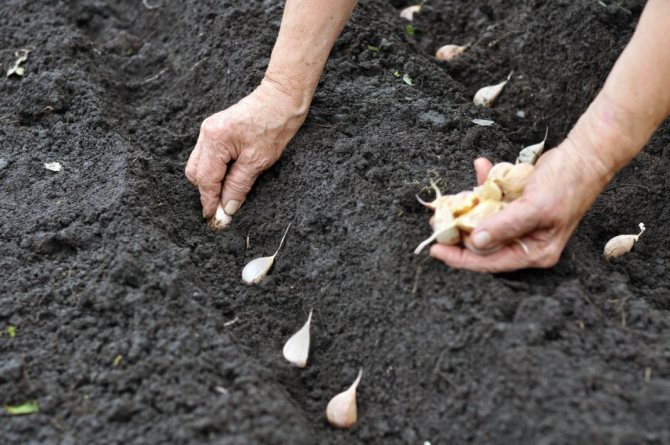
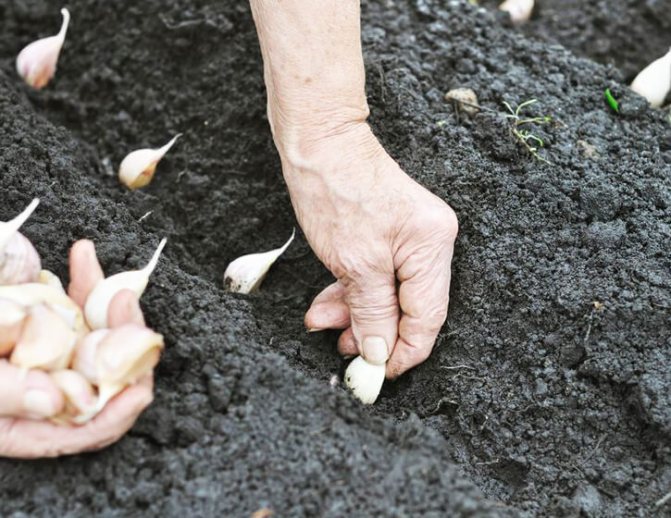
Garlic is one of the oldest crops that have been used since BC. The plant contains phytoncides that repel insect pests and have a beneficial effect on human health, acting as antiseptic and anthelmintic agents.
Garlic is also used as a seasoning for various dishes. The plant reveals the taste of food and fills with useful properties. Therefore, such a culture must necessarily be in every garden.
Biological features of garlic
The root system of garlic is fibrous, but individual roots can reach a meter depth. The high stem is false, formed by leaf sheaths of leaf blades. As the plant develops, the lower part of the leaf thickens and forms into fleshy scales. Some of the outer scales, drying out, turn into the integumentary scales of the bulb. Due to the very short internodes, a real stalk of garlic is flattened to a thin bottom. On it are fleshy scales-teeth, closed on top by integumentary scales. Inside the clove there is a bud with one or two growth points and rudimentary leaves. After resting, the teeth germinate into a new plant. Chives are used for food and as a material for vegetative propagation.
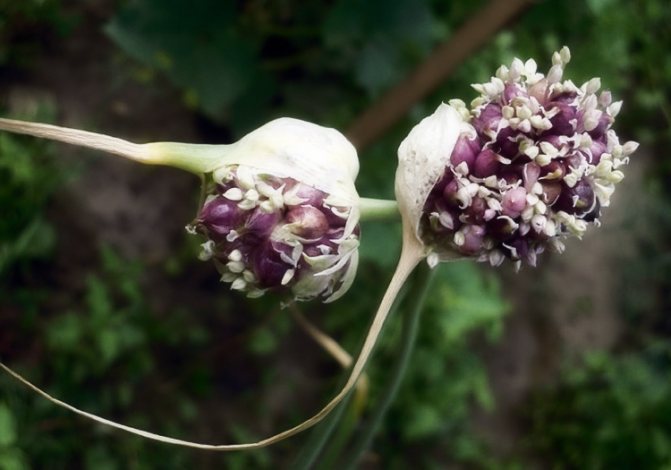
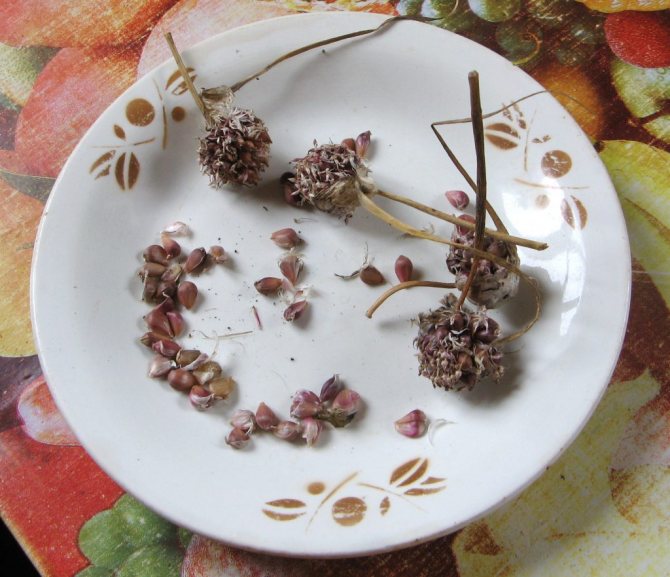
The inflorescence of garlic is a simple umbrella, located on a flowering shoot from 0.5 to 1.5 m in height, which is called an arrow. In the inflorescence, sterile flowers and airy bulbs (bulbs) develop, the number of which, depending on the variety, ranges from 10 to 500 pieces. The entire inflorescence of garlic is covered with a dense cover before flowering. Garlic inflorescences form seeds only under strong ultraviolet radiation. Under normal conditions, air bulbs are formed. Ripe bulbs of garlic crumble and germinate with one-toothed bulbs (one-toothed). Sowing a single clove will produce a regular multiple clove garlic bulb. When propagated by bulbs, the culture is considered a two-year-old, that is, in the first year, one-tooth is obtained, and their sowing the next year forms an ordinary multi-clotted garlic bulb.
