What does it look like
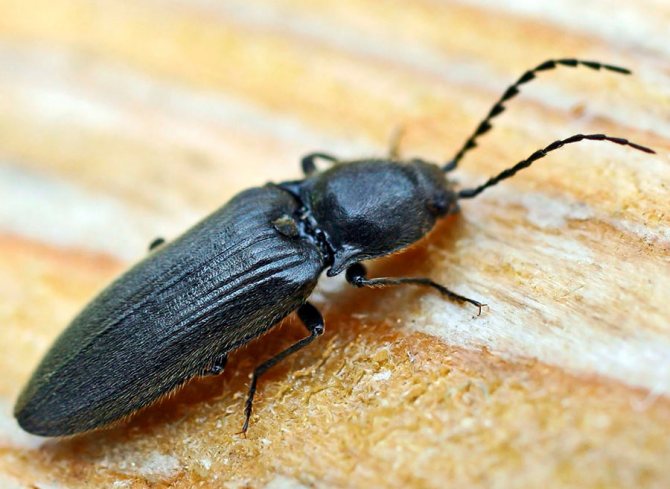
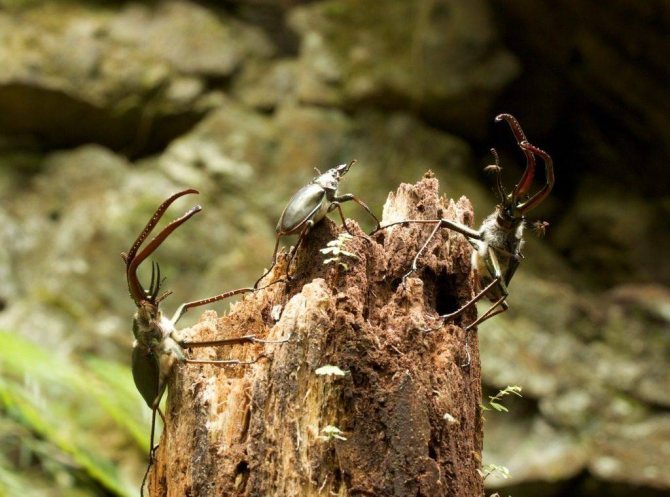
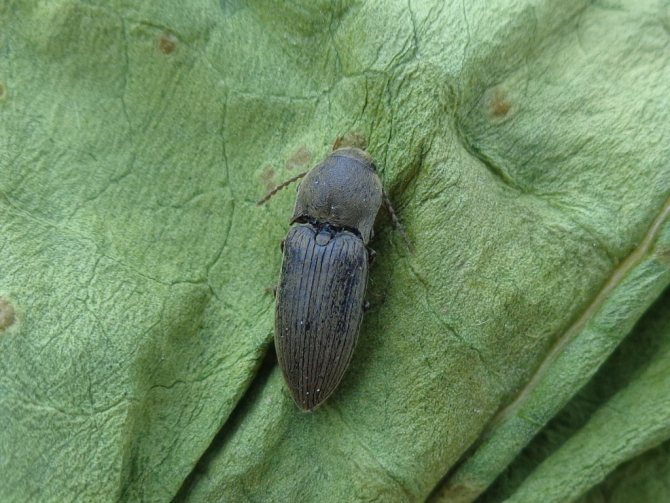
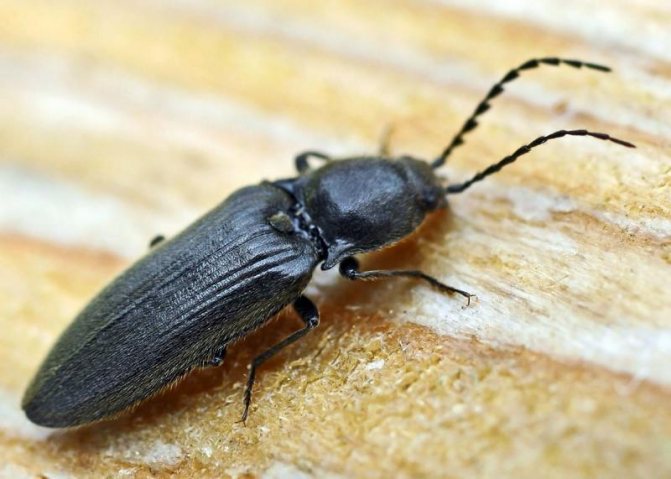
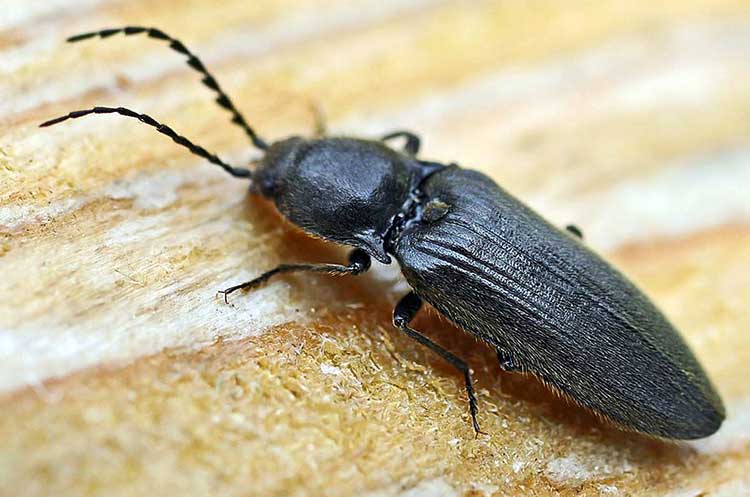
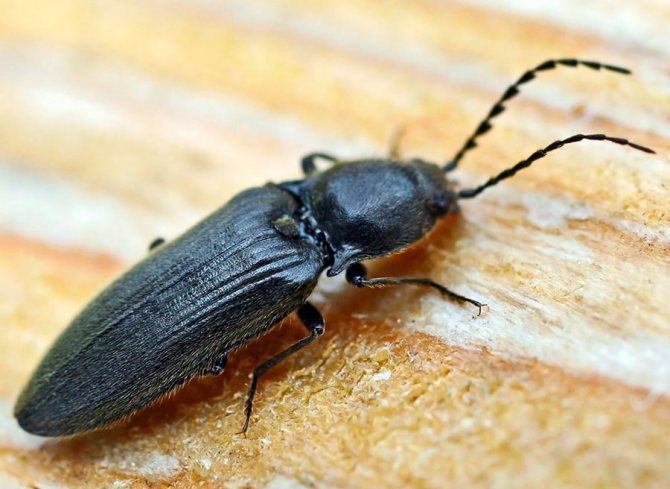
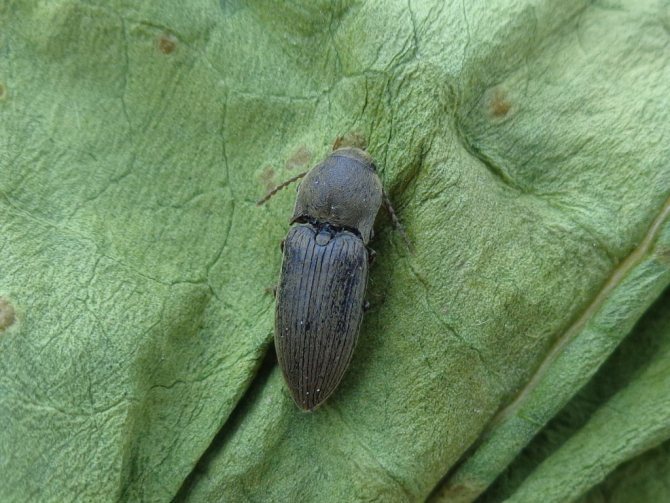
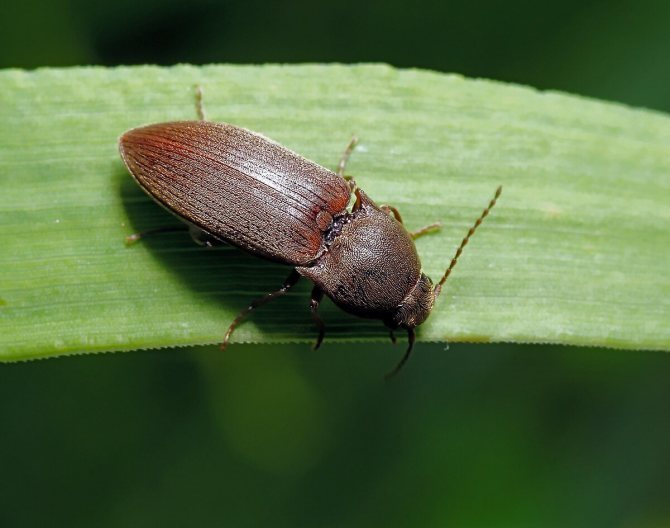
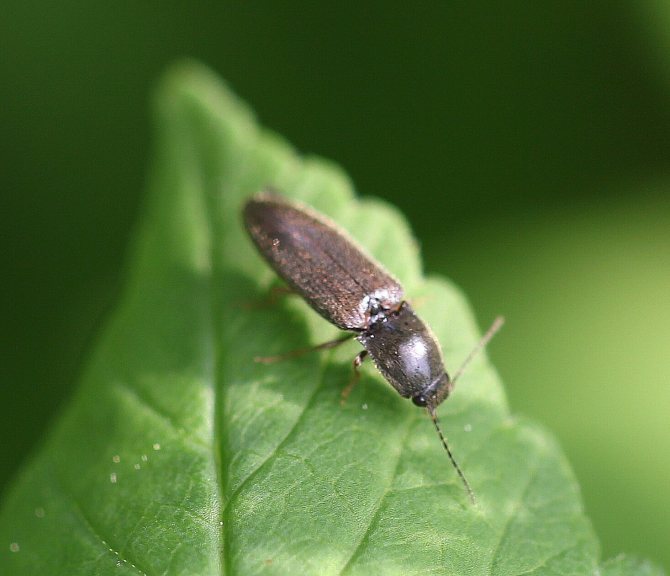
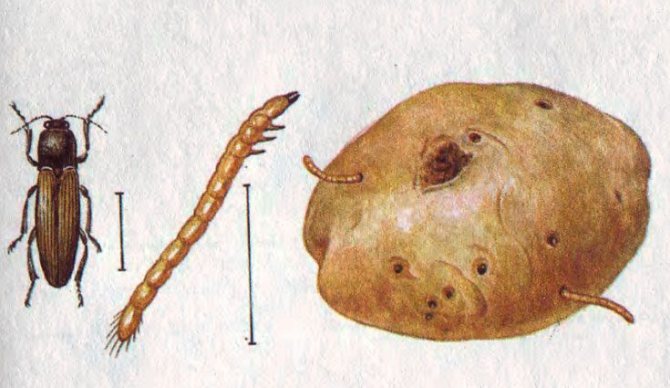
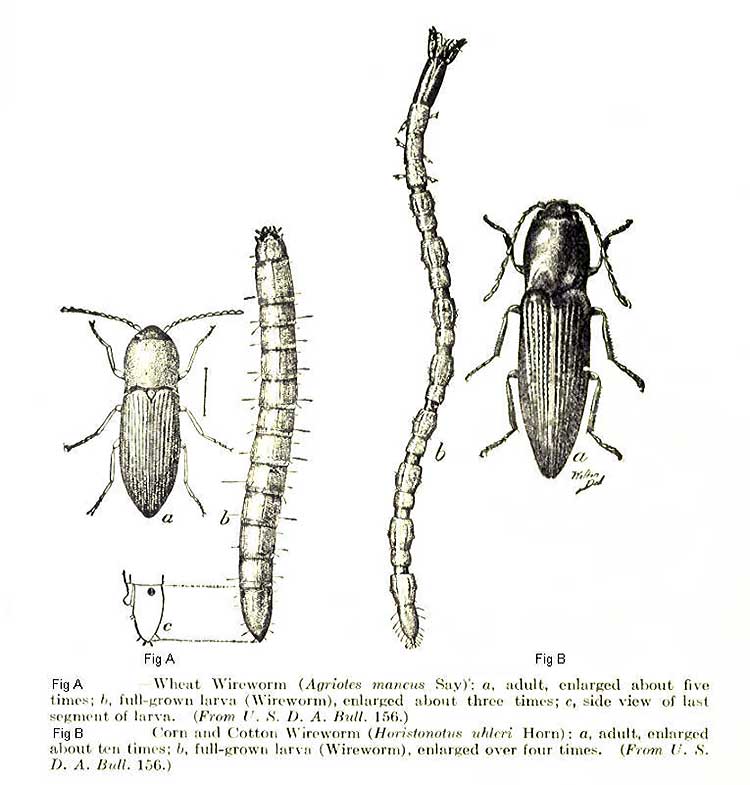
The wireworm beetle is a typical Coleoptera. The body is oblong, elongated, from a few millimeters to 2 cm long. One-third of the part is occupied by the chest. There is a long, even mustache on the head. Many species are brown, black with a metallic sheen, streaks, spots all over the body. A photo of the clicker beetle is presented below.
A special characteristic that distinguishes the clicker from other beetles is the presence of a hopping mechanism. It is formed by the front, middle part of the chest. The wirewheel mechanism is set in motion when it is in the supine position. Initially, it bends the front of the chest, pushes off with its hind legs, turns over in the air.
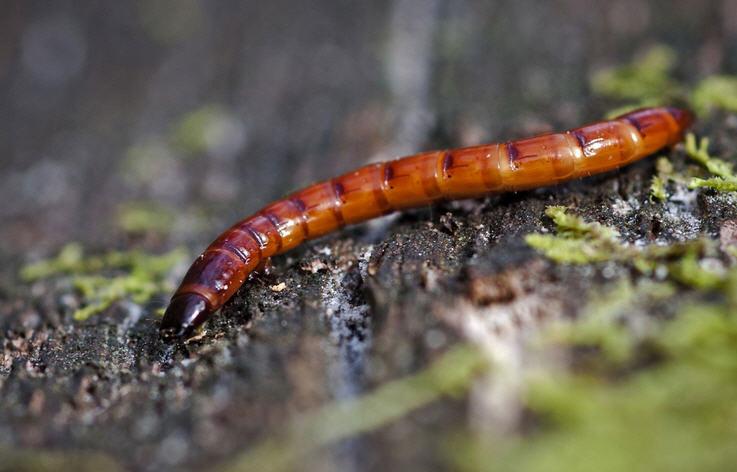
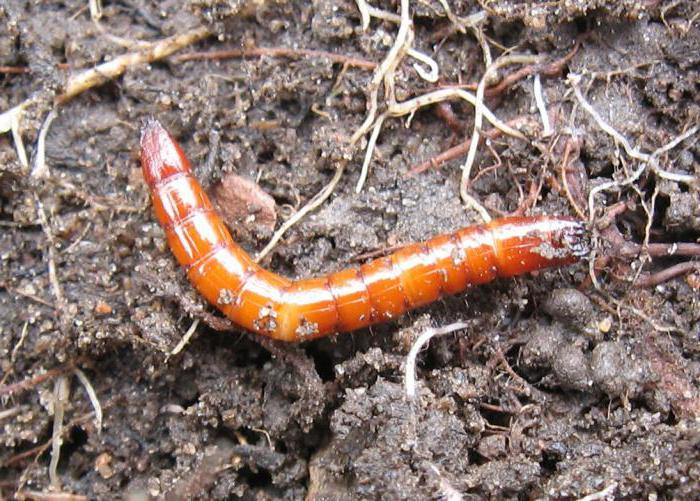
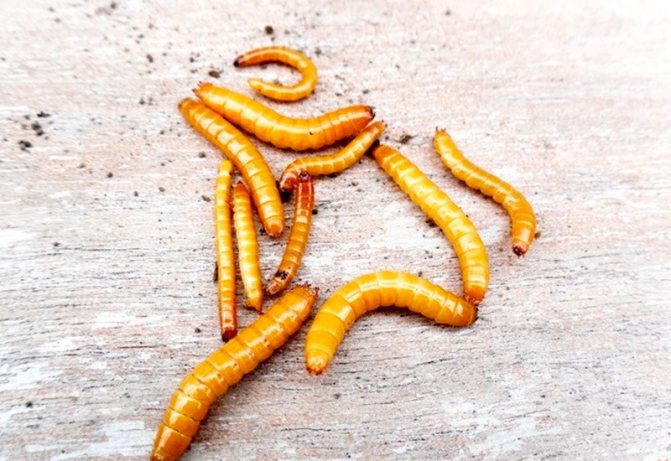
The larvae of the click beetle have an elongated cylindrical body. In some species, the caterpillars are practically naked, in others they are densely covered with hairs. The color is dark brown, light yellow. The photo of the developmental stage of the snake beetle is located further. The pupa is elongated, the body does not have a strong chitinous cover. Beige, yellow or white.
In Central America, there are species of crackle beetle that use bioluminescent light. Females emit light to attract males, wireworm larvae to attract prey.
Varieties
In total, there are about 12,000 species of click beetles, of which 700-750 are found in the CIS countries. Many varieties of the click beetle cause irreparable harm to garden crops.

