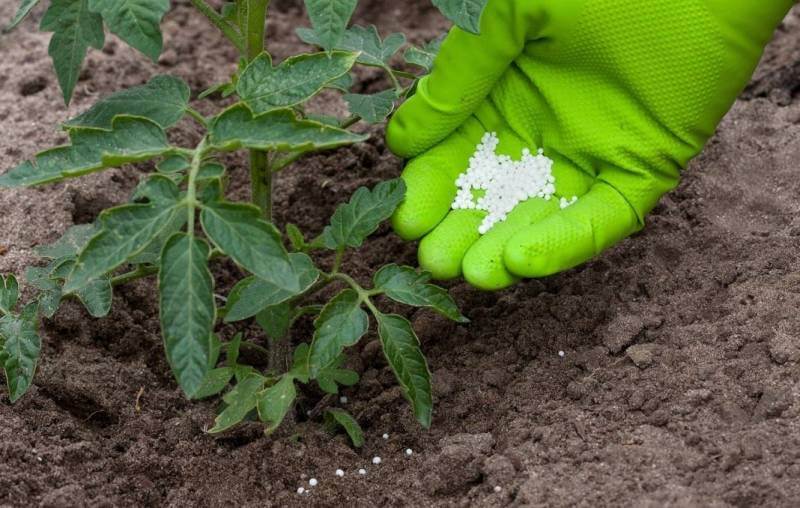
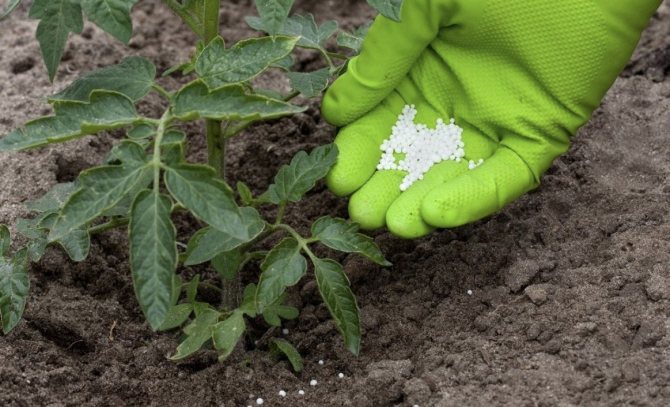
The goal of any gardener when growing tomatoes is to obtain a high yield of varietal fruits with excellent taste and marketability.
The desired result can be achieved only if balanced top dressing is introduced into the soil in a timely manner..
For growth and development, maintaining a healthy state and, as a result, high yields, this crop needs good nutrition.
Top dressing of a tomato during fruiting and flowering: what and how to fertilize
Tomatoes need macronutrients and nutrients. For a strong seedling and a rich harvest, three elements are needed: nitrogen (N), potassium (K) and phosphorus (P). When feeding tomatoes during flowering and fruiting, they should also receive magnesium, calcium, manganese, sulfur, iron, boron, molybdenum, cobalt and zinc.
Macronutrients in tomato feeding during flowering and fruit setting play an important role:
- enrich the soil and improve seed germination;
- activate the life processes of the plant;
- improve fruit set, reduce the number of barren flowers;
- participate in the synthesis of vitamins, proteins and carbohydrates;
- increase the resistance of crops to sudden changes in temperature, drought, disease and pests.
We focus on the stage of tomato development
Any plant, including a tomato, at different stages of development, consumes nutrients in different quantities. For example, an actively growing tomato needs an increased amount of nitrogen, and in the budding and fruiting phase, a constant supply of potassium.

Only with an accurate knowledge of the needs of the culture at a certain period of development, it is possible to make a balanced top dressing, which will not harm the bushes, but, on the contrary, will provide them with the necessary nutrition.
All feeding of tomatoes should be carried out in a strictly defined order.
Randomly introducing a particular substance under the bushes can provoke its excess or deficiency.
As a result of improperly carried out dressings, tomatoes weaken and are easily affected by pests and diseases, the crop (if any) loses its varietal characteristics - even the largest-fruited hybrids can produce small unsightly tomatoes.
Signs of deficiency of macro- and micronutrients in tomatoes
The appearance of the bushes will make it clear whether you need to feed the tomatoes:
- The leaves become smaller and turn yellow, the veins on the underside turn blue-red - there is a lack of nitrogen.
- The stem is thin, the underside of the leaf is red-violet, the ovary is crumbling, the vegetables are small - there is a lack of phosphorus.
- New shoots are wrinkled, covered with bronze spots, the crop ripens unevenly - potassium deficiency.
- Leaves are brittle, curl upward, fall prematurely - little magnesium.
- The growth of the stem stops early, the flowers fall - lack of calcium.
- The lower old shoots turn yellow sharply, the stem thickens - lack of sulfur.
- The growth point of the stem turns black, the fruits acquire an ugly shape, tissues in vegetables die off - there is little boron.
- Pale yellow spots appear on the upper young leaves - a lack of manganese.
- Yellowing of leaves with iron deficiency is similar to nitrogen starvation.
What substances are missing?
The main elements that tomatoes need are nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
The lack of the first of them manifests itself in the gradual yellowing of the leaves. Moreover, this process begins with the oldest of them and gradually climbs up.
When the tomato leaves turn purple, the summer resident should check the temperature. If the plants are not cold, then they do not have enough phosphorus.
In a situation where the edge of the leaf (starting from the very tip) has acquired a light color, and over time it becomes brown and dries, it is necessary to exclude the lack of potassium. If it appears at the time of fruit ripening, then the tomatoes will be sour with an unripe center.


