After how many days the hunt repeats (the cow walks)
Hunting is the period of a cow's sexual cycle when she is fertile. In the same cow, the hunt is repeated at regular intervals - most often after 18-24 days... If the cycles are irregular, then this indicates a violation of reproductive function. It can be cysts of different etiology, inflammation, ovarian hypofunction and other diseases.
From practice (!): If your cow or heifer has oestrus at different intervals, it is not necessary to immediately call the veterinarian. It happens that the cycles are restored by themselves. Track the hunt and try to cover. If two or three more cycles are not covered, then start to understand the problem.
When is the first hunt after calving
After calving, the first heat begins normally in 18-24 days, but it is too early to fertilize.. The best time to cover (inseminate) is during the second or third cycle after calving.
Firstly: one cycle is skipped to allow the cow to recover from childbirth. This way you reduce the risk of postpartum diseases (paresis, acidosis, ketosis).
Secondly: inseminating cattle in the first hunt after giving birth is irrational, due to the high percentage of unsuccessful attempts.
When to cover a heifer
The main criteria for the readiness of a heifer (biological and physiological) for pregnancy and bearing healthy offspring are:
- Weight - when they reach 70% of the body weight of the weight of an adult animal of the same breed (mother, for example).
- Age - from 14 to 18 months.
- The height at the withers is a sufficient indicator of 122-128 cm.
- The number of full-fledged hunts. It happens that heifers begin to hunt very early, for example, at 5-6 months, usually 9-11 months, and it is not recommended to miss a large number of hunts (maximum 5).
By the combination of these factors, the age of the first coating may shift.
Recommend(!): The first fertilization (and all subsequent ones as well) is better done artificially, since this reduces the likelihood of injury from being covered by a bull and contracting sexually transmitted infections.
You can read more about the benefits of artificial insemination in this article.
Inseminator selection
The bull is ready for mating when it reaches 8 months. High-quality offspring is possible only from a healthy male, which must have:
- a good pedigree, when the father's female offspring are distinguished by high productivity and attractive appearance:
- strong physique and a tendency to gain weight;
- thoroughbred thoroughbred;
- quality seed;
- a large number of successful intercourses and conceptions;
- healthy offspring.

Bull inseminator
A quality inseminator is considered to have about 50% of successful fertilization attempts. During the year, bulls are capable of covering up to 80 females. Before mating, a special diet enriched with proteins and vitamins is developed for males. It is important that the bull maintains physical activity for 2 months, alternating with periods of good rest.
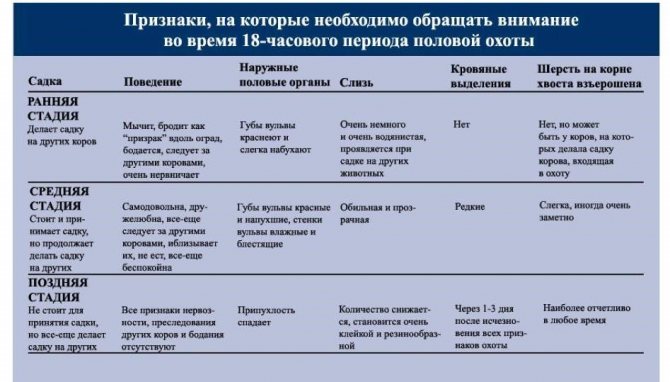
How to understand that a cow or heifer will soon come to hunt
The best period for fertilization is always preceded by a preparatory stage - sexual arousal.
Here's how you can spot an impending hunt:
- the animal is agitated;
- behaves playfully;
- restless;
- sometimes hums for no reason;
- picks up neighbors, jumps on his back, wipes himself about them;
- obsessive, fondles the owners.
The duration of the preparatory period before the hunt is different for cows. The above-described signs of cattle owners are observed most often during the day, the permissible range is within 10-12 hours and up to 2-3 days before the start of the hunt.
