Vegetable growing »Tomatoes
0
1049
Article rating
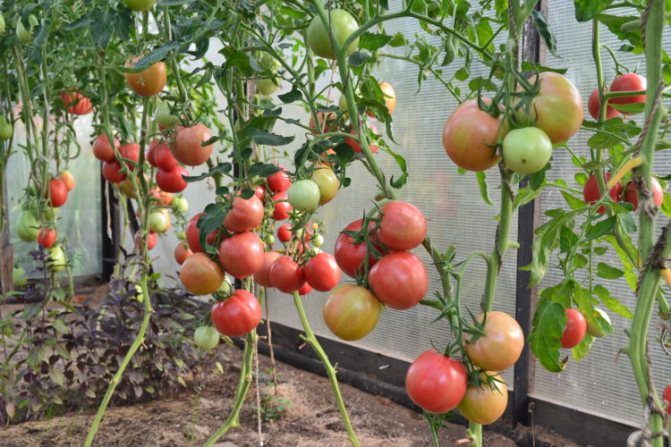
Many people mistakenly believe that growing tomatoes in a greenhouse is easier than growing outdoors. There are a number of rules you need to follow to get good yields of greenhouse tomatoes. But if everything is done correctly, indoors, the same variety will yield 2 times more harvest than outdoors.
Tatiana Orlova (Candidate of Agricultural Sciences):
Growing vegetables in a greenhouse is more costly and difficult than growing vegetables in an open field. Not even worth mentioning the cost of the greenhouse itself! The factors that complicate the work include the fact that in a closed room, the spread of infection or pest occurs much faster.

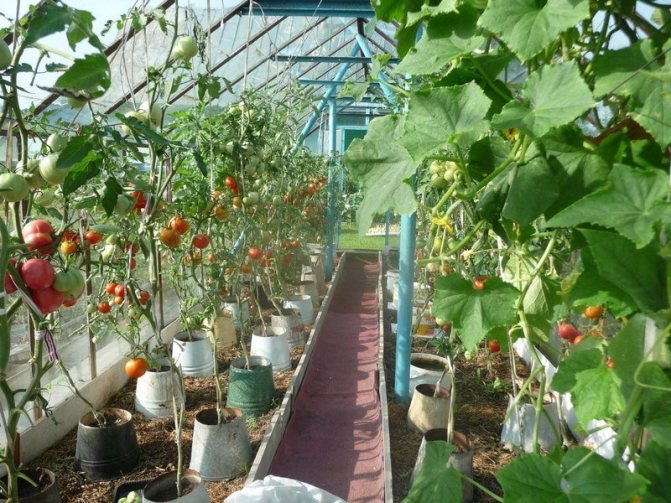
Growing tomatoes in a greenhouse
Benefits of using a polycarbonate greenhouse
The main advantage of polycarbonate is its ductility and strength. A greenhouse of any design can be made from this material. Most often, domed greenhouses are built, on the roof of which snow does not linger. Polycarbonate greenhouse:
- withstands snow load and hailstorms, unlike glass and film;
- transmits light, but does not focus it like a magnifying glass;
- polycarbonate, due to its cellular structure, maintains the difference in temperature inside and outside the structure of 7-10 degrees.


Polycarbonate greenhouses are durable. With proper use, they can last 10 years or more.
Collection and storage of tomatoes
Now a wonderful time has come when the harvest of tomatoes, lovingly grown in the garden, must be harvested.
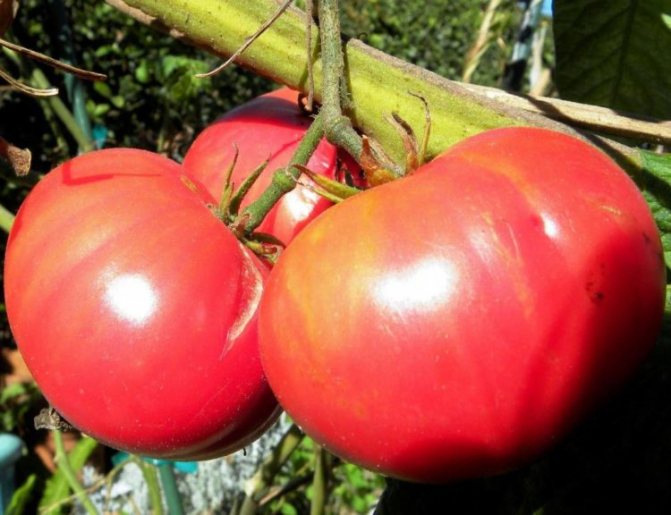
The collection of fruits depends on their further use. If you use varieties for fresh consumption, then they are harvested fully ripe, that is, red. In all other cases, especially for conservation, it is necessary to remove the fruits at the technological stage, when they are not yet fully ripe, but have already acquired the color corresponding to the variety. At this stage, the tomatoes will ripen for about a week.
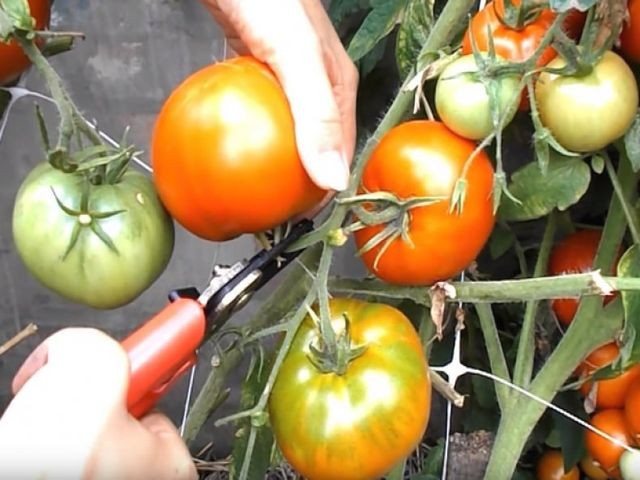


