Potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus are three chemical elements, without which the full growth and development of any plant on the planet is impossible.

Phosphorus is the most important component involved in the chemical reactions of photosynthesis and plant respiration. Phosphorus is also called the source of energy, which is necessary for the normal course of these processes. Not a single life stage of plant growth and development is complete without the participation of phosphorus:
- At the seed stage, phosphorus increases seed germination.
- Accelerates the normal development of seedlings.
- Promotes the development of the root system of the future plant.
- Promotes favorable growth and development of the ground part of the plant.
- Promotes the full flow of the flowering process and the formation of germinating seeds.
The success of all the above stages is possible only if the required amount of phosphorus is found in the soil. All crops grown in the garden, both fruit and flower, need feeding with phosphorus fertilizers.
Phosphate fertilizers in stores today are represented by a wide range. Differences in their compositions will also have different effects on seed germination and development of mature plants. Therefore, it is so important to navigate the variety of phosphorus fertilizers and know their features, as well as the rules for their use.
Potassium monophosphate
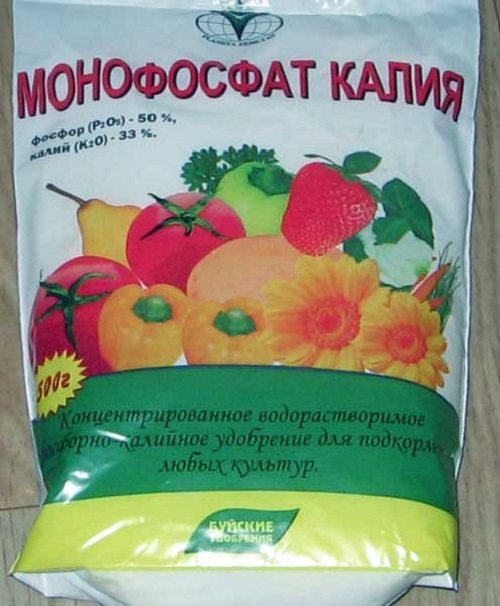


Two-component mineral fertilizer contains phosphorus in half of its composition and slightly less potassium. It is used to prepare solutions for watering seedlings of flowering plants (10 g of the drug per bucket of water). Flowers growing in open ground are periodically fed with a more concentrated solution - 20 g of the drug per 10 liters of water.
Fertilizers
It is difficult to find a universal fertilizer for indoor flowers. Based on the signs of a lack of basic nutrients in the plant body and the individual characteristics of the flower, they decide what type of feeding can be applied. According to the state of aggregation, fertilizers are:
- Liquid. They are represented by concentrated solutions that must be diluted with water before applying to the soil or spraying green mass. These are fast-acting, easily digestible substances. If used improperly, they can burn the root system.
- Loose powders. They are characterized by a high concentration of active ingredients. They are good in that you have to pay only for the dry component. Disadvantage: it is difficult to correctly calculate the required amount of a substance to obtain a solution. It is better to purchase small-sized preparations designed for 1-2 liters of water.
- "Candles", sticks are compressed fertilizers of various shapes. They must be inserted into the substrate to a depth of 2 cm, at least 1 cm away from the wall of the pot. The period of validity is 2-3 months, depending on the rate of dissolution of the main substances. They often contain insecticides (fungicides) that protect the ornamental crop from diseases and pests. Disadvantage: Difficult to tell when a nutritional supplement has stopped working.
- Granules. They are arranged so that on top of the nutrients there is a spherical membrane of a porous structure, gradually releasing chemical compounds for feeding. The dosage of the granules depends on the volume of soil in the flower pot.Disadvantage: It is impossible to tell when the membrane ball becomes empty because it does not dissolve in water and does not change shape.