During this period, clear, clear discharge is clearly visible, sometimes quite abundant. The duration of transparent abundant discharge is one to two days. There is swelling and redness of the loop (vulva).
How to know when to cover a cow with a bull
A common misconception of many breeders is to cover the cow at the first manifestations of arousal.listed above. The fact is that an egg is needed for fertilization. But in this phase, she has not yet matured and has not left the follicle in the ovary.
Important(!): If the bull covers the cow or heifer in this phase, then by the time the egg is released, there will be no living sperm and fertilization will not take place. Remember, if the cow itself jumps on others, it is too early to cover.
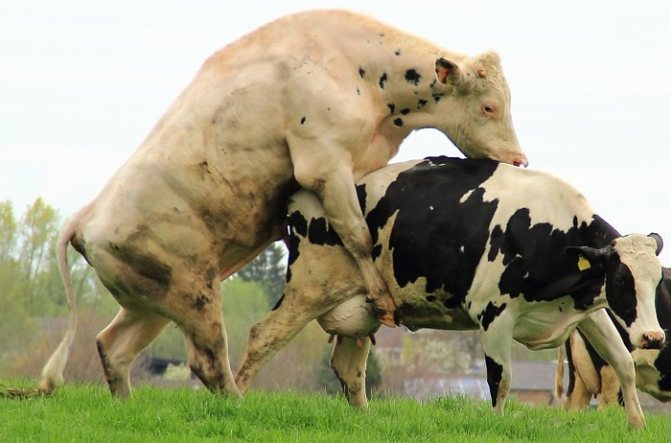
The cow (heifer) is ready to be covered by the bull when she allows other cows to sit on herself... This period is called hunting. It lasts on average from 2-6 hours to one day.
She develops a “reflex of immobility” - the animal stands motionless, bending its back and pushing its tail aside. This is the most optimal time for natural insemination by a bull.
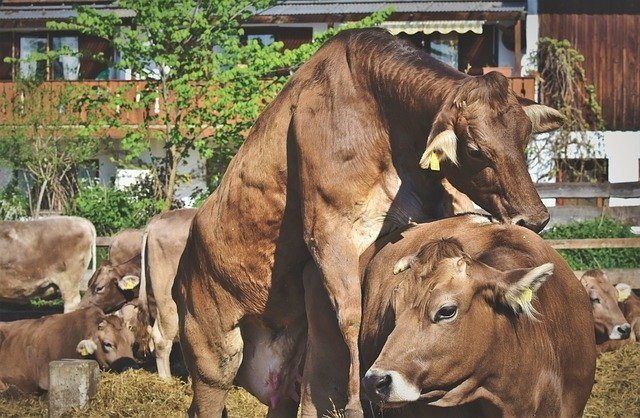


The best time to cover a cow with a bull is when she allows other cows to sit on herself.
In addition, mucous secretions contribute to the better movement of sperm through the cervix and uterus, towards the fallopian tubes, where the fusion of the two germ cells will take place.
After the effect of immobility, the cow may have some blood in the discharge after 2 days and this is normal.
Why is it important to determine readiness to reproduce
Timely identification of the beginning of the process is important not only for young heifers, but also for cows that have already given birth. Sexual maturity in cattle appears at about 8-10 months, and physiologically, females are ready for fertilization only by one and a half years. It is impossible to let a bull near an unripe heifer. It will be harmful to both herself and the future calf.
She can become pregnant, but the development of the fetus will occur simultaneously with the formation of the mother's body. And this will inevitably harm the young cow and her cub. After such an early pregnancy, the cow will never be the record holder for milk, plus you should not expect a healthy offspring from her.


It is also bad if the cow walks. There can be two reasons for this. The first is that the owner deliberately did not bring her, wanting to optimize the time of delivery. The second - the burenka went on a walk due to the inexperience or negligence of the owner. In both cases, walking cows are significantly more likely to develop ovarian problems. And this is a direct road to infertility.
