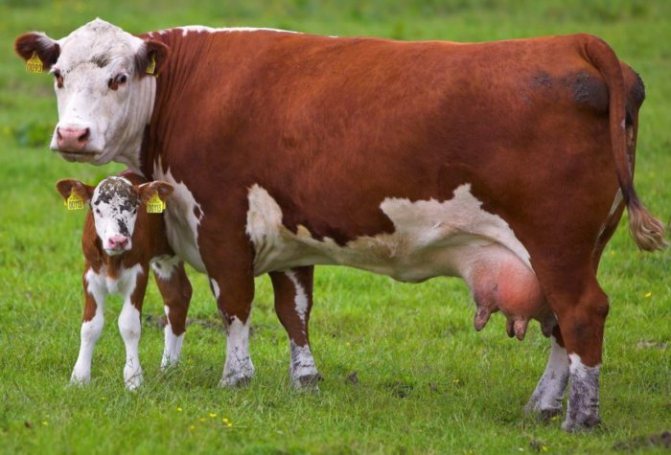
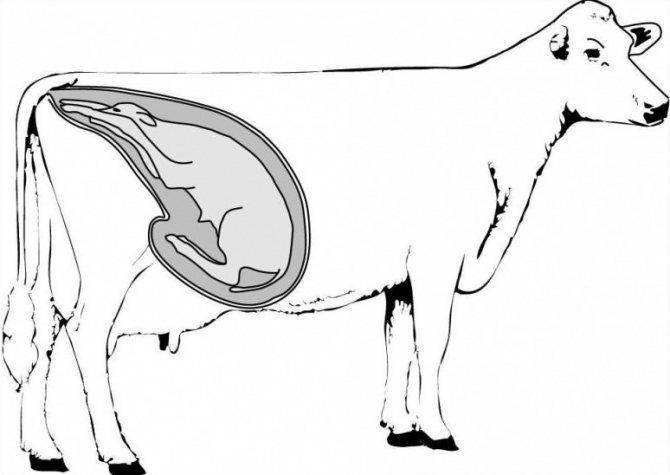
The first definition of the fact of pregnancy
After it became clear that the cow became pregnant, the owners must change her diet. The earlier it became known about pregnancy, the better. Understanding how much a cow is carrying a calf and what needs to be done in order for it to be born viable, the owners will be able to go through this period calmly, without unforeseen losses, nervous experiences and financial costs. The conditions for keeping the animal must also be changed. The health and proper development of the fetus depends on how all the requirements for caring for a pregnant cow are met.
The first thing to do is to know how much a cow is carrying a calf and to calculate the timing of labor. Various methods have been developed for this:
- Reflexological examination, when a bull is brought to the cow in the morning and evening. This is continued every day until it becomes clear if the cow is pregnant. If she does not have sexual desire, then she is pregnant, that is, pregnant.
- A laboratory study performed on milk samples. Laboratory milk is taken for research from the 19th to the 23rd day after mating. This method helps to determine progesterone - the hormone of pregnancy.
- Determination of pregnancy with the help of a veterinarian doctor who uses the rectal method. This becomes possible within 1.5–2 months from the moment of conception.
How long does a cow's pregnancy last?
Pregnancy, or pregnancy, in cattle lasts, as in humans, for 9 months. The average value for cows of all breeds is 230-311 days. The variability of time depends on the quality of care, nutrition (vitamin supplements are introduced into the diet, the amount of juicy feed increases).

Pregnancy, or pregnancy, in cattle lasts, as in humans, for 9 months.
Dates of cow pregnancy
A cow's sexual cycle lasts an average of 21 days., consists of two phases: hunting (11-20 hours) and ovulation (10-15 hours). To avoid early or unplanned pregnancy, the young are kept separately after maturation. Cattle happen annually during sexual hunt: 2 consecutive times with an interval of 12 hours (before milking).
Pregnancy in cattle is not divided into phases... But it is necessary to withstand the dry period. All breeds give birth at different times, so the recommendation to stop milking a cow 60 days before calving is inaccurate. According to scientists, it is better to leave milk to the cow starting from the 7th month, it will go to strengthen the fetus, the formation of fatty colostrum.
After 230-300 days, the first signs of an impending birth will appear. Mood changes, the animal is restless, aggressive.
The udder is poured, swells; the loop, on the contrary, softens, transparent mucous discharge appears... The hips rise, diverge by 10-20 centimeters. The little heifer picks up hay for herself, builds a "nest". It is important for the owner to keep an eye on the cow so that in case of difficulty in the birth process, they can quickly help.


Be sure to read:
Diet of fattening bulls for meat in a short time for rapid growth and weight gain of calves
How to calculate the exact duration of pregnancy
Insemination does not always lead to pregnancy, therefore, artificial insemination of the female is often used. 30 days after the hunt, you can determine whether the cow is with a calf or not.
This will be indicated by signs:
- Light discharge from the reproductive organs.
- Behavior change (the heifer becomes calm or agitated).
- The end of the sexual hunt.
Attention! There is a reflexological research method. The cow is brought to the bull every day, if she does not show interest, then the sexual hunt is over, the gestation period has begun.
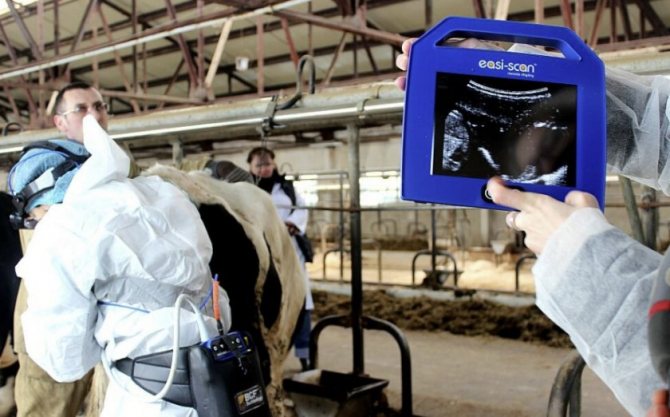
An accurate analysis is done by a veterinarian. The laboratory method determines the level of progesterone in milk or palpates the abdomen. Pregnancy tests are available. Ultrasound gives the best efficiency, but pregnancy is determined in this way not earlier than the 2nd month.