Mineral
Chemical compounds of inorganic origin that contain nutrients for plants are called mineral fertilizers. They are designed to replenish the soil with elements that are a source of nutrition for ornamental crops. Classification of mineral fertilizers:
| View | Subspecies | Name | Description |
| Nitrogen or nitrate | Ammonia or ammonia | Ammonium sulfate or ammonium sulfate | Contains nitrogen and sulfur. Used for neutral and alkaline soils. Promotes the development of the root system. Strengthens the effect of nutrients in mullein and poultry droppings. When dissolved in water, it is absorbed by plants by 70%. Converts to nitric acid, which leads to the accumulation of nitrates in the soil. |
| Ammonium chloride or ammonium chloride | Contains chlorine (67%) and nitrogen (25%). Increases soil acidity. Not recommended for indoor crops due to its high chlorine content. | ||
| Ammonium nitrate | Ammonium nitrate or ammonium nitrate | Contains 35% nitrogen. Instantly absorbed by plants. Strengthens seedlings. It goes well with potassium salt and superphosphate. Used for slow growing crops, palms, ferns. Cannot be mixed with peat due to its spontaneous combustion potential. | |
| Nitrate | Sodium nitrate or sodium nitrate | The nitrogen content is 16%. Has an alkalizing effect. Not compatible with superphosphate, it goes well with potassium salt. | |
| Calcium nitrate or calcium nitrate | Contains 15.5% nitrogen and 19% calcium. Cannot be mixed with superphosphate, ammonium nitrate, manure. Alkalizes the soil. Stimulates the growth of bulbs, germination of seeds. Strengthens cell membranes, contributing to the resistance of the culture against diseases. | ||
| Amide | Urea or urea | The compound is quickly absorbed by the root system from an aqueous solution. Strengthens stems and leaves, enhances crop growth. Under its influence, the green mass acquires a rich color. An overdose of the compound threatens to destroy the soil microflora. | |
| Phosphoric | Water soluble | Simple superphosphate or monophosphate | Contains 15-20% phosphorus. Promotes the flowering process. Increases winter hardiness of bulbs, accelerates bud opening. The compound must not be mixed with urea and ammonium nitrate. It is used for root feeding and spraying. |
| Double superphosphate | Contains phosphorus - 50%, a number of trace elements: magnesium, manganese, boron, molybdenum. Strengthens the root system, promotes the growth of green mass, the accumulation of moisture in the tissues of the culture. | ||
| Semi-soluble | Precipitate | Contains 35% phosphorus. Suitable for any soil. Strengthens the root system, increases the immunity of the culture. Similar to superphosphate, but longer lasting. Absolutely harmless. | |
| Sparingly soluble | Phosphorite flour | Contains 30% phosphorus. Alkalizes the soil. Combines with urea and manure. | |
| Potash | Concentrated chloride salts | Potassium chloride or potassium chloride | The potassium content is 60%. The aqueous solution of the compound is easily absorbed by the root system. The substance acidifies the soil and is compatible with any fertilizers. Due to the presence of chlorine, it is not suitable for all plants. Good for ornamental cereals. |
| Concentrated sulfate salts | Potassium salt | Contains 38% potassium. Consists of potassium chloride and ground sylvinite. Due to the high chlorine content, it is rarely used in floriculture. | |
| Potassium sulphate | The substance is used as the main fertilizer and for top dressing. It dissolves perfectly, but is quickly washed out from light sandy soils. Increases crop resistance to disease. The potassium content is 50%. | ||
| Complex | Complex | Nitrogen phosphate | Obtained by chemical interaction of phosphoric and nitric acids, neutralized with ammonia. Suitable for all soils and crops. |
| Ammophos | Nitrogen content - 10-12%, phosphorus - 45-52%. The substance has a universal effect. | ||
| Combined | Nitrophoska | Obtained by mixing simple fertilizers. One granule of the compound contains three main components: potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus. Not suitable if the soil needs to be replenished with one of these elements. | |
| Carboammophos | |||
| Mixed or fertilizer mixtures | Ammophos + ammonium nitrate + potassium chloride | Received by dry mixing of simple fertilizers, taking into account their compatibility. Do not use if the culture lacks one of the three components: potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus. | |
| Microfertilizers | There are many brands of products. For example, Aquarin, Vuksal, Ecolist. | The preparations contain trace elements necessary for the vital activity of cultures: zinc, boron, copper, iron, magnesium. |


Organic
Organic fertilizers include humus and slurry. Horse, cow, rabbit and chicken droppings are used to feed flowers. They contain large amounts of potassium, phosphorus and nitrogen, which are necessary for ornamental crops for normal development and flowering. Fresh manure cannot be used as fertilizer because it burns the roots of the plant. Because of its nutritional content, horse feces are called "rose marmalade". To prepare a bioactive mixture, you need:
- Pour manure with water in a ratio of 1:10.
- Insist for a day, stirring the solution from time to time.
- For watering indoor flowers, the nutrient liquid is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10.
An aqueous solution of cow dung is called mullein. This type of feeding causes active growth and flowering of ornamental plants. To prepare it you need:
- Pour manure with water in a ratio of 1:10.
- Infuse the solution for 10 days, stirring constantly.
- Before watering, dilute the finished slurry with water 1: 5.
- To replenish the nitrogen evaporated during the infusion of the solution, ammonium sulfate (20 g per 10 l) must be added to the mullein.
- To stimulate flowering, you need to spray the plants with manure infusion diluted with water 1:20.
Due to the content of nitrogen (6 g / kg), phosphorus (6 g / kg), potassium (4 g / kg), rabbit droppings stimulate the formation of buds and the rapid growth of ornamental crops. Crushed dry manure is laid in the soil (1 tbsp. Spoon per 3 kg of soil). To get slurry, you must:
- Mix droppings with wood ash (1: 1).
- Add water (1:10).
- Leave the solution to ferment for 3 weeks, stirring every day.
- To water the flowers, dilute the slurry with water (1:10).
Chicken droppings are the most nutrient-dense organics. It contains nitrogen (16 g / kg), phosphorus (16 g / kg), potassium (8 g / kg). To prepare slurry from chicken manure, use the method described above (from rabbit excrement), but without adding ash. Add the additive to well-moistened soil. If there are pets in the household plots, manure is readily available and does not require material costs. The disadvantage of such a fertilizer for flowers is the preparation time and an unpleasant odor.