When to inseminate a cow
From my long-term practice of artificial insemination (AI) of my own and other people's cows, the best time for artificial insemination is 10-12 hours after the appearance of the "immobility reflex".
The fact is that thawed bull semen is capable of fertilization in about 24 hours or less, not 2 days, as fresh. By the time of ovulation, when a mature egg is released, the thawed sperm simply will not survive and the AI attempt will be unsuccessful.
Note(!): Remember, if a cow begins to allow other cows to jump on it and stands calmly, then artificial insemination should not be carried out now, but after 10-12 hours. Otherwise, by the time the egg is released, the sperm will have died.
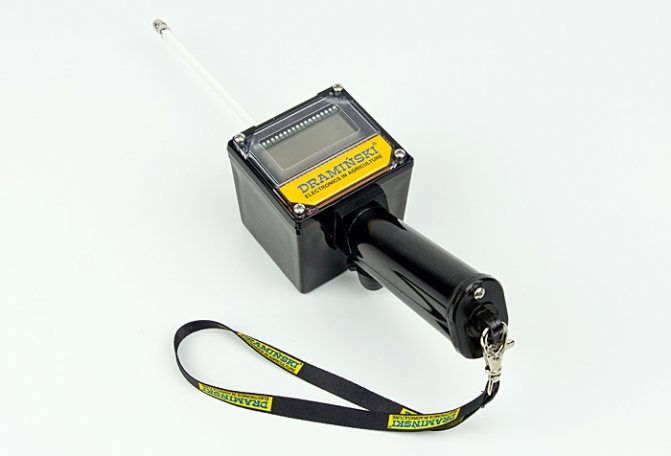
COUNTING STEPS
“When a cow is approaching sexual heat, then, in addition to the visually observed changes in the vagina and mucous membranes, an increase in her motor activity can be noted as a clear sign,” says Vasily Atamanenko, a specialist at Westfalia-Surge. - This is the basis of the Rescounter device, which has a built-in pedometer or activity meter. The device is placed on the leg of a cow or built into a collar. The activity of the cow generates electrical impulses in the pedometer, which are counted and entered into the memory of the DairyPlan computer system.
With the help of such a system, it is possible to calculate the individual average value of activity for each animal for 10 days. This indicator is used for comparison with current values, noticeable deviations from the average indicate hunting.
“The average activity of cows over 10 days should be calculated based on the same two-hour period,” Atamanenko explains. - For example, if from the first to the tenth day in the period from 10 to 12 o'clock the average activity value in a cow was 10, and on the 11th day in the same period of time the activity value was 15 and after that two more increased values were noted , then the system will alarm the operator. The advantage of using such a device is that you can monitor the animal regardless of its location - both in the pasture and in the milking parlor.
According to Atamanenko, if the Rescounter is located on the animal's leg, then it detects up to 92% of cows in heat, and if on the neck, then 77%. The fact is that the collar usually fixes a lot of unnecessary movements (neck bends, blows from other animals). And the accuracy of determining a "quiet" hunt with Rescounter reaches 70%. If the "quiet" hunt is determined by an inseminator, then the accuracy ranges from 10-30%.
A similar device is included in the Afifarm farm management system.
- The pedometer does not cause any stress or discomfort to the animal. All information about the motor activity of a cow per day goes to the central computer to the dispatcher, and he sees which cow needs to be sent to the veterinarian, and which one to the artificial insemination technique, '' says Evgeny Korshunov, director of the Kaliningrad branch of Bauer Techniks.
The activity sensor offers and. Located on the collar, it records the behavior of the cow 24 hours a day, and also analyzes the behavior of each animal over several days. The information from the activity sensor is transmitted via the antenna to the central processor of the system, which processes all the information and, in the event of high activity registration, gives the user a warning that the animal has shown high activity. In this case, the inseminator should check the presence of hunting in this animal and, if the result is positive, inseminate it.
