Much depends on the correct placement of tomato plants - yield, ease of care, the presence of pests and diseases and, of course, the good mood of the gardener. When choosing the optimal planting scheme, take into account the biology of the tomato culture and the characteristics of a particular variety, its growth force and developmental characteristics. In this article, I tell you in detail at what distance to make beds and rows in the greenhouse, plant standard, determinant and tall tomatoes, what are the disadvantages of thickened and too sparse plantings.

The device of greenhouse beds ↑
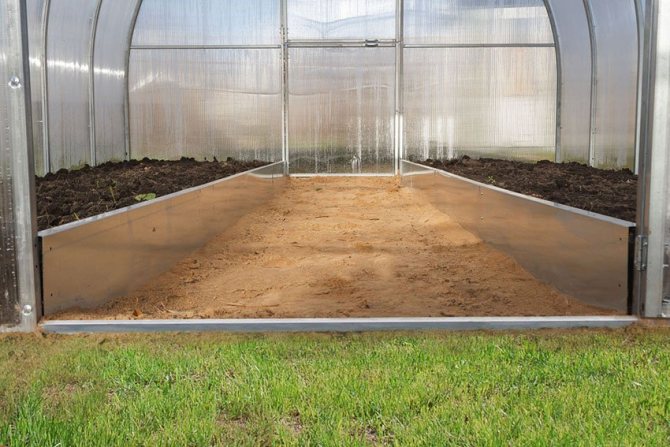
In small suburban and suburban areas, small greenhouses with an area of 3x6 m are usually laid.
- Place the greenhouse in an open area with a comfortable approach.
- The long side of the greenhouse always faces east to west, which contributes to better and longer illumination.
- In the greenhouse, the ridges are always located along the long sides of the structure.
- The height of the ridges relative to the tracks should be easy to maintain, no more than 30-40 cm in height relative to the tracks.
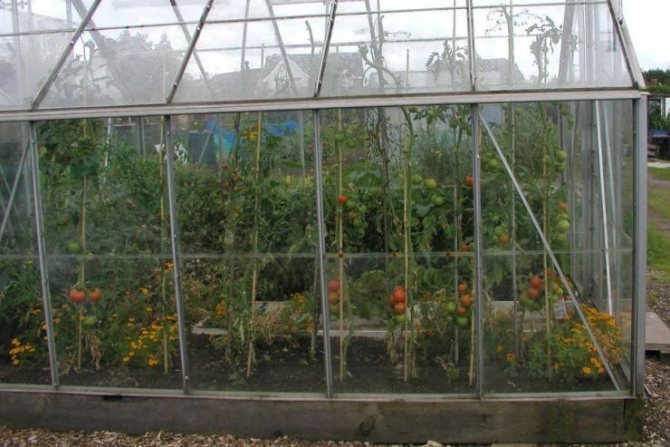
- The optimal width of the beds with a one-sided approach is 60-65 cm, with aisles from two sides (double is more profitable) - 90-100 cm.It is better to leave aisles at least 45-50 cm.Convenient width of paths for work in the greenhouse is 60 cm or more. Narrow paths are inconvenient, the edges of the beds are constantly violated.


Beds and paths - In greenhouse conditions for tomatoes, it is imperative to use the phytowall principle, that is, plants are placed on trellises, which can be permanent or temporary.
Views
In theory greenhouse - is a heated, illuminated structure equipped with an artificial irrigation system, which has large dimensions. Greenhouse on the contrary, it has a more modest size, is not heated or lit. In practice, the greenhouse differs from the greenhouse only in size.
Today there is a wide selection of greenhouses of different designs, sizes and materials.


Build greenhouse you can do it yourself using the materials at hand. Greenhouse structures in shape are arched, hipped, polygonal, wall and gable.
They should be mounted either on a pre-prepared foundation (which significantly increases the service life), or directly into the ground.
There are also hydroponic greenhouses.
It will be more expedient to install the greenhouse on south side plot.
This will additionally protect the building from wind and plants will be enough natural sunlight... Materials include glass, polyethylene, polymer films, spunbond, polycarbonate.
From glass
A glass greenhouse has a very high light transmittance and thermal insulation properties. Durability - a huge plus of this material. However, fragile glass can crack, and even during the hot season, the temperature inside the greenhouse can reach unfavorably high temperatures, which is not very good for growing crops in greenhouses.
From film
Polymer film - this is a lightweight version that can be used without a foundation, which saves time and moves the greenhouse to a convenient place. The light under the material is evenly scattered, which is an advantage of this structure.
but wear resistance leaves much to be desired.The formation of internal condensation also plays an unpleasant role for growing plants in a greenhouse.
Polycarbonate
Early planting in the greenhouse made of polycarbonate:
Polycarbonate has collected the best properties of glass and film at the same time. Differs in high transmission capacity of sunlight evenly scattered inside the structure. Has high heat insulating properties.
