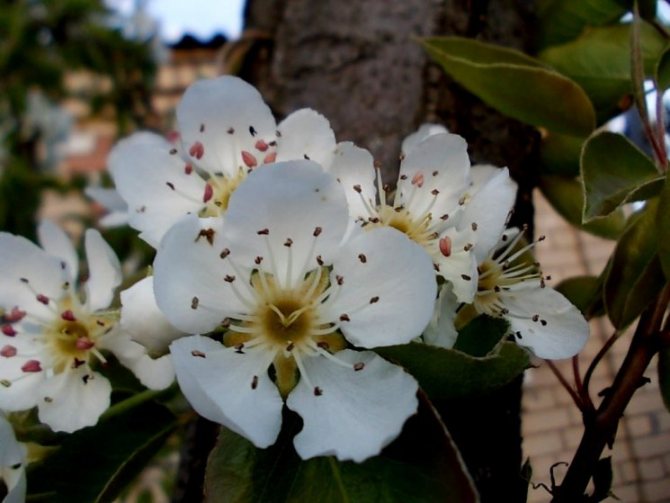
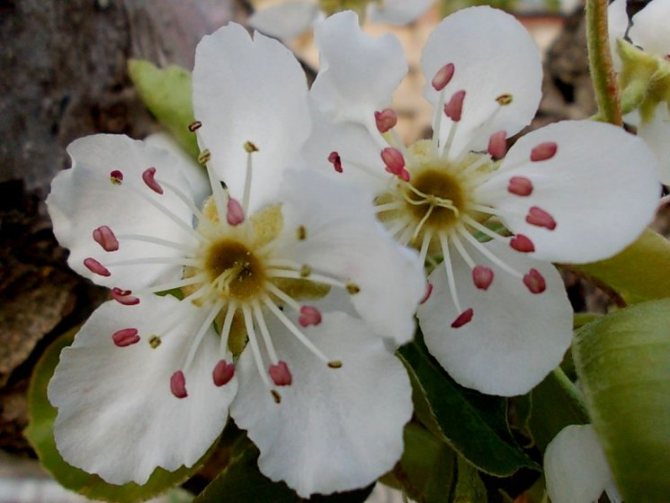
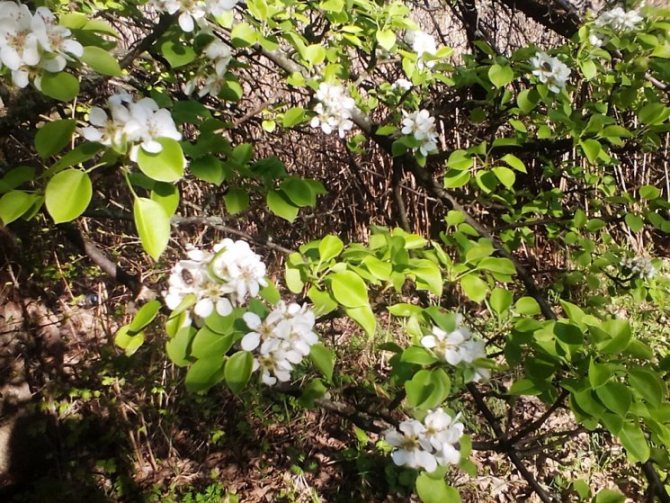
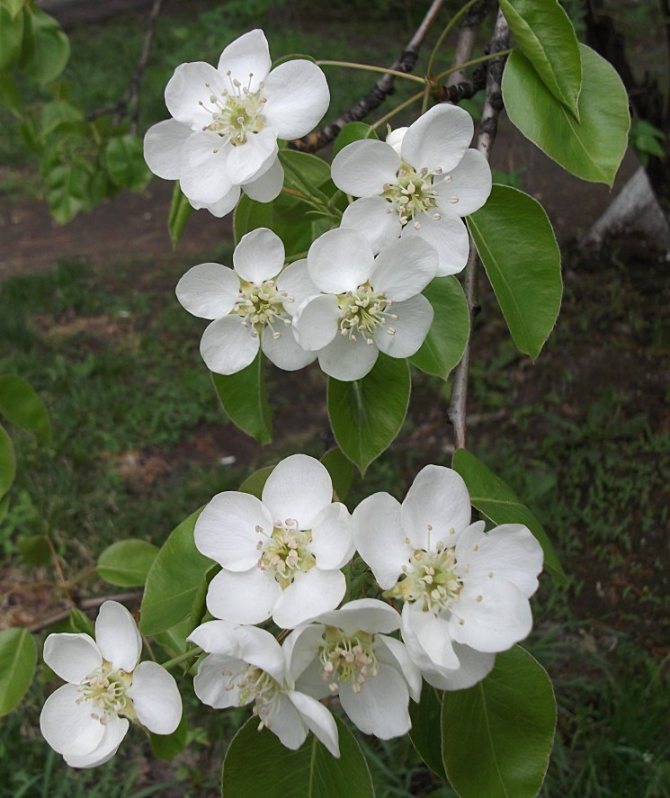
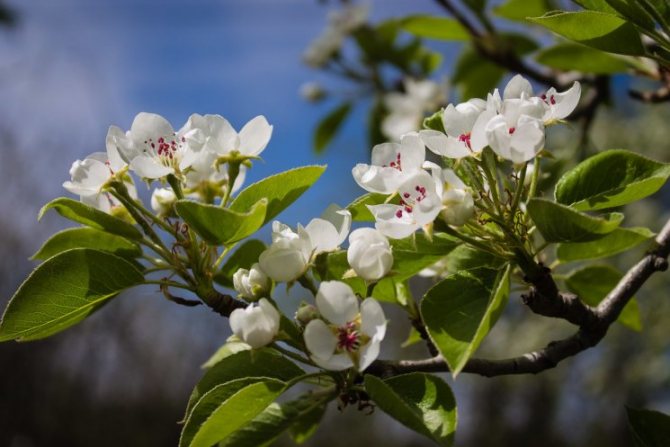
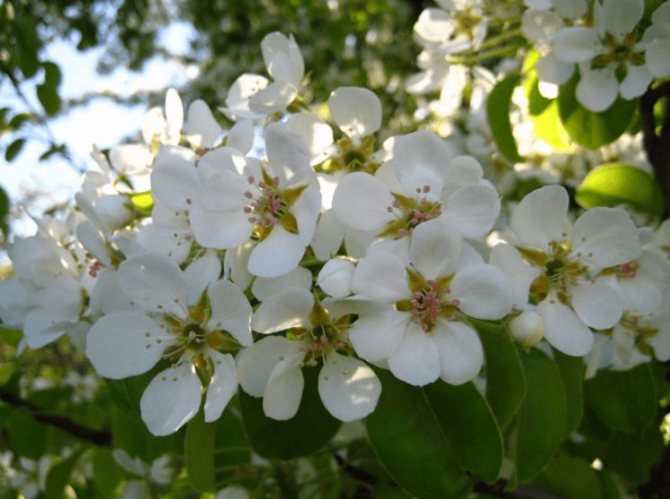
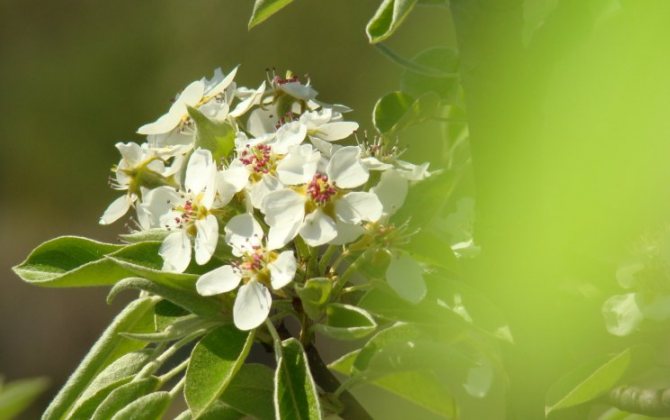
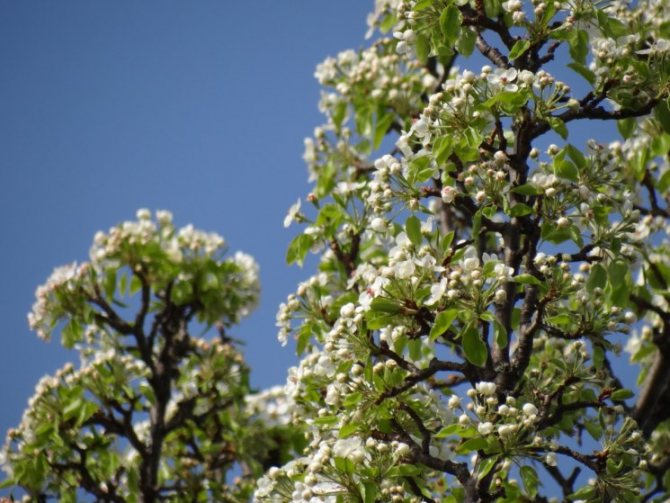
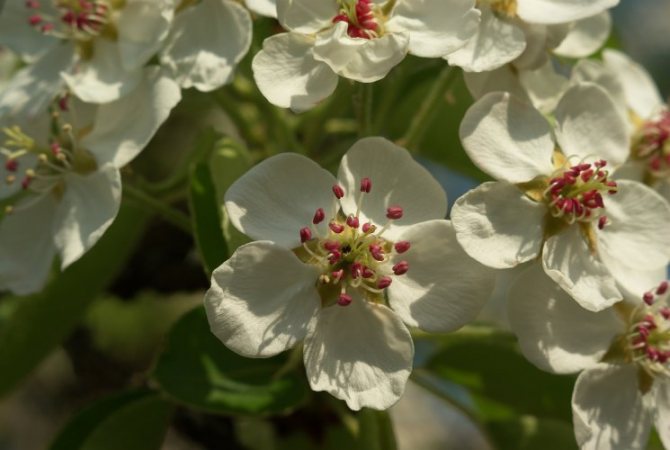
Time and form of flowering: April-May, white flowers, 3 cm in diameter, 5-petal, 3-9 in umbellate racemes. Pistils in gynoecium are from 2 to 5. Their ovaries grow together with each other and with a flower bed, which takes the form of a circle; the petals in the bud are tiled.
The nests of the fruit are lined with a dense shell (nutcarp).
The buds of a pear, like other trees in the family, are of two types: vegetative and generative. Vegetative buds are smaller and sharper, generative ones are larger and dumber. External differences between the two types of buds increase from the time of formation of these buds to the exit of shoots from them.
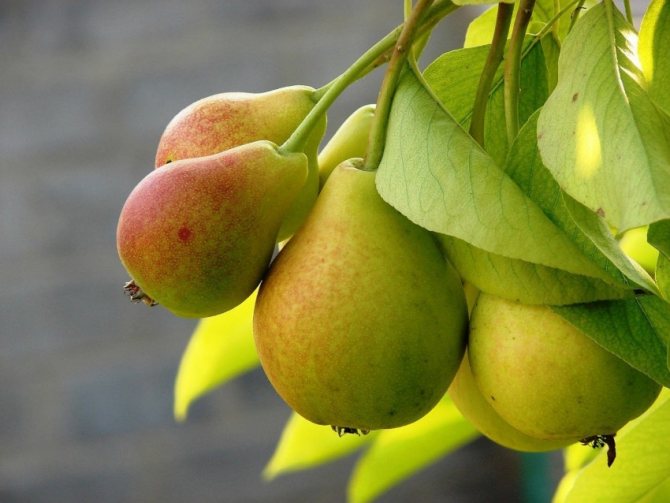
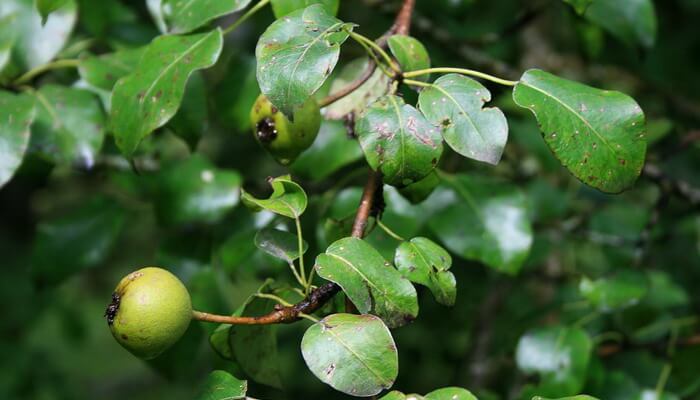
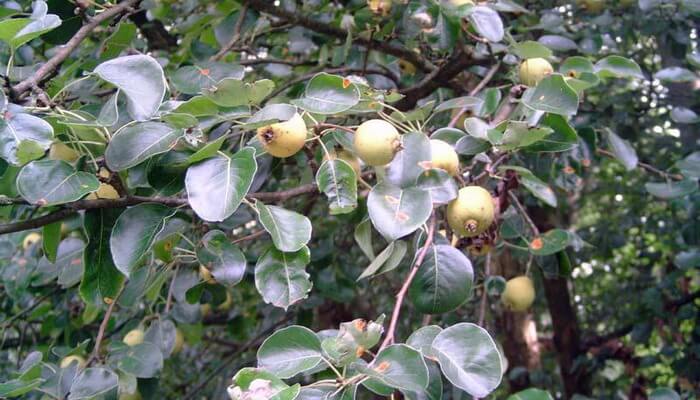
The fruit, as a rule, is of an elongated shape with an expansion in the lower part, there are varieties with spherical fruits.
Basic information
The homeland of the pear with such an intriguing name is China. However, in the vastness of Russia, the decorative pear did not particularly take root due to the peculiarities of its care.
Important! A medium-sized tree with a conical crown changes its beautiful green foliage to bright red in autumn.
The decorative curly pear is very fond of sunny areas. It is not winter-hardy, so it cannot be grown in regions with a harsh climate. The culture is represented by perennials, but there are also annual varieties.
Decorative Chinese pears have many varieties that differ in the color of the green mass, the size of the fruit, and appearance. The most famous varieties are Ivolistnaya, Beach Hill, Bradford.


