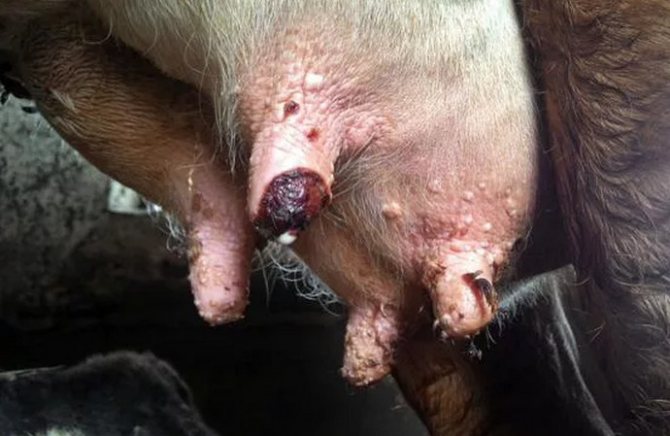
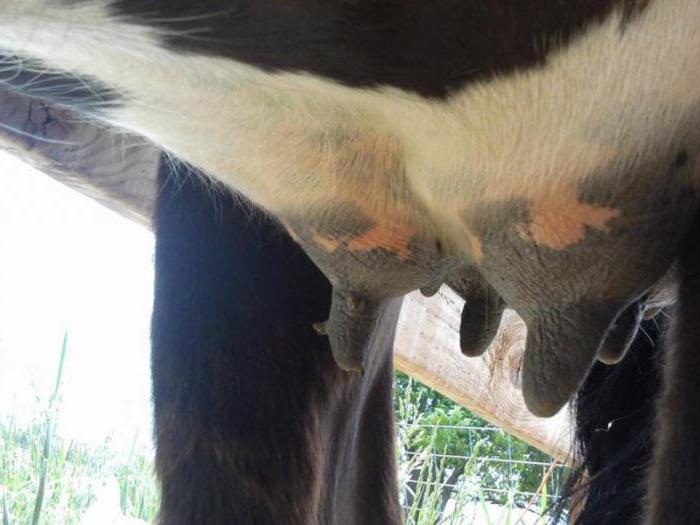
Warts on the udder of cows are papillomas of a benign nature. The place of localization of neoplasms is the nipples and udder bowl; young individuals are at risk. Formations cause inconvenience to both animals and service personnel.
The size of the tumor can range from a small pea to a plum. The milk flow process is complicated by the pain that the cow experiences during milking. Before treating the problem, it is necessary to establish the causes of its occurrence.
Reasons for the appearance
Papillomatosis - multiple warty growths on the mucous membranes and dermis. Neoplasms are referred to as benign tumors. The main reasons why cows have nipple warts are:
- accession of a secondary infection in the presence of microcracks on the skin and mucous membranes;
- improper care;
- feeding calves by a sick cow;
- insect bites;
- natural insemination: bulls are carriers of the sexually transmitted papillomavirus;
- eating poor-quality feed;
- decreased immunity;
- overcrowding of livestock in a small barn that does not meet hygienic standards;
- not properly treated mechanical damage.

A viral infection penetrates the skin through microscopic wounds when grazing in meadows with tall grass and thorny plants. Scanty feed leads to vitamin deficiency, which significantly accelerates the development of the disease and leaves the cow's body open to infection. The main vectors of infection are adults, sexually mature individuals. Failure to comply with the rules of hygiene in the barn also leads to damage to the skin and the development of infection.
How does the infection take place
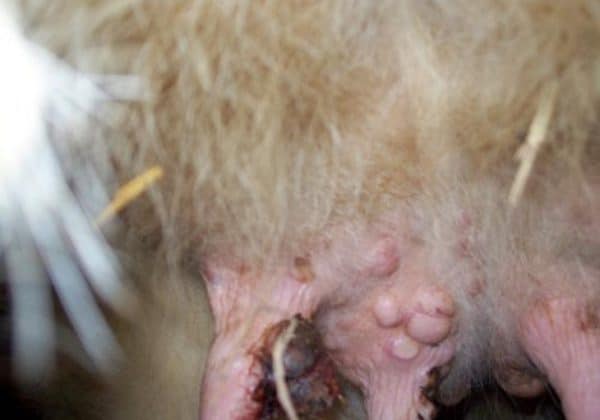