Harvesting in different regions of Russia starts at different times. It all depends on the climate and the type of tomato. In the middle lane, for example, the collection begins in mid-July.
The harvested fruits, which must be intact and not damaged, are laid out for ripening in wooden boxes. The room where the fruits will be stored must be warm and ventilated. The temperature here must be at least 25 degrees. In addition, it is desirable that it be dark indoors, then the tomatoes will ripen evenly.
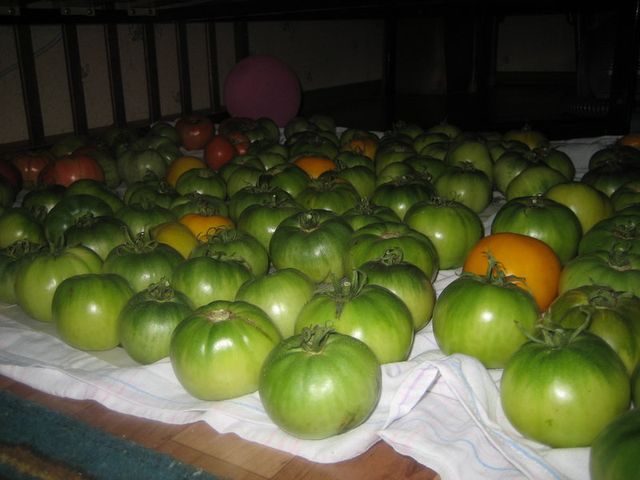


For long-term storage, fruits are used in the biological stage of ripening, i.e., green. It is best to store them in wooden boxes sprinkled with sawdust in a dark room at a temperature not lower and not higher than 10 degrees.
Proper storage of tomato fruits will provide you with tasty fruits for a long time.
Good luck!
Author of the publication
offline 1 week
Review of the best varieties
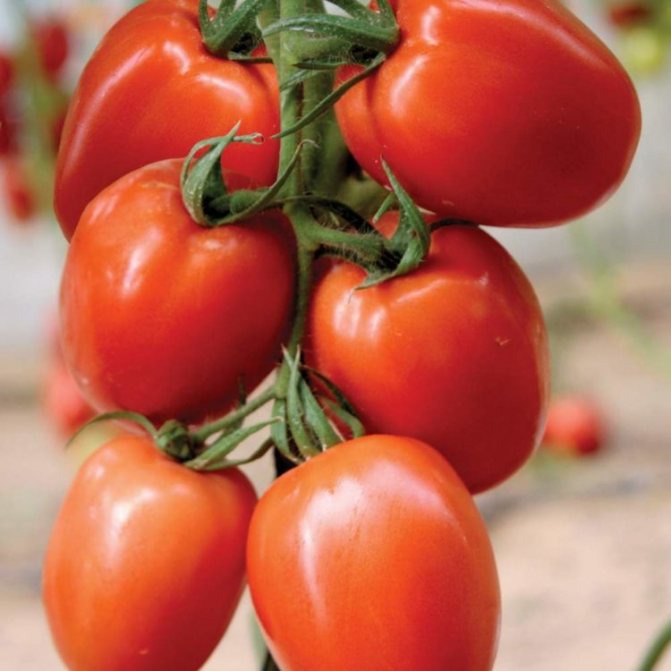
Experienced gardeners have chosen several of the best varieties of tomatoes for cultivation in a polycarbonate greenhouse. The varieties are united by high productivity and unpretentiousness.
Asterix
An early ripe hybrid. The crop is ready for use 90–110 days after germination.The plant grows up to one and a half meters, the bush is densely covered with rough leaves.
Fruits are oval, slightly pointed, weighing 70–90 g. Color red, firm flesh. The variety is valued for its good transportability. Productivity in a greenhouse - 10-12 kg per 1 sq. m.
Suomi
Mid-season hybrid suitable for open field and greenhouse cultivation. The plant grows up to 1 m in height. Fruits are formed 110 days after sprouting.
Suomi fruits are plum-shaped, weighing 70-80 g, numerous (up to hundreds of tomatoes per bush). The purpose of the fruit is universal.


