Home / Pests and diseases
Back to
Published: 27.02.2019
Reading time: 6 minutes
0
440
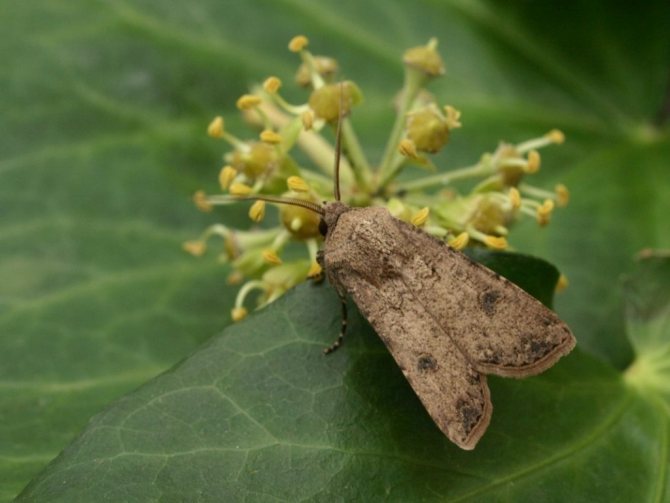
Scoops do not live except at the poles. They can be seen in all climatic zones of the Earth, including tundra or deserts. In nature, there are about 35 thousand species and varieties. The name is associated with a bird and at first evokes positive emotions. So, the white-faced scoop is a feathered predator, there is also a collar, a scops owl - they are interesting to nature lovers. African, North American, West American - these are also birds! But the insect destroys crops.

All species of this insect are pests for the plant world. So, the cotton scoop easily settles on tomatoes or corn. A smart pea will not disappear among the weeds. There are types of meadow, grain, alfalfa ... The most harmful are the so-called gnawing scoops.
Have questions? Ask and get useful advice from professional gardeners and experienced summer residents. Ask a question >>
- 1 General information on gnawing scoops 1.1 Winter scoops
- 1.2 Garden scoop
- 1.3 Cabbage scoop
Step-by-step instruction
The fight with the scoop has a number of characteristic features that must be taken into account depending on the age of the individuals.
How to deal with butterflies?
REFERENCE: If the above methods do not bring the desired result, you must use chemical insecticides.
Adult scoops lay larvae on plants, which soon begin to devour leaves and young shoots... The main methods of dealing with butterflies:
- Using pheromone traps. These devices show the gardener and gardener the exact time of the appearance of butterflies and, accordingly, caterpillars;
- Fighting butterflies with the help of their natural enemies - poaching and trichograms;
- Using proven folk recipes;
- Digging up the soil in the fall, since the moths hibernate in the soil;
- Biological products against insects.
The easiest way to protect your cabbage from pests is a gnawing scoop:
How to get rid of scoop caterpillars?
Fighting scoop caterpillars has its own characteristics... The main methods include:
- Deep digging of soil in spring in order to reduce the number of overwintered moths;
- Elimination of weeds - it is these plants that serve as the main base for feeding the larvae;
- Hand-picking the first larvae and caterpillars;
- Using folk remedies;
- The use of biological products;
- Treatment of plants with chemical insecticides;
- Autumn digging of soil for the destruction of individuals that remain for the winter.


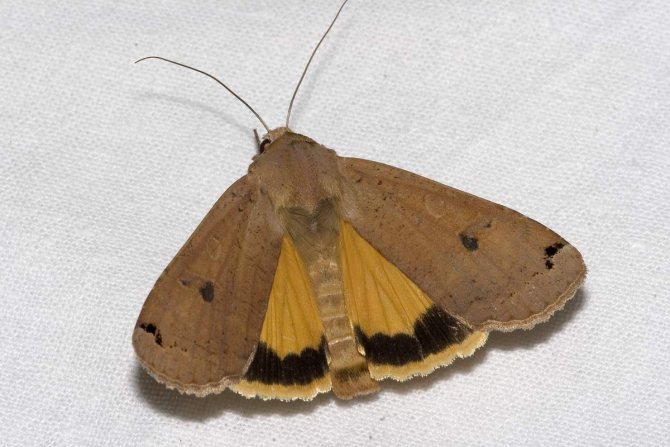
Pea scoop
These pests damage legumes and grains. They inhabit many areas. Pea moths parasitize peas, alfalfa, clover, sugar beets and legumes.


Some of the scoops feed on animal blood.
The butterfly measures no more than 42 millimeters. The front wings are black-brown in color. There are transverse lines on the wings. Caterpillars are yellow in color, the body size of the caterpillars reaches 4 millimeters.
Pea scoops fly in June-September. These butterflies feed on succulent plants. One female lays up to 400 eggs. The caterpillars eat the leaves. 2 generations are developing in a year.
How to destroy a scoop and its caterpillar on different vegetables
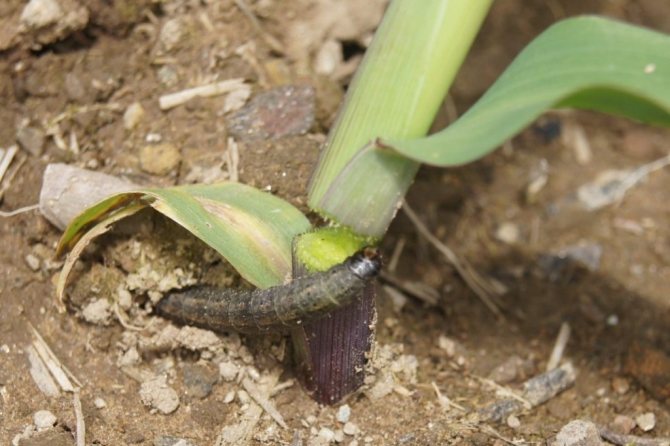
The moth larvae prefer to feed on tomato leaves, cabbage seedlings and young potato shoots. If you do not start to fight the pest in a timely manner, you can lose the entire crop on the site.
Potato scoop
In addition to the general methods of exterminating insects, the main features of the fight against the potato scoop should be noted:
- Regular weeding of potato beds from weeds, especially cereal plants;
- The use of insecticides twice a season - for soil cultivation and spraying of plants.
IMPORTANT: Do not plant tomatoes next to potato beds - the scoop can easily jump from one plant to another.
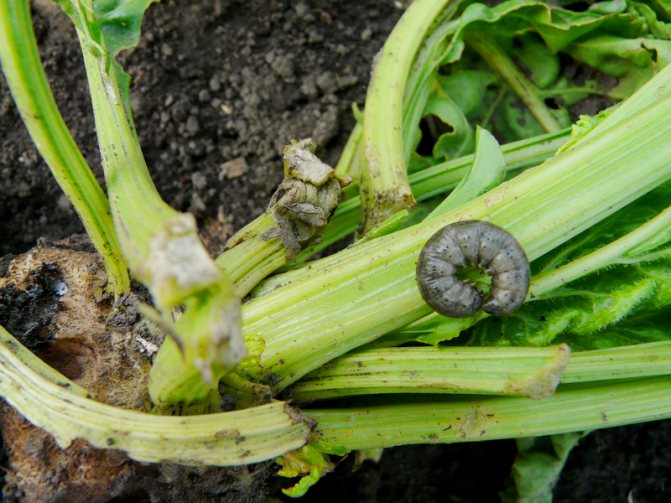
Butterfly cabbage scoop
Insect control on cabbage consists of the following actions:
- Deep digging of soil after harvest and before planting seedlings;
- Try to plant cabbage seedlings in open ground as early as possible in order to avoid mass infection of young plants;
- Regular inspection of cabbage and collection of manually found larvae (caterpillars);
- Top dressing of cabbage seedlings with potassium chloride and superphosphates;
- Using folk recipes and biologics.
IMPORTANT: Chemical processing of cabbage is recommended only when the above methods do not work.
Scoop on tomatoes
The set of measures for the destruction of butterflies and caterpillars is generally similar to the above-described methods of fighting on potatoes and cabbage. However, some salient features should be noted:
- Weed the weeds regularly, pay special attention to the loboda and nettles;
- Do not allow weeds to reappear in tomato beds;
- Use biologicals - only if there is no effect, use chemicals.


Control measures
All means of fighting the scoop can be divided into two groups:
- Biological preparations;
- Chemicals.
Let us consider in more detail the principle of action and the method of using these drugs.
Biological agents

Biologics are divided into two main types:
- Bacterial agents - contain toxins of various microorganisms that destroy pests;
- Avermectins - the results of the vital activity of pathogenic fungi Streptomyces avermitilis. They destroy not only the scoop, but also ticks and aphids.
The following drugs are widely used to combat the scoop:
- Dendrobacillin Is a bacterial agent against scoops, intended for spraying crops and garden plants. To prepare a solution, 30 g of the drug must be diluted in 10 liters of water;
- Bitoxibacillin is a waste product of microorganisms that disrupts the digestive system of the scoop and has a pathogenic effect on subsequent generations of the insect. You will need only 20 ml of the preparation for a bucket of water;
- Lepidocide is a bacterial preparation that destroys the moth caterpillars. The consumption rate is about 35 g per 10-12 liters of water;
- Entobacterin is a microbiological substance against larvae and caterpillars of the moth. To treat 1 hectare of area, you will need 3.5 kg of the drug;
- Fitoverm is a bacterial agent that affects a large number of pests. For a bucket of water, 1 to 4 ml of the drug is enough;
- Agravertine is a waste product of fungi. To destroy the scoops, it is necessary to dissolve 3 ml of Agravertine in 1 liter of water;
- Natur Guard is an insecticide with neurotoxic effects on the scoop. The consumption rate is 10 ml for half a bucket of water.


Chemicals
There are these types of chemicals:
- Pyrethroids;
- Neonicotinoids;
- Organophosphorus compounds.
REFERENCE: The latest generation of drugs are often produced in a combined composition.
The most effective remedies:
- Zolone is a highly toxic organophosphate drug. For spraying on 5 liters of water, 2 ml of the substance is enough;
- Decis pro. The product is intended for spraying both the plant and the soil around it. For 10 liters of water, only 1 g of the drug is needed;
- Bazudin is a soil treatment chemical. A hectare of crops requires 20 kg of the drug;
- Proteus is a two-component preparation that effectively eliminates caterpillars and moths. Consumption - 7 ml per 5 liters of water;
- Karate - Zeon. This insecticide is designed to eliminate caterpillars and pest larvae. To treat a hectare of crops, 100 ml of the drug is enough.
Experienced summer residents also recommend the following chemicals:
- Danadim;
- Fury;
- Dursban;
- Fufanon;
- Kinmix;
- Stefesin.
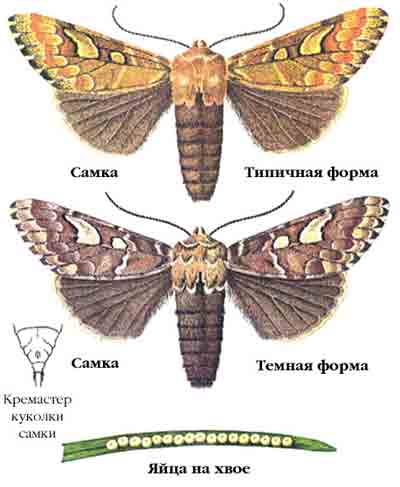
Description and photo
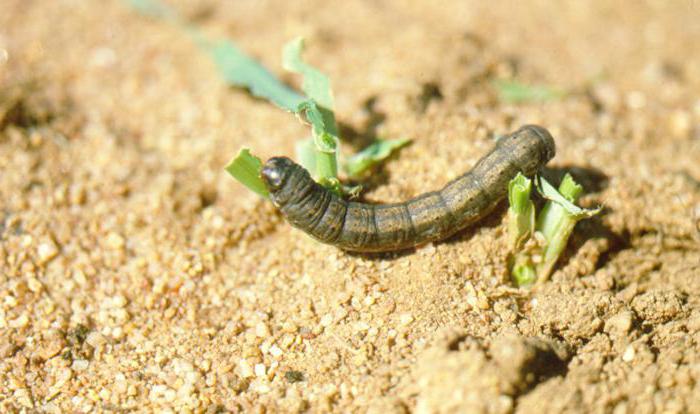
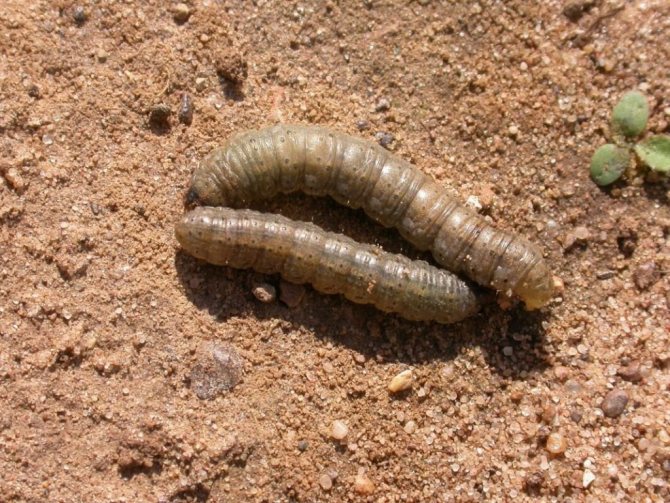
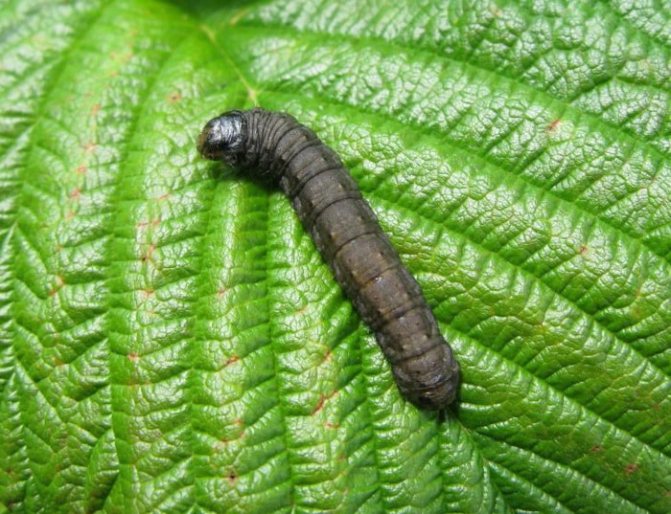
The scoop butterfly is an insect with a wingspan of up to 5 cm. When folded, the brown or brown wings are tightly pressed to the body. The scoop lives for about a month. The female butterfly lays several hundred small eggs, attaching them to the underside of the leaves. After 10 days, larvae (caterpillars) hatch from the eggs, which immediately begin to feed on greens, gnawing out the delicate tissue of the leaf, leaving the veins intact.