Wear resistance here, too, at the same level, and the increased flexibility of polycarbonate sheets allows you to effortlessly install such greenhouses on the land.
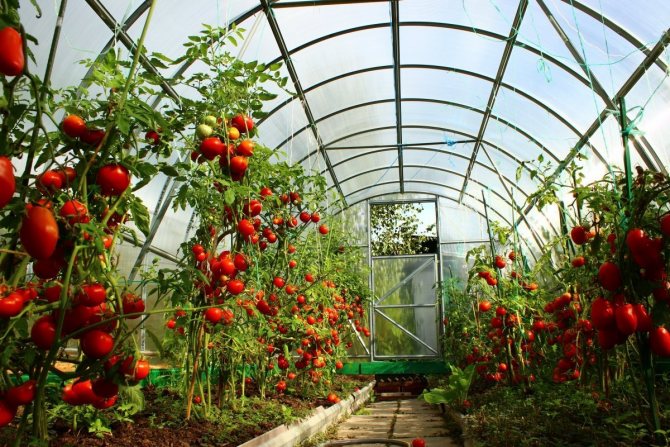
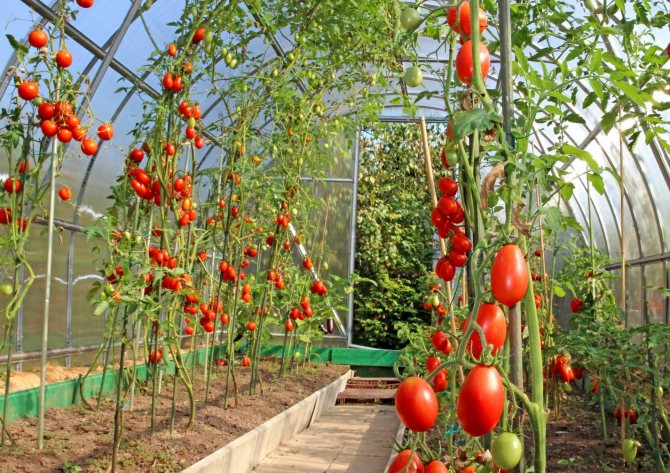
The structure of the installed structure can be either simple or complex, the dimensions can also vary. From cellular polycarbonate, it is possible to build both a small greenhouse for seedlings and a huge greenhouse for growing fruit and vegetable crops and flowers. What can be grown in greenhouse made of polycarbonate? Everything described above. You can see in the photo below what to plant in the greenhouse.
Growing in a greenhouse - photo:
Now you know what is grown in greenhouses from polycarbonate... But very often greenhouses are used as business... How? Consider below:
What types of tomatoes to grow
You can grow any type of tomato, better early ripening varieties, especially in small greenhouses. For the successful cultivation of a crop, it is imperative to plant the plants so that everyone receives maximum nutrition, light and air. Therefore, for greenhouse tomatoes, the type of bush is important, on which the planting schemes depend.
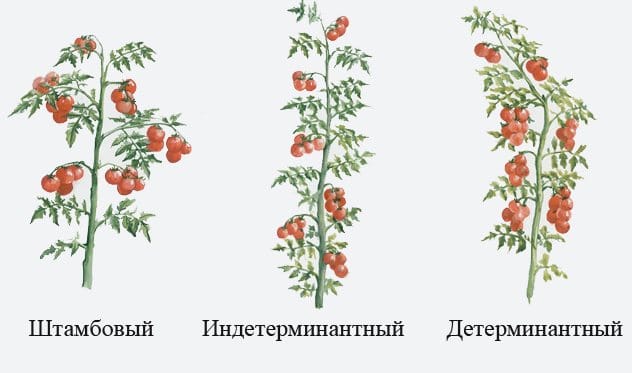
Indeterminate plants grow indefinitely and can form up to 50 clusters of fruits on a central shoot when formed into one stem. The varieties and / or hybrids of this type are suitable for the greenhouse conditions of central Russia. In more northern regions, they are more suitable for industrial greenhouses.

Types of tomato bushes
Determinant tomatoes are more convenient for home use by novice greenhouses. This type is characterized by early and ultra-early varieties and hybrids, and the latter do not require pinching, that is, the formation of a bush. Plants have limited growth, which ends in 4-5 clusters of fruits. Usually the bush is formed by pinching in 2 or 3 stems. These are very convenient varieties and hybrids for small greenhouses.
For planting in small greenhouses, standard varieties can be recommended, which are a type of determinant. They are of short stature with a strong stem that does not require a garter and pinching, which means that they are easier to care for.
Features of caring for greenhouse tomatoes
Getting a bountiful harvest depends on many factors. Timely planting of strong seedlings is important, you need to water and feed it correctly, provide protection from diseases and pests.