The variety is resistant to diseases and high air temperatures.
Silhouette
A mid-early ripening hybrid. The bush, up to 170 cm high, is formed into 2 stems. The hybrid is able to set fruit even in stressful situations (sudden temperature fluctuations, absence of insects).
Fruits are red, flat-round, weighing 150 g. They can be stored well for up to 1.5 months. Up to 8 kg of fruit can be harvested from one bush.
Lezaforta
Tall hybrid for greenhouses. The harvest ripens in 90 days after germination. Vigorous plant, medium leafiness. The clusters contain 4–6 fruits. The plant is resistant to diseases and unfavorable growing conditions.
Fruits are red, weighing 250-270 g. The skin is dense. Beef is a tomato with dense pulp and few seed chambers.
Pink Lady
Tall hybrid from Holland. Stem height 2 m. Tomatoes ripen in clusters, 5–7 pieces each. Fruit weight from 220 to 280 g. The color of the tomatoes is pink, the peel is dense. The pulp is tender, juicy. The tomato is suitable for processing and fresh consumption.
Productivity up to 25 kg per 1 sq. m.
Afen
A hybrid reaching 180 cm. Fruits are round, weighing 200–240 g. The color is raspberry-pink. Purpose - salad, fleshy and sweet fruits.
Productivity 9-15 kg per 1 sq. m.
Batianya
An early ripe tall variety bred in Siberia. The plant reaches a height of 2 m, it is formed into 1–2 stems. Productivity in the greenhouse is 16-19 kg per 1 sq. m.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Fruits in shape and size resemble a "bull heart". Fruit weight up to 350 g. The pulp is juicy, sweet, dense, few seeds. The color is pink-red.
Klondike
Mid-season variety of yellow fleshy tomato. Plant height 100 cm, sprawling bush, requires a garter. Productivity is 3 kg per bush.
Fruits are large (up to 350 g), flat-round, slightly ribbed. The pulp is tender, juicy, used for salads and processing.
Katya
An early ripe hybrid with carpal fruiting. Plant height 70 cm. Up to 8 fruits ripen in a bunch, weighing 80–120 g. Tomatoes are red, round, of pleasant taste. Up to 3 kg of fruit can be harvested from one plant.
The hybrid is resistant to disease and cracking.
Queen Margo
An early hybrid of cherry tomato. It begins to bear fruit on the 95th day after germination. The height of the bush is 120 cm. Up to 20 red fruits ripen in the cluster, weighing 20 g. The taste is pleasant, the fruits do not crack.
De Barao red
Plant height exceeds 2.5 m. The bush is powerful, with large leaves. The crop ripens 130–140 days after germination. Productivity up to 9 kg from 1 plant.


Fruits in the form of cream, weighing 100 g. Tomatoes are well stored, suitable for salads and preservation.
Alexia
An early hybrid forms a harvest 90 days after germination. The height of the tomato stem reaches 250 cm. Fruits are large (up to 250 g), red, round. Productivity 12-14 kg per 1 sq. m.
Ivanhoe
Dutch hybrid for greenhouse cultivation, yields one hundredth day after sowing. Stem height up to 2 m, moderately spreading bush.
Fruits are red, rounded, weighing 170-190 g. They do not crack, the flesh is tender, sweet and sour taste. Productivity up to 10 kg per plant.
Demiros
An early ripening hybrid (95–100 days). The height of the tomato is 190–270 cm. The hybrid is resistant to disease and stress.
The weight of pink fleshy fruits is up to 250 g. The skin is firm, tomatoes can be transported and stored for up to 3 weeks without compromising the quality of the fruit.
See also Tomatoes Yamal 200: characteristics, planting rules and variety care
Growing problems
The influence of unfavorable conditions often leads to problems:
- Tomato fruits crack when over-watered after a long dry period.
- Tomatoes do not turn red with a lack of light, a large amount of green mass, and excess nitrogen nutrition. You need to take care of the bush constantly, removing two or three leaves a week and in a timely manner punch the stem.
- Tomatoes turn black when affected by apical rot or late blight.
- Spots on tomato foliage appear when brown spot disease occurs in conditions of high temperature and high humidity. Leaves can become stained with micronutrient deficiencies.
- Rotting of fruits occurs when affected by various types of rot, anthracnose, alternaria. Excess moisture, temperature changes, and poor ventilation lead to the disease.
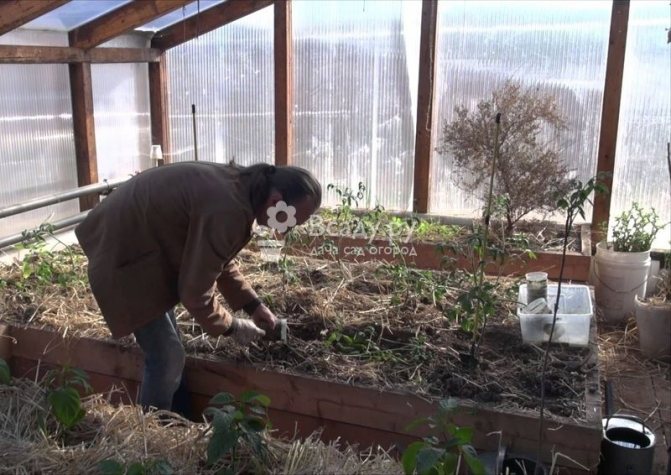
Greenhouse preparation
Before placing tomato seedlings in the greenhouse, it must be prepared for the meeting of residents: washed and disinfected.
Washing
Polycarbonate is easy to clean with water and simple soap. Cleaning powders and other abrasives cannot be used, they can damage (scratch) the polycarbonate.
You need to wash the greenhouse inside and out.
Disinfection
During the cultivation of plants, pathogens and parasites can accumulate inside the greenhouse. To destroy them, special disinfectants are used. It is necessary to process all structures inside the structure: walls, joints of polycarbonate sheets, vents, doors, inventory.
Lime
Lime powder is poured with water to the state of liquid sour cream. The lime mass is applied with a brush to the greenhouse frame without touching the transparent walls.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Bleach powder is used against pests inhabiting the soil. It is sprayed over the dug up soil in the fall, spending 2 glasses of the drug per 1 square meter. m.
Formalin
A drug with a strong effect. Its disadvantage is the effect on all, without exception, microorganisms, useful and harmful. The greenhouse is treated with formalin only in the most extreme cases.
Important! When working with the drug, you must wear a respirator, goggles and gloves.
Formalin is sprayed on the walls of the greenhouse and on the ground, consuming 20-25 ml of a 40% solution per 1 sq. meter. After spraying, the greenhouse is kept closed for 1 day.
Sulfur
Effectively disinfect the greenhouse with sulfur bombs. The gas not only destroys microorganisms on open surfaces, but also penetrates 8-10 cm deep into the dug soil.
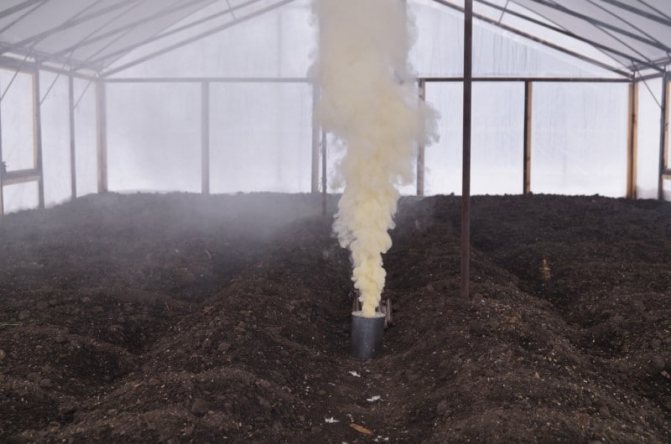