How to independently determine soil parameters?
A type
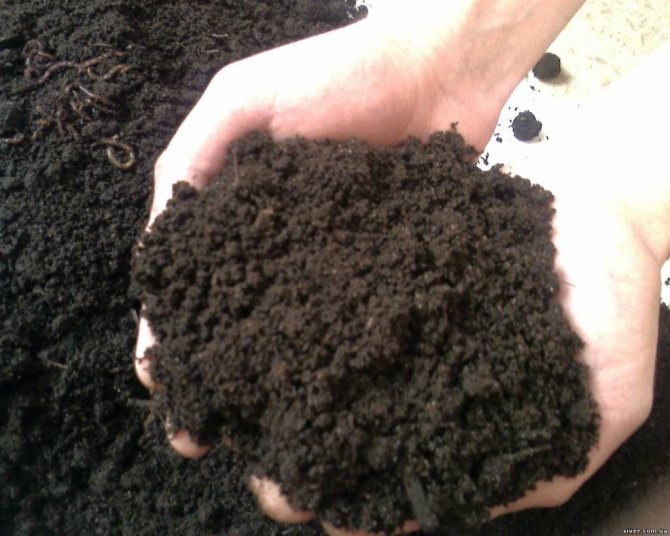
To independently determine the mechanical composition of the soil on the site, you need to take a handful of soil, moisten it evenly to the consistency of a thick paste, then try to roll it into a "sausage" about 3 mm thick, make a ring out of it, evaluate the result:
- In the presence of clayey soil, heavy in structure, the ring will roll well, differ in plasticity, and keep its shape.
- The loamy soil circle will crack.
- Sandstones, sandstone light in structure, will simply crumble, it will not work to roll them.
Fertile soil-chernozem is a black substrate with a granular-lumpy structure. All vegetable crops grow well on such soils, not only garlic.
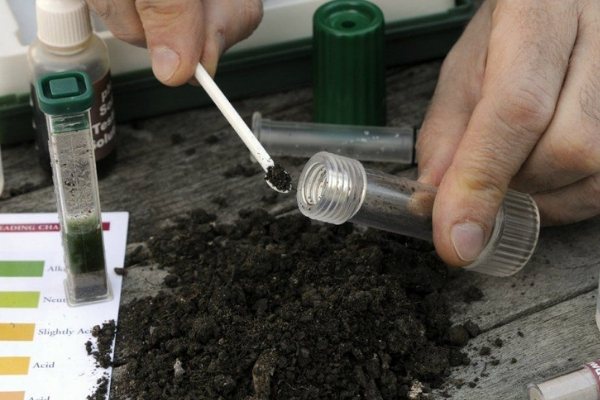

Acidity
An important parameter for the cultivation of vegetables is the acid-base medium of the soil. It is determined most accurately, of course, in laboratory conditions using chemical analysis, special Alamovsky devices or a soil meter, but these methods are expensive.
You can independently find out the acidity of the soil in several ways:
- Using the purchased litmus strip kit.Soil samples (from 10 to 30) are taken from different depths and different beds, the soil is wrapped in three-layer gauze, and dipped into a test tube or jar of distilled water purchased from a pharmacy. Shake the contents in the container, lower the litmus strip for a few seconds, wait until it changes color. Acidity is determined by the insert from the kit according to the acquired shade of the used reagent.
- A handful of earth is watered with a small amount of vinegar, when small bubbles form on the surface, the pH is considered normal, but in the absence of a reaction, the acidity is considered increased, the soil will need to be treated with lime.
- Use currant, cherry or bird cherry leaves. Take a glass liter jar. Prepare a broth in a saucepan. Add 4–5 leaves per liter of water. They give the liquid to boil, pour hot water into a jar, cool. Only then put a pinch of the selected soil. When the color of the water changes to a red tint, the medium is acidic, to blue - slightly acidic, to green - neutral.
- The soil is lowered into a glass with grape juice, when the color of the juice changes, the presence of bubbles on the surface for a long time, it is argued that the medium is neutral.
- A large spoonful of chalk, two tablespoons (tablespoons) of soil, 5 large tablespoons of water (room temperature) are poured into the bottle, and the neck is closed with a fingertip (without air). Wrap the container with paper so that there is no heating of the liquid from the hands. During the chemical reaction, carbon dioxide will be released. The result, when the fingertip straightens completely, means that the soil environment is acidic, if it straightens in half - slightly acidic, in the absence of a reaction - neutral.