Decorative pear
Wood


Hard, heavy and resilient pear wood is widely used for small crafts. Due to its low resistance to decay, it is only used for indoor products. The specific gravity of this wood is approximately 740 /. Like any other heavy and dense wood, when dried, a pear is prone to cracking and warps strongly, as well as beech wood with the same density. When dried, this wood is very dimensional stability. This resistance is associated with the presence of the so-called "stone cells" that distinguish the pear as a fruit and as a wood. These cells are woven into the structure of the wood. The specific heat of combustion of pear wood is slightly lower than that of beech wood, although these species are very similar in density. The pear wood texture is very fine, uniform, with barely discernible growth rings. Around the damage of a living tree, wood can change color, taking on colors from purple-brown to black-brown. Hot steam treatment, for example in veneer making, changes its color to reddish and darker. With aging, this wood acquires a very beautiful dark brown amber color, which is its hallmark. The pores are visible to the naked eye only in the cross section.
Despite its hardness, the pear is suitable for cutting, thanks to the "stone cages" it can be cut without splitting in different directions. In Germany, this wood has long been used in the manufacture of various printing boards for molding special types of cookies, called "springerle" (German. Springerle
).
In Russia, for a long time, carved boards have been made from pear wood, which are used in the production of printed gingerbread as a relief base K: Wikipedia: Articles without sources (type: not specified) [source not specified 1208 days
].
After being treated with black stain, this wood is also used as a substitute for the very expensive ebony.
The benefits and uses of pears
The pear contains many useful substances, therefore it is very useful. Especially high content of potassium in fruits (mainly in the skin). They are recommended for people with high blood pressure, obesity, bowel disease. It is not advised to use this fruit for patients with ulcers, gastritis, pancreatitis, because it takes a long time to digest.
The pear contains a lot of iron, therefore it is advised for anemia. Juice mixed with rosehip decoction and honey treat colds and bronchitis. Fruits have a diuretic and antiseptic effect, therefore they are recommended for inflammatory diseases of the urinary system. To refresh the skin, use a pear cosmetic mask, which is easy to make at home.
The fruits of varietal pears are widely used in the food industry. They are dried, used for the production of juices, jams, preserves, marshmallows, jam, compotes. Manufacturers often combine different fruits. Very tasty and original juice brand "Ya" pear with banana and vanilla. You can also see juices in combination with apple, plum, grapes.
In the Caucasus, dried fruits are ground and added to flour, then flat cakes are baked from it. Certain types of seeds are roasted and made into coffee substitutes. An important area of application of fruit trees is the production of honey. From 1-1.5 hectares of plantations, up to 20-25 kg of this tasty product are obtained. The wood itself has a good value. It is used for the production and decoration of furniture, artistic carvings, floor coverings.
Classification
The genus includes 69 species [7], which are distributed in two sections Pashia
and
Pyrus
[8].