The cow has warts on the udder
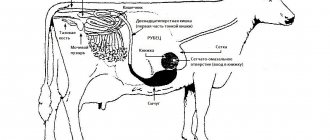
The effectiveness of therapeutic measures largely depends on the ways in which the papillomavirus enters the body. Infection occurs through open wounds and injuries in the abdominal cavity and udder.
After entering the circulatory system, the virus quickly spreads throughout the body. After a while, the first clinical manifestations appear in the form of small formations.
Ways of transmission of papilloma virus
Sources of the disease are inventory, food containers, buckets and other devices that are used when keeping livestock.
In rare cases, the disease is transmitted through contact with a veterinarian if he neglects the rules of hygiene. At a young age, the calf becomes infected as a result of suckling. One of the methods of transmission is sexual contact between a healthy heifer and a sick bull.
With herd keeping, the disease becomes widespread, passing from one individual to another. Insects, including horseflies and mosquitoes, are capable of transmitting the papilloma virus. The breeder needs to regularly clean the containers with water and food to reduce the likelihood of the occurrence and spread of pathology.


Be sure to read:
Why cow's milk is bitter, how to get rid of bitterness
Why does the papilloma virus affect the udder zone?
Papillomas can affect any part of the cow's body and even the head. In areas of skin without hair, growths are best traced.
They are immediately noticed during milking because the mammary glands are examined and massaged.The rest of the body is usually not examined, so warts are rarely noticed (especially when grown on an industrial scale).
Disease development
Once in the animal's body, the virus is able to remain in an inactive stage for a long time. In this case, the presence of the disease does not manifest itself in any way outwardly. Full-fledged immunity is able to keep pathological microorganisms in a dormant mode. In the presence of favorable factors for the development (lowering immunity), microorganisms begin to actively synthesize their own kind and leave their waste products in the tissues, as a result of which warts are formed.
Important! The intensive development of the disease occurs in animals with a history of chronic diseases, young cows under 2 years of age and calves. In sexually mature individuals that are carriers, it often proceeds in a latent form.
Keratinous growths are a collection of dead skin cells, waste products of microorganisms. They grow slowly. The maximum size of 15 cm in diameter is reached after 8 months. Neoplasms squeeze small vessels, which interferes with normal blood circulation in the udder and leads to stagnation of lymph and milk. Gradually, lymph and dead plasma cells are converted into pus.

The inflammatory process in the tissues leads to the spread of pathological microorganisms to other organs with blood flow. If the skin growth is damaged, bleeding comes off, purulent exudate pours out. The advanced stage of papillomatosis is characterized by the formation of multiple growths not only on milkings, but also throughout the body.
Delete or not?
Based on the foregoing, the question: "Should we remove warts" can be answered with confidence: "Yes."
If, through carelessness, you did not notice the neoplasm or simply decided to ignore it, in a good case, the cow will get sick with vaginitis, its treatment will require a lot of time and money. In a bad scenario, papilloma will develop into purulent peritonitis, in the event of which, in most cases, the life of livestock is cut off within a few months.
What is the danger of the appearance of warts
Damage to the warty growths causes the infection to spread. In this case, only the upper stratum corneum is removed, and the bulk of microorganisms remains inside and continues to actively multiply, which leads to serious suppuration and abscess. The penetration of a viral infection into the deep layers of the skin provokes the emergence of benign and malignant tumors.
When a growth is formed in the inner part of the nipple, milk flow stops. This leads to the development of mastitis and associated pathologies. The spread of infection to the mucous surfaces of the genital organs makes conception impossible.


Folk remedies
You can cure warts with folk remedies. For example, a decoction of lungwort is prepared, for two weeks, 5 or 6 times a day, the cow's udder is washed with a healing liquid. As a result, the warts dry out and fall off. Wipe the warts and celandine broth.
It will take only 15 minutes to prepare an infusion of potatoes, and a starchy vegetable is available in all farms. A pot with peelings on which there are sprouts should be set on a low heat. A dark liquid is required to wipe off the area with warts 3 times a day. Raw potatoes can be cut into slices for lotions. Juice is prepared from sour apples, and areas with warts are carefully treated with it. Garlic gruel is also made. Take 3 or 4 coarse teeth and a fine grater. The resulting garlic gruel is mixed with lard, and a compress is made in places with warts.
Papilloma treatment methods
What to do with papillomas on the udder, the doctor decides after a thorough examination and taking tissues for analysis.The basis of treatment is an integrated approach that includes surgery and medication. The main task is not only to remove visible growths, but also to increase the protective functions of the body.
After calving, warts may disappear on their own. In such cases, additional treatment is not required, but this does not mean that the viral infection was not in a dormant mode. Another decrease in immunity will lead to the resumption of the activity of the virus and the appearance of new growths. To avoid this, routine vaccinations are carried out. The indication for the operation is the presence of growths that impede milking and bring significant discomfort to the animal.
Important! Only large warts can be removed. Removing small growths by surgery inevitably leads to a relapse and spread of the infection.
Small warts are cauterized with acids:
- acetic,
- chrome,
- nitrogen.