According to Oleg Bespalov, the location of the sensor on the collar is better than on the leg, because it gives the animal less discomfort. According to him, the DeLaval activity sensor detects heat with an accuracy of 95%, but in any case, a visual inspection of the animal is also required. - Usually 3-5% of cows in a herd are in a state of "quiet" heat. And if, with an average sexual cycle of 23-24 days, bursts of activity are recorded every 5 days, then this most likely indicates a cow's illness. Therefore, the use of pedometers makes it possible not only to detect hunting, but also to timely identify and treat sick animals, - says Victor Gridin, consultant at Profimilk.
What should be the discharge from a cow before and after insemination
Consider what should normally be a cow's discharge at different periods of the sexual cycle:
- In the first day or two from the beginning of the manifestation of arousal, the discharge is abundant, transparent, clean (sometimes scarce or absent altogether). The average duration of mucous discharge is a day or two.
- On the second day after the hunt, there may or may not be blood in the secretions. The color and quantity can be very different - from scarlet to brown, from abundant to scarce. This happens due to the fact that at the time of the rupture of the follicle and the release of the egg at the end of the hunt, a small vessel could be damaged. Blood does not appear immediately after ovulation - it takes a long time to move to the exit.
- Further, the discharge gradually decreases and disappears completely.
- After covering, after 7-10 days, there may be a scanty cloudy thick discharge.They indicate the possible implantation of the embryo into the wall of the uterus and the formation of a cervical plug.
Important(!): If during any period of hunting a cow's discharge is yellow, white, green, transparent with cheesy inclusions, with a smell, blood (before ovulation), then it is impossible to cover or inseminate - this is a symptom of a disease of the reproductive system. First you need to treat the animal, and in the next hunt, inseminate.
General rules for caring for a cow at home
The cow is a rather whimsical animal. Quickly begins to lose weight and shed milk if it stays for a long time in a stuffy, cold or damp room. When caring for an animal at home, it is important to create optimal conditions for keeping:
- It is better to place the room near the garden, vegetable garden at a distance of 15-18 m from the house.
- As a material for the barn, it is worth using logs, planed boards, bricks, foam concrete with excellent thermal insulation.
- The floor is filled with concrete for durability and hygiene.
- It is imperative to equip ventilation with a pipe for air outflow.
- Cows are raised on farms for the purpose of making a profit in the form of calves. Burenka should choose a thoroughbred one with good milk yield. The best breeds: Kholmogorskaya, Yaroslavl, black-and-white, Lebedinskaya, Dutch. When buying, it is worth examining the cow physique. The body should expand towards the rear. Outwardly, the cash cow looks angular, not too fat and does not look like a bull.
- When keeping cattle, the barns are periodically disinfected. In winter, it is important to keep animals warm with adequate lighting, and in summer, in areas under a canopy from the sun and rain.
For your information! Approximately 50% of cows in Russia are kept on private subsidiary farms at home. Cattle breeding is a thriving, highly profitable industry if all organizational issues are approached correctly. There is no need to use expensive equipment to breed cows; in the summer they successfully graze in the meadows, eating free grass. The main thing is to economically use feed for calves in winter, because often a walked cow gives birth in summer in February-April, when there is still no green grass in the meadows.
When not to fertilize a cow
The inseminator or the owner himself can check the cow for gynecological inflammation before fertilization. This must be done because a sick animal:
- harder to inseminate;
- has a greater risk of miscarriage and fetal mortality;
- it will be more susceptible (like the fetus itself) to various pathologies of pregnancy;
- with untreated diseases, they are more prone to pathological childbirth (delayed placenta, weak labor, etc.)
It is interesting(!): Against the background of inflammatory diseases, sperm is perceived by the cow's body as a foreign protein and antibodies are produced to it. Then it is impossible to cover such a cow - the more attempts, the more actively the cow's immunity works. In this case, only skipping a few hunts and treatment.