Top dressing of a tomato during flowering and fruiting
Before the buds appear, a healthy seedling already has 6 - 8 pairs of leaves. Bushes should be dark green, not overgrown, with a thick stem and large leaves. This will serve as a signal that the nitrogen content in tomato feeding needs to be reduced. With an excess of nitrogen, the seedling will develop a green mass, extra stepchildren will form, the fruits will not be tied.
Video: Excellent top dressing that increases the number of ovaries in a tomato
For this vegetable, when the crop ripens, phosphorus is needed, as well as potassium. It is necessary to feed tomatoes during flowering and fruit growth every twenty days. The best way to introduce potassium and phosphorus preparations at this stage is to water the diluted concentrate at the root.
How can you feed tomatoes during flowering and ripening of fruits:
- "Potassium monophosphate". Contains 46% phosphorus, 34% potassium. Consumption rate 10 - 15g per 10 liters.
- Diammophos. As part of - N9: K25: P25. Dilution scheme - 20g per bucket of water.
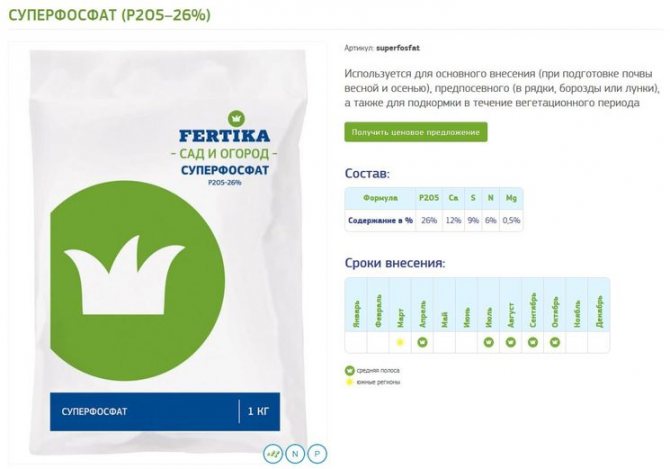
- "Superphosphate double". Contains phosphorus 46%, as well as calcium sulfate, ammonium and iron phosphates. Dilute 100 g of superphosphate in 10 liters of warm water.
Complex fertilizers


What fertilizers do tomatoes need for good fruiting? If the bushes develop normally, they have no signs of an excess of nitrogen, then complex preparations can be used. They dissolve easily in water, are suitable for leaf cultivation and for irrigation under the root, contain trace elements in the right concentration. Experts recommend:
- Kemira Lux. Packing - 100g. Suitable for outdoor and greenhouse use. Contains nitrogen 16%, potassium 27%, phosphorus 20.6% and trace elements. Dilute - 10g per 10 liters.
- "Blank slate for tomatoes." Packaging - 1.2kg, 350g and 100g. Mineral concentrate with nitrogen 16%, phosphorus 8.7%, potassium 20%. Consumption - 10g per 5 liters.
- "Fasco Baby for Tomatoes". In the composition of phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium and organic matter. Available in 50g and 250ml packaging. Consumption rate - 10 g per bucket of liquid.
Fertilizers for foliar processing
Top dressing of tomatoes during the fruiting period includes spraying fertilizers on the leaf. They contain all trace elements in an easily accessible form for plants, which are absorbed by 90% after application. Preparations for foliar feeding of tomatoes during the growth of fruits in the greenhouse and in the open field are produced in liquid and powder form. The role of such trace elements is great:
- accelerate the ovary;
- improve taste;
- increase the shelf life of the crop;
- increases resistance to disease.


