The rose is considered the queen of the garden for its beautiful flowers, a variety of shapes and shades, and a delicate aroma. Many flower growers dream of pink plantations, because it not only brings aesthetic pleasure, but also a good income. All rose lovers carry out cuttings of roses in autumn, this is the best time to obtain quality material to increase the number of plantings.
Brief description of the plant
General characteristics of roses:
- the height of the bush is 25–90 cm, depending on the variety;
- the bush consists of a main shoot, skeletal branches of several orders and bisexual flowers;
- on each shoot, from 5 to 15 leaf plates are formed, predominantly of a dark green color, in some varieties a copper or purple hue may appear;
- the surface of the sheet is matte or glossy;
- all shoots are covered with large or small thorns;
- flowers form at the tops of the shoots or over their entire area;
- the color palette of the buds can vary from snow-white to almost black.
Did you know? The smallest rosebuds are produced by a variety called C. Their size does not exceed 1 cm.
When to start? Best time
Before growing a rose from a cutting, it is important to choose the most suitable time for the procedure. In order for the seedling to be able to form normally and take root, the cutting must be fully ripe, which means that it must be cut before the petals are completely dropped from the inflorescence, but not before a full-fledged bud is formed.
At other times, the wood of the cutting will be underdeveloped and not suitable for rooting. In terms of numbers, the most suitable moment for the procurement of such planting material will be the interval from September 15 to 25.
Important! Choose annual shoots so that on each segment, as a result, there are at least four buds (a straight cut should be made above the upper one, and an oblique cut above the lower one). If the leaves have not fallen yet, then they can be trimmed a little.
Many growers prefer autumn cuttings of a rose, since it is much easier to root such planting material in autumn.


It is not difficult to explain this phenomenon: in preparation for the winter season, the rose bush tries to accumulate nutrients as much as possible, especially since, by cutting off the shoots, you will have the opportunity to choose the most suitable planting material.
Cutting roses in the fall is a relatively simple process, but you need to know not only the nuances of the procedure, but also the rules for further caring for the cuttings obtained at home, which we will discuss below.
As far as possible grafting of Double Delight, Pierre de Ronsard, Sophia Loren, Falstaff, Pink Intuition, Blue Perfume, William Shakespeare, Sins Thomas, Mary Rose, Abraham Derby, Chopin, New Dawn, see the characteristics of the variety.
Rules and optimal growing conditions