Inflammation of the genitourinary system is determined by the presence of discharge - purulent, bloody, with cheesy inclusions, abundant. Alert should be frequent urination, redness of the vulva (nonspecific), the presence of bubbles and pustules on the mucous membrane of the vulva.
Advice and guidance from experienced breeders and veterinarians
If the reason why the cow does not want to walk is not pregnancy, then experts advise:
- Revise the diet, the daily feed intake, taking into account the weight of the animal.
- Add vitamins and minerals if the cow is thin and not ready to mate.
- Contact veterinarians for the appointment of drug therapy in order to stimulate hunting. Perhaps experts will prescribe hormonal treatment.
- Check the cow for endometritis 1-2 weeks after calving, because it is this disease that often causes a decrease in the functions of the reproductive organs.
- It is not recommended to allow the cattle to constantly mate, so it is important to relieve excessive excitement, monitor the condition of the cow and her sexual relations.
Timely detection of pregnancy by the hormonal composition of the biological fluid is a win-win option. An ultrasound scan will help you find out the condition of the reproductive organs and the uterus. The method of palpation or feeling is effective. You can put a drop of milk in a glass of cold water. Complete dissolution will indicate pregnancy, spreading over the surface - the absence of fertilization.
If you follow all the recommendations of experts, then the cow is unlikely to have problems with hunting. However, it is important to monitor the well-being of the animal, regularly contact veterinarians, creating acceptable conditions for mating.
Behavior of a cow after insemination
After cover (or AI) and the end of the hunt, the behavior of the cow does not change in any way. It is impossible to tell by the behavior of a cow whether she is pregnant or not. A pregnant cow or a heifer will simply stop hunting until calving.
You can accurately determine pregnancy in two ways:
- Within a month after hunting with the help of ultrasound;
- 3 months after hunting by rectal examination.
Remember, if after covering the cow in the next cycle did not come into heat, this does not mean 100% pregnancy. Pregnancy must be confirmed.
How to determine the calving date?


It is important for the cattle owner to know exactly the expected date of birth. This will allow you to determine whether an early or normal calf is born, as well as how much the pregnancy has passed.
How to find out when a cow will give birth is well known: it can be calculated in two ways.
It is convenient to use any of them to determine the date. The choice depends only on the personal preference of the owner of the animal.
Using the formula
Calculating the estimated calving date using a formula is a fairly simple task.
The formula looks like this: D = (H + 11) (H-3), where:
- D - date of the alleged calving;
- H - the number when the mating occurred;
- H is the month in which the cow was covered.
To understand how to determine the calving date using a formula, you need to consider an example of such a calculation.
So, if the female was inseminated on September 9, then the result will be as follows: (9 + 11) (9-3) = 20.06.
Thus, according to the formula, it is determined that the calf should be approximately born on June 20.
Using the launch and calving calendar
A special calendar is also kept to determine the calving date. This is a calving table for cows, in which the month and day of insemination and calving are marked.
In such a calendar, 5 dates are usually allocated in each month (1,5,10,15,25).
Also in it, breeders mark the launch date of the cow before calving, so as not to get lost and not to miss this period.
This table is especially useful for cattle if the farmer has several cows.


Cow pregnancy calendar
Can a pregnant cow bleed?
Normally, blood in the secretions appears on the second day after the start of the hunt. If the cow is bred one day after being covered by the bull, then you have correctly calculated the coverage period and fertilization may have occurred.
When there was blood in the discharge during coating or immediately after it, then, most likely, ovulation occurred earlier and the egg had time to die before the sperm arrived.
If blood appeared 12-24 hours after AI, then the time of the procedure was calculated correctly, just in time for the release of the egg. In this case, there is a high probability of pregnancy.
When blood appeared only on the third day, it is possible that ovulation was delayed and the sperm did not live to see it.


It is interesting(!): A pregnant cow should normally not bleed. Or she is not pregnant and the cycles continue, or there are hormonal disorders, or pathology of the reproductive system.