Watering and feeding
When watering tomatoes, they are guided by the state of the plants. Gardeners advise to provide drip irrigation in greenhouses. Do not use the sprinkling method, as tomatoes suffer from leaf wetness. The right time for watering is the first half of the day.


Important! After watering, the soil in the beds is loosened, carefully working around the bushes so as not to damage the root system.
The first feeding is applied in a week and a half after transplanting seedlings. Nitrogen mixtures are used to stimulate the growth of green mass. A solution of ammonium nitrate is suitable (30–40 g of powder are diluted in a ten-liter bucket of water).
Garter
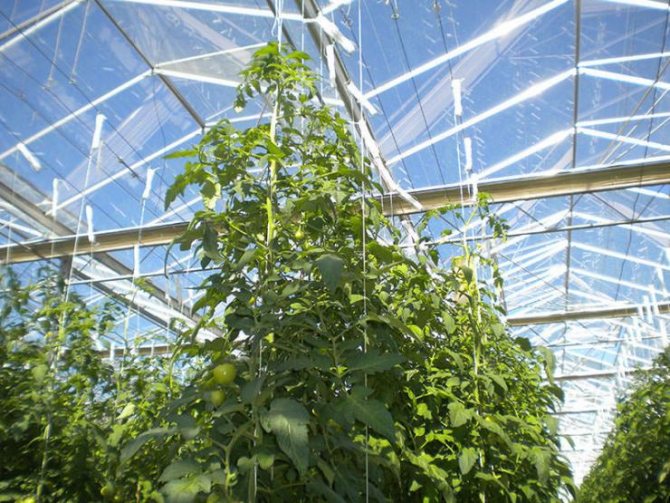
Not all tomato varieties need tying. Support for undersized and early maturing varieties is not required. Naturally, tall tomatoes will not do without garters. When planting indeterminate varieties, they practice the arrangement of vertical supports. Plants are tied to trellis nets or to separate vertically stretched strings.
Gardeners use different support options.When growing medium-sized varieties in small greenhouses, it is easiest to deepen individual pegs near each bush.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
The general requirement remains for the quality of the garters. The best option is to use fabric tapes 1.5–2.5 cm wide or twine, jute.
Formation
They begin to form bushes in early June, when lateral shoots appear in the leaf axils. The stepsons are removed to exclude thickening of the bush. Acceptable frequency of pinching is 10-12 days.


Common schemes for the formation of bushes:
- single-stem is practiced when growing tall varieties;
- two-stem is used in the cultivation of determinate tomatoes, sometimes for the cultivation of indeterminate;
- superdeterminate tomatoes form three-stemmed, but not necessarily.
Some undersized varieties do not feed at all.
There are no strict rules for the formation of bushes, since climatic conditions, the parameters of the greenhouse, and the preferences of gardeners are the determining factors.
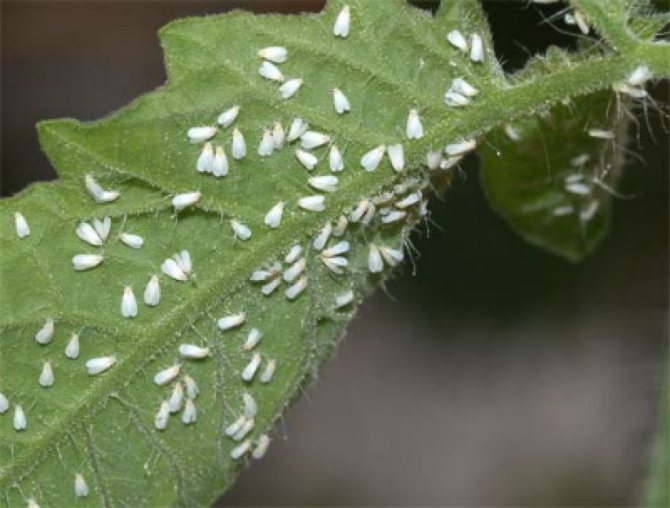
Protection against diseases and pests
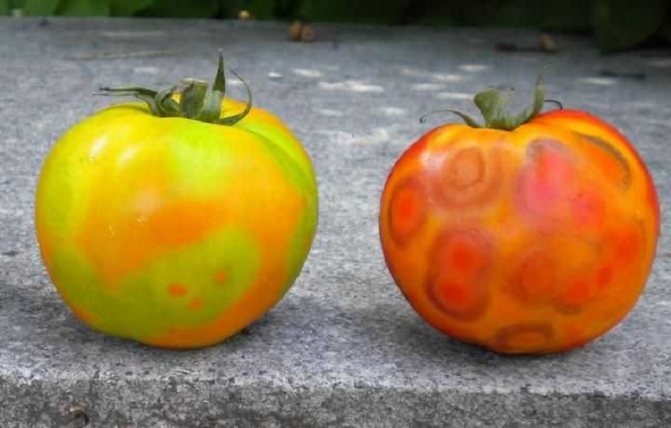
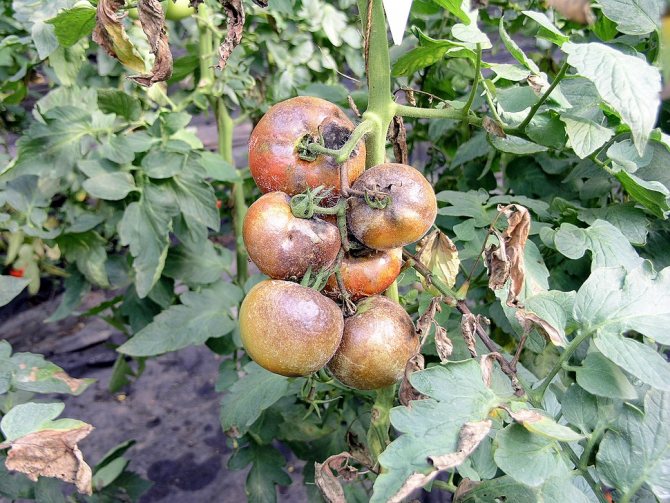
The most common tomato diseases are brown leaf spot, mosaic, leaf mold, white bloom. It is known that it is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it. The main preventive measures:
- planting disease resistant varieties;
- disinfection of seeds before planting;
- greenhouse and soil processing at the beginning of the season;
- processing of tomato bushes with special means ("Bayleton", "Aktellik").
