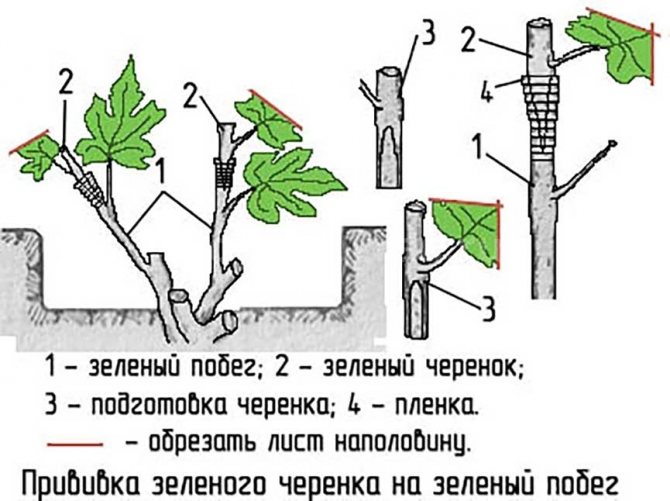
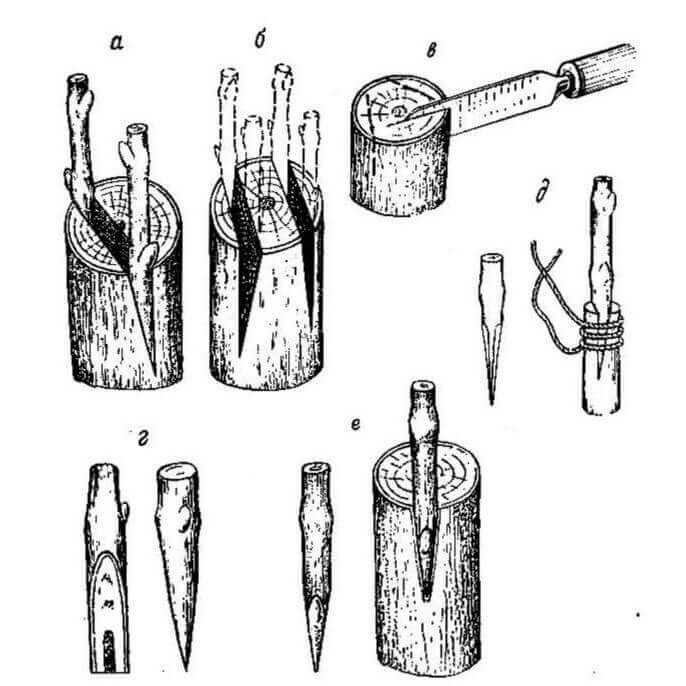
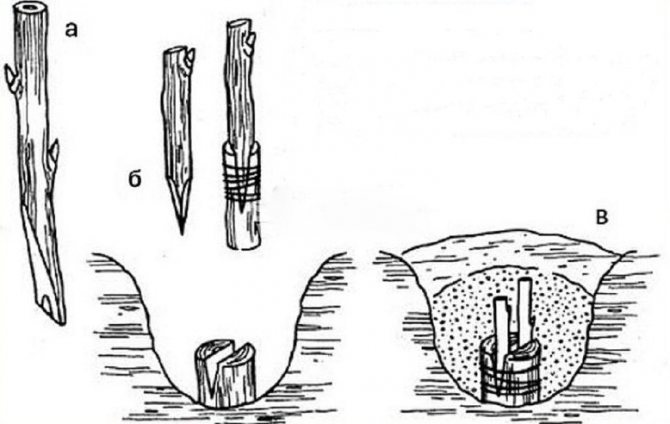
What is the vaccine for?
Some gardeners do not know why they are grafting plants. Therefore, it is recommended to figure out in advance why such a procedure is being carried out. Grafting is done to:
- Strengthen the stems. After grafting, the plant stems are strengthened by increasing their diameter.
- Adapt to new conditions. Grafted bushes quickly get used to the soil in which they grow and to the weather conditions.
- Give grape seedlings certain properties. These include immunity to most insects and diseases, earlier ripening of fruits, accelerated growth.
- Form the most suitable growth shape. Vaccination allows gardeners to independently give the bushes one form or another.
- Grow several different varieties of grapes at once. This saves space in the garden.
- Renew cultivated varieties. Features of the procedure allow you to renew old or diseased grapes by means of grafting.
Why plant grapes

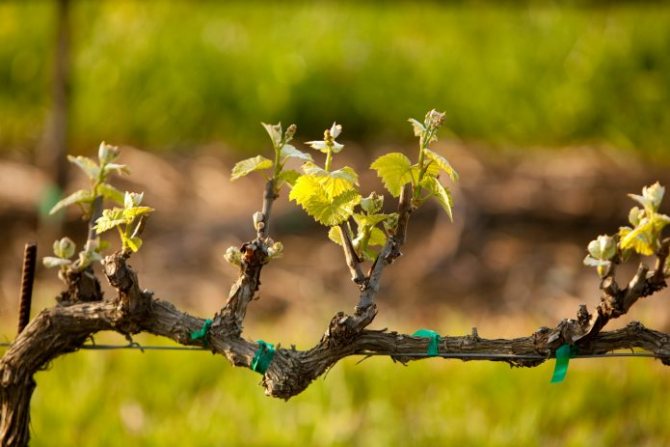
If the vineyard has suffered over the winter, grafting can restore the entire ground part of the bush within one to two seasons.
Grapes are planted for the following purposes:
- obtaining in a short time new grapes for partial replacement of plantings;
- complete change of variety;
- increased yield;
- reproduction of the variety you like.
Basic rules of vaccination
Grafting is considered a difficult procedure that many inexperienced growers cannot handle. If you do not know how to do this correctly, you can damage the bushes, because of which they will die.
Therefore, it is better to familiarize yourself with the basic rules of vaccination in advance and figure out what you should pay attention to.
The basic rules that will help to carry out the procedure successfully include the following:
- when grafting grapes, methods are used green to green or black to black;
- in order for the scion to take root well, use only the most suitable grape varieties for certain climatic conditions;
- for grafting, a scion with resistance to pests and diseases is selected;
- the growth rate and ripening time of the fruits of the scion and rootstock should not be different;
- if grafting in a stem is carried out in spring or late winter, then the scion will have to be harvested in early autumn;
- when carrying out the procedure in the summer, they use recently cut branches;
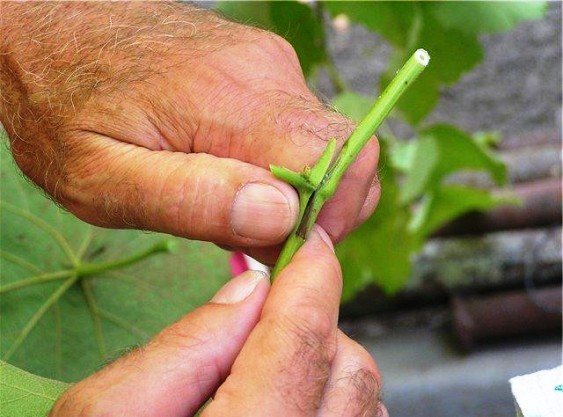
- to cut the scion, use a knife disinfected in an alcohol or manganese solution;
- when trimming cuttings, the knife blade is directed away from you so that the cut does not turn out to be concave;
- vaccination should be done when the temperature is more than 15-17 degrees Celsius.


