At this time, the gardener is trying to do something to prevent the culture from drying out. To help himself, he takes not only drugs to combat pests and diseases, but also fertilizers. Indeed, the cause of the painful state of plants can be both insufficient soil fertility and infrequent fertilizing with fertilizers.
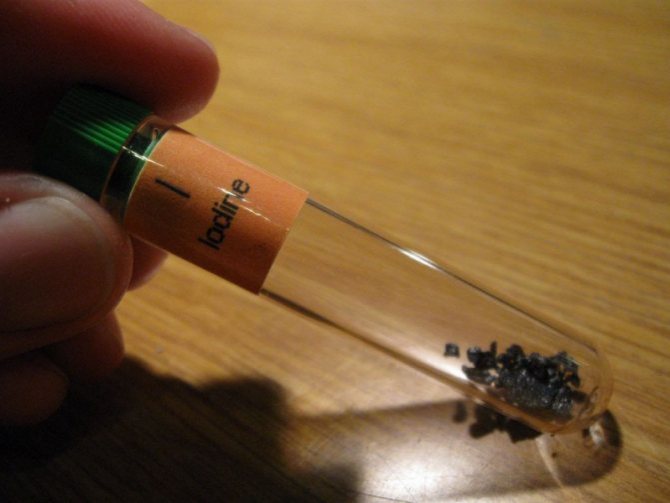
Among the substances that are considered fertilizers and which all living things on earth cannot do without, there is iodine - a chemical element from the group of halogens. Some organisms store large amounts of iodine, such as seaweed, but for most, the need for iodine is minimal.

Nevertheless, iodine deficiency affects the viability of both plants and animals. With a slight excess of iodine, most people can survive without much unpleasant consequences. For plants, iodine can sometimes be toxic even when its concentration in the nutrient solution is in the range of 0.5–1.0 mg / kg.
Fertilizer Science Facts
In the open field, iodine comes from precipitation, therefore, crops growing outdoors receive this substance naturally, at least in small quantities. At home, you need to saturate the soil yourself. Scientific experiments were carried out, during which it turned out that with proper feeding, all indoor flowers reacted positively: the plants recovered faster from diseases, the buds became more lush and beautiful, and the color of the leaves was brighter.
There is no exact explanation as to why iodine, as a top dressing, gives such excellent results. Scientists have suggested that this element regulates the work of enzyme systems, thus improving the metabolism in plants. But no matter how many controversies there are around feeding with this element, the fact is obvious: the benefits of this substance are enormous.
Iodine is able to "revive" plants even in the most hopeless cases. Studies were carried out on indoor flowers infected with diseases. Here are some examples:
- The use of iodine as a fertilizer literally "extended the life" of the anthurium. The plant has already lost all the leaves, but after several waterings with the solution, recovery has occurred. Within a couple of months, anthurium became a healthy, beautiful flower with lush green leaves.
- On the leaves of gladiolus and snapdragon, red bulging spots appeared. The fungus has already spread throughout the stem. The use of iodine saved the flowers from death, there was no trace of "rust".
- An experiment was carried out with chrysanthemums affected by nematodes. Feeding flowers helped to get rid of harmful parasites.
Also, iodine has a positive effect, as a fertilizer, and garden crops. A significant increase in the number of fruits was noted, as well as an improvement in their taste.
How to prepare a solution for feeding with iodine?
It is best not to experiment with your green pets, but to carry out disease prevention in a timely manner. Iodine will become an indispensable tool for plant care.This element is actively involved in the synthesis, has antiseptic and antifungal properties. The solution can be prepared at home or you can buy special preparations from the store.
How to use iodine so as not to harm the plant? To prepare the fertilizer, you will need 7 liters of water and 20 ml of iodine. The liquid is required to mix and water the plants along the sides of the pot. This solution stimulates growth and protects against powdery mildew. You can cure indoor flowers affected by late blight by adding hydrogen peroxide to the mixture.
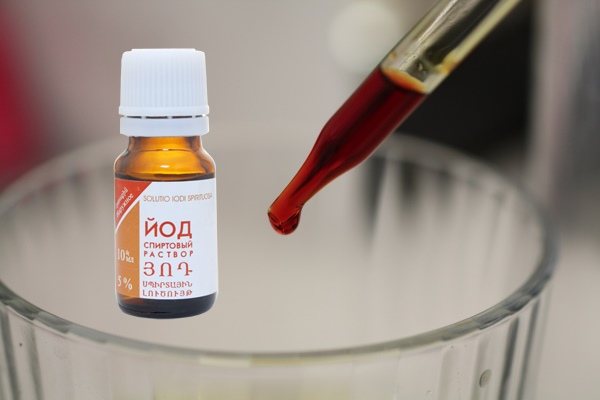


