Livestock »Pigs
0
1885
Article rating
African swine fever is a viral disease with a very high mortality rate that is harmless to humans. Synonyms - Montgomery's disease, African fever, South African swine fever, ASF. Pathology is very dangerous, spreads quickly and leads to large economic losses. Clinical symptoms are mild; laboratory diagnostics can confirm the final diagnosis. Sick animals today are not subject to treatment; preventive measures are taken to prevent them.
African swine fever
General characteristics of the disease
African plague is also known as Montgomery disease - after the name of the researcher who proved its viral nature. This is an infectious process, in which inflammatory processes develop, fever occurs, and the blood supply to internal organs stops.
The disease-causing DNA virus of the Asfarviridae family spreads to all livestock, regardless of the age of the pigs.
In individuals who died from this disease, the following pathological changes in the body are observed:
- multiple lesions of the connective tissue;
- numerous sources of hemorrhage;
- severe pulmonary edema;
- an increase in the size of the spleen, kidneys, hepatic gland;
- serous-hemorrhagic fluid in the respiratory system and in the stomach;
- the content of blood clots in the lymph.
The virus that causes this serious disease is resistant to external conditions. It survives temperature extremes, multiplies when it dries, crystallizes and decays. The virus is also resistant to formalin and alkaline environments, but sensitive to acids.
In pickles and smoked meats, this virus can persist for several weeks or months. In feces, it remains active for about 160 days, in urine - up to 60 days. In soil, the virus can persist for 180 days, in bricks and wood - from 120 to 180 days. It remains in meat for about 5-6 months, in the bone marrow - up to 6-7 months.
The first time a case of this formidable disease was reported in 1903 in South Africa. The infectious process spread to wild boars. Subsequently, the disease spread to many African countries in the southern part of the Sahara.
In the middle of the twentieth century, a case of African plague was recorded in Portugal. This happened after meat products from Angola were brought into the country. In the future, the infectious process spread to Spain, Cuba, France, Holland, Malta.

In Russia, as well as Ukraine, Georgia, Armenia and Abkhazia, African swine fever was first detected in 2007.
The statistics for outbreaks of African plague by year are as follows:
- Kenya - 1921
- Portugal - 1957 and 1999;
- Spain - 1960
- France - 1964, as well as 1967 and 1974;
- Italy - 1967, 1969, 1978-1984 and 1993;
- Cuba - 1971
- Malta - 1978
- Dominican Republic - 1978;
- Brazil - 1978
- Belgium - 1985;
- Holland - 1986;
- Russia - 2007;
- Georgia - 2007;
- Armenia - 2007.
Analyzing the reasons for the rapid spread of infection, the researchers concluded that in most cases contaminated food waste contributes to this.
The plague was brought to Russia from Georgia. In turn, the virus spread in Georgia due to the misuse of waste from international ships that transported contaminated meat and products from it. The media covered information that the corpses of animals that died in this country were found in ordinary landfills, river banks and on the seashore.
In areas that are considered stationary unfavorable for African swine fever, there is a frequency of outbreaks: in Africa, this viral process occurs every 2-4 years, in Europe - after 5-6 years.