Justification of the need for grafting grapes
At horticultural fairs, nurseries and shops, there are now many native-rooted varieties with excellent characteristics, cuttings take root well: so why then use grafting? For example, in Europe, it was possible to stop the invasion of the grape aphid - phylloxera, imported from America, by grafting local varieties on American rootstocks that are resistant to this pest. Our latitudes are not afraid of such an attack, then what benefit can be derived?
Grafting helps the grower win on the following points:
- avoid uprooting a bush that has completely lost its shoots (due to frost, damping, damage by mice, etc.), and restore the crown within a couple of seasons;
- quickly multiply inaccessible, rare or expensive varieties;
- replace a boring or disappointing variety with a new one, using an already developed root system;
- reduce susceptibility to disease;
- to increase the winter hardiness of the vineyard using cold-resistant rootstocks;
- to increase the tolerance of some varieties to unsuitable soils - excessively acidic, calcareous, arid, or, on the contrary, with a high level of groundwater;
- get earlier harvests by grafting early and early ripening varieties on rootstocks - this is especially true in the northern regions;
- to create family bushes that combine shoots of different varieties on one root - this not only saves space, but also looks very decorative;
- to some extent improve the commercial characteristics of berries: certain combinations of rootstock and scion can influence the taste and size of the grapes.
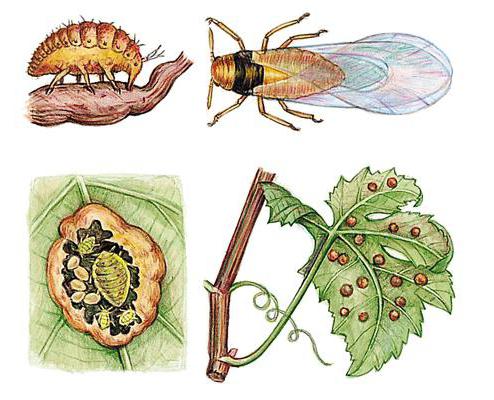


The grape aphid that led to the need to graft vineyards in Europe
After reading such an impressive list of benefits, many growers will surely be excited to start grafting immediately, but in fact grafting grapes is a little more difficult than grafting fruit trees. First of all, do not forget about such an important concept as affinity, or the compatibility of the rootstock and the scion:
- The stock is the basis of the fruit tree, then ON what is grafted. The type of root system, plant resistance to diseases and adaptability to external factors (cold, drought, unpleasant soils), as well as some qualities of the fruits (size, ripening rate, etc.), depend on its characteristics. The stock organizes nutrition and growth.
- Graft - a stalk or bud, which is grafted onto the stock, determines the varietal qualities of the fruit and the yield.
In the latitudes not so long ago covered by viticulture, the topic of affinity for local varieties has been little studied, unambiguous recommendations are given for individual groups of varieties, but for most there are a lot of doubts and disputes. Therefore, you should be ready for experiments that involve both failure and joyful discoveries.
What tools and materials are needed for vaccination?
Grafting begins with the selection and preliminary preparation of special tools. Choosing the right tools should be taken seriously. If they are not sharp enough, then the scion or rootstock can be damaged.
To complete the procedure, you will definitely need a knife. There are several types of knives that you can use:
- Garden. Such a tool is ideal for cutting the stems and unclogging the cut.
- Oculating. It is used when carrying out budding with the help of the kidney. The features of such a knife include the concave shape of its blade, which makes it easier to trim the bark.
- Copulation. It is considered the best knife for grafting plants by grafting. The copulating tool has a perfectly straight blade, with which it is possible to make straight cuts.
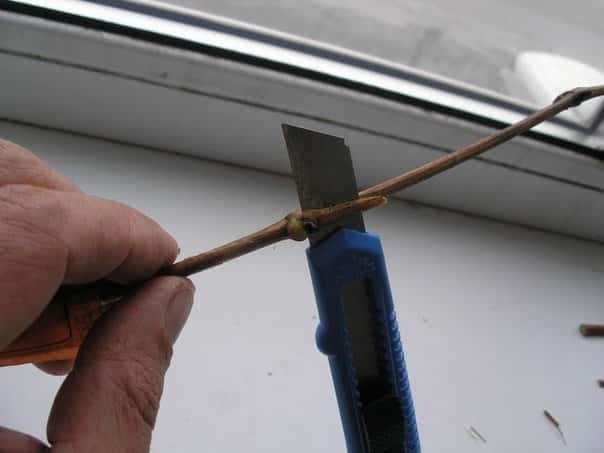


