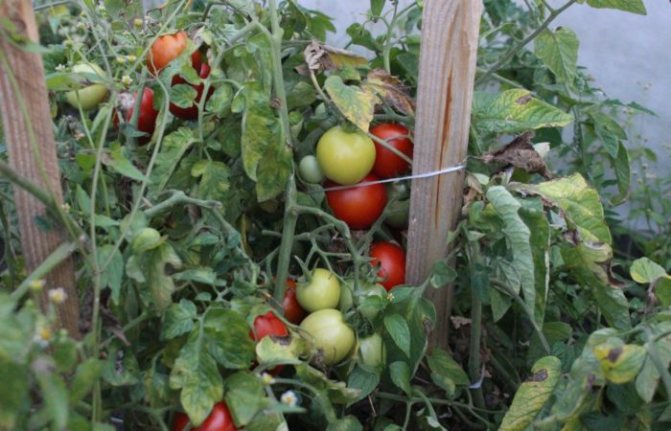
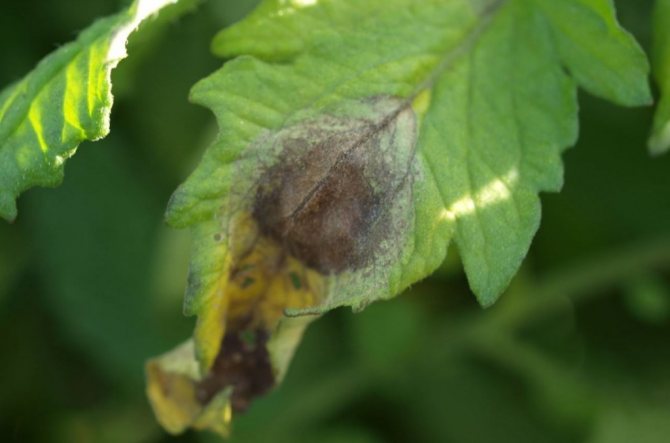
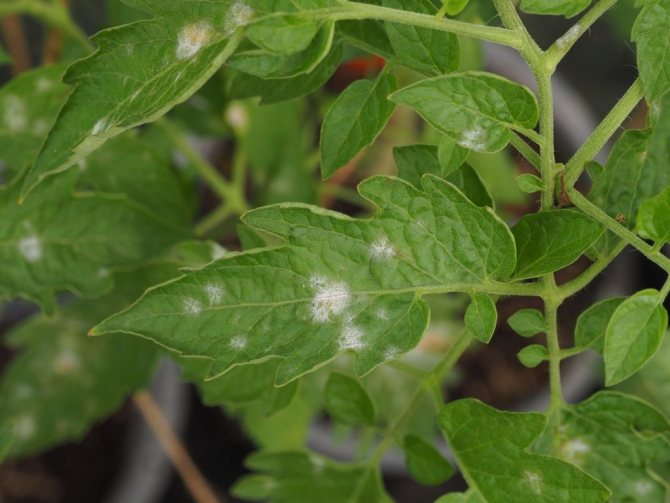
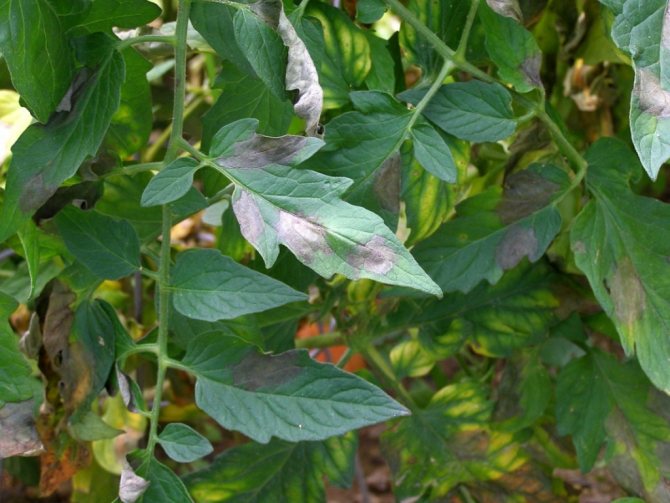
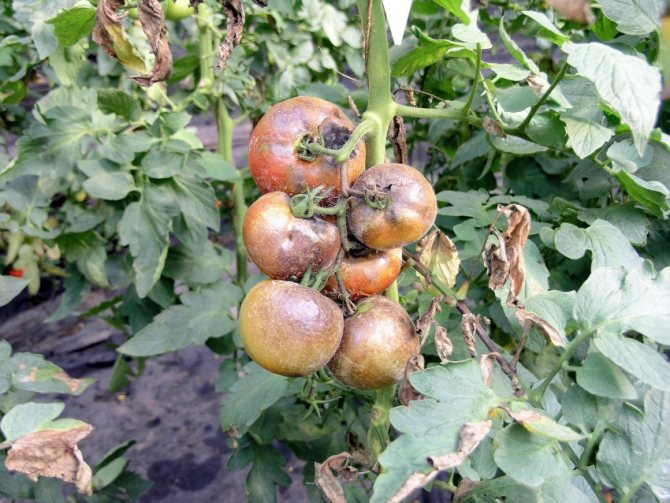
How to recognize late blight
A characteristic manifestation of the fungus is the darkening of the tops. It is affected much earlier than the fruit. The main signs of the disease:
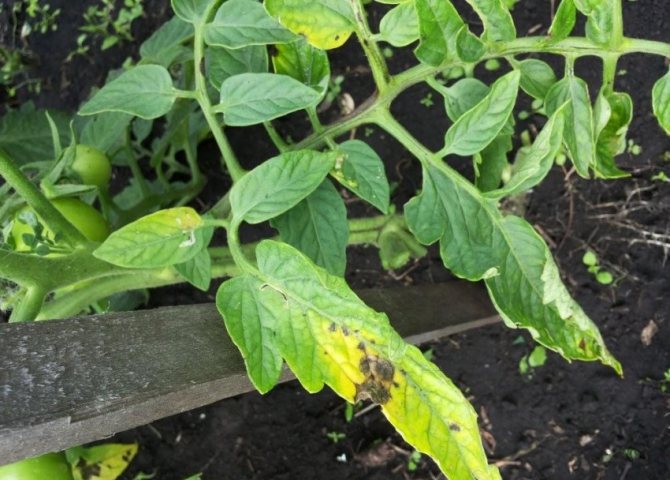
- individual dark brown uneven spots appear on the foliage;
- the affected greenery dries up, the edges are curled into a tube;
- fruits of waxy ripeness are covered with brown spots;
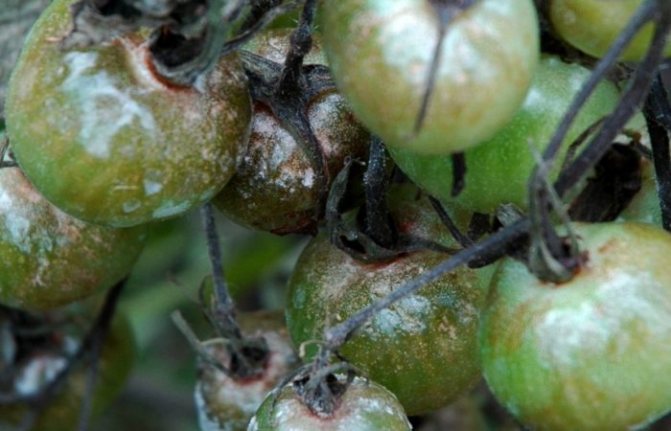
- filamentous white mold appears on plants in places of damage;
- when cutting a tomato, a rotten core opens;
- the trunks become covered with black spots, begin to rot, the bush dies.
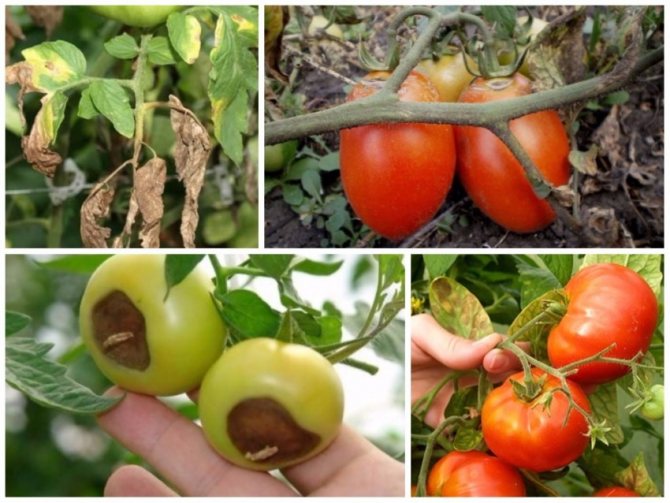

Preventing disease means saving crops
It is very difficult to treat phytophthora, therefore it is very important to carry out activities that prevent the development of a harmful fungus:
- Avoid thickening of the plantings, timely remove the lower leaves to improve ventilation, as well as leaves and fruits with signs of the disease.
- Use mulching to maintain soil moisture without increasing air humidity.
- Avoid the proximity of other crops that are distributors of phytophthora, especially potatoes.
- Observe the crop rotation.
- Timely carry out preventive spraying and apply chemicals as needed.
- Provide intensive ventilation and low air humidity in the greenhouse.
- Immediately dispose of diseased plant waste, do not use nightshade crops in compost heaps.
Prevention measures
Affected potatoes and eggplants can become a source of infection. These crops should not coexist with tomatoes. To disinfect the soil after harvesting tomatoes, rye is sown. In the spring, sprouts of winter cereals are buried in the ground.
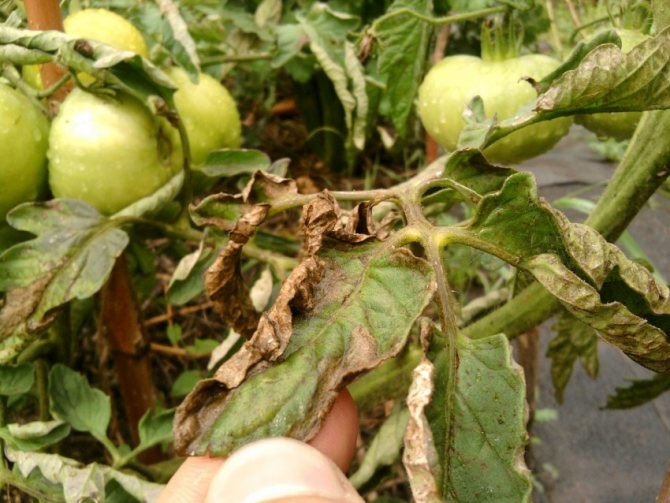


With a decrease in night temperatures to + 10 ° C, preventive treatment of tomatoes from late blight with biological preparations and folk remedies is carried out. It is recommended to treat only infected tomatoes with chemicals and antifungal solutions.


Mass pruning of leaves and stepchildren is carried out. Plantings are thinned out as much as possible to provide the plants with the necessary ventilation. The soil is cleared of weeds, mulched with dry peat or covered with straw. When morning dew appears, watering is reduced.


In the open field, the soil near the trunks is covered with old newspapers to absorb excess moisture. Stop organic and mineral feeding.


Description of preventive measures against late blight
The fight against late blight is a long and painstaking work, which does not always turn into a victory. Before planting tomatoes, you should remember about preventive control methods.
Soil treatment
The soil must be cultivated in spring and autumn. Phytophthora may appear suddenly.
More often, fungal spores are activated under the influence of the following factors:
- Unfavorable weather conditions.For example, sudden changes in temperature, high humidity.
- Lingering rains or frequent fogs.
- Increased content of alkalis in the ground (excess lime).
- Deficiency of potassium, iodine and manganese.


Before planting tomatoes and after harvesting, it is necessary to cultivate the land with the following means:
- People's... Grandma's remedies are great for preventing disease (they are not suitable for treating or killing fungal spores). You can use fermented kefir, milk whey with iodine, infusion of rotted hay, broth of pine needles or ash infusion.
- Biological... They are more effective than traditional ones, but they work only at high temperatures: + 15 ° C and above. You can pay attention to drugs - Baktofit, Trichodermin, Planriz, Alirin B, Fitosporin, Baikal EM-5.
- Chemical... "Heavy artillery" comes to the rescue when the disease has already manifested itself in the garden plot. It is important to use drugs strictly according to the instructions. The most effective are Borodskaya liquid, Copper sulfate, Copper oxychloride, Oxyhom, Quadris, Pharmayod.
Pathogens gradually get used to chemicals (they develop immunity). Experienced gardeners recommend alternating preparations (buy 2 or 3 from different manufacturers with different compositions).
It is best to water the soil with hot water before planting the plants. Do not forget about the processing of those areas where peppers, eggplants, potatoes will be planted. In the last days of April or early May, cover the beds with several layers of polyethylene. In the afternoon, the sun will warm the ground under such a shelter to + 80 ° C. This is enough to reduce the number of late blight pathogens.
Disinfection of seeds
Summer residents prefer to purchase tomato varieties that are resistant to late blight. But it is better to additionally process the seeds (this will be more reliable). Disinfection can be done according to the following instructions:
- Sort out the planting material carefully. The seeds should be brown or gray in color.
- Rinse with running water.
- Soak for 15 minutes in saline, soda or manganese solution.
Solutions create a harmful environment for fungal spores, they die instantly. Experienced gardeners recommend sowing planting material immediately, without waiting for it to dry out.
Greenhouse preparation


In the fall, after harvest, the tops of tomatoes and other nightshade crops should be harvested and burned. The greenhouse can be processed:
- With bleach.
- Baikal.
- Redomil.
- Fitosporin.
In the spring, 2 weeks before planting tomatoes, you need to remember the following recommendations:
- If the disease was last year, you can move the greenhouse to another place.
- Change frame, cover, supports, pegs and garter. The fungus prefers to spend the winter on all elements of the greenhouse.
- Replace the primer. A 20 cm layer of earth should be removed and a new (disinfected) layer should be poured in instead.
In the spring, the greenhouse should be treated with fungicides.... Preparations will prevent the appearance of late blight in the beds.
Siderata
Mustard and oil radish are the best siderates for fighting late blight. Moreover, they can be planted in open areas or in greenhouses. Regardless of the place of growth, they will equally well cope with the tasks. But first things first.
The spores of the fungus will be suppressed by bacteria that like to settle on the root system of mustard and radish. Beneficial microorganisms love iron, they take it from the soil and process it into another form that is useful for tomatoes. The phytophthora fungus remains hungry, development stops and the spores die.
Here are the instructions for planting siderates:
- It is better to plant in spring. So they will fulfill their mission until late autumn.
- When tomato seedlings have taken root in a new place, you should not often sow mustard or radish (5-7 grains per 1 sq. M of plot).
- Then mulch with green organic matter.
- Sunrises will appear in 4-5 days. Siderata grow and develop rapidly.
New neighbors need to be cared for to keep the bacteria comfortable. The mustard should be pruned during flowering, leaving a stem 10 cm above the mulch. Do not forget about regular watering.
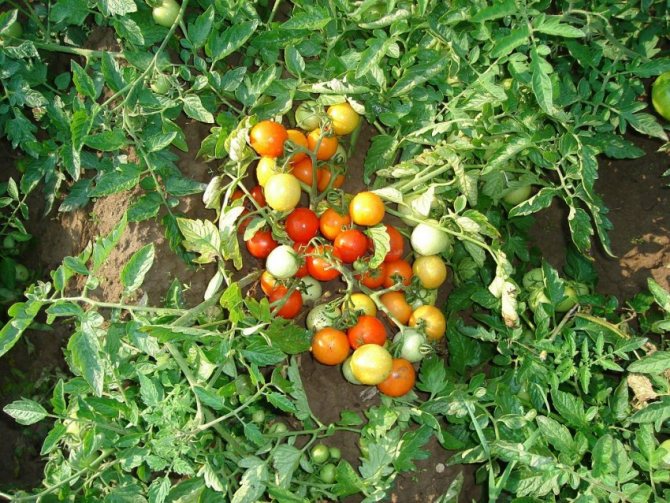
The yield loss in some years is 95-100%. There are no effective ways to combat late blight on tomatoes. Disease prevention is a good defense, but it only delays the appearance of late blight for several weeks. The main factor in the appearance of the disease is the weather.
There are two types of the disease: common late blight and southern late blight.
Plain late blight
Phytophthora on tomatoes is widespread in all climatic zones of the country, but it is somewhat more common in the middle lane and central black earth regions. In the southern regions, it manifests itself with sharp drops in day and night temperatures.
Causative agent - a pathogenic fungus that persists in the soil, on plant debris, seeds and fruits. It affects plants of the family Solanaceae. Potatoes and tomatoes are particularly affected; eggplant and pepper late blight rarely get sick.
Infection occurs through the stomata of cells even in completely healthy plants. Mycelium (mycelium) grows inside the cell and destroys it.
Infection can occur at any stage of plant development, but the first signs of late blight appear in the second half of summer. Even when sowing infected seeds, the first signs of damage can be noticed only during the period of tying the second or third brush.
Potatoes are affected first, then tomatoes in open ground, and only then tomatoes in the greenhouse. Eggplants in greenhouses get sick with late blight, although not as often as tomatoes, and the damage from it on this crop is not so great, only a few plants get sick.
Protected ground peppers are practically not affected by late blight. In the open field, peppers with eggplants suffer from the disease, but it is not so aggressive on them.
Conditions for the spread of the pathogen... Mature spores are carried by wind, water, soil particles, on clothes and working tools of the summer resident. They are stored in seeds and harvested tomatoes and potato tubers.
Conditions for the development of the disease
The disease spreads widely during humid, rainy and moderately warm or cold summers. In hot but rainy weather, the disease spreads less and affects only ground tomatoes. In dry and hot summers, late blight does not appear on tomatoes, and potatoes are slightly affected.
Other factors in the appearance of the disease are:
- The close location of plantings of potatoes and tomatoes.
- High air humidity.
- Contact of the lower leaves and brushes with the soil.
- Growing tomatoes in a place where potatoes used to grow.
- Poor ventilation in the greenhouse. Especially often late blight on tomatoes appears in the greenhouse when they are grown together with cucumbers. These crops require different air humidity: cucumbers 90-95%, tomatoes 60-75%. With high humidity, greenhouse tomatoes fall ill with late blight in the 1st decade of July.
- Sharp fluctuations in air temperature. This happens more often in the second half of August, so the crop losses are small. The main harvest is removed by this time.
- A sharp cold snap. Also happens in August. By this time, soil early-growing tomatoes are already being harvested, and the greenhouse is aired daily so that temperature fluctuations are not so significant.
Phytophthora does not spread only in hot dry summers and subject to preventive measures.
Signs of defeat
Fruits (green, in technical and biological ripeness both on bushes and during storage), leaves and stems are affected.
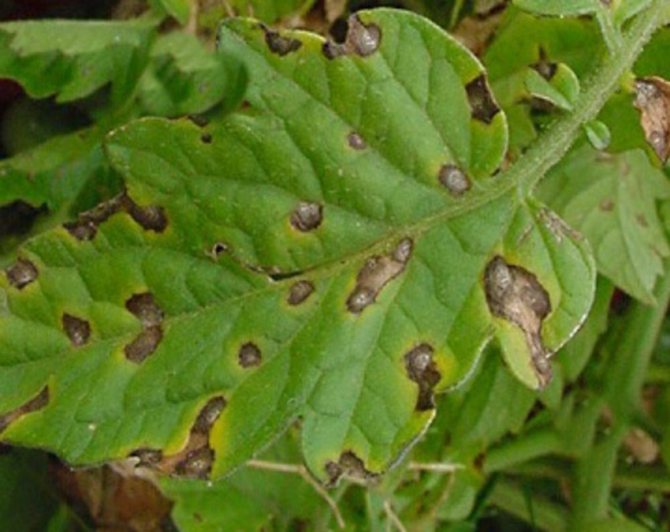
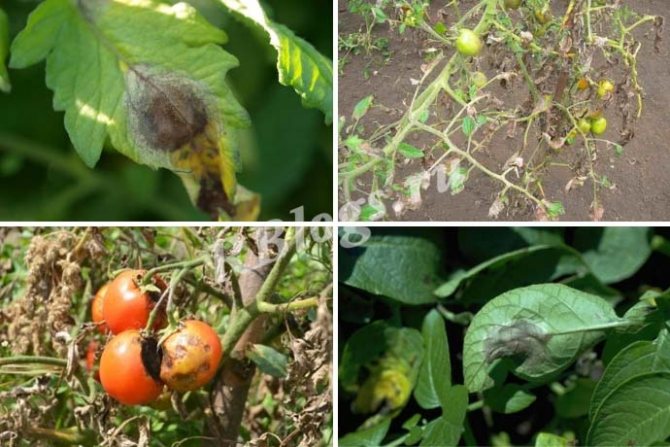
Brown blurry spots of irregular shape appear on the leaves.More often, the disease begins from the edge of the leaf blade, but it grows quickly, the leaf turns black and dries up. In wet weather, a white bloom is visible on the underside.
Brown stripes appear on the stems and petioles, which gradually grow and ring the stem. The tissue on the affected area dries out.
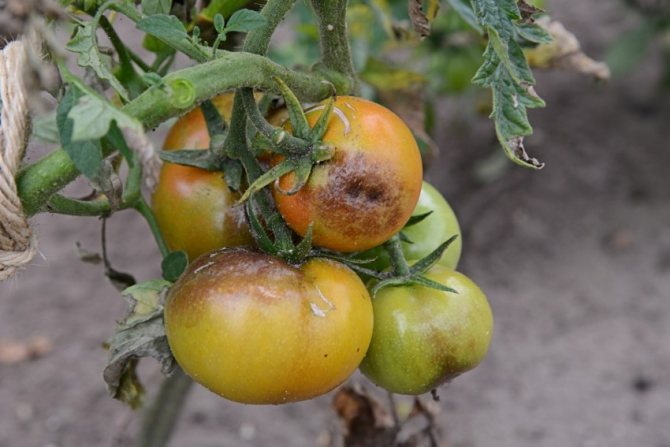
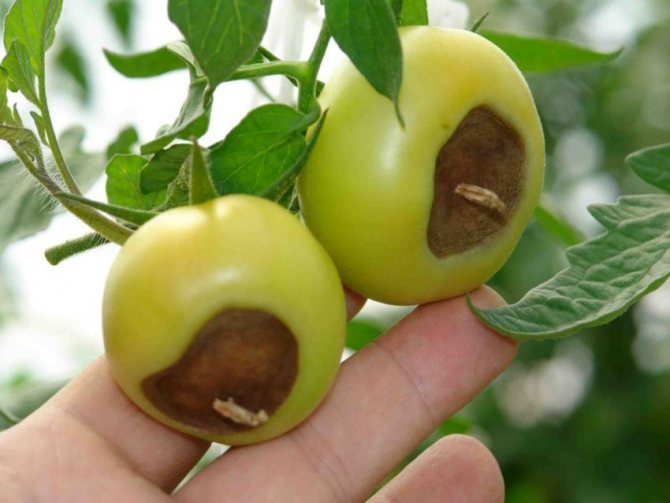
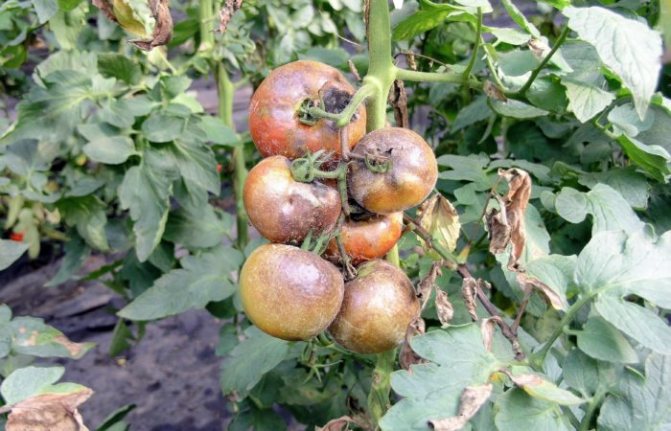
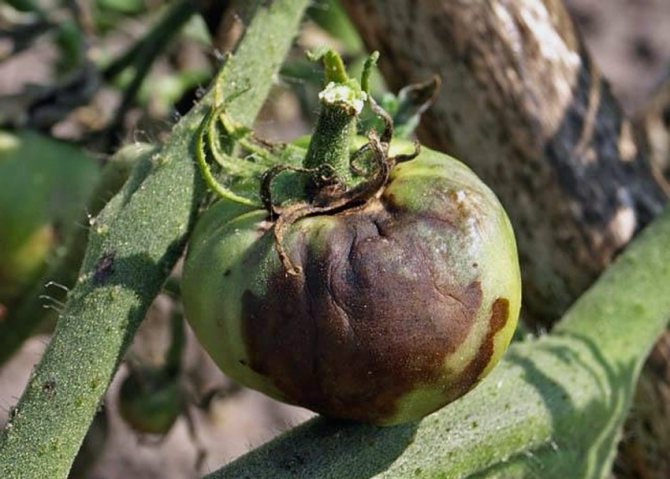
Brown-brown spots appear on green fruits, which grow very quickly, gradually affecting the entire fruit. Sometimes, with the development of the disease, the spots turn black. The fruit dries up.
During storage, late blight appears mainly on green fruits or in the phase of their technical ripeness. In the phase of biological ripeness, tomatoes are rarely affected and only when stored in a cold room with high humidity. When stored in a dry place, ripe fruits do not get sick.
Dry black-brown spots appear on the fruits of technical and full ripeness, the tissue at the site of the lesion becomes shiny, lumpy to the touch, then shrivels and dries up.
Protective measures
It is necessary to fight late blight on tomatoes throughout the season. When the signs appeared, it was too late to treat tomatoes. It must be remembered that the disease will appear anyway and the main task is to keep the plants healthy for as long as possible.
The incubation period of the disease is 3-5 days. If it gets colder and it rains, then the bushes must be processed. At the same time, peppers with eggplants in the open field, as well as potatoes, are processed.
To process tomatoes (and potatoes) from late blight begins at the end of May. These are preventive measures that allow to further delay the development of the disease by 1.5-2.5 weeks.
- Treatment of bushes with copper-containing preparations: Abiga-Peak, HOM, OxyHOM, Ordan.
- Treatment with drugs from other groups: Bravo, Previkur Energy, Consento, Metaxil, Ditan M-45.
- Treatment with Quadris. It is highly effective not only in the fight against late blight on tomatoes, but also in a number of other diseases (powdery mildew, Alternaria).
- Treatment with a new generation drug Strobitek. Processing is carried out 2 times per season, alternating with other means of protection.
- With a high risk of developing the disease, tomatoes are additionally watered at the root with copper preparations.
- If the disease has already appeared on the potato (it is affected earlier), then when spraying tomatoes, the concentration of the working solution is increased by 30-50%.
- When fighting late blight, a 10% calcium chloride solution (sold in pharmacies) is often used. 200 ml of the drug is diluted in 2 liters of water and thoroughly sprayed with tomatoes, potatoes, as well as peppers and eggplants. Plants are processed very carefully: leaves from the upper and lower sides, stems, stalks and fruits. After processing, the fruit cannot be harvested for 10 days.
Treatments are started regardless of whether the risk of developing the disease is high or not. If you do not take protective measures, then the defeat of tomatoes will occur very early and the entire crop will be lost.
Prevention of late blight
Prevention postpones the onset of the disease to mid-late August.
- 2 weeks after planting the seedlings, it is shed and, at the same time, sprayed with biological products (Pseudobacterin, Baktofit, Trichodermin or Fitosporin). Spraying is carried out every 10 days and only if signs of damage appear (especially in the open field) they switch to chemistry.
- When planting seedlings, biological products can be applied directly to the soil.
- Pruning all leaves in contact with the ground.
- Wrapping the stems with copper wire, since copper prevents the penetration of pathogen spores into plant tissues.
- Thorough ventilation of the greenhouse.
- Removal of diseased plants.
- It is desirable that the planting of tomatoes and potatoes be at different ends of the site.
- Cleaning of bleached tomatoes.
- Cultivation of resistant varieties: Cameo, hybrids Anyuta, Katya, Semko 100, Soyuz 8.
- Before sowing, the seeds are soaked in potassium permanganate, Baktofit or Fitosporin.
- Compliance with crop rotation.Do not plant potatoes and tomatoes one after another. Since late blight belongs to pseudo-fungi, it can exist in the soil for a very long time, therefore, if possible, it is advisable not to plant tomatoes (and potatoes) in the same place and after each other for 8-10 years.
In the open field
In the ground, the treatment of phytophthora is difficult, and the incidence is higher than in the greenhouse. The period of the protective action of pesticides on the street is 5-7 days, therefore 6-9 treatments are carried out per season. Simultaneously with tomatoes, potatoes are sprayed, as well as eggplants and peppers growing without shelter. If it rains within 2 hours after spraying, then the event is repeated on the same day or the next. It is important that the spraying is carried out on dry leaves.
Adhesives must be added to biological products so that they are not washed off by rain, otherwise there will be no effect from their use.
Phytophthora in a greenhouse
In the greenhouse, tomatoes get sick 2, and with proper prevention, and 4 weeks later than street ones. The period of protective action of pesticides is 10-14 days. During the season, 3-5 therapeutic and prophylactic measures are carried out (depending on the weather).
The first 3 treatments are done with biological products, and then, depending on the situation. But if late blight appears on the street (it doesn't matter if it is on tomatoes or potatoes), then greenhouse tomatoes are treated only with chemical remedies.
Measures to combat southern late blight
Distributed in the southern regions of the country, manifests itself in the Far East during the monsoon period. In central Russia, in some very hot and humid years, outbreaks of the disease can be observed. Its harmfulness is close to 100%.
Description of the pathogen
The disease is caused by a pathogenic fungus of a different class than the causative agent of ordinary phytophthora. It affects tomatoes, peppers and eggplants both outdoors and in the greenhouse. Potatoes suffer less from southern phytophthora than from ordinary ones. It is stored in the soil, on plant debris, in affected fruits and seeds.
In the photo, late blight on tomatoes
Appearance conditions
The first signs of the disease may appear even in seedlings. Massively infects tomatoes in the late spring and early summer period (end of May-June). Favorable conditions are significant temperature fluctuations (at night 18-20 ° С, during the day - 30-35 ° С), heavy rains, high humidity and air temperature.
Southern late blight on tomatoes can appear in the second half of summer against the backdrop of heavy rains and hot weather. First, tomatoes in greenhouses are affected (since the humidity is higher there) and only then soil plants. In the soil, the spread of southern phytophthora is facilitated by abundant dew and fog.
It spreads instantly. Sick tomatoes die in 2-5 days.
Signs of defeat
The signs of damage depend on the phase of plant development.
- On seedlings affects the lower part of the stem. The signs of the disease resemble a "black leg", but, unlike it, the constriction is formed not near the ground itself, but at a height of 1-5 cm, a stump remains from below. The affected tissue turns black and dries up, diseased plants die. Small brown spots appear on the leaves, which then merge, the leaf dries up. Sick seedlings are not suitable for growing.
- Before fruiting... Brown-brown strokes appear on the stems and stepsons, gradually the tissue dries up and the stem breaks. Banners can appear in several places at once. Brown spots appear on the leaves, growing, they affect it entirely. The leaf dries up.
- The beginning of fruiting... Brown-brown spots appear on green fruits, which quickly darken. On fruits, they look like bruises. The spots are watery; in very humid years, dots of white bloom appear on them - the sporulation of the parasite. The fruits gradually turn black and dry, but with incessant heavy rains they can turn into mucus.
- Technical ripeness tomatoes on bushes and during storage... Brown-brown watery spots appear on the fruits, but if the skin is pierced, there is almost no water there. Affected tomatoes shrivel quickly and turn into dust.
The leaves of diseased tomatoes remain healthy for some time. Southern phytophthora affects primarily fruits, and only then its signs appear on the leaves. Although with the rapid development of the disease, it can be difficult to establish the primary focus of infection. Southern phytophthora differs from ordinary phytophthora in darker spots, lightning-fast spread and rapid death of both the crop and the bushes.
Southern phytophthora does not lend itself to treatment. If signs of damage appear, diseased plants are immediately removed, the rest are treated with preventive treatment.
Prophylaxis
Prevention begins with preparation for sowing. The seeds must be treated with Pseudobacterin, the ground is spilled 2 times with boiling water or a raspberry solution of potassium permanganate.
The land, both during the seedling period and after planting in a greenhouse or soil, is not waterlogged. In heavy rains, regular loosening is carried out so that water does not stagnate in the upper soil layer.
All watering is carried out strictly at the root, sprinkling of tomatoes is prohibited.
All leaves in contact with the ground are removed as the tomatoes grow.
All affected plants are immediately removed from the plot. Even if there are signs on only a few fruits or stems, the whole bush is thrown away, it is sick and is a source of infection. Plant residues are not composted, not taken out of the site, but burned.
Prophylactic treatments are carried out with the same drugs as with conventional late blight (OxyHOM, Previkur Energy, Strobitek, Bravo).
In case of heavy precipitation, the concentration of the working solution is increased by 50%.
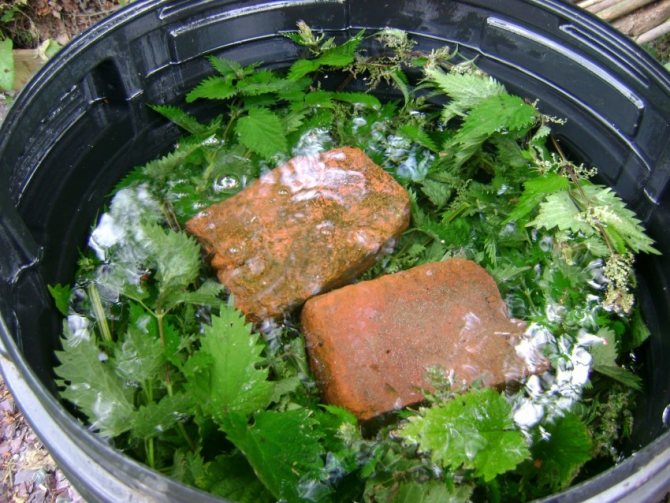
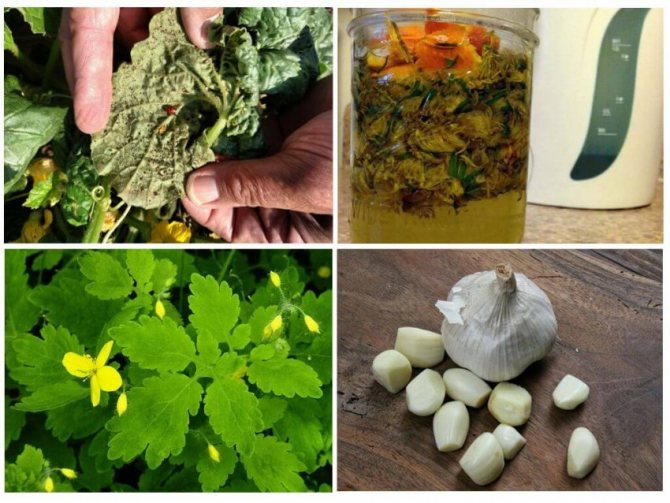
Folk remedies
There are no folk remedies to combat late blight on tomatoes, but there is a good way to prevent it. Use oven ash, which is sprinkled on the leaves and soil around the tomatoes. A lot of ash is needed, so that the leaves turn gray, and there is a thick layer of ash on the soil.
Phytophthora does not like alkaline reactions and does not affect tomatoes. But, alas, it is difficult to get such an amount of ash for a city dweller. Those who have baths are the winners. The method is unacceptable in open ground, since ash is easily washed off by precipitation (not only rain, but even abundant dew).
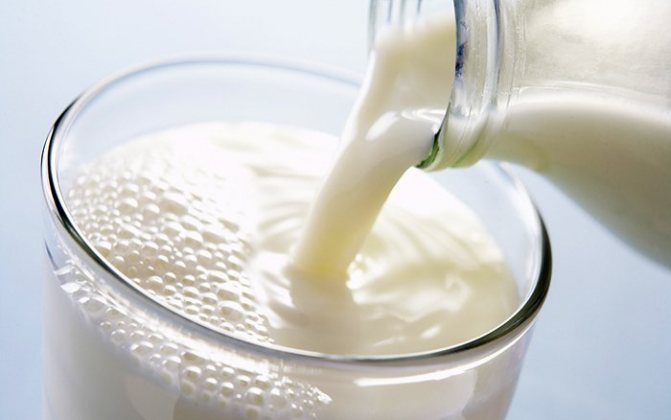
Another simple and effective method: mix 1 liter of milk or milk whey with 9 liters of water, add 20-30 drops of iodine there and stir well so that the iodine dissolves in the water. Tomatoes should be sprayed in the evening in calm weather once a week. If you alternate such spraying with Fitosporin treatment, it will be even better.
Biological protection of tomatoes
Phytophthora is not quite a mushroom, it has signs of the simplest, now it is referred to as pseudo-fungi. Therefore, effective fungicides, which are excellent at fighting fungal diseases, do not work on it, but the means to combat protozoa are also ineffective.
Biological products give good results. The most effective of them are preparations containing Trichoderma, pseudobacteria and preparations based on hay bacillus (Fitosporin, Alirin B, Gamair, Baktofit).
Using them, you can fight late blight on tomatoes at a very early stage, but many do not know how to use them correctly, so they neglect them, but in vain.
Biological products are living organisms, bacteria or fungi that are competitors of phytophthora for their habitat. In order for them to work, they must first be settled on tomatoes (potatoes, eggplants, peppers).
And for this they need a nutrient medium, so they are either grown independently at home, or adhesives are added to an aqueous solution of biological products, which are this medium for microorganisms. Biologicals are never dissolved simply in water - the likelihood of their further growth on the plant is small, since they have nothing to eat.
If, after spraying, white spots appear on the leaves, this is an indication that the colony of beneficial microflora is growing. Most summer residents take these spots for powdery mildew and immediately carry out treatment with chemicals that completely destroy phytophthora antagonists.
The appearance of white spots 2-3 days after spraying with biological products is a natural process, and if there are no signs of powdery mildew, it means that useful microflora is growing.
After treatment with biological products, chemistry is not used. 3-4 sprays are carried out with the same preparation, or alternate between them.
Trichoderma
A fungus that competes with late blight on tomatoes and displaces it from the soil and from plants. For the prevention of disease, treatments begin after planting seedlings in the ground.
The most important factor for the survival of Trichoderma on plants is the nutrient medium, which is also an adhesive, without which the antagonist mushroom will not take root on tomatoes.
In the photo, the drug Trichoderma
It grows well on carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC, is a part of wallpaper glue). You can also use fat milk, starch glue in this capacity. You can not use toilet soap, since it is not a breeding ground for the fungus, as well as laundry soap, which has a strongly alkaline reaction and in such an environment Trichoderma dies.
After processing, white blurry spots appear on the leaves - an indicator that Trichoderma has taken root. Processing is carried out every 10-14 days in a greenhouse and every 7 days outside, and in case of rain every 5 days during the entire growing season. Spraying with Trichoderma cannot be alternated with treatment with chemical fungicides, since they destroy it.
Trichoderma treatment is very effective even when the first signs of the disease appear. Under favorable conditions, it completely destroys the foci of the disease on tomatoes. In heavy rains, the biological product stops the development of the disease, although it does not completely destroy the parasite.
Pseudobacterin
The bacterial preparation contains live bacteria Pseudomonas aureofaciens /. Bacteria actively suppress not only phytophthora, but also a number of other pathogenic fungi, and also have a growth-stimulating effect. The drug is used with CMC adhesives, starch glue, oat broth.
In the photo Pseudobacterin
Processing is carried out early in the morning or late in the evening, since the bacteria cannot stand direct sunlight. In cloudy weather, it can be processed at any time.
Pseudobacterin reliably protects tomatoes from late blight. It is effective at the initial signs of the disease, but at high temperatures (especially in the south in greenhouses) bacteria die.
Hay stick (Bacillus subtilis) preparations
These are bacterial drugs that antagonize phytophthora. An excellent breeding ground for them is gelatin, so it is better to use it as an adhesive. The working solution is carried out preventive spraying with an interval of 7-10 days during the entire growing season.
At the onset of the disease, a solution of a higher concentration is prepared. Hay stick protects tomatoes well from disease, but it is less effective for treatment than Trichoderma and Pseudobacterin.
Biological methods are effective in combating both types of late blight, and they are also preferable to chemistry, since tomatoes can be eaten on the day of processing.
Summary table for common and southern late blight
| Indicator | Common late blight | Southern late blight |
| Causative agent | Phytophthora infestnas | Two pathogens: Phytophthora cryptogea. Phytophthora nicotianae |
| Spread | Northern and central regions | South and East of Russia |
| Favorable conditions | Rainy and cool weather | Heat and heavy rains; large fluctuations between day and night temperatures |
| Period of mass infection | Second half of summer | Seedling season and first half of summer |
| Signs of defeat | Dry brown or black spots on leaves and fruits | Watery brownish-brown, rapidly blackening spots on fruits. On the stems - brown stripes |
| Harmfulness | 80% | Close to 100% |
| Control measures | Therapeutic and prophylactic | Preventive |
| Preservation of the pathogen | On plant debris, soil, seeds, tools, clothing, potato tubers | On plant debris, seeds, fruits, soil, tools and clothing |
Continuation of the topic:
- How to properly form tomato bushes
- Diseases of tomatoes in the greenhouse and OG, description and methods of treatment
- What to do if tomato leaves curl
- Growing tomatoes outdoors
- How to care for tomatoes in a greenhouse from planting seedlings to harvest
- We fight the whitefly in the greenhouse and the exhaust gas
- How to deal with vertex rot on tomatoes
Cause and risk factors of late blight
Late blight, or late blight (from other Greek words "plant" + "destructive, destroying, fatal") is a common plant disease caused by fungal infection.
Phytophthora (Phytophthora) - lower fungi, leading a parasitic lifestyle. In the process of life (ontogenesis), they exhibit pathogenic properties in relation to most plants. All these fungi, without exception, are phytopathogens and cause dangerous plant diseases - late blight. Outwardly, this manifests itself in the form of drying out and wilting, in most cases in the form of rot. The grown tomato crops are most often susceptible to late blight.
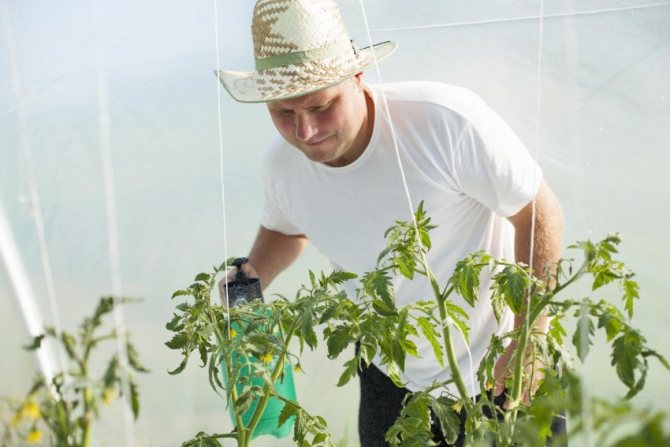
How to carry out the processing correctly
After processing, the fruits will remain toxic for 5 to 12 days, therefore, before spraying, all mature and partially unripe tomatoes are harvested.


Basic rules for spraying plants:
- glassware is used to prepare solutions;
- processing of plants is carried out in dry, calm weather, in the evening, to avoid burns;
- personal protective equipment must be used: gloves, masks, goggles, it is especially dangerous to get chemicals on mucous membranes: in the eyes, nose, upper respiratory tract
- processing of tomatoes from late blight in the open field is carried out in a directed manner in order to avoid the ingress of solutions on neighboring crops;
- in greenhouse conditions, in addition to plants, all surfaces are processed: glass, doors, visible frame of the foundation, trellises, soil;
- the frequency of treatments is not more than 1 time per week.


- How to care for tomatoes - planting, watering, feeding and the main nuances of growing. Tips and secrets of tomato care for beginners (110 photos and videos)


Feeding tomato and cucumbers with yeast: recipes and video instructions on how to properly feed vegetables with yeast (105 photos)


Boric acid for tomatoes: methods of application as fertilizer for the garden and vegetable garden. Expert advice and detailed technology for the application of boric acid to tomatoes (90 photos + video)
Tomato varieties for open ground, resistant to late blight
Late-ripening tomato varieties or plants of late planting dates most severely suffer from late blight, since favorable conditions for the development of the disease usually occur in the second half of summer and early autumn.
Many varieties and hybrids of tomato are quite susceptible to late blight, they are considered relatively resistant:
- Siberian early ripening;
- Khabarovsk pink;
- Khabarovsk standard;
- Harvestable;
- Oak;
- Gavroche;
- Krasnodarets;
- Cold resistant;
- Mars;
- Stresa;
- Semko 98 and others.
Due to their early maturity, they often escape from a strong defeat of the variety:
- Lightning;
- Ground Gribovsky;
- White filling 241;
- Lunar.
To protect a tomato from disease, you must:
- plant seedlings at a distance of 30-35 from each other;
- pinch the plants in a timely manner, avoiding thickening inside the bush;
- to carry out top dressing during the growing season with phosphorus and potash fertilizers, which increase the resistance of the tomato to late blight.
Biological preparations
Broad-spectrum phytosporin contains bacteria that multiply on phytosporosis spores.


Bactofit is a less effective fungicide (65-70%) and is used for preventive treatment.


Baikal-Em increases resistance to phytosporosis, has a beneficial effect on beneficial microorganisms.


Planriz or Rhizoplan is effective against all types of rot.
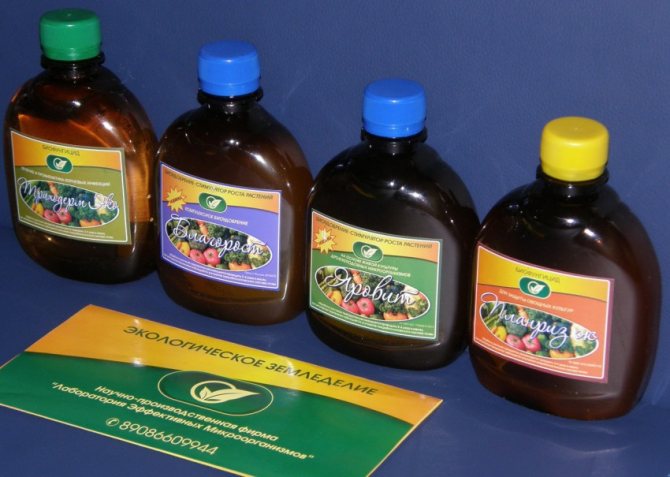


Alirin-B tablet analogue of phytosporin. Contains strains of active bacteria.




Dieffenbachia - home care tips. How to properly maintain and use a plant in interior design (125 photos and videos)

Drimiopsis - photos, videos and home care methods. Growing an ornamental plant with your own hands (110 photos)


Fitosporin for tomatoes: methods, processing methods, video instructions and 105 photos of the result of application
The reasons for the appearance of late blight
There are zones with a high degree of susceptibility to this disease and with a lower one, but in any case it is better to prevent the disease than to fight it later and lose the crop.
Good conditions for the growth of fungi are:
- If there is an excess of lime in the soil, most often this is due to the fact that gardeners, fleeing the high acidity of the soil, introduce into it an uncontrolled amount of lime mixtures and solutions.
- Tomatoes that have not received sufficient nutrition lose their immunity and become prone to various infections, including late blight.
- A humid greenhouse environment is an excellent tool for the development and spread of the disease.
- Dense plantings create conditions under which air does not reach the plants and constant stagnation of moisture is observed.
- Sharp temperature drops, which are not uncommon at the beginning and at the end of the summer period. Because of what a lot of dew falls out, it acts as an additional source of moisture.
- Lack of iodine, potassium and manganese in tomatoes significantly increases the chances of late blight.
- Heavy rains contribute to the development of the disease.
- Tomatoes can receive fungal spores from nearby infected plants, from which they are washed with water into the soil, and then spread throughout the garden.
In dry sunny weather, late blight does not develop, at this time you can get rid of all infected stems and leaves and save the harvest.
Chemical means of protection
This group of fungicides has a suppressive effect on phytosporosis spores and limits the spread of the disease.


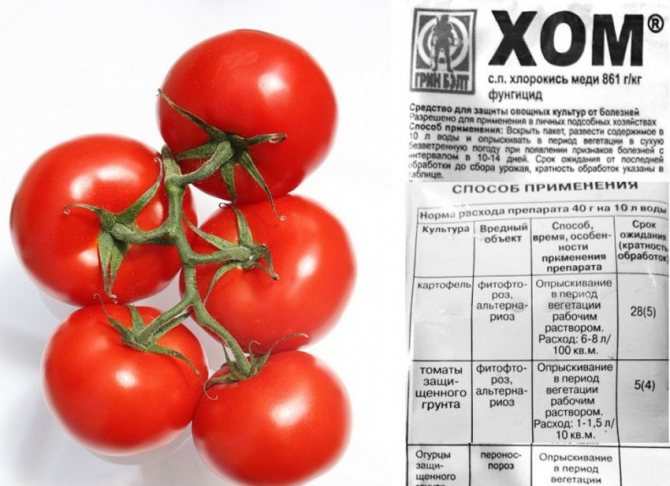
Hom contains copper oxychloride, remains toxic for 5-7 days. It is often used for preventive purposes.

Ordan is a synthesized oil-based fungicide, highly toxic.


Quadris is a new generation drug with a wide spectrum of action, medium toxicity.


Valuable Tips
- Can I take seeds from diseased tomatoes?
To collect seeds, you need to choose the best specimens. This is the basic rule of seed production. If it becomes necessary to collect tomato seeds from a bush damaged by late blight, this is possible, given that the spores of the fungus require living tissue to survive. The seeds are thoroughly dried and disinfected before planting.


- How to save infected tomatoes?
If preventive measures did not work and the disease began to spread, it is almost impossible to stop the process. It is urgent to remove healthy fruits. To save them, you can:
- immerse for 5-10 minutes in a solution of one of the copper-containing preparations in doses used for spraying;
- immerse in boiling water for 1-2 seconds with a sharp movement.
After processing, the tomatoes are dried and stored for some time.
- Can contaminated tomatoes be eaten?
For canning, healthy fruits should be used so that during storage they do not provoke the development of microorganisms harmful to health. Eating fresh or after heat treatment of fruits, from which damaged areas have been removed, is allowed.
Timely implementation of preventive measures and identification of foci of late blight in tomatoes, competent use of drugs, will prevent the development of the disease and maintain a high-quality, safe harvest.
Unconventional methods
Many gardeners use folk remedies for late blight on tomatoes. They have been tested in practice and are quite effective.