Roses should be placed in southern, well-lit areas, closed from drafts. Plants thrive better when planted in higher elevations, where the distance to groundwater is more than 1.5 m.


The optimum temperature for the full development of roses in the warm season is + 15 ... + 35 ° С. For the winter, the plants are cut and covered with sacking to ensure the air temperature is within 0 ... + 7 ° C.
During the period of growing the root system by cuttings, the moisture content should be maintained within 70-80%. For adult plants, this indicator is insignificant. They develop normally even when the air humidity is in the range of 40-60%.
Benefits of autumn breeding and how to determine the timing
The technique of growing from a cuttings has a number of advantages over the conventional grafting technique:
- vegetation that has appeared in this way does not form the root growth of a large number of stems, and this significantly reduces the difficulty in care;
- such a seedling will survive the winter much better, and in the event of freezing of the upper part, growth will go from the basal buds that are asleep;
- the starting material can be any rose from the bouquet that was presented to you.


Reproduction of roses by cuttings in autumn
Carrying out the cutting method takes place approximately at the same time as cutting off the stems of already growing flowers. This is the period from late October to early November.
What kind of roses should you prefer for breeding:
- miniature and hybrid polyanthus varieties are suitable;
- semi-leafy species;
- climbing varieties of roses belonging to the rambler group;
- excelsa flowers;
- large-flowered view Flammentants;
- representatives of the Floribunda group belonging to the Iceberg and Rosalind varieties;
- specimens of hybrid tea roses take root quickly, but their root systems are less developed, so they should be bred by grafting.
For your information! Park varieties of roses and remontant roses are difficult to graft.
Preparing cuttings
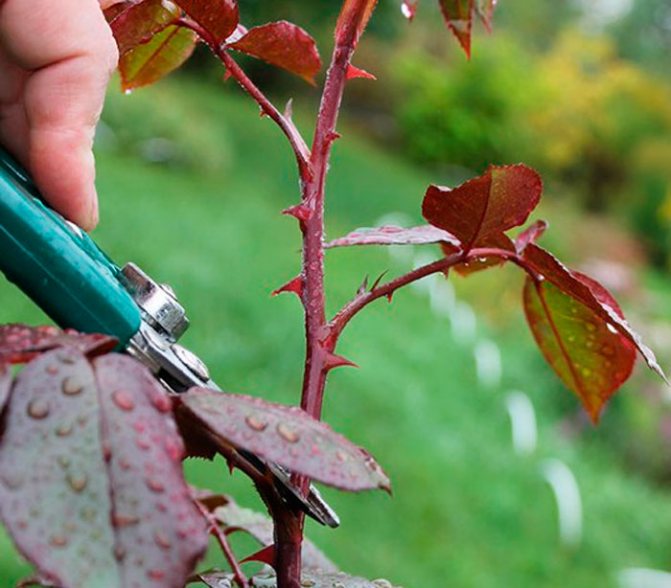
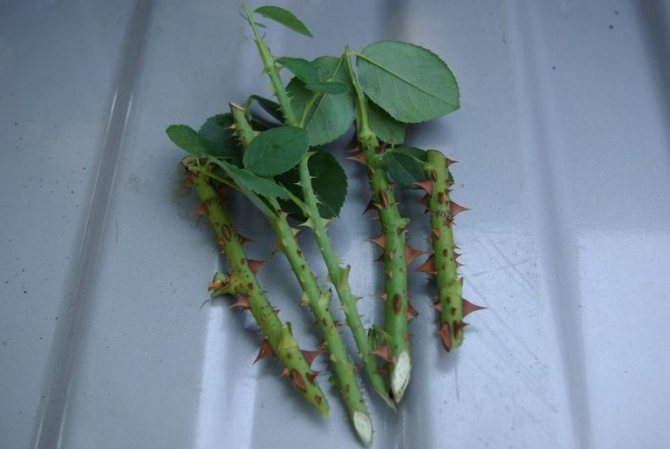
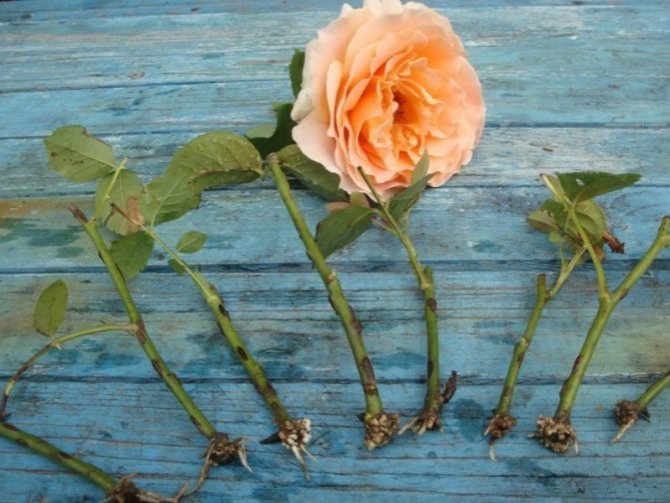
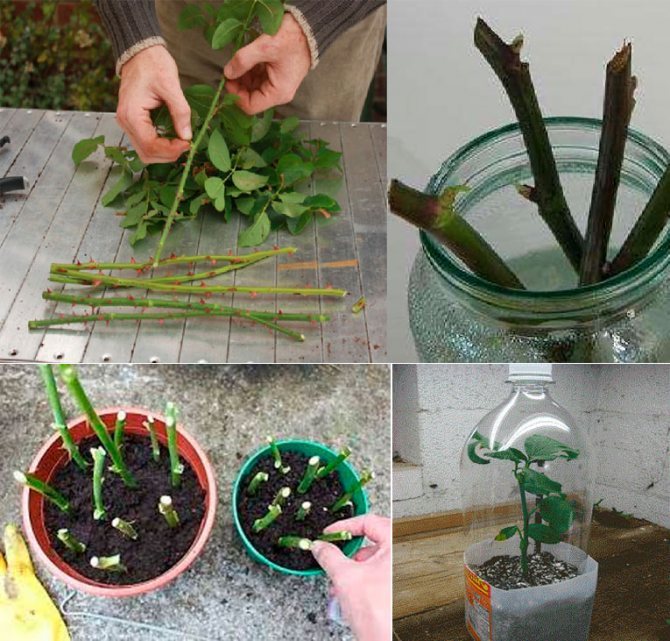
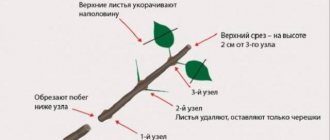
Cutting coincides in time with the autumn pruning of plants, if planting is planned for the spring. When planting cuttings in the autumn, the planting material is prepared in July or August. Shoots are cut that have reached a thickness of 5 mm, without visible traces of mechanical damage, with 3–6 healthy buds.
Check out the basic ways to grow roses from cuttings at home.
Thicker or thinner shoots will not produce a complete root system.
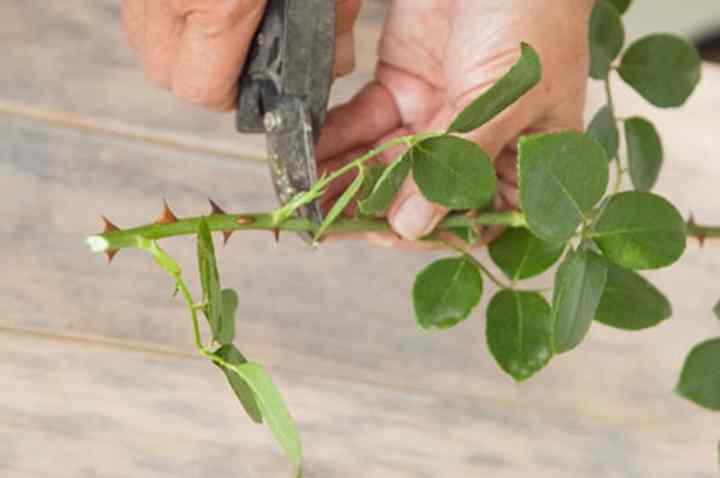
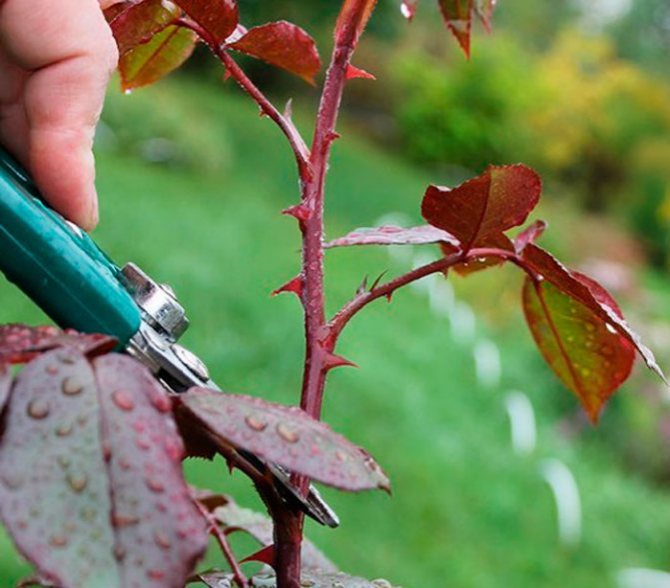
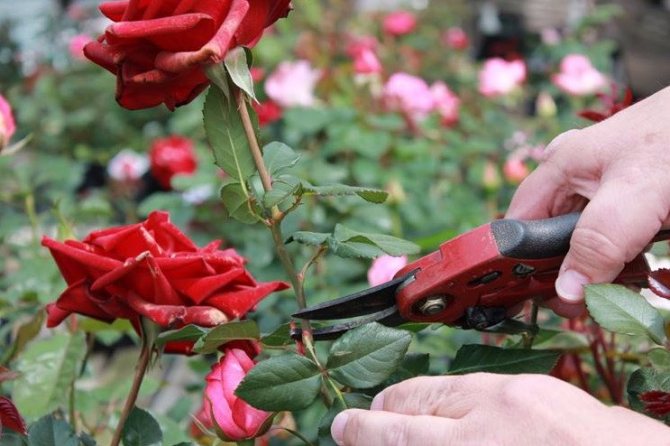
The cut must be done at an angle of 90 ° with a sharply sharpened secateurs, pre-treated with alcohol. After each plant, the instrument must be re-processed to avoid the spread of fungal diseases.
