Rosehip berries can give a person a charge of health. In order not to doubt their benefits, it is necessary to grow shrubs on your own personal plot. Rosehip propagation is possible in several ways. Each of them has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Before choosing the optimal breeding method, you need to analyze the climatic conditions, pay attention to the plant variety, and have a certain level of skill. The shrub adapts well to home flower beds and, with proper care, begins to give a bountiful harvest in a short time.
There is a legend about the bright color of rose hips. Aphrodite, having learned about the death of her lover, rushed to that place. On the way, she tore her body with thorns of rose bushes and knocked her legs against stones, but did not notice the pain and blood oozing from the wounds. Red berries appeared in place of the drops.
Rosehip description
The plant is a two-meter shrub with slightly drooping branches. However, there are other species, on the contrary, low cushion shrubs.

Lat. Rōsa
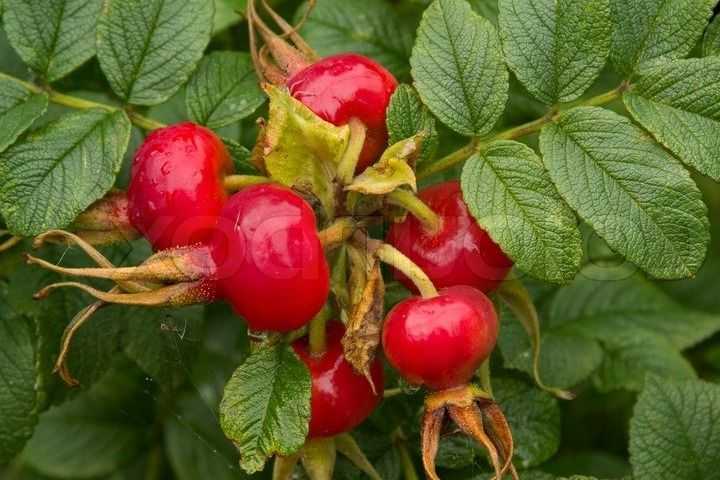
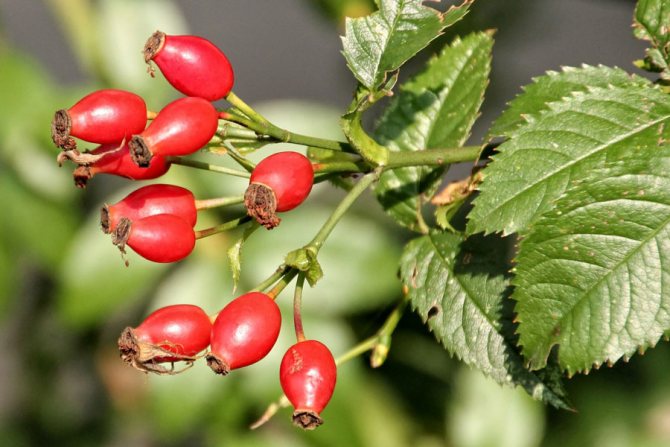
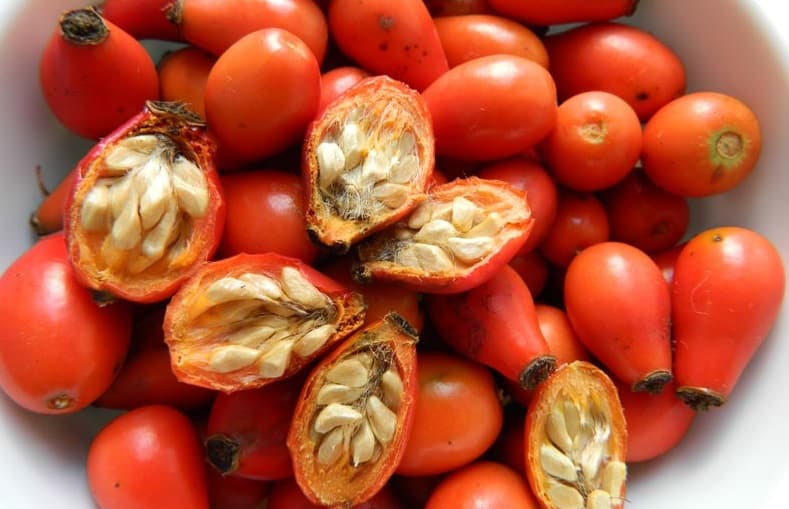
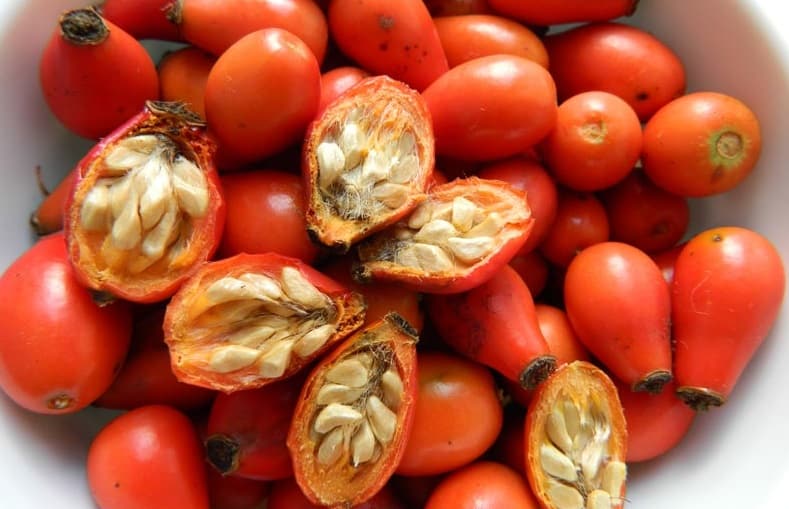
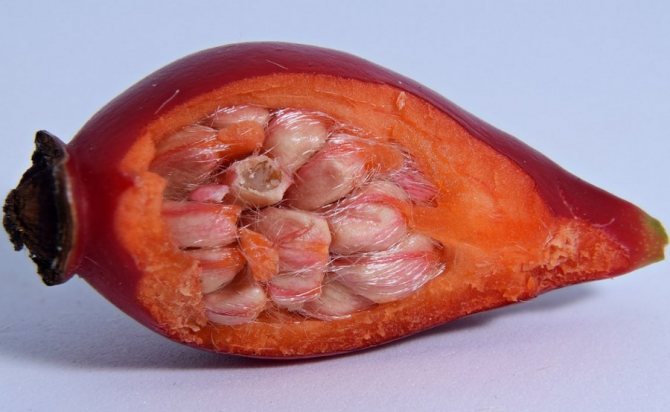
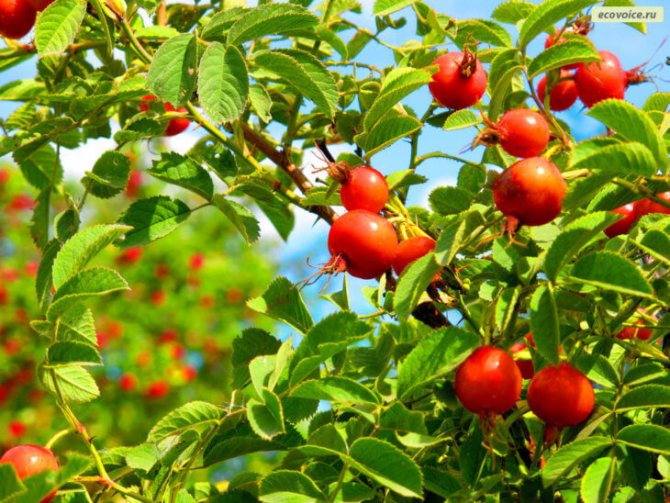
The fruits are spherical or ovoid. Their color is usually orange or red. The fruits are fleshy with a high content of internal seeds.