The degree of acidity of the soil can be indicated by weeds common in untreated areas. For example, sorrel, nettle, mosses grow in an acidic environment. In slightly acidic soil - creeping wheatgrass, field birch, clover. On neutral soils - field bindweed, white sweet clover, sow thistle. In alkaline - field mustard.
Types of aboveground mass of garlic
Garlic forms two types of aboveground mass.
- Flowering or arrowheads. They form a shoot with an inflorescence (arrow).
- Non-colorless or non-shooting. This type forms only a leaf mass during the growing season.
Shooting garlic will not lodge. Straight peduncle (arrow) and leaves turn yellow by the end of the growing season. On the arrow, the common cover of the inflorescence is opened and the bulbs fall to the ground.
In non-shooting garlic, the leaves, as they ripen, lose their turgor, turn yellow, lie on the soil and dry out.
Video


Garlic is one of the most widely recognized crops among gardeners. Its popularity is incredibly high on all continents. And this is a well-deserved price for those wonderful qualities that allow this plant to combine two hypostases at once. Garlic is not only a fragrant spice that gives any dish a unique and piquant taste, but also a wonderful natural remedy that allows you to cope with a wide variety of ailments.
Therefore, the question of how to properly grow a miracle vegetable does not lose its relevance for many, many years, if not centuries.
Types of garlic
Garlic is divided into 2 types, which differ in planting time and the size of the formed bulb. In autumn, cloves of winter garlic are planted. Spring garlic cloves. Winter garlic has both forms: arrow and non-arrow, and spring garlic - only non-arrow.
In the country, it is better to grow both forms. The winter crop forms the harvest earlier, the heads are larger, the yield is higher. But it has a low keeping quality. By January-February, the winter garlic cloves dry up and need additional measures to preserve the seed. It is also best to grow arrow-headed winter garlic varieties.
Differences between winter and spring garlic
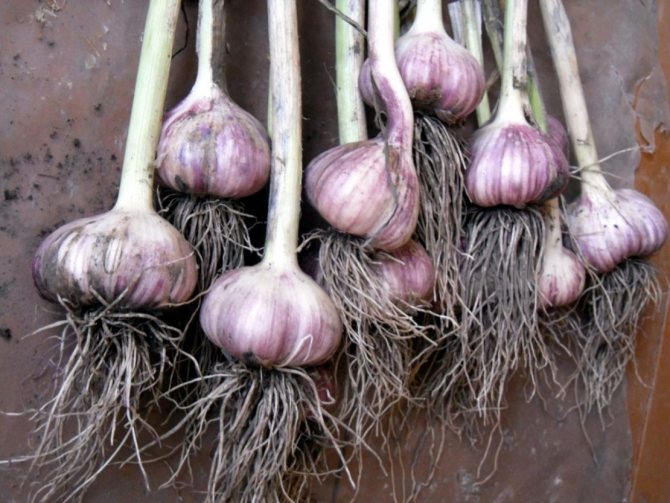
Winter garlic forms cloves around the stem located in the center of the bulb. When separating the cloves, the stem remains bare.
Spring garlic does not have such a stem. The teeth are more curved due to the tight fit in the garlic bulb. The largest denticles are located in the outer rows, smaller in the middle.
For consumption, both types of garlic are absolutely identical. According to biological characteristics, they differ in terms of planting. Spring forms a crop only when planting in spring. Winter garlic produces the largest and healthiest harvests, ripening by July, when it is planted in autumn. When planting cloves in the spring, even if it forms a crop, it is not high-quality and not good-quality.
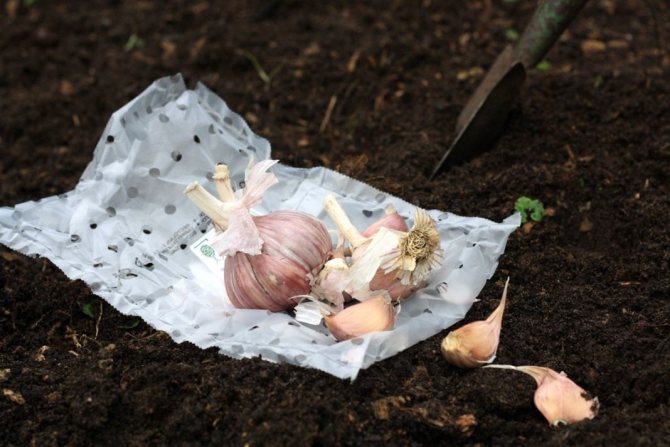


Sowing garlic (Allium sativum).
Garden bed preparation
It is good to plant winter varieties in loose soil, and spring varieties in clay soil with a small content of sand.
Garlic needs a lot of incoming light. Ridges should not be shaded by trees or covered with covering material. Under such conditions, by the end of autumn, summer residents will enjoy a good harvest.


It is worth paying attention to the landing height. The best place is to be in a high area, as garlic does not like standing water and will rot if planted in a low area.