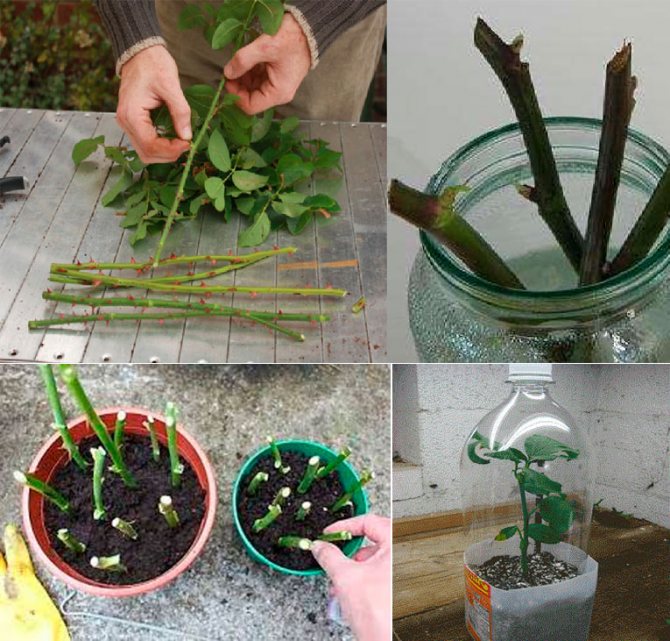
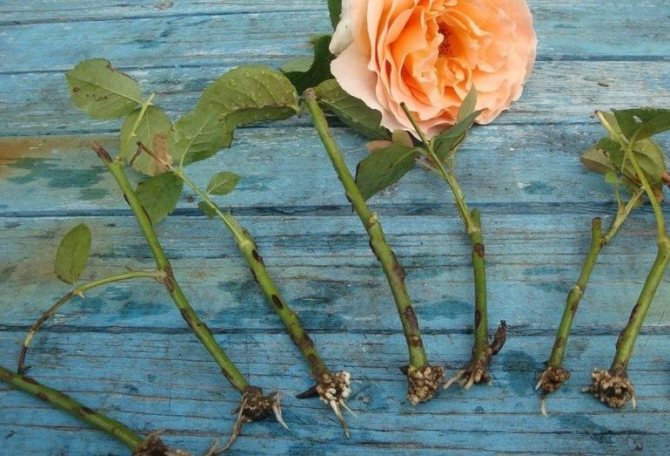
Sections on plants are treated with wood ash. The cut shoots are cut into cuttings 10-15 cm long. The cuts are made at a distance of 0.5 cm to the first bud and from the last one. Each cutting should have at least 3 healthy buds.
Then all the lower sheets are removed, and the upper ones are shortened by 2 times. The top of the cutting is dipped in molten wax to reduce moisture loss. The lower part of the cutting is treated with a root former before planting. For this you can use "Kornevin".


In order not to burn the cut, 4 g of the preparation is mixed with 4 g of crushed activated carbon. To increase the resistance of plants to fungal infections, 1 g of "Fundazol" is added to the resulting mixture. After processing with such a composition, the cuttings are immersed in water or in loose soil to build up the root system.
Important! "Kornevin" cannot be stored in torn packaging. Pour the powder into a glass container after opening the original packaging and place it in a dry, dark room - this will extend the shelf life of the drug.
How to propagate a rose bush using cuttings in the fall
Cutting roses has its own advantages and certain nuances, having studied which each grower independently decides whether he is suitable for him to obtain planting material.