Sulfur checkers ("FAS", "Climate") are purchased in garden stores. The number of blocks required for processing depends on the volume of the greenhouse (multiply the height, width and length of the structure). Processing principle.
- The required number of checkers is evenly laid out inside the room.
- Close the vents tightly.
- Checkers are set on fire, going from the far corner of the greenhouse to the exit.
- Keep the room tightly closed for up to 3 days.
When working with checkers, you must use personal protective equipment.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Advice. So that sulfur does not cause corrosion on metal structures, they are lubricated with grease before processing.
Soil preparation
After harvesting all plant residues, the soil is dug up. Various solutions are used for soil disinfection:
- "Fufanon" (10 ml per bucket of water);
- Marshal (7 ml per bucket of liquid);
- "Fitosporin" (5 g per 10 liters of water);
- "Copper sulfate" (30 g per 10 liters of water).
The solutions are sprayed on the surface of the dug soil or the soil is watered from a watering can with a sprayer. Treating the entire structure with a sulfur checker will reliably disinfect the soil.
Important! These drugs also destroy the beneficial microflora in the ground. Before planting seedlings in spring, the soil is not only filled with fertilizers, but also watered with special solutions, enriching the soil with microorganisms.Apply "Baikal EM", "Shining", "Phoenix", vermicay.
Requirements for greenhouse varieties
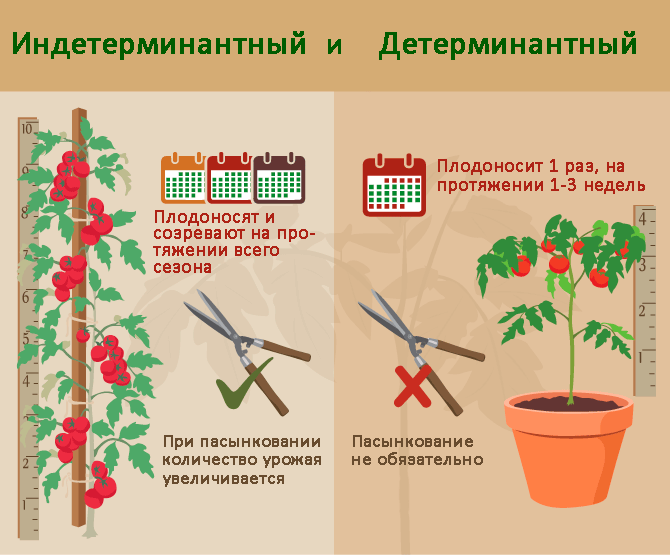
Productivity. From 1 m2 of seasonal film greenhouses, 5-9 kg of tomatoes are harvested, winter heated greenhouses - up to 20-25 kg, when growing indeterminate varieties in extended culture. The type and size of the bush. By the size of vegetative organs, tomatoes are divided into:
- standard;
- semi-determinant;
- determinant;
- superdeterminant;
- indeterminate.
Ripening time. By the number of days from sowing to harvesting, tomatoes can be:
- super early;
- early;
- medium early;
- late.
Taste characteristics of the fruit. The taste is determined by the content of sugar, dry matter, fatty and organic acids. The most delicate and delicious are traditional, thin-skinned and fleshy tomatoes. Varieties that produce both small and large fruits can provide a good harvest of tomatoes in the greenhouse.
See also Cardinal Tomatoes: characteristics of the variety and the specifics of cultivation
Disease and pest resistance. There are no varieties and hybrids that are 100% unaffected by weather conditions and disease, but must be selected with a high degree of resistance. These are, first of all, hybrids and new varieties, in which resistance to diseases and pests is inherent at the genetic level. Tomatoes in a greenhouse, even for novice vegetable growers, are suitable early-ripening, yielding until the weather conditions deteriorate, creating the prerequisites for the development of diseases.