| sect. Pashia | sect. Pyrus |
|
|
Hybrids
- Pyrus × bretschneideri Rehder - Central Asian pear
- Pyrus × canescens Spach [= Pyrus × nivalis × Pyrus salicifolia]
- Pyrus × complexa Rubtzov
- Pyrus × lecontei Rehder [= Pyrus communis × Pyrus pyrifolia]
- Pyrus × michauxii Bosc ex Poir. [= Pyrus amygdaliformis × Pyrus × nivalis]
- Pyrus × nivalis Jacq. [= Pyrus communis × Pyrus elaeagrifolia]
- Pyrus × phaeocarpa Rehder
- Pyrus × serrulata Rehder
- Pyrus × sinkiangensis T.T.Yu
- Pyrus × uyematsuana Makino [= Pyrus dimorphophylla × Pyrus hondoensis]
Hybrid childbirth with the participation of representatives of the genus Pear
- × Sorbopyrus
- Sorbopirus (=
Sorbus
×
Pyrus
)
Japanese pears, or Neshi (Pyrus serotina, Rosaceae family)
Synonyms: ours, Japanese, Asian or sand pears, Japanese ours of the 20th century The homeland of Japanese pears, more often called neshi in Russia, is the territory of northern China, Korea and Japan. Representatives of this species are also found in New Zealand. Works on the selection of Pyrus serotina began only in the 20th century (hence one of the names of the fruits).
The most successful results were obtained in Japan, where most of the best Neshi varieties were bred. They are currently cultivated in Japan, Korea, Taiwan, China, New Zealand, Australia, Spain, France, Italy, USA and Chile. Japan is one of the largest fruit producers (200 000 tons per year). Their main cultivation region is Tottori Prefecture.
In Japan, neshi are very popular, despite the high cost due to a complex agronomic process, including artificial pollination and wrapping ripening fruits in paper. To ensure uniform fruiting and fruit growth, all flowers are manually pollinated with a brush.
Wrapping each fruit in waxed paper protects the fruit from damage by insects and birds, as well as from the appearance of undesirable yellowish-gray or yellow-red color, or blush on the fruit, and thereby increases the yield of marketable products. The main varieties of Japan are 20th Century, or Japanese Golden Neshi, Nijseiki, Shinsui, and Hosui. The main period of fruit supply on the domestic market falls on September-January.
The first supplies of Neshi from Japan to the European market (to Germany) were made in 1964. In New Zealand, the first industrial plantations of Neshi were established only in 1984. However, in a short time, it managed to become one of the largest producers and exporters of fruits in the world.
The main varieties cultivated in the country are Hosui, 20th Century, Nijseiki, Kosui and Shinsui. Fruit collection is carried out from January to March. The largest Nash cultivation areas in Australia are in Central Victoria (Goulboum Valley, 200 ha) and New South Wales (150 ha). Harvesting takes place at approximately the same time as in New Zealand. In the USA, nash is produced mainly in the states of California and Washington. One of the most important varieties is Kikusui.
The harvest period lasts from late July to early September, the offer of fruits to the world market is from August to October.In recent years, due to the growing popularity of Neshi pears in Europe, Spain, France and Italy began to allocate more and more areas for this culture.
Currently, four varieties are cultivated: Shinseiki, Nijseiki, Hosui, Kosui. Fruit picking in Italy begins with the Shinseiki variety (early August), and then continues with the Kosui varieties (from mid-August) and Hosui, Nijseiki (from the beginning of September. Fruits enter the European market from Italy and Spain - from August to December, from France - from October to February Nash is supplied to the Russian market from New Zealand (February-August), Chyush (January-April) and Korea (October-April).
Fruits of Japanese origin (October-March) are extremely expensive on the world market and therefore, despite their excellent taste, they practically do not come to the Russian Federation.
A small demand for fruits, due to both the fact that Nash is unknown to a wide range of consumers, and their high price 2-3 times higher than the price of pears), is satisfied by re-export from Holland. General information. Neshi pears are the closest relatives of common and Chinese pears. Nashi is a relatively new fruit, since in its modern form they were bred only in the 20th century. The shape of the fruit is the same as that of apples, but the rind is denser and tough.
The average weight of the fruits is 250 g. To obtain larger neshes, flowers or set fruits are thinned out. Skin color varies from greenish yellow to yellow or brownish. The flesh of the fruit is white, firm and crunchy, but juicy, and may contain a large number of stony cells. It is no coincidence that in a number of countries Neshi call the apple-pear: the taste of the fruit is soft, from moderately sweet to sweet, and resembles, depending on the variety, a pear or an apple.
Their refreshing taste is especially pleasant in hot weather. To-eat is mainly used fresh, and takaw is used to make marmalades and confiture. The best varieties are "XX century" (20 Century), Hosui, Kosui, Nijisseiki, Shinseiki ("New century"), Shinsui, as well as Ichiban Nashi and YoinnskL The name of the varieties already speaks about the appearance of the fruit.
The varieties ending in "seiki" have a smooth skin, and those ending in "sui" are rough. These varieties synthesize ethylene in medium quantities (at 0 ° C - 1-3 μl / kg per hour). Fruits of the climacteric type, when ripe, are sensitive to even extremely low concentrations of ethylene in the atmosphere of storage (1 ppm), in the presence of which the destruction of chlorophyll is accelerated and the density of the pulp slightly decreases. Japanese pears have a low respiration rate during storage.
At 0 ° C, it is 1-4 ml CO2 / kg per hour, but it increases markedly when the fruits are warmed, reaching 10-15 ml CO2 / kg per hour at 20 ° C. Unlike European pears, Japanese pears are sensitive to high concentrations of carbon dioxide. Storage in an atmosphere with a carbon dioxide content of 2% for a number of varieties is possible no more than one month, since longer storage leads to physiological damage to the fruit. Japanese pears (especially varieties "XX century") are extremely sensitive to static mechanical stress and shock, therefore, when working with them, a more careful attitude is required than for traditional pears. Quality requirements. Despite the absence of an international standard for neshes and, accordingly, their division into commercial varieties, almost all fruits supplied by producers to the international market can be attributed to the first or extra grade.
This is due to the fact that the national standards of the exporting countries and the internal standards of producers and exporters impose extremely stringent requirements on the quality of fruits: integrity, unconditional freshness and purity, pulp density, absence of mechanical damage, damage by agricultural pests, as well as physiological and microbiological diseases, absence of defects shape and skin, affecting the quality of the fruit, their appearance and presentability of the whole package. Packaging and labeling. Naches are extremely sensitive to pressure and pressure, so each fruit is placed in a styrofoam net, wrapped in waxed paper or packed in special row packages - trays with an individual place for each fruit, usually in no more than two rows.
For packaging, corrugated cardboard boxes are used, designed for 4 kg of fruit (New Zealand, Australia, South Korea and Chile), as well as for 8 (Australia), 10 (France, Spain, USA, North Korea) and 15 kg (Japan, North Korea, Taiwan and others). The label contains the name of the product, the pomological variety, the country of origin, the address of the packer or importer, and the size or number of fruits in the box. A four-kilogram package can contain 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 23 or 25 fruits. Storage and transportation carried out at 0 ° C.
Some varieties of pears
The cultivated varieties of pears mostly belong to the species Pyrus communis [syn. Pyrus domestica].
- 'Bergamot'
- ‘Bessemyanka’
- ‘Williams’ - Pyrus communis ‘Williams’ Bon Chrétien ’
- ‘Duchess’
- ‘Svetlyanka’
- 'Siberian'
- ‘Skorospelka from Michurinsk’
- 'Subject'
- ‘The same age’
- 'Rogneda'
- ‘Memory of Zhegalov’
- ‘In memory of Yakovlev’
- ‘Petrovskaya’
- ‘Chizhovskaya’
- ‘Yuryevskaya’