Table: advantages and disadvantages of growing roses by cuttings
| Benefits of cuttings roses | Disadvantages of cuttings roses |
| Roses from autumn cuttings tolerate wintering better in the future, as they are considered hardened. | The main disadvantage is that young plants do not have time to grow full-fledged roots, which is why the first years winter worse or they need to be stored in a shelter. |
| A full-fledged stalk can be driven out of a bouquet rose, and at any time of the year, including autumn. | Imported hybrids that have undergone transportation and long-term storage are not suitable for this procedure. Their survival rate is much lower. |
| Cuttings prepared for autumn propagation are, as a rule, in sufficient quantity. Since the event takes place just at the time of the autumn pruning of rose bushes. In addition, at this time, the prevention of pests and diseases is usually carried out on roses, that is, the planting material was taken from presumably healthy bushes. | They take root better by cuttings and further vegetate their own-rooted varieties. Roses obtained by grafting are not advised by experts to be chosen as donors for grafting. |
| Roses obtained by cuttings have a longer lifespan than grafted rose bushes. |
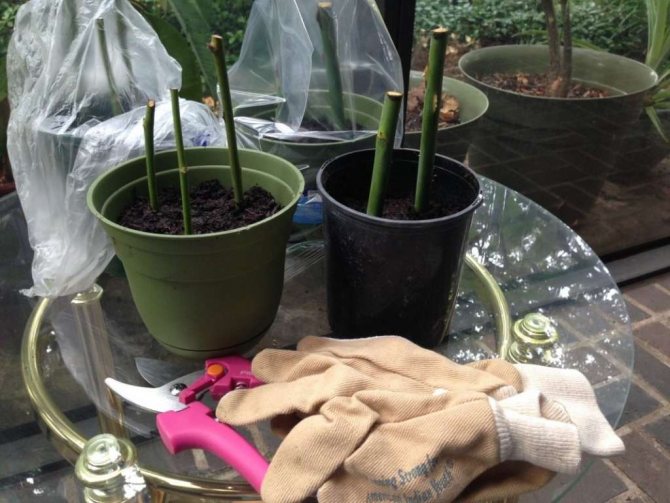
And it is also believed that roses obtained from cuttings rarely have root shoots and they are easier to recover in spring after wintering as full-grown full-fledged bushes. As for the main drawback associated with wintering at the initial stage (immediately after autumn cuttings), it is solved quite simply: in the first year, the seedlings are dug out with a clod of earth and transferred to winter indoors. More on this below.
When the aboveground part of the rose freezes (due to severe frosts, for example), the preserved living part of the cuttings activates the lower dormant buds, as a result of which the variety can be restored, which is not always the case with grafted roses.
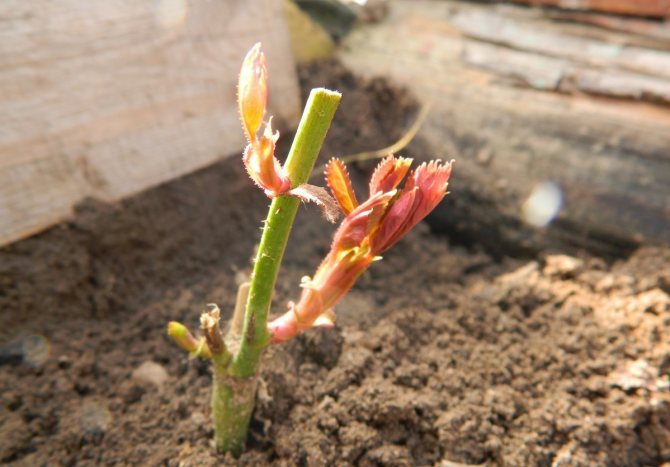


Already next spring, cuttings clearly show active vegetation with their young leaves.
Why are all trading floors "overwhelmed" with grafted roses, and you need to look for your own rooted ones? There is only one answer: after vaccination, the rose through several. months is ready for sale, because it has a root of a two-three-year-old seedling (stock). And if the stock is also bought, then the process goes even faster. In turn, a self-rooted seedling can be grown in 3 months, but it will only become full-fledged by the end of the second growing season, when the root one is formed, and in the third year it is in no way inferior to the grafted one. By the time of vaccination, the stock is usually two years old. Plus one year - growing - 3 year old sapling. Naturally, in the first years, he will overtake the rooted one in development. And by the age of 10–12 the plant weakens (because you have to either cut out the root shoots, or deepen the seedling, otherwise the rose “runs wild”). But rooted by this age bloom very profusely. And they live, in my opinion, much longer. Of course, for sale it is more profitable to propagate roses by grafting, but cuttings are better for yourself.
Martha
What garden roses can you graft
In addition to hybrid forms that have immigrated to the domestic market, you can choose almost any other types of roses for autumn cuttings. Ideal for growing from cuttings are considered miniature - Pomegranate bracelet - and old varieties, for example, Floribunda Iceberg. Large-flowered hybrid tea and remontant tea (blooming throughout the summer season until frost) take root a little worse.
The luminaries say that hybrid varieties do not take root well, as well as remontant and weaving with yellow flowers. And best of all, dark burgundy and bright red varieties of various types from miniature, climbing, ground cover and floribunda species take root.
How to keep rose cuttings in winter
If planting cuttings is postponed until spring, care must be taken to maintain their quality.
There are 3 ways to save shoots until spring:
- The first method is to dig a 15 cm deep trench on the site. Lay burlap on the bottom and distribute the cuttings on it at a distance of 2-3 cm from each other. Cover the shoots with a second layer of burlap on top and sprinkle with soil. In this case, both sections must be treated with melted wax.
- The second method is to store the cuttings in the refrigerator. To do this, you need to dilute the drug "Fitosporin-M" in a 1: 2 ratio with water and treat it with sphagnum moss. Then wrap the cuttings in moss, fold them in a bunch, fix them, put them in plastic and place them in the refrigerator.
- The third way is to lower the cuttings into the cellar. Before doing this, fill a bucket with garden soil mixed with peat and perlite in a 1: 2: 1 ratio. Stick the cuttings into the ground and cover the container with a black bag. Check the condition of the seedlings once a week and, if necessary, spray the soil with a spray bottle with water.
The main mistakes when planting roses at home
We list the common mistakes made by those who are engaged in cutting roses for the first time:
- allow cuttings to dry out in newspaper or soil;
- forget to spray the cuttings under the hood;
- do not remove the cap for ventilation, and the roses begin to rot;
- the lower oblique cut is made incorrectly;
- put the pot in direct sunlight;
- allow the soil to dry out.