The drug "Autumn"
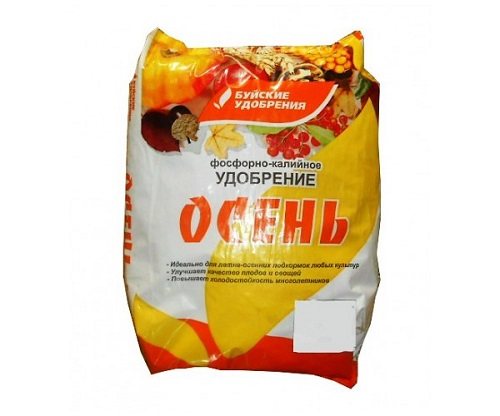


The preparation contains 18% potassium, 5% phosphorus, as well as calcium, magnesium and boron. Dry powder is introduced into the soil during the autumn digging of the site where it is planned to grow ornamental plants, at the rate of 35 g per 1 sq. m.
During flowering, 15 g of the drug per 1 sq. m, and to improve the winter hardiness of perennial crops after flowering, they are fertilized with 30 g per the same area.
The seeds are soaked in a solution of the drug before planting, and they are also watered with flowers at the root.
When you need to feed indoor plants
Fertilizers for indoor flowers are presented on the market in a huge assortment. They contain nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium - elements vital for any representative of the flora. Depletion of the soil leads to negative consequences in floriculture. There are several signs that help to understand what nutrient is lacking in flowers:
- nitrogen starvation: growth slows down, leaves begin to turn yellow;
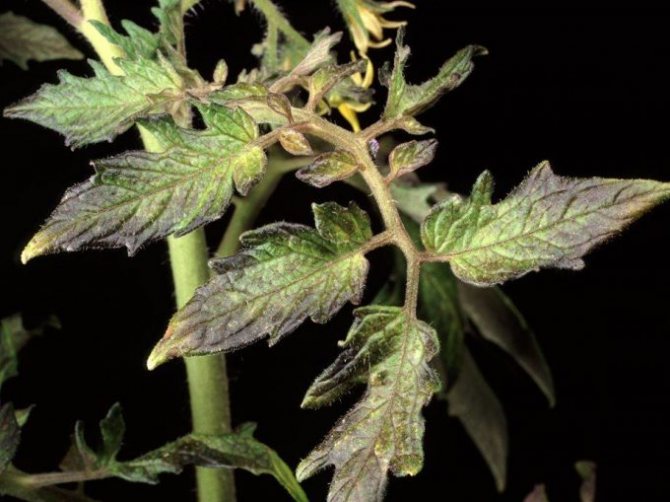
- lack of phosphorus: dark green and yellow-green spots form on the leaf plates, the shoots become thinner, and the stems bend, the flowering process is delayed, the root system becomes weak;
- lack of potassium: the tips of the leaves turn yellow and gradually die off, the seedlings weaken and dry out, and a gray-brown spot appears on the leaf plates.
- calcium starvation: weak thin shoots die off, the edges of the leaves turn yellow, the roots become weak and short, and the leaf blades curl inward.
Causes and signs of phosphorus deficiency
Plant cultures react extremely hard to insufficient concentration of a microelement in the soil, because all metabolic processes are disrupted in them. In the outward appearance of plants, the deficiency of the element is manifested by the following signs:
- all parts of the landings are first painted in a bright green hue, then in purple (crimson);
- deformation of the leaves and their premature fall are observed;
- the leaf plates of the lower row undergo necrotic changes, dark spots are formed;
- crop growth slows down;
- rhizome development is inhibited;
- the retaining part of the root dies off, plantings often fall.
All these menacing signs require fertilizing the earth with nutrient compounds. Phosphate starvation in plants occurs as a result of various negative reasons. The most common:
- heavy earth with clay;
- oversaturation of the soil with potassium;
- increased soil moisture;
- lack of useful microflora.
It is necessary to apply phosphorus-containing fertilizers after the true cause of the element deficiency has been established.
Features of feeding some types of indoor flowers
There is no universal fertilizer for all types of indoor flowers. For the successful cultivation of a specific ornamental crop, you need to know its vegetative phases of activity and rest. In each such period, the plant must be additionally fed with nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium. This should be done in accordance with the rules described above.
Spathiphyllum
Potassium is necessary for the spathiphyllum to activate the process of photosynthesis, protein-carbohydrate metabolism, and increase the resistance of the plant organism to diseases. An additional source of this element is wood ash, potassium sulfate, potassium nitrate. They are used for root feeding twice a month, starting at the end of March. Nitrogen additives block the bud formation process, so they need to be used in the spring and after flowering. Spathiphyllum is responsive to the nutritional effects of mullein and compound fertilizers.