If cabbage, peas or pumpkin grew on the beds before planting, then the soil will be fertile, saturated with fertilizers and nutrients.
From the editorial board... Since ancient times, garlic has been cultivated in India, and the Aryans brought it. Used for therapeutic purposes, but did not eat because of the sharp and specific smell.
And vice versa, if there were previously tomatoes, cucumbers or carrots on the beds where the cloves are planted, then such soil will become unfavorable for garlic, it can lead to the development of diseases and many harmful insects.
Expert opinion
Elena Pchelkina
Horticultural Expert
It is necessary to change the planting sites every year to update the soil composition and fill it with minerals.
Winter garlic growing technology
Planting time of winter garlic
Winter garlic is planted in the fall. In the south, with a warm, long autumn, planting can be postponed to the end of October, and even November-December. In 2020, I sowed winter garlic in the first decade of December (more precisely, on December 3). The teeth have taken root, the tops of future leaves have turned slightly green. This development is a great transition to winter recreation. If sown early, when warm weather often returns in the south up to +10 .. + 12 ° C, garlic manages to form leaves up to 5-6 cm, which freeze with the onset of cold weather and the plants meet damaged in spring, which subsequently leads to crushing of the heads ...
Frequent temperature fluctuations in the autumn period required a revision of the timing of planting winter garlic cloves in the middle zone of the Russian Federation and the CIS countries. In the middle regions, the optimal period was considered to be the period from the second half of September to mid-October. Currently, the optimal autumn planting time has moved to mid-October. It is better to start landing when the air temperature at night approaches +8 - + 10 ° С. Garlic will have time to form a developed root system without green above-ground shoots. Thus, a very important point is to most clearly determine the time of planting cloves and sowing bulbs for reproduction. If the teeth and bulbs form leaves in the fall, they may die in the spring during recurrent frosts or constantly hurt throughout the growing season.
Lighting for garlic
The next condition for obtaining a good harvest is the intensity of the lighting. If the garlic beds are shaded by taller crops, the heads will be shredded. Large heads are not formed when growing garlic in partial shade.
Predecessors
To prevent garlic from being re-infected with infectious diseases, the culture is returned to its former place of cultivation after 4-5 years. Prior cultures are equally important. The best predecessors are crops of the nightshade family (tomatoes, peppers, eggplants), pumpkin (pumpkin, cucumbers, zucchini), cruciferous (cabbage, salads).
Winter garlic is a good neighbor for a number of fruit bushes: black currant, raspberry, gooseberry, strawberry and wild strawberry. It has a good effect on the growth and development of cucumbers, potatoes. Protects them, like roses, gladioli, tulips from slugs, borers, caterpillars. The smell of garlic for moles is intolerable. Garlic planted next to the rose reduces the likelihood of black spot damage to the culture.
Soil disinfection
The level of the infectious background is very important for garlic. The higher it is, the less hope for the formation of healthy heads of garlic. Therefore, always before planting garlic, you need to carry out disinfecting measures.
The main one is the sowing of phacelia green manure. Phacelia is an excellent green fertilizer, Heals the soil from almost all types of fungal diseases (late blight, root rot), destroys pests (wireworm, nematode, locust). Phacelia successfully deoxidizes the soil. Suppresses the growth of weeds (wood lice, etc.).
The introduction of ammonium forms of mineral fertilizers, including ammonia water, ammonium sulfate, potassium sulfate, removes the wireworm well from the site.
If the bed for garlic occupies a small area, you can spill the area with a solution of potassium permanganate.
Preparing the soil for planting garlic
Garlic prefers light soils with neutral acidity. If the soil is acidified, add 1 glass of lime or dolomite flour per 1 sq. m. Garlic does not tolerate flooding and fresh organic matter. When fresh organic matter is introduced directly under the planting of garlic, there is a strong defeat by fungal diseases, the quality of garlic bulbs decreases. Therefore, if necessary, it is better to loosen heavy soil, humus and manure under the previous crop, and under the garlic - moor peat, sand, sawdust of deciduous trees (conifers acidify the soil).
For autumn digging (25-30 cm), a complex mineral fertilizer is used - 35-50 g / m² or a mixture of a glass of ash and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers - 30 and 20 g / m², respectively. The soil is carefully leveled. They start planting in 1-2 weeks so that the soil fluffed by digging settles. Literally 1-2 days before planting, add 15 g / m² of ammonium nitrate or shed the grooves with a root solution. This procedure is especially desirable when there is a delay in seeding in order to accelerate the formation of the root system.
Preparation of planting material
Planting material can be purchased at specialized retail outlets, but it is better to use a sample of the crop grown in the current year. For planting, the largest heads are chosen and on the day of planting, they are cut into separate one-size teeth. If the cloves are prepared in advance, then the bottom of the clove dries up and, accordingly, the germination energy decreases. With long-term storage of separated cloves, they may not sprout.
The cloves are disinfected in a solution of potassium permanganate (30-40 minutes) and planted. Cloves can be disinfected in a 1% solution of copper sulfate. The teeth are kept in the solution for no more than 1 minute. Some experienced gardeners recommend first rinsing the cloves for 1-2 minutes in a salt solution (40-50 g / 5 l of water). Then immediately immerse it in a 1% solution of copper sulfate for 1 minute and, without rinsing, start planting the planting material.
