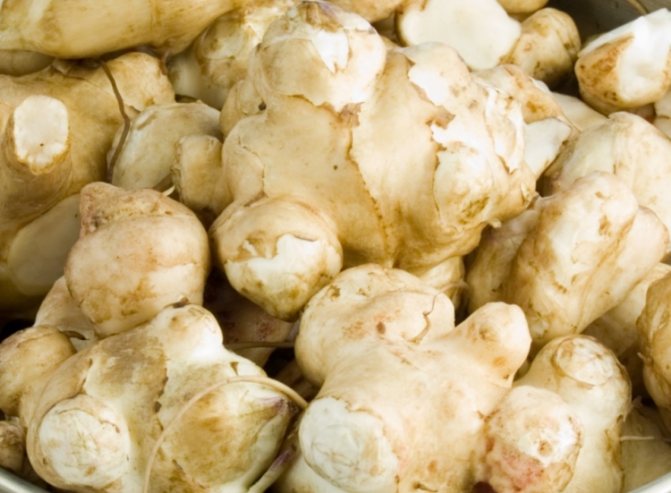
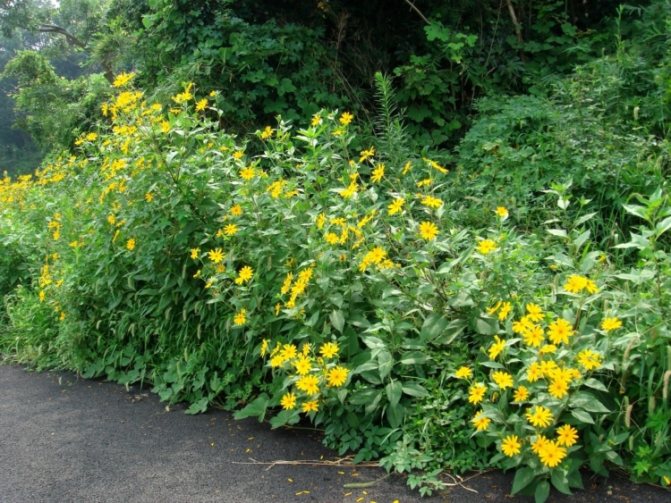
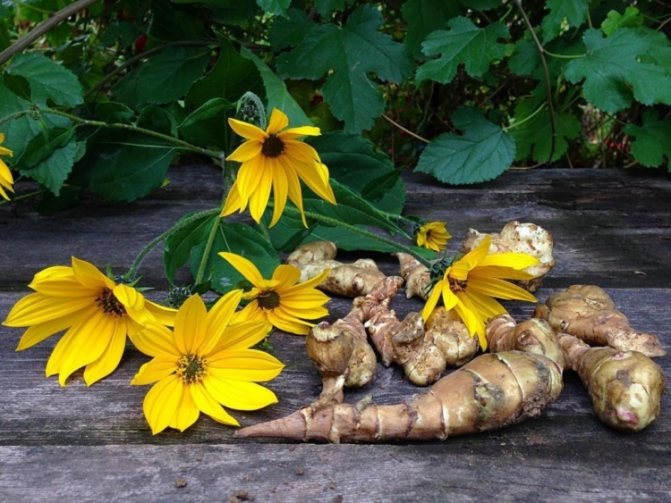
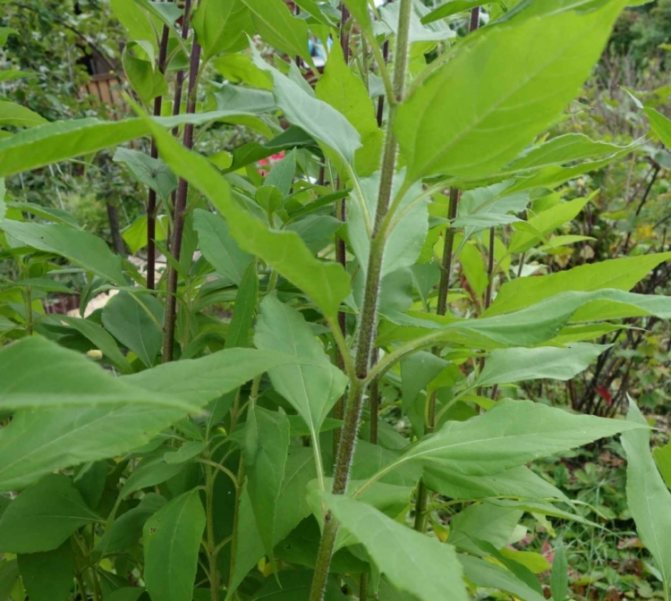
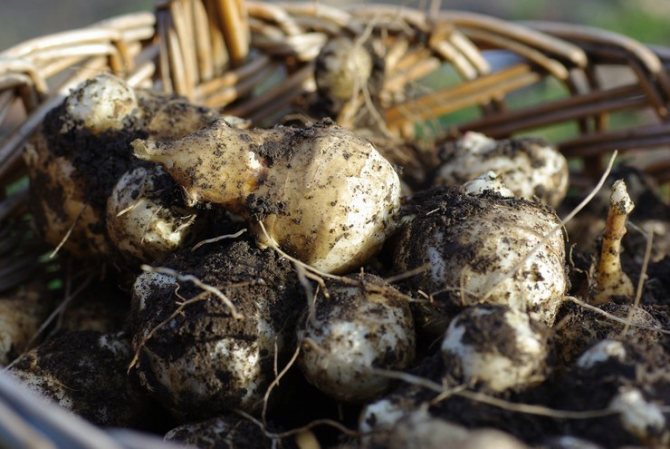
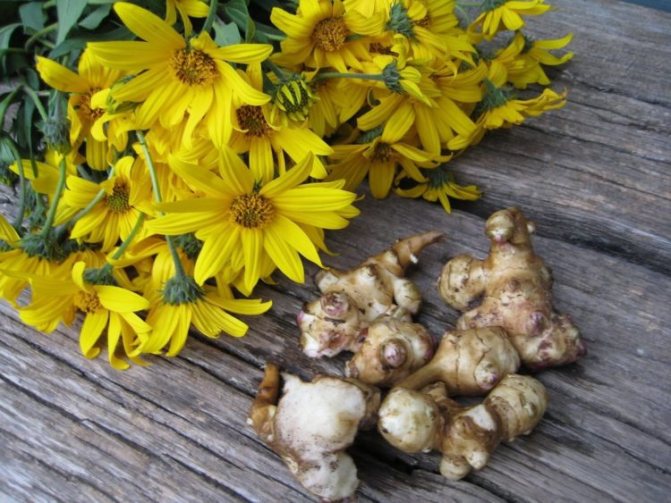
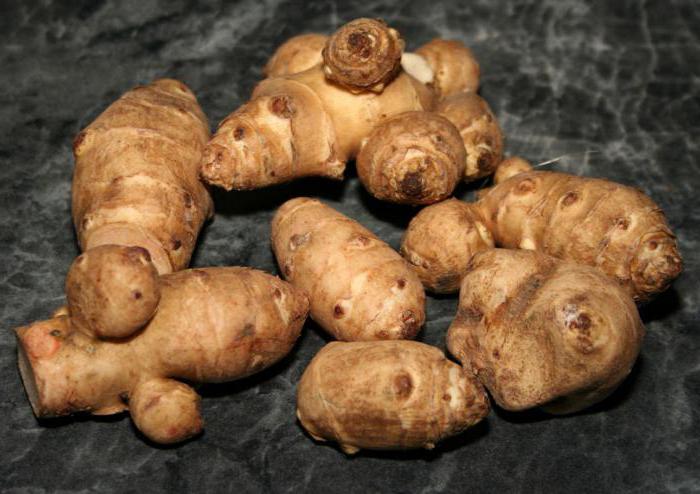
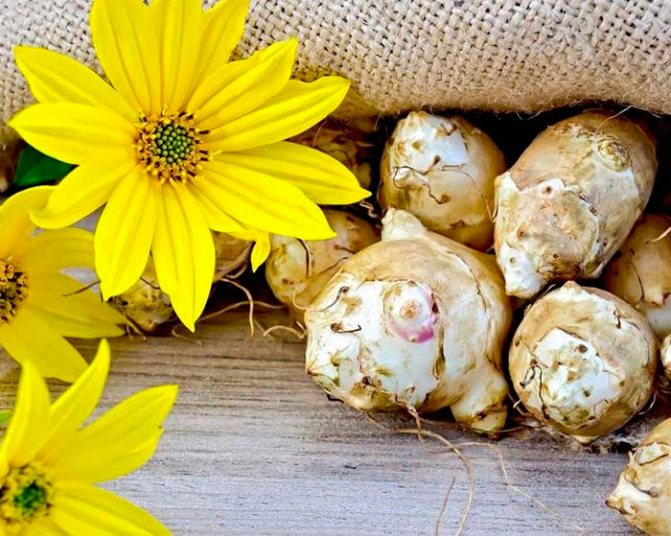
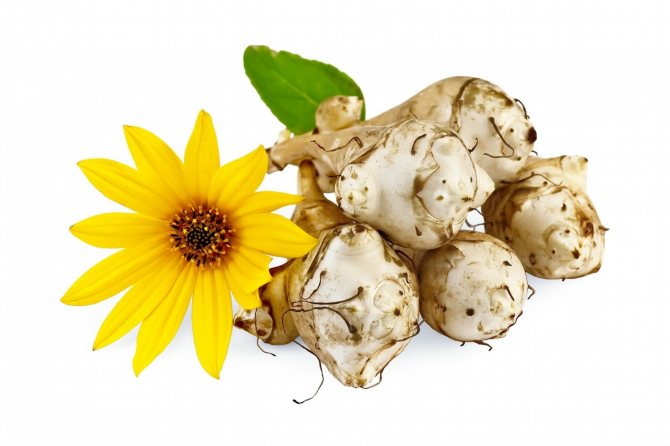
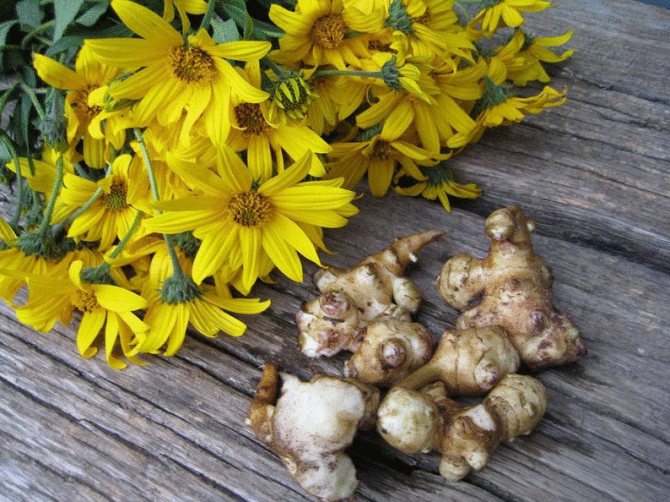
This culture is a herbaceous plant, belongs to the genus Sunflowers. He is a prominent representative of the Astro family. This plant was first discovered in the territory of today's Brazil. Jerusalem artichoke came to Europe through countries such as England and France, back in the 16th century. Jerusalem artichoke began to be used as a food element in the middle of the 19th century. In its natural habitat, this plant is found in the northern part of the United States. As for the targeted cultivation of Jerusalem artichoke, it is grown in many countries. These include Australia, Switzerland, Japan. It should be noted that in many countries this crop is perceived as a weed. The fact is that Jerusalem artichoke easily adapts even to the most unfavorable conditions, tolerates low temperatures well, is not too whimsical to grow, and also has high productivity rates.
What kind of plant is this?
Definition
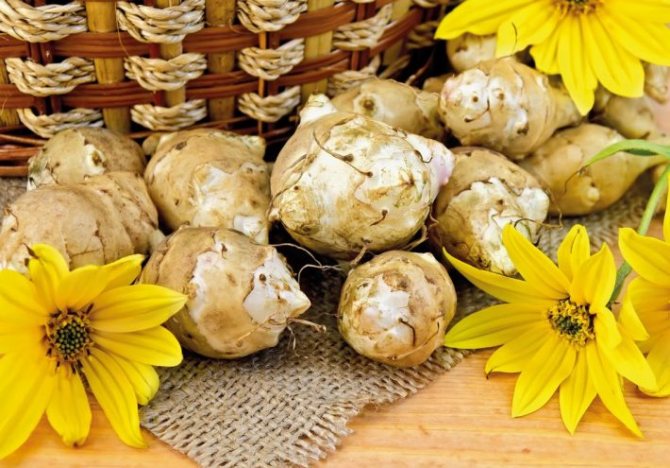
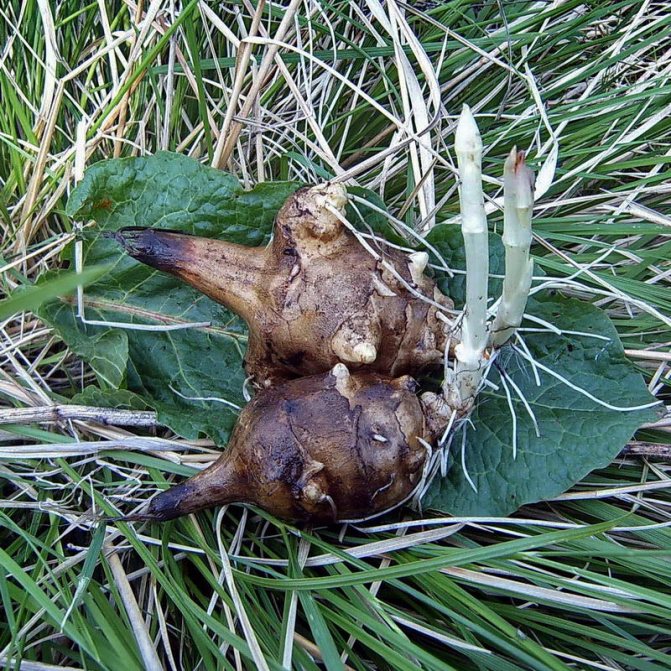
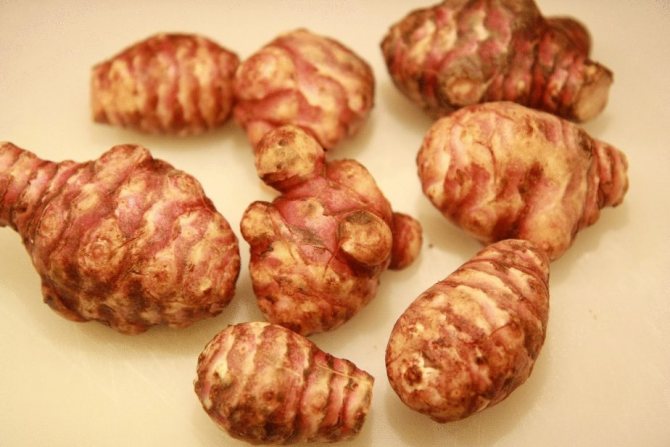
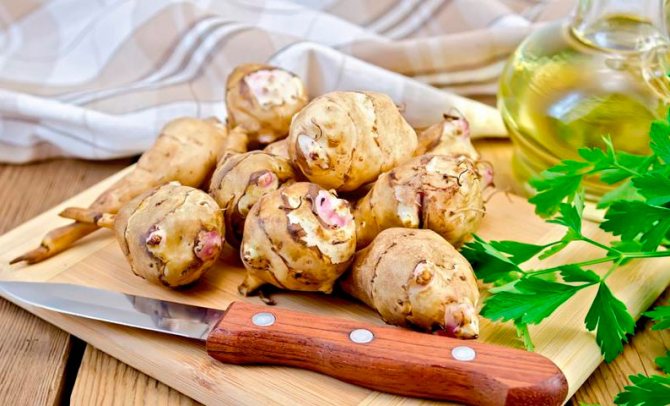
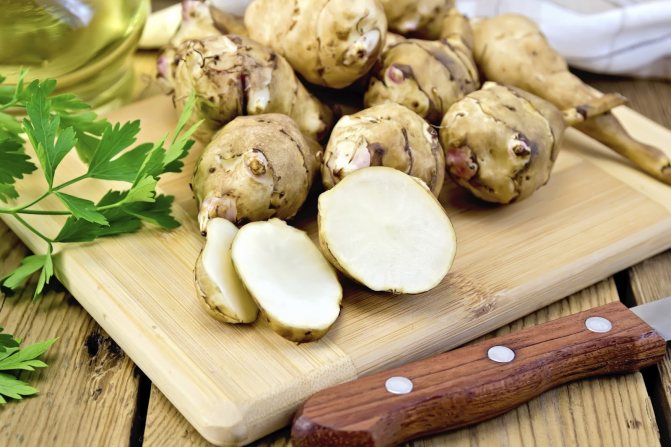
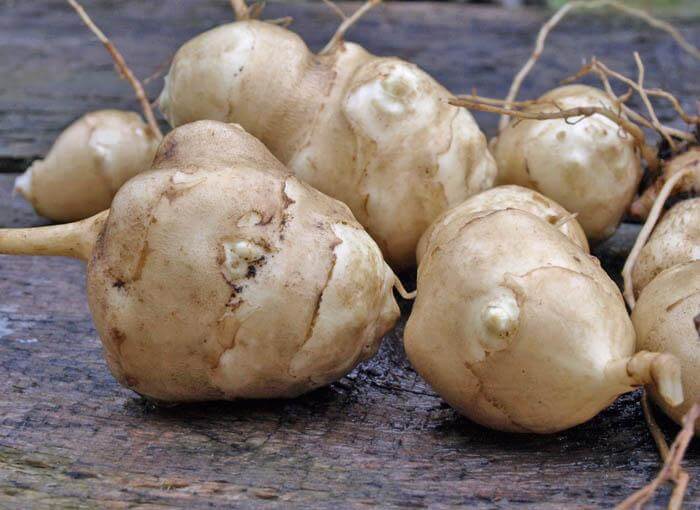
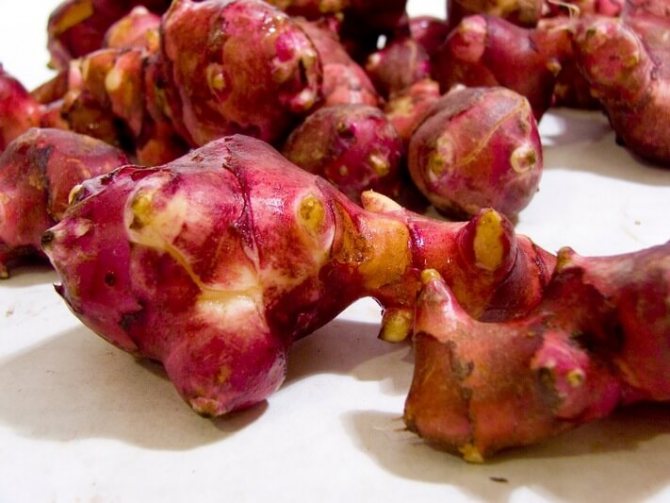
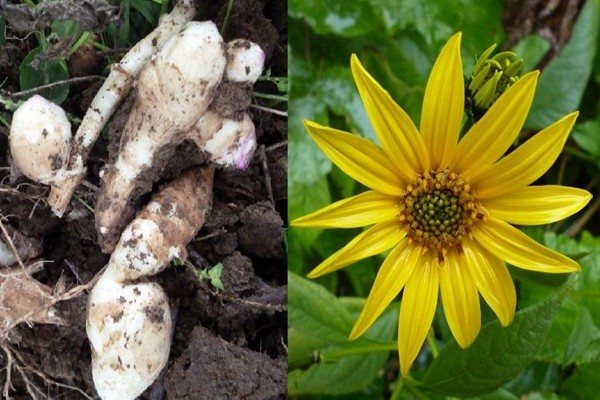
Jerusalem artichoke is a herbaceous plant of the genus sunflower, the tubers of which have an elongated pear-shaped shape with tubercles.
What else is it called and why?
According to one version, this plant was popular among all the peoples of North America, and in the Iroquois tribes who lived near the Great Lakes, it was called Jerusalem artichoke, which translated as solar root.
Another most common name is the earthen pear - the vegetable received due to the similarity of its tubers with this fruit.
But it also has another name - Jerusalem artichoke. Jerusalem artichoke has nothing to do with it, just in Italian sunflower - girasole, and this word has been transformed into a more understandable - Jerusalem.
At one time, potatoes were called an earthen apple.
What an earthen pear looks like: description and photo
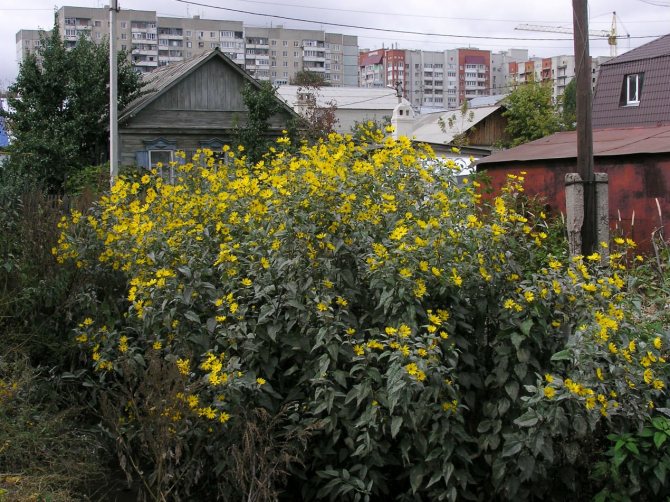
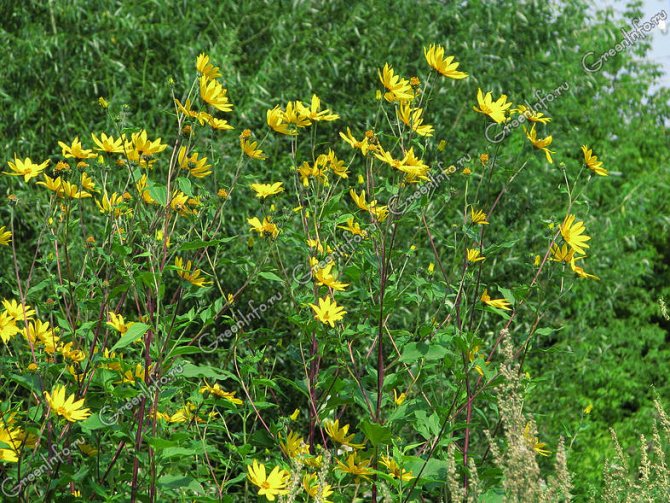
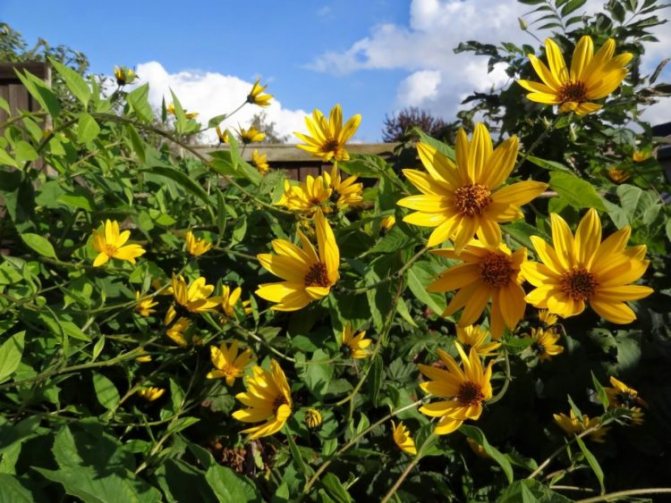
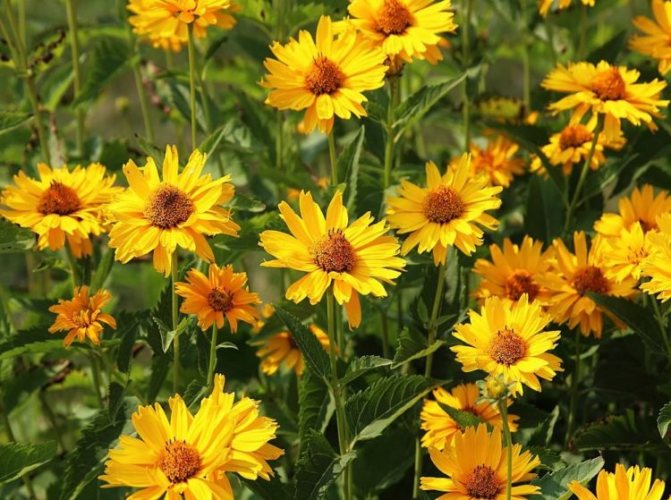