Pregnancy in cattle is not divided into phases
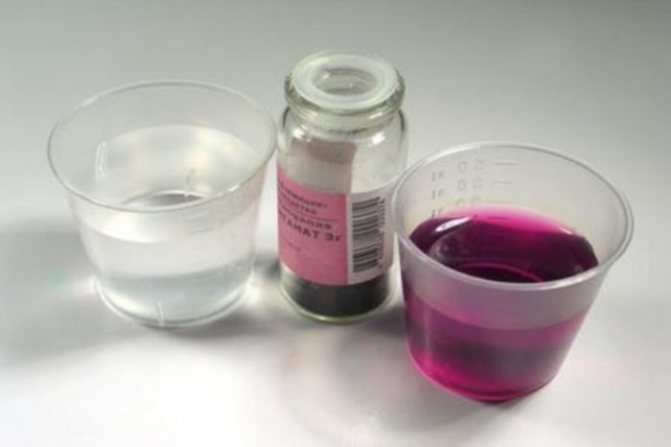
At home, a coagulation test is performed. Milk is added to alcohol (5 ml) in a test tube. Pregnancy will be confirmed if it curls up.
The rectal palpation method will give the exact time. It is carried out by veterinarians by inserting a disinfected hand into the rectum of the animal.
The stage of pregnancy is determined by the change in the reproductive organs:
- ovaries are normal, the uterus is in the pelvis, the horn is enlarged - 1 month;
- the neck descends into the belly, the horn increases 2-3 times - 60-80 days;
- the furrow between the horns of the uterus is determined, the diameter is about 20 cm - the 3rd month;
- at the 4th month, the fetus is already probed;
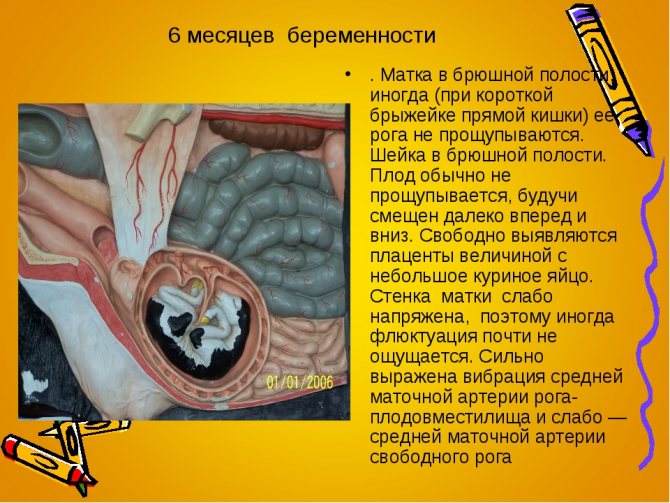
- from the 5-6th month, a simple palpation of the abdomen is performed, the uterus descends completely into the pelvis;
- 7-8 months - the calf is well felt;
- 9th month - the cervix rests against the pelvis.
In the middle of the term - 120-150 days - there are changes in the appearance, behavior of the female. The sides increase significantly, the cow eats a lot, can attack neighbors in the stall.
Determination of pregnancy at a later date
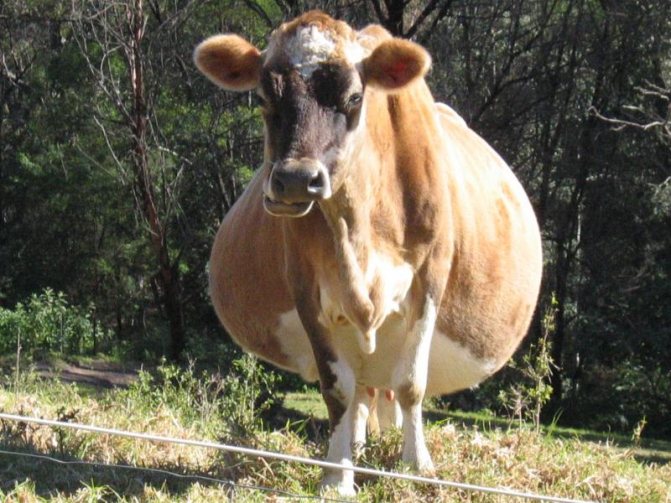
Having learned how much a cow is carrying a calf, the owners calm down a little. Since there is still time to be sure of pregnancy and stop milking her for sure. After 5–6 months, the cow's pregnancy is determined visually, by an external method. The cow's sides are compared. On the left side, it has a scar, and the area of the belly that stands out the most is in the middle. On the right is the fetus. Therefore, the bulge of the belly at the bottom will be stronger there.
You can find out about a cow's pregnancy by feeling the lower part of the belly, on the right side, the area that protrudes most. The cow's head and neck are turned to the right. This technique reduces the tension on the peritoneum. After that, very carefully, using a fist, press in the area slightly below the depression in the side. This should be done with short and quick clicks. This method is not always effective, since the fetus may be under the intestines, and then it will not be possible to probe it.
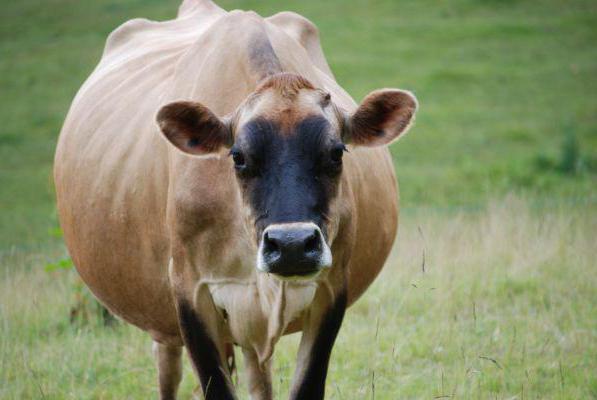


Examination through the anus
It must be said that examination through the anus is used more often than others. The fact is that it can be used at home without using any special methods, that is, without much experience. In addition, even in the very early stages, it turns out to be effective. Also, the method is often used in order to determine the cause of infertility of cattle, if the cow cannot become pregnant for a long time.
Some veterinarians argue that rectal examination in many cases is more informative than ultrasound, so its popularity does not decrease.
The course of the pregnancy period
How much a cow bears a calf, that is, the period of her pregnancy, depends on the speed of fetal development. He himself develops depending on the nutrition and maintenance of the cow. When the fetus is ripe and can already be called a calf, the hormonal background of the cow changes. The rate of growth of the fetus is influenced by whether the cow is in the stall or in the herd.
Once pregnancy is established, the cow can no longer be milked. It is believed that milking should be stopped 2 months before the birth. But how many months a cow carries a calf can range from eight to ten (pregnancy lasts from 240 to 311 days).