Diathermocoagulation is a progressive method for removing warts. Warts are exposed to high frequency alternating current. Infected individuals are transferred to separate stalls, and the room is disinfected with a 1% solution of copper sulfate. The animals are regulated by their diet. Introduce more fresh herbs and fortified feed.
Medication
Medications will help to remove papillomas at the initial stage. The treatment uses:
- antibacterial ointments with a drying effect;
- intramuscular injections of vitamins and immunomodulators.
To avoid trauma to the udder, change the pasture. Areas with low grassy cover are selected. Before milking, the udders are thoroughly washed with warm water, then with a 3% manganese solution and again with water.
Ointments
With the disease, such ointments are effective:
- Sulfur-salicylic ointment allows you to quickly remove papillomas and disinfect the affected area. The main active ingredients of the drug are salicylic acid and sulfur. Designed for outdoor use. The ointment is applied to the affected areas of the skin 4-5 times a day. The course of treatment is 5-7 days.


- Oxolinic ointment helps not only to get rid of warts, but also to increase the skin's resistance to infection, to strengthen small blood vessels. The main active ingredient is oxolin viruscide. It is applied to the skin and mucous membranes affected by the virus 3-4 times a day. Penetrating into the deep layers of the dermis, the active substance is embedded in the DNA chain of the virus and blocks its synthesis. By increasing the resistance of skin cells, it promotes the release of active substances that destroy viral compounds, and accelerates the regeneration processes. The course of application is 2-4 weeks, depending on the stage of the disease.


- Interferon ointment is an immunomodulatory drug. Once in the tissues, it helps to increase the production of immunoglobulins necessary to fight the virus. Relieves puffiness, eliminates dryness and irritation. The course of treatment is 1-2 weeks. The ointment is applied 4-5 times a day to the affected areas.
In advanced cases, combine sulfur-salicylic ointment and interferon. This allows you to quickly reduce warty growths and increase the skin's resistance to infection.
Intramuscular injections
Novocaine blockade is used in advanced cases with a course of 3-5 days. A 0.5-1% solution of novocaine is injected intramuscularly at the rate of 1 ml / kg of live weight once a day. The method of introducing a 0.5% solution under the base of the wart is considered more effective. The procedure is carried out for 3 days in a row, then they take a break of 2-3 days and repeat the course. A combination of novocaine injections with iodoforms is practiced.

After the introduction of a 0.5% solution of novocaine into the base of the papilloma in 10 minutes. repeat the procedure using a 10% iodoform solution. A single dosage of novovain is 0.3 ml, iodine solution is 0.5 ml.To increase immunity, injections of vitamins B6 and B12 are given. This approach allows you to accelerate the regeneration processes and accelerate the synthesis of immunoglobulins in the body.
Folk ways
People have been breeding cattle for centuries, and it was not always possible to receive treatment from a specialist. Traditional healers knew how to remove warts using the power of plants. Folk remedies will help to quickly cure papillomatosis without surgery. Hanging growths are tied with a hair from the tail of a cow.
Several knots are tightly tightened under the base of the wart and wait for it to fall off. During this time, external ointments of their own manufacture are used, which have a drying effect and a disinfectant effect.
Means for external use
Ointments based on garlic juice act positively on the animal's body. The plant extract contains phytoncides - substances that have a powerful antibacterial effect. Mix 100 ml of juice or pulp of garlic pulp with honey and 100 ml of cabbage juice. The ointment is applied 3-4 times a day until the papillomas disappear completely. Garlic juice is added to cows' drinking in the proportion of 50 ml of juice per 10 liters of water. This drink is given every 3 days.