One of the most common species is the dark nutcracker. His chitin is brown-black, occasionally rusty-brown in color. The upper elytra are framed by gray hairs. The larvae are yellow-brown, can reach 25 mm in length. The last segment of the wireworm is equipped with spiracle-like dimples.
The larvae of black cracker and turf mainly damage potatoes and vegetables. The larvae of the striped, dark and shiny beetles damage sunflowers and all cereals.
An equally dangerous pest is the small nutcracker (sowing). Its body length can reach 6-9 mm, width - 1.2-2.8 mm. Chitin is brown. It damages mainly cereals, peanuts, beets, sunflowers.
The striped (bread) nutcracker has an oval elongated body 7-10 mm long. Elytra are dark brown. It feeds mainly on the roots of cereals.
The steppe nutcracker damages almost all agricultural crops. The body reaches 9-13 mm in length, the width varies between 2.9-4.5 mm. The head is large punctured. Pronotum black, elytra brownish black.
Another omnivorous species of beetle is the black nutcracker. The body is completely black, and a metallic hue may appear. Body length varies between 10-14 mm.
In Central America, there is a species of clicker that is capable of emitting a fairly bright light. The Indians tied beetles to their feet to illuminate the path at night.
The Parreis nutcracker is considered the largest nutcracker in the fauna of Russia. Its body length can reach 35 mm. It is included in the register of the "Red Book of Russia".
Lifestyle
Adults lead an open lifestyle. Most of the time they spend on plants, woody vegetation, or hide in secluded places - forest floor, manure, compost pit, wood cracks, bark, stones.
Imagoes do not feed at all throughout their adult life, or they eat the green part of plants. Their main purpose is to lay eggs. For one clutch reproduces up to 1500 eggs, places them in piles of 5 pieces.