The walls of the berries are covered with fine hairs from the inside. Fruits are a source of minerals, vitamins and other trace elements that a person needs.
The plant begins to bear fruit from the age of three. Peak fruiting occurs when the plant is 10-12 years old.
Rosehip flowers open at 4-5 pm and close at 7-8 pm. The root system is very developed and goes far in depth and breadth. Fruits are most often harvested for the winter in the form of jam, jam, compote or dried.
The name of the plant comes from the presence of thorns on the bush that can harm humans. Thorny bushes can be found throughout Russia, with the exception of the Far North.
Rosehip refers to light-loving plants, therefore, it can be found in nature most often on open edges, river and lake shores, and mountain slopes.
It is impossible to grow one specimen on the site, since the plant is not pollinated by the pollen of its flower, more bushes are needed.
Why are gardeners increasingly planting a "wild rose"?
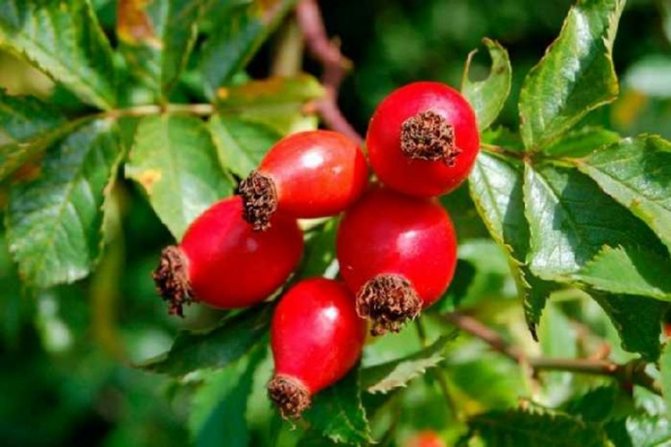


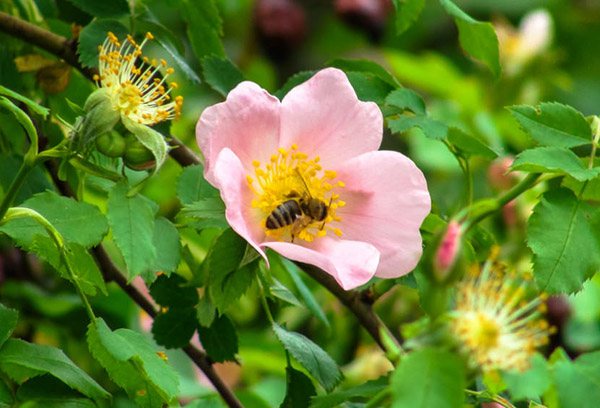
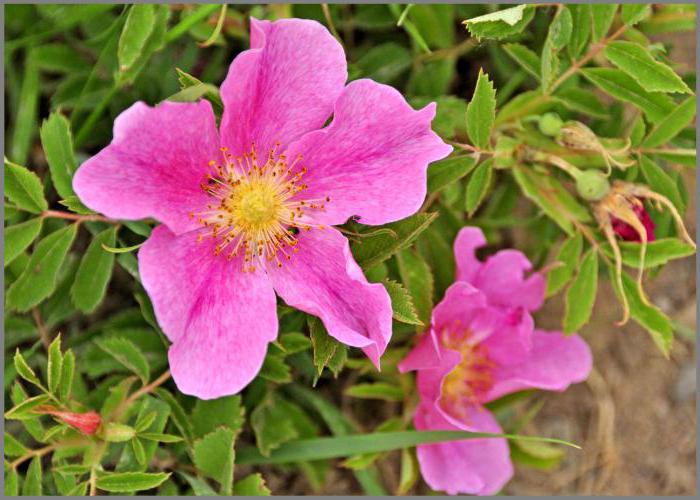
Wild rose belongs to the class of dicotyledonous plants, the order Rosaceae, the Rosaceae family. Rosehip flowers are simple and double. Terry varieties are not inferior in beauty to varieties of roses. The color of the petals can be scarlet, bright crimson, pale pink, lemon yellow, white, pale peach. According to various sources, the number of varieties varies from 10,000 to 20,000.