Pear pruning rules for each season
Each period has its own climatic characteristics, and the development of the plant in spring, summer and autumn is very different. Therefore, when pruning in each of the seasons, you must strictly follow the rules.
Note! In winter, pruning is strongly discouraged. The cuts will not have time to heal, there is a high probability of death of the branches from frost, which will affect the health of the entire tree.
Spring pruning
After the end of severe frosts and before the beginning of the growing season (before the buds swell), spring pruning should be carried out. Work should be started when the temperature reaches 5 ° C.
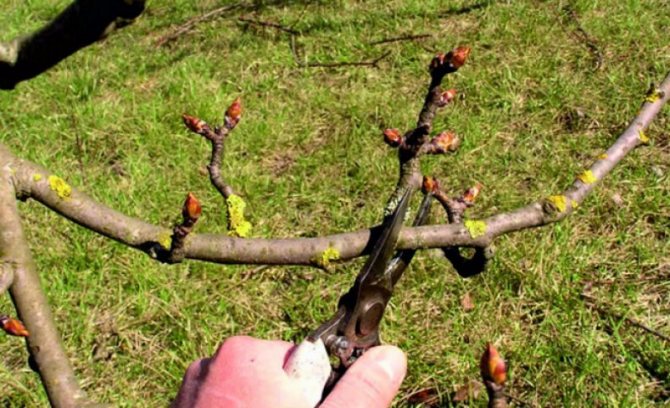


Spring pruning should be done before buds begin to bloom.
Before starting work, remember the basic rules that must be adhered to so as not to harm the tree and get the most positive result from it.
- Use a pruner to work, making sure that its blades are very sharp. It is better to cut large branches with a hacksaw. Be sure to disinfect the tools with alcohol-based products before and after trimming.
- First of all, the crown is thinned out. This will provide sufficient light and air for the tree.
- The next is the shortening of the central trunk. It is recommended to cut it by about ¼ part. Thanks to this, the tree will not grow and a bowl-shaped crown will form.
- All the places where the cuts were made should be lubricated with a protective substance as soon as possible. It can be Rannet, oil paint, garden varnish or drying oil. It is also recommended to soak any damage on the surface of the tree with a runnet.
- Traditionally, pruning methods such as cutting into a ring and pruning are used. In the first case, the cut is made in the area where the branch grows from the trunk, at the very base, “under the ring”. To prevent scuffing up of the bark, first make an incision at the bottom, and then cut off the branch from the top side. The second method accelerates the growth of lateral shoots and the awakening of the buds, which are located under the slices.
- Pear branches can grow both horizontally and vertically. It is recommended to remove vertical shoots and provide horizontal support with a support if necessary. In addition, it is imperative to cut branches growing in the downward direction: their productivity is too low.
- When pruning in the spring season, it is not necessary to feed the pear with nitrogen fertilizers: now it receives enough nutrition from the soil.
If the spring pruning is done correctly, by the next season all the cuts will heal, the tree will be healthy and ready to harvest.
Video: rules for pruning pear trees in spring
Summer pruning
In the summer, pruning for pear trees consists of pinching, or pinching. This is the name of the removal of shoots extending from the top of the plant. You can easily pinch it with your nails, and if you need to remove most of the young branch, use a pruner.
We spend much more time for pinching than for pruning. But this procedure, as experience has shown, really has a very good effect on the plant: as a result, nutrients coming from the soil are used sparingly and evenly. I think this is because, thanks to the pinching, the growth of the shoot is stopped, and its optimal length is achieved. At the same time, in the spring of next year, we shorten the one-year shoot, removing its significant part, for the growth of which useful substances were consumed.
Pinching can be done at different times during the summer, and depending on the time, the plant can react differently.


Pruning pears in the summer season can be done if young shoots have thickened the crown too much.
A pinch carried out in June during an active growing season will retard the growth of the shoots. Thanks to this, premature, summer, shoots are formed faster from the axillary buds, and the weakened branches located nearby will get stronger and strengthen growth. The leaf buds will turn into fruit buds. But remember that pinching during this period can have a bad effect on the growing season of the tree and its wintering.
If you pinch at the end of July, when the growth of the shoots ends, you can achieve an improvement in the ripening of the shoots and a better development of the axillary buds.
Video: rules for pruning pear trees in summer
Autumn pruning
The optimal time for the last of the year, autumn pruning lasts from the last decade of August to mid-September. It is used on early and mid-season pear varieties.
- It is recommended not to prune the plant too much: it will begin to spend a lot of energy to recover as soon as possible, and may sprout many vertical shoots. It is better to carry out the process in stages: remove some of the branches this fall, another next, etc.
- Autumn pruning should be done before it gets colder and the temperature drops to 0 ° C.
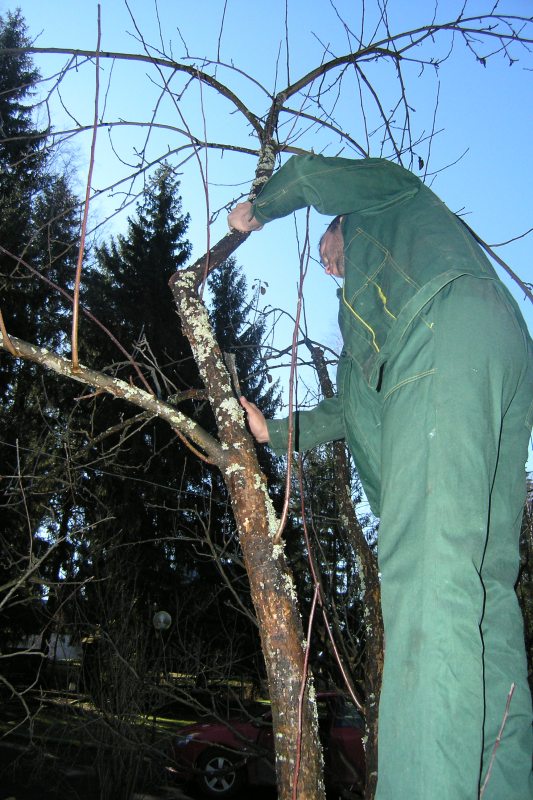


Hurry up to carry out autumn pruning before the temperature drops to minus indicators
- Start removing shoots that grow at right angles to the trunk. When finished, trim off those that run parallel to the trunk or in a vertical direction.
- An annular bark flow will serve as a guide for pruning. It is clearly visible between the base of the branch and the trunk. It is undesirable to make an incision below it or leave a stump above it. In order for the wood to heal quickly, cut off the branch along the flow: it contains tissues that ensure rapid regeneration.
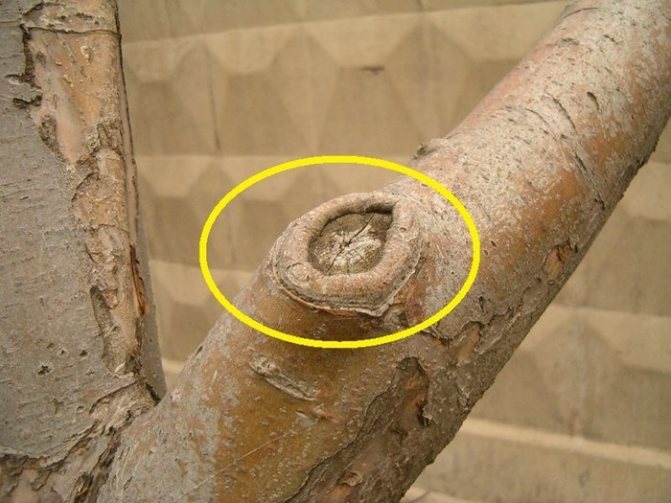