In addition to a knife, they use a grafting pruner, which is needed to cut the stems of grapes. The procedure can be carried out with the following types of secateurs:
- Standard. Most often, it is he who is used when cutting the branches of grapes, since it does not damage their surface and makes even cuts. The distinctive features of the standard models include the fact that their lower blade is slightly offset.
- Anvil. These tools do not have offset blades and are therefore not easy to cut through thick branches. Gardeners advise using an anvil pruner only for cutting off dried old twigs.
- With ratchet mechanism. It is a versatile model ideal for pruning dead and young branches. Due to the ratchet mechanism of the tool, cutting the stems requires little effort.
See also
Instructions for the use of "Ridomila Gold" for the processing of grapes, dosage and waiting timeRead
Useful Tips
- The stalk should not be very long - 1-2 buds.
- Several cuttings can be grafted onto a thick stock. So there will be a high probability, if one of the shoots dies, still get a healthy bush.
- The soil under the stock will be under a plastic wrap for the first two years, therefore, before grafting, it is advisable to saturate the soil with oxygen by loosening.
- If there are roots on the scions, then they must be removed from the surface of the plant in order to prevent them from rooting on their own.
- Before grafting, it is recommended to properly fertilize the soil around the stock.
- It is important to remove any growing points around the graft, otherwise the plant will be weak.
As you saw from this article, grafting of grapes in autumn is an excellent way to update the type of culture, if you do not like the one that is taking place, also restore an old bush or damaged vine, and also propagate rare and valuable grape varieties, therefore, before to destroy the bush you do not need - think, is it worth it?
Happy vaccination!
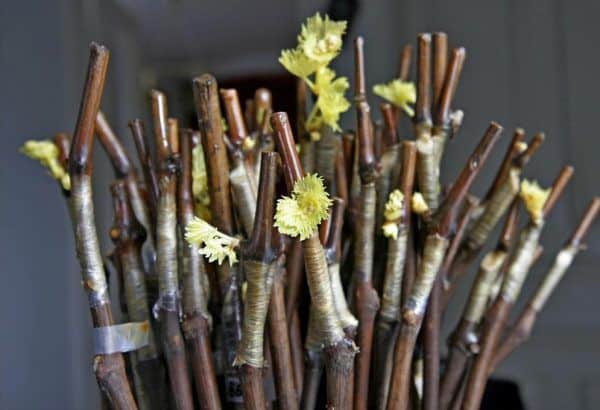
Harvesting cuttings
Before grafting, they are engaged in preliminary harvesting of cuttings. It is recommended to do this in early autumn, before the first night frost. Cuttings cut in winter or the second half of autumn are not suitable for grafting.


When preparing, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Cuttings are cut with pruning shears only from healthy bushes that bear fruit well. At the same time, you cannot cut them off from the top of the shoots, since such branches will not take root well. Therefore, a part of a healthy shoot is cut off at a distance of about 30-40 cm. It is also an important condition that the cut branches do not have mechanical damage and are not too thin.
- A sharpened pruner or knife is used to cut the branches. The length of the cut cutting should be 10-12 cm.
- If you cut the twig unevenly, then in the future it will not take root. Therefore, it is recommended to practice a little on old branches before harvesting. When pruning, make an incision 5-6 mm deep and then carefully insert the knife blade to the end of the branch so that the cut is even.
- The cuttings are placed in a large container filled with copper sulfate. This is done to disinfect the cut site.
Mistakes that beginners make
In order for the stalk to take root successfully, we try to avoid the following mistakes:
- Incorrect storage of the scion. Cuttings must be treated with paraffin or stored in a bag. Otherwise, they will lose a large amount of moisture, dry out and not take root.
- Cleavage too deep. This can lead to moisture rot.
- Rough and rough cut. It must be sanded, otherwise the stalk will not take root, and bacteria will form on the cut.
Vaccination in spring
Some gardeners are busy grafting grapes in the spring. The procedure should be carried out in mid-April, when the soil warms up to 10-12 degrees.


Budding
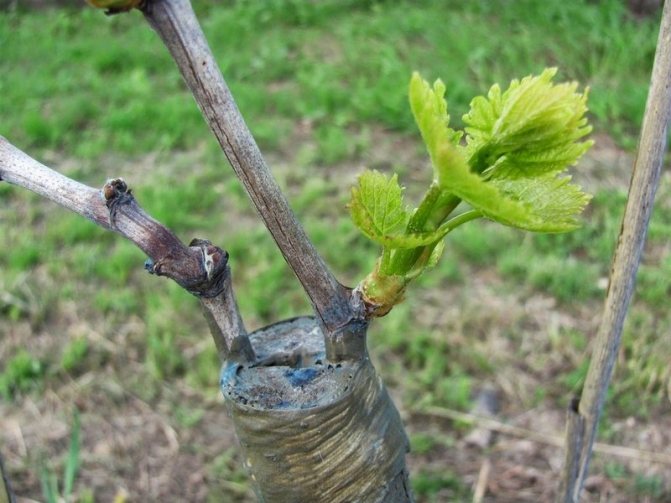
When budding is carried out, you will have to cut off a small shield on the stem. Then a cut is made on the stock with the same dimensions so that the scion can be combined with the stock. After crossing the branches, the place of their connection is carefully wrapped with a plaster.
Cleavage grafting
The method of grafting grapes in the split is considered the simplest and most common among winegrowers. To carry out the procedure, you will have to select in advance the blackest and thickest branch from which a 6-7 cm long stalk is cut off. Then a 2-4 cm deep incision is made on the rootstock, to which the cut off branch is applied. The junction of the branches is carefully wrapped with a tourniquet.
Split grafting into an underground wellbore
A few days before grafting grapes, the harvested stems are placed in a solution prepared from "Epin".Then the stem of the plant, to which the stems will be grafted, is dug in to a depth of 15-20 cm.After that, the roots that are on the surface of the soil are cut off, and a 3-5 cm long incision is made in the center of the trunk. A scion is inserted into the created incision, after which it is lubricated clay and wrapped in cloth.
Drill grafting
Before grafting, the drill is disinfected in a manganese solution for half an hour, after which a hole is drilled in the grape trunk. Its depth should be about 5 cm. Then a handle is inserted into the drilled hole and the joint area is carefully lubricated with clay.