In conclusion, we suggest watching the process of cutting roses in the video:
We sincerely hope that you will not make any mistakes, and in the spring a real rose garden will move to your garden.
Step-by-step instructions for grafting
In open ground, seedlings can be planted immediately in a permanent place or in a cuttings. The first method is good because the plants will not need to be repotted. But if some specimens do not take root, there will be an uneven distance between the roses, which does not look very beautiful.
When planting in a cuticle (in spring), you can transplant all the established plants, forming a beautiful flower bed, and reject plants that have not taken root. In addition, the cuttings are much easier to cover for the winter than a ready-made flower bed.


The procedure for planting in open ground in the fall must be carried out at least 2 weeks before the expected frost. Rooting in closed ground is carried out when the weather conditions change, when the moment of laying the planting material in open ground has already been missed.
Did you know? Japanese roses of the Chameleon variety are able to change the color of the petals by the time of day. They are scarlet in the morning and white in the evening.
In the open field
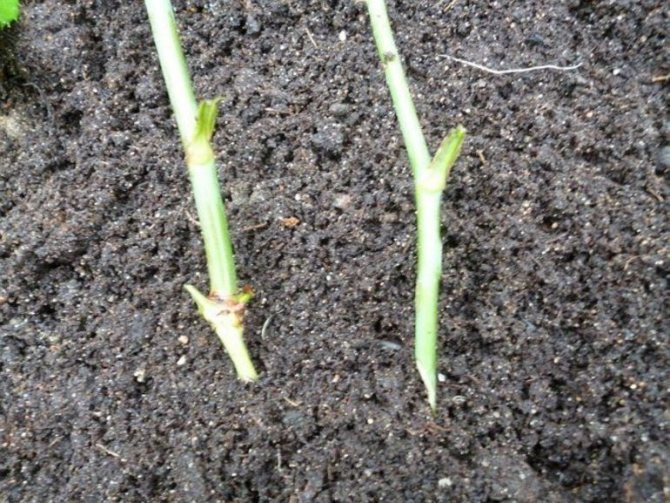
Cuttings are ready for planting immediately after cutting.
After proper processing of both sections, you can start planting work:
- Dig planting holes 25-30 cm deep at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other.
- Fill the holes by a third with cut grass.
- Place a layer of compost on top of the grass.
- Pour 1 liter of warm water (+ 20 ° C) into the pits.
- Once the moisture has been absorbed, center the cuttings at an 85 ° angle.
- Fill the voids with soil and compact.
- Cover the soil around the seedlings with peat.
- Cover the seedlings with transparent glass jars - they can be removed only immediately before transplanting to a new location.