This is what a ring bead looks like after the branch is cut to the base.
- If there are branches with a thickness of 3 cm or more that need to be cut down, do the following: cut from below approximately to the middle, and then finish off from above. Otherwise, you can damage the bark under the branch being cut, and the unfinished part will simply break under its own weight.
- Immediately after completing the procedure, lubricate the cuts with pitch or other means, as when pruning in the spring. Unmasked wounds begin to secrete sap, which attracts pests and vectors of diseases that are dangerous to the tree.
- In this case, feeding during pruning is also not carried out.
Video: rules for pruning pear trees in the fall
The nutritional value
| Untreated pear (Nutritional value per 100g) | |||
| Water: 83.71 g | Inorganic substances: 0.33 g | Dietary fiber: 3.1 g | Energy value: 58 kcal |
| Monosaccharides: 9.80 g | Carbohydrates: 15.46 g | Proteins: 0.38 g | Fat: 0.12 g |
| Trace elements | |||
| Potassium: 119 mg | Phosphorus: 11 mg | Calcium: 9 mg | Magnesium: 7 mg |
| Sodium: 1 mg | Iron: 170 µg | Copper: 82 µg | Zinc: 100 µg |
| Vitamins | |||
| Vitamin C: 4.2 mg | Vitamin B1: 12 µg | Vitamin B2: 25 µg | Vitamin B3: 157 µg |
| Vitamin B5: 48 µg | Vitamin B6: 28 µg | Vitamin B9: 0 µg | Vitamin B12: 0 µg |
| Vitamin A: 23 UI | Retinol: 0 µg | Vitamin E: 0.12 µg | Vitamin K: 4.5 µg |
| Fatty acid | |||
| Saturated: 6 mg | Mono-unsaturated: 26 mg | Poly-unsaturated: 29 mg | Cholesterol: 0 mg |
Hairpin "Kraken"
Pear wood properties
Pear wood has pleasant warm shades, ranging from pinkish-yellowish-white (in young trees) to brownish-red (in older trees).
Under the influence of bright sunlight, pear wood begins to darken. The gloss data for pears is quite high, comparable to those for conifers. At the same time, pear wood is also characterized by higher strength values in parallel with maple, oak, ash and other hard-deciduous species, in some ways slightly inferior to them, and in some even clearly superior. And yet, in no case should we forget that it is the wood of the wild pear that is much stronger and more durable than the wood of cultivated varieties.
The impact hardness of such wood is a very significant quality for parquet and furniture (the reasons are quite clear). The abrasion (in fact, wear resistance) of pear wood can be assessed as high. Its performance is very close to that of tree species such as oak, ash and maple. It easily lends itself to bending and other types of processing, it is quite easy to paint, polish and grind. At the same time, experts estimate the resistance to pulling out of fasteners as high, approximately at the level of birch.
The pear is a nuclear-free, diffuse-vascular, ripe woody breed. Ripe woody species, in fact, differ from sapwood species in the fact that the most central zone on a growing tree has less moisture in comparison with the peripheral one. It is customary to call such a peripheral zone as ripe wood. Core rays and annual rays on longitudinal sections hardly differ. When cross-sectioned, the vessels are virtually invisible due to their small volumes.
Pear bark
Pear bark was often used in dyeing. It is customary to paint wood and fabrics in a brown shade with a decoction from such bark. A well-deserved fame among carpentry specialists is homogeneous, dense, slightly knotty and hard pear wood. It must be dried with great care. During drying, it warps and cracks a little, but dries well. Wood with a slight lilac shade is pinkish, the older it is, the darker it is, highly valued in the production of high-quality furniture. Straight-grained wood is excellently polished and pickled.
It is also important that the pear tree is processed with great difficulty with special tools, but the cut from the chisel or chisel comes out quite clear, with a velvety clean surface.
Pear wood is the favorite material of sculptors and carvers. The polished wood has a glossy matte surface and a beautiful shade. It is customary to make models for casting, veneer veneers, rulers, race tires from pears. The finest lines and the smallest details are most well worked out. This characteristic is very successfully applied by engraving artists. This is very important for making cliches for end engraving, that is, woodcuts.
How to eliminate the problem with the formation of flowers
To exclude a delay in flowering, it is necessary to correctly approach the choice of a tree variety and caring for it. So, it is preferable to stop at pears, which will bear fruit in the sixth year after planting.


Don't buy trees from strangers. Most often, such acquisitions appear through acquaintances who can honestly say about the advantages or disadvantages of the variety.


Most pears require pollination. Since insects in this case may not be enough, several varieties of trees should be planted nearby. It is believed that cross-pollination will significantly increase yields.


When choosing a pear, climatic features should be taken into account. In areas with harsh winters, the choice should be stopped on frost-resistant varieties.


If frosts are frequent in the area, it is better to plant late-ripening varieties, the flowering period of which begins later.


The main factor is the determination of the landing site. For a tree, you should choose sandy loam or loamy soil. Drainage should be used on clayey soils.


During the growth of the tree, attention should be paid to watering. It is especially important during dry periods. For the procedure, you should choose the evening time or cloudy weather.


Some gardeners recommend preparing a ditch near the tree, which must be filled with water when watering. In order to provide enough light to the branches, a crown must be formed during the growth of the seedling.


To avoid nutrient deficiencies, the tree needs feeding twice a year. Humus, dung or ash are most often used as fertilizers.


Complex additives, including urea or ammonium nitrate, are an alternative to organic fertilizers. Potassium phosphate fertilizers are also useful for pear fruiting.