Grafting methods
For grafting grapes, the same technologies are used as for other fruit trees:
- split / half split,
- simple copulation,
- improved copulation,
- budding with an eye,
- on the omega-shaped thorn and others.
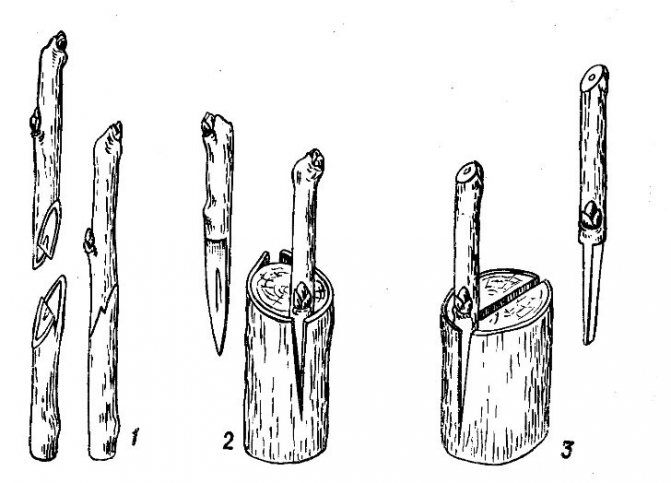
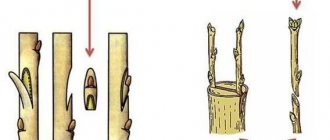
These are the ways in which parts of the rootstock and scion are cut and applied to each other. Many gardeners constantly use the easiest ones - copulation and splitting, and are satisfied with the result: it is with these methods that it is worth starting to learn grafting. So, a simple copulation is available to anyone who knows how to handle a sharp knife:
Everything is extremely simple: cut, connect, fix
There are three secrets to success:
- equal diameter of the scion and rootstock;
- a sharp and clean (up to sterility) knife - all grafting instruments must be clean in order to avoid contamination of the sections with bacteria or fungi;
- coincidence of cambial layers at the junction of the grafting.
The last point needs some explanation. Consider the structure of the cutting:
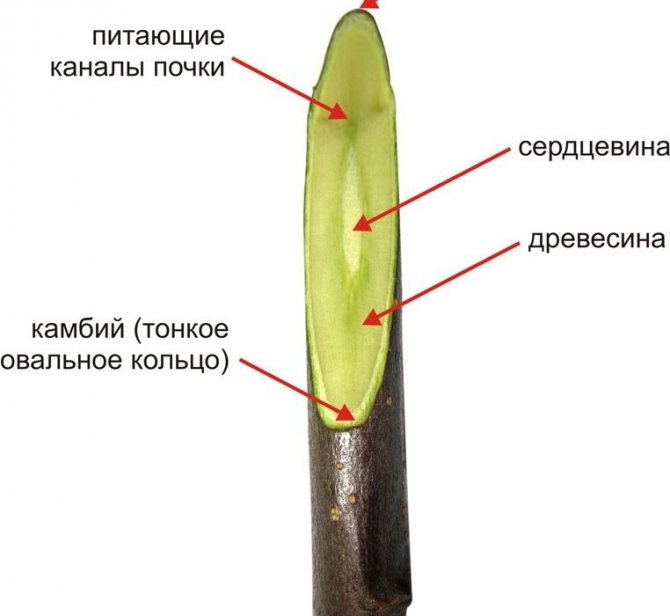

Cambium - a thin transparent layer under the bark of a tree
Cambium, also known as the cambial layer, is a thin, slippery structure that we can find by removing bark from a tree. It is he who is responsible for the growth of shoots in thickness and the formation of vessels that feed the plant. Cambium is especially active in spring, during the period of sap flow, which explains the greatest popularity of spring grafting. Touching, the cambial layers of the rootstock and scion grow together into a single whole (form an adhesion), and the formation of common vessels begins: nutrition is established in the grafted plant, the buds start to grow. Therefore, the contact of the cambium on at least one side of the joint is a prerequisite.
Improved copulation is a method that provides a more reliable fixation of the cuttings. On the cut, the so-called. a tongue that keeps the scion from slipping off at the slightest movement of the joint:
A little more effort - and the scion is fastened much more securely
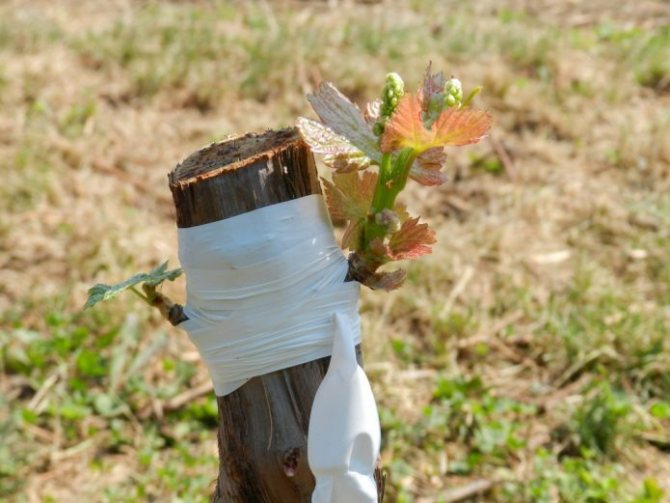
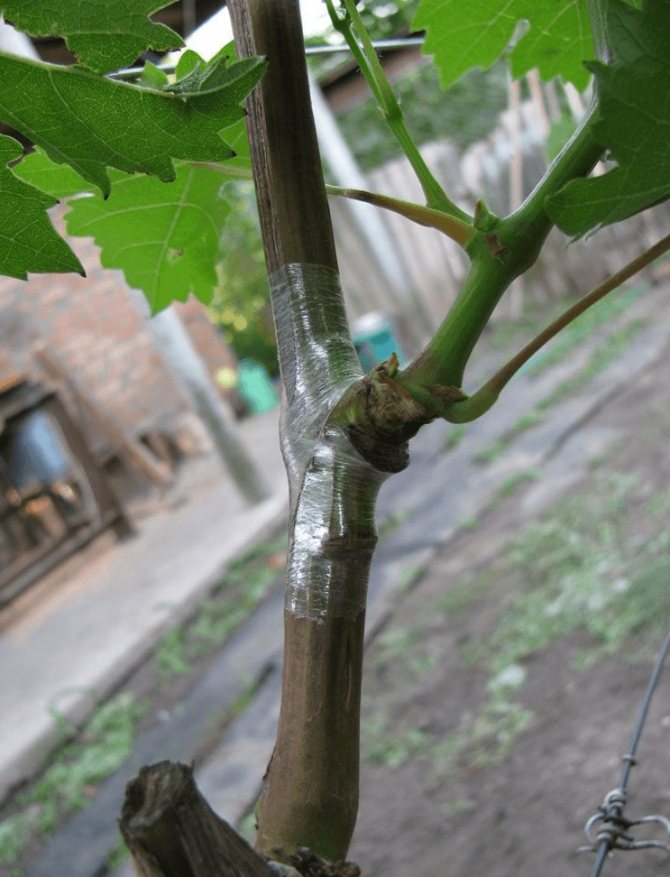
The junction of any graft is always fixed with a film (sometimes also with electrical tape), and the upper cut of the scion is covered with garden varnish or waxed.
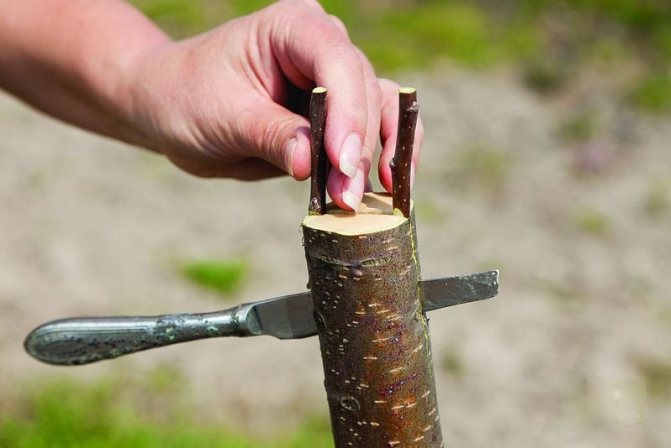
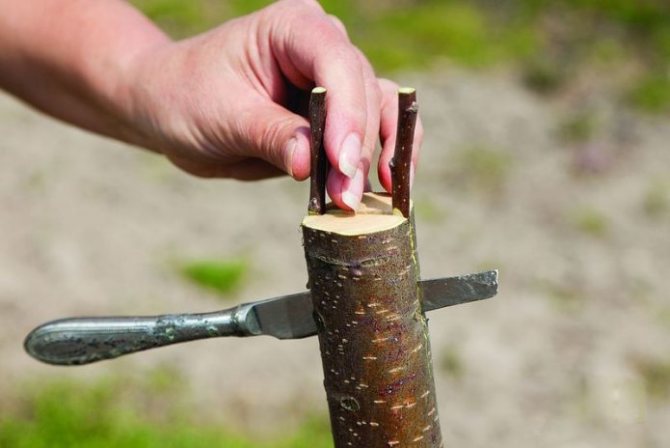
The cleft grafting method is also popular. At the same time, one stock is inserted into a stock split to a depth of 3-5 cm, and if the stock diameter allows, two two-three-eyed (ie with two or three buds) cuttings sharpened with a wedge. The cambial layers should touch here along the edge of the cleft. The cleavage is pulled together with twine, wrapped with foil, waxed or coated with clay:
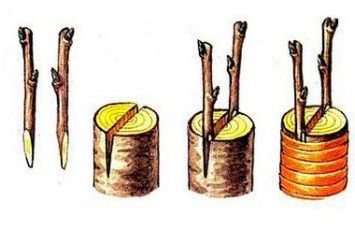