If these materials are not available, the planting material can be disinfected with an alkaline solution. 400 g of ash is poured into 2 liters of water, boiled for 0.5 hours, cooled. The cold solution is filtered and the cloves are kept in the prepared concentrate for 1.5-2.0 hours. They are washed with boiled cold water and planted.
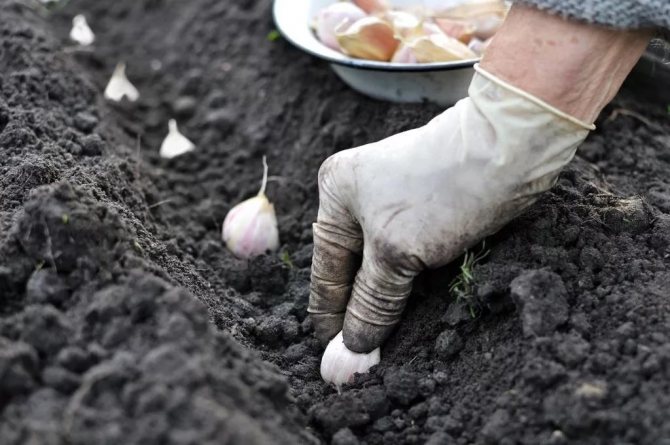
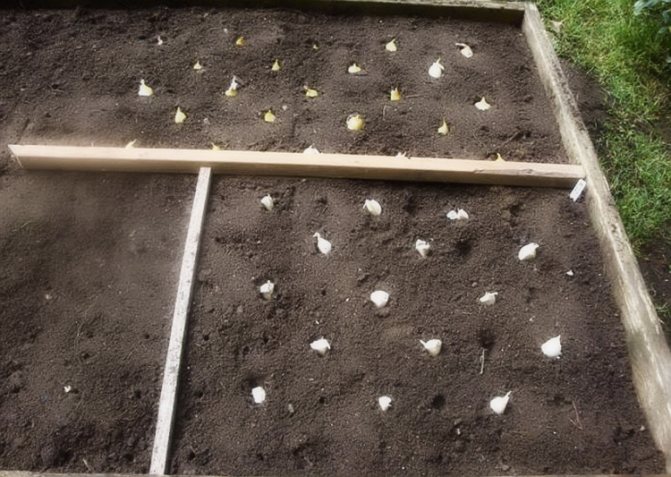
Planting winter garlic
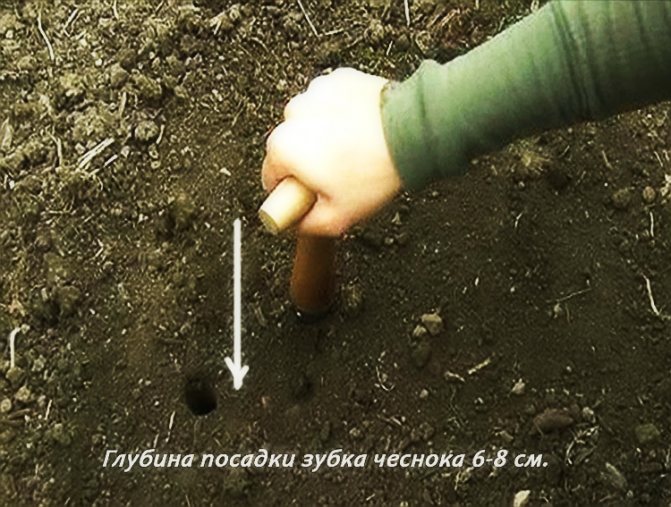
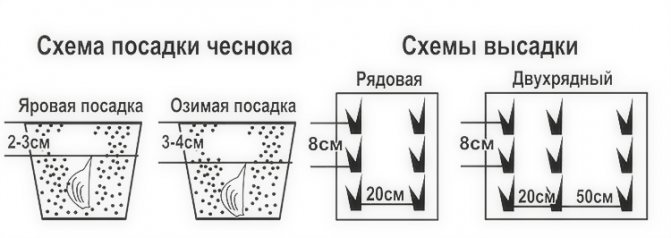
The optimal scheme for planting garlic is ordinary or two-row (two-row). The width between the lines is 10-12 cm, between the rows is 25 cm or the width of the hoe's blade. Distance in a row 8-10 cm or the length of a standard matchbox. When the plantings thicken, the cloves and bulbs become smaller. The seeding depth is 2 tooth heights or at least 5-7 cm. In case of shallow planting, the rapid heating of the upper layers of the soil in spring will lead to crushing of the heads and cloves. If the soil is dry, the bottom of the furrow is pre-watered from a watering can. Cover and level the soil. Despite the sufficient frost resistance of winter garlic (-18 ..- 25 ° С), plantings of any fine mulch must be mulched. From crows, you can cover the bed with spruce branches or dry branches.