Excerpt from Pear
The Emperor, with the excitement of a personally insulted person, finished the following words: - To enter Russia without declaring war. I will make peace only when not a single armed enemy remains on my land, ”he said. It seemed to Boris that the emperor was pleased to say these words: he was pleased with the form of expressing his thoughts, but was dissatisfied with the fact that Boris heard them. - So that no one knows anything! Added the emperor, frowning. Boris realized that this applied to him, and, closing his eyes, slightly tilted his head. The sovereign again entered the hall and spent about half an hour at the ball. Boris was the first to learn the news of the crossing of the Niemen by the French troops, and thanks to this he had the opportunity to show some important persons that much that was hidden from others happens to him, and through that he had the opportunity to rise higher in the opinion of these persons. The unexpected news of the French crossing the Niemen was especially unexpected after a month of unfulfilled expectations, and at the ball! The Tsar, at the first minute of receiving the news, under the influence of indignation and insult, found that, which later became famous, a saying that he himself liked and fully expressed his feelings. Returning home from the ball, the sovereign at two o'clock in the morning sent for the secretary Shishkov and ordered to write an order to the troops and a rescript to Field Marshal Prince Saltykov, in which he certainly demanded that the words be placed that he would not reconcile until at least one the armed Frenchman will remain on Russian soil. The next day the following letter was written to Napoleon. “Monsieur mon frere. J'ai appris hier que malgre la loyaute avec laquelle j'ai maintenu mes engagements envers Votre Majeste, ses troupes ont franchis les frontieres de la Russie, et je recois a l'instant de Petersbourg une note par laquelle le comte Lauriston, pour cause de cette agression, annonce que Votre Majeste s'est consideree comme en etat de guerre avec moi des le moment ou le prince Kourakine a fait la demande de ses passeports. Les motifs sur lesquels le duc de Bassano fondait son refus de les lui delivrer, n'auraient jamais pu me faire supposer que cette demarche servirait jamais de pretexte a l'agression. En effet cet ambassadeur n'y a jamais ete autorise comme il l'a declare lui meme, et aussitot que j'en fus informe, je lui ai fait connaitre combien je le desapprouvais en lui donnant l'ordre de rester a son poste. Si Votre Majeste n'est pas intentionnee de verser le sang de nos peuples pour un malentendu de ce genre et qu'elle consente a retirer ses troupes du territoire russe, je regarderai ce qui s'est passe comme non avenu, et un accommodement entre nous sera possible. Dans le cas contraire, Votre Majeste, je me verrai force de repousser une attaque que rien n'a provoquee de ma part. Il depend encore de Votre Majeste d'eviter a l'humanite les calamites d'une nouvelle guerre. Je suis, etc. (signe) Alexandre. " [“Sovereign brother! Yesterday it dawned on me that, in spite of the straightforwardness with which I observed my obligations towards Your Imperial Majesty, your troops crossed the Russian borders, and only now received a note from St. Petersburg with which Count Lauriston notifies me about this invasion, that Your Majesty considers himself to be in hostile relations with me since the time when Prince Kurakin demanded his passports. The reasons on which the Duke of Bassano based his refusal to issue these passports could never have led me to suppose that the act of my ambassador was the pretext for an attack.And in reality he did not have a command from me, as he himself announced; and as soon as I found out about this, I immediately expressed my displeasure to Prince Kurakin, commanding him to fulfill the duties entrusted to him as before. If Your Majesty is not inclined to shed the blood of our subjects because of such a misunderstanding, and if you agree to withdraw your troops from Russian possessions, then I will ignore everything that happened, and an agreement between us will be possible. Otherwise, I will be forced to repel an attack that was not initiated by anything on my part. Your Majesty, you still have the opportunity to save humanity from the scourge of a new war. (signed) Alexander ". ] On June 13, at two o'clock in the morning, the sovereign, having summoned Balashev and read him his letter to Napoleon, ordered him to take this letter and personally hand it over to the French emperor. Sending Balashev, the sovereign repeated his words to him that he would not make peace as long as at least one armed enemy remained on Russian soil, and ordered him to convey these words to Napoleon without fail. The sovereign did not write these words in the letter, because he felt with his tact that these words were inconvenient to convey at the moment when the last attempt at reconciliation was being made; but he certainly ordered Balashev to hand them over to Napoleon personally. Leaving on the night of June 13-14, Balashev, accompanied by a trumpeter and two Cossacks, arrived at dawn in the village of Rykonty, at the French outposts on this side of the Neman. He was stopped by French cavalry sentries. A French hussar non-commissioned officer, in a crimson uniform and a shaggy hat, shouted at Balashev, who was approaching, ordering him to stop. Balashev did not immediately stop, but continued to walk along the road. The non-commissioned officer, frowning and grumbling some kind of curse, advanced with the chest of a horse on Balashev, took up his saber and rudely shouted at the Russian general, asking him if he was deaf that he did not hear what was being said to him. Balashev identified himself. The non-commissioned officer sent a soldier to the officer. Not paying attention to Balashev, the non-commissioned officer began to talk with his comrades about his regimental business and did not look at the Russian general. It was unusually strange for Balashev, after closeness to the highest power and power, after a conversation three hours ago with the sovereign and generally accustomed to honors in his service, to see here, on Russian soil, this hostile and, most importantly, disrespectful attitude towards himself by brute force. The sun was just beginning to rise from behind the clouds; the air was fresh and dewy. On the way, the herd was driven out of the village. In the fields, one by one, like bubbles in water, larks were sprinkled with a chiming. Balashev looked around him, expecting the arrival of an officer from the village. The Russian Cossacks, the trumpeter, and the French hussars occasionally looked at each other in silence. The French hussar colonel, apparently just out of bed, left the village on a beautiful well-fed gray horse, accompanied by two hussars. The officer, the soldiers, and their horses had an air of contentment and panache. This was the first time of the campaign, when the troops were still in good working order, almost equal to observation, peaceful activities, only with a touch of elegant militancy in clothing and with a moral touch of that fun and enterprise that always accompany the beginning of campaigns. The French colonel could hardly restrain a yawn, but he was courteous and, apparently, understood the full significance of Balashev. He led him past his soldiers by the chain and said that his desire to be presented to the emperor would probably be immediately fulfilled, since the imperial apartment, as far as he knew, was not far away. They drove past the village of Rykonta, past the French hussar hitching posts, sentries and soldiers saluting their colonel and examining the Russian uniform with curiosity, and drove to the other side of the village.According to the colonel, the division chief was two kilometers away, who would receive Balashev and escort him to his destination. The sun had already risen and shone merrily on the bright greenery. They had just left the tavern on the mountain, when a group of horsemen appeared to meet them from under the mountain, in front of which, on a black horse with a harness shining in the sun, was riding a tall man in a hat with feathers and black hair curled up to his shoulders, in a long legs protruding forward, like the French ride. This man rode at a gallop towards Balashev, glittering and fluttering in the bright June sun with his feathers, stones and gold braids. Balashev was already two horses away from a horseman in bracelets, feathers, necklaces and gold galloping towards him with a solemn theatrical face, when Yulner, a French colonel, respectfully whispered: "Le roi de Naples." [King of Naples.] Indeed, it was Murat, now called the King of Naples. Although it was completely incomprehensible why he was the king of Naples, he was called that, and he himself was convinced of this and therefore had a more solemn and important appearance than before. He was so sure that he was really a Neapolitan king that when, on the eve of his departure from Naples, during his walk with his wife through the streets of Naples, several Italians shouted to him: “Viva il re!” [Long live the king! (Italian)] he turned to his wife with a sad smile and said: “Les malheureux, ils ne savent pas que je les quitte demain! [Unhappy, they do not know that I am leaving them tomorrow!] But despite the fact that he firmly believed that he was the King of Naples, and that he regretted the sorrow of his subjects, who were leaving them, recently, after he was ordered to re-enter the service, and especially after a meeting with Napoleon in Danzig, when the august brother-in-law said to him: “Je vous ai fait Roi pour regner a maniere, mais pas a la votre” [I made you king so that reign not in his own way, but in my opinion.] - he cheerfully set to work familiar to him and, like an eroded, but not fattened, fit for service horse, sensing himself in a harness, played in the shafts and, having discharged himself as colorful and expensive as possible, cheerful and contentedly, he rode, not knowing where and why, along the roads of Poland.
Reasons for delayed flowering
If flowers and fruits have not formed on the tree in due time, the growing conditions of the tree should be checked. These include:
- temperature regime;
- illumination of the site;
- soil type;
- planting depth;
- watering;
- state of the crown.


So, strong and prolonged frosts can adversely affect the condition of the kidneys. And in the spring, you should not expect a lush flowering.


After a very cold winter, the tree is likely to die, as evidenced by the lack of foliage, brittle branches and damaged bark.


If the pear was planted in the shade, the tree's development will be slowed down. This is due to the delay in fruiting.


Pear trees need pruning. This allows you to reduce the forces that are required to feed the branches, provide ventilation of the crown, and also open the access of sunlight to the buds. In this case, incorrect cropping will have the opposite effect.


The tree will begin to waste energy on crown restoration, which will lead to weak flower formation or a complete lack of flowering.


Access to water is important in the life of a tree. Therefore, with sufficient moisture, flowering occurs quickly. In arid areas, the tree will not begin to bear fruit until the root has grown to the aquifer of the soil.


At the same time, high humidity can cause rotting of the roots, causing weakening and death of the upper part. This happens in heavy soils. Or in soils in a close location of groundwater, which wash out useful substances.


Another factor why the pear does not bear fruit is the planting depth. The root collar should be at ground level.Otherwise, the gardener should shake off the earth from it, or huddle it up.