Fertilizers recommended by experts:
- "Quantum for Vegetable Crops". Complex, highly concentrated chelate. Contains nitrogen 5%, phosphorus 5%, potassium 7%, iron, zinc, copper, magnesium, boron and humic and amino acids. Apply twice: before budding and three weeks after the first treatment. The consumption rate is 30 ml per 10 liters of water.
- "Reakom for tomatoes". Chelated concentrate with a content of phosphorus 40%, potassium 60%, sulfur, iron, molybdenum, magnesium, copper, boron. Consumption rate - 25 g per 10 liters of water.
- "Boric acid". Consumption rate - 10 g per 10 liters of water. What is the microelement boron for:
- promotes pollination and formation of the ovary;
- increases yield up to 20%;
- promotes better absorption of calcium.
The role of humate for fertilizing tomatoes
Humates are substances with humic acids. Humic substances are extracted from peat and contain about 50 macro- and microelements. Some elements of these acids are not assimilated by crops from the soil, so they are converted into water-soluble potassium or sodium salts.
You need to introduce humates three weeks before the first harvest.... For spraying, use a filtered concentrate without particles of raw materials.
How humates affect the plant:
- prevent shedding of the ovary;
- accelerate the ripening of vegetables;
- reduce the content of nitrates and radionuclides in the crop.
What humate preparations can be used to feed tomatoes for quick ripening of fruits in June - August:
- "Potassium humate", "Sodium humate" and "Humate + 7" - produced in dry and liquid form. The concentration of the active substance differs from manufacturer to manufacturer, so you need to follow the instructions on the package.
- "Hera for Tomatoes" is a humated, granular substance. Contains the main elements and salts of humic acids. The drug is applied dry at a dosage of 5g per bush.
Video: How to feed tomatoes with potassium humate
Organic fertilizer for tomatoes
Such substances are obtained as a result of the processing of waste products of plants and animals. All types of organic fertilizers are suitable for feeding tomatoes during fruiting. Consider the main types of organic matter:
- Wood ash. It is obtained in the process of burning wood, therefore there is no nitrogen in it. Contains high concentration of potassium, as well as calcium, magnesium, molybdenum, manganese and boron. Method of application - watering at the root of 100 g of ash per 10 liters of water.
- Biohumus. Foliage, grass or manure processed by earthworms. Contains a water-soluble form of elements, amino acids and humic substances. For feeding during flowering and growth of tomato fruits, you can use the drug "Gumisol". It increases productivity, enhances taste. The spray rate is 250 ml per 10 liters of water.
- Cow and horse manure. Contains the necessary elements for crops. Use dry manure. Insist 1 kg of humus in 10 liters of water for 5 days. Next, dilute each liter of the resulting liquid with a bucket of water. Add 1 liter of ready-made liquid under the bushes.
- Bird droppings. It contains three to four times more useful trace elements, so you need to dilute the concentrate 1 liter per 20 liters of water.
Mineral fertilizers
Balanced mineral fertilizing promotes the harmonious development of the plant and provides targeted nutrition for the tomato bush that needs support. During flowering, tomatoes are fertilized with the following substances:
- superphosphate and double superphosphate, a feature of which is slow solubility - the required dose of the agent is put into hot water, insisted for a day, and then mixed with the rest of the water;
- potassium salt and potassium chloride are used strictly according to the instructions, not exceeding the recommended volume due to the chlorine content in the dressing;
- potassium sulfate - the optimal fertilizer, which, if possible, is better to replace potassium compounds with chlorine;
- potassium nitrate, which has good solubility.
Ammophoska, nitrophoska, potassium monophosphate and other complex mineral preparations are widely used for feeding tomatoes in the flowering phase. For efficiency, they often use ready-made complexes or mix substances on their own, guided by the instructions. The dosage of dressings varies depending on the phase of development:
- at the very beginning of flowering, 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 10 g of potassium chloride and 40 g of superphosphate are taken on a bucket of water;
- 2 g of potassium permanganate and 20 g of potassium sulfate are added to a bucket of water to 25 g of superphosphate diluted in advance;
- in the flowering phase of the third and fourth brushes, the following composition is selected - 30 g of ammonium nitrate, 70 g of superphosphate, 20 g of potassium;
- after 2 weeks, top dressing is carried out in this proportion - 30 g of ammonium nitrate and potassium agent, 45 g of superphosphate;
- fertilization of 5 g of urea and the same amount of potassium preparation, 20 g of double superphosphate accelerates fruiting, while for weak tomatoes at the flowering stage, the proportion of the nitrogen component is doubled.
Foliar dressings with different microelements are also used:
2 g of boric acid, copper and zinc sulfates, 4 g of manganese sulfate are dissolved in a bucket of water. The consumption of the specified amount of fertilizer is per 100 sq. m. To increase the amount of ovary, fertilizing with boron is carried out, which is part of various preparations: boron-magnesium fertilizer, borosuperphosphate, borofosk and others.
Fertilizing tomatoes during flowering, they comply with the requirements of agricultural technology in terms of the number of dressings and the timing of their implementation. Using mineral preparations, they study the features of fertilizers and their use. Before or after feeding, the bed must be watered. They give preference to products in liquid form, which are more easily and quickly absorbed by plants. If dry fertilizers are applied, the granules or powder are spread over the soil surface so that they do not come into contact with the roots. Different types of soil require a certain dose of mineral fertilizers. On clayey heavy soils, they take a large rate of funds, because in such areas minerals are absorbed slowly. On light structured soils, the applied top dressing quickly approaches the root shoots.
Attention! With the intensive development of tomato tops, instead of flower brushes, the proportion of the nitrogen component is reduced. To get the harvest faster, the dosage of potassium and phosphorus is increased.


Useful tips for feeding tomatoes in the greenhouse and in the open field
- Choose complex formulations with potassium, phosphorus, boron, magnesium. Use preparations with a minimum nitrogen content in the composition.
- Alternate the introduction of mineral and organic substances.
- To accelerate the growth of fruits, remove the leaves on the stem to the first brush with an ovary and pinch the tips of the shoot on which the vegetables are formed.
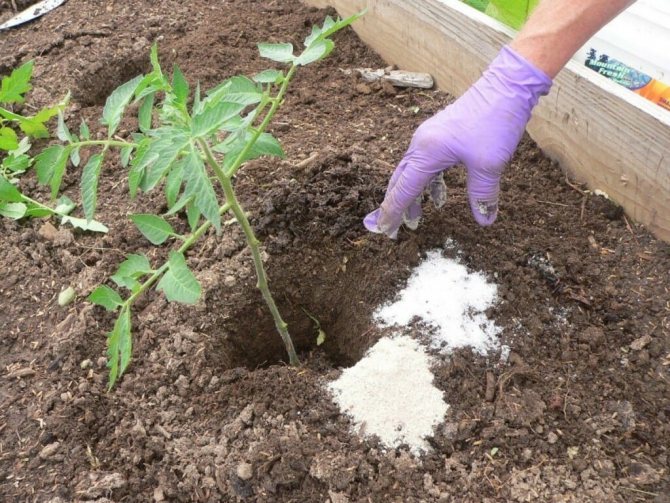
- Apply fertilizer for digging the soil in the fall. Use 50 g of superphosphate and 20 g of potassium sulfate per square meter of land.
- In the spring, when planting seedlings, add 10 g of nitroammophoska to each well.
- Plant green manure in the place where this vegetable will grow. Plants such as oil radish, lupine, phacelia, mustard, alfalfa improve the structure of the soil, accumulate nutrients in it.
- In polycarbonate greenhouses, after sheet processing, it is imperative to ventilate the seedlings; close the greenhouse when the leaves are completely dry.
- Observe the norms for the dilution of chemicals according to the instructions, do not exceed the number of treatments.
- Provide regular and sufficient watering during budding and ripening of the crop. With a lack of watering, a barren flower is formed, and the ovary crumbles.
Video on how to make an infusion of nettle for cucumbers and tomatoes
Nettle-based bait is gaining popularity among experienced gardeners. Thanks to the organic composition, such an infusion can significantly increase the yield and increase the resistance of cucumbers and tomatoes to external factors.
All types of baits help plants to develop well and give a rich harvest. A competent approach to the choice of fertilizers guarantees a positive result and you can enjoy healthy vegetables. Follow our advice and be healthy.
Author of the publication
offline 44 minutes
How to feed tomatoes during fruiting
Top dressing of tomatoes during the fruiting period is a prerequisite for growing vegetables. It is important to apply fertilizers not only in sufficient volume, but also taking into account the needs for certain elements at different stages of plant development.Top dressing is also necessary because tomatoes are very demanding on the quality of the soil. Each plant tries to take all the elements necessary for growth and development, thereby impoverishing it. To ensure high rates of growth and ripening of fruits, it is necessary to pay attention to the correct preparation of the nutrient mixture.