The flight of the scoop butterfly in the Moscow region and the middle lane begins in mid-June, in the southern regions the pest is active since May. At the end of August, scoops disappear.
Types and differences
In total, there are several thousand species of these butterflies in the world. The greatest harm to crops is caused by gnawing scoops. A group of pests, which include potato, winter, exclamation scoops. Butterflies are active in the evening and at night, laying eggs on the leaves from the underside. Caterpillars damage seedlings of beets, carrots, cabbage, sunflowers, peas and other plants. In poured root crops and potatoes, the larvae gnaw through the passages without damaging the skin.


Winter scoop. Yellowish-gray moth inhabiting the entire European territory of Russia. Active flight starts in May and lasts until the end of July. Winter moths are very fertile, capable of laying up to a thousand eggs. Caterpillars hatch after 5 - 7 days. In the early stages of development, it lives on the lower leaves and on young seedlings of plants, and later goes into the upper layers of the soil. The adult caterpillar is shiny, thick, greenish-yellow in color, up to 5 cm long. One voracious individual can damage up to a dozen plants per night.
In areas with a warm climate, the winter moth gives two generations. Caterpillars hatched in early autumn feed on grain and seedlings of winter crops.


Exclamation scoop. A small gray butterfly, with a wingspan of up to 3.5 cm. Caterpillars up to 3 cm in length, dark gray. It develops in the same way as winter. Causes severe damage to seedlings of carrots and cabbage.


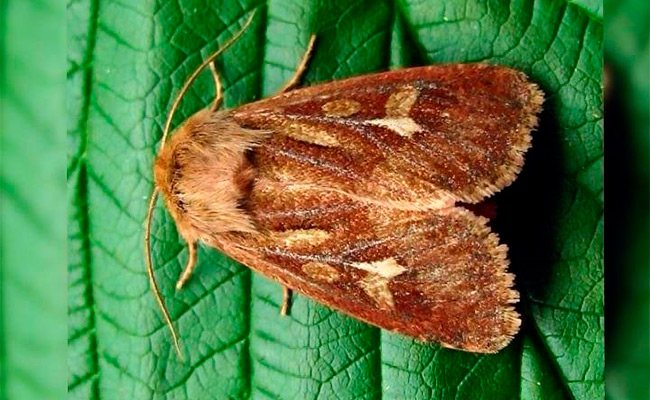
Garden scoop. Butterflies of this species are brown-brown, caterpillars can be light green or brown. Appears at the end of May, butterflies lay 50 - 70 eggs on leaves from the ground. The caterpillar menu is extensive: radishes, beans, peas, cabbage, turnips, peppers, tomatoes.


Cabbage scoop. A dangerous pest from the group of leaf-eating scoops. Large dark gray butterflies with scalloped wing edges begin to fly from mid-May. Each season is capable of producing two generations. The female lays eggs on cabbage leaves, although she does not disdain other crops: peas, tobacco, beets, salads.
Caterpillars hatch after 10 - 12 days and gnaw holes of irregular shapes on the leaves, leaving rigid leaf veins not eaten. Caterpillars often bite into the head of cabbage, contaminating it with their excrement.
Folk ways
The safest ways to combat a pest are folk methods.
These include herbal infusions, decoctions of plants, as well as the use of various substances, deterrents and traps.
Decoctions of such plants as:
- Sagebrush;
- Pepper Highlander;
- Black and red elderberry;
- Tomato tops.
Infusions of red bitter pepper and Sarepta mustard powder are also effective against scoops.
It is recommended to spray agricultural crops with infusions:
- Burdock (burdock);
- Onions;
- Garlic
- Large-flowered delphinium;
- Black elderberry.
IMPORTANT: You need to use folk methods regularly, until the pest disappears completely.
Scoop gamma
These pests are polyphagous. They are ubiquitous in Russia. Gamma scoops damage field crops such as beets, potatoes, flax, hemp, legumes and the like.
Butterflies measure up to 48 millimeters. The front wings can be from purple to gray, they have a spot in the form of a "scale", hence the name. These scoops fly during the day and feed on flower nectar. One female lays 500-1500 eggs. During a year, 2 generations of scoops of scales can develop.



