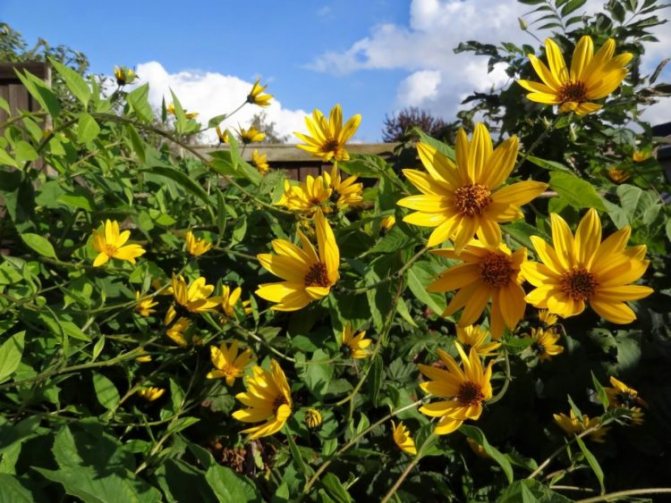
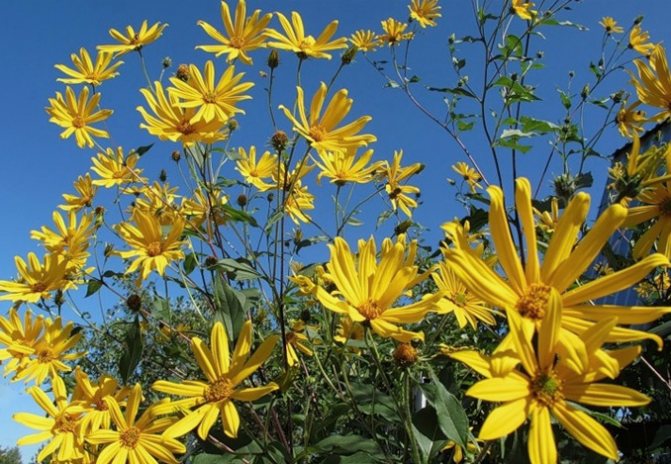
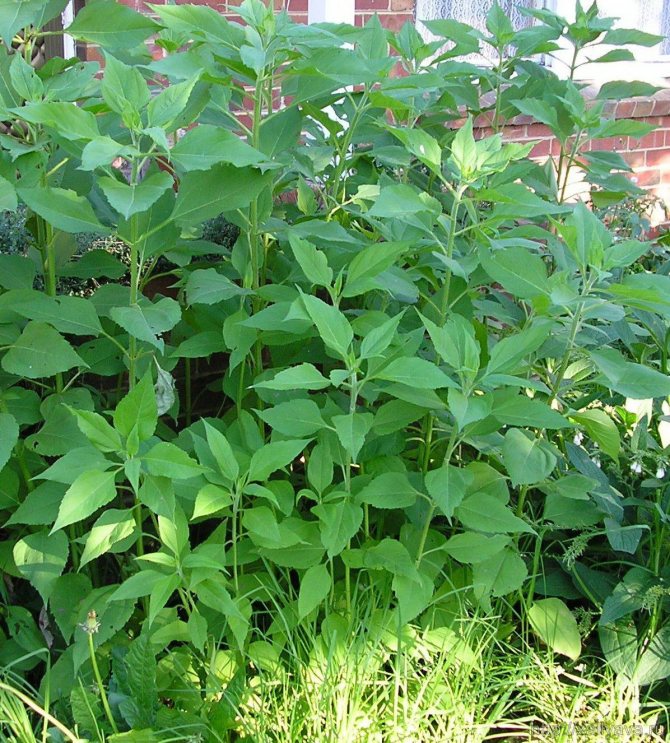
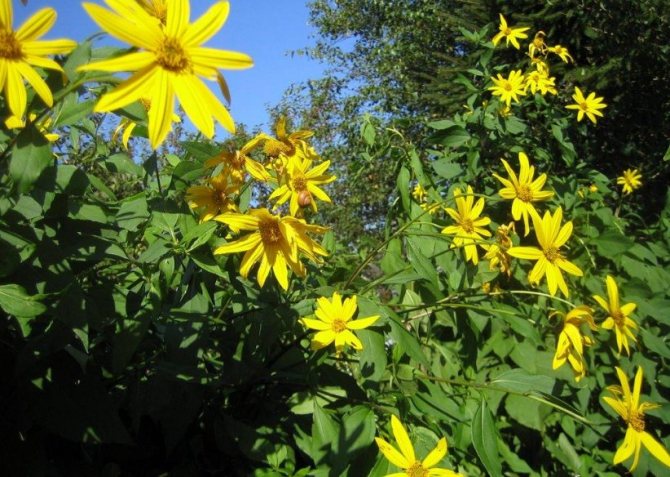
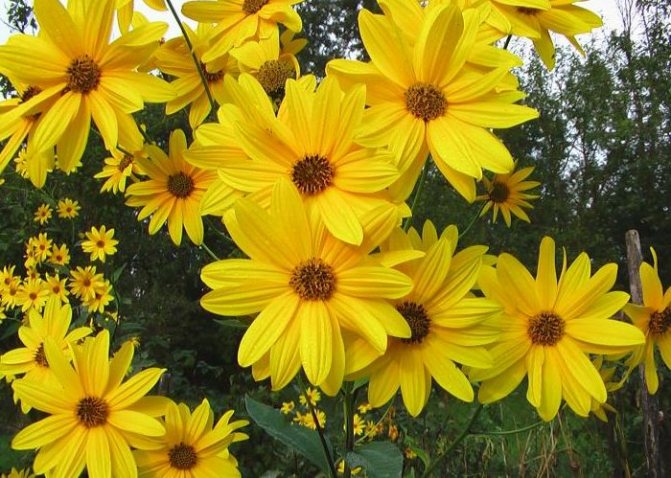
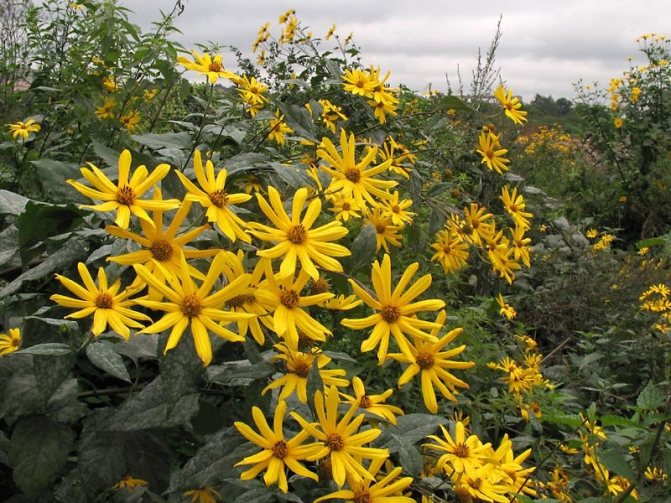
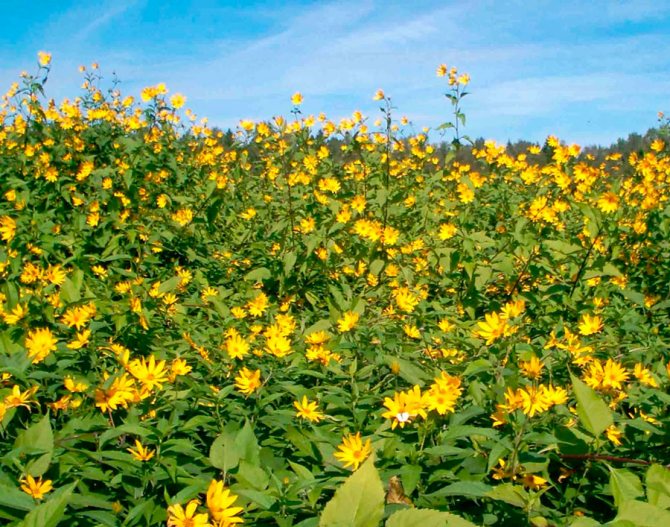
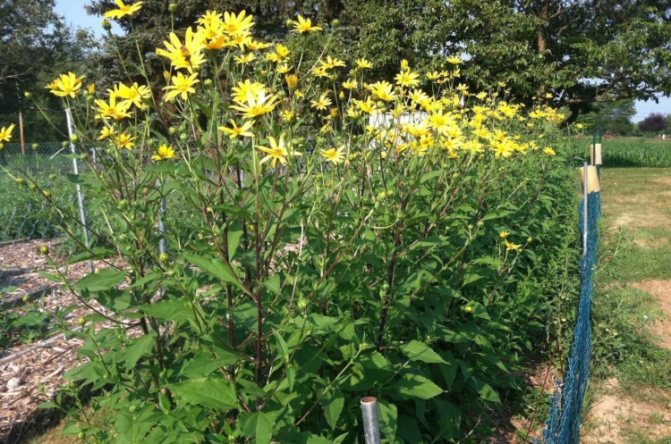
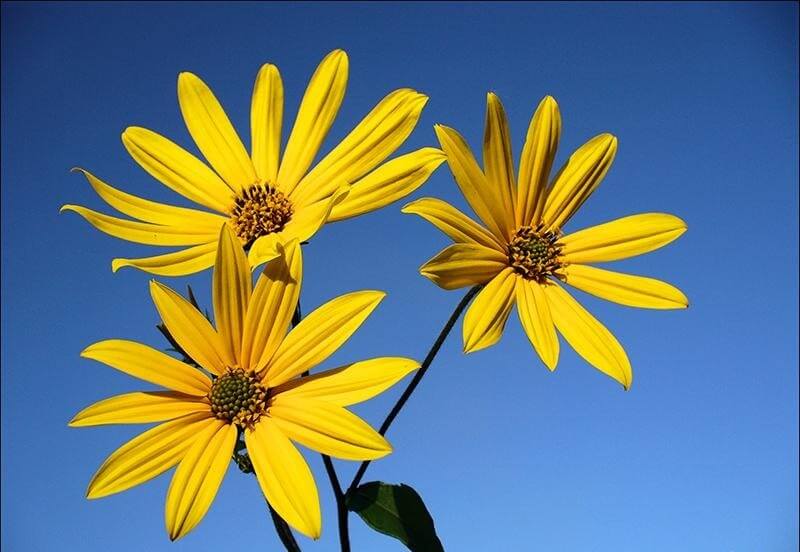
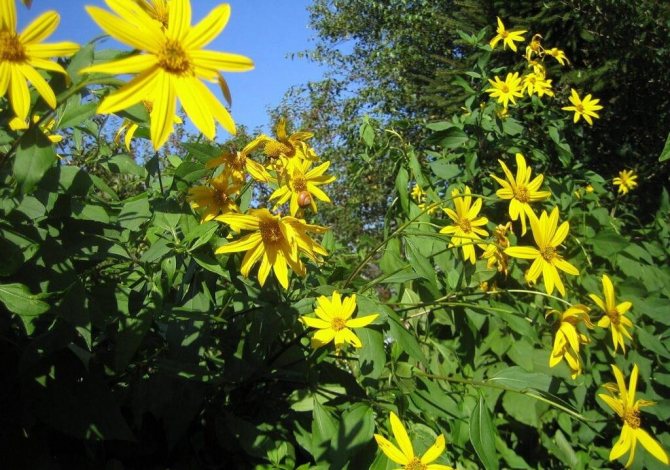
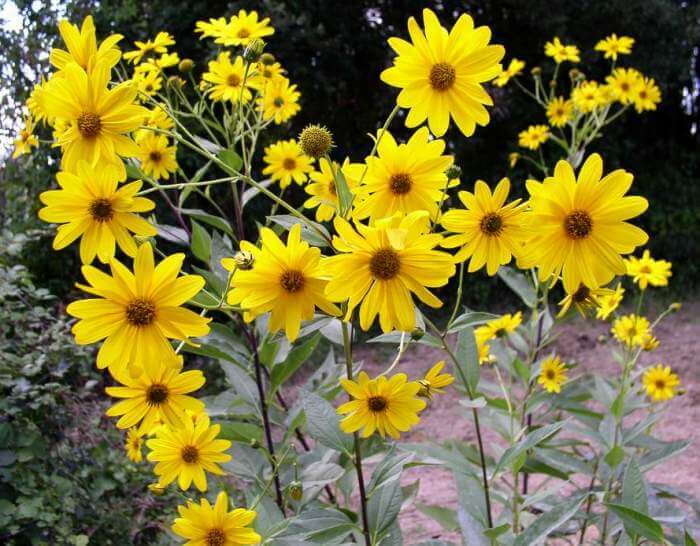
An adult Jerusalem artichoke plant looks very impressive., because the stem can reach a height of 2 to 4 m, while it branches densely and has good strength. An earthen pear is believed to withstand gusts of wind without breaking - even better than corn. The top of the stem of this plant is crowned with large yellow flowers.
Next, you can see how the plant itself looks in the photo, as well as its flowers, fruits, leaves and tubers.
Which family does it belong to?
Tuberous sunflower (Latin Heliantus tuberosus) is a perennial tuberous herb of the Compositae family.
Structure
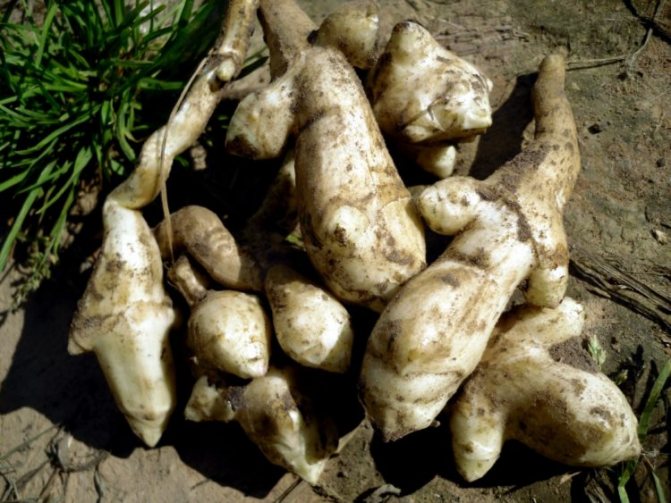
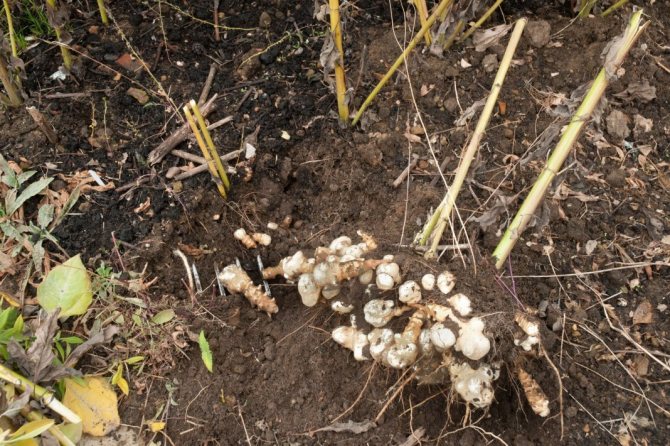
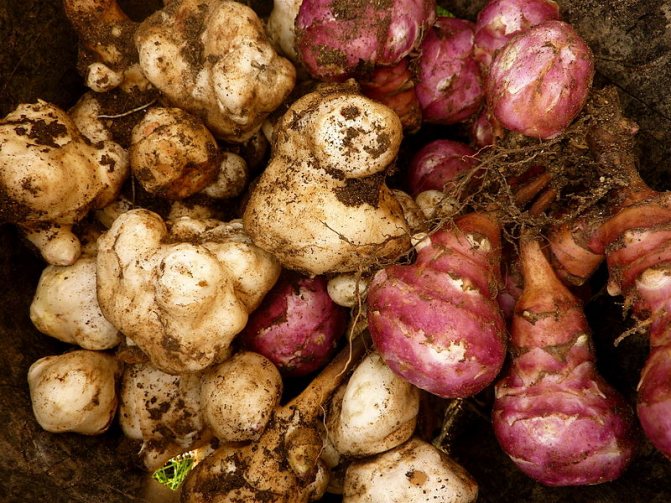
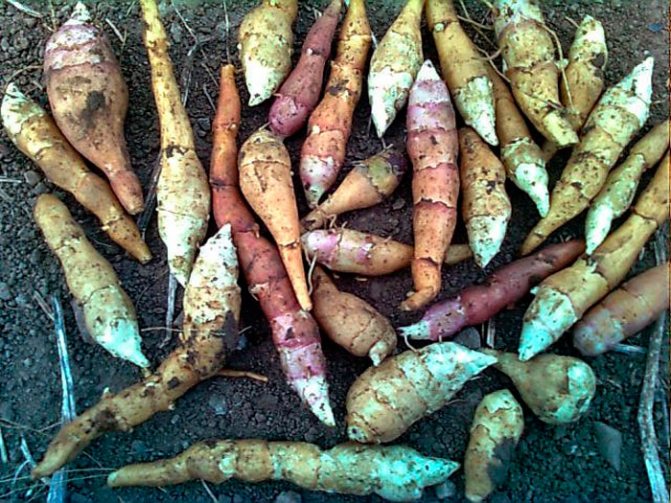
- The root system is fibrous, on short underground horizontal shoots (stolons) tubers are formed that have a different color - white, yellow, red, purple - depending on the variety.
- On an erect stem, the lower leaves are heart-ovate.
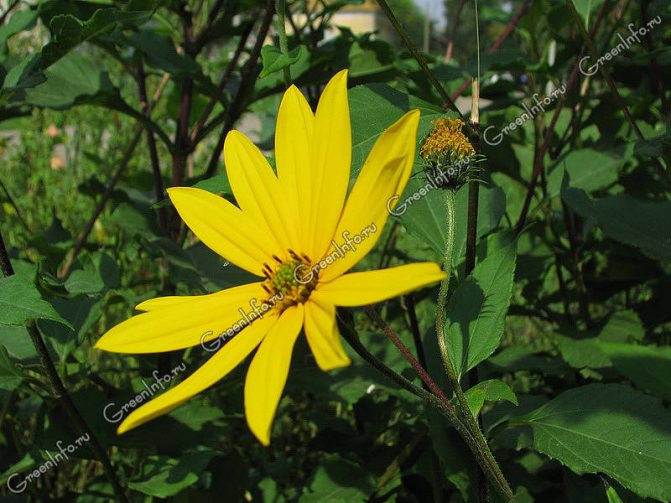
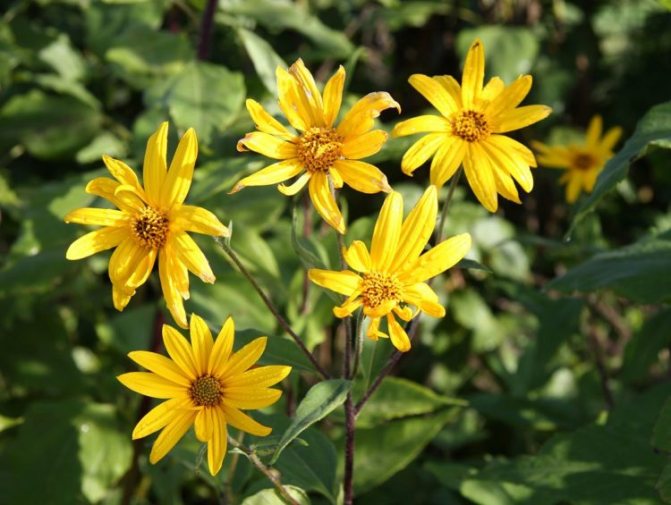
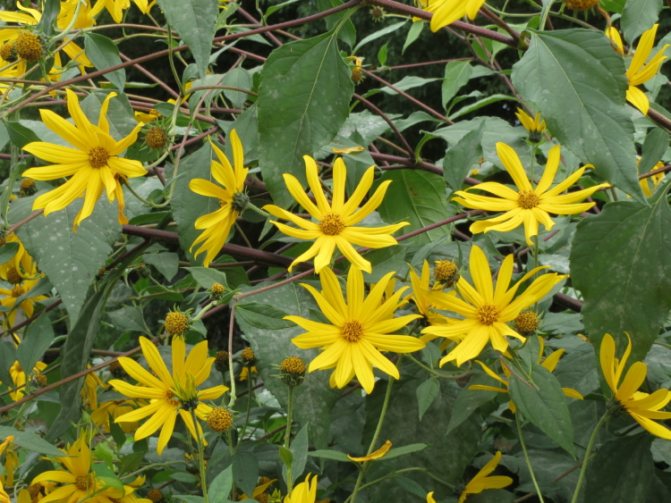
- During flowering, yellow complex inflorescences are formed - baskets with outer reed and inner tubular flowers.
- The fruit of Jerusalem artichoke is achene.
Biological features
Jerusalem artichoke can grow in one place for over 30 years... This plant tolerates low temperatures well (greens can withstand frosts down to -7 ° C) and does not degenerate during drought. The earthen pear prefers fertilized loams, but yields good yields on other neutral soils.This short-day plant thrives in an open, well-lit area, but can grow in the shade as well.
How and where does it grow?
Due to its unpretentiousness to soil and climate, Jerusalem artichoke has spread like a weed in many countries. It is cultivated in limited areas in:
- USA;
- Canada;
- Australia;
- Japan;
- England;
- Germany;
- Kazakhstan;
- Russia.
Basically, the earthen pear is a fodder plant, as well as technical raw materials for processing into alcohol and fructose.
In Switzerland, Jerusalem artichoke is considered a plant that threatens biodiversity.
How is it different from sweet potato?