Top dressing of tomatoes during fruiting
What fertilizer is best for seedlings of tomatoes and peppers on the windowsill
Tomatoes and peppers belong to the nightshade family, therefore they are very similar in terms of care and feeding. With a well-chosen top dressing, you will get a rich harvest of healthy and tasty vegetables.


So, tomatoes need the following types of food: mineral, organic and cooked according to folk recipes. All of them have a positive effect on plant development and fruit growth. However, don't overdo it. It is worth carefully observing the plant in order to understand what minerals and micro-elements it lacks. An excess of nutrients can lead to the death of the vegetable or fill the fruit with a large amount of nitrates.
- Mineral dressing. Seedlings of tomatoes and peppers can be watered with solutions of urea, superphosphate, epin, etc. The most effective is a nutritional formula called "Bogatyr". It contains a whole complex of minerals, micro-elements and nutrients for root and foliar feeding. There is also an additive "Hera", which stimulates the growth of fruits, improves immunity, gives a pleasant taste to vegetables and does not contain harmful chlorine.
- Organic food. They are used in the form of infusions, solutions and in pure form. Thanks to them, not only the condition of the vegetables improves, but also the quality of the soil itself. Organic matter includes compost, manure, humus, mullein, bone meal, yeast, and bird droppings. It is worth noting that fresh manure is not allowed for tomatoes and peppers. It is used to prepare infusions and solutions for complementary foods.
- Folk dressing recipes. The most commonly used are iodine, yeast, peroxide, eggshells and wood ash. All these ingredients can be found in your home and will enrich the soil with all the necessary substances. A solution is prepared from iodine: 1 drop of the substance per 3 liters of water. Leaves are treated with this mixture 2-3 times during the entire period of growth. An infusion is prepared from the eggshell: 500 g per 3 liters of water. The mixture is defended for 3 days and used if there is a suspicion of a lack of calcium in the plant.
When to feed?
It should be borne in mind that too frequent feeding can damage the tomatoes. Therefore, it is recommended to carry out this procedure during the following periods of the plant's life:
- After planting seedlings in the ground.
- Just before flowering.
- When the first ovaries appear.
- During fruiting.
For the full ripening of the fruits, when the tomatoes have not yet poured, the third and fourth feeding are most important. The third feeding contributes to the formation of full-fledged fruits. It is carried out during the period of active flowering and ovary formation. The next top dressing, carried out during the fruiting period, is aimed at increasing the yield of the bush. In poor soil conditions or with prolonged rains, tomatoes need more frequent feeding. For greenhouse plants, this procedure should be done less frequently to avoid excessive moisture. During the ripening of fruits, the amount of nitrogen fertilizers should be reduced - an excess of nitrogen will provoke the formation of green mass, which will take away all the nutrients.
Connection with peppers and cucumbers
The joint cultivation of tomatoes and sweet peppers, including at home, is permissible and does not cause antagonism, since the conditions for the growth of crops are the same, but it is better to differentiate tomatoes and cucumbers for the following number of reasons:
- Tomatoes and peppers need moderate warmth and dryness. Cucumbers, on the other hand, love high humidity.
- At high humidity, tomatoes are affected by fungal infections, dryness for a cucumber threatens the appearance of a spider mite.
- Frequent watering is vital for cucumbers; watering tomatoes and peppers is often not recommended.
Top dressing based on mineral salts
Mineral fertilizers contain various chemical elements necessary for plants at different periods of growth and development. These are mainly sodium, phosphorus and potassium (also referred to as NPK). It is convenient to use ready-made mineral fertilizers such as Kemira Universal or Solution. They can be purchased at specialist gardening stores. Such fertilizers help to improve the taste and increase the yield of tomatoes. However, if necessary, fertilizers can be made independently. During ripening, tomatoes are most in need of potassium, so top dressing must necessarily contain this element.


The feeding solution should be prepared correctly
Even when using compound fertilizers, it is recommended to add potassium sulfate in a volume of 20 grams per 10 liters. The lack of potassium is indicated by the appearance of red specks on young leaves, which merge into solid brown spots at the edges of the leaf. Soon the leaves fall off, and the fruits become unevenly colored. When the first signs of potassium deficiency appear, you need to feed with 1% potassium sulfate solution. Poorly developed fruits and bluish tinge of leaves indicate a lack of phosphorus. To prepare a phosphorus-containing fertilizer, you should dissolve superphosphate in boiling water in a ratio of 35 grams of fertilizer (about 2 tablespoons) per liter of water.
To completely dissolve the superphosphate, the resulting solution must be infused for at least 8 hours, after which it is diluted in 10 liters of water and applied at the rate of 0.5 liters per tomato bush. Lack of calcium during the fruiting period is characterized by the appearance of apical rot, in which the top of the fruit darkens and begins to dry out. In this case, it is recommended to spray the plants with a special solution, at the rate of 20 grams of calcium nitrate per 10 liters of water.
What ready-made products can you buy?
- Ammophos, nitroammophos, diammophos (contain nitrogen and phosphorus).
- Potassium nitrate (contains nitrogen and potassium).
- Calcium nitrate (contains nitrogen and calcium).
- Magnesium sulfate (in the composition of magnesium and sulfur).
- Potassium monophosphate (phosphorus-potassium fertilizer).
- Nitrophoska, nitroammofoska.
- Kemira Universal 2, Kemira Lux.
- Station wagon.
- Solution.
- Tomato crystal.
There are other ready-made dressings for tomato seedlings, about the most popular of them, such as "Athlete", "Garden World" and others, you can read in this article, and here you will learn about such means as "Baby", "Red giant "," Mage boron "and others.
Organic feed
To replenish potassium, you can also use ordinary wood ash; you need to feed it with the loosened soil under the bushes. However, an ash solution with the addition of iodine and boric acid will be more effective. To prepare it you will need:
- Ash 1.5-2 l.
- Boric acid 10 g.
- Alcohol solution of iodine 10-15 ml.
First, the ash is mixed with 5 liters of boiling water. After the mixture has cooled down, add water to it so that the final volume of the solution is 10 liters. Then iodine and boric acid are added to the solution (for better dissolution, boric acid is preliminarily diluted in a small amount of warm water). In a day, the fertilizer solution will be ready for use.
Before using the solution, a liter of the mixture is diluted in 10 liters of water. Each individual bush requires 1 liter of fertilizer: greenhouse plants - once every 2 weeks, and for tomatoes grown in open ground - once a week.
The active content of potassium and other trace elements in ash significantly accelerates the fruiting process, iodine protects plants from fungal and bacterial diseases, and boron promotes the setting of new fruits.The use of potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate) instead of iodine has a positive effect on the formation of fruits. Experienced gardeners recommend alternating fertilizing with manganese and iodine for a more even plant development.
Boric acid as fertilizer for tomatoes
Boron itself is very important at all stages of the growing season of tomatoes. It promotes active cell growth and helps to synthesize nucleic acids. Boron primarily affects the young parts of the plant: ovaries, points of growth and flowers.
If tomatoes do not receive the proper amount of a trace element, then this contributes to the accumulation of toxic substances in the plant, which poison it and lead to death. Consider a number of signs of a boron deficiency in tomatoes:
- In the initial stages, the ovaries, foliage and poor maturation of the vegetable fall off.
- In the second stage, young shoots twist and the foliage changes color at their base. In this case, the tip still retains its natural green color.
- Then, young leaves that have just appeared begin to acquire a light green or whitish color and curl towards the base.
- At the final stage, the veins of already diseased leaves darken, the stems break easily, the growth points die off. If the plant has already begun to bear fruit, then dark spots form on the tomatoes.
If an excessive amount of fertilizing with nitrogen and lime content was introduced, then the boron deficiency will only increase.