Terms of labor
If the insemination of the cow was planned and everything took place successfully and on time, then the birth will take place in the tenth month. In such cases, veterinarians recommend, and strongly, to start stopping milking in 7.5 months. Understanding how many days a cow carries a calf and calculating everything correctly, the animal is left without milking for 2 months before giving birth. That is, most cows are idle without milking, being pregnant, for about 60 days (maybe more). And only about seven percent of livestock have a shortened period of non-milking.
The cow needs to take a break from milk production long before giving birth. She needs energy for the development of the fetus. If the milk yield is removed, then the processed food will go all the energy production, so necessary for the future calf. It will help to find out how many a cow is carrying a calf, the table (calendar) of start and birth in cows, which is at the veterinarian's.
Table (calendar) of gestation and pregnancy of cows
| date | date | date | date | ||||
| Insemination | Calving | Insemination | Calving | Insemination | Calving | Insemination | Calving |
| January | October | April | January | July | April | October | July |
| 1 | 7 -12 | 1 | 5-10 | 1 | 6-12 | 1 | 7-12 |
| 5 | 11-17 | 5 | 9-15 | 5 | 10-16 | 5 | 11-17 |
| 10 | 16-22 | 10 | 14-20 | 10 | 15-21 | 10 | 16-22 |
| 15 | 21-27 | 15 | 19-25 | 15 | 20-26 | 15 | 21-27 |
| 20 | 1.11 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 1.05 | 20 | 1.08 |
| 25 | 31.10-6.11 | 25 | 29.01-7.02 | 25 | 30-6.05 | 25 | 31-6.08 |
| February | November | May | February | August | May | November | August |
| 1 | 7-13 | 1 | 4-10 | 1 | 7-12 | 1 | 7-12 |
| 5 | 11-17 | 5 | 8-14 | 11-17 | 5 | 11-17 | |
| 10 | 16-22 | 10 | 13-19 | 10 | 16-22 | 10 | 16-22 |
| 15 | 21-27 | 15 | 18-24 | 15 | 21-27 | 15 | 21-27 |
| 20 | 26.11-2.12 | 20 | 23.02-1.03 | 20 | 26-1.06 | 20 | 26-1.09 |
| 25 | 1.12-7.12 | 25 | 28.02-6.03 | 25 | 31-6.06 | 25 | 31-06.09 |
| March | December | June | March | September | June | December | September |
| 1 | 5-11 | 1 | 7-13 | 1 | 7-12 | 1 | 6-12 |
| 5 | 9-15 | 5 | 11-17 | 5 | 11-17 | 5 | 10-16 |
| 10 | 14-20 | 10 | 16-22 | 10 | 16-22 | 10 | 15-21 |
| 15 | 19-25 | 15 | 21-27 | 15 | 21-27 | 15 | 20-26 |
| 20 | 24-30 | 20 | 26.03-1.04 | 20 | 26-2.07 | 20 | 25-1.10 |
| 25 | 29.12-4.01 | 25 | 31.03-6.04 | 25 | 1.07-7.07 | 25 | 30-6.10 |
If you do not adhere to this, then the cow can get sick, and the calf is born unviable. Owners need to know that the calf develops especially intensively in the last 3 months of its gestation.


Signs of labor
The table (calendar) of cow pregnancy is accurate in 90 out of 100 cases, that is, in 90%. When it is clearly known how many days a cow is carrying a calf and it is clear that the time of birth is approaching, you need to be vigilant. This significant day can be identified by the following signs:
- The pelvic ligaments are weakened.
- Mucus is secreted from the genitals in the form of leashes.
- Colostrum appears.
Colostrum is called milk, which differs from the usual in its fat content. It is necessary for the calf in the first days from birth. If a cow grazes with a herd in a field, it is necessary to separate it in the last days, and in case of the beginning of labor, help to give birth. Be careful: childbirth in the field is quite common!
Generic process
Thanks to the calendar, the farmer knows approximately how much a cow is carrying a calf, this document helps to prepare in time for his birth. The first step is to take care of the arrangement of the calving place. What measures need to be taken before this important event:
- Clear the stall.
- Provide clean, soft hay bedding.
- Treat the manure grooves with a solution of lime.
- Disinfect the cow's hooves using a 2% creolin solution.
Recommendation. The place intended for calving and staying there of a cow with a calf should be free of dampness and draft. Good lighting is also worth taking care of.
Signs of approaching calving
Shortly before delivery, the cow begins to behave restlessly. She feels discomfort, so it is easy for the farmer to determine the approach of the birth process by the following signs:
- The calf looks back, shifts from foot to foot.
- She is shy.
- The animal eats much less, drinks little.
- The external genitals are slightly enlarged.
- A mucous secretion is secreted from the vagina.
- The udder swells, colostrum begins to drip.
- A few hours before giving birth, the cow twitches its skin.
- In summer, the animal can separate from the herd and try to hide in the bushes.
- The sacrum descends.
- The pelvic ligaments relax.
- The cow lies for a long time and hums.
A sure sign of the onset of labor is that the cow lies on its side (usually on the left). At this time, it is necessary to prepare everything that may be needed during calving - towels, warm water, soap, a solution of potassium permanganate in a concentration of 1%, an iodine solution (5%), scissors.
How to receive a calf correctly?
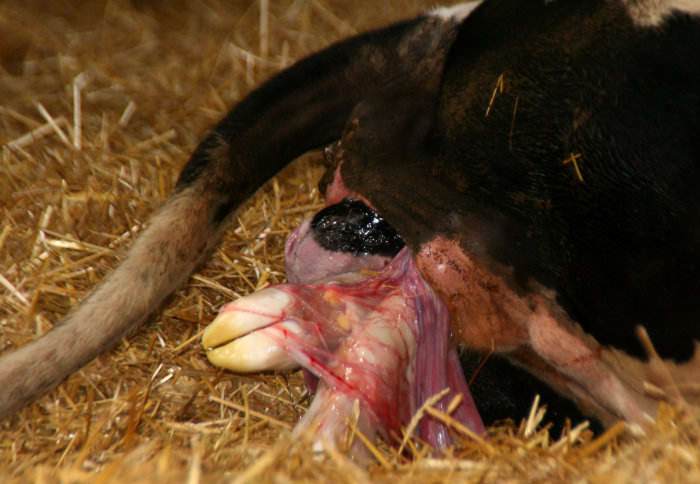
At first, a fetal bladder will appear from the cow's vagina. It will burst on its own if the animal has intense attempts. If labor is weak, then help is needed. The fetal bladder should be ruptured or incised. If the calf walks with its limbs forward, this is considered normal. In this case, he will not need additional help. Normal labor activity lasts from half an hour to an hour (in first-calf heifers).
The intervention of a veterinarian will be needed if the cow has weak attempts, and more than half an hour has passed since the water left. A slower calf emergence and an incorrect direction of fetal movement are alarms. The help of a doctor in this case is necessary. The calf is taken neatly and laid on a soft bedding, freeing its respiratory tract from mucus. The umbilical cord is tied and cut with sterile scissors. Its remaining end is dipped into an iodine solution. Then the calf is shifted to the mother's face, giving her the opportunity to lick it.
Every farmer should know how long a pregnant cow walks. Accurate fertilization information should be recorded in the calendar. This will help to correctly determine the time of entry into the deadwood and prepare for calving.
Help for a woman in labor
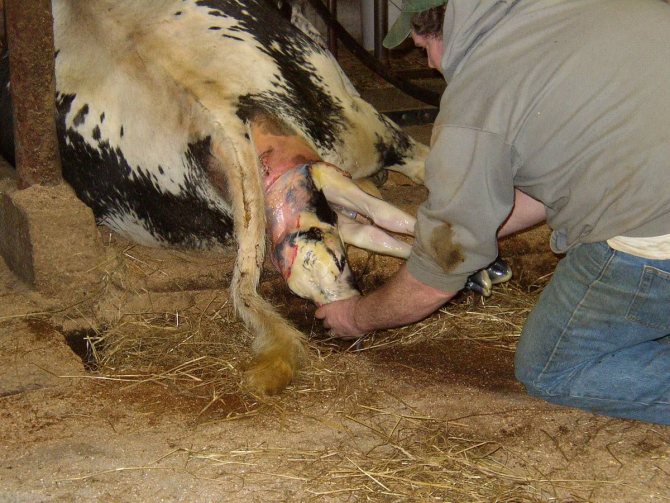
To help a giving birth cow, a person is tied with a rope around his belt and tied to the calf's legs that appear. They do this in the case when they know how long the cow is carrying a calf, and the birth has come, and the fetus does not come out for a long time so that it does not suffocate. A man, leaning back on the cow, helps in childbirth.
If there can be two people during childbirth, then everything will go easier. They grab the legs (front) of the calf with straw (rag) and help it to come out into the light. For this, the calf is carefully pulled out. Sometimes, very rarely, a cow needs to have a caesarean. But this operation is done by a veterinarian.
Complications during childbirth occur in young cows, whose owners still do not clearly understand how long a cow's pregnancy lasts, and she is carrying a calf for the first time (first calf). Such young women in labor, pregnant for the first time, require special attention and care. As a rule, they receive vitamins, improved feed.
But here, too, there is one peculiarity: the cow must not be allowed to overweight. It is necessary, of course, to look at the cow at night, because this is a very favorable time for childbirth. A pregnant cow in a stall runs the risk of dying or killing a calf during childbirth if she stands close to a wall. A woman in labor needs space!
Calving
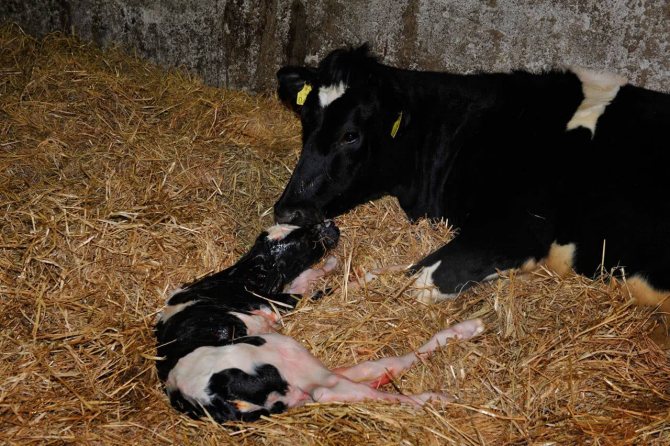