All varieties of rose hips are distinguished by abundant flowering, the beginning of which, depending on the region, occurs in May-June. The wild rose blooms for about three weeks. The size of the flowers depends on the variety; in some Far Eastern varieties, they reach 15 cm.
How can you propagate rose hips
Rosehip propagation occurs in several ways. Each gardener chooses the one that he likes best:
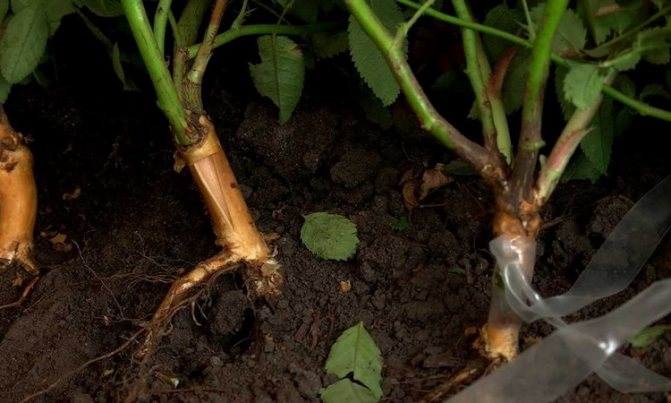
- With the help of root growth. The method is considered common and simple. The harvesting of offspring is carried out in the fall, they are selected from the most productive bushes. The root part for planting should be at least 15 cm, the aboveground part - no more than 5 cm.
- Seeds.
- Layers.
- By dividing the bush.In order to use this method, you need to take a plant that is already 5-6 years old.
- The bush is planted and divided into 3-4 parts. Each piece should contain 2-3 shoots. Planting in a permanent place should occur immediately, until the roots are dry.
- Green and root cuttings.
Rosehips, like all living plants, absorb toxins well, so you cannot plant shrubs along roads.
Care features
Regardless of which variety of rose hips is planted, it must be properly cared for. Many questions arise: can it be watered often and how to get a good harvest.
- Watering a young plant is done as needed. You need no more than two buckets at a time. An adult bush is watered less often, 3-4 times a season. Moistening must be done in the spring, during flowering and fruit development. Up to 5 buckets of water are poured under each large bush.
- Feeding with chicken manure, diluted in a ratio of 1 to 50, is carried out in the first year of life: during the growing season, before ripening of berries and after harvesting. Adult plants are fed once every 3 years.
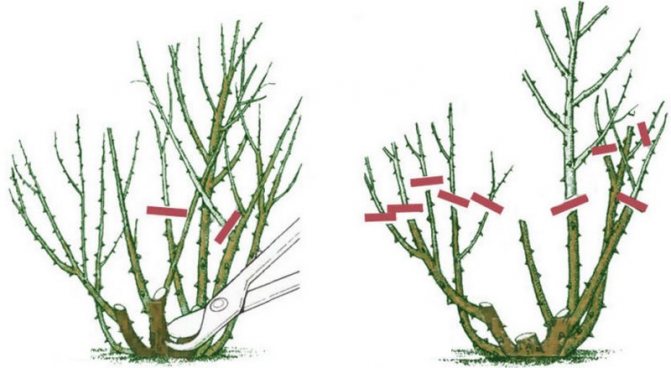
- Pruning is mandatory in the first year of life. All branches are removed. Further, the crown is leveled every 3 years. It is necessary to eliminate drying and freezing shoots. It is required to leave branches of different years, but not older than 7 years.
Plants tolerate spring pruning better. They are very sensitive to this procedure, so they may not tolerate the winter cold if it is carried out in the fall. Pruning the branches too much will not help increase the yield. The plant will drive away the greens, which will lead to a reduction in fruit.