Boric acid can be used at all stages of tomato growth, including when preparing seeds for planting.
- Preparation of a solution for seed treatment and soil irrigation. Before planting seeds, it is recommended to soak them for faster germination in the following mixture: 0.2 g of boron powder and 1 liter of water. The seeds are soaked in a solution for 24 hours, and then immediately planted. The same liquid, prepared with the same proportions, can be poured over the soil before planting seedlings. But you need to do this if you are sure that the soil needs additional boron. Most often, this element is low in podzolic, waterlogged and calcareous soils.
Boron powder is readily soluble only at t +55 - +60 ° С. Therefore, it is advisable to dilute the required amount of powder in a small volume of hot water. Then bring to the required displacement with water at room temperature.
- Preparation of a solution for foliar feeding. Everything is quite simple here: you need to dilute 1 g of boric powder in 1 liter of water. The whole bush is sprayed with this solution. This feeding must be repeated at least 3 times per season: during budding, flowering and fruiting. This type of complementary food helps not only to adapt tomatoes to environmental conditions, but also prevents late blight and fungal diseases.
Top dressing based on organic-mineral mixtures


Top dressing will help the fruit develop faster.
During the period of active formation and development of fruits, good results are obtained by using fertilizers from a mixture of organic and mineral fertilizers. For the manufacture of fertilizers, you must:
- Mullein 1 l.
- Complex mineral fertilizer 16-18 g.
- Copper sulfate or manganese 1 g.
As a mineral fertilizer, you can use Kemira Universal or Solution. All ingredients are dissolved in 10 liters of water. The resulting mixture is watered at the rate of 1.5 liters per bush of determinant varieties or 2.5 liters per bush of tall varieties.
Potassium sulfate solution
It is a synthetic analogue of bird droppings or liquid mullein. Many gardeners use compost heaps for the same purposes - they collect mowed grass and weeds torn from the beds, which, having rotted in a warm temperature, begin to actively release the same chemical compound.
Any of these types of fertilizer is applied under tomato bushes at the rate of a liter and a half for each plant.Some experts argue that before and after feeding with such organic fertilizer, it is necessary to properly water the soil around the plants in order to ensure maximum access to the roots of tomatoes of nutrients. This is especially true in arid regions with a hot, dry climate and a predominantly clay or sandy soil type in which you grow tomatoes.
Top dressing of tomatoes during the ripening period
The tomato harvest is formed in several stages. Top dressing is carried out so that the plant has enough nutrients both for the formation and ripening of fruits, and for the further growth of the bush.
The first brush is poured
After the formation of an ovary on the first brush, it is necessary for the plant to send nutrients to future fruits. Potassium and phosphorus help redistribute the carbohydrates accumulated in the leaves. To do this, root feeding is carried out with potassium-phosphorus fertilizer. Under each bush, depending on the size, pour from 0.5 to 1 liter of solution (15–20 g of potassium monophosphate per 10 liters of water).
What elements are needed for tomatoes
The first flower cluster grows on tomatoes after 6–8 pairs of true leaves appear, so the tomatoes no longer need nitrogen.
Attention! Nitrogen is required if the stems are very thin during flowering, the leaves are pale, if the bushes hardly grow.
But usually, when blooming buds, bushes need phosphorus (P) and potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), boron (B), iron (Fe), sulfur (S).
It is required not to forget that to fertilize tomatoes when budding:
- the amount of potassium and phosphorus must be higher than nitrogen;
- it is desirable that boron (B), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sulfur (S), iron (Fe) are present in the feeding;
- it is recommended that the feeding contains humates or humic acids;
- it is bad if there is chlorine in the fertilizer.