In a hotel that runs smoothly, human intervention is minimal.
At the same time, even a novice livestock breeder can cope with the task. In the same case, if complications are observed, the help of a veterinarian or an experienced farmer will be required.
The cow should be washed with warm water and laundry soap, and the external genitals should be wiped with sterile oil.
Do not make noise around the cow, as this will frighten her.
The owner should note the time of the onset of labor in order to be able to understand if they are delayed in time.
Firstborns usually produce a calf lying down, while re-birth cows can stand.
Contractions before the full opening of the cervix become much more frequent and turn into attempts. A fetal bladder appears from the genital slit, inside which there is a calf.
The bubble may burst itself, or it may need to be cut open. The calf is born with the front legs forward. After its complete release, the placenta leaves with a small volume of blood and mucus.
Advice! The afterbirth is inspected to make sure that it has come out completely.
Natural
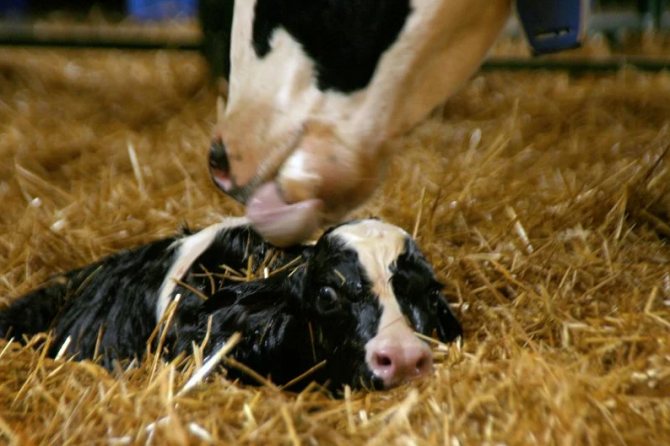


Natural calving takes place with little or no human intervention. The owner will only need to accept the born calf, wiping it of mucus and clearing its nostrils.
Also, to facilitate childbirth, if the fetal bladder does not break itself, it is cut with scissors.
With intervention
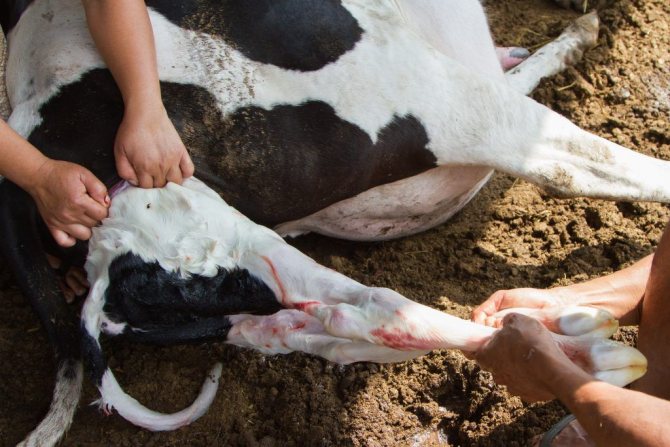