Terry and smooth rose hips give up to two hundred flowers on one mature bush. It has been cultivated from time immemorial for its beauty and abundance of berries. The benefits of rose hips are invaluable for strengthening human health. It will not be difficult to grow a shrub in your garden if you follow all the rules of planting and care. Rosehip will delight with its flowering in the summer and give useful fruits in the fall for many years.
Seed propagation
For this, ripe fruits are used, which are already beginning to wrinkle. Next, the following steps are taken:
- The fruits are placed in pots filled with moist soil. In this form, the fruits are left to winter for successful seed germination.
- After frost, the berries are taken out of the pots, the seeds are separated and, with the help of water in the vessel, they are checked for germination.
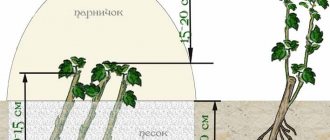
- Drowned seeds can be sown in a box and grown in a cold greenhouse.
- Seeds are sown in open ground to a depth of 2 cm.
- Water and mulch with manure or sawdust.
- In the spring, cover the sowing with foil, but periodically ventilate.
- When the weather has stabilized, the film must be removed.


Dog-rose fruit
When three leaves appear in seedlings, the plant is thinned out.
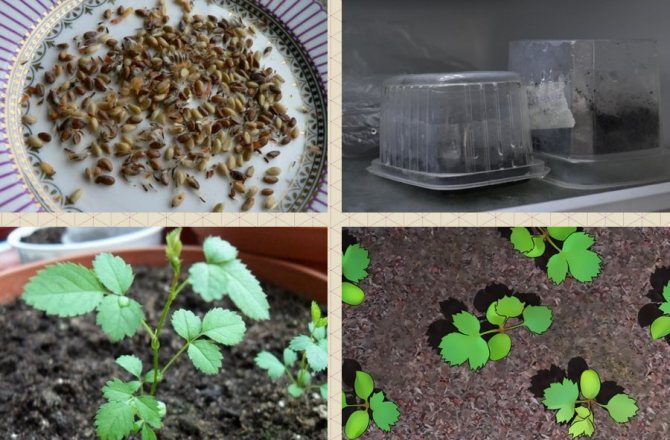
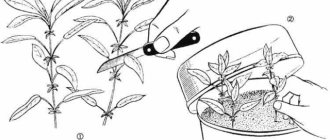
Laying seeds for stratification
The collected berries are opened without drying, the seeds are taken out and washed with water at a temperature of 37-40 o C. Washing helps to wash off the essential substances that prevent the development of the embryo and its germination. The seed is then dried using a hair dryer set to a cool temperature. It is necessary to obtain a free-flowing mixture, which is mixed with wet clean river sand. The ratio of sand to seeds is 3: 1.
The mixture of seeds and sand is placed in a container, slightly moistened with a spray bottle, covered with a plastic bag and put into the vegetable compartment of the refrigerator, or in a cellar or snowdrift for up to 6 months. The temperature during the period of such storage should be constant: from 0 to 4 o C. This procedure is called stratification, and it is, in fact, copied from natural conditions, when the seeds in the soil survive the cold season, and then sprout together.
The seed is a living organism, and biochemical reactions are actively going on in it. First of all, breathing.With prolonged cooling during stratification, the embryo activates its growth, and the seed coat becomes thinner, giving all the nutrients to the future sprout. When stable warm weather sets in, it begins its development and forms a strong, hardened plant.