Keeping quality of fruits. The storage time depends on the density of the peel, the dry matter content and the structure of the pulp. It is better stored firm, firm fruit with a strong skin that is resistant to damage. In order to extend the implementation time and maintain commercial qualities, breeders are constantly working on developing hybrids for greenhouses with improved performance.
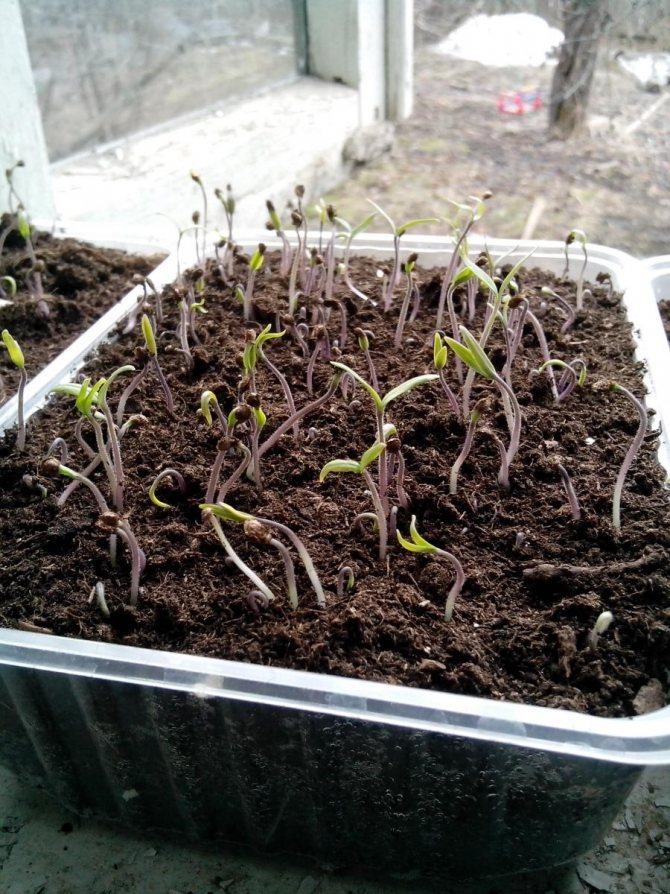
How to grow seedlings
To accelerate the harvest, tomatoes are grown through seedlings. Seedlings for greenhouses are prepared from December to February, depending on whether the building is heated or not.
Vegetable seeds are laid out in separate cups, to a depth of 6–8 mm. The substrate for tomatoes should be loose and nutritious. It is made up of equal parts of humus, sand and peat. For every 10 liters of the mixture, add 10 g of complex mineral fertilizer.


Seedlings are kept at a temperature of +16 degrees at night and + 22 ... + 24 degrees during the day until they are planted in the greenhouse. The duration of daylight hours is at least 12 hours. Plants are regularly watered with cold water.
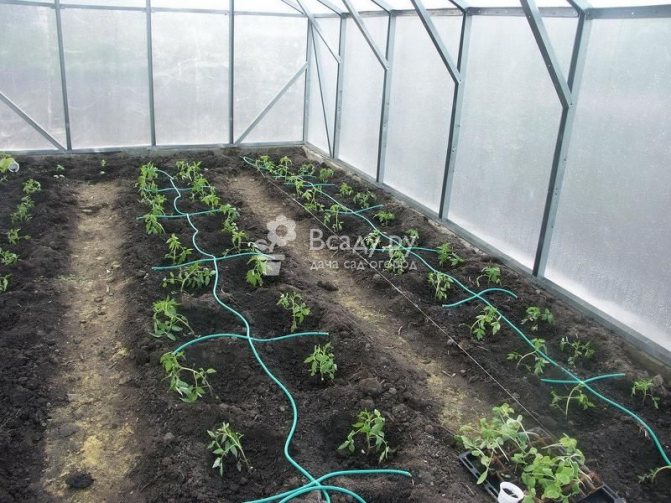
Tomatoes are transferred to the greenhouse at the age of 55–65 days.
The timing of planting seedlings in a polycarbonate greenhouse depends on the temperature outside. Tomatoes can be planted in an unheated greenhouse when the temperature outside does not drop below +10 degrees. Plants are additionally protected from frost with a covering material, and heaters are installed inside the room.
The choice of planting material
In order to grow tomatoes in a greenhouse made of film or polycarbonate to give the desired result, you need to choose the right vegetable variety. Since there is no access to closed structures for insects pollinating plants, self-pollinating hybrids should be preferred.
Also, before buying seeds, you should pay attention to the manufacturer's recommendations. Today there are many varieties available for indoor cultivation. The hybrid varieties "Evpator", "Palenka", "La-la-fa", "Gift", "Cherry", "Aksinya", "Flamenco" have shown themselves well.
Pay attention to the height of the bush. If there is little space in the greenhouse, give preference to undersized or medium-sized plants. If the height of the greenhouse is 1.5-2 m, tall bushes can be grown.
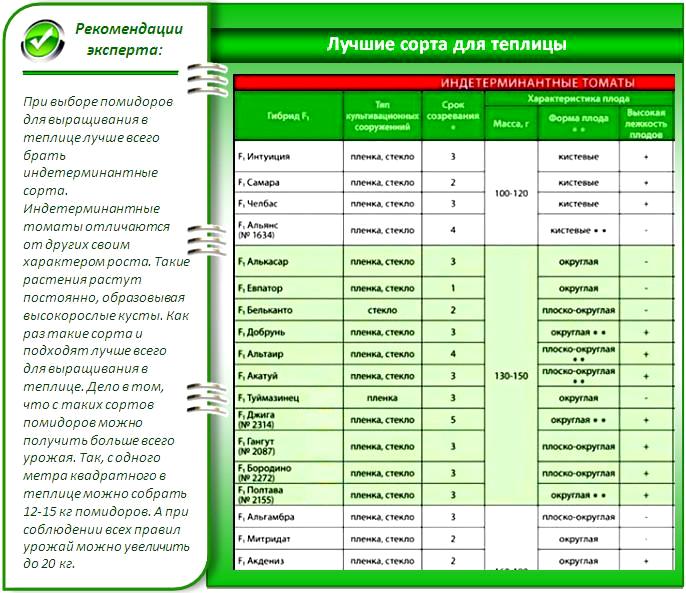
Tatiana Orlova (Candidate of Agricultural Sciences):
As a rule, only tall (indeterminate) tomato varieties are grown in greenhouses. This is done in order to use not only the area, but also the entire volume of protected soil.Even if vegetables are grown not for sale, but for personal consumption, you always want the costs of installing a greenhouse to quickly pay off. Therefore, cultivars for greenhouses are chosen for the intensive type, with potentially high yields and an extended harvest period. These requirements are met not by varieties, but by modern tomato hybrids F1.
Scheme of planting tomatoes in a greenhouse
Depending on the height of the plant, you need to plant tomato plants at different distances.
- Tall tomatoes, which form into 1 stem, are placed at a distance of 30-40 cm in a row. Gaps of 60 cm are left between the rows.
- Indeterminate tomatoes, formed into 2 stems, are arranged in a 50 by 70 cm pattern.
- Low-growing bushes, up to 120 cm high, are planted more spaciously. Leave gaps of 70 cm between them.Plant plants sparingly in a checkerboard pattern, observing gaps of 50 cm in a row, with row spacing of 70 cm.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
When starting planting at the recommended time, they pay attention to the weather - plants planted on a cloudy day take root better.
Tomatoes are planted in holes, where a mineral complex fertilizer is placed ("Kemira", "Hera", "Agricola"). The stem is buried in the soil until the first true leaves. This technique promotes the formation of new roots on the stem. After planting, the bushes are watered abundantly. It is useful to mulch the soil surface with straw, tree bark, chopped grass.
How to properly collect and store fruits
Tomatoes are harvested as they ripen every 3-4 days. It is better to harvest a little unripe, since the presence of overripe fruits on the bush reduces the yield. For ripening, tomatoes are laid out in a dry, ventilated room. Fruits of late-ripening varieties are more suitable for storage. Storage temperature: more mature (pink) - 1–2 ° С, brown - 4–6 ° С, milk and green - 10–12 ° С.