It is advisable to buy seed from reliable agricultural firms that independently process the seeds before selling.
Formation of standing density ↑
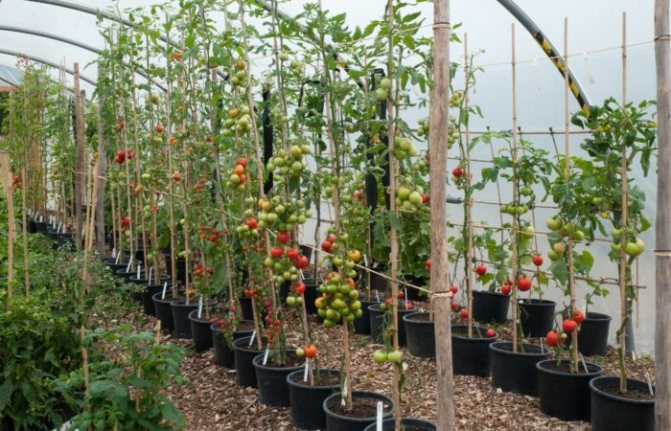
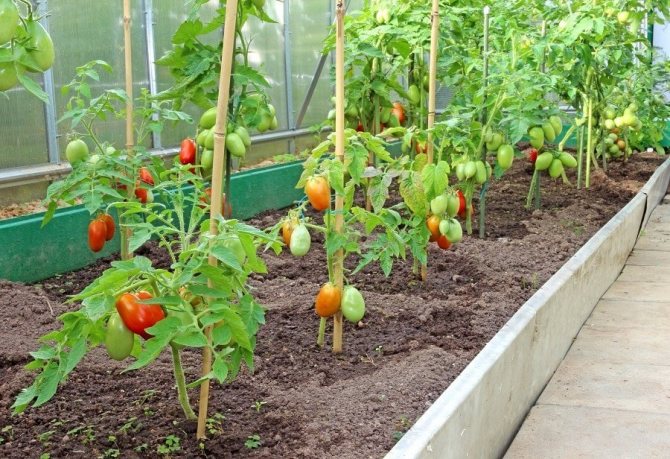
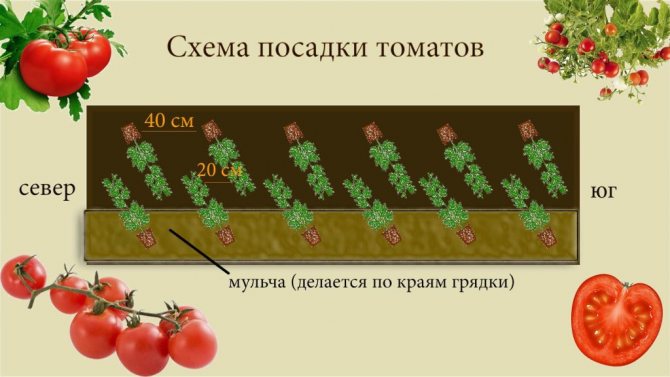
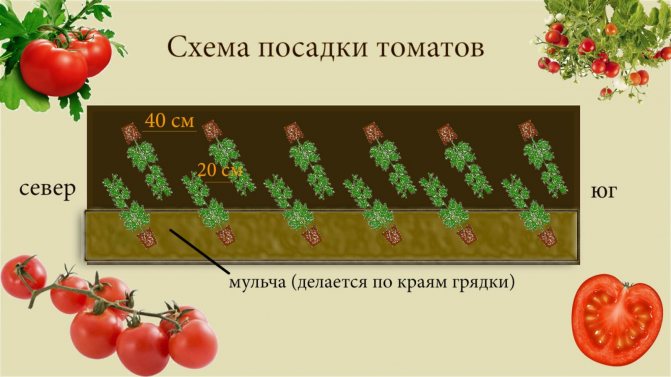
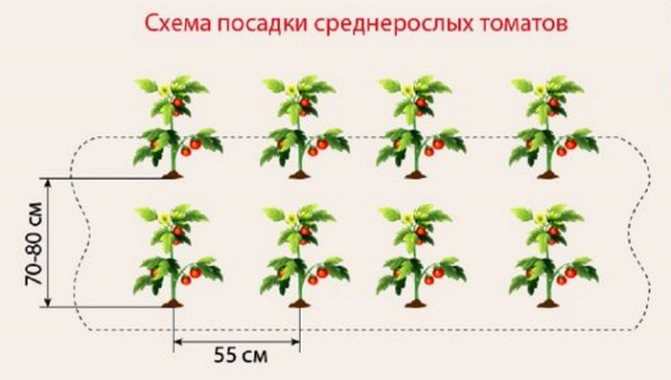
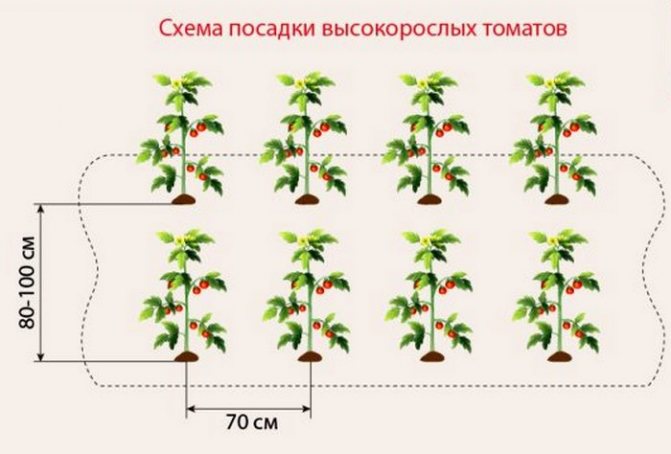
For the correct operation of polycarbonate greenhouses with a complete arrangement (heat, moisture, lighting, nutritious soil, etc.), it is better to grow tomatoes of tall indeterminate varieties and form them into one stem. With a single-stem