Ficus
A distinctive feature of ficuses is their need for feeding only in spring and summer. In stores, you can buy complex preparations designed specifically for this culture, for example, Agricola, Pocon. Using solutions of mullein and poultry droppings for ficus activates its growth. Top dressing based on coffee grounds, "citrus cocktails", sugar-yeast water are suitable for him. After spraying with succinic acid, the ficus leaves acquire a beautiful green color and shine.


Succulents and cacti
A characteristic feature of succulents and cacti is a long dormant period - from September to March. At this time, you can not use additional food, so as not to disrupt the growing season. Such plants are contraindicated for feeding with slurry. From it, the leaves of the culture grow fat and burst.It is better to purchase special complex fertilizers for succulents and cacti (Good Power, Pocon, Bona Forte, Etisso). The nutrient solution prepared according to the instructions is added every 14 days from April to August.


Bamboo
Bamboo (a type of dracaena) in a vase thrives in aquarium water. If this is not available, it is imperative to add a mineral additive for decorative deciduous crops, diluting the obtained (according to the instructions) rate with water in a ratio of 1: 5. The ideal fertilizer for bamboo is one in which the combination of potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus is in a ratio of 3: 3: 1. The potted culture is fed with complex fertilizers once a month from spring to autumn. In summer - every 14 days. There is no need to fertilize bamboo for the first 2 months after purchase.


Indoor violet
To build up green mass, violets need more nitrogen (nitrophoska, ammophos, ammonium nitrate). To activate and prolong flowering, you need to feed the culture with potassium and phosphorus (superphosphate, potassium salt). Of the complex fertilizers, Etisso, Bona Forte, Master are ideal for violets. The plant is fed every fortnight in the spring and summer.


Dragon tree (dracaena)
In order for the dracaena to have a gorgeous look, it is necessary to feed it with a root and foliar method (alternating) twice a month from April to August. At other times, the nutrient solution is added once (monthly). The best composition of top dressing for dracaena is a combination of nitrogenous potassium (1 g), ammonium sulfate (0.6 g) and potassium phosphate (0.4 g). The mixture is dissolved in 2 L of water. You can use such industrial drugs as:
- Rainbow;
- Ideal;
- Giant;
- Master;
- Stimulus.


How to fertilize indoor plants correctly
In the absence of certain knowledge from the grower, feeding can cause the opposite effect. In order not to harm, fertilizers for flowers must be applied correctly:
- Strictly follow the instructions for preparing the formula on the manufacturer's packaging.
- Strictly observe the dosage and feeding schedule.
- Adhere to the timing of the introduction of bioactive additives (morning and evening).
- Apply any top dressing only with a moistened substrate.
- Feed the transplanted plants no earlier than after 4 weeks.
- Fertilize new crops only one month after purchase.
- Do not feed a strong, healthy plant.
- Do not add nutritional supplements if rot is present in the soil, the flower has a fungal disease or is affected by pests.
- Stop fertilizing before the plant should bloom, and only resume after flowering.
Foliar dressing requires no less knowledge and care than fertilizing the soil. Basic rules for irrigating crops with nutrient solutions:
- Foliar top dressing is carried out 10 days after root dressing.
- Flowers with large leaves (monstera, croton, etc.) can be sprayed with a nutrient solution every 3 weeks.
- Dust should be removed from the sheet plates before sprinkling.
- It is best to use a beneficial spraying on the day you water.
- It is important to observe the seasonality: in winter, you should not use nutritious irrigation, so as not to disturb the dormant period.
- It is forbidden to spray during bud formation and flowering.
- The leaves are watered on both sides.
- The ingress of moisture into the succulent rosette can cause rotting.
- Sick crops must first be cured, and fertilized at the stage of rehabilitation.
Other sources of potassium - what are the names?
Other types of preparations are also used to feed plants with potassium:
- Potassium nitrate (potassium nitrate) is a complex fertilizer made from potassium in the amount of 44% and nitrogen in the amount of 13%. It is used for most horticultural crops, and it is introduced during the growing season, flowering and fruit setting.A small percentage of nitrogen does not cause an unnatural build-up of green mass, but only strengthens the plant. Potassium nitrate is loved by root crops and berry crops.
- Potassium salt is an analogue of potassium chloride, which is of little use for feeding some plants due to the high percentage of chlorine. Potassium contains 40%.
- Kalimagnesia is another complex consisting of potassium (up to 30%), magnesium (about 10%), sulfur (17%). Sold in the form of a pinkish powder or granules. It dissolves quickly in liquid, but gives a precipitate. The advantage is a minimum of chlorine (1-3%), suitable for almost all crops. Kalimagnesia is well accepted by potatoes, legumes, fruit bushes and trees. With proper use, the level of starch in potato tubers increases, in berries - sugar, ascorbic acid. A noticeable result is observed on sandy soils, peat, on loams only with sufficient moisture.
- Potassium carbonate, nitrophoska, nitroammofoska and liquid complex fertilizers also serve as a source of potassium.
Video about the terms and norms of using wood ash for feeding.
From natural sources, it is worth highlighting wood ash. Potassium in it is 10%, the composition contains magnesium, phosphorus, iron, copper and other elements. Ash is applied throughout the growing season. In autumn and spring, the additive will improve the nutritional properties of the soil, and in summer it will strengthen the developing plant.
How to determine the lack of minerals in the soil
Plants cultivated in light peatlands need the supply of potassium the most. Signs of insufficiency of such an element are especially pronounced in the summer season:


Potash fertilizer
- brown spots appear on the leaves;
- foliage changes color, becomes yellow or bluish with a bronze tint;
- "edge burns" are observed - the tips and edges of the leaf begin to die off;
- the veins are deeply buried in the green tissue;
- the stem becomes thin;
- planting stops intensive growth;
- wrinkles appear on the leaves, they curl;
- the bud formation process is suspended.
Fertilizers with phosphorus do it yourself
The basis of phosphorus mineral fertilizers is phosphorite. To make your own nutritional mixture, such as superphosphate, bones must be calcined over a fire in order to rid the material of organic compounds. After the calcination procedure is over, the result is calcium phosphate and phosphorite. The next step is to separate from the total amount of clean pieces of calcined bone, followed by grinding into powder. For convenience, use a hammer, and then transfer it to a mortar and grind to a powdery state.
Pounded bones in an amount of 50 g are combined with chalk (3-5 g), the resulting mixture is placed in a clean glass container and 70% sulfuric acid (20 g) is poured into it. When adding acid, stir gradually with a stick. As a result of heating the mixture, you will first get a paste, and then a dry white powder called superphosphate. Cooking time 1 hour.
Phosphorus fertilizers are effective on acidic soils (podzolic, peat). It is best to lay them in the holes when planting crops.
Phosphate fertilizers for cucumbers, tomatoes and other horticultural plant organisms are a vital composition of useful elements. When using them, you need to take into account the type of crops planted and the condition of the land on a particular site.
How to identify a phosphate deficiency
Liquid phosphorus, in the form of fertilizer, should be used to prevent deficiency of this element. Mild to moderate phosphorus deficiency is difficult to recognize. Plant growth can be slower than healthy plants without identifiable symptoms of phosphorus deficiency. A mild deficiency is often associated with a darker-than-usual bluish-green foliage.
In contrast to nitrogen deficiency, young leaves remain dark green at all levels of development. The first sign of phosphorus deficiency is premature aging of the leaves. In most cultivars, yellowing is preceded by the appearance of purple anthocyanin pigments causing a range of yellow tints in the leaves.
Necrotic lesions can develop in chlorotic zones, and necrosis spreads spots until the lamina is completely brown and dry. In some varieties, yellowness precedes necrotic lesions that appear on the green tissue of the leaf. Some varieties may develop purple pigmentation on the surface of young leaves.


The importance of phosphorus for plants
Phosphorus is essential for plant nutrition. He takes an active part in most metabolic processes - energy, metabolic, reproduction and division. Without it, the course of the processes of respiration, photosynthesis, fermentation is impossible. Helps regulate the permeability of cell membranes.
Phosphorus is especially needed for fruits and flowers, for example such decorative flowering as violets. It accelerates their formation, improves the decorative qualities of plants.
The root system ensures good branching and correct growth, as a result of which the plant acquires all the necessary substances in sufficient quantities. Increases cold resistance and lodging resistance.
Application technology for plants
There are three known options for the use of fertilizers:
- pre-sowing;
- pre-sowing;
- post-sowing.
Most used in the fall, as many of its varieties contain chlorine. The dosages are set taking into account the depletion of the earth.
It will be better if you scatter the fertilizer several times over the surface, maintaining a distance of fifteen centimeters from the roots. Liquid formulations work effectively, they should be prepared according to the instructions.
The supplement is really popular. It is only necessary to remember that an excessive dose of potassium or violations in the use of the composition harm not only plants, but also the soil composition. Particular care should be taken with formulations containing chlorine.
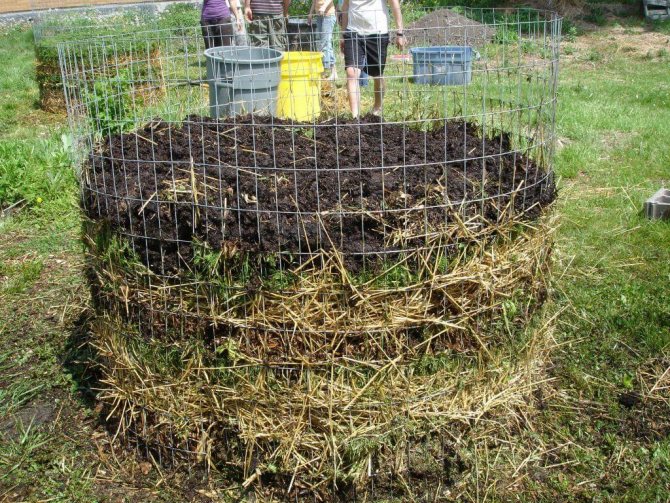
How to make the mixture yourself
For composting, ready-made additives with phosphorus and potassium are used. They are simply sprinkled with compost ingredients. Its basis is garden grass. It contains nitrogen and practically no phosphorites. But not all weeds are free of phosphorites. This will help give the compost natural plant matter.
Among the weeds, the most phosphorus is contained in the berries of mountain ash, wormwood, hawthorn, thyme, etc. With their help, you can make compost yourself, and the composition of the fertilizer will be completely natural and non-toxic to plants. Fertilization with phosphorus is not effective immediately, but such additives have a prolonged effect. If the plant develops fully, then it blooms in a timely manner, ripens and gives a bountiful harvest.
Now read:
- Planting to decorate the site with three types of conifers
- Effectively Get Rid of Whitefly Butterflies on Plants
- Choosing cucumbers for open ground according to your preferences
- Delicate, easy-care coniferous bushes in garden plots
About
Agronomist of the state agricultural enterprise "Garovskoye" of the Khabarovsk region of the Khabarovsk region.
Learn more about the composition of phosphate fertilizers
By enriching the soil with minerals and salts, plants receive the necessary nutrition for growth and cyclical development. Gardeners believe that, even overdoing it with the amount of the active ingredient, it is difficult to damage the plant. It will take from the soil as much as it needs. Fertilizers are divided into three categories: sparingly soluble, water soluble, and insoluble.
Those compositions that are difficult to dissolve should be used for an acidic substrate or chernozem. They should be used to enrich the soil in the autumn months. They are buried in the substrate.
Compounds that dissolve in aqueous media are more versatile. They should be applied to any soil and any plant. Insoluble compounds are diluted in water acidified with citric acid. They enrich any soil, but usually acidic soils are fed with them.
Top dressing with potash fertilizers by crops
Cucumbers
Cucumbers need potassium. Potassium-containing fertilizers are applied three times: the first time when sowing, the second time - when 2-3 leaves appear, the third time - during abundant flowering and the formation of ovaries.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes not demanding on potassium, prefer more phosphorus and nitrogen. Potash fertilizers for tomatoes are scattered along with sowing, after planting seedlings in the ground before flowering, a second top dressing is carried out. You can carry out one more dressing in the phase of fruit formation.
With a lack of potassium in tomatoes, corrugation and dome-shaped curling of the leaves are observed - "edge fuse". The fruits are covered with yellowish-bronze spots.