The owner's help is required only if complications develop during childbirth, the main of which are the following:
- weak attempts;
- the calf does not come out within 30 minutes after the fetal bladder has opened or was opened;
- exit of the calf with hind legs.
In all these situations, it is advisable to call your veterinarian.
Experienced livestock breeders can often solve the problem themselves by pulling the calf out on a push with the help of a loop of rubberized rope thrown over the legs.
Such work is hard, and a woman can rarely cope with it. If you are not sure to carry out everything successfully, then you need the help of a specialist.
Also, a veterinarian is indispensable when a cesarean section in a cow is required (giving birth to a calf using an operation).
Surgery is necessary if the calf is too large to pass through the cow's birth canal, or the cervix does not open correctly.
What to feed the cow after that, the specialist will recommend.
Care in progress


The cow does not need any special care at the hotel. During the period of contractions, the animal is washed from behind with a warm soapy solution and wiped off.
If a cow gives birth on its side, then a pillow is made of hay for her, which is placed under her head. The first calving of a cow may require additional constant calming of the cow.
Advice! If the animal is very nervous, then the owner can try to calm him down by combing the sides with a stiff brush.
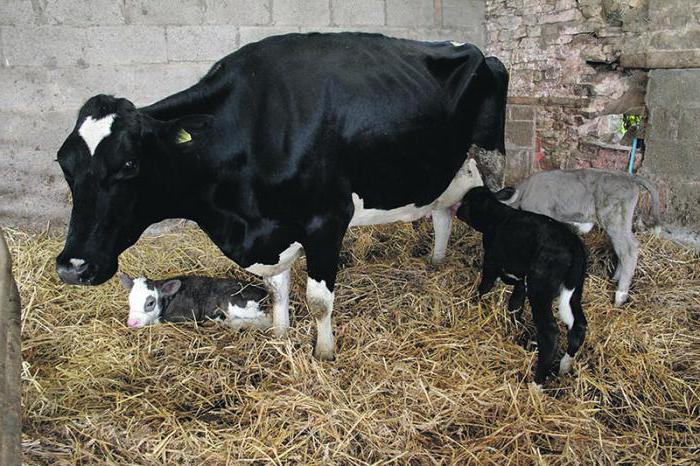
Birth of twins
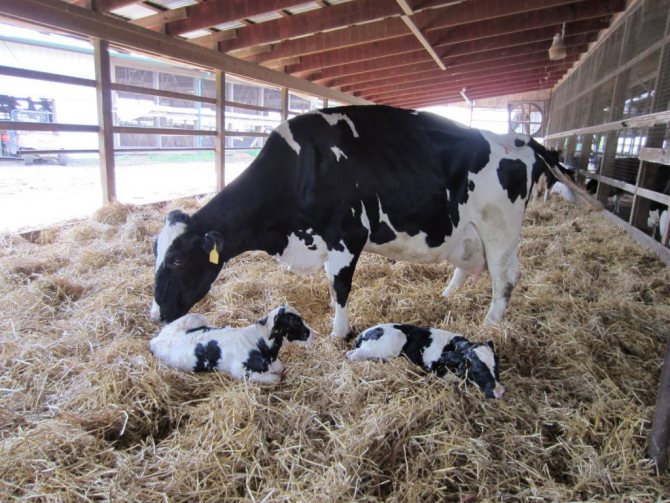