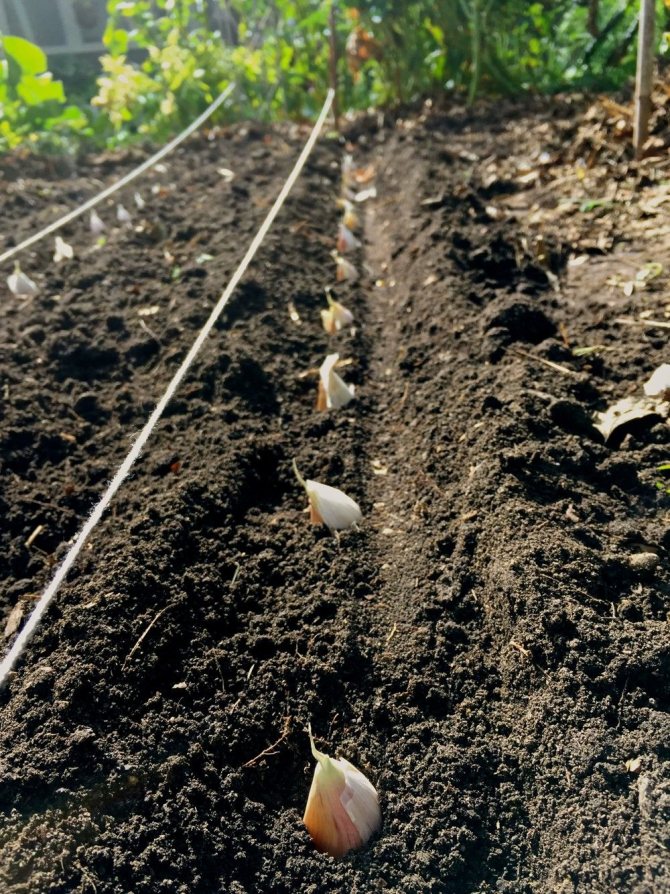


Planting garlic cloves.
Basic soil preparation work
Before, how to prepare a bed for planting garlic in the fall,
make sure it is in a sufficiently lit dry place. Excess moisture is one of the most unfavorable factors for the development of culture.
Important! If water stays in the ground for too long, the cloves begin to rot, gradually infecting each other.
Preparing a bed for garlic in the fall
occurs in two stages: disinfection and nutrition.
Disinfection
Firstly, if the composition of the soil is still acidic, which can be evidenced by the activity of such weeds as woodlice, white clover, buttercup, then the easiest way to "acidify" it. You just need to sprinkle the soil with ash. Secondly, preventive disinfection should be carried out in any case, since traces of specific bacteria and diseases can remain even in healthy soil.
Preparing the garden for garlic
Garlic care
Loosening the soil
In the spring, after the snow melts, the planting of garlic must be loosened. Loosening will remove the soil crust, remove the rudiments of weeds, and increase the access of oxygen to the roots of plants. The presence of a soil crust retards the development of the garlic bulb. They are stunted in growth and form crushed heads.
Watering
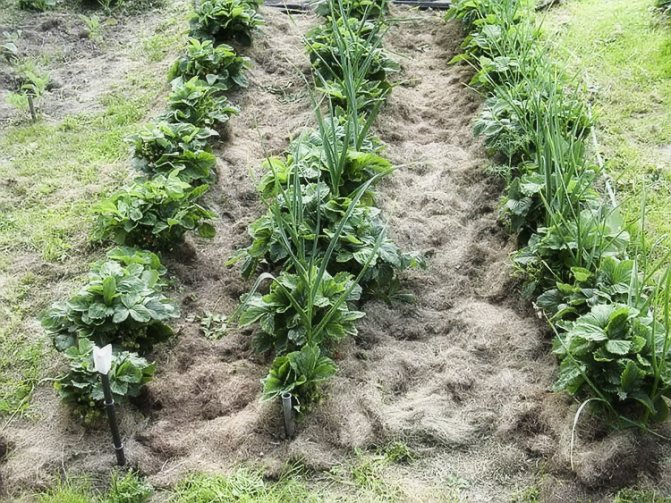
An active increase in the aboveground mass of garlic takes place in May, June and the first half of July. Watering is carried out 3 times a month in normal weather. In hot summer, watering is increased up to 5-6 times per month. If the summer is humid, don't water the garlic. Plants during the period of active growth need high humidity, but the coincidence of rains and abundant watering lead to fungal and bacterial diseases with root rot, leaf rust. To reduce the amount of watering and keep the soil moist for a longer time, it is necessary to loosen and mulch the soil after each watering. In hot summers, when the soil dries out quickly, large heads of garlic cannot be obtained without mulching.
From about the first decade of July, when the pre-harvest ripening of the heads of garlic begins, they switch to maintaining soil moisture or cancel watering. Do not dry out so that dry soil does not take moisture from ripening cloves.
Garlic dressing
To make top dressing more effective, they are combined with watering. Garlic heads are capable of storing nitrogen, therefore, the additional supply of nutrients to the culture must be carefully considered. During the growing season, garlic is fed 2-3 times, no more.
The first feeding of winter garlic is carried out on wet soil in the phase of 3-4 leaves with a solution of urea (20-25 g / 10 l of water) with a consumption rate of 3 l of solution per 1 sq. m area.
The second dressing of garlic is carried out after 2 weeks with nitrophos, nitroammophos or other fertilizer at the rate of 2 tablespoons per 1 m². Top dressing can be applied dry or in solution (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water, per 2 m²).