Jerusalem artichoke and sweet potato are similar in only one thing - their tubers are eaten.... Otherwise, these 2 herbaceous plants are different.
Sweet potato is an annual plant of the bindweed family, therefore it looks like a vine with creeping stems up to 20 cm high.
The sweet potato blooms with pink or white flowers, and its fruits are four-seeded capsules. The tubers have a smooth surface and are distinguished by their high weight, shape and taste from those of an earthen pear.
About pests and diseases of Jerusalem artichoke


This culture has a very good resistance to various diseases. However, with improper care and conditions, Jerusalem artichoke can be affected by powdery mildew, white rot, and also Alternaria. Let's consider each problem in more detail.
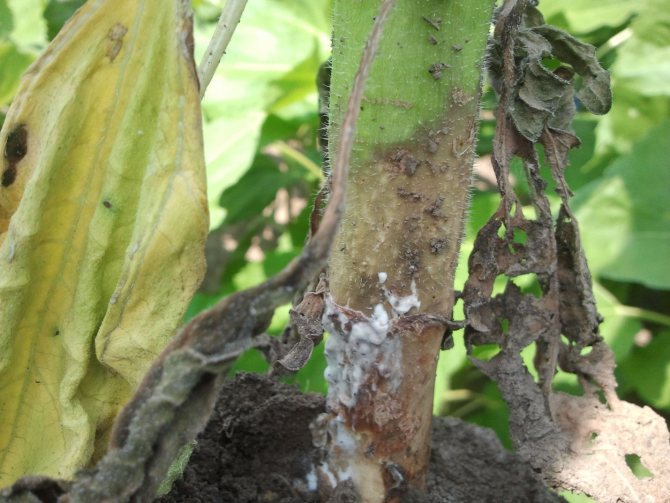
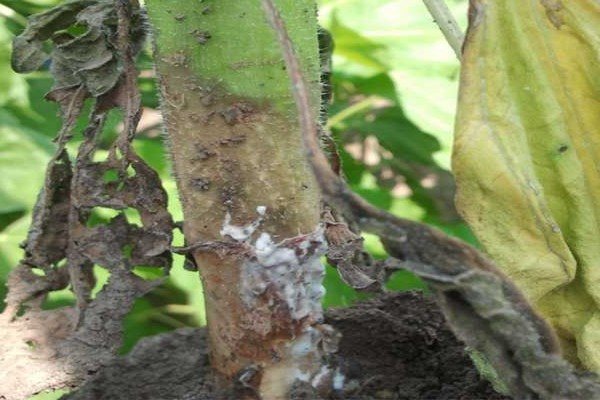
White rot.
This disease is also sometimes called sclerotinosis. The main symptom of this problem is the appearance of plaque on the stems of the plant, which is very similar to mold. The inside begins to become covered with black growths. This culture, as a rule, is affected through the root system in the ground. Sclerotinosis occurs when the ambient humidity level is too high. Such a problem may appear if the temperature changes are too sharp. Treatment is practically useless. Those plants that have been affected must be removed from the site and burned away from the garden.
Alternaria.
This disease occurs quite often in Jerusalem artichoke plantings. Because of it, the part of the plant that is above ground level suffers. It can be identified by its characteristic dark or light brownish patches on the foliage. Such spots have a pale yellowish frame. After a while, the spots become larger, and then the foliage begins to dry out. The same goes for the petioles. To combat this ailment, it is recommended to use drugs - fungicides. Plants are processed when the street is at least +18 degrees. As a rule, if Alternaria is still at the initial stage of development, one spraying is enough. But it is better to carry out the treatment again, after ten to thirteen days.
Powdery mildew.
Jerusalem artichoke is affected by this disease during the second half of the growing season. A whitish bloom-like coating appears on the surface of the leaves, which has a loose texture. As the disease progresses, the color of the plaque changes. It takes on a brown or prodigal pinkish color. At the same time, the leaf plates become brittle. This disease can occur due to too hot weather with not smooth temperature fluctuations. In addition to this reason, powdery mildew can occur due to an excess of nitrogen, as well as due to an incorrect environment humidity regime. This problem can be dealt with with fungicides. Experienced vegetable growers most often use Topaz, Topsin, Bayleton, Quadris and other similar preparations.
Pests
As for harmful insects that can harm Jerusalem artichoke, most often such a culture is affected by slugs, bears and other larvae. To prevent slugs from pestering your Jerusalem artichoke plantings, it is recommended to put a granular agent on top of the soil, which is aimed at fighting slugs.
If you saw a scoop, May beetles, a bear on the future garden bed, then before planting the plants in the ground, you need to dig it up and add special means. For this purpose, you can use Diazonon or Foxim.