Calving is the birth of a cow of both one calf and twins. This phenomenon is rare and accounts for no more than 4% of the total number of calving.
The definition of twins is carried out using ultrasound. If this procedure was not carried out, then the exact number of calves will only be known at the hotel.
A Burenka needs special control at the birth of two calves. If calving proceeds without complications, then both calves survive. In the uterus, they are located so that one turns out to be hind legs to the vagina.
Most often, the calves are on top of each other. To prevent the death of one of the fetuses, a person inserts his hand into the uterus and determines the position of the upper calf.
At the birth of the first cub, the second should be carefully pushed into the uterine cavity.
When stretching the calf is required, it is important not to confuse the legs and not to grab one from one, and the other from another fetus. Calves are born from twins, usually with human participation.
Important! Trying to give birth faster by stretching the calf as soon as the legs appear, as this is likely to mutilate it and injure the cow.
Possible complications
During the calving process, complications can develop that pose a threat to the calf and mother.
The main complication of the hotel is its delay. The calf should be born within 30-60 minutes after the full opening of the uterus. If this does not happen, the animal needs help.
Also, complications include stopping the advancement of the fetus at any stage of labor. In this case, urgent specialist assistance is required.
Important! The owner of the cow should have a veterinarian's phone at hand, who can come at any time of the day if complications develop during calving.
Birth
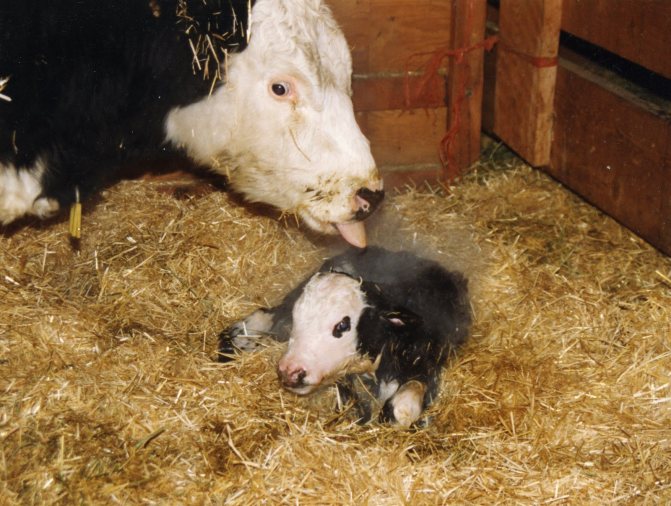
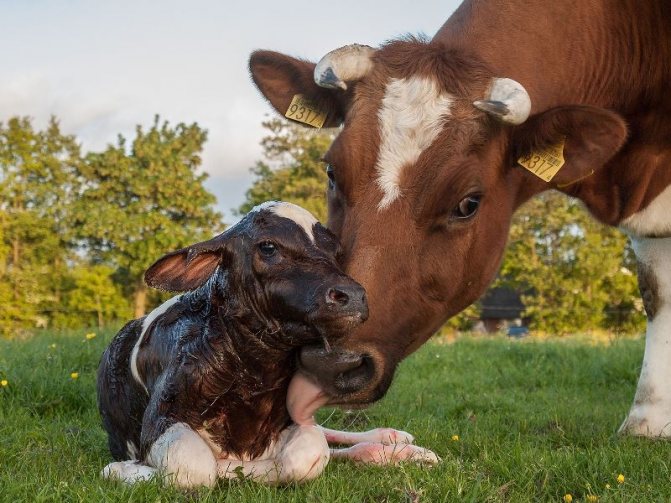
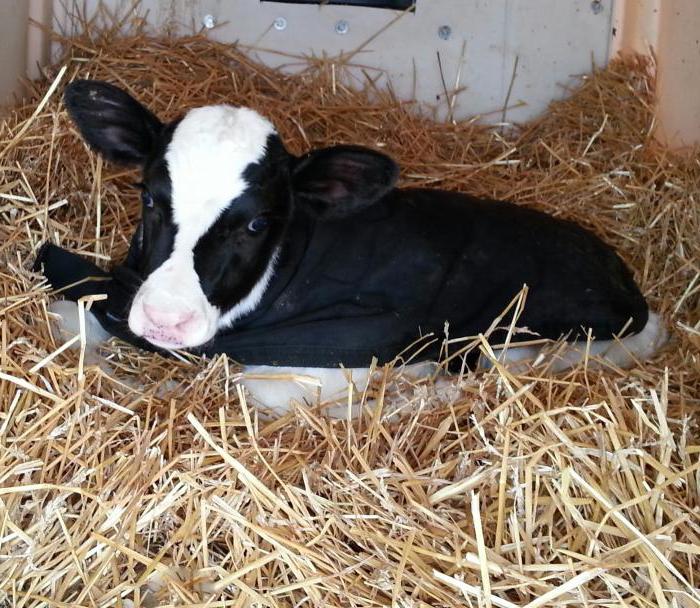
At the birth of a calf, you need to take dry straw and wipe it, clean it from the mucus from the mouth and nose. You need to give the newborn a massage. When a cow is able, she does it herself. She will lick it with her tongue for a long time and clean it.
It is imperative that after wiping the calf, the placenta (placenta) must be removed from the barn. If the cow eats it, then there will be no problems! You need to be very careful, the animal may start eating rags and polyethylene - the cow may die in this case! Therefore, you need to once again treat childbirth very carefully and seriously!
The most important day is the first 4–5 from birth of the calf. At this time, you need to give him warm boiled water between main meals.The calf drinks the first colostrum after about 1.5 hours. On the 5th day, mineral supplements are slowly introduced into the diet of the calf, since colostrum is valuable for the first 5–7 days. The vitamin and mineral supplements that the calf should receive per day are divided by two to three times.
Breeding and care rules
In a cow, the sexual cycle is cyclically repeated. The schedule consists of the following parts:
- Heat occurs first.
- Then - hunting.
- After that, the female ovulates.
In the event that mating occurs during the period of ovulation, pregnancy occurs. On average, its duration is 285 days. In practice, slight deviations from this period are possible. It is considered normal when the gestation period lasts from 285 to 300 days.
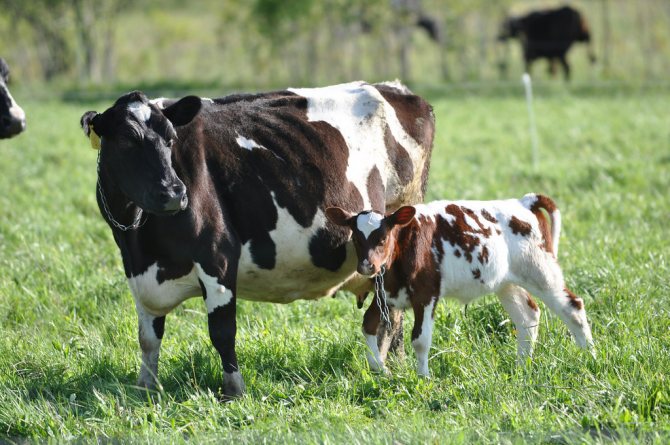
Cow and calf
At a certain stage, a pregnant cow starts up. From now on, she must follow special rules for calving to be successful.
It is important to correctly determine the launch day. In this case, one of the simplest ways to determine it is that you need to count seven and a half months from the moment of conception.
It is necessary to control the fact of pregnancy of cattle. If she is expecting a calf, she is usually additionally fed from the very beginning of pregnancy. When the fifth month begins, the milk yield of the cows gradually decreases.
At the same time, you need to change the diet of the animal. From this point on, it is necessary to feed the cow only with dry wood.
Note! It is necessary to control the amount of milk produced. As soon as it becomes less than four liters, milking must be stopped. It will be possible to renew it only after the calf is born.
For those cows that are characterized by high milk production, the termination of milking occurs in a slightly different way. When the milk yield per day is equal to four liters, the number of milkings is reduced to two per day. Then the amount of milk received will continue to decrease. It is only necessary to stop milking after the milk yield has dropped to one liter.
It is customary to start launching approximately 70 days before the expected calving date. A cow, feeding on dry wood, regulates the composition of the necessary vitamins and minerals it receives.
During this time, it is not allowed to give the animal green grass or feed concentrates. The cow continues to be taken to the pasture, however, gradually the time spent there is reduced.
If the launch time falls on the hottest period of summer, the cow continues to be taken to the pasture. When it starts up during the winter, it is allowed to pasture for three or four hours.
Important! When there are two weeks left before calving, the cow should be looked after especially carefully. This period is the most crucial in the process of preparing for the birth of a calf. During this time, in particular, it is necessary to ensure the cleanliness of the stall, remove the manure and disinfect the floor. It is also recommended to treat the hooves with a 2% solution of creolin.
How long can you walk?
The problem of overstepping the calving dates worries many farmers. It is more accurate to determine how long a cow has been carrying a calf, using the entries in the pregnancy diary. With a short period of walking of 10-15 days, you should not worry, since these two weeks may be nothing more than an error in determining the day of conception of the fetus. If the period of crossing is too long and has exceeded 20 days, an urgent need to consult a veterinarian. Only an experienced specialist will be able to determine the reason for the delay in calving and, if necessary, provide qualified assistance. This is a rather serious matter and in no case should it be allowed to take its course. The reason may lie in the freezing and even mummification of the fetus, which will require immediate surgical intervention.
Calving time of the cow after insemination
In order to find out approximately the date of birth of a calf, you can calculate it using the following formula:
(Calving date) = ((Day of month) + 11) / (Number of month - 3)
In the formula under consideration, the following designations are used:
- calving date - a calf is expected to be born on this day;
- day of the month is the day of the month when fertilization took place;
- the month number is equal to the ordinal number of the month from the beginning of the year (January corresponds to one, February to two, and so on).
Let's give an example of the calculation. Let's say a cow was inseminated on September 15th. In this case, the formula is applied as follows:
(Calving date) = (15 + 11) / (9 - 3) = 28/6
With the help of calculations according to this formula, it was obtained that calving will occur approximately on June 28th.
Calving time of the cow after insemination
A situation is possible when the first amount exceeds the number of days of the month. In this case, the number must be reduced by the indicated amount.
Example. If the number 25 and 11 are summed up, then the result will be 36. From it it is necessary to subtract 30 (the number of days in a month) and write down the result of the subtraction.
The number of days in different months is different, but remember that this is an approximate date, not an exact date.
In addition to using the formula given here, there is another way. In this case, the calving calendar is used to determine the desired date.
How to determine your due date
Knowing the mating date of your ward, you can determine the date of the expected birth using a simple formula. Values for the formula:
- "H" - mating date;
- "D" - term of calving;
- "M" - calendar month of insemination;
- unchanged numbers 11 and 3.
The calculation is carried out as follows: D = (H + 11). (M-3)
Let's take an example: insemination was carried out on April 16, April according to the calendar is the fourth month. Therefore, the formula looks like this: D = (16 + 11). (4-3) = 27.01 - January twenty-seventh.