Lack of potassium in cucumbers and tomatoes
Grapes
Grapes picky about potassium. If grapes don't get enough potassium, they can pull potassium from older leaves, redirecting it to younger shoots. Fruiting bushes of grapes are annually taken for the growth and formation of fruits up to 10-12 g of potassium.
Impact of organic fertilizers on the soil
Top dressing of organic origin contains micro- and macroelements necessary for the full growth of plants and in the proportions required for them. The basis of such fertilizers are plant products that have undergone a certain processing. But these fertilizers are not recommended to be used in their pure form, this can lead to a burn of the root system. To maximize the benefits of organic matter, plants should be mixed with wood dust, husks, straw, or diluted with water before use.
When organic matter enters the soil, it enriches its structure with the necessary elements. These elements include:
- Nitrate nitrate, which is required by the plant for the development of stems and leaves. For the full assimilation of nitrogen, a sufficient amount of potassium is needed, which also enters the soil from these fertilizers.
- Due to the presence of potassium, the stems become strong during their development, and the plant bears high-quality fruits.
- The ability of plants to resist various diseases is provided by phosphorus. It is also necessary for the growth of the root system and flowering.
- So that the plant does not absorb nitrogen more than the norm it needs in the soil, the presence of calcium is necessary, which, in addition, ensures the speed of root development.
- Also, organic substances are sources of such important elements as copper, magnesium and iron, the lack of which is the cause of plant diseases.


Personal safety measures when working with mineral fertilizers
- Use protective goggles and gloves when working. For example, phosphate rock has a dusty composition - if it enters the respiratory tract, it adversely affects the mucous membranes. May cause burns to the skin.
- Wash tools thoroughly. After work, you should thoroughly rinse protective equipment, containers, tools with running water.
- Be careful when handling potassium nitrate. The chemical compound causes spontaneous combustion. Do not keep fertilizer near flammable substances or use fire nearby. Potassium nitrate is an oxidizing agent. Causes burns and ulcers on the skin.
- Always follow the directions for use. Excessive application of drugs leads to the concentration of chemical elements in the fruits of plants. This can adversely affect human health.
Characteristics and introduction of PKU
Superphos