History of origin and country of origin
It is believed that in Europe the earthen pear appeared thanks to the French explorer Samuel de Champlainwho studied the northeast coast of America in the 17th century. While visiting the village of local Indians, Samuel tasted these wonderful tubers and, appreciating their taste, brought them home. This product quickly spread throughout Europe, but was supplanted by potatoes in the 18th century.
In Russia, Jerusalem artichoke became known as a remedy in the 17th century, and in cooking it began to be used from the end of the 18th century.
Photo
The photo shows what Jerusalem artichoke looks like.
Chemical composition
100 g of the edible part of an earthen pear has a caloric value of 61 kcal and contains:
| Nutrients | Weight (g) | Vitamins | Weight (mg) | Macronutrients | Weight (mg) |
| Protein | 2,1 | AT 4 | 30 | Potassium | 200 |
| Fats | 0,1 | AT 5 | 0,4 | Calcium | 20 |
| Carbohydrates | 12,8 | FROM | 6 | Silicon | 8 |
| Org. acid | 0,1 | E | 0,2 | Magnesium | 12 |
| Alimentary fiber | 4,5 | H | 0,35 | Sodium | 3 |
| Water | 79 | RR.NE | 1,6 | Phosphorus | 78 |
| Ash | 1,4 | Niacin | 1,3 | Iron | 0,4 |
The chemical composition of the vegetable is discussed in this publication.
Useful Jerusalem artichoke recipes
Tea for weight loss and diabetes
Jerusalem artichoke leaves.
Pour 1 tbsp. a spoon with a slide of dried leaves 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let it brew (preferably in a thermos) for 2-3 hours. Drink 150 ml 20 minutes before meals.
Vitamin salad
Jerusalem artichoke, carrot, daikon. dill, vegetable oil, salt.
Grate in equal proportions Jerusalem artichoke with skin, carrots, daikon or radish. Season with salt, add vegetable oil, sprinkle with dill herbs.
Benefit and harm