The third top dressing on fertile soils can be skipped. On sandy loam and light soils, they are fed in the phase of formation and growth of heads (second decade of June) with superphosphate - 30-40 g / m².
If it is noticed that the plants are slowly building up the aboveground mass, additional foliar feeding with an infusion of ash or bird droppings, water-soluble fertilizers with a set of microelements can be carried out.
Prepare solutions of the following concentration:
- 1 glass of ash or poultry droppings are diluted in 10 liters of water, filtered and sprayed on the plants,
- you can use a spoon of crystallin with a microelement set (buy in a store) for 8-10 liters of water.
Foliar dressing of garlic can be used in any combination, but in low concentration, since it complements, and does not replace, the main dressing. If you overfeed the plants, the taste and quality of the bulbs will noticeably deteriorate.
Garlic is capable of degeneration. Over time, it is no longer possible to obtain large heads from long-term selection. Therefore, the material must be updated in 3-4 years. For this, ripe inflorescences are removed, large bulbs are selected and sown around September - early October. The next year, one-toothed garlic is obtained, which, when sown in autumn, form full-fledged healthy large heads of winter arrow-headed garlic.
See also our material: Growing garlic from bulbs.
Winter garlic forms large heads if the arrows are removed in a timely manner as they appear. Arrows are removed at 10 cm height. They are broken off or cut off, leaving a 2-3 cm column.
Protecting garlic from diseases and pests
Diseases of garlic
Like all vegetable crops, winter garlic is susceptible to infection with fungal, microbial and viral diseases. Chemical preparations for protection against diseases and pests on garlic are not recommended for use. It is most practical and without a threat to the health of the owners of the dacha, children, animals, it is better to use biofungicides. They can be used to process plants from the first days of their life until harvest, which will allow you to get healthy products.
If, with the timely fulfillment of all agrotechnical requirements, the winter garlic changed color, spots, dots, arrows appeared on the leaves, growth stopped, then the plant is infected. The most common diseases are leaf rust, root rot, fusarium, powdery mildew, white rot of the bottom, etc. It is necessary to immediately start treating plants and soil with alirin, gamair, phytosporin, glyocladin, planriz. The preparation of working solutions and their use are given in the recommendations; one cannot deviate from their requirements. Self-increasing concentration, spraying at low temperatures will not have the expected positive effect on plants.
Garlic pests
The most harmful pests are the onion fly, whose larvae eat the flesh of the cloves, stem nematode, onion hoverflies, thrips, ticks, lurkers and others.
The main methods of control include the obligatory dressing of the planting material and the treatment of plants and soil with bioinsecticides. Due to the natural biological basis, bioinsecticides do not have a negative effect on human health and do not cause addiction to pests.
These include the most commonly used actofit, avertin-N, mycoafidin, lepidocid, bitoxibacillin, nemabakt, bicol, pecilomycin (from nematodes) and others.
Effective as a preventive measure, planting calendula and marigolds along the edge of the garden bed and between wide aisles of garlic. The larvae of the nematode, sliding down to the smell of flower crops, use the juice of their roots for nutrition, which is poisonous for nematodes and leads to the death of pests.
Site selection
For planting, an elevated, sun-drenched area is suitable, where there is no stagnation of moisture and snow melts quickly in spring. Low-lying places where melt water accumulates will not work.
In the absence of a choice, high beds will help save the situation, which will allow excess water to go into the aisles, protecting the rhizomes of garlic from decay.
It is important to consider the rules of crop rotation.It is not recommended to plant garlic in the same place for several years in a row. The frequency of planting in one place is once every 5 years. Indeed, diseases and pests accumulate in the soil, which will easily destroy the new crop.
Strawberries at home all year round! These veneers are 100 times better than a false jaw! And there are pennies! Up to 15 kg of strawberries every month! False dental veneers for a penny! Up to 15 kg of strawberries every month! Famous overhead veneers are now in Russia!
Legumes, cabbage, cucumbers, greens are perfect as predecessors. But sowing garlic after onions and potatoes is not recommended.
Harvest
Harvesting begins in late July - early August. The dug out plants are dried in the shade for 3-5 days. Then the above-ground part is cut off, leaving 5-6 cm of the column. It should be noted that almost all varieties of winter garlic are distinguished by large bulbs. So, the Komsomolets variety forms heads weighing up to 80-110 g, Sofievsky - 90-110 g, Otradnensky - up to 100 g.


Planting garlic cloves. <>
Varieties of winter garlic for growing in the country
Early maturing varieties: Bashkir (non-firing), Broadleaf -220 (non-firing).
Mid-season varieties:
- Alkor - for the conditions of Western Siberia,
- Moscow Region (non-shooting) - for Moscow Region and those close to them,
- Lyubasha - for Ukraine and middle regions of Russia,
- Nazus is intended for the Urals and nearby regions,
- Komsomolets - for the northern regions.
From other mid-ripening varieties of garlic, it is possible to recommend for cultivation in the middle zone and cold regions: Nadezhny, German, Dubkovsky, Antonik, Gribovsky jubilee, Gribovsky-60, Novosibirsk (non-shooting), Zubrenok, Losevsky, Sofievsky, Skif, Danilovsky and others. All varieties can be grown in the southern regions for high quality yields.