- Also cover the soil between seedlings with peat or dry foliage.
When disembarking directly to a permanent place, all actions are identical to those described above.
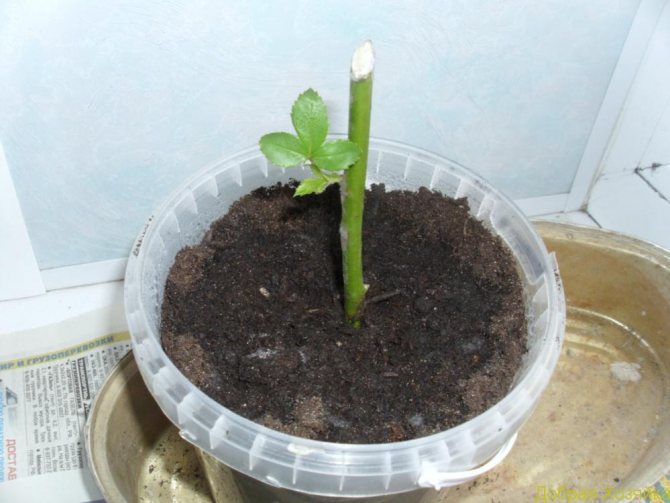
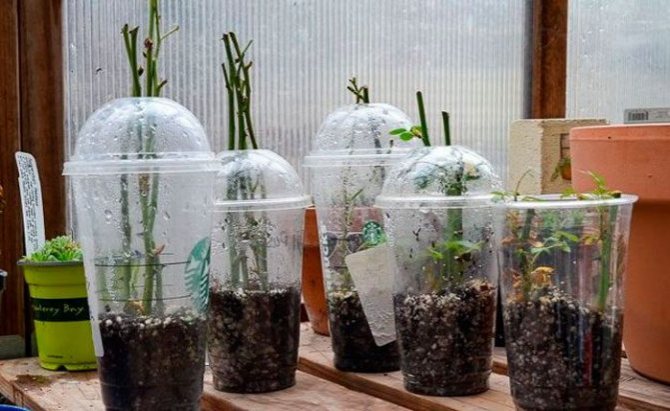
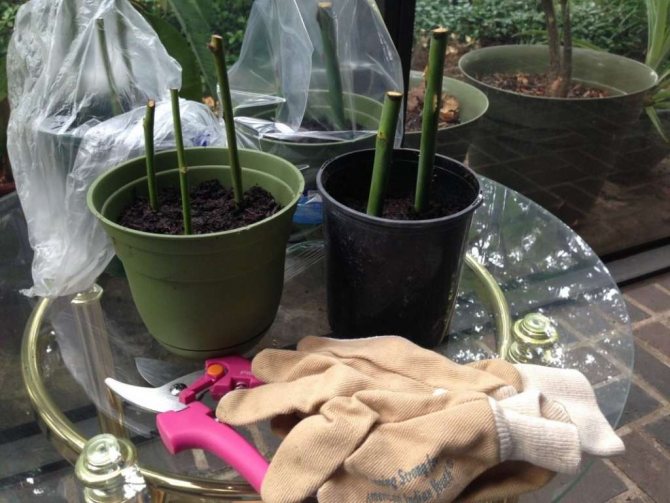
Indoors
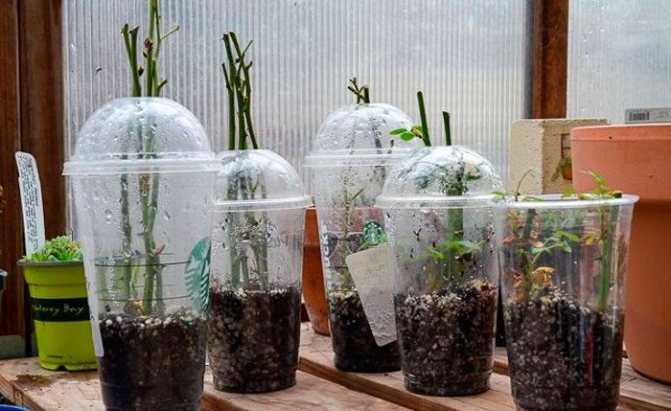
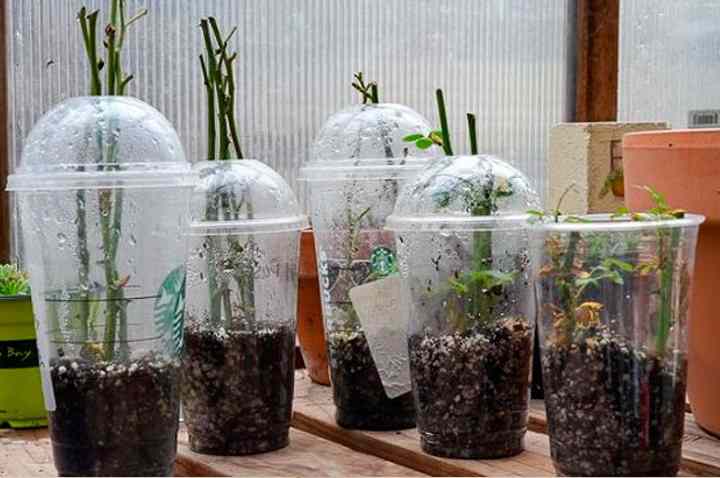
For rooting, a deep, spacious container is required. It is best to use plastic buckets in this case.


Step-by-step instructions for rooting rose cuttings indoors:
- Make drainage holes in the bottom of the container using a 1 cm diameter screw, heated over the fire.
- Cover the bottom of the container with expanded clay.
- Mix soil with peat in a 1: 1 ratio.
- Add 20% vermiculite to the resulting substrate.
- Fill containers with substrate and add 0.5 l of water.
- Mark the holes with a wooden stick at a distance of 10 cm from each other.
- Insert cuttings into the holes and compact the soil around them.
- Cover the container with a transparent bag, securing securely at the edges to create a vacuum effect.
- Move the containers to the glazed balcony.
Did you know? An even number of flowers does not always symbolize a mourning event. For example, in England, to receive 2 yellow roses as a gift from a man means a declaration of love.
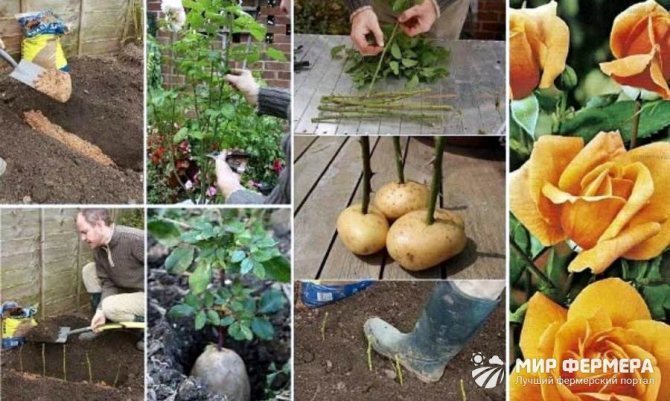
Rooting by different methods
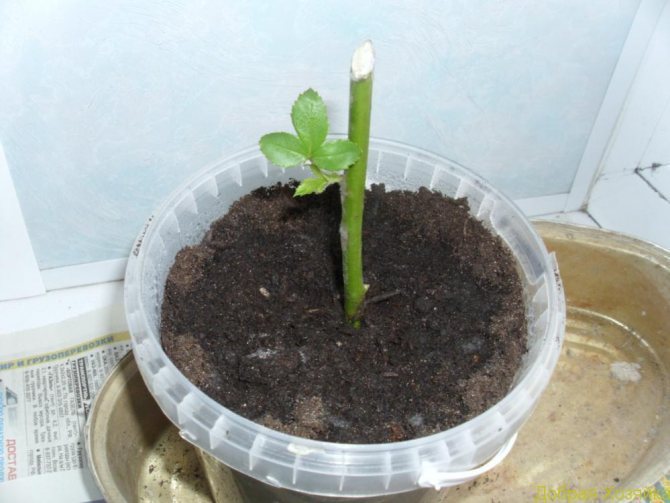
There is another unusual but effective method of rooting cuttings in potato tuber... The preparation of the cutting is carried out according to the usual scheme. Previously, it is kept in a weak solution of manganese, then soaked for 12 hours in a mixture of equal parts of aloe juice and pure water. After this time, the cutting is removed and inserted into the potato tuber. Potato with a shoot is placed in a pot, 2/3 filled with a nutritious substrate. The soil is thoroughly watered with a strong manganese solution, the potato is lightly sprinkled with earth on top.