Jerusalem artichoke is useful due to the content of vitamins and macronutrients not only in tubers, but also in the entire aerial part of the plant. Earthen pear helps:
- in strengthening the immune system;
- in the normalization of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract;
- fight overweight;
- get rid of accumulated toxins;
- recover faster from overwork;
- when used in cosmetology.
This product can only cause harm if abused, since individual intolerance is extremely rare.
PORTRAIT
It is a perennial herb with straight, strong pubescent stems, in favorable conditions
RARE PLANT SEEDS FOR YOUR GARDEN - FREE SHIPPING. PRICES ARE VERY LOW. THERE ARE REVIEWS


reaching a height of 3 m or more. Leaves are opposite, broadly lanceolate, pubescent, 20-25 cm long. Blooms from August to October. Inflorescences are single yellow baskets up to 8 cm in diameter, fruits are achenes (they do not ripen in the Middle Lane).
Jerusalem artichoke treatment
- Jerusalem artichoke leaves contain inulin - a plant analogue of insulin, so the plant in its raw form is useful for patients with diabetes mellitus.
- Official medicine recommends Jerusalem artichoke in tablets for atherosclerosis, and the extract of this plant - for diseases of the liver and gallbladder.
- Powder from dried ground pear root suppresses pathogenic organisms in the intestines (how to dry Jerusalem artichoke?).
Jerusalem artichoke root powder promotes blood thinning, therefore it is not recommended to use it before surgery.
We wrote in detail about the medicinal properties of Jerusalem artichoke here.
Contraindications
The plant is absolutely safe. The only contraindication is individual intolerance. If you are using Jerusalem artichoke for the first time, limit yourself to a small dose to start.
Please note that Jerusalem artichoke can cause flatulence. Do not use it during an exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases.
Don't mix Jerusalem artichoke with sage and lemon balm. Interaction with these herbs leads to the loss of all the healing properties of Jerusalem artichoke.
Application of different parts of the culture
Flowers
Jerusalem artichoke flowers are most often used to brew medicinal tea, which the:
- normalizes blood pressure;
- improves metabolism;
- relieves headache;
- cold even helps treat heartburn.
Leaves
- Alcohol or vodka tincture from the leaves is used as a prophylactic agent for cholecystitis and as an antioxidant to remove toxins and toxins.
- An aqueous infusion of stems and leaves helps well with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and colds.
- Green gruel has a wound healing and anti-inflammatory effect.
In this video, you can learn how to make tea from Jerusalem artichoke leaves:
The juice
The unique biochemical composition of the juice makes it useful:


- with food and alcohol poisoning;
- with chronic lead poisoning and when working in an area with increased radiation;
- to reduce muscle tone and eliminate arrhythmias;
- to restore early changes in the myocardium;
- for the treatment of amnesia and allergies;
- for pregnant and nursing mothers.
Roots
A decoction of dry Jerusalem artichoke roots is used:
- for the treatment of hypertension;
- increase in hemoglobin;
- lowering blood sugar levels.
reference... For drying, the roots are chopped with a knife, and then dried in the oven for 2 hours at a temperature of 50 ° C.
See how to properly dry Jerusalem artichoke roots:
DRUG PROPERTIES OF TOPINAMBUR
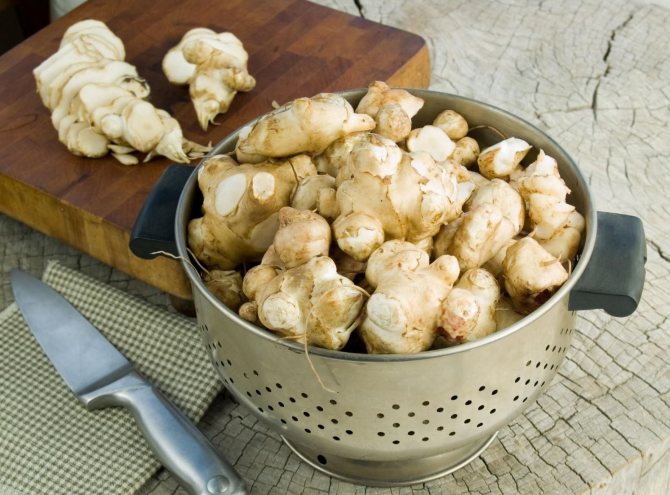
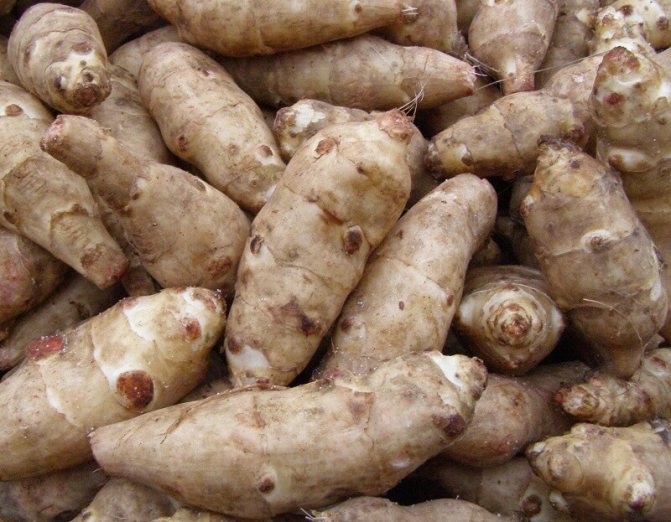
Jerusalem artichoke tubers are rich in carbohydrates. They also contain up to 3% protein, up to 18% inulin polysaccharide, mineral salts, iron, phosphorus, zinc, vitamins B1, C, carotene.
The tubers taste like a slightly sweet potato, but, unlike him, are poorly stored. Jerusalem artichoke is useful for diabetes, obesity, gastritis, loss of energy, vitamin deficiency.
It is also used as an anti-inflammatory agent for rheumatism and joint diseases. The juice promotes rapid healing of wounds, burns, external and internal ulcers, reduces the degree of radiation exposure. Tubers are eaten raw in salads, boiled, baked, salted, a coffee drink is made from dried ones, and tea is made from the leaves.
Varieties and types
Jerusalem artichoke varieties are divided into early, mid-season and late ripening periods.
| Variety | Ripeness group | Tuber yield (c / 1 ha) | Productivity of greens (hay) (kg / 1 ha) |
| Volzhsky 2 | Early | 150 | 200 |
| Skorospelka | Early | 250 | 268 |
| Leningradsky | Middle | 498 | 420 |
| Vylgotsky | Middle | 107 | 346 |
| Interest | Late | 265 | 436 |
| Solar | Late | 400 | 320 |
What material for planting to choose?
As already written, the earthen pear reproduces both by seeds and tubers. If you decide to plant seeds, then you will not get a large harvest by the fall. The bush will grow small, and only a few small tubers are formed, it is from them that you should expect good fruits, but by next fall.
There is nothing better than planting Jerusalem artichoke tubers in spring. In the first year, you can enjoy good, large fruits. That is why, most often, in order to get a full harvest, and not planting material, tubers, or their fragments, are planted.
Growing
Landing
Jerusalem artichoke is planted from late April to early May, using small tubers, according to the scheme:
- depth - 12-15 cm;
- distance between tubers - 40 cm;
- row spacing - 60 cm.
You can find out about the planting time of Jerusalem artichoke here.
Care


Caring for an earthen pear is very simple.
- Water the plant once a week during the dry season.
- Weeding and loosening is carried out after watering or rain the next morning.
- In the spring, mineral fertilizers containing nitrogen and potassium are annually applied to the soil.
- During the flowering period, Jerusalem artichoke is fed with green manure infusion, and once every 3 years in the fall, organic matter is introduced into the soil.
Depending on the variety, 150 kg of tubers and 180 kg of greenery can be harvested from 1 hectare.
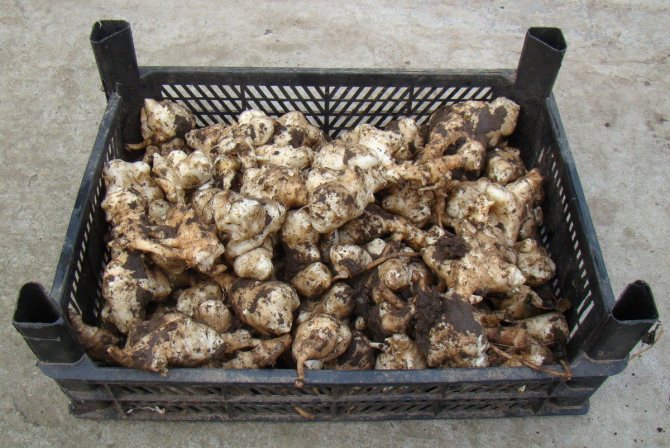
Harvesting and storage
Harvested in late autumn... Store in boxes, sprinkled with sand, after washing and drying thoroughly.For storage, a cellar or a glazed balcony is suitable.
We offer you to watch a video about growing and harvesting Jerusalem artichoke:
How to grow Jerusalem artichoke in a nutshell


Jerusalem artichoke: photo
As a rule, this culture is planted before the first frosts come, about fifteen to twenty days. The so-called "winter landing" is carried out. In this case, the tubers are planted directly in the open ground.
A plant needs quite a lot of light for a plant to thrive.
The composition of the soil is not so important, rather it is worth paying attention to the level of acidity of the soil. Neutral or slightly alkaline earth is best, with a pH of six to eight. Jerusalem artichoke will not grow or develop on land that is high in salt. A soil with a too heavy structure is not suitable for this purpose.
It is not often necessary to water Jerusalem artichoke, this procedure is mandatory in case of prolonged drought in the summer. About one - one and a half buckets of water are consumed per plant.
In the spring, Jerusalem artichoke should be fed annually. For this, mineral-based dressings are used. Organic fertilizers are recommended to be applied in autumn, once every two to three years.
This culture propagates, as a rule, with the help of tubers on which they have eyes. Tubers can be whole or divided into parts. Less commonly, Jerusalem artichoke propagates using seeds.
From time to time, this plant can be affected by harmful insects: bears, slugs, wireworms. As for diseases that can harm plantings, it is worth noting powdery mildew, white rot.
How to give to children?