How to grow spring garlic
Unlike winter garlic, spring garlic is sown in spring, when the soil warms up in the upper 15 cm layer to + 5 ... + 8 ° С. Spring garlic is distinguished by the formation of small heads. To get larger heads, it is sown as early as possible. The culture is quite frost-resistant and develops better at low temperatures. Therefore, if it is not possible to measure the temperature of the soil, then usually gardeners, focusing on the period from the melting of snow, and also depending on the region and climate, start sowing in early - mid-April.
Shoots of spring garlic are not afraid of recurrent spring frosts and appear at an air temperature of + 3 ... + 4 ° С.
The soil for spring garlic is prepared in the fall, so as not to mess around in the cold, semi-frozen ground in the spring.
Agrotechnical requirements for environmental conditions, soil preparation and planting material do not differ from winter garlic.
Temperature requirements of spring garlic
The temperature requirements of spring garlic change during the growing season. You can adjust it by the planting depth of the cloves. In order for the temperature to be optimal in the zone of development of the root system (+ 5 ... + 10 ° C), the cloves are planted to a depth of 5-6 cm and the sowing is mulched so that the soil in this layer warms up more slowly. At low soil temperatures, the cloves start growing more actively, and the development of the root system proceeds faster. In a month (from the stage of laying the garlic bulbs) the best air temperature is + 15… + 20 ° С, and later, when the bulbs are ripe, + 20… + 25 ° С.
It is possible to regulate the temperature of the air and soil (of course relatively) with the help of mulching and light fog-like sprinkling. In cold weather, dark colored mulch (high moor peat) is used, in hot weather - light colored mulch (sawdust, shavings). Can be mulched with mown wilted grass. The loose layer allows air to pass through well and prevents the soil from heating. A layer of mulch is recommended at least 4-5 cm. With this technique, you can reduce the temperature in the soil from 1 to 3 ° C and even more.
What conditions are needed for the normal development of garlic
Garlic is a cold-resistant crop. At temperatures below 1 degree, roots are already beginning to grow. But the optimum temperature for growth is 8-12 degrees. The ground part of the plant begins to grow at temperatures from 5 to 10 degrees above zero.
At the beginning of its growth, bright garlic needs small above-zero temperatures. Otherwise, the aerial part may begin its strong growth, and the formation of the bulb will not be successful. Therefore, the sooner you plant the garlic, the better. During the period when the chives begin to root, it needs moisture. If it is not enough, then the root system will dull its growth.
Top dressing of spring garlic
Spring garlic is fed 2 times during the growing season. It is impossible (like winter crops) to overfeed the crop. When overfeeding, the nitrite form of nitrogen compounds (toxic to humans) accumulates in the teeth, the quality of the teeth decreases sharply. For feeding spring garlic, if the soil is well filled with fertilizers during basic preparation, you can use nitrophoska or an infusion of 1 glass of fresh mullein or bird droppings with 2 glasses of ash per 10-12 liters of water. Stir the solution well, strain and add to the aisles for watering, followed by mulching.
Soil characteristics
The soil for garlic is selected light, loose. Heavy, loamy soil is diluted with sand, expanded clay is used. It is useful in areas with excessive moisture.
The acidity of the soil for onions and garlic is the same. Preference is given to neutral or slightly acidic soil. If possible, soil analysis should be done with a pH value greater than 6.5 (neutral). The level of acidity is judged by the weeds growing on the site. Plantain, horsetail, mint, woodlice, or buttercup indicate acidity. Nettle, chamomile, cornflower and clover grow on neutral and slightly acidic soil.
Increased acidity will lead to the fact that the plant does not absorb nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium and other elements, in high doses it will absorb toxic substances. Plants develop poorly with it, especially their root system. If high acidity is found just before planting, wood ash can be added to the soil. The use of mineral and organic fertilizers can be carried out no later than two weeks before planting.
Harvest
By August, the leaves turn yellow, lodge, the culture is ready for harvesting. Garlic is dug in, shaken off the ground and, after drying, intertwined into braids. As such, garlic is stored in a cool dry place. The shelf life of dry-resistant garlic bulbs is up to 1.5-2.0 years. The vast majority of varieties are stored for up to 10 months.
Varieties of spring garlic for growing in the country:
- The Aleisky mid-season variety, zoned for the conditions of Western Siberia.
- The Sochi-56 variety is early maturing, resistant to weather extremes in the southern regions and diseases. It is successfully grown in the middle climatic zone.
- The Permyak variety is mid-season, intended for the northern regions.
- The Degtyarskiy variety is mid-season for the northern regions.
How do you grow your garlic? Share your proven secrets and tips in the comments!
Tips for Harvesting Large Garlic
A few more tips from experienced gardeners:
- Responsible approach to variety selection: Seed from a fine-toothed variety will not produce the desired result.
- Compliance with the rules of crop rotation: prepare the site in advance, plant it in the ground and harvest in a timely manner, water, fertilize and mulch.
- Growing garlic in one area no more than three seasons in a row, otherwise the culture will degenerate.
- Planting material update every three years.
- Systematic cutting off of arrows will provide the bulbs with additional nutrients.