Rules for the care of greenhouse tomatoes
Indoor plant care includes regular watering, feeding, forming shrubs and treating diseases.
Watering
At the stage of growth, flowering and fruit setting, tomatoes are watered at least 1 time per week. The dose of liquid for each plant is from 5 to 15 liters, depending on the height of the bush.
Starting from the reddening phase of the fruit, watering is reduced to 1 time in 10-12 days. Excess moisture delays ripening.
Water the plants at the root.
Garter
All tomatoes need a garter. Low-growing plants are tied to stakes, tall ones are grown on trellises. A strong nylon twine is used for the garter.
Temperature regime
For full development, tomatoes need a temperature range from +18 to +26. At temperatures above +35 degrees, plant pollen becomes sterile.
Airing
Tomatoes are among those plants that cannot tolerate high humidity and respond well to drafts. The greenhouse must be ventilated by opening not only the vents for the day, but also the doors in order to reduce the temperature and humidity to comfortable ones.
Stealing and shaping
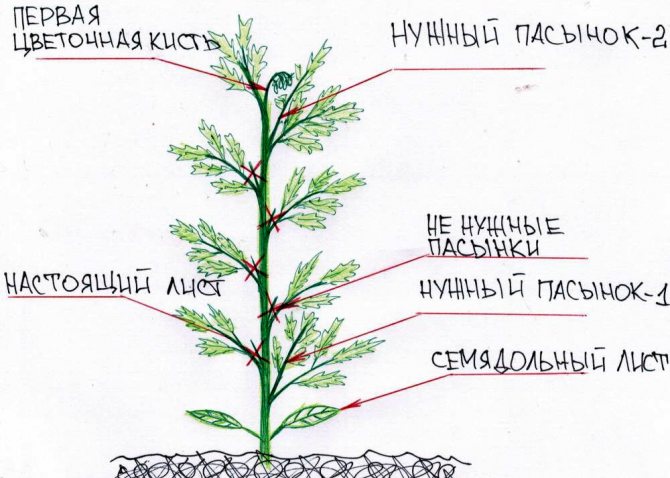
Tall tomatoes form 1–2 stems, removing all other shoot buds. 3-4 stems are left for determinant plants.
The stepchildren (young shoots growing in the leaf axils) are removed until they reach 4–5 cm. They pinch the shoots in the morning so that the wound dries up in the evening.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
After the formation of the crop on the lower brushes, all the foliage is removed up to the first brush.
Top dressing
Greenhouse tomatoes are fed every 3-4 weeks, alternating organic matter and mineral fertilizers.
- 2 weeks after planting the seedlings, the tomatoes are fed with mullein infusion (1 kg of manure per 10 liters of water). The infusion is poured at the root.Nitrogen can be added with urea by dissolving 30 g of fertilizer in 10 liters of water.
- In the budding phase, phosphorus-potassium fertilizing is carried out with a complex mineral fertilizer or with such a mixture: 30 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium chloride per 10 liters of water.
See also Labrador Tomatoes: yield and cultivation rules
For better fruit setting, flowering bushes are sprayed with the preparation "Ovary".
- Nitrogen and potassium will help speed up the filling of fruits after flowering. The plantings are fed with manure infusion, grain fertilizer, wood ash, or a mixture of urea (30 g) and potassium nitrate (10 g) is given.
- Until the end of fruiting, tomatoes are fed every month with a full complex mineral fertilizer with microelements ("OMU", "Agricola", "Hera").
Preventive treatments
For the prevention of fungal diseases in the greenhouse, tomatoes are sprayed three times during the growing period. Use:
- iodine solution (10 ml per 10 l of water);
- Fitosporin;
- milk whey (1 glass per bucket of water).