Earthen pear even more useful for children than for adults.
Indeed, vitamins and minerals contained in this plant are vital for a growing organism.
The use of Jerusalem artichoke in any form will be useful for enhancing immunity, and overweight children will also help to lose weight.
For children under 1 year old, Jerusalem artichoke is best given in the form of syrup.sold in pharmacies.
Where and for how much can you buy seed?
In each region there are companies, private entrepreneurs, Jerusalem artichoke lovers who are engaged in plant breeding and offer planting material for sale. Sales offers are easy to find on the Internet.
For example, from the city of Sapozhok, Ryazan Region, he sells Jerusalem artichoke in a package of 30 kg, the price ranges from 5 to 15 rubles per kilogram. In Moscow, Jerusalem artichoke planting material can be purchased at a price of 27 to 35 rubles per kilogram (AV Gorobets, IP, Starominskaya. Veselaya Rat, IP, Moscow). In St. Petersburg - the cost of an earthen pear is from 25 to 150 rubles per 1 kilogram (the order is accepted from 10 kg), the plant sells.
Feeding the tops and tubers of the culture of domestic animals
In terms of nutritional value, green tops and succulent earthen pear tubers are superior to fodder beets.
- For feeding chickens and rabbits the green part of the plant is used in the summer, and the dried part in the winter.
- To increase milk production in cows and goats, as well as to improve the quality of wool in sheep, both green mass and tubers are added to their diet.
- For pigs mainly tubers are used.
Jerusalem artichoke is a very valuable crop that cannot take a leading place in agriculture only because of its short shelf life. But for this there are breeders, and an ordinary person can independently grow this wonderful plant and not only enjoy the novelty of the dishes, but also use it for healing.
How to use Jerusalem artichoke for feeding animals is described in this article.
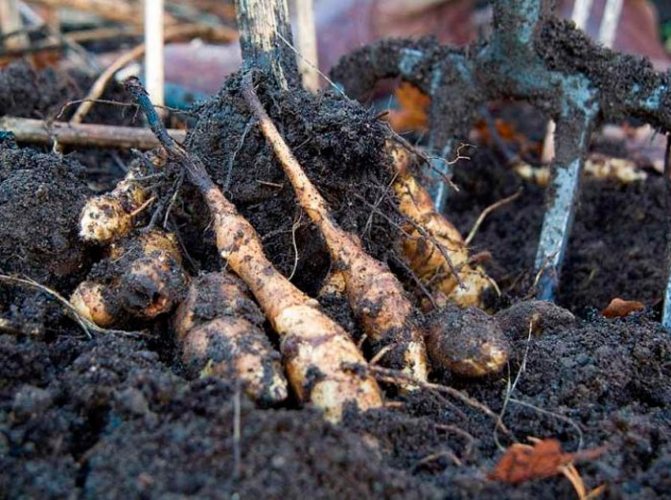
How to harvest and store Jerusalem artichoke
The tubers of this culture reach their maturity in about one hundred and twenty days. Before this time, it makes no sense to remove them from the ground. They simply will not be able to reach the required quality level of maturity.
It is best to get tubers out of the soil in spring. It is worth noting that the soil should warm up well. This procedure can be carried out in the fall, when the earth, on the contrary, begins to "seize" by frost.
Tubers, which are located in an open area, can withstand frosts down to -38 degrees without problems. It is still recommended to cover your beds with snow or dry soil for the winter period. You can dig up tubers in parts. For example, in the fall, harvest the crop that will be used in the winter, and those tubers that remain can be selected in the spring, when the body lacks vitamins.
Harvesting should take place before warm weather. Otherwise, shoots will begin to grow, and the tubers, in turn, will lose their taste and useful properties. In addition, from a useful root vegetable, the plant will simply turn into a weed.
Jerusalem artichoke tubers are stored in the same way as other similar vegetables. They need to be placed in boxes and sprinkled with a layer of sand. Before starting storage in the basement or cellar, the root crops are washed and dried. A balcony with insulation or a loggia is good for storage. If there are not too many tubers, then you can put them in storage in the refrigerator, in the vegetable compartment.
Description of the Jerusalem artichoke plant
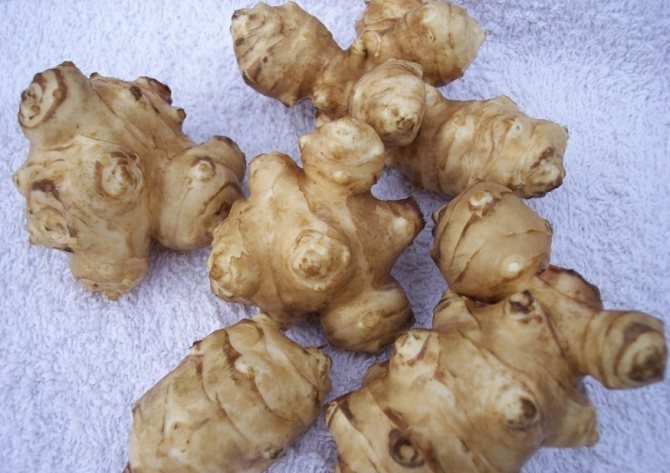
Jerusalem artichoke is a hard root vegetable colored yellow, red, lilac or white. The appearance of the rhizome resembles ginger. Earthen pear is used for food, it has a light sweetish taste. Many people compare the taste with cabbage or turnips. The surface of strong and erect stems is slightly pubescent. They can grow up to 3 m in length and have a branched crown. The upper leaf blades look oval, the lower ones are opposite ovoid. Basket flowers are formed from tubular buds painted in a yellow tone, and golden false-lingual flowers are located at the edges. Fruit ripening begins at the end of summer.
For industry, Jerusalem artichoke is grown in America, Russia and Asia. In our area, for several decades, many summer residents have been cultivating it in their garden plots. The ground pear has medicinal properties and is a very nutritious vegetable crop, the chemical composition of which is close to that of potatoes. Root vegetables are edible raw and boiled. There are many recipes on the Internet for preparing various dishes and drinks from this vegetable.
Site and soil preparation for planting
Jerusalem artichoke requires a fertile open ground. In the first year, in the autumn, before planting planting material, it is necessary to add compost or useful rotted manure to the soil, mixed with mineral fertilizers, at a rate of 15 kg / m2. Fertilizers can be diluted in the correct proportions, such as potassium salt (10 to 20g / m2), superphosphate (15 to 20g / m2). In the spring, the addition of ammonium nitrate is carried out at the rate of 10 to 15 g / m3.
For the next years of cultivation, mineral fertilizers are added as top dressing, while loosening the beds.
Growing Jerusalem artichoke at home
If desired or necessary, Jerusalem artichoke can be grown at home. They put it in a large box or pot. To plant one plant, it is necessary to allocate a container with a depth of about 40 cm and about the same diameter. Landing is done as follows:
- Drainage from broken bricks and pebbles is laid at the bottom of the box. You can use sand.


Lack of drainage combined with improper watering is the most common cause of home-grown Jerusalem artichoke diseases
- A layer (about 10 cm) of fertile soil is poured over the drainage. If you take soil from the garden, then add humus and sand to it. You can buy seedling or flower growing soil at a specialized store.
- A tuber is placed on the ground and poured over it with water.
- After that, the tuber is covered with a 10-centimeter layer of earth.
- The box is placed in a warm place, the soil is periodically watered.
- As soon as shoots appear, they begin to pour earth into the container so that about 10 cm of the plant is above the surface. The filling is carried out until the container is completely filled.
If the soil is well fertilized, then no additional dressing of Jerusalem artichoke is needed. It will be necessary to periodically water and loosen the ground a little. Now all that remains is to wait for the ripening of the crop.
Similarly, you can put Jerusalem artichoke in a barrel or other container and put it in the open air. In this case, you do not have to worry that the plant will conquer a large territory.
Jerusalem artichoke for an excellent state of the nervous system
Jerusalem artichoke tubers are a real wealth of B vitamins and magnesium, which provide a good state of the nervous system. Eating Jerusalem artichoke improves your ability to concentrate and helps you remember information better.
It also helps reduce the effects of chronic stress. Therefore, Jerusalem artichoke should be part of the diet for patients with general fatigue and exhaustion. They are also great for pupils, students, and people doing mental work.
Jerusalem artichoke also reduces the risk of dementia in older people. Silicon, which prevents brain calcification, plays a positive role in the prevention of Alzheimer's disease.
It is important to note that the silicon in Jerusalem artichoke also prevents bone disease. This reduces the risk of bone demineralization, thereby preventing the development of osteoporosis.
It has a positive effect on the cartilage, guaranteeing its correct elasticity and preventing the appearance of degenerative changes.
Jerusalem artichoke juice, in turn, is used to treat bacterial skin infections. Works great for ulcers, burns and psoriasis. Reduces unpleasant symptoms and accelerates the regeneration of the epidermis.
Brief botanical description
Jerusalem artichoke or tuberous sunflower - a perennial plant of the Astrov family, subfamilies tube-flowered. The Latin name is Helianthus tuberosus. Small flowers are combined into an inflorescence - a basket with a diameter of two to ten centimeters. The basket contains 50-60 flowers. Pseudo-lingual asexual flowers are located along the edges, tubular bisexual flowers in the middle.
Five stamens grow together with anthers, forming a tube. The ovary is unilocular, with an orange column. The stigma is bipartite. One plant can have from one to five to fifty inflorescences or more. Cross pollination, possibly with its own pollen.
Storage features
Despite the many advantages that we talked about above, the plant has one disadvantage - storage. No matter how you spray it, no matter what temperature you store it, you can be sure that it will quickly deteriorate anyway. This is due to the too thin skin of the plant, which is easily damaged. The only way to extend storage even a little is to fold the earthen pear into food paper bags and put them in the refrigerator. The product will remain fresh and usable for about 2-3 weeks.
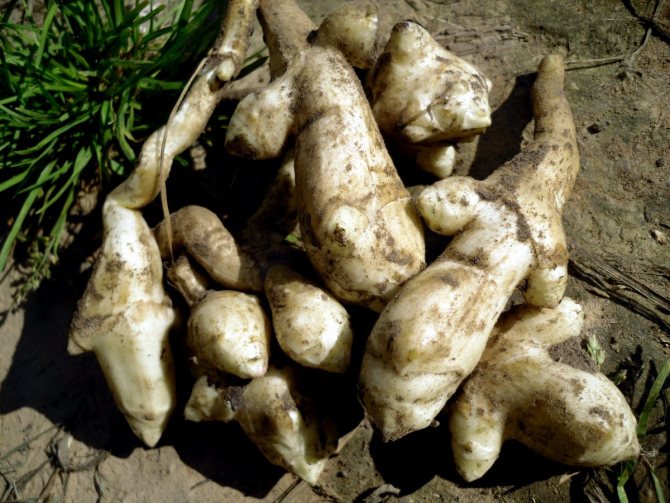


Further care
In the middle of summer, Jerusalem artichoke will grow up to a meter, and it will be difficult for him to keep heavy greens on his own. So that the stems do not break and continue to gain growth, divide the plantings into bushes, erect strong supports in the form of pillars and tie the bushes to them with strong wire or thick threads.
To further increase yields, re-raking is recommended in the second half of July. Around the same time, the plant will begin to bloom, do not leave the color on the bushes, it will take away all the nutrients from the tubers. Cut them by shortening the Jerusalem artichoke to one and a half meters. The assembled bouquet will perfectly decorate the room if you put it in a beautiful vase.
Cellulose
The human body does not assimilate all the food eaten, a certain part of it is not digested, but simply excreted from the body. For a long time, scientists were convinced that fiber is not needed by the body and even harmful. Back in the middle of the 20th century, nutritionists assured that refined foods were the most useful, and the world enjoyed refined refined food until the alarming fact was replaced: the more refined food a person consumed, the more he was overcome by gastritis, colitis, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, malignant tumors.
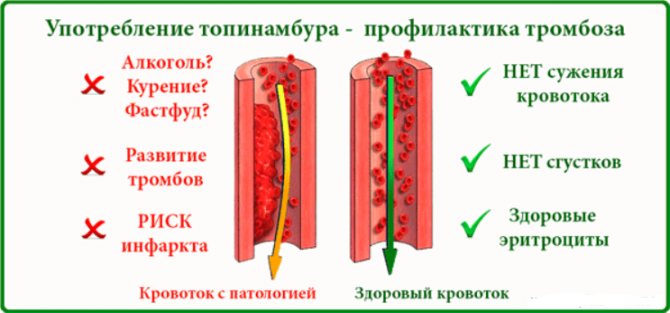
According to Bengmark S. (1998), low fiber content in food is an important etiological factor in the development of colon cancer, diverticulosis, constipation, obesity, and vascular thrombosis.
Today, fiber has finally taken its rightful place alongside proteins, fats, carbohydrates, trace elements and vitamins. It is now clear that fiber is healthy and necessary for the body. It acts like a good broom: "cleansing" the thinnest villi lining the inner surface of the intestines, preventing them from sticking together. Fiber absorbs a large amount of fluid, facilitates bowel movement, relieves colitis, gastritis and constipation.
The swollen fiber, moving through the intestines, removes from it harmful chemicals, mutagens, carcinogens, 'provoking the development of malignant tumors. It also helps to reduce blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
Food is poor in fiber, provides less satiety, and maybe that's why people started to overeat. And again the risk of obesity, hypertension, diabetes increased.
Despite the fact that fiber is found in sufficient quantities in whole grains, fruits, but they are very high in carbohydrates, so it is better to prefer fiber using Jerusalem artichoke powder.
Care after sprouting
At the moment when Jerusalem artichoke will actively grow, build up the green mass, which usually happens in the first half of summer, it is necessary to introduce fertilizing with formulations that contain a lot of nitrogen. Before planting Jerusalem artichoke, such fertilizers are not needed, there will be enough manure, but during the period of active growth, the plant will need this component. As July approaches, replace the fertilizer with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers.
Watering should be done, focusing on the weather and the condition of the bushes. This is the most important point after planting Jerusalem artichoke correctly. If the plant does not have enough moisture, then it will grow slowly, and the crop will consist of small, highly branched tubers. In addition, drought can contribute to the attack of pests on the plant. With excessive watering, Jerusalem artichoke is also in danger: it will be struck by various types of rot and slugs.
When the plant reaches a growth of 30 to 40 centimeters, it is necessary to spud it. This activity will allow additional roots to form, which will lead to a higher yield.
Before germination
An earthen pear is not a potato, and care is needed for it even the moment the first shoots appear above the ground. To get a healthy plant and a good harvest, it is important to follow some rules:
- A dense earth crust must not be allowed, which will not allow moisture and air to pass through. For this, the soil is gently loosened. In order not to damage the plant, be guided by the ridges that remained when burying the tubers.
- Measures to eliminate weeds, that is, weeding, are being steadily carried out.
- Plant care lasts from the moment of planting to harvest.
- Jerusalem artichoke is fed once a month.
From planting the plant to harvesting the tubers in the fall, it is necessary to maintain soil moisture. To do this, try to produce abundant watering if there is insufficient rainfall.
Jerusalem artichoke varieties for the Urals
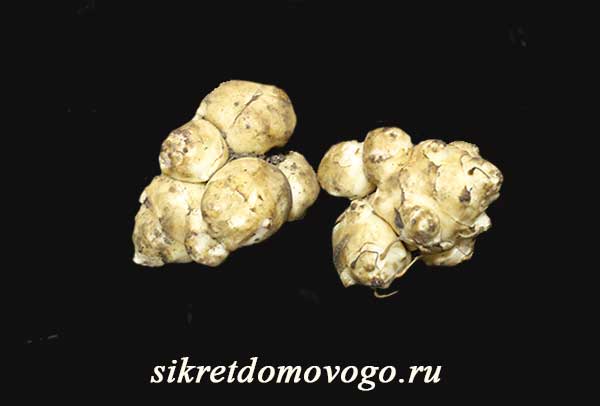