At the moment, this infectious disease of pigs is registered in 24 countries of the world.
Epidemiology
The first cases of the disease were recorded at the beginning of the twentieth century in South Africa, from there it spread to Portugal, Spain, and other countries of southern Europe. In the 70-80s, the pathology was registered in South and North America, the USSR. Now the disease is a serious threat, because of it, pigs are almost not raised in Africa, their livestock is declining in Europe and America. In 2007, the outbreak was recorded in Georgia, in 2020 - in Ukraine, since 2008, the African plague, as reported by veterinary services, has been regularly registered in the European part of Russia.
The source of pathology is sick pigs and virus carriers. Even if the animal recovers, it continues to excrete the pathogen until the end of its life, therefore, all livestock are destroyed in the epizootic focus. The natural focus is African pigs, especially wild pigs. Their infection is latent and chronic, very rarely - in acute. Domestic pigs are more susceptible to the virus, especially European breeds. Even among wild boars in Europe, mortality is at the same level as among domesticated ones.
The African swine fever virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, alimentary. The main objects and things through which pigs become infected are water and food (especially feed that uses animal meat), care items, contaminated bedding. The virus can be transmitted through the clothing and shoes of people caring for sick pigs. Often, the virus enters the bloodstream through ticks, which are its natural reservoir. Flies and other blood-sucking insects can carry the infection. Often, the pathogen is mechanically carried by domestic birds and rodents.
Virus transmission methods
The source of the virus is a sick pig. Also, African plague is transmitted from virus carriers, which can be people, insects, birds and animals.
This disease, which affects domestic pigs, is transmitted in the following ways:
- as a result of close contact of a sick animal with a healthy one: infection occurs through the oral cavity, skin, mucous membranes of the eyes;
- through contaminated food waste, as well as equipment intended for the slaughter of pigs;
- from domestic animals, birds, rodents, insects and people who have stayed in the infected area - a slaughterhouse or warehouse;
- through the bite of a tick carrying the virus;
- through vehicles that have been contaminated when transporting sick pets;
- through food waste that is added to pigs' feed without having previously processed it appropriately.
The duration of the incubation period of the disease is about 5-10 days.
For the human body, this disease does not pose a danger, since it is not sensitive to a virus of this type. However, a person is able to act as a virus carrier and infect pigs upon contact with them.
The pathogenesis of the disease
The susceptibility of domestic pigs to the virus is very high, which is why the disease is so dangerous. The pathogen enters the body through mucous membranes and skin, even with microscopic damage, sometimes enters the bloodstream with insect bites. From the site of penetration, the virus enters the cells of the immune system (macrophages, neutrophils, monocytes), as well as the endothelial cells of blood vessels. Reproduction of the pathogen takes place in these structures.
After replication, the virus leaves the cells, destroying them. In the vessels and lymph nodes, foci of necrosis appear.The permeability of the vessels increases sharply, blood clots form in their lumen, and inflammation develops around the damaged structures. Anesthetized lymph nodes are found in various organs. Due to damage to the immune system, the ability of the pig's body to protect and resist other diseases is sharply reduced. Symptoms of the African plague are manifested, quickly leading to the death of the animal.
Symptoms of African swine fever
The disease can take three forms:
- Lightning fast. In this case, the disease develops for 2-3 days and inevitably ends in the death of the infected animal.
- Sharp. This form of the disease is characterized by severe clinical manifestations.
- Chronic. This form is poorly manifested, it is very rare. Most often, this kind of African plague is observed among wild boars.