Complex concentrated nitrogen-phosphorus, neutral granular fertilizer. Chlorine free. A complex of three components: precipitate, ammonium sulfate and ammonium phosphates.
The best application on sod-podzolic soils for feeding any plants. Fertilizer is applied before plowing and digging in the fall or when planting plants. It can also be used at any time of the year.
Potassium-demanding crops
Where is potassium found inside plants? "Favorite" areas are the cytoplasm and cell sap. Roots, seeds and tubers contain less mineral than young leaves and stems. If flowering plants are not fertilized, budding may stop or the flowers will be small.
With a significant lack of potassium, ovaries may not form at all. Particularly sensitive to the mineral content in the soil are: sunflower, buckwheat, beets, potatoes, carrots. Most cereals are not so demanding on the deficiency of potassium salts.
Testimonials
Maria, Moscow
I have never used fertilizers before, and did not understand how to achieve good harvest results. Then I bought ammophos fertilizer. The results were not long in coming. The growth went up the hill, the yield increased. Now I will continue to experiment with phosphate fertilizers.
Ivan, Moscow region
For a good harvest of potatoes, I constantly use superphosphate. I like this fertilizer because it is very easy to plant and it is enough just to water the bush. The price matches the quality. Satisfied with the result.
How to feed indoor flowers at home
The soil in flower pots depletes over time. Transferring plants to a new substrate requires a lot of time and experience. Feeding flowers at home is an excellent alternative to transplanting. They require additional care during flowering, because during this period the maximum of vitality is consumed. You can replenish them with the help of nutritional supplements that you can prepare yourself at home according to folk recipes.
Humus
Dung humus (humus soil) is formed from the excrement of domestic animals (cows, horses, pigs) and plant residues (leaves, stems, bark, fruit peel), which are re-heated in compost heaps under the influence of aerobic, anaerobic decomposition. This earthen mixture is an effective organic fertilizer, without which truck farming, horticulture and floriculture are unthinkable. Humus contains many micro-, macroelements and beneficial microorganisms important for plants.
It is used as one of the main components of the potting medium. It is readily available fertilizer, free of charge or requiring a minimum of material costs. It has no drawbacks, but the advantages are obvious:
- The soil is enriched with a complex of nutrients.
- Top dressing promotes rapid growth and abundant flowering of indoor plants.
- The heat capacity of the soil increases.
- The moisture content of the soil mixture increases.
- Heavy soil becomes looser, and light soil is bound by humus soil into a homogeneous substrate.


- Top dressing of tomato and pepper seedlings with folk remedies: fertilizers for a good harvest
- Mineral fertilizers for plants
- Eggshells as plant fertilizer
Sugar or glucose
Sugar is one of the most affordable and popular nutritional supplements for ornamental crops among flower growers. The glucose included in its composition is able to replenish the energy costs of indoor flowers, especially in the autumn-winter time with a short daylight hours. Sweet water prolongs the flowering period, the leaves of the culture acquire a richer color. Large ficuses, dracaena, roses are especially fond of a useful additive. To prepare a nutrient solution, dissolve 1 teaspoon of sugar (glucose tablet) in 0.5 liters of water.
This top dressing has one drawback: increased growth of pathogenic fungi and rot.To avoid this, experienced flower growers simultaneously use the drug "Baikal - EM 1". Microorganisms contained in it inhibit the action of harmful bacteria. When using sugar water, you need to adhere to the rules:
- You can use it no earlier than 2 months after the flower transplant.
- The soil should be well moistened before applying the nutrient.
- Water diseased cultures with a weakly concentrated solution (0.5 tablespoons per 1 liter of water).
- It is recommended to use the nutrient solution no more than once a month.


Watering indoor flowers with yeast
The yeast solution for indoor flowers acts as a natural growth biostimulant. Phytohormones and B vitamins contained in yeast promote active cell division of the plant organism. Once in the soil, the nutrient additive accelerates the breakdown of organic substances into inorganic ones, activates the activity of microorganisms in the substrate. In the process of chemical reactions, carbon dioxide is released, which contributes to the rapid absorption of glucose by the tissues of the root system.
To prepare a nutrient mixture, 10 g of yeast is dissolved in 1 liter of warm water, add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of sugar, insist 2 hours. Sugar-yeast solution is used once every three months. It is not used in winter because most plants are dormant. Ash (5-10 g) or 1 g of potassium sulfate are an excellent addition to yeast solution. They are added so that the soil does not lose potassium and calcium under the influence of yeast fungi.


Onion peel
A medicinal and nutritional supplement for indoor plants is an infusion of onion peels. It is rich in B vitamins, carotene, trace elements and phytoncides. Onion infusion has the following beneficial qualities:
- promotes the rapid assimilation of nitrogen and sulfur;
- protects the plant from rot, pathogenic fungi and other diseases;
- normalizes redox processes in the plant organism;
- when planting strengthens weak shoots;
- stimulates flowering.
The tool is used for watering and spraying all indoor crops, except for succulents and ficuses. You can feed the culture in this way no more than 1-2 times a week. To prepare a biostimulant from onion peel, you need:
- Pour 50 g of raw materials with boiling water.
- Cook for 10 minutes.
- Infuse the broth for 3 hours.
- Strain.


Slept coffee
An excellent bioactive additive for ornamental plants is coffee grounds. All you need to do is pour the cooled gruel into a flower pot and loosen the soil. Coffee contains calcium, potassium, magnesium, nitrogen, phosphorus. Coffee grounds are an excellent baking powder, but you need to use it wisely. You should not send all the drunk coffee to the flower pot. This dressing is not suitable for all colors, but only:
- azaleas;
- begonias;
- ferns;
- roses;
- lilies;
- coniferous crops.