Treatment


The benefits of pears have been known for a long time, they are used in folk medicine. For example, the substances that are in fruits help soothe a cough and bring down the temperature during infectious and viral diseases.
On the basis of pears, various infusions and decoctions are prepared, which help to improve the condition with inflammation of the urinary tract. Perhaps this is due to the diuretic effect of the fruit on the body. People who suffer from urolithiasis are advised to consume pear compote.
The treatment of many diseases takes place not only thanks to the pulp of fruits, in folk medicine they also use the leaves of the plant, which, when dried and crushed, help to cope with increased sweating. Young leaves can be used to relieve inflammation, and they also fight fungi.
Compote, which is cooked on the basis of dried fruits, helps with intestinal disorders. Pear seeds also have a useful property: they can be used to cope with worms.
Pears are very useful for humans, and therefore supporters of traditional methods of treatment are advised to use this fruit to get rid of many diseases.
| Disease | Method of treatment |
| Prostate adenoma | Steam the dried fruit with boiling water in a thermos and leave overnight. Drink an infusion of fifty milliliters up to four times a day. |
| Anemia | Wash, peel, chop and mash a couple of pears. Then add fourteen milliliters of honey to the fruit puree and mix well. This puree should be eaten after dinner. |
| Bronchitis | Add a dessert spoon of rosehip syrup to two hundred milliliters of pear juice. Consume one hundred milliliters three times a day. |
| Gastritis, cholecystitis and liver disease | You need to eat two pears daily to get rid of heartburn and severe pain, as well as eliminate intestinal discomfort. |
| Diarrhea | Pour half a glass of dried pears, forty-eight grams of oatmeal flakes into a shallow container and pour four hundred milliliters of boiling water. Boil the mixture for at least twenty minutes. Then the broth should be infused for about an hour, after which it must be filtered. Drink one hundred milliliters up to four times a day before you sit down to eat. |
| Stones in the kidneys | In five hundred milliliters of water, boil for ten minutes a glass of dried and ground pears. After the broth, you need to brew for four hours. Drink one hundred milliliters no more than four times a day before eating. |
| Urolithiasis disease | Every day in the morning on an empty stomach, eat a couple of pears (preferably wild) and drink pear compote, but without added sugar. |
| Rheumatism | Steam a couple of tablespoons of dried pear leaves with a two-hundred-gram glass of freshly boiled water and set aside to infuse for a couple of hours. Filter the infusion and drink two tablespoons no more than three times a day. |
| Diabetes | You should drink seventy milliliters of pear juice daily about half an hour before eating. |
| Cystitis | A couple of pears must be lightly sprinkled with sugar and baked in the oven, and then eaten. |
As you can see, pears bring tremendous benefits to the body. However, you should not abuse self-medication if your illness persists. In this case, it is best to consult a doctor for advice.
Pharmacological properties
The fruits of the common pear have diuretic, anti-febrile, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antipyretic and astringent properties. Kissels and compotes from dried pear fruits strengthen blood vessels, remove excess salt, water, toxic substances, heavy metals from the body, and cleanse the digestive tract. Pear fruits are the best prevention of multiple sclerosis. Pear seeds have an antihelminthic effect. In the experiment, quinine exhibits acaricidal activity (Lee H., 2007).Pear fruits have a tonic effect, they have a positive effect on the heart and central nervous system during stress.
Decorative curly annual pear - what is this "fruit"
Decorative pears are actively used in landscape design in almost all countries of the world. There are several known varieties: Bradford pear, Beach Hill, Willow. Many sources on the Internet often add to this list a kind of "decorative annual curly pear". This name immediately intrigues: how can a tree be annual and even curly. All attempts to find more detailed information or a photograph of the mysterious plant turn out to be fruitless. All articles on Russian-language sites mentioning a curly pear represent as a photograph ... a pumpkin! True, these pumpkins look like a pear. In the text, however, the curly annual pear is usually mentioned, but the description of the varieties is given for ordinary ornamental pears.


The cute pear-shaped fruits belong to the pumpkin and can be used for decorative purposes.
The study of foreign sites leads to the conclusion that they do not know about curly pears there either. There is a term "ornamental pear" - "ornamental pear", but you will not be able to find the term climbing pear. It can be assumed that someone mistakenly translated the expression pear curling leaf - a symptom of a disease that occurs in ornamental pears, and since then a myth has arisen about a curling pear that no one has ever seen.
So, we are talking about completely different plants: decorative pears (full-fledged large trees) and decorative pumpkin, which gives pear-shaped fruits.
How to make pears ripen at home?


How to make pears ripen at home? The fruit should be plucked from the tree when the skin of the fruit has just begun to turn yellow or red. After unripe pears should be stored for about five days in a relatively cool room, where the air temperature will reach about twenty degrees Celsius. During this period, the fruit should be examined twice a day. If some pears are not yet fully ripe, then they need to be taken to a cooler place, where the thermometer will show five degrees Celsius.
In order for the pears to ripen faster, the fruits should be kept in the refrigerator for a day, and then stored at room temperature for several days. In this way, pears can ripen much faster.
How else can you store pears so they ripen quickly? For example, some gardeners recommend folding pears, apples and bananas into a single paper bag. A special substance (ethylene), secreted by the last two fruits, allows the pear fruits to finally ripen in a short time.
Video
Growing rules
The willow pear is propagated by cuttings, layering or root shoots. Often used as a graft for wild-growing crop varieties. The place under the tree is allocated sunny, without shading, on well-drained soils. Planting of seedlings is carried out in spring or autumn in a pit 80 cm / 1 m, using a fertile substrate. A prerequisite for the landing recess is that the bottom is covered with a drainage pad. The material is taken at least one year.
Important! When planting a pear, the root collar is left above the soil level.
Agrotechnology for willow pear is standard, care is oriented to the biological characteristics of the culture:
- Watering is moderate, for an adult plant, drying out of the root ball is quite acceptable. The plant is drought-resistant, the root system, completely deepened, provides the tree with the necessary moisture. In the dry season, the pear is watered 3 times: after flowering, in July and September with a large volume of water. Seedlings up to 2 years old are watered 2 times a month.
- When planting, a fertile mixture is placed on the bottom of the pit, the nutritive elements of the willow pear are sufficient for 3 years.Then the tree is fed every year: at the beginning of the growing season - with compost or superphosphate.
- The crown is formed in the spring, according to the design concept, when creating a trunk, the lower branches are trimmed in the 3rd year of growth, the crown is thinned out for subsequent years. If the formation of the crown occurs naturally, sanitary pruning is carried out in the spring, frozen and dry branches are removed.
When growing willow pear in temperate climates, the plant is prepared for winter. Abundant watering is carried out, the stem is wrapped in burlap and the trunk circle is mulched.
Caucasian pear (Pyrus caucasica)
The plant is widespread in the Caucasus. It is a tall tree reaching 25 m. It has a spreading, pyramidal crown of medium density with a smooth, gray bark. Branches are prickly, arcuate, brown. Shoots are maroon. The kidneys are conical, smooth, slightly bent.


Leaves are wide, round or oval, up to 4 cm long, short-pointed, dark green, smooth. They keep on a long petiole. The flowers are white, collected in scutes, with rounded petals.


The fruits are lumpy, pear-shaped, greenish-yellow. The peduncle is medium, thick, curved. The pulp is oily, juicy, tender, sweet, aromatic. Contains sugars, titratable acids, ascorbic acid. Fruit ripening begins at the end of August. The duration of their storage is 1-1.5 months. Pears removed one week before full ripening tolerate transportation well. The Caucasian pear is self-fertile, it needs pollinator varieties "Klappa", "Williams", "Red-cheeked", "Korsunskaya". Fruiting begins at the age of 7-8 years. The yield is high. The fruits are dried and processed, used fresh.
Possibilities of forming a decorative pear
Since decorative pears are not grown for the sake of fruit, you can embody any of your fantasies during their formation. To obtain interesting shapes, you need trellises made of wooden or metal lattices or wire stretched in several rows or strong rope. Metal trellises need to be braided with plastic so that the metal does not damage the branches in frost.
Various forms of growing decorative pears - photo


Trees located in the same plane look very unusual


Trellis make it possible to form a pear in two tiers
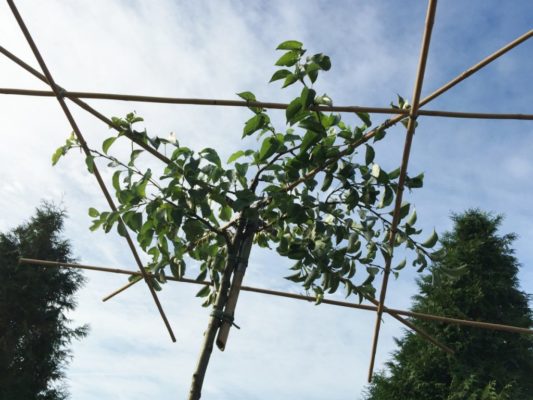


The flat support structure created from the slats allows you to get an interesting shape of the pear crown
Decorative pears can even be shaped like an arch by guiding and fixing their branches on curved trellises.