If the diameter of the stock allows, two cuttings are grafted at once
It is by this method that grafting of grapes is most often carried out - this is the grafting of an adult plant in order to rejuvenate or completely change the variety. Its main advantages are the accelerated receipt of a new crop and the absence of the need to spend efforts on uprooting the old root, in the place of which, moreover, it is undesirable to plant the same crop for several years later (the so-called soil fatigue). In this case, they are grafted into a stem or root.
It is impossible not to mention such a method as budding with an eye - also popular, but more painstaking, requiring skill. At the same time, a bud with part of the bark and cambium is cut from the scion and placed in a T-shaped incision in the bark of the stock. After the scion grows, the stock above the grafted bud is cut:
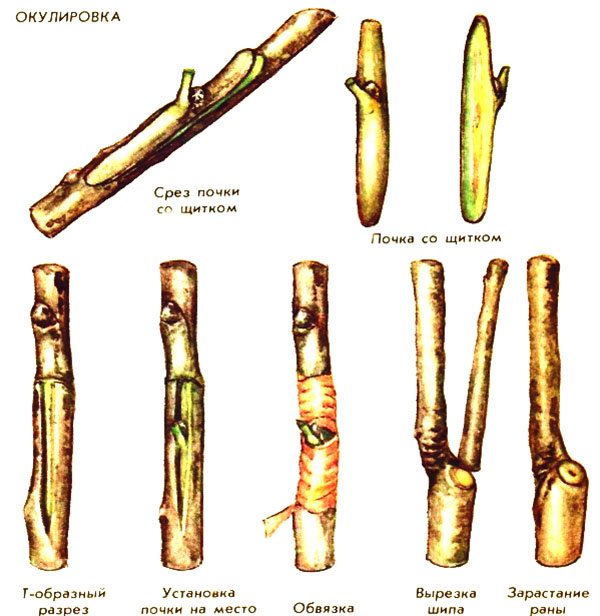

You need to carefully cut the bud of the scion and place it under the bark on the stock
Having gained the experience of successful vaccinations with these methods, you can begin to master the more complex ones, which are willingly described by experienced winegrowers on the forums.
However, simplicity and good results are also promised by advertising of grafting secateurs, which allow grafting cuttings on the so-called. omega-shaped thorn. However, negative opinions prevail about them:
This device is a toy for amateurs who, for some reason, need to make several hundred "factory" vaccinations - on absolutely identical rootstock and scion. If it touches to graft cuttings, then they are all different ... And density, and thickness, and hump .... Sharpening such a pruner is a problem. Those cutting edges that are straight are still possible to sharpen, and bent iron is impossible in principle, not to mention the finishing straightening on a leather belt with GOI paste.
Nikolajvse-o-vinogradnoy-loze-koroleve-sada-3987.html
... and the strength of the grafting is also apparently low. We have normal grafts with a long cut and a tongue that breaks with the wind, then the bird sits down, and then there is no need to talk about breaking strength at all. IMHO, this is pampering. Although the business is certainly the master's.
I will not say
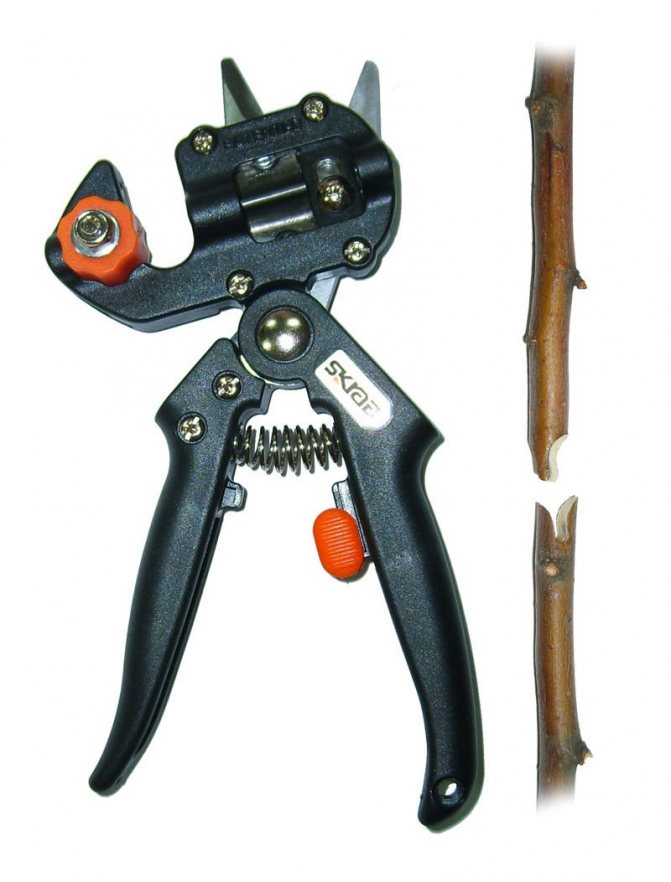