This pathology is characterized by the following manifestations:
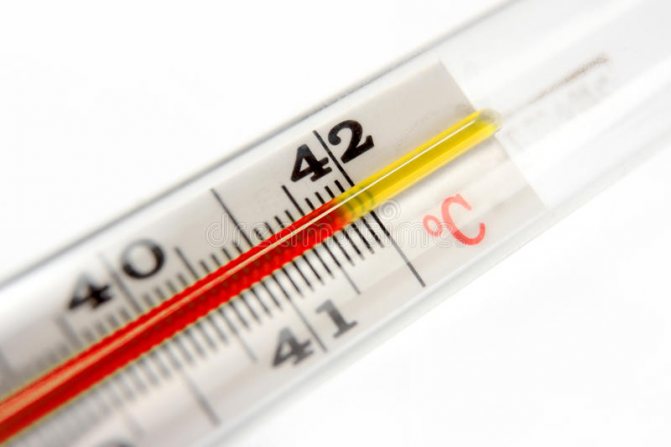
- an increase in body temperature up to 42 degrees, such indicators hold until the moment the animal dies;
- general depression;
- weakness;
- cough;
- serous conjunctivitis;
- increased thirst;
- lack of appetite;
- discharge of purulent masses from the nose and eyes;
- severe shortness of breath;
- paresis of the hind limbs;
- vomiting;
- fever;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- exhaustion;
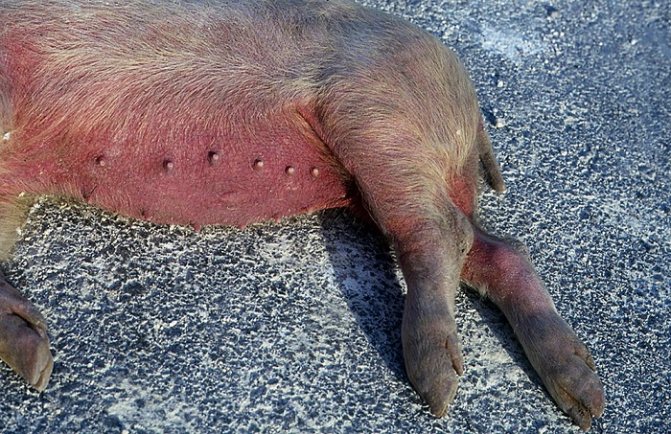
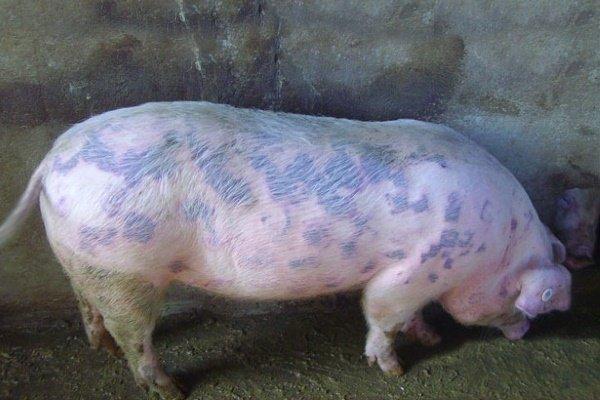
- discoloration of the skin on the abdomen and under the breast to red or dark purple;
- constipation or bloody diarrhea;
- impaired motility;
- punctate hemorrhages in the lower abdomen, neck, ears.
Sick individuals huddle in the far corner of the barn, constantly lying on their side. Infected pigs' tail is unwound. If African plague infects pregnant sows, they will have a spontaneous abortion.
Some individuals can survive, but they remain carriers of the virus for a long time, therefore they threaten other animals. In this case, immunity is not developed: pigs that have undergone African plague will fall ill with it again.
Atypical form of ASF
Symptoms vary from individual to individual, due to a mutation in the virus. ASF can also occur in an atypical form, in which pigs suffer from profuse diarrhea, variable fever. Bruises are noticeable on the ears, tail, limbs, patch, and on the body. Animals weaken, lose weight, do not gain weight. The skin is covered with wrinkles, strongly compacted. Signs of conjunctivitis, gastroenteritis are clearly manifested. The infection is fatal, usually on the third day after the first symptoms appear. The mortality rate is 30-65%.
The atypical form of ASF is most often diagnosed in suckling piglets that were weaned early from the sow, in young animals that had contact with virus carriers or were infected with mildly virulent strains of the virus. At the same time, some of the piglets recover without treatment. The rest die or are life-long virus carriers. The disease can be complicated by secondary infections.
Diagnostic methods
It is possible to identify African swine fever by the characteristic symptoms of this infectious process, which manifest themselves externally.
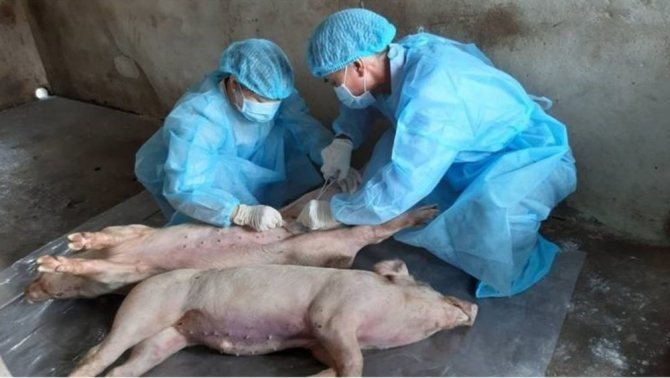
The diagnosis is made in a comprehensive manner, based on laboratory data, as well as the results of postmortem examination. In the diagnostic center, samples of the lungs, spleen, lymph nodes, blood and its serum are examined.
To identify the pathogen, PCR, hemadsorption, fluorescent antibodies are used.