The treatment is carried out by covering the entire surface of the plant with the preparations, including the reverse side of the leaves.
Prevention of tomato diseases
When growing tomatoes in a polycarbonate greenhouse, it is critical to take measures to prevent disease. Fungal and bacterial lesions of the tomato easily develop in the specific humid and warm microclimate of the greenhouse.


In addition to airing, maintaining an acceptable temperature and humidity, tomatoes must be protected with chemical protection.
Tilling the soil before planting a tomato with preparations of copper and potassium permanganate is one such technique. But don't stop there.
A couple of times during the summer months, it is worth repeating the processing of tomatoes under polycarbonate with a Bordeaux mixture or a solution of copper sulfate. You need to spray the foliage, and the stem, and the soil. Such treatment prevents the development of late blight, protects both leaves and fruits - tomatoes from disease.


In the prevention of the invasion of pests on tomatoes, spraying with garlic and ash extracts has proven itself well. 100 g of chopped garlic or a glass of ash is infused in a liter of water for several days. Then add this infusion to a bucket of water and spray the plants.
Disease Control Ways
For the treatment of most ailments of tomatoes, preparations based on copper are used, as well as antifungal drugs.
Late blight
The disease is manifested by yellowing of the foliage and the appearance of brown spots on the fruit. With the development of the disease, the foliage dries out, and the fruits begin to rot. Phytophthora develops in conditions of high humidity and low temperatures.
The affected fruits are removed from the bushes, the foliage is cut off and burned. Plants are sprayed with:
- "Fitosporin" (5 g per 10 liters of water);
- "Furacilin" (10 tablets per 10 liters);
- "Ordan" (50 g per 10 l), apply until the fruit ripens.
From folk remedies use milk whey, iodine solution, garlic infusion.
Stem necrosis
Viral disease is characterized by cracking and blackening of the stem at the base. The source of infection is soil and seeds. There is no cure. The diseased plant is removed from the garden and burned. The soil is shed with "Fitolavin".
Septoriasis
Fungal disease, which is also called "white spot". Spots appear on the leaves with a white center and darkening towards the periphery, subsequently the leaves turn brown and dry.
After removing the diseased foliage, the plants are sprayed with the preparations "Skor", "Ditan", "Acrobat".
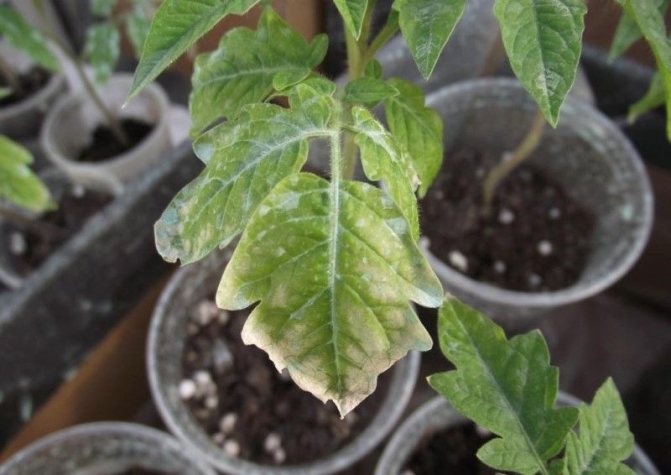


Important! Fungicide is diluted strictly according to the instructions! Processing is carried out no later than 2 weeks before harvesting. When working, use a respirator, glasses.
Top rot
The disease is manifested by decay of the tip (top) of the tomato. It occurs due to a lack of calcium during the period of mass fruiting. Tomatoes are fed with calcium nitrate (10 g per 10 l), powdered with wood ash. It is useful to close up 1 teaspoon of crushed eggshell in the root zone of the tomato.
Root rot
A fungal disease affects the base of the stem. The stem rots and the plant falls. It is too late to treat a tomato when the stem has turned black. Prevention is the treatment of bushes and soil with antifungal drugs.
Fruit cracking
Occurs due to excess watering and dressing at the time of fruit pouring. The fruits of modern varieties of intensive cultivation have a dense skin that does not burst.
Dangerous diseases and pests
The technology of growing tomatoes in a greenhouse is aimed at preventing the development of diseases and pests that reduce the yield and marketability of products:
- The caterpillar emerges from the eggs of the scoop. Tomatoes are affected by almost all types of scoops, which eat not only leaves, stems, but also buds, ovaries. Caterpillars also spoil the fruit, gnawing holes.
- The whitefly weakens the plant by feeding on its sap. Lives on the seamy side of the leaf, is a carrier of viral diseases. The secretions of flies are a breeding ground for the sooty fungus, which can kill the plant.
- The bear gnaws at the roots and stems, and can completely destroy the seedlings.
- Wireworms, or click beetle larvae, cause irreparable damage to the root system.
- Fusarium, or fusarium wilting, first affects the root and vascular system of tomatoes, rises up the stem. A fungal infection develops during the fruiting period and leads to the death of the crop.
- Phytophthora, or brown rot, is a fungal disease that affects the entire vegetative system. The disease develops very quickly with a large difference between day and night temperatures, dew and frequent fogs.
- Macrosporiasis (brown or dry spot) affects the stems and leaves, and sometimes the fruit. The leaves, starting from the bottom of the bush, are covered with large, brown spots that grow throughout the leaf blade. Over time, the leaves may die completely.
- The viral mosaic infects the leaves of tomatoes, which become variegated, become stained, then curl. Light, viral spots appear on the fruit.
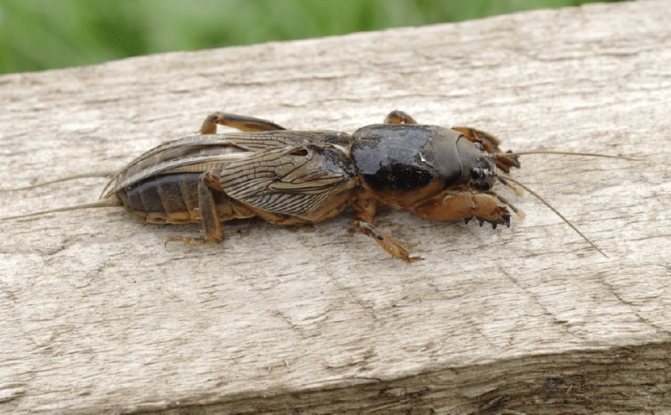