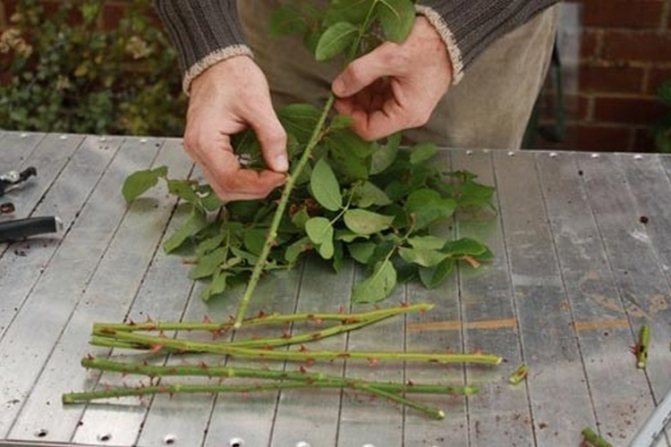
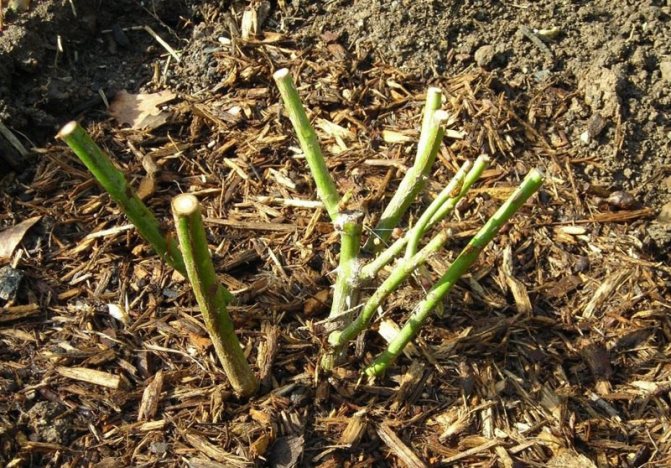
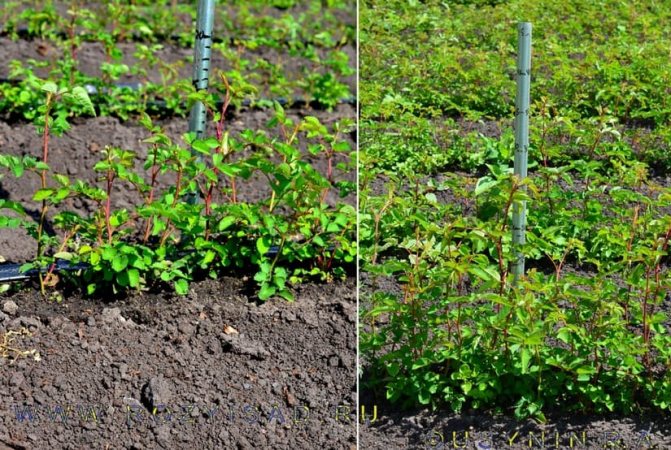
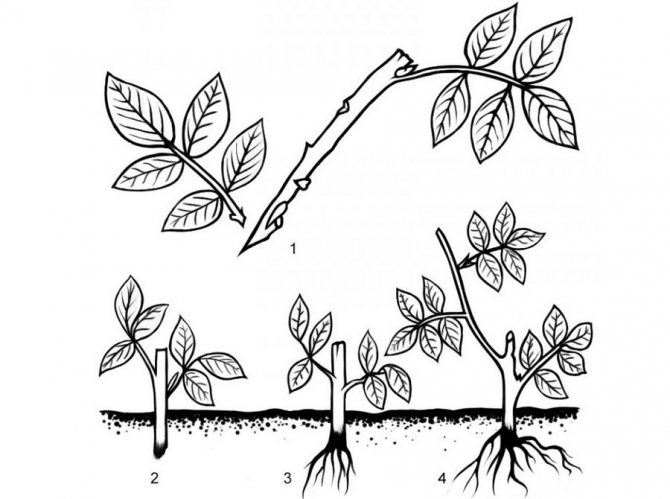
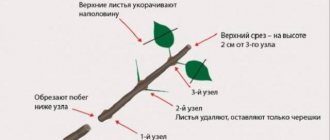
Propagation by cuttings
Cuttings are carried out during the period of active growth of shoots. This happens in the second half of June - early July. The landing pit is made 0.2 m deep.
The soil must first be limed, since the rose hips do not like high acidity. You can add compost or rotted manure to the pit.
Some gardeners recommend short-cutting the seedlings with an oblique cut before planting. The roots can also be shortened, since after the cuts on the roots, the plant takes root better. The bottom sheet is removed.