If insemination took place in January or February, then "12" is added to the month number. This formula gives only an approximate value, the timing of calving depends on the age of the female, the number of previous pregnancies and the characteristics of the body.
Cow pregnancy and calving calendar
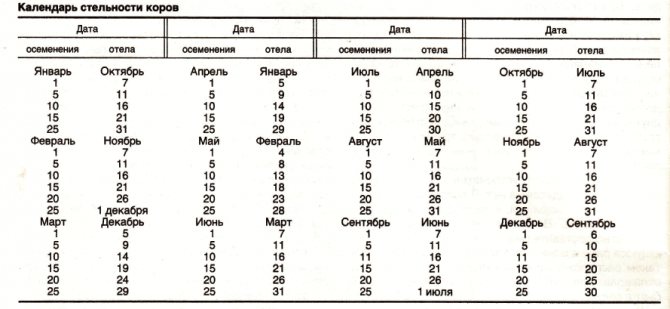
When determining the expected date of birth of a calf, you will need a table - a calving calendar of cows by the date of insemination. In this case, there is no need to carry out calculations using any formulas.
The calving and insemination table for cows has four columns. The first and third are the month and date of the day the insemination took place. The second and fourth columns indicate the month and date of the day on which calving is expected to occur.
When you look at the cow pregnancy calendar, you can see that it does not indicate any insemination dates, but only those that fall on the first, eleventh and thirtieth numbers. This is done so that the size of this table is not too large.
In addition, it must be remembered that it is hardly possible to accurately predict the date of calving in seventy days, the table indicates it with an accuracy of ten days. Therefore, it is not necessary to indicate all possible dates when insemination could have occurred.
On a note! In order to use this table, it is necessary in the first or third column to find the month and the approximate, nearest of the indicated dates, when insemination took place. Then in this line in the column of the calving calendar, which is located on the right side, the date when the birth of the calf is expected will be indicated.
Calving calendar
The following is a table that you can use to determine the date a calf should be born.
Time of delivery table
The values in parentheses here are for leap years. If a number is specified without parentheses, then it refers to a year that is not a leap year.
How the fetus develops
Once insemination occurs, the calf does not exist yet. The embryo gradually develops until it is born.
This is how it works:
- During the first month, various parts of the body begin to form: eyes, mouth. At this time, instead of the skin, you can see the vascular network. The embryo weighs no more than one gram.
- The second month is the time when the organs of vital activity begin to be created. At the same time, the placenta begins to appear. The size and weight of the embryo increases. At the end of this month, the size can reach 8 cm, the weight can reach 20-30 g.
- During the third, fourth and fifth months, testes form, horns begin to grow. When the fifth month ends, the embryo can already be called a calf.
- Over the next three months, active formation of internal organs occurs, and wool begins to grow.
The calf is born 285 days after conception.
Tips & Tricks
An individual calving calendar is drawn up for each cow, depending on when she was bred. If everything is done in accordance with the existing rules, this will allow you to get the lactation period as productive as possible.
Seven days before delivery:
- The ligaments located at the root of the tail and near the pelvis begin to descend.
- At the same time, the udder should be covered with a liquid that looks a bit like sugar syrup (colostrum).
- The cow often lies down and bellows loudly.
- You can see that the udder of the cow is increasing.
- In the summer, the cow tries not to be in the herd, looking for a secluded place. If you don't look after her, she can give birth to a calf in one of these nooks.
- The genitals swell a little.
- The belly becomes saggy.
Note! When only a day is left before calving, the animal becomes especially restless.
It is important to monitor the appearance of these signs in order to know when exactly calving will occur.
Cow calving calendar with table


What is a personal cow pregnancy calendar and why is it needed at all? Knowing the mating date, you can calculate the time the calf appears. But not everything is so simple. The cow still needs to be prepared for calving, otherwise problems cannot be avoided during childbirth or in the postpartum period. In addition, you should not count on high milk yield without preparation. It is just about the correct preparation for calving that we will continue to talk about.
Feeding pregnant cows
When carrying a fetus, cows need a special diet. Note that at the end of pregnancy, the weight of a newborn can reach 20 kilograms. It will be too difficult for a cow to bear a healthy calf, so the farmer is faced with the task of providing her with a balanced diet. The feed should contain a large amount of proteins and useful microelements. Do not forget about the mandatory availability of water. A water hole is needed 2-4 times a day.
Deficiency of basic vitamins can lead not only to fetal pathologies, but also cause miscarriage. During the dry season, it is best to feed with herbs and silage. You shouldn't skimp on high quality feeds, which are specially designed to prepare for pregnancy.
In winter, coniferous supplements in the form of flour or branches will be useful. This is a good source of vitamins to help prepare for childbirth. Eliminate moldy hay and frozen vegetables. Due to improper nutrition, the condition of the animal and the taste of milk significantly deteriorate. Such ingredients can be fatal to the fetus and the cow.
How the fetus develops
A cow's personal pregnancy calendar is based on the stages of fetal development. Therefore, before talking about the diet and the intricacies of starting cows, you need to have an idea of how the calves develop inside the womb. It is customary to divide the stages of fetal development by months.
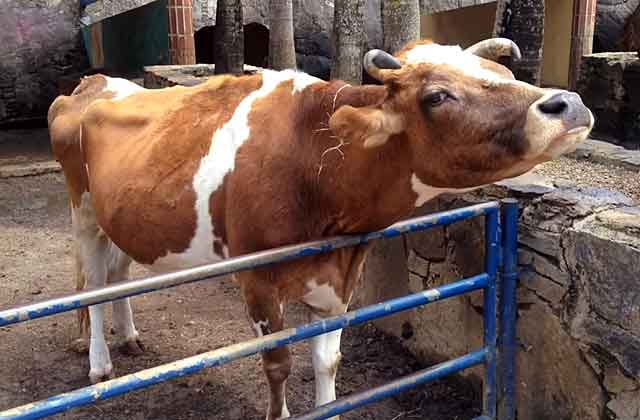