On the right is a sample of cuttings treated with secateurs.
Thus, the classical methods still seem to be more reliable and effective.
Autumn grafting
Grafting of grapes on an old bush is most often done in the autumn. By crossing young stems with old bushes, they increase the level of fruiting of the plant, thanks to which a tasty harvest can be obtained within a year. Grafting of grapes in autumn is carried out at the beginning of September, when the summer heat subsides. In this case, you will have to monitor the minimum daytime temperature. If it falls below 15 degrees, the scion will not take root.
First, the thickest stems are cut from the old bush. To do this, use a sharp pruner or saw if the branches are too large. All sections must be treated with a manganese solution to disinfect them.
See also
Instructions for the use of fungicide "Quadris" for the treatment of grapes, waiting time and actionRead
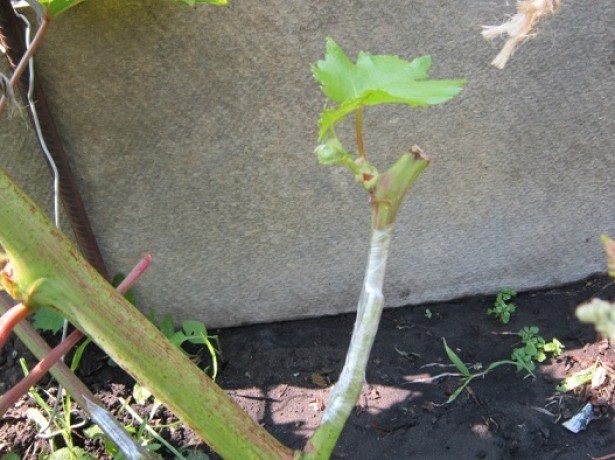


After pruning the old bushes, they begin to prepare the cuttings. They are treated with a liquid to improve growth and soaked in water for 2-3 days. When more than three swollen buds appear on them, they are carefully inserted into the prepared incision on the stem of an old grape bush. Then the junction is filled with sawdust and tied with a tourniquet. Some gardeners wrap it with plastic oilcloth.
How to care for a grafted grape bush
Gardeners are advised to adhere to the following care rules:
- constant observation of the bush - after 14 days new shoots should appear on the shanks, if they are absent, then all procedures are repeated;
- young roots that do not come out of the stock are regularly excised - otherwise it will not be a graft, but a standard planting of grapes;
- when the junction is clamped, juice flows out of the plant abundantly - the dressing should be loosened, otherwise the process will not take root;
- in order to avoid the weakness of the bushes around them, you need to periodically remove weeds;
- if the process took place in autumn days, then the vineyard is covered with straw, creating additional protection from the cold.
After a certain period of time and after the complete engraftment of two parts of the vine, the plants need regular treatment for fungal infections. Infection can negatively affect the health of the bushes and the future harvest. Newbies can easily cope with grafting grapes - subject to the work scheme.
Summer vaccination
Grapes are grafted in summer with green or black cuttings. In the latter case, twigs harvested in the autumn are used. They are soaked in water in advance to speed up the swelling of young buds.
August is great for grafting. Some growers perform the procedure in July. During grafting, the scion is carefully trimmed at an acute angle. Then a split is made in the largest stem of the stock, into which a grape branch is inserted. It is carefully wrapped in twine and wrapped in a film.
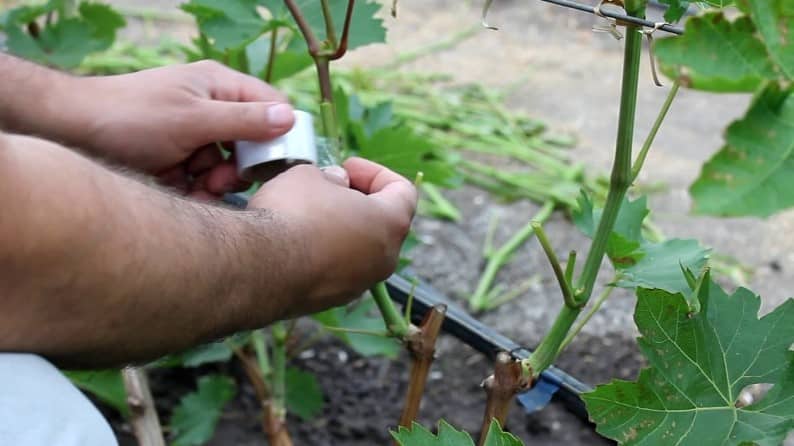


Sleeping bud budding
Many consider this method of budding the most reliable, since the survival rate of plants is about 90%. To vaccinate, it is enough to prepare one grape bud. It is cut from the ripe branch itself, and it is cut off along with a piece of wood and bark. The cut kidneys are wrapped in a damp cloth and soaked for 3-4 hours. Then an incision is made on the surface of the rootstock bark, into which the prepared bud is placed.
The area with the cut is carefully lubricated with plasticine, which is necessary to retain moisture.
Improved copulation: technology
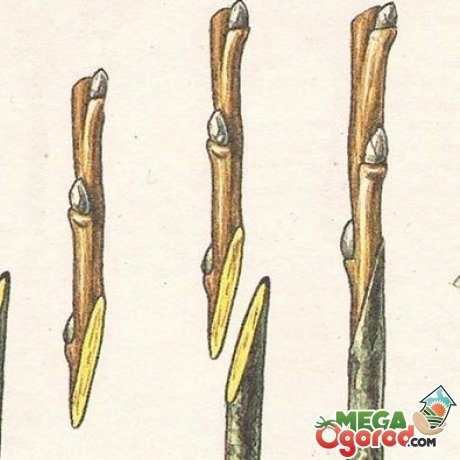

Procedure for winter grafting:
- Choose a scion and rootstock equal in diameter.
- On them with a sharp knife, cuts are made obliquely. They should be even, length - 3 cm.
- The chubuk is shortened by 2 kidneys.
- On fresh cuts of both grape varieties, cuts are made with a knife. The result will be "tongues".
- The stalk is connected to the base so that the grooves of the tongues "go" into each other, and the cambial layers coincide.
- The vaccine is hidden under polyethylene.
- The top of the cutting is treated with garden pitch.
- It is recommended to apply waxing of the junction.
- The grafted culture is put in boxes and left warm for 15-20 days. Rhizomes are sprinkled with wet sawdust.
With knowledge of copulation, the plant can be successfully grafted. A not-so-good or damaged grape does not have to be uprooted. Winter grafting is a great way to bring your shrub back to life.
More information can be found in the video.
Winter grafting
Inoculation in winter is most often used for crossing bushes over two years old. This is done in the last week of February or in the first half of March, when the frost is weakening. Some also plant young seedlings in pots in winter. In this case, you will have to vaccinate at the end of December.