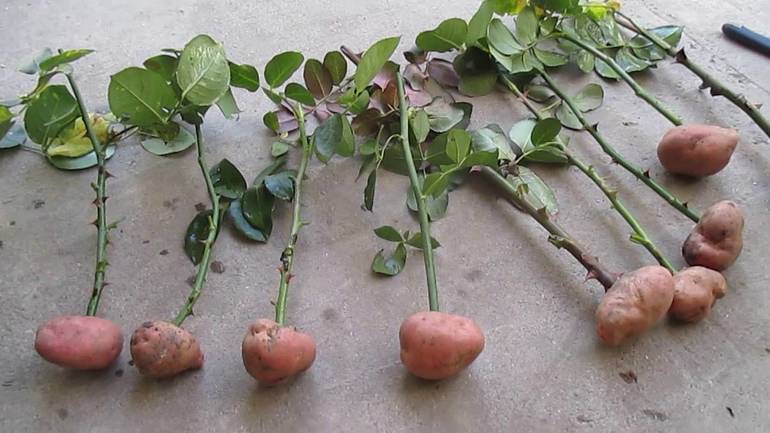


Important!
In the future, the soil in the container will need to be watered regularly as the topsoil dries out. It is best to use pre-settled water with the addition of a small amount of sugar (about 10 g per glass of water). You need to water every 5 days.
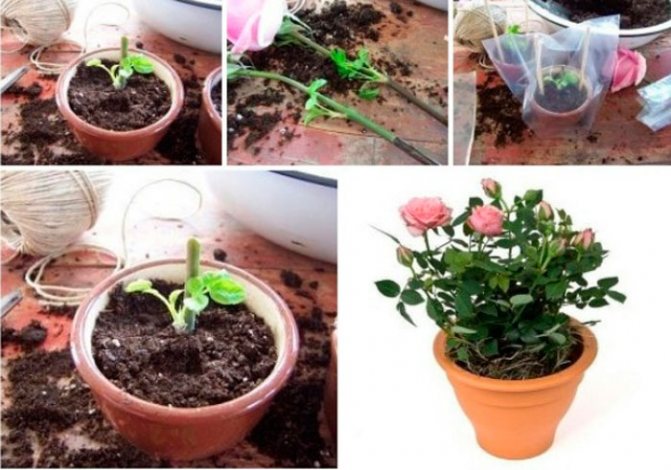
Those who want to once again enjoy the beauty of a withered rose from a bouquet, you can graft it and grow a young bush. To do this, prepare cuttings from a pink stem in the usual way. The resulting segments can be rooted in flower pots. This can be done at any time of the year. Instead of soil pots, you can use plastic bags filled with fibrous peat or moss. The substrate is abundantly moistened with a mixture of pure water and aloe juice in a ratio of 9: 1.
Packages with cuttings are slightly inflated, tied and hung from the window frame. A greenhouse effect is formed inside due to the increased air humidity. This will lead to rapid root formation. The humidity of the air and soil must be maintained constantly. In order for the plant to form healthy, powerful roots, new leaves and buds must be pruned before the rose is transplanted into open ground in the spring.
Plant care after cuttings
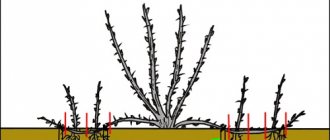
When planting cuttings in open ground in the fall, you need to take care of a reliable shelter for the cuttings.
To do this, build a mini-greenhouse according to the following scheme:
- Cover the plantings with coniferous branches.
- Install at a distance of 50 cm from each other metal arcs above the landing.
- Cover the top of the arc with agrofiber.
- Press down the hanging edges of the agrofibre with boards or bricks.
- Sprinkle some fallen leaves on the mini greenhouse.
- As soon as it snows, cover the greenhouse with it.
When planting in a permanent place in the open field, such shelters must be built over each plant. With the arrival of spring, the shelter is removed in layers, focusing on the temperature regime. As the temperature rises to + 10 ° C, the first layer of the shelter is removed, and then one layer at a time every 5–7 days.


When landing in containers, it is important to ensure that the temperature on the balcony is 5 degrees higher than the outside temperature. When the temperature in the room drops to -5 ° C, it is better to cover the plantings with old clothes or bring them into the apartment for a short time.
Did you know? To make 1 liter of rose oil, you need to spend about 3 tons of petals.
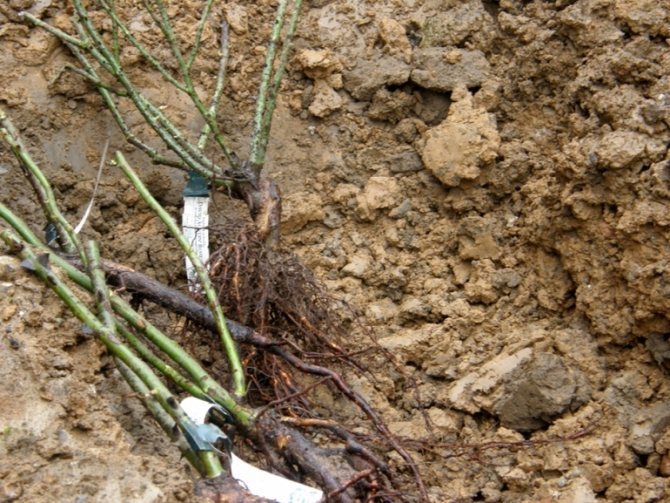
In the spring, 2 weeks before transplanting the rooted cuttings into the ground, dig up the area, pour a 1% solution of copper sulfate. After 2 days, dig up the soil again, add 10 kg of sand and compost for each 1 m². After 10 days, dig up the soil again, level the area and make a marking for the flower bed that is convenient for yourself.
Add 10 g of superphosphate to each well.
For planting, mix the soil from the holes with rotted manure, add 400 g of wood ash for every 10 kg of soil. Water the plants 2-3 hours before planting. After removing the seedlings from the soil, assess the condition of the root system, treat with "Kornevin" mixed with activated carbon and "Fundazol".