In the first month, there is no calf as such. In the embryo, eyes are just beginning to form and, in part, the mouth is visible. The gills are still clearly visible, instead of the skin, the vascular network. The embryo weighs up to 1 gram.
The second month is devoted to the laying of the vital organs. In the same period, the placenta is formed.The embryo is actively growing and with sizes up to 8 cm should gain 20-30 g.
From 3 to 5 months, testes are already formed and cotyledons are clearly visible. Horns are formed by the 4th month. By the 5th month, the size of cotyledons reaches 4 cm.During this period, the fetus can already be called a calf. He grows up to 45 cm and gains in weight up to 4 kg.


At 6 months, signs of hair on the legs appear, and at 7 and 8 months, the calf is completely covered with short and smooth hair. Also, from 7 months to the very birth, internal organs and incisors are actively formed.
On average, a cow's pregnancy or pregnancy lasts 285 days.
What happens in a cow's body
Of course, bearing a fetus dramatically changes the nature of the life of any living creature, including a cow. The first thing worth mentioning is the acceleration of metabolism. For this reason, the cow will need enhanced nutrition and a revision of the calorie content of food. This is especially true in the early stages of pregnancy.
In addition to metabolism, the following also changes:
- there is an additional load on the heart;
- the tone of the vascular system appears;
- the circulatory system receives a double load, in particular, only the uterine veins can increase in size by 2-3 times;
- blood biochemistry during the analysis is changed.
It is also worth mentioning that the main reproductive organ is increasing: the uterus can stretch to incredible sizes, multiplying its dimensions by 12-16 times. Accordingly, in parallel with the uterus, the volume of the sternum also grows, which makes the animal breathe more often.
Diet of pregnant cows
Starting from insemination, and the entire period of pregnancy of the cow, the diet is selected with an eye to the stages of fetal formation. For the first 6 months, the animal needs to be given everything. So the daily ration of a cow weighing up to 500 kg is at least 10-14 kg of hay from herbs. The amount of succulent feed reaches 20 kg.


In winter, they are given in an assortment: silage, fodder potatoes, beets, carrots. In summer, green grass in pastures makes up the lion's share of succulent fodder. Concentrates are given separately, but not more than 2 kg. Plus, table salt should always be near the feeders, and chalk should be added to the feed.
Cattle cannot be milked continuously; in the last 3 months before giving birth, the body of a pregnant cow must be given rest. And about 70 days before calving, the animal is transferred to dead wood and milk is stopped altogether. This is called launch. By the appointed date of birth, the weight of the cow should be about 50 kg more than usual.
One week before calving


A week before the expected calving, constant monitoring of the cow is required, since it is impossible to accurately determine the day on which the calving will take place.
The owner must also fully equip the stall in which the cow will give birth and further stay with the calf.
It is advisable to carry out such preparation in advance, even a month before the expected calving, so as not to face a problem if it happens early.
Feeding a week before giving birth needs a special one. Nutrition needs to be balanced. Hay feeding is stopped as soon as lactation stops.
In order to understand how well a cow is eating, she is weighed.
A week before calving, she should gain about 65 kg. If more than 75 kg of weight is gained, then this means that the animal is overfed, which will negatively affect the process of giving birth to a calf.
Underweight, when its weight gain is less than 50 kg, indicates a reduced appetite of the cow or inadequate feed quality. Insufficient weight gain of a pregnant cow has a negative effect on the calf's condition.
A week before the expected calving, the cow should be washed with warm water and her hooves should be treated with a 2% strength creolin solution. The animal must be kept as clean as possible.
How the launch is done
The launch should begin no later than 45 days before calving. The norm is 2 months, and for primiparous and highly productive cows, the launch begins in 70 days. But the animal still needs to be prepared for it.
Gradually, within 5-7 days, juicy feeds and concentrates are excluded from the diet. At this time, the cow is not even taken out to the pasture. At the same time, the amount of fluid consumed is reduced. The udder massage should be stopped and the number of milkings should be reduced to 2.


By the time of launch, the udder sags and wrinkles appear on it. In order for the cow to stop milking, she is completely transferred to hay.
In high-yielding dairy breeds, it is possible to stop milking and start a cow at a productivity of 4 liters per day. And for beef cattle, the milk rate at start-up is 1 liter. As soon as the cow was started, that is, transferred to dead wood and stopped milking, the daily ration and the range of conventional feeds are returned in 3-4 days so that the animal gains weight.
Transfer of a cow to dead wood
The dry period is the time period before calving, when the cow is resting, gaining strength for lactation. At this time, her milk yield decreases, milk production gradually stops. However, it is important to correctly transfer the animal to dead wood. To do this, you need to know exactly how long is a cow's pregnancybecause heifers need about 60-70 days of rest before calving.
To transfer an animal to dead wood, various methods are used:
- About 70 days before the expected calving date, the cow's diet is changed.
- Reduces the number of milkings per day.
- Milking is carried out at a different time, unusual for a cow.
Start-up power
To reduce milk production, it is necessary to remove juicy feed from the animal's diet. They are replaced with hay. Concentrates are also excluded for a while. In the warm season, when the heifer grazes in the pasture, they stop feeding her with green mass and concentrated feed. If milk yield does not decrease, it is recommended to leave only roughage in the diet. During the stall period, it is permissible to add flax cake, oatmeal, and wheat bran to the menu of cows during the dead time.
Reducing the number of milkings
Changes in the schedule of expressing milk lead to a violation of conditioned reflexes. The cow's nervous system reacts to such changes by reducing milk yield. Sometimes it is enough to change the usual mode of expression, as milk production is noticeably reduced. Many farmers use this technique very successfully. In some cases, it is not even necessary to change the diet of a pregnant cow.
Attention! When starting, you need to be more attentive to the udder. At this time, the likelihood of developing stagnant processes, mastitis is high.
Once the milk has stopped arriving, which usually takes about 7-12 days, the cow's nutrition should be adjusted to include all the necessary vitamins, minerals and trace elements. The last two months of pregnancy are very important - during this time the calf is gaining weight and develops very rapidly. Lack of nutrients can lead to various health pathologies.