Pathological changes and diagnostics
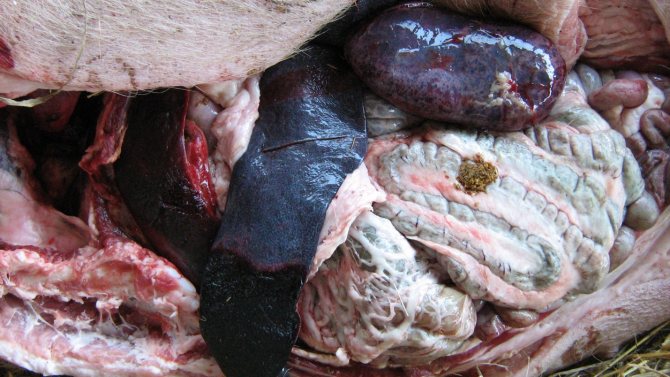
If ASF is suspected, a random examination of the corpses is mandatory. Pathological changes and histological signs of African plague are as follows:
- The skin on the abdomen, under the breast, behind the ears, on the inner thighs is red or dark purple.
- The mouth, nose, trachea are filled with pink foam.
- The lymph nodes are greatly enlarged, the pattern on the cut is marble, multiple hemorrhages are visible, sometimes the node resembles a continuous hematoma with black clots.
- The spleen is large, with multiple hemorrhages, areas of necrosis.
- The kidneys are also enlarged with hemorrhages in the parenchyma and on the walls of the dilated renal pelvis.
- The lungs are full of blood, a shade of gray with red, there are multiple bruises in the parenchyma, there are symptoms of pneumonia, fibrous cords are found between the alveoli (signs of fibrotic inflammation).
- The liver is full of blood, significantly enlarged, the color is gray with a clay tinge, uneven.
- The mucous membrane of the intestine and stomach swells, they reveal hemorrhages.
- In chronic pathology, bronchitis is found on both sides, an increase in lymph nodules in the lungs.
- In the asymptomatic form, only changes in the lymph nodes are visible: they have a marble pattern.
African swine fever has symptoms similar to common swine fever. To distinguish between 2 diseases, laboratory diagnostics are required. The method of PCR, fluorescent antibodies, hemadsorption is used. Also, biological tests are carried out, the material of sick animals is injected into pigs vaccinated against common plague. If they show pathology, the diagnosis is confirmed.
Ways to solve the problem
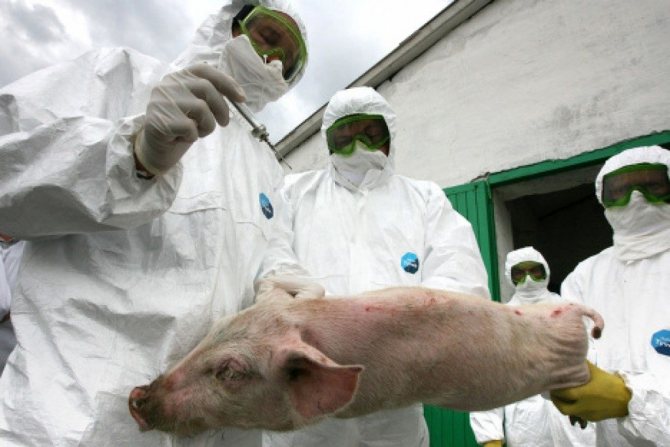
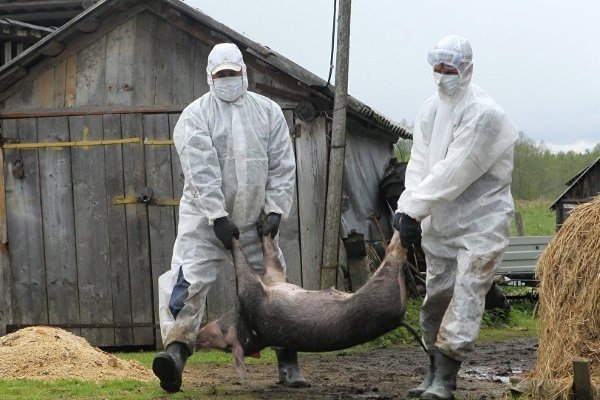
The African swine fever virus is spreading at a high rate. It is prohibited to carry out medical measures, the only way out is the complete destruction of infected individuals. There is currently no adequate treatment for swine with African plague.
With the spread of an infectious process, it is first of all necessary to determine the boundaries of the focus of the spread of infection and declare a quarantine regime.
All individuals infected with the African plague must be destroyed by a bloodless method. The area where the slaughter of animals affected by the virus is planned must be isolated.