Citrus or banana peels
To increase the immunity of plants and activate their growth, once a month, you can use fruit water for irrigation. It compensates for the lack of trace elements and enriches with vitamins. At home, you can prepare a citrus cocktail dressing:
- Chop the orange (tangerine) zest.
- Fill 1/3 liter jar with it.
- Pour boiling water over.
- Insist content for 24 hours.
- Take out the cake.
- Top up the jar with settled water.
Banana peel infusion has the same effect. It is prepared according to the recipe described above. Banana peels are an organic fertilizer rich in potassium and trace elements. In a crushed and dried form, they are added to the soil mixture before planting. You can also combine beneficial ingredients to obtain a nutritional supplement:
- Grind banana peels and orange peel.
- Fill a third of a three-liter jar with ingredients (1: 1).
- Fill the container with warm water.
- Add 2 tbsp.tablespoons of sugar.
- Infuse the contents for 3 weeks, shaking occasionally.
- Strain.
- Keep refrigerated.
- Dilute the top dressing with water 1:20 before use.


Ash
Wood ash is an organic food containing many useful substances. She is able to saturate indoor plants with potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, zinc. Ashes are laid in the soil during the preparation of the substrate or used for watering flowers (1 tablespoon per 1 liter of water). It can disinfect the transplanted culture because it has antiseptic properties. The liquid version is used for foliar feeding - irrigation of green mass (except for leaves covered with villi and flowers).


Aquarium water
Do not pour out the green water when cleaning the aquarium. It is a source of large amounts of organic matter. Aquarium water is a bioactive additive that is especially useful for indoor plants in the spring, when many of them wake up after winter rest. You can use it no more than 1 time a month, so as not to provoke the reproduction of microscopic algae in a flower pot. Aquarium water is suitable for all indoor flowers without exception.


Amber or citric acid
Succinic acid is a natural substance obtained from amber. It is not a nutrient, but it promotes the absorption of microelements from the soil by plants, and has a strengthening effect on the plant organism. The use of a solution of succinic acid for indoor flowers has the following advantages:
- stimulates growth;
- when irrigated, it dissolves whitish calcium bloom on the leaves;
- gives the foliage a rich green color by accelerating the production of chlorophyll;
- activates the ejection of peduncles and the opening of buds;
- promotes seed germination;
- accelerates the rooting and adaptation of the plant after transplantation;
- normalizes the acidic environment of the substrate;
- neutralizes pathogenic microflora in the soil.
Succinic acid can be purchased in pure form (crystals) and as a pharmaceutical preparation (the tablet contains 0.1 g of active ingredient and 0.5 g of talc). To prepare an amber solution, you need to dilute 1 g of crystals in 5 liters of water (1 tablet per 1 liter). The solution is used for irrigation. Such feeding is best perceived by begonias, citrus fruits, ficuses, chlorophytum. It should be used no more than 1 time per month. For fat women and cacti, a solution of succinic acid is used once every 3-4 years. For spraying green mass, the concentration of amber water is reduced by 2 times.
- How to water flowers and houseplants
- Succinic acid for indoor plants: application
- Fertilizer for feeding strawberries
Lemon contains 8% citric acid and many vitamins. For foliar feeding, add 1 teaspoon of lemon juice to 1 liter of settled water. Irrigation with a solution of leaves will remove calcium deposits from them, saturate them with vitamins and microelements. It is recommended to spray the leaf plates on both sides with acidified water no more than once a month.


Features of PKU application


Application rates depend on many factors. In this case, the average recommended doses can be:
- for potatoes 20 g;
- for a tomato 20 g;
- berry bushes (raspberries and blackberries) 35 - 40 g per square meter;
- trees 70 - 90 g per trunk circle;
- berry bushes (currants and gooseberries) per bush 65 - 70 g.
Complex phosphorus-potassium fertilizers can be explosive and require special handling.
They are stored in dry, cool stone rooms at a temperature not exceeding 30 degrees and an air humidity of not more than 50%. The shelf life is no more than six months.
Manifestation of lack of phosphorus
Phosphorus is one of the most important elements of this living thing. Without this element, the plant will not be able to participate in the process of photosynthesis. Also, phosphorus is part of the nucleus of the plant, and its plasma. The main indicators of phosphorus deficiency in plants are:
- The color of old leaves turns purple;
- Dark spots appear on the leaves;
- Flowers and shoots are deformed;
- Seeds germinate slowly;
- Leaves dry, especially not at the tips.


Also, due to the normal amount of phosphorus, the plant can fully feed and absorb moisture. If we talk about root crops, phosphorus is a key element in the formation of fruits.
In order to avoid the lack of nutrients and trace elements, any plant needs timely feeding. For each plant, you need to select your own complex of fertilizers, taking into account their characteristics. Timely fertilization can increase yields and save crops from possible diseases.