Clicker beetle (wireworm)
Wireworm larvae turn into adults for 5 years. From the second year they turn into real pests of agricultural crops. Omnivorous, feed on roots, buds, roots.
The wireworm beetle chooses acidic soil for egg laying. Infection of the site occurs due to non-observance of the rules of crop rotation, improper care of the land.
Appearance conditions
Pests appear on garden plots for various reasons. Firstly, it can easily penetrate from neighboring areas and lay eggs. Often the owners themselves are to blame for the fact that a clicker beetle appeared on their site. As a rule, in garden plots, few adhere to agrotechnical rules, planting crops in one place every year. This is especially true for planting potatoes, since the weight volume of such plantings is always greater in comparison with other crops. Potatoes have to be planted every year and there is simply nowhere to move the plantings of this culture, given how much land a gardener has. Even in villages where people have more land, no one seriously thinks about this problem: potatoes were planted in one place, and they continue to do this from year to year.
Reproduction - photo and description of the click beetle at all stages of development
In early spring, the female lays eggs in the soil, climbing into cracks. Larvae appear after 28 days. The first stage of their development begins. They live in the ground, feed on small microorganisms. From the second year, they begin to actively eat root crops, roots, swollen buds of plants, thereby causing irreparable harm to crops.
The full development cycle lasts 5 years. In the last year, puberty occurs, the wireworm beetle makes its way into the upper layers of the soil, pupates. A full-fledged insect is published.
Favorable conditions for the development of the larvae of the larvae of the click beetle are high humidity, acidic soil.
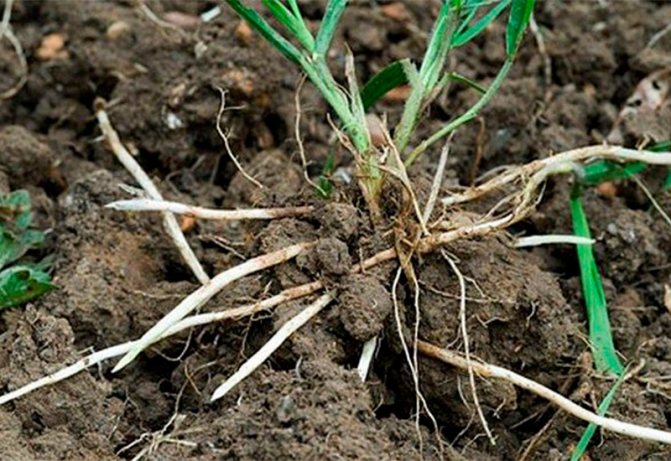
Wireworm on potatoes
Among all the root crops in the garden, the drotyanka likes to concentrate in areas where potatoes grow.
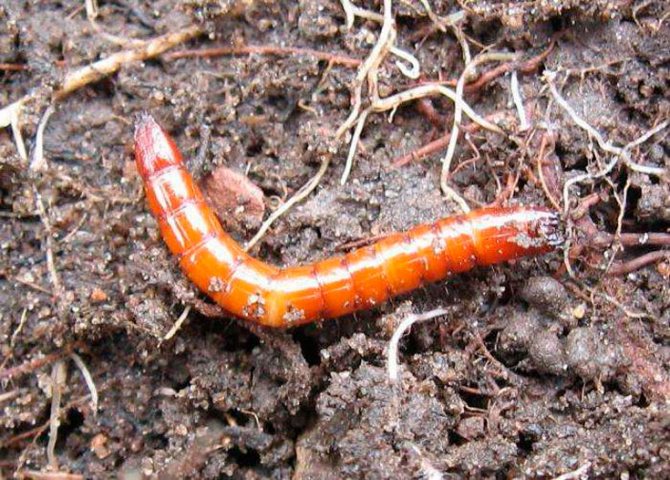
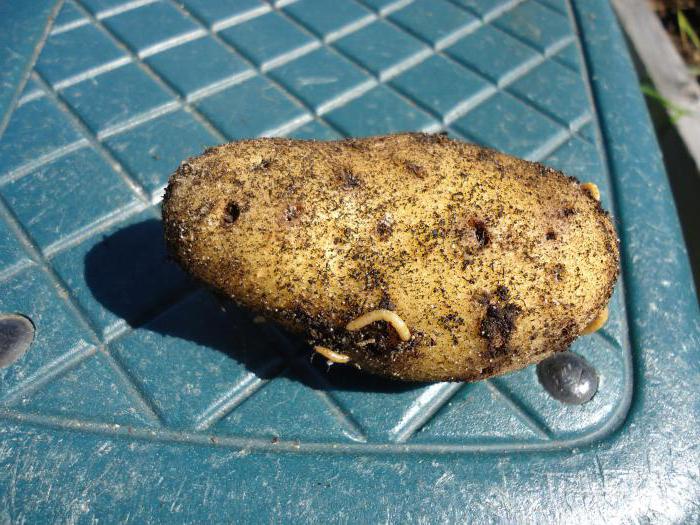
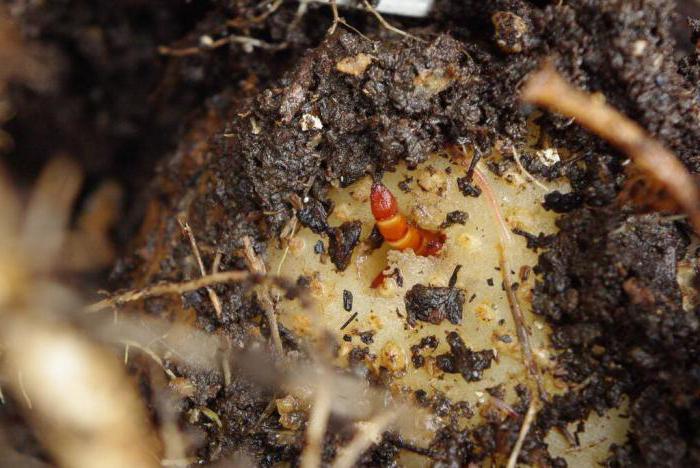
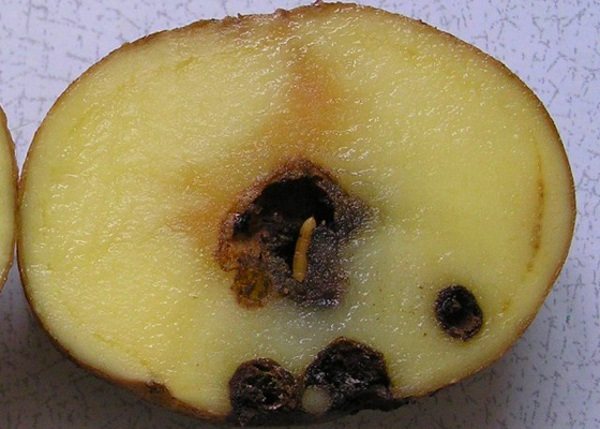
Photo of a wireworm larva in a potato:


In the cool season, it lives at great depths, but with the onset of spring heat it rises almost to the very surface of the soil.
That is why, from the moment of planting the tubers, they become vulnerable for the wireworm beetle.
It bites into the peel of the root vegetable, penetrating deeply into it, as can be seen in the photo. At the same time, outside on the potatoes remain visible and unpleasant tracesresembling the dying off of the outer tissues of the plant.
In addition, a destructive process of rot and spoilage begins inside the potato, which can lead to complete rotting of the fetus... The larvae of the click beetle also feed on young tubers, thereby destroying almost the entire crop of potatoes.
What does the insect eat
The adults do not eat anything or feed on the juices of the green parts of plants. They don't do much harm. The larvae are the real destroyers of crops. The thin, strong structure of the body allows them to easily break through the peel of root crops, roots.
In our area, there are about 750 species of cod beetles. The diet of each of them is slightly different.
- The wireworms of turf and black cracker prefer potato tubers and vegetable crops.
- The larvae of the shiny, striped beetles eat cereals and sunflowers.
- Small nutcracker, sowing eats peanuts, beets, carrots, cereals.
- The steppe wireworm damages almost all crops.
Insects do not disdain weeds. Leek and burdock are eaten with great appetite. If you do not take proper measures, pests will completely destroy the entire crop, all vegetation on the site.
What plants are affected by the pest
Most often the pest lives in the fields with root crops, but its reproduction occurs in any area with vegetation. The favorite places of the parasite are:
With great difficulty growing vegetables on their land plot, how much disappointment people experience when collecting spoiled and unusable crop.
The main reason for this is all kinds of pests living in the earth.
One of the central places among them belongs wireworm... How to kill a wireworm?
Control methods
It is possible to destroy larvae, adults in different ways, ways. The desired result comes faster when several are combined.
Agrotechnical control methods
They are highly effective, long-lasting, but the result will have to wait a year or even more.
- Dig up the soil in late autumn. The larvae, eggs, caught at the top, die from the low temperature.
- During the growing season of plants in sunny weather, the soil should be loosened. The larvae do not tolerate high temperatures and die. The same thing happens with wireworm eggs.
- You should not plant a crop for two years in a row in the same place, you need to follow the rules of crop rotation. Beans and buckwheat will help get rid of the nutcracker in potatoes. When planting potatoes, beans are planted every 3 bushes.
- If the land is empty for a year, it is recommended to plant it with buckwheat, peas. From such crops, all wireworms will crawl to neighboring areas.
- One of the most effective ways to combat wireworms is to lower the acidity of the soil. Mineral fertilizers, ash, hydrated lime, chalk, eggshells are added to the soil.
- During planting of potatoes, onion peels are thrown into the holes, mustard powder is poured between rows of beds with beets, carrots.
- Marigolds will help scare away the nutcracker from the site, if you plant them around the perimeter of the garden, between the beds.
- A few weeks before sowing, oats, barley are planted, then they are removed.


Fighting the wireworm
It is imperative to remove weeds, periodically loosen the soil. If it is difficult to fight with agrotechnical methods, you can use insecticides, then take preventive measures to prevent re-contamination of the soil.
Chemical methods
In the garden, potatoes suffer more from the wireworm than other crops. Insecticidal preparations are used to treat soil, planting material, and the green part of the plant.
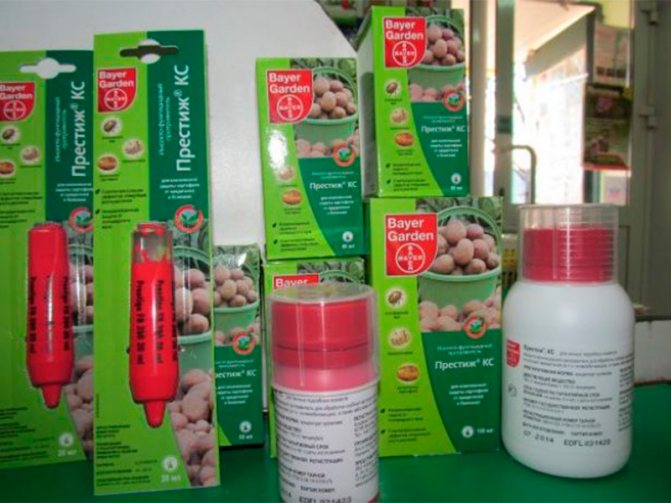
- Prestige. Poison with a broad spectrum of action, long lasting effect. The solution is prepared immediately before use. 10 ml of cold water will require 10 ml of the drug. Stir thoroughly for 10 minutes. Potatoes are treated in a solution, allowed to dry, planted in holes. The duration of the poison is 50 days, after which the insecticide is split and neutralized in the soil. In Prestige, you can also soak the roots of plants, seedlings before planting in open ground or greenhouses.
- Aktara. A universal remedy for many agricultural pests. Used for spraying the green part of the plant, soil treatment. The solution is extremely easy to prepare. Dissolve 10 ml of the concentrate in a bucket of cold water. Stir well. Water the holes before planting potatoes, beets, seedlings. 10 liters of solution is enough to process 10 sq. m. vegetable garden. The poison is neutralized after 60 days.
- Taboo. Insectoacaricidal agent is used to treat sowing material, seeds. Apply immediately before planting. Dilute 10 ml of the product in 1.5 liters of water. This amount is enough to process 125 kg of seeds.
Description of the pest
Wireworm Is the larva of the click beetle.When turned over, this beetle makes a specific click. An adult is about 1.5 cm in size, painted brown. An adult insect does not harm the crop. The life cycle is about 4-5 years. The pest is in the larval stage for 3-4 years. Therefore, there are individuals of different ages in the soil.
In the first year of life, the larvae are practically inactive. In the second year, they turn yellow, acquire a dense chitinous membrane. Outwardly, they resemble wire. The beetles overwinter at a depth of 15-30 cm. In warm weather, they are active in the evening. Beetles feed on leaves.
To get rid of this harmful insect or reduce its number, it is imperative to carry out a number of measures to combat it.
Beetle appearance and residence


There are more than 2,500 pests all over the earth. They come in different sizes, from 1 mm (larva) to 2 cm (adult). In the steppe zone, they have a bright color - rich brown. It is very difficult to confuse them with other types of insects, but if difficulties arise, you can see the photo and description of what the beetle looks like. Here are the distinctive features and species characteristics:
- pronounced stripes on the back of the click beetle, as in the photo;
- fine hair on the body;
- there are small antennae;
- oblong body;
Note!
Wireworms hibernate in the ground (if there is moisture in it), and in the spring they wake up and go hunting. Of all garden plants, beetles are more fond of potatoes. They feed on the tubers and leaves of the plant, therefore, if at least one parasite is found on the bush, measures must be taken to destroy not only the beetle itself, but also the larvae.
In addition to potatoes, beetles like to eat leaves:
- carrots;
- radishes;
- beets;
- celery;
- cabbage;
- tomato;
- Luke;
- corn.
The main reasons for the appearance of a wireworm in potatoes:
- acidity of the soil;
- soil moisture;
- a lot of vegetation.
The most dangerous time for plants is the beginning of spring until the end of August. During this period, beetles actively spread throughout the garden, if they are not destroyed, then soon the territory will be completely dried up. Pests are very dangerous for crops.
The larvae themselves in the first year of their development are not dangerous to plants, since they feed only on leaves and in small quantities. But for 3-4 years of life, the body of the larva hardens, it becomes like a real beetle. Then you need to stock up on various means against the fight against them. Every gardener should be able to distinguish a healthy bush from a beetle-infested one:
- wilted or dried bush;
- there are small passages in the potato tuber;
- the larva itself on a plant, in the ground or in a fruit;
- black spots from piercing passages on the tuber itself.
The fight against the wireworm should be started at the first sign of defeat.
Preventive actions
- Compliance with a crop rotation that includes legumes. Alternation of planted legume strips with main crops.
- It is recommended to plant corn, lupine or sunflower between the potatoes.
- Autumn digging of the soil to a depth of about 25 cm. The larvae on the surface will die at low temperatures. Shallow spring digging.
- Liming the soil with an acidic reaction. Dolomite flour is added every 3 years.
- Weed control (wheatgrass).
- Planting should not be thickened.
- Marigolds and calendula among the plantings frightens off the pest.
- Autumn sowing of mustard as green manure. When the mustard reaches 10 cm, it is cut and embedded in the soil. You can also use sweet clover or buckwheat.
- Timely harvest. Do not leave unharvested roots in the ground for the winter.
- It is advisable not to import land from other sites, it can be contaminated.
Chemical methods
- When planting, you need to shed the wells with a solution of potassium permanganate (2 g per 10 l).
- In the fall, potassium chloride can be added for digging.
- Liming.
- Application when planting nitrogen fertilizers. They are toxic to the beetle.
- Use of ammonia water.
Insecticides:
Wells or planting material should be treated with insecticides. Insecticides can be applied to sawdust, which is later used for planting in furrows or holes.
A biological method of combating the pest has been developed - the drug "Nemabakt". It is a symbiosis of nematodes and bacteria.
Folk ways
Folk methods are considered the most benign measures. They include the use of various traps, herbal infusions.
The wireworm trap can be potato tubers or other root vegetables.
Traps:
- At the end of a 20 cm long twig, put half a potato or other root vegetable and bury to a depth of about 10 cm. After a few days, remove the trap and remove the wireworms. After refreshing the cut and moistening it, place the trap back in the ground.
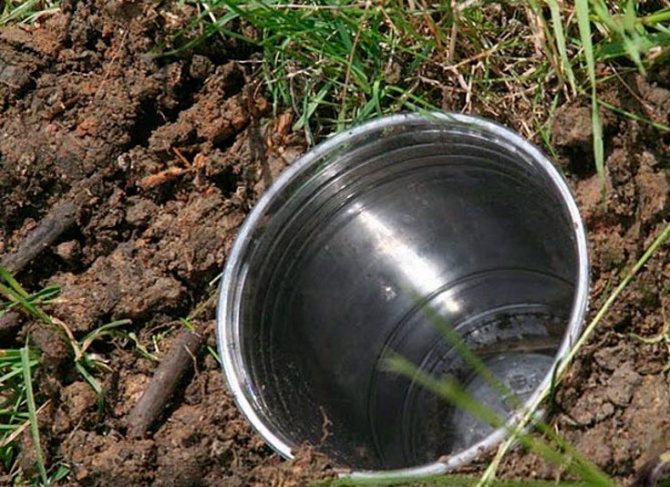
- Dig cans up to half a liter in shaded place along the neckline. They need to place pieces of potatoes or root vegetables. Inspect the traps and replace the bait every few days.
- Distribute evenly throughout the entire area small piles of manure, potato tops or straw. Pests prefer to settle in them. After a week, they must be destroyed.
- The rest of the thick kvass should be placed in a nylon sock and bury, leaving the end on the surface. A few days later, the trap is examined.
Description of a wireworm with a photo and how to deal with a wireworm
To understand what the wireworm of each type of clicker looks like, one would have to study entomology.
The dark nutcracker wireworm reaches 2.5 cm in length and has a dark yellow color of the chitinous cover. With a high degree of probability in the photo, the wireworm of the dark clicker beetle.
The wireworm of the steppe click beetle 3.5 cm long, brown-red.
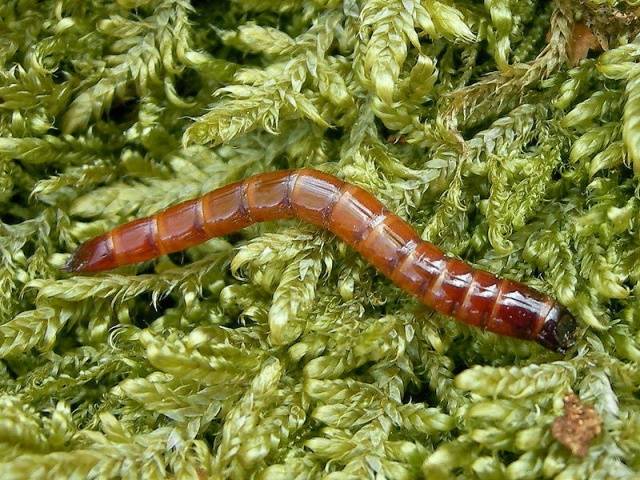


Wireworms of striped nutcracker up to 2 cm long and no more than 2 mm in diameter.
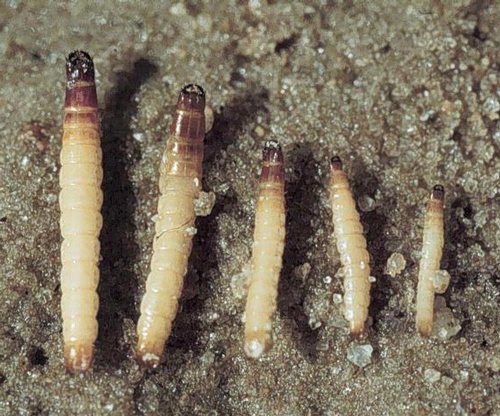


In this case, the larvae of the same click beetle can be of different ages and vary in size, like the wireworms in the photo.
They have a very tough chitin in common, which makes it almost impossible to crush the wireworm.
The fight against the wireworm for the gardener is even more important than the fight against the Colorado potato beetle. Colorada can be assembled by hand, the wireworm is not visible underground. In addition, Colorado eats only nightshade plants and does not touch others. The wireworm spares nothing. He drills any root crops and eats up the roots of any plants.
Colorado, by eating the foliage, reduces the yield and the size of the tubers. But they can be stored potatoes. Roots perforated with wireworm are no longer suitable for long-term storage. And they are no longer very suitable for eating because of the internal passages.


Almost all gardeners are trying to find a reliable remedy for the wireworm, since if the female nutcracker laid eggs in the garden, then the whole garden will be infected and for more than one year. Even if the wireworm has disappeared, this may mean that the larvae have pupated and, after a few years, adult beetles will emerge from the pupae, which will again lay eggs in the garden. One female can lay up to 200 eggs per year.
How harmful the wireworm is
Female click beetles, waking up at the end of April, start laying eggs. From one adult individual, from one to one and a half hundred eggs are produced. After 2-3 weeks, larvae appear from them. In the first year of life, they are harmless and unable to harm the crop. But from the second - this is a real disaster for gardeners. They live in the larval stage for 3-4 years, then pupate, turning into an adult insect.
Capable of spoiling seedling stems
The true face of the wireworm
The strong structure of the body of the larva makes it possible to punch through tough root crops, crush them, thereby rendering them unusable. Damaging the stems and root system of young plants, destroying swollen buds, they cause significant damage to the crop.
Habitat
As a rule, these beetles settle in fields planted with root crops. But they breed in any area where there is vegetation. A favorite place for laying eggs is in the weeds.
There is an opinion that these beetles do not live in exemplary areas.
They prefer areas with acidified soil, densely planted, not weathered and not thinned plants, rotten grass.
The developed wireworm larvae move to the upper layers of the soil, which are rich in nutrients and have a degree of moisture suitable for their existence.
Can get into an apartment with root vegetables
Both the click beetle itself and the wireworm may end up in your home. These beetles also penetrate the dwelling. They enter the apartment from the street through open windows or doors. They must be immediately eliminated from the dwelling before the female has laid eggs.
In the apartments, you can also find wireworms that have fallen along with food supplies: potatoes, beets, carrots, etc. The root crops affected by them must be urgently removed.
Weaknesses of the wireworm
There are exceptions to their omnivorousness. They hate beans, flax, buckwheat.
The beetle itself and the wireworm - its larva, do not tolerate the smell of beans. Where they grow, these insects do not lay eggs.
Such "spices" as onion husks or fresh pine needles are also not respected in their diet.
Nutrient base
The larvae of this beetle are omnivorous. They can pretty much ruin beets, carrots, onions. They easily gnaw through a large number of moves in a potato.
Gnawing the roots and stems of cereals, corn, sunflowers, seedlings, they can nullify the results of the harvest. Weed roots are also preferred.
These omnivorous insects feel comfortable even in heavy clay soils.
Wireworm larvae are completely capable of destroying crops. They cause significant damage to seeds that are sown in insufficiently heated soil.


