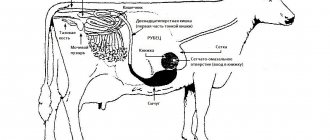
In order to properly prepare a cow for calving, to run it in dead wood on time, it is necessary to be able to predict the date of birth of a calf. Sexual maturity in females begins to appear at 7-8 months. The time of the first mating or artificial insemination depends on the breed of cattle.
Early maturing individuals quickly gain weight, their reproductive organs form early and hunting begins. They are taken for mating at the age of 14-16 months. In late-maturing cows, weight can increase rapidly, but the reproductive organs are formed closer to 2 years. Meat breeds are most often late ripening.
Females are led for the first mating at 22 months. After mating, it is important to determine the pregnancy of the female. This is necessary in order to predict the time of calving. The first signs of pregnancy are not visible from the first months. The belly begins to increase only by the 5th month of pregnancy.
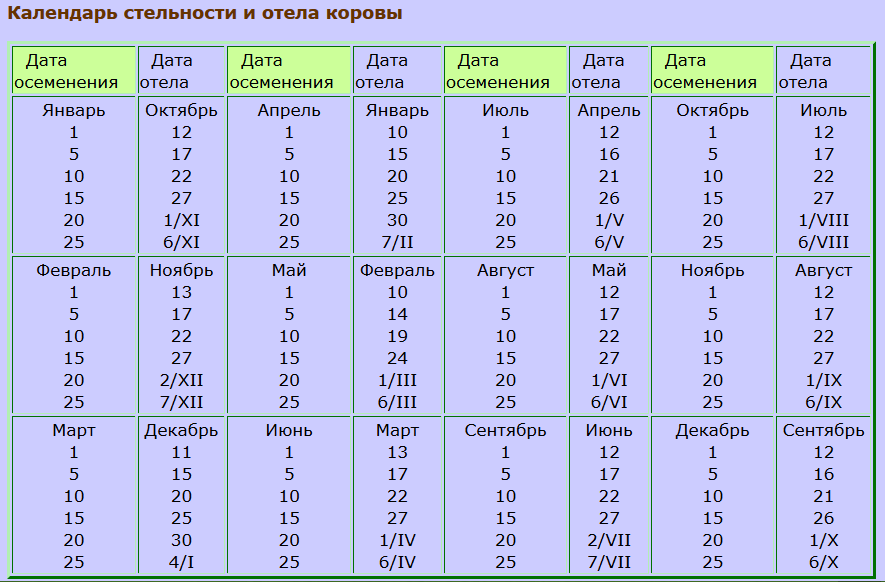
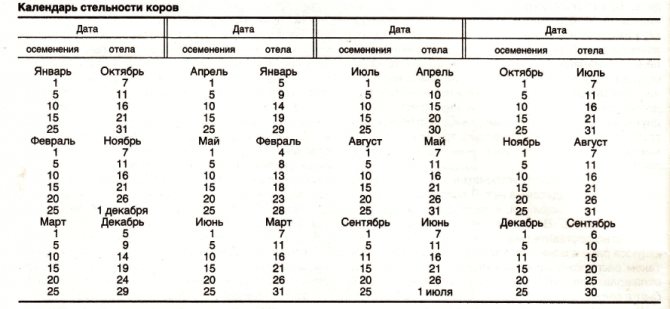
Pregnancy tests can be wrong. However, veterinarians make pregnancy schedules. They indicate the dates of mating and expected calving. How to draw up a calving schedule for cows correctly? What should be considered when doing this?
Conditions of detention
The most common problems due to poor containment conditions include:
- decrease in the reproductive qualities of the livestock;
- the occurrence of limb diseases, metabolic disorders;
- unfavorable genetic correlations (diseases that reduce production and health indicators).
Subject to certain maintenance conditions and the purchase of high-quality feed base, the economic efficiency of this line of production increases by 80%. Despite all the measures taken to improve the physiological parameters of the herd, 60-90% of all calving cows develop postpartum complications. Intensive and prolonged treatment does not always give the expected results. Experts in the field claim that most of the diseases are caused by stables.
When treatment is carried out in the postpartum period, the results may not meet expectations - re-fertilization occurs later than the standard time, the service period is increased to 150 days or more.
The solution to such problems is based on the active participation of veterinarians in the prevention of gynecological diseases. At the same time, the output of calves increases by 90-95%.
How the fetus develops
Once insemination occurs, the calf does not exist yet. The embryo gradually develops until it is born.
This is how it works:
- During the first month, various parts of the body begin to form: eyes, mouth. At this time, instead of the skin, you can see the vascular network. The embryo weighs no more than one gram.
- The second month is the time when the organs of vital activity begin to be created. At the same time, the placenta begins to appear. The size and weight of the embryo increases. At the end of this month, the size can reach 8 cm, the weight can reach 20-30 g.
- During the third, fourth and fifth months, testes form and horns begin to grow. When the fifth month ends, the embryo can already be called a calf.
- Over the next three months, active formation of internal organs occurs, and wool begins to grow.
Read also: How to beautifully place shelves on the wall
The calf is born 285 days after conception.
Mass features
Despite the fact that the weight of the female ready for insemination plays an important role, the parameter is not decisive. Approximate indicators of the mass of animals:
- 15-16 months - 380-42 kg;
- 14 months - 356 kg.
The main task is to raise livestock in the right conditions for fertilization at the most optimal time. At the same time, foreign specialists rely on the growth parameter. The average option is 125 cm at the withers. Based on weight, Russian representatives are often mistaken. In practice, cows weighing more than 430 kg are fertilized worse, and if insemination was successful, their weight exceeds 550 kg, which entails certain problems already at the stage of pregnancy.
The reproductive function of cows is greatly influenced by leptin, which is a peptide hormone. It is capable of suppressing appetite, so lowering its rate leads to the risk of obesity. In addition, delayed ovulation and lack of insemination are possible. Accordingly, these factors postpone the date of birth and entail a later fertilization. Preparing cows and heifers for calving includes complex measures.
Calving a cow and preparing for it
About 10 days before calving, the cow's diet is changed. Dispensing of succulent feed is stopped, the amount of concentrates is reduced. The main fodder base during this period is made up of leguminous and cereal hay. A pregnant cow is given warm water to drink.
Preparatory containment measures:
- the room in which the cow is kept is thoroughly disinfected;
- the floor is covered with a thick layer of straw mat.
Disease prevention should be carried out already a month before the launch of the female. Calving preparation includes regular check-ups. Correct insemination and calving of cows is only possible if the veterinarian's recommendation is followed.
Zoohygienic norms
Compliance with hygiene in calving cows allows you to avoid infectious diseases and improve the condition of the entire livestock. The health of a cow that has given birth is influenced by indicators of air exchange, humidity and room temperature. When transferring a female to dead wood, mechanical cleaning of her wool is always carried out. If necessary, veterinary control is carried out for weakened individuals.
Since it is possible to start a cow before calving only after diagnosis, at this stage it is recommended to carefully monitor her physiological state and diet. As part of the prevention of metabolic disorders, fortification and additional research are carried out to identify hidden infectious processes.
Treatment of mastitis and other diseases
At the moment, about 60-80% of all milk-producing livestock have a latent course of mastitis. But this depends solely on the maintenance of the farm and regular inspections. Preventive measures and veterinary examination allow you to avoid the deterioration of the animal's condition and to detect breast diseases in a timely manner.
The cow must be completely healthy before calving. 10-14 days before calving, the cow is checked by a specialist. The procedure includes:
- inspection;
- palpation;
- organoleptic assessment of the secret;
- trial milking.
It is also recommended to do a check when starting animals. When cows are started at once, they mainly use long-acting drugs aimed at stopping the disease in the embryo. In this case, the livestock is always checked for subclinical mastitis, it is treated in 5-7 days.
If intensive care is planned, the cow will need therapy consisting of warming udder ointments and the internal administration of prescribed medications.
With regular diagnostics, it is possible to significantly reduce the percentage of various diseases, including not only mastitis, but also long-term pathologies, for example, vestibulovaginitis.
Calving dates and calf reception
The female carries the calf for about 285 days, that is, approximately 10 months. More precise timing is carried out through the pregnancy calendar. This indicator is influenced by the age, housing conditions and breed of the cow. The term can be shifted by 10 days. How many days a cow calves depends on the presence of diseases and pathological processes in her.
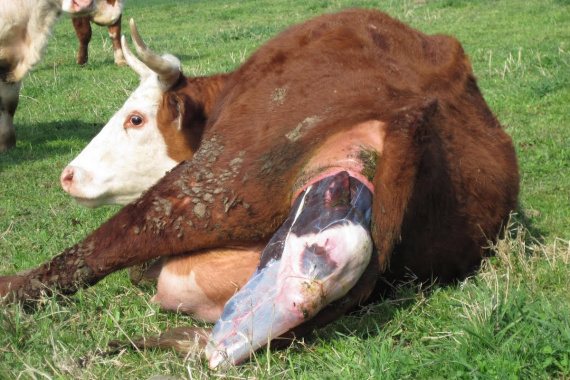
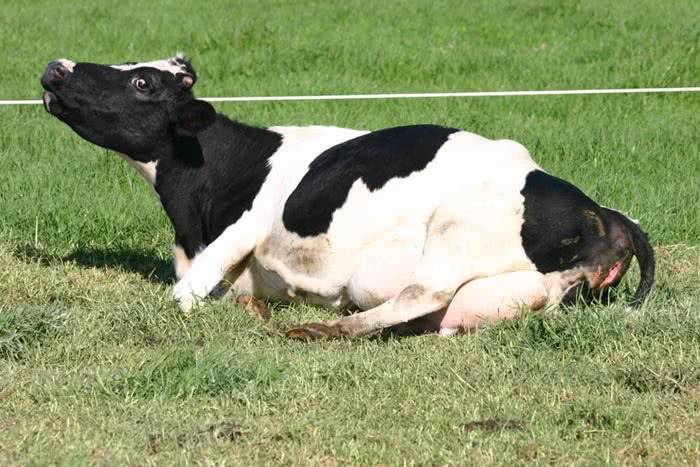
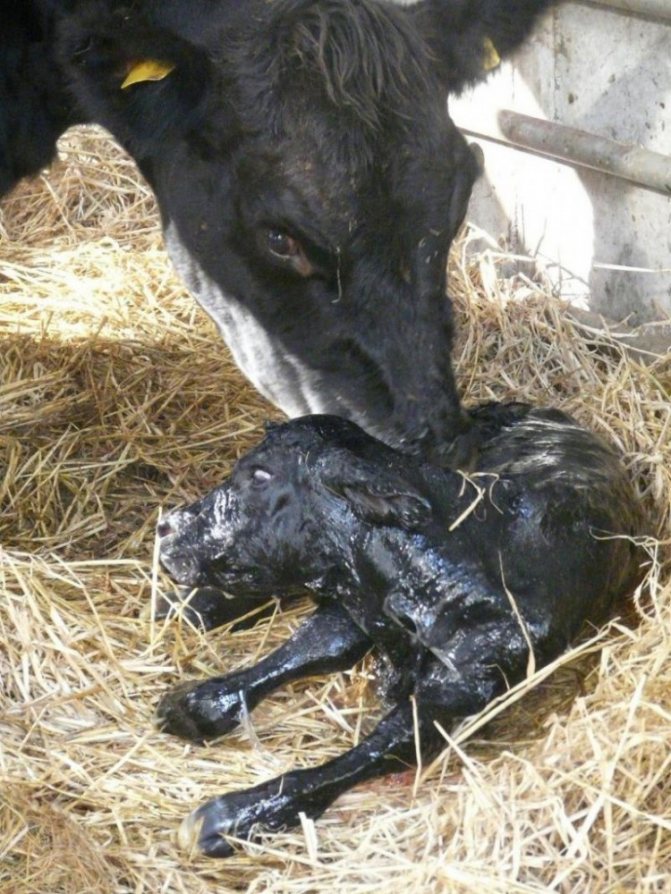
The female calves lying on her side. A normal process takes 30-60 minutes. First of all, the amniotic sac ruptures, the legs and head come out.
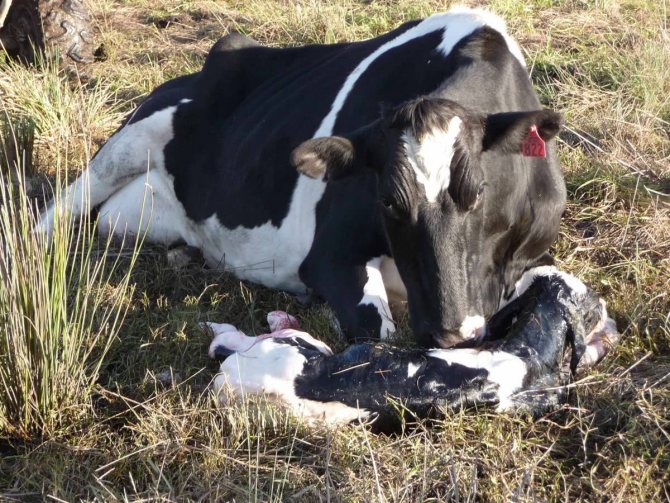
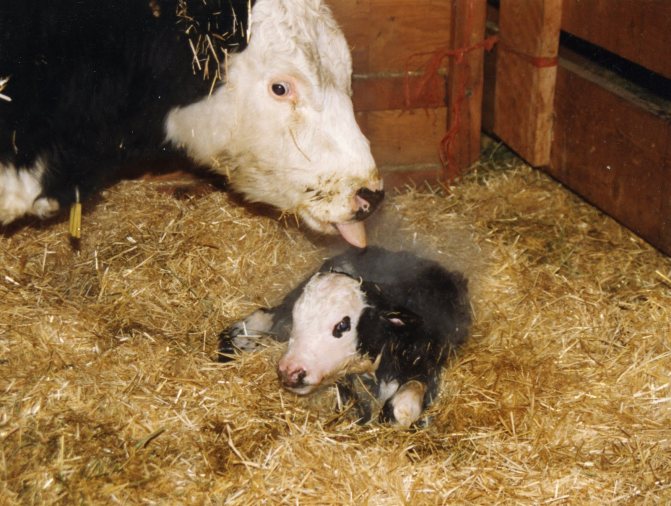
In some cases, the cow prefers to stand. It is then advisable to hold on to the emerging calf so that it does not hit the floor. After birth, the umbilical cord is cut off and placed on a clean burlap next to the female's head so that she can lick it. This is done to clear up mucus. How long it takes cows to calve depends on their physiological parameters.
If the cow refuses to lick the calf, you cannot force it. It must be wiped with clean burlap and left to dry in a warm place. After drying, the calf almost immediately rises to its feet. He is placed in a separate cage.
If the calf takes the wrong position (head back) inside the cow, then the veterinarian takes over the birth, who changes the position of the fetus on his own.
What it is?


Calving is giving birth to a cow. The calf birth process begins with contractions during which the cervix opens.
Further, attempts arise, in which the fetus is expelled from the uterus and goes out through the birth canal.
The duration of the entire process depends on several factors:
- having calved earlier - firstborns calve longer;
- the general state of health of the cow - a weakened animal gives birth longer than a completely healthy one, properly prepared for childbirth;
- fetal size - a large calf takes longer to hatch than a small one; number of calves.
Typically, a cow gives birth within a few hours. From the moment of development of attempts to give birth to a calf, it takes about an hour. In primiparous, this lasts longer.
The need for veterinarian help can be said if labor in a re-giving birth cow did not end within 10 hours, and in a primiparous - within 12 hours.
Some females have an individual feature in which the birth of offspring lasts longer, but only a veterinarian can detect this property when examining the animal.
The veterinarian or experienced livestock breeder will determine exactly how the cow is giving birth in a particular case - normal or too long.
Signs
The back of the cow is washed with warm water with lysol solution. After the outer part of the vagina is treated with potassium permanganate.
The main signs are:
- sagging belly;
- swelling of the external genital organs;
- divergence of the vertebral bones, relaxation of the tail ligaments;
- swelling of the udder and milk flow from the teats;
- expansion of the genital gap and the release of mucus from the vagina;
- increased anxiety of the cow, attempts to lie down.
After the onset of symptoms, it is necessary to provide the animal with peace and quiet. Attempts occur at regular intervals.
The first sign of calving in a cow in the near future is the release of milk. Occurs several hours before delivery.
Retention of the placenta
Diseases associated with the labor of cows are noted. With poor maintenance of cattle, if the diet is not followed, childbirth can take place with complications. One of the most common pathologies is the retention of the placenta. With a lack of vitamins, nutrients and minerals, the walls of the uterus become flabby. They cannot function fully. A complication can occur if a cow has two fetuses in the womb or the calf is too heavy.
Normally, the placenta is separated 2-4 hours after calving.12 hours is considered acceptable, but if the placenta has not separated at the end of the maximum period, then the help of a veterinarian is required. Possibly surgery.
The complication is noticeable in the behavior and appearance of the cow. Her belly is tightened, her back becomes hunched over, her coat is tousled. The animal struggles from time to time. His appetite decreases, there is a poor production and delivery of milk. The individual's body temperature rises, a fetid odor is noted from the vagina.
To prevent the complication from manifesting itself, the following measures are carried out:
- for prevention, after the appearance of the calf, the cow is drunk with warm water with 500 g of sugar; after 8 hours, the watering is repeated;
- cool tea leaves are added to sweet warm water; give up to 7 liters of liquid to drink;
- before calling the veterinarian, the animal is given amniotic fluid to drink: they are diluted with warm water in a 1: 1 ratio; the amount of solution is 4 liters; watering is repeated after 6 hours.
If no measures help, then call the veterinarian. The life of a cow depends on timely help. Milking is carried out, but the milk is discarded. The calf is fed with milk formulas.
Another serious complication can occur immediately or 2 days after calving. This is postpartum paresis. Certain signs are noted in cows already at start-up. Complications are associated with improper nutrition of the animal. The examination diagnoses hypocalcemia and low blood sugar. A dairy cow with large milk yields is at risk. Calcium is washed out with milk.
If an individual already before calving tries to lie more, tightens the limbs, she has convulsions of the limbs, then this indicates the development of hypocalcemia. The symptoms of the disease do not go away after calving, but on the contrary, are aggravated:
- the animal stops holding its head. She falls with her all the time;
- body temperature decreases: body, horns and nose are cold;
- pupil dilation occurs;
- the sensitivity of the skin decreases;
- the mouth is open, the tongue falls out. The cow is not fed in the usual way. Fluid is injected through a tube into the esophagus.
Cow Veterinary Medicine notes that postpartum paresis is not a rare disease. It is found not only in cattle, but also in all farm animals. At start-up, the cow's diet is monitored. Limit the amount of concentrates and juicy feed. 2 days before calving, the cow is fed with sugar water. Immediately after giving birth, she is given salt water: a solution is made with 120 g of salt. During the dry period, the animal is added to the feed ammonium chloride, 100 g.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: If you picked up a stray cat first aid and further actions
With postpartum paresis, seek the help of a veterinarian. It can carry out inflation. Air is pumped into the udder of the cow through the teats. To do this, use the Everas apparatus or a bicycle pump: the tip is wiped with alcohol and burned with fire. Air irritates receptors and makes muscle tissue work.
Air is pumped into all 4 lobes of the breast. At the same time, the state of the udder is monitored. It should not be too tense and extended. After blowing in, the nipples are massaged. If at the same time air comes out through the channel, then the nipples are tied with a bandage. Recovery can come within 30 minutes. After 5 hours, the animal can stand up, but tremors are observed in the limb.
| № | Helpful information |
| 1 | If there is no improvement in the condition, then after 8 hours a new injection is made. |
| 2 | Massage the peritoneum and sides of the body |
| 3 | Knead the withers and back |
| 4 | Subcutaneously injected with caffeine and glucose |
| 5 | It is recommended to do an enema with warm water to free the intestines from feces |
| 6 | A cow is injected with fresh milk from other cows |
Postpartum paresis in cattle, most often, is cured, the symptoms gradually disappear. Otherwise, the animal is discarded.
If the time has come for a cow to calve, but no signs are observed, then this should alert the owner. You can invite a veterinarian who will determine the reasons for the absence of labor. If calving has already occurred, then complications sometimes arise after it. Most of them require the consultation of a veterinarian.
Complications may be related to the age of the wet nurse. It has long been noticed that older cows are harder to calve and they often have problems later. Young cows are also often difficult to give birth. The main reason for the appearance of pathologies is improper preparation of the animal for calving. At risk are emaciated and obese cows, as well as cows with gynecological problems.
Calving for the cow ended well, the calf is healthy and well fed, but it's too early for the owner to relax. Within a maximum of 10-12 hours, separation of the placenta should occur, only after that the birth is considered completely completed. If this does not happen, then the owners should call the veterinarian.
The reasons for the detention of the placenta can be:
- unbalanced feeding during pregnancy;
- lack of vitamins;
- lack of exercise;
- stress.
Before the doctor arrives, the owners can give the cow sweet water. If you managed to collect amniotic fluid, then you can give them too. The veterinarian must examine the cow and administer the medication. If all these actions did not give results, then the afterbirth is separated manually.
This pathology is most common in older cows. The postpartum cut usually starts within the first 3 days after calving. First, the cow's gum disappears, then tremors in the limbs begin. Soon the cow falls on its side and does not get up again. The disease begins suddenly, the owner should call the veterinarian as soon as possible and bring him to the farm.
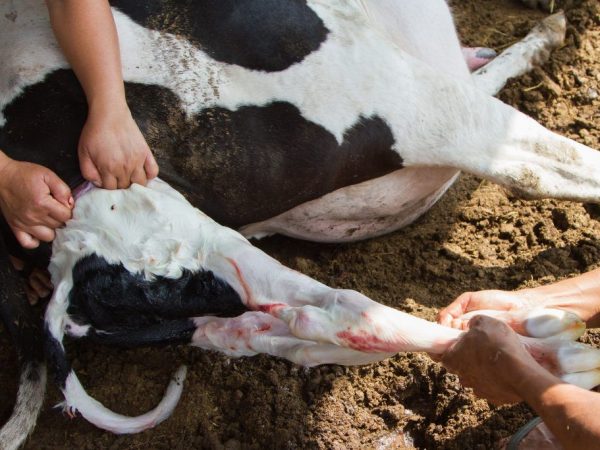

Without treatment, the cow dies in a couple of days. The doctor examines the cow and prescribes drugs. Droppers with glucose and calcium are usually used. In the scheme with these drugs, additional drugs can also be used. In some cases, the doctor inflates the udder according to Evers.
| Signs | Disease | What to do |
| The animal does not get up after childbirth, the back is bent, the contractions continue, mucus is secreted, the remnants of the afterbirth, loose stools or bleeding are visible. | It is worth thinking about incomplete cleaning (the afterbirth did not come out completely). | Here you need to act with lightning speed - call a veterinarian, because the amniotic tissue will decompose, which will lead to inflammation of the reproductive system, which is problematic to treat. |
| Careful movement, desire to constantly rest, lack of desire to eat for several days. | Symptoms of postpartum paresis, which in its advanced form provoke paralysis. | It is important to keep an eye on the individual, quietly make it move and feed it properly. The right care is the right treatment. |
| The animal does not want to move, but eats well. | Hypocalcemia should be suspected. | Call a veterinarian, because without the introduction of special drugs (d0 and d1) and adjusting the diet, the cow will die. |
When fixing any symptoms, you need to call a veterinarian to eliminate complications and save the life of the cow.
Calving a cow and receiving a calf are significant events that should be approached consciously: prepare in advance (watch photos and videos, know how many cows have already calved, be able to identify signs of imminent birth, keep a calendar of insemination, follow the above recommendations and use the services of veterinarians ).
Taking care of animals after calving
The postpartum period requires careful care. After giving birth, the female is watered with salted water and given some hay. The udder is washed with warm water and a disinfectant solution. The first milking takes place - the first trickles of colostrum are not given to the calf, but are milked.
How much milk a cow gives after calving affects feed volume. With abundant milking, its amount decreases if the indicators do not return to normal within a few days.


In the postpartum time, the cow lies on a bed, which must be monitored for dryness. The vulva is disinfected twice a day until the loch disappears completely. If the female does not have any postpartum complications, the first walk is carried out after 3-5 days. A week after giving birth, the animal is examined by a veterinarian to rule out complications and pathologies in the body.
Good health factors:
- the presence of appetite;
- normal temperature;
- general behavior and mobility.
Emerging complications
If the contractions are weak, and within half an hour the fetus does not come out, the owners have to remove the calf themselves, tying a loop of strong and well-disinfected twine and throwing it on the calf's legs.


For each bout, the calf is pulled a little by this rope. This work is not easy and requires a lot of physical effort from the owner. Ideally, a veterinarian should do this. He will be able to remove the fetus with minimal risk to him and the mother.


Important: Particular attention should be paid to childbirth of first-calf heifers and a cow passing her pregnancy.