form, the distance between the bushes can be 30 cm, it is optimal to leave 50 cm between the rows. With a line planting (in 2 rows), seedlings or sowing in holes are best done in a checkerboard pattern. This technology will make better use of the greenhouse space and plant more bushes.
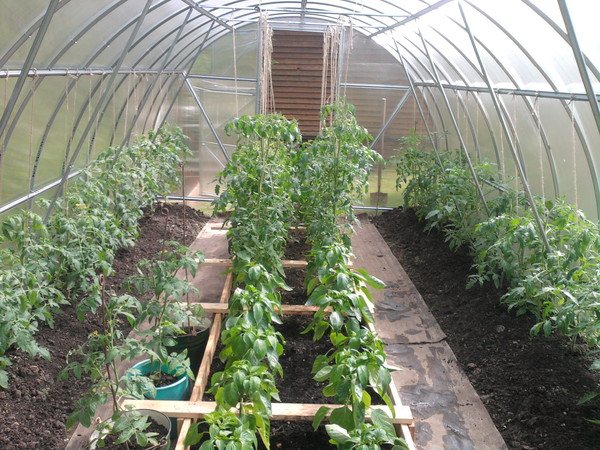


Rational arrangement of beds
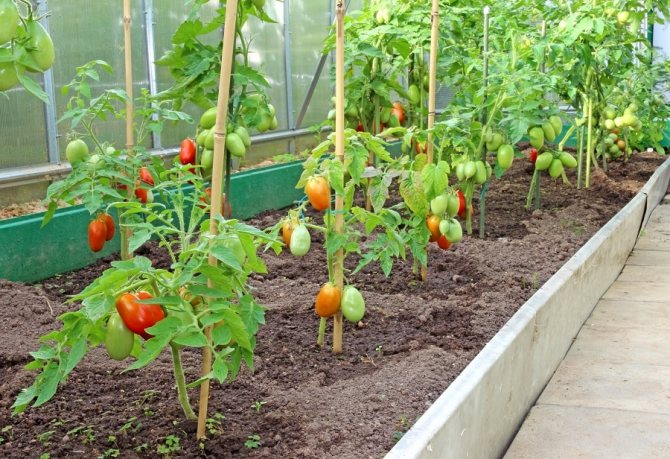
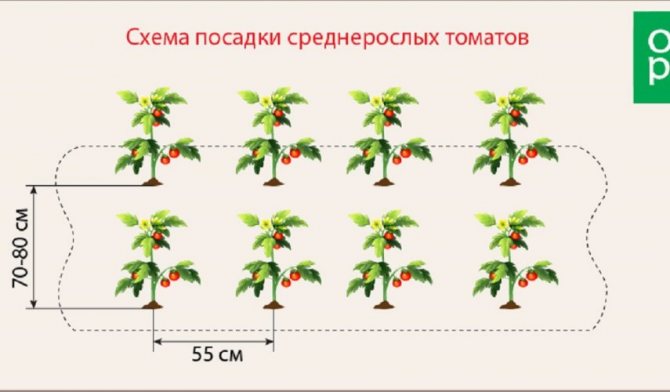
Tall varieties, formed in several stems, can be planted in one or two rows, always observing a checkerboard pattern. The gap between the bushes is 45-70 cm, between the rows 70-80 cm.