After transplanting, water the plants with a little water, about 300-400 ml per well.
Carry out the first full watering after transplanting in 2 weeks. At the same time, you can carefully remove the layer of wax with which the upper end of the seedling was processed. Start applying fertilizers a month after planting. You can use universal rose dressing.
For the first time, dilute them at a concentration 2 times less than indicated in the instructions. With each successive time, increase the dosage by 10%, bringing it to the maximum.


Plants develop well and bloom when mineral complexes introduced by the foliar method alternate with organic root feeding (slurry diluted with water in a 1: 2 ratio). At the budding phase, it is best to feed the plants with phosphorus compounds, abandoning nitrogenous fertilizers.
In this regard, potassium monophosphate has proven itself well. It is diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 3 and used as root and foliar feeding. Watering is carried out moderately, about once a week, after the upper earthen coma has dried to a depth of 3-5 cm.
It will also be helpful for you to learn how to properly grow roses from seeds.
Some subtleties
In order for the cultivation of roses from cuttings in the fall to be successful, you need to know and observe some subtleties. This will help speed up their growth in the autumn and winter and avoid the development of diseases. The rules for preparing the material are as follows:


- Shoots for making cuttings are best obtained from a rose flower when pruning old bushes.
- Rose is a plant that does not thrive on all types of soil. Acidic soil and soil with a high clay content are not suitable for it. For planting in pots and open ground, it is necessary to prepare a mixture of humus with turf soil and river sand.
- Before planting, the soil must be disinfected.
- As the top layer dries out, the soil needs to be moistened.
- The film or plastic jar is periodically removed from the cutting to ventilate the plant.
Disease and pest control
Roses can suffer from diseases such as:
- Powdery mildew - progresses in the second half of July, quickly spreads to all plants. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of a white coating on the leaves and shoots. If the first symptoms are found, treat with the "Skor" preparation (2 ml / 10 l of water), cutting off the previously affected parts of the plant. For prophylaxis in the spring, treat with a solution of copper sulfate (100 g / 10 l of water).
- Rust - caused by fungal spores. Signs of the disease are the appearance of orange cushion-like seals on the leaves and shoots. Spraying with Hom (40 g / 10 l of water) will help to cope with the disease.


Among the pests for roses are dangerous:
- Aphid - to get rid of the pest will help three times spraying with an interval of 10 days with the drug "Agrovertin" (2 ml / 1 l of water).
- Spider mite - carry out 3 treatments every 7 days with colloidal sulfur (40 g / 10 l of water).
- Leaf roll - a one-time treatment with Iskra (1 tablet / 10 l of water) will help.
- Clicker beetle - you can get rid of the pest by introducing the preparation "Bazudin" (20 g / 1 m²) into the soil.
Important! After pollination, roses form fruits in place of flowers. The wilted bud must be removed from the bush, otherwise the formation of ovaries will jeopardize further flowering this season, since the plant will direct all its forces to planting seeds.
Useful Tips
To get beautiful rose bushes, take on board some practical tips:
- Water not at the root, but in a ditch (depth 10 cm), dug at a distance of 20 cm from the main stem of the rose - this will help to avoid root rot.
- Loosen and mulch the soil with compost after watering to maintain soil moisture and further nourish the plants.
- When planting grafted roses, deepen the budding site into the ground by 3-5 cm.
- Carry out the last top dressing in September with potash fertilizers - this will help to increase the winter hardiness of the plants.
The best way to propagate roses is considered to be cuttings, which coincide with autumn pruning. The main task of the gardener is to provide future plants with a reliable shelter for the winter. To do this, you can use any of the above methods.
Alternative way
Some growers prefer other methods to propagate roses by cuttings in the fall. The shoots are placed in boiled cold water, which changes every 2 days. In this state, the cuttings are kept for 15 days. During this time, a whitish ball should form at the tip of the shoot - this is the embryo of the future root. You can transplant the cutting into the ground already at this stage, or you can hold it in water for another week to form full-fledged roots. However, this method of rooting also has some disadvantages - the roots lack oxygen in the water and they can begin to rot.
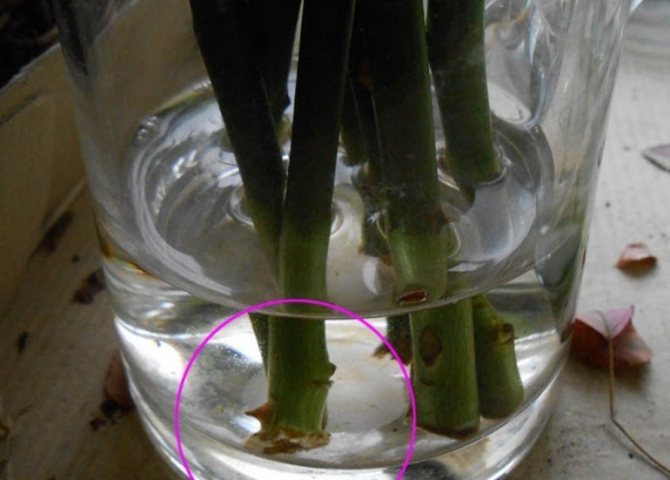


Important!
For the shoot to form healthy, viable roots, it needs a sufficient amount of oxygen. In addition, it is important to maintain an optimal level of air and soil temperature, as well as a sufficient amount of sunlight.
During the first 2 years, it is necessary to remove all formed leaves and buds from a young cutting. If this is not done, the rose bush will spend all its energy on them and will not be able to form a good root system. The resulting seedlings must be regularly watered and ventilated. After the formation of strong roots, you can move the rose to a permanent pot.