How to get an early harvest
In order to grow a crop in an unheated polycarbonate greenhouse by the beginning of summer, you must adhere to several rules:
- grow ultra-early ripening varieties of tomatoes;
- sow seeds in February;
- plant seedlings in the greenhouse with a flower brush;
- carry out intensive feeding.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
As a top dressing, yeast infusion is used. It is correct to cook it like this: dissolve 100 g of dry yeast and 40 g of sugar in warm water (10 l). The mixture is infused for a day, then diluted with water 5 times. Tomatoes are watered with a nutritious composition under the root at the time of pouring the fruits.
Basic requirements for a greenhouse
A protective structure for tomatoes must be reliable, as durable as possible, ventilated, adapted to the conditions of the region. The cost of building it should pay off. For the construction of greenhouses and greenhouses, both polycarbonate, spunbond, and polyethylene film of various thicknesses are used. The earliest vegetables are produced in heated facilities, but additional lighting will be required in winter. It is possible to grow good tomatoes in an unheated greenhouse during the spring and summer period.
Common mistakes
It is useful for novice gardeners to consider common mistakes in growing tomatoes in a greenhouse.
Unsuccessful variety selection
Indoors, varieties and hybrids of intense and extended fruiting are grown. Plants must be resistant to low light, high humidity and cracking.
Neighborhood with cucumbers
Cucumbers and tomatoes require different moisture levels during the growing process. You cannot combine crops in one greenhouse. Tomatoes can be grown alongside peppers and eggplants.


Landing in one land for several years
Lack of crop rotation leads to the accumulation of harmful insects and pathogens in the soil. The soil in the greenhouse is disinfected every year, completely changed every 3-4 years. After harvesting tomatoes, you can plant mustard to cleanse the soil from fungi.
Thickened or sparse fit
With a thickened planting, the bushes are poorly lit and ventilated. This leads to the development of diseases. Placing tomatoes spaciously is unprofitable from an economic point of view.
Lack of ventilation
High humidity and temperature make the pollen sterile. Fungal diseases spread faster.
Pinching and pinching errors
Stepsons need to be cut or pinched so as not to damage the tomato stem. The wound is sprinkled with ash powder.
Garter too tight
Tomatoes are tied up, taking into account the growth of the stems, not tight. The twine can grow into the stem or pull it over, blocking access to food from the roots.
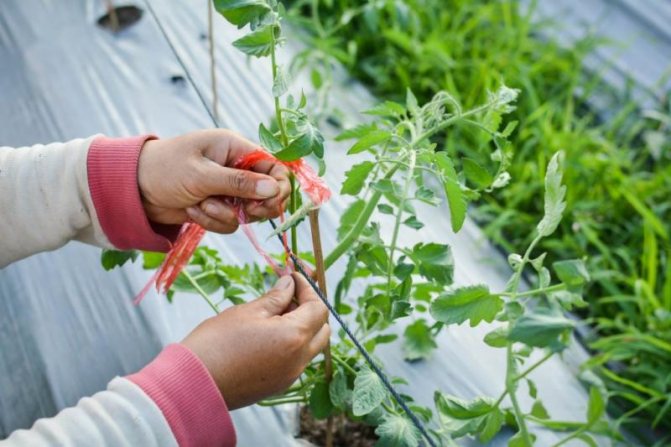


Removing too many leaves
No more than a third of the green mass can be removed from the bush at a time. Foliage tearing is performed every 3 weeks.
Excess or lack of moisture
With a lack of watering, tomatoes grow slowly. Fruits are not set well, they are small.
Excess water leads to rapid growth and cracking of the fruit. Fungal diseases and rot develop.
Ignoring disease and pest prevention
In the confined space of the greenhouse, the infection develops rapidly. Pests, having no natural enemies, multiply quickly. Without the necessary treatments, there is a high risk of losing plants in a matter of days.
Late harvest
The fruits are harvested in the greenhouse every 3 days. A delay in picking will slow down the ripening of the tomatoes.
"Tomato" indoor microclimate
So, let's figure out what conditions need to be created in the greenhouse for the successful cultivation of tomatoes.
Illumination
Tomatoes are light-loving enough, and feel great with long daylight hours. But it is important not to overdo it with lighting for seedlings: with an excess, the number of leaves between the inflorescences will increase significantly, but the fruits will not tie.
Temperature
The most favorable temperature for growth and fruiting in tomatoes is 22-25 ° C during the day, and 16-18 ° C at night. And here there is a danger of being left without a crop at all: if the air temperature in the greenhouse rises above 29 ° C, the pollen will become completely sterile, and the flowers will crumble. Of course, there will be no more fruits. Although at the same time, tomatoes are able to endure a short night temperature up to 3 ° C.
Humidity
The optimum air humidity for this crop is up to 60%. At higher humidity, the fruits crack quickly.
By the way, today it is fashionable to grow tomatoes in pots: