Bordeaux liquid is an effective broad-spectrum cellular poison against fungi and bacteria that damage plants. The effectiveness of Bordeaux liquid has been tested by more than a century of experience. Bordeaux liquid is a preparation for immediate use: during its preparation, the main compounds of copper sulfate CuSO4 and calcium oxide hydrate Ca (OH) 2 (lime) are formed, see fig.
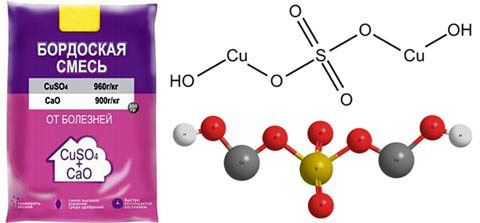
Formation of the active principle of Bordeaux fluid
The CuSO4 + Ca (OH) 2 complex adheres well to the plant and gradually decomposes in the air, releasing the active principle - Cu ++ ions. After 2 weeks, there is no active copper in the plant; sulfur and calcium are partially absorbed by it, and partially washed out. Therefore, Bordeaux liquid is applicable for both prophylactic (eradicating) and current medical treatment of diseased plants. The multiplicity of processing with Bordeaux liquid per season can reach 6 times without compromising the consumer qualities of the crop, which allows you to fight plant diseases flexibly and quickly. But the advantages of Bordeaux liquid are fully manifested only with its correct preparation and application, in which inexperienced summer residents and in general small private farmers make many mistakes, and even describe them on amateur forums and show them on YouTube. This article is intended to help beginners figure out how to make Bordeaux fluid and how to handle it.
Note: free 2-valent copper is a strong poison and for warm-blooded animals, incl. and for you and me. Therefore, you need to use Bordeaux liquid with all the necessary precautions, see below.
Abiga Peak
Abiga Peak is perhaps the most common contact fungicide. It earned its popularity with a wide range of actions. Thanks to copper oxychloride, which is part of its composition, the drug copes well with a large number of infections caused by fungi. It does not cause resistance, it can be used in various conditions, including at home.


Abiga Peak
The drug is produced in the form of a suspension, which is easily diluted in water. Diseased indoor plants are recommended to be sprayed with Abiga-Peak fungicide 3-4 times with an interval of 10 days. To prepare the solution, you will need 5 ml of the product per 1 liter of water. Preventive treatments should be carried out before flowering plants.
What is insecticide?
Insecticides are chemical or biological agents that kill insect pests. Biological agents are not as dangerous. Any insecticide must be tested on one plant before use. If after 24 hours the condition of the flower has not become worse, then you can use the product on all plants of this variety. So that the plants do not become addictive, it is advised to alternate insecticides for indoor plants.
Process all plants, making sure to follow safety precautions. It is necessary to wear at least a respirator when using insecticides, since the drug is very quickly absorbed into the blood through the lungs. Read the instructions carefully and follow them when using the drug.
Oxyhom
Another widely used copper-containing fungicide. In addition to copper hydroxide, manufacturers included a new agrochemical, oxadixil.Due to this combination, the drug received not only contact, but also systemic action. By acting on pathogens, it simultaneously destroys them and suppresses cell division, which stops the development of spores. The pesticide is a fast-acting substance (the effect on the infection begins already in the first 2-3 hours), while it has a long-term prophylactic effect.


Oxyhom drug
Produced by Oxyhom in the form of a wettable powder. For spraying indoor plants, a solution of 2 g of the agent is usually used per 1 liter of water; to treat a red bulbous burn (amaryllis, hippeastrum), 2 times more of the drug will be required. Processing is carried out up to 3 times every 10 days. Since copper hydroxide tends to settle, the finished liquid must be periodically stirred during the procedure.
Classification of drugs
Fungicides are divided into several groups, due to differences in chemical characteristics, principle of action and method of distribution.
By chemical properties
According to their chemical characteristics, fungicides are:
- Organic or biological. Produced on the basis of nitrogen-containing compounds. There are no heavy metals in the composition, due to which the funds are rather unstable. They dissolve quickly in water and do not stay in the soil for a long time.
- Inorganic or chemical. They consist of chemicals: sulfur, copper, mercury, etc. The effectiveness of their use is associated with long-term accumulation in the soil.
By the nature of the action
According to this criterion, drugs are classified into:
- Immunizing. Once in plant tissues, active components change metabolic processes and prevent the occurrence of fungal diseases.
- Protective. They are used for prophylaxis during periods when the risk of infection with pathogenic fungi is especially high. The products protect crops and help increase yields.
- Medicinal. They are relevant in cases where the first symptoms of a fungal disease are observed. The active components contained in the preparation violate the pathogenesis of the disease and contribute to the early recovery of the plant.
By way of distribution
As a rule, according to the method of distribution, these funds are classified into:
- Systemic. Penetrating into plant tissues, the active substances spread very quickly, gradually destroying pathogenic bacteria. Some drugs are used for prophylactic purposes, but most of them are aimed at treating an existing disease.
- Contact. They act on a pathogenic microorganism superficially, without being absorbed into plant tissues. Contacting with the active substance, the fungus dies, being in the "embryo" phase.


Spraying fungicide in the greenhouse
Vectra
For protective and therapeutic action, contact-systemic fungicide Vectra is also used. The pesticide contains dichlorophenyl and triazole. The active substances stop the further development of the infection, drown out the sporulation of pathogens and heal plants. The drug is low-toxic and economical to use.
The agrochemical is supplied on sale in ampoules of 2 and 5 ml of a ten percent suspension concentrate. For home use, dilute 1-1.5 ml per 5 liters of water. Treatment is carried out by spraying 3 times every 10 days.
Ant remedies


The drugs can be used to get rid of garden pests and ants that have bred in the house.
Muracid
It is an emulsion, which is watered in a diluted form on an anthill. For enclosed spaces, bait is made by mixing with sugar.


Thunder-2
Small granules of the substance are scattered over the soil surface; 2 - 3 cm of the top layer of the soil is removed beforehand. Dangerous for fish and birds.
Anteater Super
Highly effective bait for garden and red house ants. It is used dry and as a paste.To prepare a paste, a few drops of water are added to the granules.


The industry produces a wide variety of products for all types of pests. They should be used strictly in accordance with the instructions, not forgetting about personal protective equipment.
Vitaros
This contact-systemic fungicide is used only for prophylactic treatment of seeds, bulbs, tubers and other planting material. Thiram and carboxin, the main substances of the drug, provide growth-regulating and long-lasting, up to six months, protective action.


Fungicide Vitaros
The product is available in the form of a concentrated suspension in 2 ml ampoules and in vials with a volume of 10 to 100 ml. The biomaterial soaking procedure takes 2 hours. To prepare the solution, 10 ml per 5 liters of water is required. Thanks to the bright dye included in the pesticide, the processing process is noticeably easier.
The use of Vitaros in the treatment of orchids
The treatment with Vitaros common for all plants is not suitable for delicate orchids, since the maximum possible exposure of these flowers in the working solution is no more than 10 minutes. If foci of infection with Alternaria or phyllosticosis are found, the damaged areas are smeared with a fungicide solution, and they also come with rhizomes when black rot appears. In cases where the infection has spread over most of the plant, but the root system can still be saved, the root is cleaned of diseased areas and planted in fresh soil, after spilling it with a solution of the drug.
The principles of drug selection
Before purchasing this or that drug, you need to determine:
- the area of the lesion;
- type of plant culture;
- the degree of damage;
- the level of toxicity of the agent.
Some types of fungus are capable of forming a kind of immunity to one or another component of the fungicide. Therefore, long-term use of the drug becomes practically useless. To prevent this from happening, fungicides must be replaced periodically.
Discore
A systemic chemical fungicide is actively used in indoor floriculture. Its active ingredient, difenoconazole, has a high degree of activity and quickly suppresses the vital processes of pathogens. The drug can be used at any stage of plant development, including during the period of swelling of the buds and during flowering. Depending on the infection, treatment is possible by spraying and watering the soil. Also, seed dressing is recommended as a preventive measure and to increase germination.


Discore
Discor is produced for home use in the form of an emulsion concentrate, with a volume of 2 and 10 ml. For spraying in the treatment of most diseases, 1 ml of the product is enough for 5 liters of water, for combating gray mold - 2 ml, and for bacterial spots, 2.5 ml is required for the same volume of liquid. The repeated procedure is carried out two weeks later, reducing the concentration of the solution by 2 times.
Houseplant pests
Midges or sciarids (mushroom gnat)
Small insects, they grow in pots in winter when the flowers are less watered. Adult midges lay their eggs in the ground, from which larvae hatch, which eat the roots. For prevention, water the plants as the flower requires, do not water very often. Fertilize plants with tea leaves, there is tannin in it, which destroys sciarid larvae and eggs. Be sure to repot the flower every 3 years.
How to save flowers from midges... Transplant the plant into new soil, first thoroughly washing the roots of the flower. Stick 6 matches into the ground with sulfur heads. Water the pots, then the sulfur will be absorbed into the soil, and will destroy the sciarid larvae. You can also water the flowers with a solution of soap or potassium permanganate. Since midge larvae mostly grow in moisture, reduce watering. This method is suitable for succulents, cacti.Cover the top with ash or calcined sand. When transplanting a plant, pour boiling water over the soil.
Mealybug
People also call the pest "hairy lice", as the insect emits a waxy substance similar to cotton wool. The photo shows that the adult worms are oval and slightly crimson in color. Adult larvae gather on young shoots, below the leaves and buds, they suck out the juice, because of this, the flowers grow very slowly.


Adult worms move quickly, their eggs are placed in a pouch that resembles a piece of cotton wool. The pest secretes honeydew, on which a sooty fungus appears afterwards. Inspect the flowers periodically and water them systematically, as the worm grows in dry places.


How to get rid of a mealybug... When you see a diseased plant, isolate it, tear off the infected leaves. If the plant just got sick, then you can moisten a cotton swab in soapy water, wipe the leaves, as well as the gaps between the trunk and the leaves. Then spray with a solution of 10 g of green soap per 1 liter of water. After a week, repeat spraying. And after another 7 days, spray again. Can be sprayed with tobacco or garlic infusion, cyclamen broth. Spray the plant with insecticides or lepidocide.
Indoor aphid
Aphids are small insects that suck the sap of plants with their proboscis. There are 4000 species of aphids. Pests are 2-3 mm in size, but they are larger up to 5-6 mm. They come in red, green, brown and black. Aphids can be easily seen, they are found on flowers and leaves. In flowers affected by aphids, the shoots are deformed, the leaves dry, and shrink. Honeydew is also visible - secretions from aphids.


It is recommended to ventilate the room and light the plants well. It is necessary to pinch off the damaged leaves. Flowers need to be examined carefully. Water the plant with a shower.
How to get rid of aphids... If you see an infected plant, separate it from the healthy ones. Treat the flower with a soap solution. Spray the plant regularly. If there are a lot of aphids, then the plant needs to be treated with insecticides.
Spider mite
Ticks are very small insects up to 1 mm. Red spider mites appear on indoor flowers, they are located on the underside of the leaves.
Adult females can lay hundreds of eggs in their lifetime. Eggs lie for up to 5 years, after which ticks appear, so you need to fight them. In diseased plants, small white dots are visible on the leaves, after which the leaves dry out and fall off. Some types of mites lay a thin cobweb.
How to protect flowers from spider mites... You can spray with water, then pollinate the flowers with pyrethrum powder or ground sulfur. To fight the plants are sprayed with "Intavir", "Derris", "Fitoverm", "Fufan", "Aktellik" and "Karbofos".
Whitefly
This is a medium-sized yellowish moth, it carries viral diseases. Its larvae appear from the bottom of the leaf as small grains, they are oval-oblong and light green in color. Insects suck the juice, the leaves turn yellow, fall off. After them, sugary secretions remain, and a sooty fungus soon appears on them.
How to save flowers from a whitefly... You can try to catch adult butterflies by hanging fly sticks near the flowers. Thoroughly rinse the leaves of the diseased plant to rinse off the larvae and eggs. Spraying with a solution of 10 g of green soap per 1 liter of water helps. Do this 3-5 times a day.
The plant then rests for 6 days. After spraying is repeated. Garlic solution works well. The whitefly is destroyed with a solution of 3 cm³ "Nicotine sulfate" per 1 liter of water, "Parathion" 1 cm³ per 1 liter of water, sprayed once every 3 days.
Beetle "grape elephant"
The beetle has a long proboscis, eats leaves, the larvae are in the ground. Most of the beetles appear on cyclamens and primroses. Creamy larvae are up to 2.5 cm long and eat tubers and roots.
The beetle loves to settle on maiden beauty (fuchsia), begonias, ram (primrose), cyclamen.The indoor flower withers, its leaves droop and fall. It is possible to determine that an adult beetle is present on the plants by the holes in the leaves, damaged edges, wilted buds.
How to destroy the "grape elephant"... The land is treated with insecticides: Fitoverm, Aktelik, Aktara. Pour gravel on the ground with a layer of 2 cm so that the beetles do not get to the ground. Beetles do not fly or swim, so you can put a diseased plant in a pot of water.
Drosophila. These are very small brown midges, about 2-3 mm, appear on rotten plants. They transfer pathogens. They can appear on perishable foodstuffs. Airing the room in winter helps. The soil is watered with any available insecticide.
Shields
Small insects up to 5 mm, covered with a shield, they feed on sap.
How to save flowers from scale insects... Sick flowers isolate. Wipe the leaves with a cotton swab smeared with insecticide made from 2 ml of Actellic per 1 liter of water.
After the flowers are treated with soapy or tobacco solution. Then rinse the solution. At the end of the procedure, spray the flowers and soil again with insecticide. Wrap the plants in polyethylene. After 30 min. remove the film. After 3 days, rinse the flowers with warm water.
Thrips
Very small insects on the inside of the leaf. White dots are visible on the outside of the sheet. First, yellow or whitish spots, stripes appear on the flowers, then they merge. The leaves wither and fall. The flowers are falling. If there are many thrips, you will see “silvery” parts on the plant.
How to deal with thrips. You need to wipe the flowers with a soap solution. Then wash the plant in the shower. Dissolve 2 ml Fitoverma in a glass of water. Treat the flower, then put a plastic bag over it, remove it after 24 hours. Alternatively, dilute 2.5 ml of Vermitic in a bucket of water (10 l). Spray the flower, put on the bag, you can take it off after 24 hours.
Nematode
These are white worms 0.5 mm long, are in the ground, feed on juices. The nematodes that form cysts burrow into the roots and attach to them. After fertilization, the body of such females becomes a cyst, that is, a reservoir with eggs. Free nematodes can crawl along the roots. Gall nematodes crawl into the rhizomes, they secrete galls - thick nodules on the roots, in which they live and reproduce.
How to save flowers from nematodes... The diseased plant is isolated. The earth is heated for 10 minutes. in a water bath at a temperature of + 55C. In order to kill nematodes, 1 tablet of "Decaris" is placed in 1 liter of water and the flower is shed 4 times.
Fitosporin-M
Systemic fungicide Fitosporin-M refers to drugs of biological origin. The waste products of Bacillus subtilis, which constitute the active ingredient of the pesticide, inhibit the multiplication of pathogens that cause diseases. The breadth of application of biofungicide is noted by both gardeners and home gardeners. At the same time, it is low-toxic to humans and animals and is absolutely non-phytotoxic. It is possible as spraying plants in any growing season, and watering for soil treatment, and soaking before planting seed and root system of seedlings.


Fitosporin
Three forms of the drug are available, differing in the number of bacteria per unit of substance and solubility in water.
- The powder has the largest number of spores and living cells, but it does not dissolve well, requires preliminary soaking 1-2 hours before processing. For prevention, spraying is performed with a solution of 0.5 teaspoon (1.5 g) per 2 liters of water, for treatment: the same amount of the drug, but for 1 liter of water. For soaking and watering, dilute 2 grams in 1 liter of water.
- The biofungicide is easily diluted in a pasty form, but it has the lowest bacterial titer. For watering the soil for 1 liter of water, 15 drops of the substance are used, for spraying - 10.
- The middle between the two previous forms is an aqueous suspension, which has a softer effect on plants. The solution for all types of its application will be the same: 10 drops of fungicide in 1 glass of water.
About the sprayer
On-call professionals spray Bordeaux fluid from a conventional electric pneumatic sprayer. It does not burn them - the electricity is the master's, and the increased wear of the apparatus is included in the processing cost. But it is expensive for a summer resident or small private owner to buy a new sprayer every 2-3 years.
The point here is that atmospheric air is pumped into the tank with the working substance. Under the influence of oxygen from it, the nanoparticles of the suspension very quickly aggregate (stick together) into larger lumps, which wear out the sprayer. Therefore, it is necessary to process plants with Bordeaux liquid from a gas sprayer, where the pressure in the tank is created by carbon dioxide. By the way, it also increases the effectiveness of literally all liquid agricultural chemicals due to the absence of the same oxygen under pressure.
A gas sprayer can also be made with your own hands from a plastic tank with a sealed lid for 1.5-2 bar overpressure (PE wall thickness - from 2 mm) and a fitting for a household carbon dioxide cartridge. Such cartridges are used to saturate soda in siphons, and in ship and aircraft modeling - to drive micro-pneumatic motors. The fitting itself is a steel conical hollow needle (the cone is very shallow) and a holder for a cylinder with a threaded plunger cap. When the cap is screwed on, the cylinder is pierced with a soft alloy stopper on the needle, the gas flows from the tank - that's all.
Note: the sprayer is more powerful for a larger area, you can use a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher for 0.5-2 kg of solid carbon dioxide (dry ice).
Baktofit
Biofungicides include a broad-spectrum drug "Baktofit". Its active ingredient is Bacillus subtilis strain IPM 215. The bacterium is also called "hay stick" in another way. She produces an antibiotic, which becomes fatal to pathogenic fungi. But this requires certain conditions. The air temperature should not exceed + 25 ° С, and the microorganism needs additional nutrition, which can be applied in the form of mulch, for example: crushed bark or wood chips. Also, the bacterium does not tolerate chlorine, therefore it is recommended to let the tap water settle before use.


Baktofit
The preparation is produced in the form of a powder and a suspension concentrate. For watering indoor plants, the solution is prepared in the ratio: 3 ml (1 g) of fungicide per 1 liter of water. For spraying against various stains, 1 ml (1 g) per liter of water is used for the working fluid. The procedure is repeated up to three times with a frequency of 10-12 days.
Precautions
Copper as a trace element is essential for all living organisms. But free copper in a concentration slightly higher is a strong poison. Although copper as a toxin is not cumulative, like all cell poisons, it has long-term systemic effects. Therefore, it is necessary to work with Bordeaux liquid and any other copper preparations in compliance with the entire set of precautions.


Precautions for handling Bordeaux fluid
The young people on the left in fig. simply ruin their health - for the future. When spraying Bordeaux liquid, a complete set of PPE must be used. A respirator mask often comes with a sprayer, but a vapor-proof coveralls (center in the picture) are not cheap. It can be replaced with a plastic raincoat (right), tight-fitting shoes for trousers outside and latex gloves for long sleeves. Work clothes should be stored in a separate non-residential area (for example, a utility block); in the same place and change clothes. In addition, in the processing area there should be no strangers (especially children), and the employee there must not eat, drink, smoke and take off PPE while standing upwind from the treated plants: the wind must blow from him to them.
If signs of copper poisoning are noticed: nausea, headache, fever, fever, tachycardia, nosebleeds - you need to immediately stop work, drink 1-2 liters of a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate or just warm water and induce vomiting. Then drink a glass or two of warm milk (preferably with honey), and consult a toxicologist. To avoid the long-term consequences of systemic poisoning, systemic treatment with special medications is also required.
Agat-25K
Biofungicide "Agat-25K" can be called a drug of multisystem action. It was created on the basis of the waste products of the bacteria Pseudomonas aureofaciens H16, in addition, the manufacturer added bioactive substances, micro- and macroelements, active fractions of coniferous extract to the composition. Thanks to this complex of components, the immunity of plants increases, due to which resistance to infection is developed, as well as the growth of crops is activated and their resistance to unfavorable factors increases. The fungicide is safe for both humans and animals, and the environment, has a beneficial effect on the root zone, acting as a fertilizer. The drug combines well with other agrochemicals, and when used together with herbicides, reduces their negative effects.


Agat-25K
In the retail network, the agent is presented in a dark-colored pasty form, placed in a syringe with a measuring scale. The solution is prepared in two stages, first the required amount of biofungicide is diluted in a small amount of water, then the resulting liquid is added to the filled sprinkler. To treat indoor plants for 10 liters of water, only 3 g of the drug is required. Spraying is carried out 2 times a month.
The table below shows the most common fungal diseases, the houseplants they attack, and the most popular fungicides.
| Disease | Plants | Fungicides |
| Alternaria and dry spot | Hybrid petunia; Pelargonium; Gerbera; Zinnia; Orchids; Dracaena | Abiga-peak, Oksikhom, Vitaros, Agat-25, Baktofit |
| Downy mildew (Peronosporosis) | Bulbous plants; Roses; Wisterias; Begonias; Palms and other monocots; Saintpaulias and plants with dense pubescence | Abiga Peak, Oxyhom |
| Powdery mildew | Laurel; Saintpaulia; Gloxinia; Roses; Gerberas; Kalanchoe | Vectra, Oxykhom, Vitaros. Prevention: Fitosporin-M |
| Septoria | Hydrangeas; Anthurium; Rose flower; Rhododendron; Azalea; Small-leaved carmona | Abiga peak, Discor, Vitaros |
| Gray rot | Decorative ferns; Asparagus; Homemade chrysanthemums; Eastern hyacinth; Myrtle tree; Monstera; Ficuses; Flower Male happiness; Spathiphyllum; Gloxinia; Violets; Cyclamen; Begonia | Fitosporin-M |
| Leaf rust | Gerberas; Fuchsia; Carnation; Cyclamen; Pelargonium; Rose flower; Geranium; Chrysanthemum; Asparagus; Citrus bushes; Palms of different types | Abiga Peak, Vectra, Oxyhom. Doesn't help: Fitosporin-M Baktofit |
| Phylosticosis (brown spot) | Hibiscus; Roses; Orchids; Begonias; Dracaena | Vectra, Abiga peak, Discor, Vitaros |
| Root rot | Orchids; Saintpaulia; Cactus | Baktofit, Oksikhom, Vitaros |
| Mottling | Any indoor plants | Prevention: Fitosporin-M, Baktofit. Treatment: Abiga peak, Oxyhom, Vectra, Vitaros |
| Black spot | Palm trees; Orchids; Camellias; Anthuriums | Abiga Peak, Vectra, Oxyhom, Vitaros |
| Verticillary wilting | Chrysanthemums; Hibiscus | Vectra, Agat-25K |
| Fusarium (Fusarium wilt) | Orchids; Begonias; Fuchsia; Balsam; Azalea; Pelargonium; Chrysanthemum; Cyclamen | Vectra, Vitaros |
Plants insecticides
Black henbane... The flower is poisonous because it contains alkaloids. The roots and leaves of an annual plant are the most deadly. They are harvested in early spring or autumn. The two-year-old henbane is completely poisonous and is harvested when it blooms. Belena must be hung up to dry. 100 g of crushed henbane are poured into 1 liter of water.If dried leaves and rhizomes are available, then pour 50 g in 1 liter of water. Leave for 12 hours, then filter. Pour 4 g of soap per 1 liter of infusion. Other plants are pollinated with dried henbane powder.
Marigold... An infusion from aphids is prepared from them. Dry marigolds are ground, poured into a bucket of warm water, left for 48 hours, filtered. Pour 40 g of soap. Sprinkle flowers.
Datura ordinary... It protects against aphids, herbivorous bugs, suckers, spider mites, cabbage moths. When flowering, the aerial part or leaves, buds, flowers are cut off. Dry by hanging in the air. 100 g of dry crushed henbane are poured into 1 liter of water and left for 12 hours. Pour 4 g of soap into the strained infusion.
Bulb onions helps to get rid of copperheads, spider mites, aphids. The scales are cut off from the onion, 1 liter of water is poured into 20 g. Water the flowers three times every 5 days.


Garlic destroys ticks, aphids, sawflies, lungwort. Grind 100 g of garlic, add 1 liter of water, mix. Add water to 2 liters. Then, when spraying, 0.3 liters of the resulting composition are further diluted with 10 liters of water. Flowers are processed after 3 days.
Dalmatian and Caucasian chamomile... It is used to kill aphids, leaf-eating caterpillars and ticks. The substances do not have a harmful effect on humans, mammals and birds, but they kill insects. The baskets of the Caucasian chamomile are robbed when it blooms. Dalmatians collect stems, inflorescences, leaves. They are poured in a layer of 2 cm and dried, stirred every day. Dry parts of chamomile are ground into powder.
For Dalmatian chamomile, use 1 part of inflorescences and mix with 2 parts of dust or chalk, kaolin. For Caucasian chamomile, take 1 part of the flower and 1 part of the filler: chalk. After that, 200 g of powder is poured into a small amount of water and a bucket of water (10 l) is poured. After the plants are sprayed.
Yarrow... Destroys aphids, spider mites, honeydews, leaf-gnawing caterpillars, thrips. When the plant blooms, the aerial part is cut off. Yarrow is dried and crushed. 80 g of dried herbs are scalded with boiling water, 1 liter of water is poured, and left for 36 hours.


Creeping gorchak... Kills aphids, ticks. At the beginning of flowering, bitterness is harvested, dried, and crushed. In 200 g of bitterness add 1 liter of water, then wait 2 days.
Plant treatment recommendations
With the introduction of effective insecticides into practice, the fight for the health of window residents has ceased to be futile. A well-chosen preparation will completely rid indoor plants from insect pests in a matter of days. The main thing is to observe the following rules:
- strictly follow the instructions when preparing working solutions;
- process plants with fresh mixtures;
- buy funds from trusted suppliers;
- do not use expired insecticides.
Bordeaux liquid
This fungicide was included in the list of the most powerful drugs against pathogenic microbes and fungi. It can be purchased ready-made, or you can cook it yourself.
To do this, in separate non-metallic containers, pour 300 g of quicklime and copper sulfate with boiling water (not steep). Then, in each bowl, bring the composition to the required volume (up to 5 liters) using cold water.
After filtering the lime solution through a gauze folded in several layers, slowly add the contents of the second dish to it. The result should be a bright blue 3% mixture with active copper and acid-neutralizing lime.
Be careful: Failure to keep the proportions will harm the plants. For example, if you do not add lime powder, the flowers will get severe burns after being treated with this remedy.
The given ratio of components is intended for volumetric foci of infection. At the initial stages of the disease, it is recommended for flowerpots to prepare Bordeaux liquid in a ratio of 100 g: 100 g: 10 liters.
If after processing the solution remains, it can be stored for 24 hours by adding a teaspoon of sugar (10 liters).
Orchid infectious diseases
It is very interesting to listen to experts and flower growers about the proper care of orchids. And how to deal with various diseases of these plants. But how do orchids cope with such a horde of sores in real habitats? Or are there fewer of them? After all, the conditions are natural.
We ourselves are mostly the culprits of their diseases... I overflowed, then underfilled. Hot and cold.


The main cause of illness is improper care.
The main reasons for the appearance of fungal diseases of orchids:
- Root damage. As with transplants. So it is with different pests;
- Excessive watering and moisture stagnation;
- Poor ventilation of the room;
- Supersaturation with nitrogen fertilizers;
- Poor quality substrate. Especially its salinity;
- Inadmissible lowering of soil temperature;
- Lack of trace elements that provide protective functions of plants.
All parts of the plant can be affected by infections. Regular inspection of plants allows you to discover in a timely manner that not everything is in order with the plant.
Leaves can signal this:
- Darkening;
- Drying out and stains;
- Bumps and swellings.
A close inspection of the transparent containers will help determine the health of the root system. Most often, at home, you have to deal with infectious diseases of orchids, which we will discuss below.
Various rot
Gray
Gray rot more often appears on adult plants in the form brown spots on flowers... Stagnation of cool and humid air is most conducive to the development of fungi of this disease. In the autumn or spring.
Infection occurs fairly quickly: 12-15 hours is enough for other nearby plants to get sick.
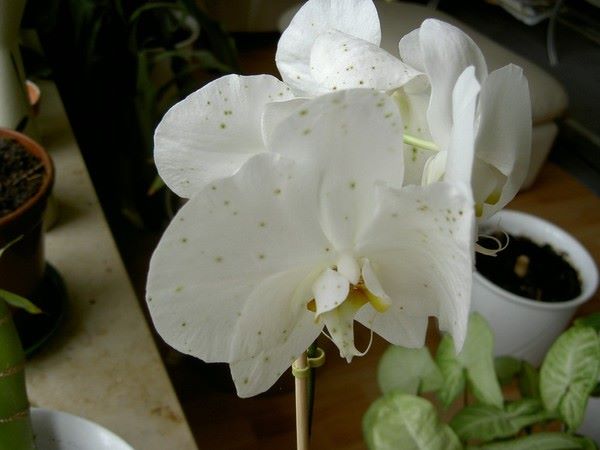


Gray rot.
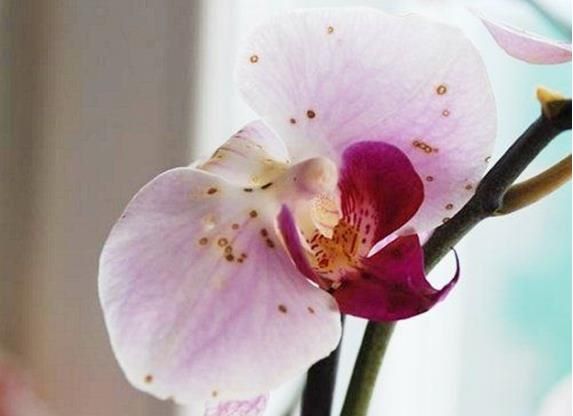


Black rot
The appearance of this disease in an orchid is very promoted by pests (scale insects, aphids, scale insects). And high humidity, oversaturation of nitrogen in the soil only helps its spread.


Black rot.
Anthracnose
Distinct small, rounded brown spots on leaves... It is they who testify to the disease of the plant with anthracnose:


- In the future, the leaves are covered with black bloom or mold with a pinkish tinge;
- The affected area is rapidly expanding. If delayed with treatment, they can both join and form dents;
- High humidity and stagnation of moisture in the axils of leaves and cores of pseudobulbs can be the cause of the disease;
- Miltonia, Oncidium, Pafiopedilum, Phalaenopsis are more often ill.
Powdery mildew
She is characterized by white coating of leaves and buds... As if flour were sprinkled on top:
- If you do not take action, the plant may die;
- Greenhouse conditions (high humidity and high temperature) of the content can most often be the cause of the development of this disease;


- Affects most indoor orchids.
Fusarium
Dangerous disease of orchids with fungi of the genus Fusarium. There are root and stem forms:
- More often, infection can come from newly acquired plants or seeds;
- It all starts with reddening of the roots;
- Then depressions appear. The roots darken and begin to rot.


Fusarium.


Very important! The effectiveness of treatment depends on early detection and timely action. And the correct use of the remedies. A diseased plant must be removed from other flowers without delay.
Insecticide groups by chemical composition


The above substances are used as a preventive measure, active extermination of parasites, in the cultivation of the vast majority of crops, flowers, trees. The insecticidal effect has a detrimental effect on parasitic insects that oppress vegetation, which can destroy most of the crops.Almost all means belonging to the new generation affect individuals that have already grown, their larvae, eggs, and fight bedbugs.
The composition is selected individually each time. It is important to consider:
- type of insects;
- their number in the treated area;
- saturation of the solution with active ingredients;
- place of application.
Those gardeners who have struggled with a similar problem and have successfully dealt with it will help to choose the most effective substance.
Consider the most commonly used pest control products:
- Aktara is a systemic agent, contact action, the main component of thiamethoxam. Form - soluble granules, ready-made solution. Helps against a wide range of pests. Resistant to the sun and rain.
- Actellic is a class 2 agent with pirimiphos-methyl, contact effect, penetrates the leaves. The efficiency of treatments at high temperature and humidity indicators of the air is significantly increased. Too often Actellic is not used as resistance develops.
- Akarin is a contact intestinal preparation, effective against ticks, Colorado potato beetles, moths, etc. It decomposes well in soils.
- Bazudin is a class 3 contact type insecticide that has a targeted effect on soil-dwelling insects. Form - granules. In order to treat indoor plants, the agent is used, but it is not safe for children, pets, it has an unpleasant persistent aroma.
- Decis with deltamethrin is a contact-intestinal insecticide that destroys the nervous system of the pest. Resistant to precipitation.
- Thunder-2 is a granular gardening agent based on diazinon, distributed over the soil surface. Helps against bear, ants. Class 3. Protection is created for several months after treatment.
- Inta-Vir is a popular contact insecticide for killing a wide range of pests. Release form - tablets used to prepare the solution. Up to 3 treatments can be done per season, they are not produced less than 3 weeks before harvest, and during the flowering period too.
- Spark is a contact agent against whiteflies, aphids, and other parasites. Hazard class - 3. More often than once every 3 weeks, you cannot use the product.
- Kleshchevit is an acaricide with aversectin in its composition, it helps against leaf-eating insects, ticks, is relatively low-toxic. In order to avoid the development of resistance more than three times per season, the drug is not used. Alternation with biological insects is possible.
- Tanrek is a strong systemic drug with imidacloprid for the Colorado potato beetle, whitefly, and aphids. The duration of the protection after treatment is 4 weeks. Can be used during drip irrigation.
- Fitoverm is a biological product based on Aversectin C, sold in the form of ampoules. It has a pronounced effect on the Colorado potato beetle, tick, aphid, apple moth. Hazard class 3, the action is intestinal. The phytotoxicity is low. Mixing with other formulas is not allowed.
- Fufanon is an aqueous solution with malathion. It is used against ticks, winged insects. The effect lasts up to 10 days, the active substances can be washed off by rain. Do not spray the plantings during flowering, do not combine with other preparations. Fufanon is dangerous for bees, class 3.
Preparations based on imidacloprid. (Biotlin, Golden Spark, Commander, Extra Confidor)
The drug belongs to systemic insecticipids. Plants freely absorb the substance and absorb it. It enjoys considerable popularity due to the successful fight against such a well-known pest as the Colorado potato beetle. In addition, it is used to kill aphids, whiteflies, thrips, spider mites.
Biotlin application
Biotlin serves to protect many fruit and flower crops from pest damage. Already after a few hours, it begins to act, interfering with the prevention of young growth. Plus - insects don't get used to it.
Affects aphids, whiteflies, thrips, penetrating the body through the intestines of the insect.Among its advantages - it is enough for a large volume (1 ml per 100 m), a long period of use, resistant to climate change - it tolerates hot weather well, is not washed off by rain. Interacts with insects through plant roots, leaves and stem.
The drug is effective against the Colorado potato beetle, aphids or whiteflies due to systemic effects. Protects potatoes, vegetables. It also acts through the intestines. The period of action of the substance is 2-3 weeks, 95-98% of the elimination of the Colorado potato beetle. It is diluted in the following volume: 1 ml per 10 liters of liquid.
Monsoon insecticide
It is an insecticide with a wide range of uses, but is more often used to control the Colorado potato beetle, caterpillars in small farms. The first results are noticeable after a few hours. The impact of the monsoon lasts 15-30 days. It is resistant to weather changes, temperature rise and water wash-off. Only after rain should the treatment be repeated after 3-4 hours.
A recent invention among imidacloprid-based pesticides. It is in great demand and is used in 120 countries around the world. Serves for the safety of almost 140 types of crops.
The main purpose of the spark is to get rid of the Colorado potato beetle. It is also used to remove aphids, thrips, whiteflies and other pests of potatoes, vegetables and flowers.
1 ml of insecticide is diluted with 5 liters of water, the action begins after 1-2 days. The spark of gold is not subject to precipitation and tolerates high temperatures well. The validity period is 25 days. Safe for humans, animals and fish.
It is used to remove aphids, as well as parasites on most vegetable and fruit crops. Tanrek affects the nerve cells of insects. It is produced in ampoules of 1.5 ml, the contents of which must be diluted in one liter of water. And also available in a volume of 1 and 10 ml. The term of protection is 14-21 days. It is resistant to high temperatures and precipitation. Insect pests disappear within a few hours after treatment with Tanrek.
Malathion-based preparations (Antiklesch, Actellik, Iskra M, Inta-Ts-M, Karbofos, Fenaxin-Plus, Fufanon-nova)
Malathion application
It is a non-systemic insecticide and acaricide of a wide range of applications. Its main direction: the fight against mites living on fruit crops, pests of vegetables (such as aphids, caterpillars, thrips, various types of mites).
The use of an insecticide systematically interferes with the reproduction of insects. But too frequent use of the drug is not always convenient because of its special smell. In the soil, the substance decomposes within one day, the time of withdrawal from the plant is a week. Preparations containing malathion in the base are recommended for use on any crops.
It is undesirable to use malathion in the ground: the substance is exposed to precipitation and wind, and also acts for a short time.
Anti-mite drug
It is used to remove spider mites and harmful insects on vegetable, berry and fruit crops. The effect of its use is noticeable after a few hours. Does not react to high temperatures, can be used in greenhouses. It is not dangerous for plants. The active action time is 15 days.
Serves to fight against aphids, ticks, whiteflies and other parasites on plants. It has a contact and fumigation effect (that is, through poisonous vapors).
The drug is produced in ampoules of 2 ml. One ampoule is diluted in 2 liters of water (in rare cases - per liter). Plants should be sprayed with a solution of the substance, moisten the leaves with it. Do this at a temperature of 12-25C without precipitation. It is a hazardous substance (second class of toxicity). It is better not to use it indoors. If there are plants necessary for processing there, then it is in such a place, it does not follow for a long time.
Iskra M preparation
Serves for the destruction of ticks, aphids, caterpillars and other pests of agricultural crops. Moderately poisonous (third class of danger), but dangerous for bees. Do not use near water sources.The drug is diluted in a ratio of 5 ml to 5 liters of water. Acts immediately after application, the period is two weeks.
Inta-Ts-M
It is used to fight against ticks, aphids, whitefly, Colorado potato beetle. It has a contact-intestinal effect. It is a tablet (8 g), which is previously dissolved and diluted in 5-10 liters of liquid. Inta-Ts-M is a mixture that is poisonous for fish and bees. Do not use the drug near water bodies and mix this solution with other pesticides.
Karbofos application
Insecticide against aphids, bedbugs, ticks and other productive pests. Method of application - spray plants in quiet, warm conditions. The insecticide works 3-4 hours after work. The amount of water that is needed for the solution is different, depending on the culture and type of pests - from 1 to 20 liters. The duration of the action is up to two weeks. First level of toxicity for bees. Avoid getting Karbofos into water. When working, use gloves, goggles and overalls, wear a respirator.
It is an insecticide for fighting the bear. The pest dies within 3 hours after application. The period of action is two to three weeks. Use the bait in the following amount: 3-5 granules, that is, 5-10 g every meter.
The action is similar to Karbofos. The ampoule is diluted in 5 liters of water. It works a day after use. It is poisonous for fish and bees, so it should not be allowed to get into the water.
Preparations based on pyrethroids (Inta-Vir, Kinmiks, Tsunami, Senpai, Decis)
This is a recent invention, although pyrethroids have been used against pests for a long time. For example, they have been used against fleas in hygiene products for dogs and cats. First of all, insecticides from this chemical group are used against chewing and sucking insects: aphids, thrips, whitefly. This insecticide has low toxicity and is almost harmless to the environment. It decomposes quickly and does not affect plants.
Inta-Vir preparation
Poisoning risks with insecticidal treatments
Biological insecticides are used in the prevention and control of parasitic insects along with pesticides. These are environmentally friendly drugs based on various viruses and bacteria. A delayed inhibitory effect on pests is observed immediately after treatment. These compositions are completely non-toxic, do not pose a danger to people, and will not damage the plant.
The most common:
- Fitoverm is a bacterial insecticide used against various insect pests, it is well compatible with other chemical agents, growth regulators. Deals with mites, sawers qualitatively. Processing during flowering is prohibited.
- Iskra-Bio - kills most of the known pests, including ticks. It is most effective in sunny, dry weather. The composition is safe, because this method of processing is possible 1-3 days before the harvest of berries, vegetables, fruits.
- Tobacco dust is the most popular among biological agents used for preventive maintenance and control. It is used on flower, berry, fruit plants in the form of decoctions, infusions, pollination of these crops.
The main plus of biological products is complete safety for humans, cultures, and environmental friendliness. Only its effect is not quick, therefore, in cases of severe infection, it alternates with various pesticides.
Poisoning with insecticides is not uncommon. Always look at the hazard category of the substance, use personal protective equipment.
In case of contact with toxic substances, the skin is washed with water and soap, when insecticides penetrate into the gastrointestinal tract, vomiting should be induced if possible, be sure to seek qualified medical help.
After completing the treatment, wash your face, hands with soap, rinse your mouth. It is advisable to wash clothes. It is dangerous to contact with insecticides for more than half an hour.
Insecticides are sometimes the only way to control pests and preserve crops.The main thing is to choose the right tool and use it according to the instructions.
The active ingredient in this insecticide is thiamethoxam. It is ¼ the mass of this chemical. "Aktara" gets into the vegetative mass either through the skin of the leaves, or is absorbed by the root system from the soil when irrigated with an insecticide solution. Then it spreads along the stem throughout the plant.
If this tool was not found in a specialized store, then sellers can offer the following analogues:
- Tiara;
- Adamant;
- Cruiser;
- Doctor.
"Tsineb"
A poisonous chemical for the treatment of garden, fruit and vegetable and indoor crops from root rot, scab, leaf spot, anthracnose, septoria, mildew, late blight, re-sporosis, cercospora, rust, blast, keel. Acts on parasites in a contact and systemic way.
It is produced in the form of a white or yellowish 15% soaking powder with the parallel names "Duponfungicide A", "Aspor", "Tiudou", "Ditex", "Novozir", "Zineb".
The fungicide is intended for spraying the aerial parts of plants and acts on pathogens for 2 weeks, does not suppress the reproduction of mealy fungal spores.
The suspension is recommended for processing plants during the flowering period, as it increases the percentage of the formed ovary and the development of roots.
It interacts well with organochlorine and organophosphate substances, but it cannot be mixed with Bordeaux liquid.
Prevention and treatment of plant diseases using phytopreparations-biofungicides
Phytopreparations stand out among the fungicides. It is widely believed among summer residents-gardeners that drugs that are not synthesized chemically, but that have a biological origin, cause less harm to the garden land and crops. Let's try to figure out what means for combating plant diseases come on the market under the names with the prefix phyto. There are many such fungicides: Fitosporin, Albite, Fitolavin, Trichodermin, Glyocladin, Alirin-B.
Oddly enough,… mushrooms help to reduce the amount of harmful fungi in the soil! Scientists call these useful representatives of saprophytic fungi of the genus Trichoderma suppressors. This is what is hidden under unfamiliar and obscure scientific terms. Mushrooms - saprophytes feed on the remains of organic matter of the plant and animal world, and also know how to turn myceliums of harmful pathogens into a breeding ground for themselves. The term "suppressor" in this case means "suppressor". In addition to trichoderma, this group includes several more varieties of mushrooms. All of them successfully destroy populations of pathogens in the soil.
Saprophytic fungi are propagated in laboratory and industrial conditions. They are used to prepare drugs for the treatment and prevention of diseases in open and closed ground. The most famous are Trichodermin, Glyocladin.
Fungicides of bacterial origin include an equally popular drug - Fitosporin. It includes a live culture consisting of cells and spores of a specific bacterium. A feature of these microorganisms is the ability to suppress the development of pathogenic microflora, enhance plant immunity. Fitosporin is a fungicide with a wide range of uses. It is used to prevent and cure diseases of potatoes and tobacco, root crops, cabbage, tomatoes, black currants, and flowering plants.


Fungicides - contact, systemic, their use
lit. at Art. Pesticides.)
- Forest Encyclopedia: In 2 volumes, vol. 2 / Ed. Vorobiev G.I .; Editorial board: Anuchin N.A., Atrokhin V.G., Vinogradov V.N. and others - M .: Sov. encyclopedia, 1986.-631 p., ill.
Pine seedlings, like other tree species, are quite susceptible to infection by pathogenic organisms in the first months of growth.
This is favored by the weak protective properties of young plants associated with a number of anatomical and physiological features.Among pathogenic organisms, soil fungi cause the greatest damage.
The most common disease of pine and cedar seedlings is infectious lodging
... It is caused by fungi of the genera Fusarium, Verticillium, Alternaria, Botrytis, Pythium. They are all saprophytes. They are introduced into the soil with seeds, compost, soil, as well as when crops are covered with old contaminated material, their number in the soil increases sharply during monoculture. The mycelium of the fungus passes into the stem and causes blockage of the tracheids, disrupts the supply of nutrients to the needles, and poisons the plant with the products of its metabolism. In the process of life, these fungi form and accumulate various products, due to which they change the environment in which they live. Metabolic products are certain amino acids, fats, alcohols, organic acids, as well as biologically active substances: vitamins, hormones, enzymes, auxins, antibiotics, toxins.
To recognize the causes of lodging of seedlings, I.I. Zhuravlev developed a special technique. Symptoms of the disease: near the root collar, the stem of the seedlings becomes sluggish, loses turgor and turns brown. A constriction is formed and the seedling falls to the ground and withers. The disease starts at the roots and goes up the stem. In wet weather, in the place of the constriction, you can often see the mycelium of the fungus in the form of a felt.
Read also How to melt chocolate in a multicooker
The most dangerous for seedlings are fungi of the genus Fusarium - F. oxysporum Sch., F. sporotrichioides Scherb., F. martii Appel et Woll., F. bulbigenum Cooke et Mass., Which, being saprophytic fungi, remain in the soil for a long time, and under favorable conditions, it affects seedlings, seedlings, seedlings and seeds in the soil. The disease they cause is called fusarium
... It has a focal character. With a strong soil contamination with Fusarium fungi, pine and cedar seeds die during the germination period. With a low degree of infection, seedlings lodging takes place. When the trunks are lignified, the seedlings dry up right at the root. In the cells of a plant affected by fusarium, there are abundant multicellular filaments of mycelium with oil droplets, 2-4 microns in diameter. In wet weather, seedlings affected by Fusarium are covered with a pinkish loose bloom, consisting of conidiophores. F. martii conidia are mainly 3-septate. Macroconidia are spindle-sickle-shaped, sometimes straight, with a short, slightly tapering and blunt upper cell, with a short stalk, 32-48X5-6.5 microns. Microconidia are ellipsoidal, without or with one septum, 12-15X4.5-5 microns. Sometimes chlamydospores are formed, rounded, brown, 10-14 microns in diameter.
F. sporotrichioides forms on the mycelium single short conidiophores 8-12X4-5 µm, separating oval, clavate one-, two-celled colorless microconidia 8-16X4-6 µm in diameter. Round chlamydospores with a diameter of 12-14 microns are also formed on the remains of dead seedlings, which germinate in spring.
Mushrooms are widespread in Siberia. Under these conditions, lodging of seedlings is observed in late May and early June. The outbreak fades in July. New development appears in August, but due to lignification of the stems, an outbreak of the disease is not observed. Chlamydospores overwinter.
Mushrooms Verticilliuin albo-atrum Rke. et Berth., V. terrestre (Link) Lindau cause verticillary wilting
seedlings. The vascular system of the seedling is affected, which leads to difficulty in the flow of water and the death of seedlings. The mycelium of the fungus spreads through the vessels, clogging them, the needles turn yellow, the seedlings wither. Infection occurs through the soil of forest nurseries, when stems and root systems are injured.
Conidiophores V. albo-atrum are erect, dark-colored, branching, bearing up to 8 whorls. The terminal branches bear colorless, ovate-oblong conidia at the apex, 5-12X3 µm in size. V terrestre forms white, fluffy, open tufts. Conidiophores, erect, septate, usually with whorls of four short branches, depart from the colorless mycelium. Conidia are solitary, apical, from spherical to ellipsoidal, colorless, 4.4-5X3.5-4.5 microns in size.
In addition to conidial sporulation, the mycelium of the fungus forms chlamydospores, with which it overwinters.
Mushroom Botrytis cinerea Pers. ex Fr. causes mold
seedlings of pine, spruce and larch, penetrating into the tissue of the seedling in places of injury.In these parts, a gray moldy plaque is formed, consisting of densely located, erect, branched conidiophores, separating numerous unicellular ovoid or oval conidia. The fungus overwinters in the form of nodular black sclerotia.
With a strong development of gray mold, the affected seedlings emerge from under the snow in the spring completely covered with a grayish-white cobweb bloom.
Causes of diseases
The following reasons lead to the wide spread of many fungal infections that affect almost all types of fruit, garden and ornamental plants in the country:
- The accumulation of pathogens occurs through contaminated plant debris. This is how root rot, late blight, fusarium spread. Fungal spores accumulate in the soil where the infected tops are left to winter, and are carried along the garden beds along with unripe compost.
- The shortage and high cost of manure, the main source of fertility until recently, led to its replacement by other suppliers of organic matter for the beds. The green mass of tops, mowed grass, dead leaves brought from the neighboring forest have become the most important organic fertilizers in summer cottages. Together with them, pathogenic microorganisms that cause rot and other infectious plant diseases appear in the soil.
- Inappropriate use of drugs that prevent and treat infections, instead of benefit, can lead to the emergence of fungicide-resistant microbial races. Some pathogens develop resistance (addiction) to fungicides, for example, such as Fundazol, Fundazim, Benorad. This is why it is so important to follow the dosage instructions strictly and change them from time to time.


The use of fungicides for plant diseases, list
Strawberry
The wide spread of viral and fungal diseases has greatly reduced the plantations of everyone's favorite berries in their summer cottages. By sharing planting material with neighbors, buying infected seedlings from markets, gardeners have made it almost impossible to acquire healthy garden strawberries. They tried to save the situation with the improvement of the planting material by introducing the Frigo industrial technology into amateur gardening. Many summer residents are trying to grow a healthy strawberry crop from seeds.
Fungicide treatment of strawberry beds helps in the prevention and treatment of diseases such as a variety of bacteriosis, spotting, rot, powdery mildew. Diseases have to be fought during all vegetation periods of plants.
The first spraying begins as soon as the leaves begin to grow. Repeated treatments are done every 10 days until mass flowering. At the stage of fruit setting and before harvesting, the introduction of drugs is stopped. After picking berries, fungicide treatment has to be repeated to prevent the disease next year. The end of summer, the beginning of autumn, when the defeat of these diseases is severe, we do at least two treatments. Preparations used in strawberry beds: HOM, bordeaux mix, Speed, Ridomil.


Fruit trees
The most common apple disease caused by the reproduction of pathogenic microflora is scab. The fungus especially affects apple trees in seasons rich in heavy rain. The multiplying causative agent of the disease, having overwintered on fallen leaves, is carried by the spring wind and settles on the blossoming buds. Thus, scab spores fall into the ovary. A diseased tree sheds damaged leaves prematurely and yields cracked, twisted fruit with corky skin.
A fungicide that has long been used to treat apple and pear scab is a Bordeaux mixture. It is bred for the so-called "blue spraying" in the following proportion: 800 grams of slaked lime and 600 grams of copper sulfate are added to 20 liters of water.The old recipe can be replaced with modern copper preparations from the above list.


Fruit rot (moniliosis) is a dangerous disease that causes serious damage to the harvest of the orchard (plum, cherry, sweet cherry and others). The source of the spread of spores is last year's mummified fruits that overwintered on trees. Often, spores of monilia settle in the cracks of fruits affected by scab. Copper fungicides are also used to prevent and treat the disease.
Brown leaf spot, stem rot and many other infections affecting apples and pears, in addition to copper preparations, can be treated with strobilurins (Strobe, Profit Gold, Ridomil and many others).
Stone fruit cultures suffer from a variety of infectious diseases - moniliosis, coccomycosis, clasterosporiosis. Infection with pathogens of cherry trees is massive. The infection quickly spreads around the area, infecting trees in neighboring areas. Many collective gardeners, in order to combat diseases that have entered the stage of an epidemic, are forcing summer residents to completely get rid of cherry plantings.
It is possible to prevent the spread of insidious infections on cherries and plums with the help of timely treatment with drugs. Speed, Rajok, copper-containing fungicides. To get the result, and in the summer season, you have to resort to three spraying.


Berry bushes
Often, brown and yellowish depressed spots can be observed on the stems and leaves of black currants. At the same time, the leaves curl, dry up and fall off. Most likely, the plant is affected by anthracnose. Raspberry and gooseberry bushes can also suffer from this disease. Spores of another fungus, whose intermediate host is sedge, causes goblet rust. Its striking distinguishing feature is the orange-colored spore pads on the leaves.
Vague purple spots on annual raspberry stems, in the places where the leaf petioles are attached, give out a disease called purple spot. Copper-containing fungicides cope with the treatment of most fungal pathologies in berry fields.
American powdery mildew (spheroteka) very often affects black currants and gooseberries, especially old varieties that are not resistant to this disease. A profuse white bloom appears on the tops of the shoots. The bushes look like they are sprinkled with flour. Leaves curl, stop growing, young shoots bend, berries, without ripening, fall off. In the shade and waterlogged places, the spores of the fungus are especially strong.
Since the spheroteka mycelium lives not in the soil, but on the shoots of berry bushes, before treatment with fungicides, all affected plant parts visible to the eye are cut out and burned. For treatment use Fundazol, Topaz, phytopreparations.


Protection of tomatoes from late blight and other dangerous infections
How many enthusiasts, eager to grow delicious, carefully selected varieties of tomatoes in their garden, abandoned their experiments, desperate to defeat the insidious phytophthora. Getting into ideal conditions for mass reproduction (warm and high humidity), the spores of the fungus instantly spread through the beds and greenhouses with tomatoes, not bypassing potato plantings. Their resettlement does not stop the temperature drop in August - September. In parallel, other infections of tomatoes can begin: brown spot, macrosporiosis.
The first signals of the appearance of late blight on tomatoes are small dark dots on the stems. Gradually, their area increases until they turn into brown spots. The same damage appears on the leaves. At first, late blight does not appear in any way on the fruits, they seem healthy. But the destructive activity of the fungus goes under the skin of the fruit, soon depressed brown spots appear on them.
Tomatoes infected with late blight are treated with fungicides containing copper. Add 50 g of the preparation to 10 liters of water HOM (copper oxychloride) or Abiga-Pak... Spraying is carried out with a fine spray, trying to moisten the underside of the leaves. When infected with late blight, a whitish bloom (the underside of the leaf) formed by the fungus can be observed. The best result in treatment is given by a three-time treatment. The first spraying, as a warning of the disease, should be done as early as possible - a couple of weeks after planting the seedlings.


Daily inspection and removal of affected plant parts, a short-term increase in the temperature in the greenhouse to 55-60 degrees, a reduction in watering and maintaining a dry microclimate can help in the fight against late blight. There is a known way to save tomato fruits, infected with spores, but not yet damaged, - immerse them in water heated to 60 degrees for 3 seconds, then dry them and store them in one row.


Cucumber garden treatment
The most famous and most ruthless enemy of cucumber lianas in their summer cottage is peronosporosis. Another name for the disease is downy mildew. The first signs - characteristic spots on the leaves, require immediate treatment. The most effective for the prevention and treatment of disease are the treatment with copper preparations.
For example, Ordan or its analogue Kurzat bred at the rate of 50 grams per bucket of water and sprayed with cucumber vines. The waiting time for these drugs (you cannot harvest) is 5 days. As a result of the treatment of cucumbers with copper-containing preparations, prevention of other fungal diseases is also provided - olive spot, anthracnose. The same treatments are useful for preventing diseases on plantings of other pumpkin plants - squash, squash, pumpkin.
An additional obstacle to the development of pathogenic fungi will be the raising of cucumber lashes on trellises, which will relieve them of contact with the soil, where the spores of infectious agents are located. For prevention, it is worth thinning the planting of cucumbers, more often ventilating the greenhouse or greenhouse, and in the future, select varieties and hybrids that are resistant to downy mildew.
Ornamental garden
Protection against pathogens of fungal infections is required not only for vegetable and fruit and berry crops, the ornamental garden also suffers. Luxurious pine and other conifers can be affected by rust, which cannot be dealt with without treatment. Oxychom.
Rhododendrons, like tomatoes, attack late blight. To prevent and treat it, you will need watering the soil. Fundazolespraying Ordan and its counterparts.
Many flowering perennials suffer from powdery mildew. First of all, these are autumn asters, delphiniums, peonies, shrub cinquefoil, roses. In addition to pruning and removing affected parts of plants, spraying with fungicidal preparations (HOM, Speed, Topaz).
Attention is paid to the protection of tubers and flower bulbs from diseases during winter storage. Before laying, they are thoroughly dried and treated with Maxim.


Storage and greenhouse processing
To prevent the disease next year with late blight and peronoscosis in greenhouses where tomatoes and cucumbers grew, they are treated with fungicides. Work is performed before the onset of cold weather, removing plant debris and digging up the soil. The walls, frames, glass are wiped with a solution of copper sulfate, the room is fumigated with sulfur preparations. Consumption - 50 grams of sulfur per 1 cubic meter. m. greenhouses. Remember to handle garden tools, pots, seedling boxes and other similar equipment.
In a similar way, preventive work is carried out in cellars and basements before planting a crop in them for the winter. Before processing with copper sulfate and burning sulfur, the storage facilities must be dried.
Lesions of the root system of conifers
Root system lesions cause fungal diseases: Fusarium spp, Pythium spp, Rhisoctonia solani, Phytophthora sp, Tracheomicos.
Visible signs of damage to the root system:
In pine, yew, fir and spruce, young growths droop literally in one day and dry out.
In thuja and cypress, the needles become lethargic and acquire a grayish tint.
In all conifers, the bark at the bottom of the trunk becomes soft and squeezes when pressed. If you scratch the bark a little, you can see that the color of the fabric has turned brown, not green.
Also on the trunk, closer to the soil, plaque is visible, or blotches of white or pink color. The bark shrinks and turns black.
If you cut the shoot at the bottom of the crown, closer to the trunk, then brown rings are visible at the cut.
Features of the use of fungicidal mixtures for plant protection
Usually, this disease appears on seedlings with excessive moisture and is accompanied by infectious wilting or lodging.
Mushroom A. tenuis Nees emend Neerg. causes alternaria
... Develops as black mold on seeds during storage. Once in the soil, the fungus infects the needles of the seedlings (more often already diseased seedlings are affected) and continues its development on the dead seedlings. In the initial stages, diseased seedlings stand out with yellow needles. Subsequently, the top dies off, and a black bloom is formed on the dead needles, consisting of a brown, thick-walled mycelium of the fungus. Conidiophores, forming on mycelium, are short, brown; conidia are oblique-shaped, olive-brown, with 3-5 transverse and longitudinal septa and constrictions, 30-50X14-18 microns in size. This disease accompanies lodging and wilting.
The fungus Pythium debaryanum Hesse causes white mold
seedlings. It develops on heavy, excessively moist soils on seedlings. In the affected seedlings, the stems near the root collar turn black, thin out and become covered with a white bloom. The disease is focal in nature. In places of damage on dead plants and in the soil, there are conidia (in dry weather) or zoosporangia (in rainy weather). Resting spores hibernate. Conidia form at the ends of the mycelium branches. Without falling off the conidiophoid, they can, with sufficient moisture, turn into zoosporangia. In a humid rainy summer, the fungus develops very quickly.
Opal and root collar burn
... In this disease, the death of seedlings occurs due to a violation of the most important physiological functions and an irreversible change in the physical state of the plasma in connection with the coagulation of proteins. The critical temperature of the soil surface at which damage and death occurs is not the same for seedlings of different species and varies depending on the color of the soil, air humidity, lack of wind, concentration of protein solution, and the presence of a number of salts and alkalis in this solution. The disease is observed most often in nurseries on dark soils; dry, loose, dark-colored soils are especially heated. Usually, a seedling damaged by opal or a burn is attacked by fungi of the genus Fusarium. When a pine seedlings are burned, the aboveground part is damaged, primarily hypocotyl and needles. An unlignified seedling falls if tissue death (from bottom to top with fusarium and top to bottom with a burn) spreads to the area of the root collar and base of the stem.
Read also Can lemon when feeding a newborn
Basidiomycetes Thelephora terrestris Fr. and T. laciniata cause suffocation
seedlings of pine. The defeat of seedlings is usually observed in nurseries and crops on sandy soils, where the fungus develops saprophytic on plant debris. Fruit bodies are shell-shaped or membranous, leathery, dark brown with a rough-hairy surface and slightly lumpy hymenophore. Fruiting bodies are often formed directly in the soil on fallen cones and branches. The fungus envelops the seedling, hindering growth, disrupting physiological processes (respiration, assimilation). The seedlings suffocate and die off.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
Conifers are decorative at any time of the year and have completely different sizes, shapes and colors of needles, therefore, thuja, junipers, spruce, pine, fir, cypress and even yew are planted on our sites.
Unfortunately, conifers and shrubs are susceptible to diseases and may lose their decorative effect due to fungal damage. Fungal flora affects the roots, bark and needles of plants.
How and what to treat conifers in the garden
The treatment of coniferous plant diseases is a complex process. An incorrectly chosen drug or a high concentration of it can ruin the "patient".
The signs of many diseases and the type of damage caused by pests are often similar, so it can be difficult to recognize them, but, fortunately, the measures to control them are close. Pay attention to the recommendations presented on this page - they will help you and your green pets. Use in the garden only those pesticides that are approved for use in personal subsidiary plots, and strictly follow the instructions attached to the preparation.
Table "Diseases of coniferous trees and their treatment":
| Signs of defeat | Cause | Prevention, control measures | |
| Small yellow-green insects covered with gray-white waxy pubescence. They suck the shoots between the needles. Before fledging, they switch to needles | Pubescent aphid | Systemic insecticides | |
| Colonies of large shiny aphids on branches and bark | Korium aphid | Also | |
| Sticky small fluffy snow-white formations on the underside of the needles | Hermes | Also | |
| On the bark, formations with a white sticky fluff, under which dark brown small insects hide | Measles Hermes | Also | |
| Small caterpillars on buds and (or) adjacent shoots | Bud-shoot moth | Also | |
| Caterpillars are green to brown. They eat pine needles and young growths, wrapping them in cobwebs | Leaf rollers, scoops, shoots, moths, etc. | Also | |
| Small oval cakes are initially white and then dark brown. Miniature larvae hide under the shields | False shield | Systemic insecticides. It is possible to use actellik, karbofos or other similar drugs | |
| Groups of different sizes of sticky white shaggy secretions, under which small larvae hide, on needles and delicate twigs | Juniper bug | Systemic insecticides | |
| The branches are covered with groups of the finest cobwebs. The smallest mites move inside the cobweb. The needles turn brown. Up to 3-6 generations of pests are formed during the season. | Spider mite | Acaricides | |
| On the needles and branches, fusiform swellings with yellowish mucous or gelatinous secretions of fungi | Rust | Removal of affected branches. Destruction of heavily affected plants. Disinfection of wounds. Fungicide treatment | |
| The needles in the spring, within 1-2 days after the snow melts, becomes red-brown with black transverse lines and falls off. The disease is especially dangerous for young plants. Adults are more resilient | Shute ordinary | Fungicide treatment. It is possible to use colloidal sulfur, Bordeaux mixture or other similar preparations. Removal of dead needles and dead plants | |
| The needles in the spring, after the snow melts, turns out to be a dirty green color, because, they are covered with a thin gray mycelium, During the summer, the needles become light gray with black dots and fall off. The disease is especially dangerous for young plants. Adults are more resilient. Infection occurs in autumn | Shute snowy | Fungicide treatment in spring and July-September. It is possible to use colloidal sulfur, Bordeaux mixture or other similar preparations. Removal of dead needles and dead plants. | |
| Cancer ulcers on trunks and branches. On the dead bark, white discharge 2-4 mm in diameter is formed | Stepped cancer | Removing dead branches or diseased plants | |
| Vertical cracking of the bark. Most often on young thujas, tuyeviks and cypress trees | Frostbite of the bark | Warming of trunks for the winter. Covering wounds with garden varnish, tightening and wrapping the bark until fusion | |
| Spring browning of branches and needles above the snow cover zone | Frostbite | Planting in the shade or under the cover of other plants.Warming of plants from late autumn with a light air-permeable covering material. Spring shading after removing the shelter. Spraying of affected, but live branches that have a chance to grow back. Removing dead branches | |
| Browning and shedding the needles on one side of the plant | Spring sunburn | Shading of plants in early spring from the sunny side. Planting in the shade or under the cover of other plants | |
| Sudden local browning of needles and branches, Shine on the needles. In the future, the death of branches or the death of the plant is possible. | Consequence of contact with urine of cats and dogs | Immediate rinsing of plants with clean water. Pruning diseased branches | |
| Browning of needles and small twigs in the center of the crown in spring after removing the shelter | Damping out of needles due to a strong screed or too late removal of the cover | Light scaling of branches in front of the shelter. Gradual and timely removal of the cover, Shading after removing the cover. Cleansing in early summer, after awakening the kidneys | |
| Yellowing and drying of needles and small branches in the center of the crown in late summer - autumn | Natural seasonal dying off of needles | Does not exist. In autumn, cleaning is undesirable, since dry needles warm the plants in winter. It is recommended to remove needles and cut out dead branches on a dry day in early summer. | |
The most common diseases of conifers are shown in these photos:
Instructions for use
Before starting treatment, the owners must carefully study the annotation for the insecticide.
The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the correct preparation, use of a working solution, powder or composition for fumigation. Violation of the dosage, strength of the solution, timing, frequency of processing harms the crop, reduces the effectiveness of the impact, worsens the quality of fruits and vegetables.
General rules
Effective pest control is carried out by the following methods:
- spraying leaves, stems with an aqueous solution of a certain concentration;
- fumigation - the process of sublimation of dry steam with the release of toxic components;
- dusting - a dry powder in the form of a powder is applied (scattered) over the affected plants. The second name of the method is dusting;
- laying insecticide powder and granules in the ground.
How to breed
For the success of processing, it is important to properly prepare the working solution:
- take a bucket, pour 1/3 of water, add powder or pour in the required volume of concentrated emulsion;
- stir the workpiece thoroughly for five minutes;
- add the remaining liquid, mix thoroughly again;
- use the working solution immediately or within the time specified in the instructions for a specific preparation.
Important!
The preparation of the composition, even with the third or fourth class of toxicity, is carried out in protective clothing, with a respirator and plastic transparent glasses. Inhalation of poisonous vapors or powder, contact with the insecticide solution on the skin provokes allergic reactions, poisoning.



