How to recognize the lack of useful elements?
- If the bushes lack phosphorus, then you will see that the stems, leaves from below turn purple. Then it is required to spray the bushes with a highly diluted superphosphate solution.
- With a lack of calcium, the foliage curls inward, and the fruits develop apical rot. At the same time, spray the bushes with a solution of calcium nitrate.
- If the bushes lack nitrogen, then their leaves turn pale or turn yellow, they grow very slowly, the stems are thin. In this case, the tomatoes are sprayed with a low concentration carbamide solution.
Top dressing of tomatoes
During the fruiting period of tomatoes, they pay increased attention to feeding. The taste of vegetables, as well as the degree of keeping quality, shelf life depends on their quality and quantity.
Specificity and features of the procedure
As soon as the fruiting period begins, remember the main features of the organization of fertilizing:
- When feeding tomatoes during this period, be careful with nitrogen-containing fertilizers.
The fact is that the entire effect goes to the growth of green mass, as a result of which the tomatoes themselves remain without food. Their formation and growth slows down. - Remember to cut back on the amount of water for irrigation... Add aloe juice or onion peel-based solution to the water. This will help to avoid stunted plant growth.
- Prepare potassium-containing dressings, as the tomato needs it most at this time. Avoid top dressing with potassium chloride, because the tomato does not tolerate the potassium content in the soil itself. They are fed carefully, observing the dosage.
The role of macronutrients in the development of tomatoes
Macronutrients are essential for all plants, regardless of where they are planted. Consider what each element is responsible for and what is its significance in the development of a tomato.
It is necessary for bushes for the development of green mass. The lack of nitrogen leads to the fact that the leaves do not grow, have a nondescript appearance. The upper leaves do not curl, the older plates die off, have a matte or faded shade. Because of this, fruiting is delayed. Nitrogen-containing fertilizing corrects the situation.
For example, use a solution of 20 liters of water, 1 liter of mullein and 2 tablespoons of nitrophosphate.Water the plants at the rate of 0.5 liters of liquid per 1 bush. Fertilizing the bushes is best in the morning or evening.
Such dressings are carried out no more than 2 times a month. Also, nitrogen fertilizers often contain phosphorus. It helps shrubs to tolerate cold more easily. Lack of phosphorus causes the leaves to take on a purple hue. We'll talk about this in more detail below.
Important! With a normal nitrogen content, the leaves have a color and size characteristic of each variety. In the morning, the top curls up, and in the afternoon it becomes straight.
Phosphorus
During the fruiting period, with a lack of phosphorus, brown spots appear in the leaves in the areas between the veins. An excellent remedy is a superphosphate extract. Pour 2 tablespoons of superphosphate with 1 liter of boiling water and leave overnight. Next, bring the volume to 10 liters by adding water and water the beds. Sometimes gardeners use a simpler method and simply pour 0.5 teaspoon under each bush.
Do blooming tomatoes need to be fertilized?
The main reason why you should not neglect feeding at this time is that lack of nutrition can lead to the formation of a large number of barren flowers in the plant.


They will take up nutrients from the developing fruit, which will lead to a significant decrease in the volume of the crop.
It can also be very bad for tomato seeds.... The seeds of weakened plants do not germinate well, the seedlings from them are weak and often sick.
So if you prefer to grow tomatoes from your seeds, pay attention to feeding during this period.
How to fertilize tomatoes after planting in the ground, read the material on our link.
Important: Another possible consequence of a lack of nutrition during flowering can be the sour taste of tomatoes and a hard core.
Types of dressings
How to feed tomatoes during fruiting in a greenhouse? Depending on the method of feeding, there are root and foliar. The root method is the most popular. He saturates tomatoes with vitamins using root watering.
Foliar dressing is applied directly on top of the bush. For its preparation, a weaker concentration is used to avoid burning the leaves. Both root and foliar dressing are beneficial for plants, especially if they are alternated with each other.
Purchased drugs
Gardeners love to "feed" tomatoes with the following drugs:
- «Kornevin". The name speaks for itself: first of all, the drug has an excellent effect on the root system of the bush, making it even more developed and powerful. In addition, it reduces the impact of adverse external factors. Prepare protective clothing and gloves to work with Kornevin. Sold in bags of 0.4 g. The price of one package is 11 rubles.
- «Solution»Contains nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, as well as other trace elements necessary for the plant. About 20 mg of "Solution" is added under the root. It is quickly absorbed by tomatoes, quickly eliminates the lack of any substance. Used as a solution. The price for 0.5 kg is 53 rubles.
- «Station wagon". Granular fertilizer is effective and affordable for any gardener. The best effect is achieved if applied before loosening or watering. Provides proper assimilation of nutrients by tomatoes, low levels of nitrates, good harvest. 5 kg "Universal" costs 299 rubles.
- «Orgavit". The fertilizer is based on dry horse manure. It occupies a leading position in the content of useful elements. "Orgavit" is practically not washed out of the soil. Produced in the form of granules, non-toxic. For 2 kg of funds, gardeners pay 139 rubles.
- «Biohumus". It is a liquid organic solution. Contains humic acids, biologically active substances, micro- and macroelements, amino acids. 3 liters of "Biohumus" cost 199 rubles.
Folk remedies
Among folk remedies, the following are popular:
- Chicken droppings - saturated with calcium, potassium and nitrogen. To use solutions based on chicken manure should only be introduced under the root of the bush. There are no toxic substances in the product, it increases the resistance of tomatoes to diseases, accelerates their growth. Dilute 1 liter of water and 1 liter of dry chicken manure, let it brew for 5 days in a warm place. The infusion is stored for a long time, so you can fertilize plants with it throughout the whole season.
- Boric acid - increases the amount of sugar in plants, protects against parasites and diseases. You can use the root or foliar method. Prepare a solution of 1 L of water and 1 kg of boric powder. It is better to use hot water as this will dissolve the powder faster. During fruiting, use a mixture of boric acid and potassium permanganate. This will provide the tomatoes with reliable protection against late blight.
- Suitable for feeding in a greenhouse fresh or dry yeast... Dissolve 100 g of fresh yeast in 10 liters of water and immediately pour over the tomatoes with the resulting liquid. For each plant, use 0.5 liters of solution. Yeast will not strengthen tomatoes as much as boric acid or chicken droppings, but rather have an overall healing effect.
- Ash is an excellent fertilizer at any stage of tomato cultivation. During the fruiting period, a solution based on wood ash is especially actively used. To do this, dissolve 1 glass of ash in 10 liters of water, add liquid soap to the mixture. The solution is sprayed on the bushes from a spray bottle.
Organics and folk remedies
You can get a high yield of tomatoes without the use of chemical fertilizers. Long-term experience of summer residents and technologies based on the use of new types of fertilizers not only ensure excellent fruiting of the crop, but also protect plantings from typical diseases, including late blight.


Humic fertilizers
A relatively new type of fertilizers managed to win the hearts of summer residents: they improve the structural composition of the soil and make it possible for beneficial bacteria to fully develop.
Suitable for flowering tomatoes:
- Gumi Kuznetsova;
- "Gumat-Universal";
- "Gumisol";
- "Lingogumat" and others.
Prepare nutrient solutions according to the instructions provided.


Watering tomatoes with yeast gives a tremendous effect: even the "scruffs" catch up with their strong brothers, actively bloom and tie. It is not worth considering strictly as a top dressing yeast solution - rather, it is a good stimulant of long-term action. It works well on all soils, but on fertile soils it lasts longer - up to 4 weeks.
The feeding solution is prepared according to the following procedure:
- 10 g of fresh yeast are taken for 1 liter of water;
- dissolve them in half a glass of warm water;
- insist 3-4 hours;
- bring the volume to 1 liter.
Flowering tomatoes are watered twice during flowering. Before flowering or at the very beginning, half a liter of nutrient solution is poured under each bush. Do this when the first flowers open. The second time, 1 l / bush is fed, when the flowering comes to an end, the first ovaries are formed.
At the same time, ash is added to the tomatoes, since the yeast "eats" the calcium present in the soil.


Ash use
To feed flowering tomatoes, ash is ideal - wood, straw, peat. This valuable organic matter is rich in essential nutrients (potassium and phosphorus) and contains important micro and macro elements. You can use it without fear of overfeeding in various ways.
- 1 tbsp. l. scattered on the bush under the tomatoes twice a month.
- They are fed at the root with an infusion of 100 g of ash in 10 liters of water. Each plant will need 2 cups of liquid.
- Sprayed on a leaf 300 g of sifted ash and 3 liters of water, diluted to 10 liters and infused for 30 minutes, boiled for 30 minutes.
Ash treatment of tomatoes acts quickly and efficiently, accelerates flowering.Plants also receive protection from insect pests and pathogens.


Iodine solutions
The available product increases the number of promising ovaries on the brushes, accelerates the ripening of fruits, disinfects the soil during root watering, and protects the green parts (stems, leaves) from late blight and other harmful fungi when sprinkled.
The simplest option is root feeding. For watering, a useful solution is prepared from a bucket of water and 3 drops of iodine.
For foliar feeding of tomatoes, a more complex solution is prepared:
- 30 drops of iodine are injected into 1 liter of whey or low-fat milk;
- add to the mixture 15 ml of hydrogen peroxide;
- add the mixture with water to a total volume of 10 liters.


Spraying with boric acid solution
Such dressing is especially relevant for greenhouse tomatoes: often the air temperature in greenhouses exceeds + 30 ° C. For nightshades, this is a critical temperature, since it leads to sterility of pollen - actively flowering tomatoes do not set fruits. Boric acid will help to cope with the problem, as well as make the fruits sweeter, protect the bushes from parasitic microorganisms, including the notorious phytophthora.
To spray tomatoes, a solution is prepared from 1 g of pharmacy powder and 1 liter of water. The process is carried out in stages:
- dissolve the specified amount of the substance in 100 ml of heated water;
- add water to 1 liter.
Liquid pharmacy boric acid is diluted in a proportion of 1 tsp. 10 liters of water.
Often in greenhouses, flowering bushes are irrigated with a solution of 10 g of powdered boric acid, 2 tbsp. l. sifted ash and 10 liters of hot water. The mixture is allowed to brew for a day, poured at the root.


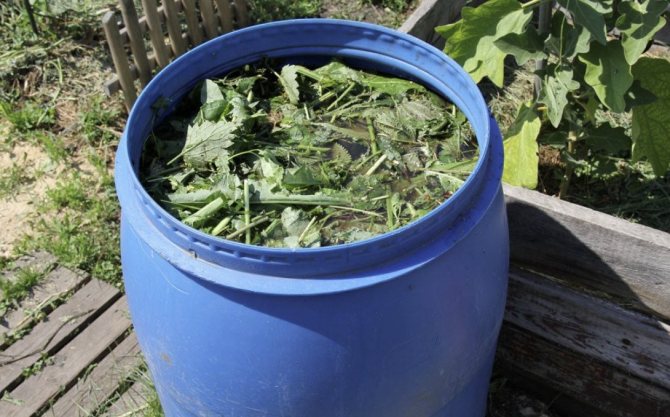
Weed infusion
The most popular way for summer residents to process tomato beds. There are many options = making healthy "tea", the best one includes several ingredients that allow you to feed tomatoes with the nutrients necessary for the formation of a healthy ovary and ripening of delicious fruits.
For a 200-liter barrel, take:
- 5 buckets of fresh weeds (the more nettles there are, the better);
- 1 bucket of mullein (or half a bucket of bird droppings)
- 1 kg of yeast;
- 1 kg of wood or straw ash;
- 3 liters of whey, preferably homemade or from a nearby farm.
The ingredients are put into the barrel without ramming, and top up with water. Insist "compote" for 1-2 weeks (the period depends on the weather, if it is stably warm, it will be ready in 5-7 days). The special value of top dressing - all important micro and macro elements have an easily digestible form. At the same time, the infusion scares off most pests, has a detrimental effect on pathogens.
Another popular option is nettle infusion. For cooking, you will need chopped nettle leaves and water in a volume ratio of 1: 3. Insist 5 days, after which the tomatoes are watered. A completely harmless agent is also used for spraying.
Timely supply of micronutrients and macronutrients during flowering is one of the most important elements of tomato care. At the same time, it is important not to direct all attention to root feeding, but to combine them with foliar feeding: this is a quick and effective way to deliver important nutrients to the plant tissues. Tomatoes, properly fed during flowering, will delight the caring summer resident with the beautiful appearance and taste of the fruits.
To obtain a good harvest, feeding the tomatoes during flowering and fruit setting plays an important role. The quantity and quality of fruits depends on how much the plant was provided with nutrients.