I grow Jerusalem artichoke for tubers, so I was interested not in fodder, but in tuberous varieties.Studying different characteristics of Jerusalem artichoke varieties, I settled on the Skorospelka variety.
Its advantage is that its vegetative period (from germination to flowering) is only 4 months. In the conditions of the Urals, this is extremely important, because only after flowering, active growth of tubers begins, and a high yield can be ensured.
In addition, the variety is characterized by sufficient frost resistance, it can withstand frosts even - 40 degrees during a snowy winter, so the tubers can safely winter in the ground. This provides strong planting material and tasty juicy tubers for early spring consumption.
The variety is resistant to heat, drought and frost, tolerates shade well, blooms profusely and serves as a beautiful decoration of the site.
The mistake of many summer residents
Most people who do not know how to plant Jerusalem artichoke correctly believe that you can dig in tubers near roads where the land is "empty". This opinion is shared by those who saw that the plant grows by itself, in abandoned wastelands. That is why, even having planted an earthen pear according to all the rules, summer residents forget about it until the fall, when it will be time to harvest. Imagine their surprise when, under strong, healthy bushes, only a few "skinny", highly branched roots, which cannot be called tubers, are found.
Jerusalem artichoke, although unpretentious, needs a specially designated area, and will not fully develop, growing in an inappropriate, untreated place. How to plant Jerusalem artichoke tubers correctly, we figured it out, now let's talk about proper care of the plant.
Photo gallery
Content
- Description
- Planting Jerusalem artichoke in open ground When to plant
- Jerusalem artichoke soil
- Then you can plant
- How to plant
- How to grow
- Diseases
- Healing properties
How to deal with pests
The most dangerous disease for Jerusalem artichoke is "White Rot" (sclerotinosis). The disease manifests itself at the very base of the stem, in the form of brownish spots. These spots grow higher and completely affect the entire lower part. After that, the decayed tissues of the stem are covered with a bloom of white, and Jerusalem artichoke begins to gradually dry. Strict and timely adherence to agrotechnical rules can prevent infection!
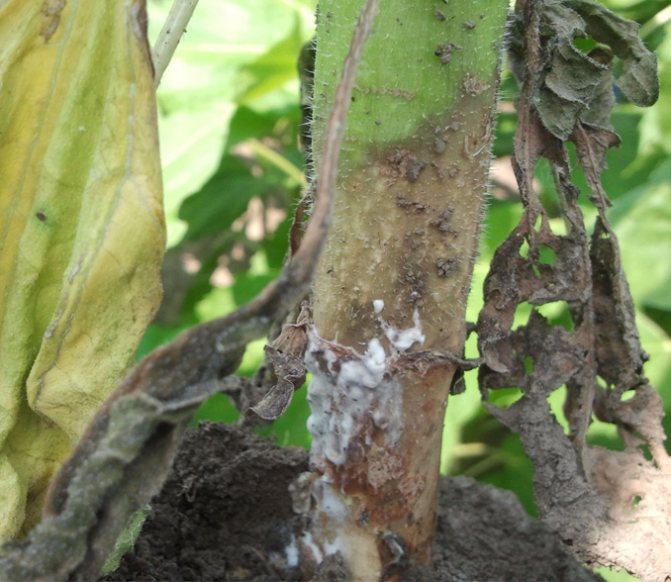


Infected bushes must be dug up and immediately burned in order to prevent infection of the entire garden.
The most popular parasites of Jerusalem artichoke are the larvae of the May beetle and the nutcracker (wireworm), as well as the bear.
Also, for the fight, there are enough primitive precautions - transplantation to another place, the destruction of all affected above-ground parts, etc.
Where to plant Jerusalem artichoke?
This plant is rather unpretentious to the soil. It will develop well if a sufficient amount of oxygen and moisture gets into the soil. If there is not enough humus in the ground, then this is not a problem. It is easily compensated for by well-chosen dressings.
Do not plant Jerusalem artichoke in dense black soil, where little oxygen will flow. In this case, even if there is sufficient nutrition, the plant will not bring a rich harvest. The soil must be well ventilated so that moisture does not stagnate.
Find an open area where sunlight can penetrate well. And its preparation for planting should begin already in the fall, because planting Jerusalem artichoke in the spring is much easier and easier if the beds are ready.
The subtleties of choosing Jerusalem artichoke
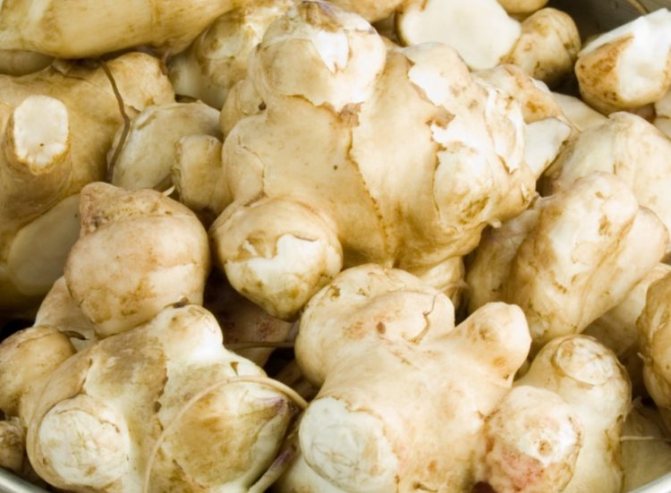
What exactly should be guided by when choosing? Not only photography, but also appearance is often deceiving. In this case, we advise you to take this product in your hands and carefully examine its skin.The presence of roughness, fine hairs and irregularities indicates good quality. In addition, the tubers must be firm. Sluggish and soft will definitely not suit you. Incomprehensible spots, wrinkled skin are already a reason to refuse to buy and look for something else.
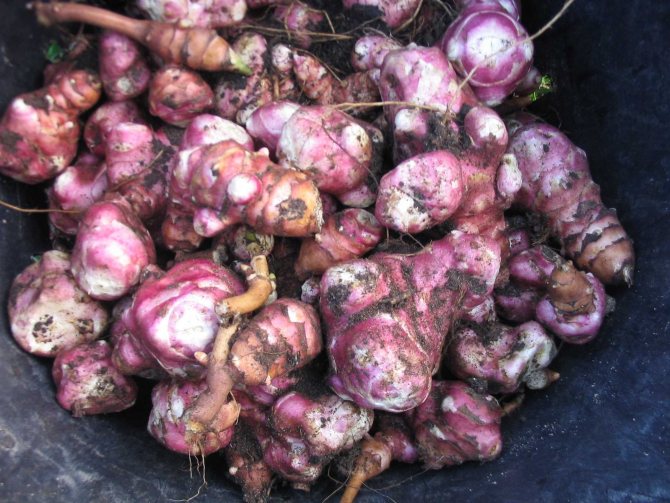


External description of Jerusalem artichoke (earthen pear), Jerusalem artichoke flowers and leaves, photo of Jerusalem artichoke


An earthen pear is a plant with a short, branching stem. Jerusalem artichoke leaves are located on it, the shape of which is different and depends on the location. The upper leaves are arranged alternately, they are ovoid. The lower leaves are similar in shape to the heart, opposite. They can be seen in the photo of Jerusalem artichoke.


The plant blooms late. His flowers are yellow, collected in baskets. Flowering begins in the second half of June and ends in September. The roots are well developed.
Some useful tips from experienced gardeners for growing an earthen pear
You should not plant Jerusalem artichoke where stunted crops grow, as well as in the center of the garden area. A tall plant will:
- shade smaller "neighbors"
- take nutrients from nearby vegetables
- obscure the perspective view into the depth of the site
- suffer without the protection of a fence, other enclosing structure (its stems tend to lie down and break under the gusts of wind)
The best place to place tall Jerusalem artichoke, grow and care for it is along the fences enclosing the site on the leeward side. In this case:
- the monotony of the fence is brightened by embossed green curtains with bright colors
- the plant will not interfere with the growth of other "inhabitants" of the garden
- next to the fence posts, it is easy to provide for the fastening of the supports for the garter of high Jerusalem artichoke stalks so that they do not break.
Edible beauty ↑
Jerusalem artichoke has earned the love of flower growers. Its massive plantings form magnificent hedges. Planted along the perimeter of the site, it becomes a reliable shield from wind and rodents. Also, it easily displaces weeds and weeds from the site.
At the same time, yellow caps of inflorescences on high stems look good in the background.
Yellow flowers can become a bright background for a country-style flower garden or a garden decorated in one color scheme.
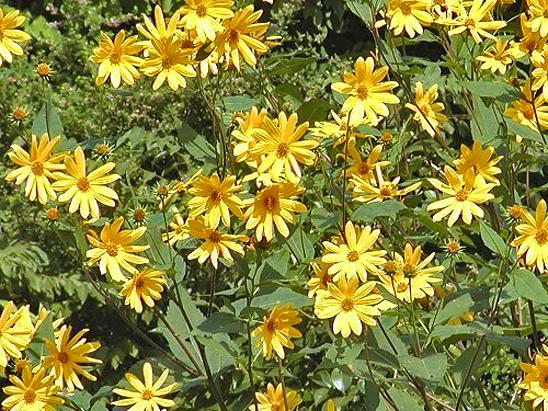


But here, like everything, if it's short. I hope you enjoyed the plant and there is a secluded spot in the garden for Jerusalem artichoke. Moreover, this is a great opportunity to combine business with pleasure. Or maybe you know how to use the properties of Jerusalem artichoke in dishes. Send recipes with photos.