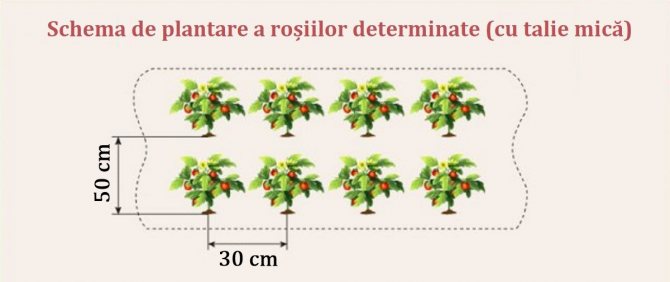
In small greenhouses with a different coating (reinforced film, ordinary double, bubble, etc.), large yields form undersized determinant varieties. They are formed bushy in 2 or 3 stems, sometimes they are not pinned at all. In such conditions, it is more expedient to grow early maturing varieties. Planting can be done in 2 rows, observing a checkerboard pattern. Free space in a row 40 cm, between rows 50-60 cm.
If greenhouse conditions allow, you can combine several varieties of tomatoes of different types. In this case, the outer beds are occupied by low-growing tomatoes, and the central bed with the highest distance to the ceiling is occupied by indeterminate ones. This technology will provide the family with fresh vegetables for a longer period.
Dates for planting tomatoes in a greenhouse
To get a bountiful harvest of tomatoes, it is important not only to select a variety, but also to plant the planting material in a timely manner. The optimum temperature in the greenhouse should be between 20-25 ° C. And the type of structure is of great importance:
- the heated greenhouse is ready to receive seedlings from the end of April;
- unheated building with double foil can be used from the beginning of May;
- unheated and non-insulated structure is ready to accept tomatoes at the end of May.
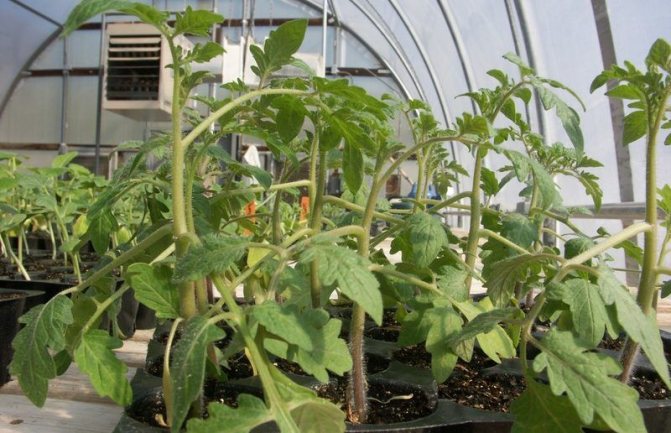


To more accurately determine the timing, you need to take into account the climatic features, the variety of tomatoes.The age and characteristics of the seedlings also matter: the seedling must have a strong trunk, a well-developed root and 8 formed leaves.
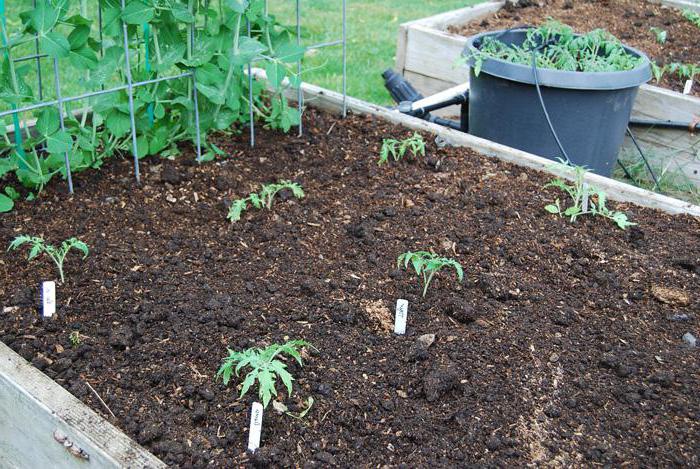
Tomato planting schemes
The location of tomato seedlings depends on the size of the greenhouse and its operation.