Top dressing of tomatoes during flowering and fruit setting
It is impossible to rashly introduce the first fertilizer that comes into the soil: the result will be the opposite of what was expected. It is necessary to accurately calculate the proportions and know what properties this or that soil has. For example, fertile black soils require significantly less fertilizers, while loam and sandy soils require them more.
Replenishment of tomatoes with coffee grounds
There is such waste in almost every kitchen. They are often used in compost. There is even a recipe for feeding with coffee leftovers as a base:
- prepare for rotting thick, straw and leaves in a ratio of parts 2: 1: 1;
- mix the ingredients;
- do not cover;
- after 3 weeks, the compost is ready for use on the site.
The coffee sediment itself is also rich in nitrogen. It also contains potassium, phosphorus, magnesium and other microcomponents. The easiest way to fertilize tomatoes is to scatter the thick around the trunk of the bush and cover it with soil, immediately water the garden. The roots will gradually absorb the valuable substances.


The effective action of dry grounds is enough for 2-3 watering tomatoes. Additionally, the substance attracts earthworms. They qualitatively loosen the soil and open air access to the underground part of the bush. The acidity of the fertilizer is neutral, which means it is suitable for tomatoes in any type of soil.
Attention! Organic is an environmentally friendly make-up. But using the mixture at a high concentration, you can harm the tomatoes. To prevent the likely negative effect of organic matter on the bushes, reduce the saturation of the solutions.
Tomato care rules
Experienced gardeners competently organize outdoor care for tomatoes, do not forget about feeding, thanks to this they manage to get good yields and avoid outbreaks of diseases.


Here are their helpful tips:
- When choosing a variety, preference is given to late blight-resistant tomatoes.
- Observe the crop rotation. Do not plant tomato bushes after potatoes, peppers, eggplants, tomatoes. The return of culture to its original place can be carried out for 3 years.
- Do not plant vegetables prone to late blight on adjacent ridges.
- Adhere to the planting scheme for low-growing tomatoes 30x70 cm, indeterminate varieties - 40x70 cm.
- Pickle tomato seeds before sowing seedlings.
- In the rainy season, do not forget about the treatment of tomato bushes from late blight.
- Keep the aisles clean, mulch the ridge with straw.
- Do not forget that mineral fertilizers are needed for tomatoes in the open field.
Three important feeding
During the season, it is necessary to feed the tomatoes at least 3 times at the root. This scheme is standard, it is used by everyone who cares about the tomato harvest:
- Fertilize seedlings 2 weeks after transplanting. Take nitrophoska (15 g), mullein infusion (1/2 l), dilute with water (10 l). Spend 1.2 liters of solution per plant.
- When the first buds appear, carry out a second feeding. Take simple superphosphate (1 tbsp. L), potassium sulfate (1 tsp. L), water (10 l), stir until dissolved, pour a liter of solution under each bush.
- Drizzle with potassium humate, adding nitrophosphate. The interval between the second and third feeds is 2 weeks.
If necessary, you can feed the tomatoes in the open field with superphosphate 2 weeks after the 3rd feeding. Fertilizer concentration 1 tbsp. l per bucket of water, consumption 10 l / m2.
Where to place the beds
The successful cultivation of tomatoes depends on where you place your beds. This place should be well lit for at least 6 hours a day. Gusts of cold wind and drafts can be detrimental to your tomatoes.
If earlier nightshade trees grew on the garden bed, then tomatoes can be grown on it only after a few years. This is explained by the fact that insect larvae from nightshades continue to live in the ground for some time and can adversely affect tomatoes.
Plots of land with deep underground streams will do. But don't choose very wet soil. The beds should be placed in an easterly direction in the southern part of the garden. Thus, the earth will be equally heated to the desired temperature. The beds can be of different heights. In the north of the country, it is better to make high beds, in the depths of which organic fertilizers.
Root feed
This method involves the introduction of fertilizers directly under the plant itself.It is assumed that in this case, valuable elements are actively absorbed by the root system and directly enter the tomatoes. However, this method contains one implicit disadvantage: the roots cannot physically absorb minerals and trace elements at once. The process takes several days (depending on the type of tomato). During this time, some of the fertilizers are washed out by precipitation or during irrigation.


Attention! The average loss with this method is up to 20%.
Top dressing of tomatoes under the root means watering with a liquid solution or embedding dry substances in the soil. These methods allow you to add both organic and mineral compositions. For the entire period of growth and development on the street, tomatoes should receive fertilization at the root 3-4 times. The interval is at least 2-3 weeks between applications. To obtain a crop on poor soils, the frequency of root dressing can be increased.
Advice. The rate for watering tomatoes with fertilizer: 1 liter per 1 plant before flowering and 3-4 liters after flowering.
Soil selection and preparation for planting tomatoes
It was already mentioned above that tomatoes came from South America. They have a lot in common with potatoes, including disease. Therefore, it is not recommended to plant tomatoes in the place where potatoes grew before. Pathogens may remain in the soil, which will prevent young seedlings from gaining strength.
A separate place in the garden should be reserved for tomatoes. The soil for tomatoes must be prepared in the fall. Apply phosphate fertilizers, since they dissolve for the longest time and react with the soil, organic fertilizers - manure or compost are also applied in the fall. By the spring, the manure will decompose and will be suitable for assimilation by plants.
In the fall, top dressing is applied to a depth of about 30 cm and dug up, leaving large clods of earth. This contributes to better moisture when the snow begins to melt in the spring.
Seedlings are planted in separate holes 10-15 cm deep at a distance of 50 cm from each other. Depending on the variety of plants, the distance may be less - up to 30 cm.
You can also make a solid hole - a trench. This is necessary so that water and liquid fertilizers do not spread, but fall directly under the root of the plant.