Pregnancy check
Pregnancy refers to the pregnancy of cows.There are a number of ways to diagnose it. However, the most win-win is visual inspection. First, they pay attention to the genitals of the female during pregnancy, the mucus has a transparent color and a viscous structure. Moreover, if impurities of pus or blood are found in the mucus, we should talk about the development of pathology.
Other signs of a cow's pregnancy include:
- swollen mammary glands;
- swollen peritoneum;
- the acquisition of elasticity and smoothness by the skin.
How to identify quiet heat in cows and heifers - the main signs
Silent hunting may not manifest itself in any way or it may appear dim. For example, there is no noticeable mucous discharge, unreasonable mooing, mood changes, or jumping on your neighbors.
It can be just an individual feature of the cow (heifer) and she is able to cover normally. Then you just need to learn how to determine the hunt in such a "quiet girl".
Here are the criteria by which I identify such candidates for insemination:
- Visually - I determine by the look. The look of such cows becomes "crazy", frightened and surprised.
- Behavior in the herd. If there are still cows, then by their behavior the hunt of the "quiet girl" will be noticeable, they will jump on it.
- Sometimes it is seen by the presence of clear vaginal discharge. Sometimes you fail to notice anything.
- If there is no such possibility, then it remains to wait for blood. Normally, blood appears on the second day after hunting. You can skip a couple of cycles and count the regularity of the hunt by blood. Then calculate the time for the next blood to appear, minus two days and expect the next hunt on that day.
It rarely happens that there are no signs at all. You need to carefully observe and at least something of the listed you will surely notice.
In addition to individual characteristics, quiet hunts may appear due to various disorders of the reproductive system. In any case, first try several times to identify a quiet heat and fertilize the cow (heifer) and only after three unsuccessful attempts call the veterinarian.
Test bull for hunting and other methods of its determination
The best way to find out if a cow with estrus is present is to launch a probe bull into the herd. This is a male with tied or clipped spermatic ducts, unable to fertilize. He clearly defines a specific smelling individual, on which he will undertake cages. The method has been used for many years, during which it has demonstrated high efficiency and reliability. So that the bull does not lose its scent, it cannot be left in the herd for more than two hours.
Other effective techniques include:
- Regular measurement of the temperature in the rectum or vagina. The effectiveness of the methods is low and is within 25%. For sexually mature individuals, the temperature is measured every day at the same time and its rise by 0.3 degrees indicates the beginning of egg maturation. The technique is ineffective for previously nulliparous cattle, as well as in the presence of diseases accompanied by an increase in body temperature, overheating in the sun.
- Instrumental examination of mucus from the vagina, carried out in special laboratories. A sign of estrus is the presence of increased levels of estrogen in the secretions. The technique belongs to the exact methods, but its implementation will require considerable funds. In this category is an old and less effective method - painting the tail root with easily washed off paint or chalk. If the owner notices that the paint has worn off, this means that the individual is allowed to do cages, and this is possible only during the active phase of the sexual cycle.
- Pedometry, which is a measurement of physical activity that increases during estrus. A special measuring device is attached to the female's neck or leg, which reads and records all motor activity.Its sharp increase indicates the beginning of the cycle. The effectiveness of pedometry is just over 90%. The device does not bring discomfort to individuals and, if necessary, can be easily and quickly removed.
- The estrus detector is a unique, highly efficient device that determines the best time to fertilize. For this purpose, the electrical resistance of the vaginal discharge is measured, for which the instrument is inserted into the female genitals. The procedure takes no more than one minute and does not bring any discomfort to the animal. Manufacturers give 100% efficiency, but provided there are no violations in the reproductive system.
The main disadvantage of accurate measuring techniques is the high cost of equipment and therefore they are not in great demand in small farms. It should be emphasized that with a small population, estrus in a female is easily recognized by external signs and behavior. On large farms, this is more problematic and accurate instrumentation becomes a good solution to the problem.