Feeding cucumbers: 110 photos of the best products. Video advice from experts when, what and how best to fertilize and feed cucumbers during growth

How to tie tomatoes correctly - quick and easy ways to tie vegetables. Tying technique and 100 photo examples of tomato garter


How to tie cucumbers in the open field - 85 photos of the main methods of garters and video instructions for beginners
Antiseptics: iodine, furacilin, hydrogen peroxide have a disinfectant. The solutions are used to wipe the fruits removed from the affected plants.
Medicinal antifungal agents are diluted at a concentration of 1 tablet per liter of water. This method has recently become popular.
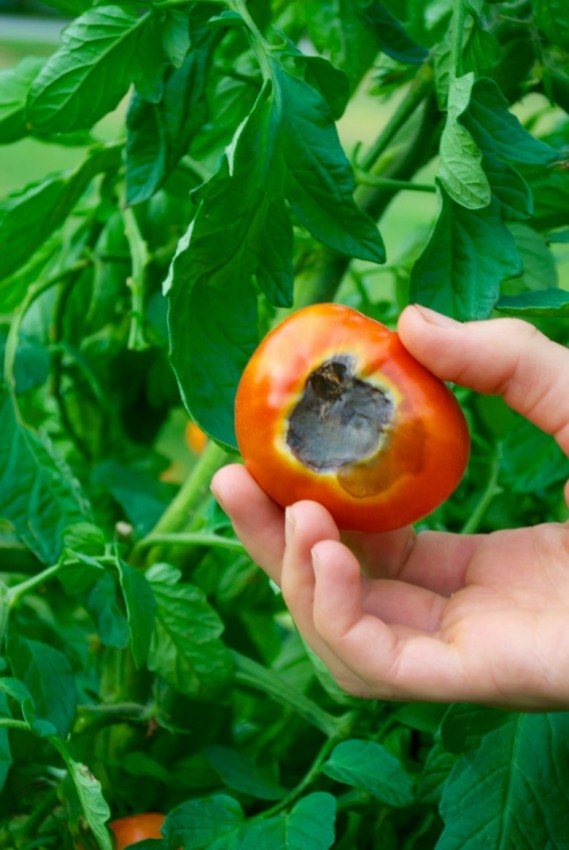


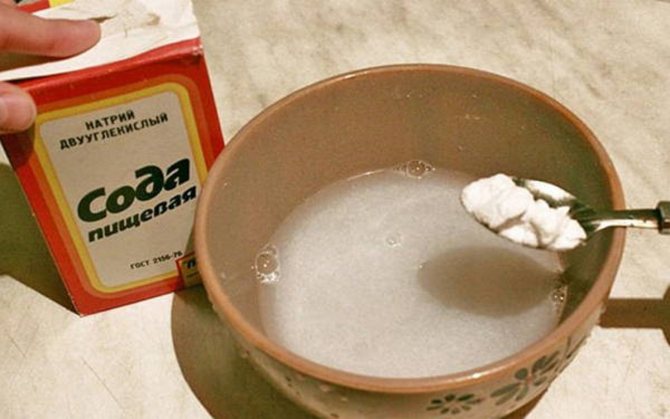
Wood ash, soda, fermented milk whey alter the acidity level. Soap is added to these solutions for better adhesion: 2 tablespoons per bucket of water.
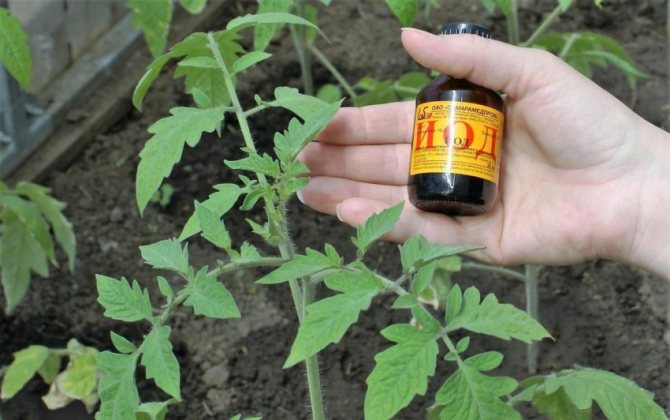


Methods for treating tomatoes from late blight
Treatment of late blight is of two types: chemical and folk.
Chemicals used to treat fungus include:
- hom;
- furacilin;
- phytosporin;
- trichopolum;
- metronidazole.
How to treat:
- Hom is a contact fungicide containing copper oxychloride. Hom can be processed 3-5 times a season in the morning or evening, but no later than twenty days before harvest. It has an effect for about two weeks, while it is easily washed off with water or rain. The solution is prepared from 40 grams of reagent per 10 liters of water, not suitable for storage. When preparing the solution, you must wear protective clothing.
- Copper oxychloride acts on the surface of the fruit and foliage, without penetrating inside. But it is more suitable for preventive actions. It does not have a cumulative effect, therefore it is not addictive to fungi.
- Furacilin is an antibacterial drug, so its solution can be stored throughout the season. For preparation, it is necessary to crush and dissolve 10 tablets in 10 liters of water. Spraying with furacilin is carried out 3 times: before flowering, when the ovary appears and when the fruit ripens.
- Fitosporin is a bacterial pesticide that is biologically safe. This drug is able to penetrate into the plant, thereby killing all harmful bacteria. For the solution, you need to stir 2 teaspoons in 10 liters of warm (no more than 35 degrees) water in a plastic bucket, metal is not suitable, and let it brew in the sun to activate bacteria. They are treated with phytospirin every 10 days or after rain.
- Trichopolum and metronidazole are antimicrobial and antifungal medicines. The solution requires 2 tablets. It is processed every ten days and after rain.
Folk remedies include whey, kefir, vinegar, salt, soda, garlic, or toothpaste.
What is the danger of late blight?
Phytophthora is terrible because the disease is invisible at the first stage, especially since the disputes are very tenacious. They can be drowsy for a long time on the structure of the greenhouse, in the ground and even on the seeds of the plant. Spots appear on the tomatoes themselves, which gradually spread to the entire fruit, while it becomes deformed and begins to rot.
During decay, a sharply unpleasant smell appears. If the disease spreads, you can lose up to 70% of the tomato crop.
First signs
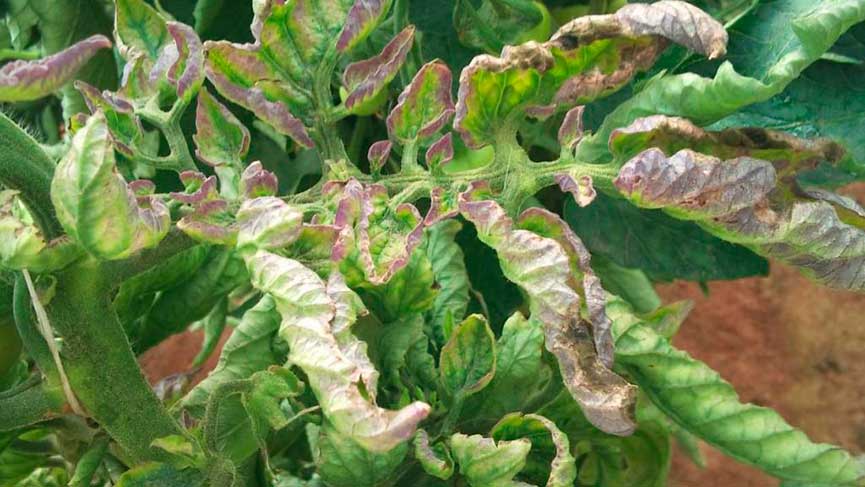
Phytophthora in the greenhouse and in the open field starts the same way. Its first signs:
- leaves curl;
- covered with tiny specks;
- the spots grow, turning into brown marks visible to the naked eye.
How to recognize phytophthora? Those who have encountered it at least once can make a diagnosis without difficulty. The spots on the leaves are so characteristic that they cannot be confused with any others. They are brown in color, of various shapes and sizes, and can be found on any part of the leaf. The lesion always starts from the lower plates and then spreads to the stems and fruits.