They have been preparing the bushes since the fall. In October, they are dug up and trimmed so that the length of the trunk does not exceed ten centimeters. Then the dug out seedlings are sprinkled with sawdust, treated with a manganese solution and transferred to the basement. 3-4 days before the procedure, they are placed in a container with warm water for two days and grafted into the cleavage.
The grafted plants stand for about a month in a room with a temperature of at least 20 degrees. During this time, you will have to ensure that new shoots do not grow on them. It will be possible to plant grape seedlings in the garden when the temperature outside is about 17 degrees Celsius.
Grafting grapes - step by step instructions for beginners
Adding an article to a new collection
Grapes still seem to our gardeners to be a very capricious culture. However, in matters of vaccination, it hardly differs from other fruit. In addition, this procedure solves many problems.
Some varieties (as a rule, their fruits are the most juicy and tasty) do not have good winter hardiness, they often get sick, are attacked by pests and die very quickly. To avoid this, a finicky grape variety can be grafted onto an unpretentious "relative". Thus, you will be able to get a rich harvest of delicious fruits.
Also, with the help of grafting, you can get several grape varieties on one bush. So you will not only enjoy the fruits of different tastes, but also get a beautiful plant that will perfectly fit into the landscape of your site.
In addition, several varieties of grapes on one bush is also a good space saving in the garden. It seems that many crops were planted, but at the same time they took up little space.
If you are tired of a particular grape variety, you can completely replace it with another one. And for this you do not need to plant a new plant and wait a long time until it reaches its fruiting age. For example, grafting into a split can replace an unnecessary variety with a more productive one.
Grafting grapes is not much different from grafting fruit trees (for example, apple trees or pears), but there are still some peculiarities that must be taken into account in order for the "operation" to be successful.
It is not so easy to plant a cultivated grape variety on an old bush, for this it is necessary to properly prepare the scion and rootstock.
For most popular grafting methods, the grape and rootstock should be the same thickness.
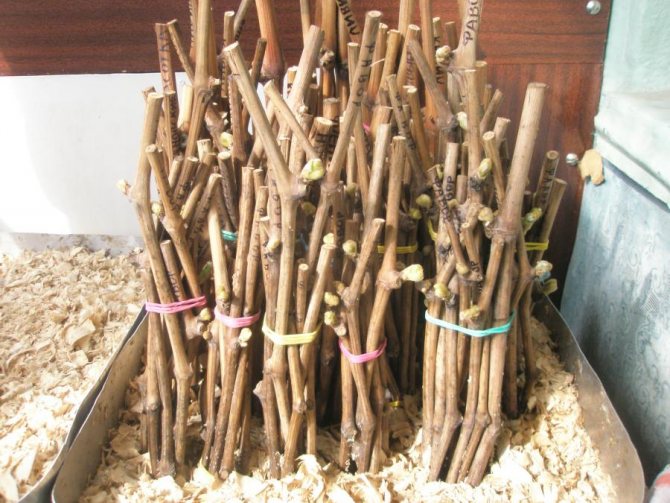
Harvesting grape cuttings
To obtain a high-quality scion, cuttings (shanks) must be harvested in the fall (in October-November), but always before the frost begins. To do this, choose a healthy bush with a good harvest of bright and juicy fruits and, using a special clean and sharp knife, cut the cuttings so that each one has 2-3 eyes. The average length of a grape shank should be 9-12 cm.
Please note that fatty, damaged, unripe, crooked and too thin cuttings are not suitable: they are unlikely to take root on the bush. It is also better not to use the uppermost part of the shoot - about 30 cm long.
For the grafting to be successful, it is very important that the cut is straight. Therefore, beginners are advised to practice on any unnecessary branches first.
Dip the chopped grape cuttings for 30 seconds in a 3% solution of copper sulfate (for disinfection), then spread them out on a flat surface and let dry. Then wrap them in polyethylene or a damp cloth and place them in a refrigerator or cold cellar with a temperature not exceeding 5 ° C.
Grafting grapes in spring
The grapes are grafted after the buds have swollen on the rootstock (most often in April). The most favorable air temperature is 15 ° С. The weather should be warm, but in the scorching sun, spring grafting is not recommended.
You can plant grapes in different ways.
- Budding. On the handle, cut off the flap, retreating 1.5-2 cm above and below the peephole, apply it to the stock, in which a similar cut is previously made. The vaccination site is tied with twine or plaster.
- Underground grafting end-to-end. The seedling, which will serve as a stock, is grown on a separate site, in the spring it is cut just below ground level (about 5 cm). Then a cross-section is made, a wooden rod 2.5-3 cm long and 5 mm in diameter, sharpened on both sides, is placed into it, on which the scion is planted. The site of inoculation is wrapped with a damp cloth and a plastic bag is put on this entire “structure”, which is then tied tightly. To prevent the tissue from drying out, it is periodically moistened with a syringe, which is pushed through the bag. After budding on the scion, polyethylene is cut, and when 5-centimeter shoots appear, they are completely removed.
But the easiest way is to plant grapes in the cleft on an underground trunk in the spring. This is done like this:
- About 2-3 days before the vaccination, take out the cuttings prepared in the fall, sharpen the tips and place them in Epin's solution.
- Dig the trunk of the bush, which will become the stock, to a depth of 15-20 cm, clean it from the bark and cut off the roots that have become noticeable.
- In the middle of the trunk, make a split with a sharp grafting knife to a depth equal to the length of the pointed tip of the scion (3-4 cm).
- Insert the graft into the cleft. If the gap in the rootstock is larger, place a second cutting on the other side of the gap.
- Secure the inoculation site with twine and cover with clay.
- Fill the hole around the trunk, and cover the part of the scion located above the ground with sand.
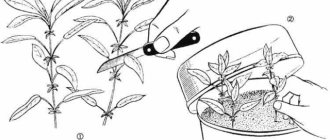
Grafting grapes in summer
Throughout the summer, you can do a combined grafting with a lignified cuttings in a green shoot (in a split):
one.On cuttings harvested in the fall, update the cut just below the bud and sharpen the tip of the cutting on both sides by about 2-3 cm.You should get a wedge. Then place the cutting in a bucket of water and hold until the buds swell on it.
If the buds of some cuttings have not yet grown, it makes no sense to use them. Inoculate only those that have "come to life."
To stimulate growth, grape cuttings can be held in Epin's solution for 15-20 minutes.
After swelling of the kidneys, you can start vaccination: it is better to do this in the early morning or in the evening after 18.00, when the sun is less active, or at any other time in cloudy weather.
2. Carefully prepare the stock - the vine on which you will graft the cutting. Cut off a part of a healthy shoot and make an incision 2-3 cm deep in the middle with a knife.
3. Carefully insert the cutting into the rootstock incision so that the eyes of the rootstock and the scion are turned in different directions, and wrap the grafting site with special grafting material or twine, and attach a plastic bag over it so that it is just above and below the grafting site.