A decoction from the following herbal collection is good in treatment:
- medicinal chamomile - 50 g;
- elecampane - 30 g;
- St. John's wort - 50 g;
- mother and stepmother - 40 g.
The collection is poured into 1 liter of boiling water and insisted for 2 hours. Lotions are made with a concentrated broth. A piece of bandage folded in several layers is applied to the affected areas, and it is fixed with an adhesive plaster. Leave for 15-20 minutes. The procedure is performed 3 times a day. The course of treatment lasts until the complete disappearance of the warts.
Did you know? At the time of the destruction of a garlic clove, allicin is formed - a strong antibiotic of natural origin that destroys carcinogenic microorganisms. The medicinal component is quickly destroyed by heat treatment, therefore, products created on the basis of fresh garlic are more effective.
the creature is also added to the drink of cows: 500 ml of concentrated broth goes to 10 liters of water. Aloe-based ointments have a wound-healing and regenerating effect. For medicinal purposes, a plant that is 3 years old and older is suitable. The juice of 1 aloe leaf is mixed with garlic gruel from 2 cloves. The ointment is applied 3 times a day.
Conspiracy for treatment
In ancient times, it was customary to treat papillomatosis with conspiracies. Bandaging warts with cow hair was accompanied by the reading of special conspiracy words: “Illness and nudota, go to Fedot, to the red mountain, beyond the blue sea. Don't push the animal, don't drive it to the churchyard. Go to the forests and swamps, there will be work for you. " As soon as the wart body fell away, it was buried next to the outhouse, saying: “It dried up, fell away, fell to the ground. The disease will be buried in a heavy piece of land, and it will no longer be found in the barn ”.


Conspiracies are read 3-7 times. To ward off the attack, bunches of wormwood and St. John's wort were hung in the cowsheds. After each milking, the udders were greased with pork fat. To reduce the warts, all the litter was removed in the barn, and then the floor was washed with a steep broth of wormwood, saying: “The spoilage of my animal does not wrinkle, it leaves at night. I close the paths to the threshold, sprinkle with salt ”. After processing, a pinch of salt was necessarily poured under the threshold, and a fresh bed of hay and straw was laid on the floor.
Important! Rituals aimed at treating diseases are performed in the waning moon phase. As the monthly sickle in the sky decreases, the disease goes away.
A few more ways
In the household, this phenomenon is unpleasant and frightening - warts on the udder of a cow. Treatment of papillomatosis, in addition to the above methods, can be done using:
- Solid oil, which is used to process cow's udder for 3 weeks after milking. Be sure to wipe the skin with warm water before the procedure.
- Sour apple juice, preferably winter varieties. Such a remedy should be applied to sore spots two to three times a day. Papillomas will become smaller, darken, and then completely disappear.
- The juice of a vine that flows out of it when cut.
Disease prevention
To prevent cows from getting sick, it is necessary to carry out preventive measures in time and follow the elementary rules for caring for animals. Prevention of papillomatosis is as follows:
- disinfection of premises for keeping animals every six months with formalin solution;
- changing the top layer of litter as it gets wet;
- selection of pastures with minimal risks of traumatizing animals;
- balanced diet;
- udder treatment before and after milking;
- enrichment of the diet with fortified elements in winter;
- vaccination of animals.


Papillomatosis is an unpleasant disease that can be effectively treated in the initial stages. Prevention and vaccination will help to avoid re-infection.
Video "Cattle Diseases"
The video discusses the most common cattle diseases, and what veterinary measures to take for prevention and in case of diseases.
Featured Articles
Methods for treating various forms of mastitis in cows Mastitis is a very common disease. It is important to detect it in time and successfully cure it. How to independently detect and carry out treatment, read the article.
How to avoid udder diseases in cows? Various diseases of the udder of a cow cause great damage to the farm. Read in the article about the symptoms and treatment of the most common diseases
An overview of possible diseases of the udder of goats and how to treat them It is good if the animal is always vigorous and mobile, but sometimes farmers have to deal with diseases of the udder of goats. How to cure them, read the article
Effects
First, the cow's udder warts look like a bunch of grapes. They are also wide at the base, rounded. They are no more than a pea or a nut in size. Then multiple papillomatosis develops, that is, there are several growths.
If the warts on the udder come into contact with other objects, they are injured, bleeding, inflammation appears due to secondary infection. When the growth is on the nipple, it interferes with milking. the animal feels pain. Because of this, milk stagnates, mastitis develops.
Udder warts are most common in young heifers. They are benign growths
The tumors are constantly growing. After 4-8 months, they reach 15 cm in diameter. Then they gradually dry out. Warts can be found on other parts of the body, although they are not always noticeable under the coat.
If the animal is not treated, the virus penetrates into other tissues, weakening the body, its immune system. Animals that suffer from papillomatosis are more susceptible to infections. Later, a malignant tumor appears.