For home use in greenhouses with three beds, a single-row scheme for planting seedlings in the outer beds (near the wall) and a two-row scheme in the central bed are often used.
- If the greenhouse has only two beds, then the planting pattern can be left single-row or, depending on the type of tomato plants, a two-row checkerboard.


Tomatoes in greenhouses
- If the greenhouse is of medium size (4x8 m), then you can use a multi-line planting method (2-3 rows form a line) for the middle bed and a ribbon-nesting method for the outer beds. When using this scheme, use the appropriate marker and plant the seedlings at the intersection of the marker bars.
When choosing a landing pattern, you need to be guided by 3 basic rules:
- optimally occupy the greenhouse area,
- create optimal conditions for the plant
- have free access to every plant.
Why thickening plantings is dangerous
If the bushes are planted too thickly, this leads to their shading, which means to late ripening of the fruits. Plants with a strong root system inhibit the development of weaker ones.
Thickening of the planting complicates care. The likelihood of the occurrence of diseases and the appearance of pests increases due to the contact of the leaves of a diseased bush with a healthy one.
Additional Information! Dense plantings can create a lack of moisture and nutrition, postpone ripening, which will lead to a significant decrease in yield.
However, with the rare placement of seedlings in the greenhouse, the use of the area will be irrational. Therefore, when purchasing seeds, it is necessary to find out which species the variety belongs to. This determines the distances that must be maintained when planting, and the care that the plant will require.
Important! The yield of tomatoes largely depends on the correct placement of seedlings and the distance between the bushes.
That is why gardeners need to know at what distance to plant tomatoes in a greenhouse, what should be the scheme for planting tomatoes in a greenhouse. The information provided will help give


Thickening of plantings
How to plant tomatoes in a greenhouse 3x6 m ↑
The greenhouse can accommodate 2 or 3 beds.
When arranging two beds ↑
The beds are placed along the long sides. If they are ground-based, then their height will be 30-40 cm from the level of the greenhouse path. The width of the beds is 90-100 cm, the rest of the area will go under the path, where the tools, a small wheelbarrow, irrigation hoses and other devices that do not obstruct the approach to the beds will be located.
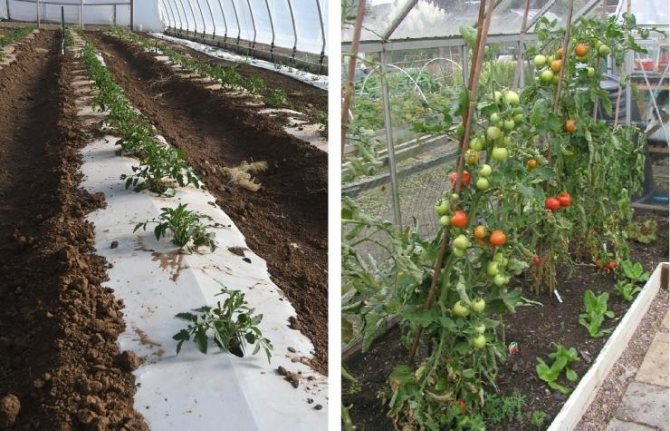
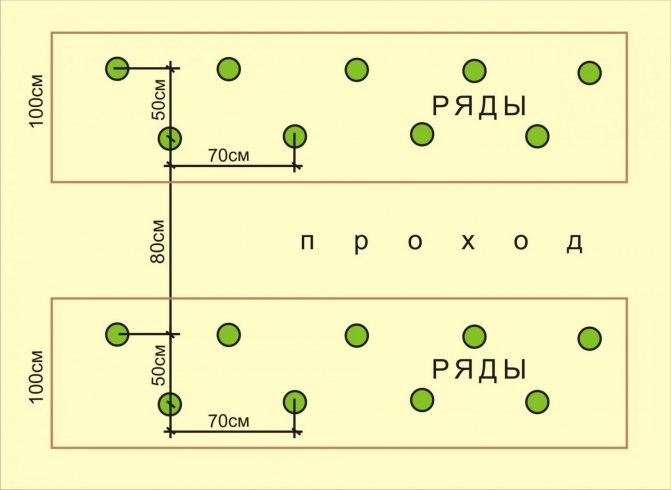
In such a greenhouse, you can use a square-nested or two-line method of planting seedlings. For ease of care, the bushes need to be staggered. If the distance between the plants is 40 cm, and between the rows 60, then 60 bushes can be planted.
Calculation: 600: 40 = 15 bushes will take 1 row of tomatoes. There will be 4 such rows on 2 beds. Calculation: 15x4 = 60 bushes.