June-July usually grafted with green cuttings on a green shoot. The technology is the same, only the cuttings do not need to be “revived” with water or a growth stimulant. They are simply cut from the bushes of the desired grape variety just before grafting. The tip of the green cutting is sharpened in the form of a wedge and inserted into the incision in the rootstock.
Grafting grapes in autumn
In the fall, grapes are usually grafted into the split bole of an old bush that is already bearing poor fruit. The success of the autumn grafting lies in the correct splitting and competent preparation of the cuttings.
- First of all, soak the cuttings in a growth stimulant (Epin, Heteroauxin, Kornevin, etc.). After 2-3 days, signs should appear that the plant is alive: swelling of the buds, pecking of leaves, the appearance of antennae.
- At the beginning of October, at an air temperature of at least 15 ° C, carefully cut off the above-ground part of the trunk, clean the cut site with a sharp disinfected knife and wipe with a damp cloth.
- Insert a slotted screwdriver in the middle of the stem and gently hammer in with a hammer. The size of the split should be small - about 3 cm deep.
- Sharpen one tip of the cutting in the shape of a cone. The cut should be no longer than 2.5-3 cm.
- Carefully insert the stalk into the cut of the grape trunk with a pointed tip. If there are gaps left, then they need to be repaired with small pieces of vine and soaked toilet paper.
- After you have closed all the gaps between the tissues of the plant, tightly tie the graft site with twine or a piece of sturdy cotton cloth and cover it with wet clay, garden varnish or other means to protect the cuttings from drying out.
If the stem of the stock is much wider than the cutting, 2-3 shafts must be grafted onto one stem.
Tabletop, or winter, grafting of grapes
In winter, young 1-2-year-old grape bushes are usually planted. Winter grafting is carried out in January-March, but the stocking of the stock and scion begins in the fall.
- Prepare the cuttings in the same way as for other methods of vaccination. When the vine has shed its leaves, dig it up, cut it to 10 cm, and disinfect the aerial part with a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate). Then place the stock in a container with sand and sawdust and take it to a basement with an air temperature of about 0 ° C.
- A day before grafting, remove the stock, clean it thoroughly, cut off the rotten roots, and shorten the healthy ones to 15 cm. Transfer it to a room with a temperature of about 20 ° C.
- After the stock is warm, place it in a large container of water at 15 ° C and wait exactly one day.
- After this time, remove the grape stock from the water, blot it with a dry rag and graft a stalk of the required variety to it in any way described above.
- Place the grafted plants in a container (for example, a glass jar), cover with polyethylene and put in a warm (25-28 ° C) place for 2-3 weeks. For example, on a radiator. Then put the plants back in the container and place it in a cool, dark place.
- In the spring, when the outside temperature rises to 15 ° C, remove the grafted plants from the container, remove the dead parts, keep them in the fresh air for 2-3 days, and then plant them in open ground.
How to care for a grafted grape bush?
Immediately after the spring, summer and autumn grafting, the stock should be watered and hilled. Do not forget to thoroughly loosen the soil in the trunk circle so that it is saturated with oxygen.
If you are inoculating into a split bole (for example, in the fall), the junction of the rootstock and the scion does not need to be covered with earth directly.
If, after 2 weeks, new shoots have not appeared on the grafted cuttings, cut off the upper part of the rootstock (with the graft) and re-graft the cutting onto it.
Check every 10-13 days how the rootstock and scion grow together. All protruding roots that are not allowed into the rootstock by cuttings must be removed so that they do not take root in the soil. Otherwise, it will no longer be a graft, but a regular planting of a plant.
You should also remove weeds in a timely manner and loosen the soil around the grafted grape bush. The grape bushes grafted in the fall should be covered with straw or spruce branches before the onset of the first frosts.
Have you tried planting grapes? Share your successes and secrets in the comments!
Vaccination care
It is necessary to properly care for the vaccine so that it takes root well. You should familiarize yourself with the peculiarities of caring for the grafted vine in advance so that it does not deteriorate and does not have to be re-grafted. There are several rules that will help when caring for grapes:
- The place of the scion should be tightly wrapped with a cloth or any other material. If juice seeps out of the junction of the branch and the trunk, you will have to rewind the plant.
- 2-3 times a week, check whether the grafted branch is taking root. There are times when the stems do not grow together well and you have to re-cross them.
- For two weeks, the bush is treated with potassium permanganate or Bordeaux liquid. It is useful for protecting against disease and stimulating fruiting.
- If the procedure was carried out in the autumn, the base of the bush is periodically covered with sawdust or straw. This shelter protects him from low temperatures.
Scion and rootstock preparation
When preparing the mother bush for the procedure, it is carefully cut off. Leave only a stem 8-12 cm high. The cut must be clean from rot, signs of other diseases, traces of insect damage. The stem is cleaned of bark, dust, dirt and treated with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, after which it is touched only with sterile instruments. The cut of the stem must be even and smooth.
For high-quality grafting of any variety, cuttings must be properly prepared. They are harvested in late October or early November, taking into account the following recommendations:
- The event is held before the start of frost.
- Choose a healthy, high-yielding shrub carefully. The vine on it should be mature, have a tough yellow-brown bark.
- The scion shanks are cut with a length of 10-20 cm.
- On each of them, 2-3 eyes are left, carefully peeling off the mustache and stepsons.
- Then the shafts are kept for 24 hours in a solution of heteroauxin - a growth stimulator (0.1 g per 1 liter of water).
- After it is dried and treated with paraffin. It protects the cutting from drying out, improves its survival rate. Chubuki are dipped in melted paraffin for a few seconds and then quickly dipped in cold water.
- If the grafting procedure is planned for the winter or spring, the scions are stored in a pit, sprinkled with sand or in a refrigerator at a temperature not higher than + 5 ° C.
To get quality grafting material, do not use the top of the vine, or damaged, thin or crooked stems.