If the center conductor of the pear is directed along an arcuate support, you can get an arch from trees
Use in landscape design
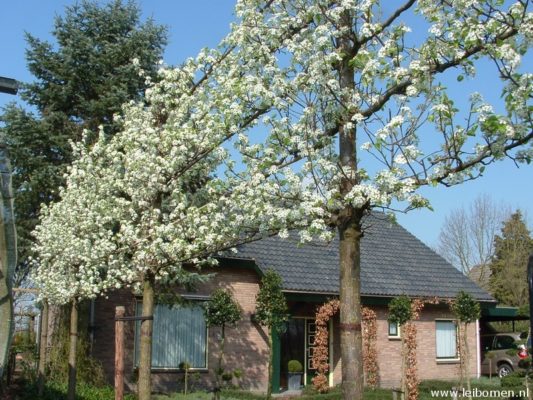
Willow pear is used for ennobling urban areas, parks and squares. Suitable for adding decorative effect to backyard and garden plots. Looks impressive thanks to its voluminous, spherical shape. The photo above shows the white flowers of willow pear along with long leaves - an original combination. In landscape gardening, the tree is used as a single growing or as an element of landscape composition. Ornamental willow pear can be used for hedges or edging plantings. Looks great in tandem with conifers.
How to choose and store?
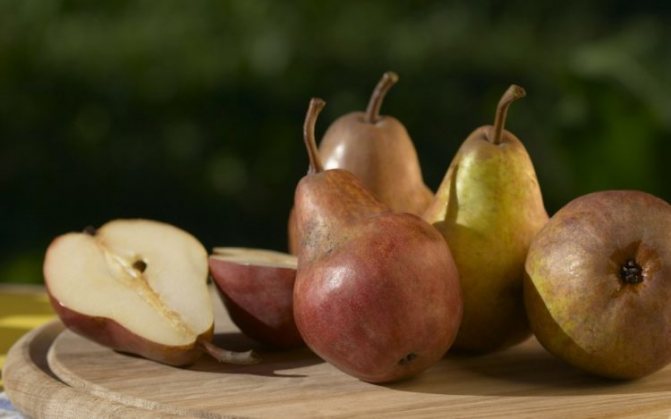


Here you need to rely on your sense of smell and tactile sensations. A sufficiently ripe and sweet pear is very aromatic, and a rather pleasant, sweet smell emanates from it.
Also, when choosing a good pear, you need to carefully examine the appearance of the fruit. The skin should be painted in a uniform shade, with a smooth surface, on which there should be no dents, cracks and traces of rot or mold.
In addition, with a quality fruit, the fruit will always be firm. If the pear is soft to the touch, then the fruit is overripe. So, we figured out how to choose a pear. Now you need to understand how to properly store the pear so that it does not deteriorate ahead of time.
Where can pears be stored?
The room needs to be chosen sufficiently dark and cool. To do this, you can use the balcony, cellar, basement and refrigerator. This type of fruit cannot be frozen.
How to store pears at home?
For any storage method, you need to use only those fruits that are not damaged and have not yet fully ripened (just started to turn yellow). The container where the fruits will lie must be with a smooth surface, some soft material must be laid on the bottom, and the walls of the container must be covered with paper. When the container is prepared, you should start preparing the fruits themselves. Each pear must be wrapped in thin and soft paper and folded into a container in three layers. It is also necessary to cover each layer with paper. The fruits must be placed diagonally in the container so that the stalks do not come into contact with each other.
How to store pears in an apartment?
As mentioned, the place should be dark and cool, so a balcony and refrigerator are best for storage. But each type of fruit has its own specific expiration date. Summer pear varieties should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than two weeks. During this period, the fruits must either be eaten or preserved. Autumn varieties should be harvested within a week of fruit ripening. Otherwise, the fruit will lose its appearance and taste. Stored in the refrigerator or on the balcony for about forty-five days.
How to store a late pear?
Winter varieties are harvested at the end of autumn (it is best to pick the fruits slightly immature) and can be stored at home until the arrival of the spring months. At what temperature should pears be stored? The most favorable temperature is from zero to two degrees Celsius.
When storing pears at home, you need to constantly inspect the fruits. If one pear has deteriorated (darkened, cracked or started to rot), it must be immediately removed from all the others.
When storing fruit in the refrigerator, keep the fruit separate from other foods, as the pear can absorb odors.
Cooking applications
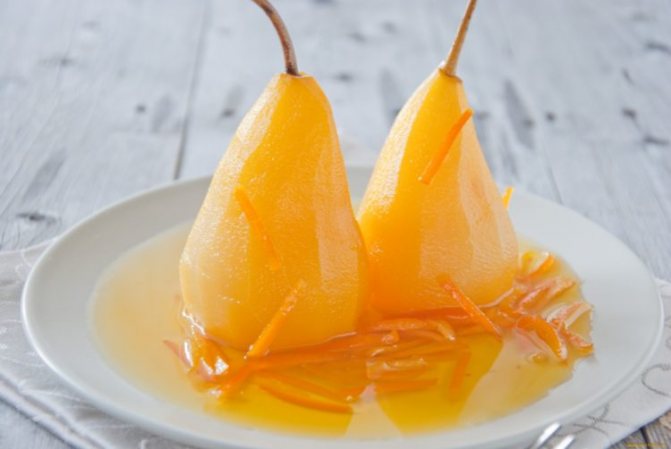


In cooking, pears are used not only fresh, they are also baked, dried, canned, etc. Very tasty juice and other drinks are prepared from the fruits, for example, compotes, jelly, etc. Pears are used to make delicious preserves, jams and jam. Fruits are added to a variety of desserts, and they are also put in salads and sauces.
In cooking, in many recipes, a pear with cheese is very often used to prepare various sandwiches, snacks, toasts, pizza, and mashed soups.
Also, a pear in the form of a filling is placed in a variety of pastries (charlotte, muffins, biscuits, pies, casseroles, pies). Sometimes a caramelized pear is taken as a pie filling.
Desserts such as baked pear with cottage cheese, pear in wine, pear with nuts, pear with ricotta, smoothies, baked pear with shrimps, pancakes with pear are very tasty and tender.
In addition, this fruit is also suitable for making meat dishes (chicken, duck, ham, chicken liver pate, lamb). Pear sauce can also be served with meat.
Sometimes a pear is used to make alcoholic beverages (moonshine, tincture).
As you can see, the pear is an essential product on the culinary table. Also, this fruit can be served as a separate snack. And here many people have a question: "What can be done so that the peeled pears do not darken?" After all, if you peel the fruits in advance, they may darken after a while, and then it will not look very beautiful on the festive table.
So, so that the pears do not darken when peeling, you can sprinkle the already cut fruit slices with lemon juice (this is done shortly before serving). Alternatively, you can dip pear slices in water with citric acid (this method is used when the product is lying for a long time). Instead of lemon juice, you can use salt (for two liters of water, you need sixty grams of salt), only after that you need to rinse the fruit under running water.
Pear. Types, features of the plant
The shelf life at this temperature is 12 weeks. Diseases during transportation and storage are the same as in common pears. However, more often, when stored in Japanese pears, physiological disorders and defects develop: a watery core, damage due to a low oxygen content in the atmosphere, as well as damage caused by an increased content of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Symptoms of a watery core are glassy, watered areas of the flesh.
Affected tissues may have a sweet taste and brownish tones in coloration. Most often, the defect appears on pears of the varieties Nijisseiki, Shinseiki and Hosui, collected from plants grown under conditions of intensive growth. Harvesting fruit at the optimum ripeness stage reduces the likelihood of a defect. Increased concentrations of carbon dioxide (more than 2%) in the air cause the core and pulp around it to turn brown.
In severe lesions, cracks appear as a result of desiccation and tissue death. The lack of oxygen (1% or less) in the atmosphere of the storages causes the appearance of small brownish depressions on the surface of the fruit. The defect develops, for example, on fruits of the "XX century" variety after 4 months of storage at 0 ° C.












