There are 2 rows in the greenhouse
Preparing soil and seeds for planting
For sowing tomato seeds for seedlings, the seed and soil mixture should be properly prepared. The pelleted seed is not processed before sowing. The rest of the planting material should be soaked in Fitosporin for 20 minutes. Then the seeds are kept in a hydrate with a growth stimulant and sown in the prepared soil.


The seed is sown in a container, the height of the sides of which is about 7 cm.The soil mixture is prepared by combining in equal parts:
- peat;
- humus;
- sod soil.
The mixture is to be moistened. Then it is enriched. Take on the bucket:
- river sand - 1 liter jar;
- ash - 1 tbsp;
- superphosphate - 1 tablespoon
You can sow the seed in ready-made commercial soil.
Distances depending on the variety or hybrid of tomatoes
When your seedlings have grown and matured enough, there will be a need to transplant them into a greenhouse or into open ground. Depending on which variety or hybrid of tomatoes is chosen, the distance between the tomato bushes will vary when planting.
The classification of tomatoes is based on their shape, the height of the bush and the level of distribution of its root system:
- the height of low-growing (they are also called standard) tomatoes fluctuates at the level of 45 cm, the roots branch out into a very compact system. It is recommended to plant such plants very densely: 6-7 bushes per 1 m2 of soil. Due to the fact that their trunks are strong and strong, standard varieties develop well without tying up;
- medium-sized (so-called determinant) varieties reach a height of 100-150 cm and have a well-developed root system. Seedlings of such tomatoes are planted 3-4 bushes per 1 m2 of soil, preferably in open and protected ground. Bushes of medium-sized tomatoes need shaping;
- the largest areas are occupied by tall (indeterminate) tomatoes, the height of which can reach 3 m. Their roots grow very extensively. The best arrangement of such tomatoes is 2 bushes per 1 m2 of soil, in no case should they be planted thicker. They also require more attention than other varieties: tall tomatoes in the process of growth and development need to be tied up, pinned and pinched.
The depth of the hole will also depend on the variety: 20 cm will be enough for undersized tomatoes, and 30 cm for a hole for tall ones.
Business
What to plant in the greenhouse profitable? You can also consider greenhouses as a business. You can make a year-round winter greenhouse and grow cucumbers, tomatoes, herbs, vegetables, strawberries, flowers for sale. Such a business can become very profitable.
You can also grow in a greenhouse to sell chrysanthemums, roses or tulips by March 8th.
This concludes our article. You already know the peculiarities of growing in greenhouse and what to plant in the greenhouse and how. By installing it on your site, you will get a huge opportunity to significantly extend and increase the summer cottage season and plants grown in greenhouse, will give you an excellent harvest of their own production. And using insulated greenhouse such a pleasure takes place all year round.
Distances when sowing tomato seeds for seedlings
The first step on the road to a rich tomato crop is planting seeds for seedlings. Tomatoes are distinguished by good germination, therefore, before planting, the seeds can not be germinated or stimulated, however, it is recommended to carry out a disinfection procedure (rinse with 1% manganese solution) and enrichment with mineral fertilizers (mixtures for this can be prepared by yourself or bought ready-made in specialized stores).


Prepared, shallow (no more than 8 cm), sterile containers should be drained (otherwise the tomato roots may start to rot), then filled with moist soil, not reaching 2 cm to the top edge. Compact it, top up the soil to the previous level and compact it again. Make several recessed rows 4-5 cm apart. Put the seeds in them every 2 cm, cover them with dry soil on top, lightly tamp with your hand. Cover with glass or cellophane and place the seedlings in a warm place.
A more thickened planting of seeds can lead to the fact that the seedlings will turn out to be frail, weak - the tomatoes will not have enough moisture and nutrients, they will put pressure on each other's root system.
Internal arrangement of greenhouses
The layout of the inner space of the greenhouse depends on its purpose and size. For the greenhouse itself, a place is selected so that the sun's rays illuminate it throughout the whole or most of the day. When growing low-growing plants (seedlings, peppers, bush tomatoes, green ones), the greenhouse is placed so that the beds are directed from north to south.In mixed plantings with growing parts of the plants on trellises (cucumbers, tall tomatoes, zucchini), it is better to place the beds from west to east for uniform illumination of crops.
Planting hole size
A hole is a hole in the soil for planting a seedling. A properly prepared hole is the key to successful engraftment of seedlings. Its size depends on the volume of the pot in which the seedling was grown.
When planting, it is necessary to keep a lump of soil around the root system, then the plant will take root quickly and painlessly.
In general, the depth of the hole should be at least 20 cm. The root system should be placed in the hole and covered with earth so that the level of the pot is slightly lower, and a depression for watering is obtained. After the seedling has taken root, this depression is sprinkled with earth.
If the seedlings in the pot have outgrown, the hole can be made somewhat freer, but the root system should not be buried, but laid in a groove up to 30 cm deep. Seedlings of indeterminate varieties are more often drawn.