The bodies of dead and destroyed pigs, as well as their waste products, the remains of feed and equipment are burned. The same must be done with feeders, partitions, dilapidated premises. The resulting ash must be mixed with lime and buried in the ground. The depth must be at least 1 m.
All rooms in which the animals have stayed must be treated with special solutions. This should be done 3 times, with an interval of 3-5 days. For disinfection, use a solution of bleach, sodium hypochlorite.
All pig farms located within 25 km of the infection zone are slaughtered, even if the pigs are healthy.
Quarantine after the detection of African swine fever lasts at least 40 days. During this period, it is forbidden to take out of the zone any products obtained from animals (even if they are not obtained from pigs). For six months after the outbreak of infection, the export and sale of any agricultural plant products is prohibited.
Activities related to the elimination of the African swine fever epidemic should be provided by veterinary services.
Elimination of foci and prevention of spread
First of all, you must take into account the entire danger of infection. Another important factor is the lack of effective treatment. Considering these aspects, the way out of the situation becomes obvious.
When signs of African swine fever show up in pigs, the only way out is to destroy the livestock. Of course, this way of dealing with the problem that has arisen causes significant damage to the country's economy and harms the development of agriculture. Moreover, both sick animals and uninfected individuals kept on the same farm are destroyed. However, today this is the only possible way out.
The measures taken to combat the infection are under the control of the veterinary service.All preventive measures are carried out in accordance with the regulations of the Rosselkhoznadzor.
Prophylaxis
Despite the fact that the infection is incurable and threatens the life of the pig, the situation is not hopeless. You need to know about preventive measures that will prevent infection of livestock and help avoid mass death of pets.
The main thing is to monitor the availability of veterinary certificates when purchasing both adult males or females, and young piglets.
When running a farm and keeping pigs, it is recommended to observe a number of conditions:
- Ensure the raising of livestock in accordance with the rules established by the veterinary service.
- Do not pollute the environment with animal waste.
- Timely implement quarantine measures.
- Isolate diseased animals immediately.
- Do not graze pigs in areas close to the infected zone.