Why is the cow or heifer not covered (constantly walking around)
The most common failures when covering (inseminating) cattle are associated with:
- from incorrect determination of coverage time (or IO). Each animal has its own cycle and it does not always fall under the standard calculation;
- diseases of the reproductive system (ovarian cysts, ovarian hypofunction, endometritis, vaginitis, etc.);
- mechanical obstacles, such as vaginal obstruction caused by an abnormality or adhesions, tears, scars, tumors. Deformation of the cervix and others;
- inflammatory diseases... For example, mastitis may have coating problems because milk flow and reproduction are interrelated;
- almost all infectious diseases... The body simply does not have enough strength to fertilize, even if the reproductive system is not directly affected. Or conception still occurs, but the embryo dies (early embryonic mortality) at a period of 15 days or later;
- errors in content... For example, acidosis caused by unbalanced feeding. With acidosis, high acidity, including the endometrium of the uterus, has an acidic environment in which the embryo cannot be implanted.
What to do if the cow is not covered
I advice continue to try to fertilize the animal for two, maximum three cycles (provided there are no obvious health problems).
If there are signs of the disease, treat and repeat insemination from the next hunt.
Then either to the synchronization scheme (hormonal drugs), or try to maneuver with different seeds, use the superfecundation effect (insemination in one hunt with the semen of different bulls for 15-20 minutes to create competition between them, causing an increase in fertility).
It is also rational to analyze the previous experience (when the blood appeared), choosing a different time of insemination. You can also use a double cover (once per hunt and repeat after 10-12 hours) and other methods.
Insemination types
Mating cows with bulls can be done in several ways. In the conditions of small farms, the use of free and manual insemination is most often used. On industrial-scale farms, artificial insemination is relevant. Let's consider each of the methods in more detail.
Free mating
This method is often used on small farms. It involves the constant presence of the female next to the inseminating bull throughout the day, after which the male is taken to a separate stall for rest.
The advantages of free mating include:
- maintaining the stability of the cow cycle;
- reducing to a minimum the likelihood of missing the sex hunt.
The main disadvantages are the lack of opportunities for breeding and calving planning.In addition, the likelihood of genital infectious diseases and injury to young females is high.
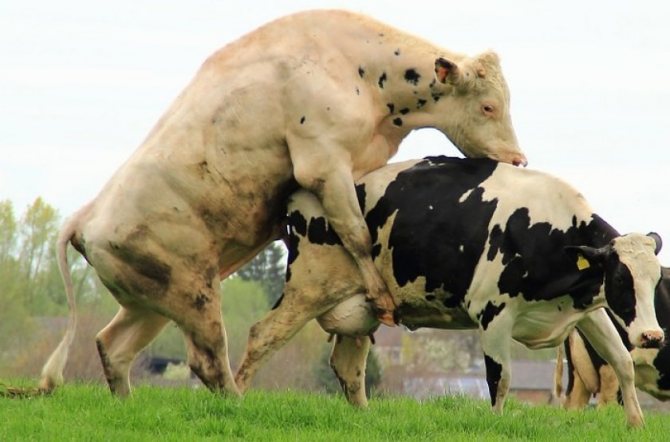


Free mating
Manual mating
This method is more reliable and is equally often used in small and large farms. The mating process takes place in a separate room, which contains the bull and several females assigned to it. A special machine is placed in the room, on which the male puts his limbs in order to avoid injury to the heifer during fertilization.
During the hunt, the female is brought to the bull twice: at the beginning and in the middle of the sexual cycle. Immediately before mating, the animals are carefully examined and washed.
Artificial insemination
The method of artificial insemination is characterized by the ability of the male to cover up to 500 females at a time. To obtain sperm, the cage is carried out artificially, the essence of which is as follows:
- a dummy version of the cow's vagina is made in a separate room;
- before taking biological material, the bull is led in a circle, and special sounds are created for it, imitating the roar of a cow during a hunt;
- after - the male is introduced into the arena, where the material is taken by means of a mechanical apparatus.