The root system is dipped in a clay mass, planted in peat pots, so as not to injure the rhizome during transplantation. Drainage is poured at the bottom, the substrate is sprinkled on top, the rhizomes are lowered and straightened.
When planting, the root collar should deepen by about 5 cm. The seedling must be watered, mulched with sawdust and peat. For 1 sq. m of earth should fall 6-7 kg of organic matter. If the planting of seedlings is carried out in the fall, feeding should be done a month before.
By autumn, the cuttings should grow by 10-15 cm, after which they begin to shade each other, so the distance between them should be increased to 0.5-1 m. If rooting is carried out in spring, it is imperative to fertilize the soil in the fall.
The most common varieties
All wild roses and species rose hips bear fruits of different shades: bright red, orange, purple, brown and almost black berries. However, not all of them are equal in quality.


Below are the most valuable (in terms of the content of nutrients) berries of the following rosehip varieties:
• May, or cinnamon, which is the most common species growing in central Russia. Individual bushes of this rosehip are found in forest glades and clearings. When grown in the garden, it is very unpretentious to any soil conditions. Usually, these species have high winter hardiness and excellent resistance to various diseases.
• The prickly rose is also a decorative wild rose, which is often planted in city squares and in front gardens. The bush is undersized, its branches are densely covered with thorns. During the flowering period, the plant is completely covered with fragrant snow-white flowers.
• Dog rose, or wild rose - is almost universally used as a hedge. Light pink fragrant flowers bloom in June, and beautiful orange-red fruits adorn the branches in autumn. This species has rather tall and spreading bushes up to 2.5-3 meters and a powerful root system. This rosehip is decorative, unpretentious, winter-hardy and disease-resistant.
• French rose hips - the ancestor of ancient garden roses, including the famous in Europe medieval pharmacy rose. This species grows in Southern Europe, Crimea and the European part of Russia. The small, undersized bushes are less than one meter high and often form dense thickets. The large flowers of this species have a magnificent bright red color.
Comments (2)
Mockina of Light
23.01.2018 at 15:51 |
We propagate rose hips exclusively by cuttings. Quite successful. We collect the fruits, dry them, grind them coarsely in a coffee grinder and in winter we brew them in a thermos with boiling water overnight. In the morning, a wonderful vitamin drink is ready! You can drink with lemon)Reply
Valya
25.10.2018 at 00:37 |
I read that a rose hip is a rose cut at the wrong time, which turned into it, but I think that if this happens, then a rose hip is also needed, especially for those who have kidney problems.
Reply
Use of suckers
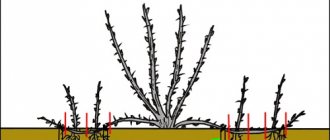
The emerging root suckers are harvested in two ways. The offspring, which have reached 31-39 cm in length, are dug up in the fall or spring. In this case, it is necessary to cut the root of the mother bush at a distance of 20-25 cm from the offspring. Such offspring are not dug out, but spud with rotted manure in a layer of 21-24 cm and watered. Adventitious roots will appear on the hilled area of the shoots.
With the arrival of autumn, in the second year, with the help of a shovel, the roots of the mother plant and the aboveground parts are cut off at a height of 13-15 cm. They are left for another year. The offspring that were harvested by the first method will require rearing and formation in a nursery for 12-24 months.
Harvesting and storage
Collecting rose hips is sometimes difficult, since there are quite a few thorny and sharp thorns on the branches. Gloves made of thick fabric should be worn before harvesting to avoid damage. The crop is harvested in several passes from August to October. When picking fruits, remember that:
- it is necessary to collect everything before the first frost, otherwise the berries will lose their healing qualities;
- do not pick all the fruits at the same time. The fiery red fruits must be removed first, and the lighter or yellowish fruits must be left to ripen. It will take longer, but the quality of the crop will be higher.
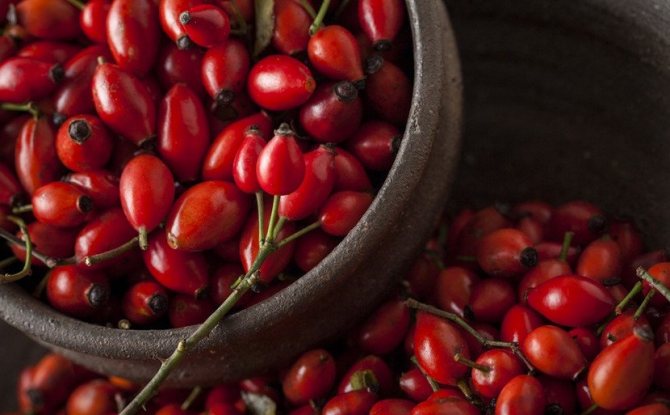


The berries are considered ripe when they reach a fiery red color.
Drying is the most common way of storing rose hips. When preparing the berries, you do not need to wash. Particularly large, it is desirable to cut in half. Then keep in the oven for 10 hours at a temperature of + 50 ° C. In the process, it is necessary to turn the fruits over so that they dry evenly. Thus, almost all chemical constituents are preserved. After the end of the process, the berries are put in cotton bags or glass jars.
About
Planting a plant
Rosehips should be planted in the spring or autumn season in the soil prepared in advance. For this, the site is being digged with the simultaneous introduction of a bucket of compost, 40 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium salt per square meter.
Advice
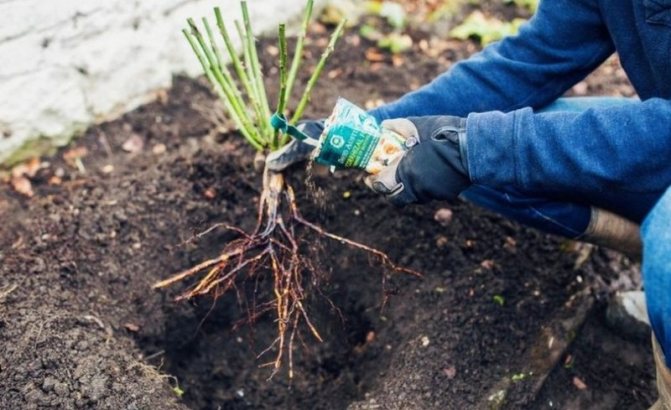
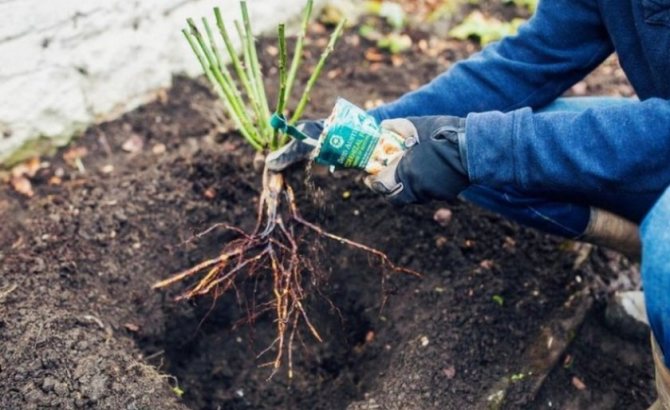
Before planting, the roots of the rose hips should be dipped in a mash made from clay and manure.
One-year or two-year-old seedlings are placed in a planting pit 40x40 cm in size, placing them at a distance of a meter. Before planting, you should carefully examine and straighten the roots, if necessary, remove the damaged areas. A seedling is placed on a soil slide prepared at the bottom of the hole, carefully straightening the roots. Gently sprinkle with a fertile substrate, gradually compacting it around the plant. After planting, the land is watered and mulched with compost, peat or rotted sawdust.
Seedlings must be watered regularly, the soil around the plant must be loosened and weeded. In early spring, each young bush should have its stem cut off, leaving three buds above the ground.