The insect can be confused with darkling beetle larvae.
Developing for 4 years, the larvae cause irreparable harm to plants. During this time, new adults appear, which will again lay the next batch of eggs. Thus, if you do not take any preventive measures or control them, you risk being left without a crop.
Description in detail
The wireworm is often confused with the false wireworm, the larvae of darkling beetles. The latter have a convex head with a straight front edge. The middle pair of legs, of the three available, is somewhat larger. The extreme abdominal segment is rounded. In the wireworm, it is carved and has teeth.
Adult Clicker Beetle
In general, there are more than 2500 species of these beetles in nature. The more common and well-known species are striped and steppe.
Their body is flat, oblong, with segmented legs. Chitinous integuments have a brown or black tint, which is characterized by a metallic luster and grayish pubescence.
The clicker beetle, a photo of which in an enlarged form allows you to see the appearance in detail, reaches a length of 30 millimeters.
Those that live in the tropics range from red to yellow, blue and green. Often on the chitinous cover of these insects, you can see a variety of patterns: spots, lines. The mustache is clearly visible. Females have shorter antennae.
Beetle eggs are mostly white. During development, they absorb large amounts of water. The female lays eggs in small heaps.
The oblong body of the larvae has dense integuments, very hard to the touch, color from dark yellow to dark brown with shine.
Wireworm control methods
In agronomy, there are two ways to combat it: agrotechnical and chemical, that is, using insecticides.
Chemical method
When using the chemical method, the soil is treated with wireworm preparations.The method is expensive and infects the earth with pesticides that kill not only the wireworm, but also beneficial insects living in the soil. First of all, due to the high cost, the chemical method is not suitable for owners of personal plots.
Nevertheless, if things are really bad and the wireworm has flooded the site, you can use the drug "Aktara", which is diluted according to the instructions, and the places of future plantings are shed on them, and tubers are soaked in it. The drug is guaranteed to destroy all living things in the soil, including beneficial larvae and insects.
Glass jars against beetles and their larvae
During the winter, you should stock up on jars, preferably glass containers up to one liter. They will come in handy in the summer to fight the pest, as gardeners know how much damage the nutcracker does to plantings. The methods of dealing with it are very different. And this one is one of them. Throughout the site, in shaded places (there is more moisture, which wireworms love), glass jars are buried to the very neck. Pieces of chopped raw vegetables are placed at the bottom. Once every three days, the contents of the container, along with the wireworms (and they will definitely be there), are removed, the bait is again put in the jar. It is advisable to repeat this procedure several times per season.
Soil liming
Wireworms love acidic and moist soil, while garden crops tend to prefer neutral or alkaline soil. Liming the soil is another way to get rid of the wireworm without resorting to pesticides or laborious agricultural techniques, or at least to reduce its amount.
Liming in order to control the population of larvae is carried out every 3-4 years. Soil acidity can be determined using a litmus test.
With a large number of nutcracker larvae, it is necessary to water the plants no earlier than the topsoil dries out to a depth of 15 - 20 cm. The wireworm does not like dry soil.
Just as with the Colorado potato beetle, there are many folk recipes for how to get the wireworm out. Some of them are very time consuming. The other involves pitfalls.
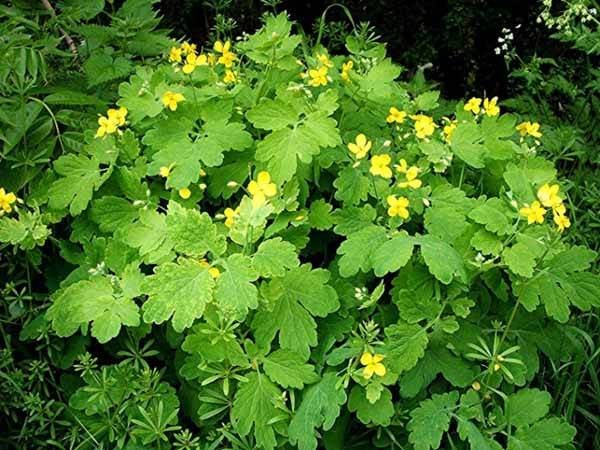
Poisonous celandine will help keep the planted tubers from wireworm. Unfortunately, celandine does not protect new tubers.


Environmentally friendly methods of dealing with wireworms
Almost all methods of protection against a wireworm are based on the manufacture of traps for it in one form or another.
Pre-sowing cereals. About a couple of weeks before sowing potatoes, oats or barley are sown on a future potato field in nests of one and a half dozen grains. After emergence, the plants are dug up and wireworms are selected. The method is very laborious.
Rotten organic traps. This way they get rid of the wireworm in the middle of spring, when the frosts have already ended, but the soil is still quite cold. Pits are dug in the soil and half-over-matured grass, straw or hay are laid in them. Then the bookmark is poured with water and covered with boards. Wireworms crawl into organic matter in search of heat and food. It takes only a couple of days to completely populate the trap with clickbearer larvae. After 2 days, the grass is removed and burned. The procedure is repeated several times.
Professional drugs "Etonem" and "Nemabakt". They are not available for retail sale, as they are designed for large areas. But perhaps this is the most effective way to protect yourself from the larvae of the nutcracker. The preparations are eggs of nematodes, whose main food is wireworm. They are able to cope with larvae within one season.


However, "Nemabakt" is already entering retail sale, which is logical, since the market for private small farmers is actually even more extensive than the market for large agricultural producers.
Catching clickers with jam. It is used only in spring, when there are no cultivated plants yet. Diluted syrup from jam, molasses or just sugar is put out on the street at night.In the morning, trapped insects are destroyed, 90% of which are likely to be pests.
How to arrange traps for clickers and wireworms with crops already planted can be seen in the video.
Traps for clickers and their larvae
Other ways to banish the wireworm
Onion peel. When planting potatoes, put a large armful of onion skins in the hole. When using this method, a calm day is chosen for planting potatoes so that the husks do not scatter over the entire area.


Dry mustard. The wireworm does not like mustard, so when planting root crops, dry mustard powder can be poured into the hole. Use this method when planting potatoes, turnips or radishes.


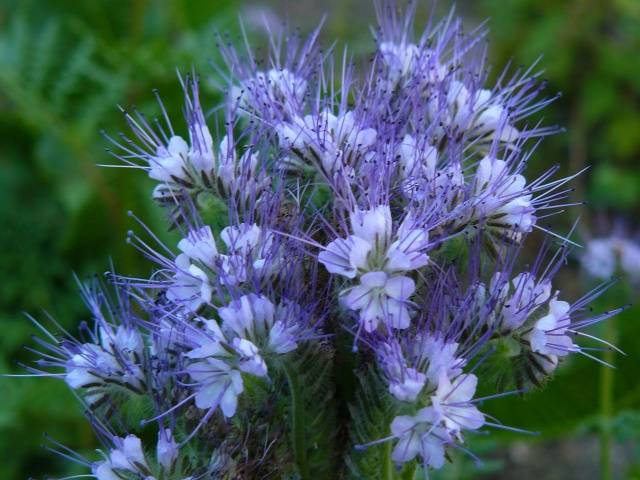
Scare plants. Clicker larvae do not like phacelia, peas and mustard. They are especially unhappy with phacelia, which has the ability to change the acidity of the soil from acidic to neutral. Thus, phacelia is useful not only for expelling the wireworm from the site, but also for the destruction of perennial weeds that love acidic soil. But growing green manure will require additional effort and money.


None of these measures will allow you to forever protect yourself from wireworms for the reason that click beetles have the ability to fly, which means that at any time a female click beetle can fly into the site. But it is quite possible to significantly reduce the number of larvae on the site.
Insect damage


Due to the fact that wireworms are polyphagous, they cause colossal damage to cultivated plants. They love to eat tender roots and stems, destroy swollen seeds and seedlings.
The larvae do a lot of harm to root crops and tubers: they drill whole tunnels in them, which leads to decay and makes the crop unsuitable for storage.
The greatest harm to the nutcracker larvae is inflicted on potatoes, wheat, radishes, corn, carrots, barley, onions, beets, strawberries, cucumbers, daikon, lettuce, cabbage.