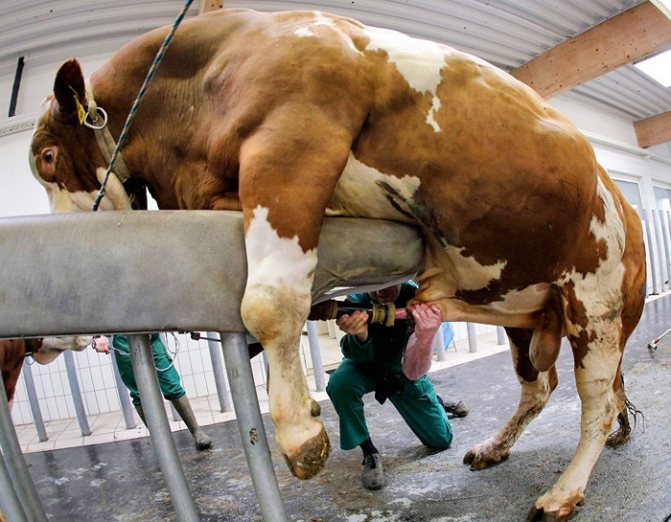


Sampling of material from an inseminating bull using a mechanical apparatus
Cooking method
This insemination method allows:
- use valuable and high quality males in the mating process;
- determine hunting and infertility in time;
- stimulate sexual function.
In this case, the cows that are in the period of sexual heat are placed in a spacious enclosure called cooking, where the bull is subsequently brought. The male independently chooses the female for mating. Bulls are admitted to the heifers twice during the day: in the morning and in the evening for several hours.
What Problems Can Be When Covering A Cow
Technical: the cow is not worth it, it is not possible to fix it. She kicks, sits down, lies down, jumps (all sorts of met).
You can read about different ways of fixing a cow in this section on the website.
Mechanical: vaginal obstruction caused by an abnormality or adhesions, tears, scars, tumors. Deformation of the cervix.
Determining the presence of mechanical obstacles on the path of sperm to the egg can only be done manually - on examination. This can be done by a veterinarian, inseminator, or just a literate person.
The cow (heifer) in the hunt does not allow the bull to not stand with IO
If the cow is hunting by all indications, but does not have a "reflex of immobility" and does not allow the bull or does not stand on the AI, it is necessary to call a veterinarian or inseminator and manually check the opening of the cervix and the readiness of the follicle (it will be clearly felt on one of the ovaries).
Artificial insemination is almost always not voluntary for cows. They have to be fixed and this has nothing to do with the hunting stage.
Here is a video on the subject of cow insemination:
Possible difficulties while hunting
Cows do not always go smoothly and without problems, and they often cause headaches and anxiety for farmers. The most common problems worth noting are:
- Mild estrus, in which all signs are blurred or not at all noticeable. This variant is more often found in young females walking for the first or second time. It is not possible to prevent the problem, since it refers to the physiological characteristics of the body.
- Latent endometritis is a dangerous disease characterized by an increase in acid levels in the uterus. As a result, the sperm simply die in a viscous consistency, without reaching their goal. It is difficult to detect the disease, since the behavior of the heifer does not change, she registers estrus, but not a single test ends with fertilization.Only a veterinarian can make an appropriate diagnosis after examination and a series of tests.
- Inability to get pregnant due to ongoing infectious diseases, pathologies of internal organs, malnutrition and maintenance. To normalize the course of estrus and increase the chance of pregnancy, you should monitor the balance of the diet, treat the identified diseases in time, seek help and advice from veterinarians.
In some cases, to stimulate or synchronize the process of egg maturation, farmers use various medicinal preparations of narrowly targeted action. We must not forget that their uncontrolled intake can cause biological castration or serious damage to the reproductive organs.