Quarantine
One of the necessary measures to stop the spread of the fatal disease. Quarantine is carried out after identifying the source of the infection that threatens the life of pigs.
Animals that are at risk of disease, as well as infected individuals, are destroyed using a bloodless method. Equipment, feed, partitions, dilapidated old premises, fences, feeders are also subject to liquidation. As a rule, everything is burned. If this is not possible, then the corpses of pigs, inventory, wooden floors, etc. are buried in the ground to a depth of at least 2 meters.
In an area with a coverage of 5 km, all pets (both piglets and adults) are registered.
Prohibited:
- take pigs out of the quarantine zone;
- sell livestock and poultry of any kind;
- trade in meat, milk, etc.
Prophylaxis
There is currently no vaccine that can protect livestock against African swine fever. Work in this direction is underway, but they are of an experimental nature. Scientists note that in the next 10 years, a vaccine against this viral disease will not be invented.


There are preventive measures that can minimize the risk of an African plague outbreak. These include:
- timely inspections of the livestock by a veterinarian and vaccination against classical plague;
- thermal processing of feed, their purchase only from reliable manufacturers;
- proper organization of the processes of disinfection of manure and wastewater, disposal of animal corpses;
- organization of fencing for livestock farms;
- a ban on feeding animals with food waste and confiscated items;
- keeping pigs in fenced areas and excluding the possibility of their contact with the livestock of other owners, as well as with domestic animals, birds, insects;
- isolated equipment of the slaughter area from livestock complexes;
- clearing the territory of the farm and adjacent areas from garbage and manure;
- restriction of free range of pigs;
- non-admission to the territory of the pig farm of unprocessed tools of labor, as well as vehicles that have not undergone special processing;
- carrying out periodic disinfection of the pig farm territories, warehouses with feed, treatment from parasites;
- purchase of pigs only in agreement with the State Veterinary Service.
If you suspect an outbreak of African plague among the pig population, you must immediately report it to the appropriate authorities - the sanitary and epidemiological station.
Preventive measures do not provide complete protection against the spread of the virus, but they significantly reduce this risk.
How does the infection take place?
There are several options for the spread of the disease and ways to enter the pork body:
- during contact with the carrier;
- transmission path;
- using a mechanical carrier.
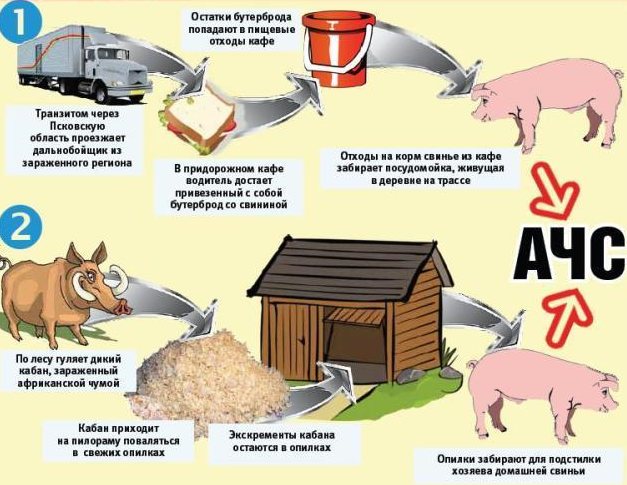

When infected with healthy animals, the pathogen passes through the mucous membranes, can penetrate through skin lesions, is in the waste products of animals, and be in common containers for feed or water.
Insects transmit disease in a transmissible manner, and this applies not only to ASF. The bite of a tick, horsefly, zoophilous fly or flea can be the cause of the disease. But the greatest danger is the attack of ticks.
Mechanical carriers include small rodents, mice, and rats. The disease can be spread through cats, dogs, poultry, geese or chickens. Wild birds pose a clear threat to livestock, as an entire pig farm can become infected from one individual. It is impossible to exclude a person from a number of dangerous distributors. He may well carry a hostile genome if he visited a place that is unfavorable for the disease.
Notification of a detected virus and responsibility for withholding information
If an outbreak of African swine fever is detected among the livestock, it is necessary to immediately report it to the Sanitary and Epidemiological Station.
For concealment of information about a sudden death or simultaneous mass diseases of animals, liability is provided in the form of an administrative fine. For citizens, its size is 3,000-4,000 rubles, for officials - from 30,000 to 40,000 rubles, for legal entities - from 90,000 to 100,000 rubles.
Administrative punishment is also provided for violation of quarantine rules and prescribed recommendations regarding the handling of potentially hazardous waste (animal corpses, feed, premises).
Watch a popular science film about the origin, spread and danger of this pig disease, which has become a real scourge of 21st century farming:
African swine fever is a dangerous disease of domestic animals that causes massive deaths in livestock. A person can act as a carrier of the virus of this disease, but it does not affect his body in any way. The African plague requires radical measures: bloodless slaughter of all infected and healthy individuals and the organization of a quarantine regime.
0
Is there a cure
The disease is life-threatening to animals. The signs of African swine fever are not clearly manifested, therefore, it is difficult to make a diagnosis. In addition, it happens that an animal becomes infected with a lightning-fast form, which proceeds in the shortest possible time and always ends in death.
The African plague has not yet been fully understood. Accordingly, the appropriate way to get rid of this scourge, which harms the economy and the development of animal husbandry, has not been identified. No effective drugs have been found for the treatment of a fatal disease.
Even in case of a favorable outcome, recovered pets remain a source of threat to the health of fellows. A pig that gets rid of the disease remains a virus carrier forever.


CSF symptoms
Symptoms directly depend on the type of disease.


Intestinal form
Many piglets become infected with intestinal disease, due to which the animal's digestive processes are disrupted. The first signs of distemper do not appear immediately, but several days after infection. Therefore, farmers are not always able to immediately determine what the mumps is sick with.
At first, animals begin to develop constipation. Problems with bowel movements continue for several weeks. Between constipation, gilts develop diarrhea. Then, other signs of the virus gradually appear, which include fever and enterocolitis. A sick piglet stops eating, which leads to weight loss. If left untreated, the infected animal will die.
Pulmonary form
This type of distemper is considered one of the most dangerous, as it often leads to the death of a sick animal. At first, the distemper does not manifest itself in any way, and therefore it is difficult to determine that the pig is sick with something.However, over time, the first symptoms begin to appear, which should be paid attention to.
See also
Instructions for the use of Tetramisole 10 for pigs, contraindications and analoguesRead

The initial signs of pneumonic plague include the following:
- cough that gradually gets worse;
- pneumonia, accompanied by an increase in body temperature;
- discharge from the nose of mucous fluid;
- shortness of breath with snoring.
Also, animals that are sick with the plague often begin to sit on their hind legs. They do this to relieve pain in the lungs.
Chronic form
Sometimes sick animals do not die from the disease, but remain alive. In this case, the plague becomes chronic. Symptoms appear from time to time. Piglets periodically suffer from fever, pneumonia and severe coughing. Sometimes sick pigs have symptoms characteristic of an atypical virus. These features include the following:
- weight loss, due to which the animal practically does not have a fat layer;
- fever due to increased body temperature;
- loss of appetite;
- conjunctivitis;
- difficulty breathing.


Acute form
According to many farmers, the acute form is considered the most dangerous, since due to the rapid development of the disease, animals die within 5-10 days. It is not easy to determine the disease in a timely manner due to the fact that it does not manifest itself immediately. In the early days, the disease does not manifest itself in any way. However, then the following symptoms appear abruptly:
- fever and fever;
- diarrhea, during which feces come out with red streaks of blood;
- nasal congestion;
- redness of the eyes;
- the appearance of yellow pustules in the ears and abdomen;
- minor subcutaneous hemorrhages.


Lightning shape
People who are raising small pigs should be wary of the lightning type of the virus. This disease most often occurs in piglets that are less than six months old. The lightning-fast form is dangerous for the weakened organism of animals. They can die within a few days after symptoms appear.
Common signs of fulminant plague include:
- Vomiting. This is the main symptom that manifests itself much earlier than others.
- Spots under the skin. They appear as a result of subcutaneous bleeding due to vascular damage.
- Temperature increase. Due to inflammatory processes in the body, the body temperature rises greatly.


Subacid form
Some animals have a conditional resistance to this virus and therefore rarely become infected with other types of the virus. Most often, these pigs suffer from the subacid type of the disease, which is characterized by symptoms of the pulmonary and intestinal forms.
The duration of the illness is two and a half weeks. After this, the subacid plague can take on a chronic form. If this does not happen, the animal will die due to the appearance of complications. The most common complication is salmonellosis, which impairs bowel function. Animals develop diarrhea with a discharge of pus and blood. Piglets also stop eating, which leads to rapid weight loss.
See also
Rules for breeding piglets at home for beginners, profitabilityRead