If the plantings do not bloom for a long time, a mixture of one liter of water and 1 drop of iodine will help. It must be poured in with extreme care so that the solution penetrates only into the soil, without touching the leaves and roots, otherwise the mixture may burn them. This fertilizer is very useful for geraniums; after such watering, bright lush flowers soon appear on this beautiful plant. The procedure must be repeated every 10 days. It is enough to use no more than 50 ml of liquid at a time. Also, such a solution is excellent for pelargonium.
The best recipes for iodine flower food
It is recommended to water indoor flowers with iodine with a solution, for the preparation of which 1-2 drops of alcohol tincture and 2 liters of water were taken. The advantages of such nutrition are sufficient: an intensive growth rate, abundant flowering and increased immunity in indoor plants. But the procedure itself must be carried out carefully so as not to harm the green spaces. It is necessary to pour the working fluid around the perimeter of the flowerpot, avoiding contact with the root collar. The optimal consumption per plant is 50 ml of diluted iodine.


Instead of water, it is good to use ultra pasteurized milk. Alternatively, you can make a solution from 1 drop of iodine, ½ liter of milk and 2.5 liters of water.
For the quick restoration of rose bushes, an iodine solution is used at the rate of 7 drops of a pharmaceutical agent and sodium humate prepared according to the instructions. For the treatment of ornamental crops, it is effective to prepare a working fluid from 2-3 drops of the main product and 3 liters of water.
For a weakened geranium, a solution of 1 drop of iodine and 3 liters of settled water is suitable. Make-up is applied at the root, but first moisten the soil with clean water. For feeding violets and saintpaulias, a similar composition is prepared, exceeding the dosage here is detrimental to the flower itself (it will not be able to cope with a highly concentrated liquid). The first procedure is carried out 3 months after the transfer of the plant to another container, and the next one after 10 days. This scheme is applied 1-3 more times.
Regardless of the type of flower crops, 5% iodine is used to prepare the working solution.
Feeding procedures are best done in summer, keeping an equal interval between treatments. The water should be soft, settled (within 2-3 days), at room temperature.
Special fertilizers with iodine
You can buy a solution with iodine in the store. These preparations treat the wounds of a green pet, and also prevent yellowing of the leaves. This contributes to the speedy recovery of the flower and the abundant appearance of foliage in bright colors.
The most popular drug among flower growers is Bioiodis. It consists of organic products and is not capable of harming the plant if used correctly. In addition to iodine, it contains vermicompost and other useful microelements.
To avoid overdose, you should strictly follow the instructions on the drug. Use "Bioiodis" for spraying leaves and fertilizing directly into the soil. To get the life-giving mixture deep into the soil near the rhizome, you can use an ordinary syringe. It is also useful for plants to pre-soak in Bioiodis before planting in a pot.
Restrictions for feeding with iodine
Fertilizers are recommended to be applied from the end of February until flower buds appear. In the spring, you need to pay special attention to indoor plants, because this time is characterized by an active growth phase. In the spring months, iodine is especially beneficial for home flowers.
It is categorically impossible to use iodine in the following cases:
- If the flower has recently undergone a transplant. The plant should take root and develop well roots in the new soil.
- Be sure to water the plant before feeding. It is impossible to pour iodine solution onto dry soil.
- Iodine is more commonly used for disease prevention rather than treatment. If the plant looks weak and withers, you need to identify and eliminate the causes, and then feed it.
Indoor plants are a real outlet for flower lovers, especially during the cold season when the garden is in hibernation. With the right care of green pets, you can turn your home into a true flower paradise. It is important to timely feed with iodine for indoor plants and not to allow an excess of it. Then the plants will thank the florists with lush foliage with inflorescences and a pleasant fragrance around the room.
Perhaps, in any country first-aid kit there are such antiseptics as iodine and brilliant green solution. Many gardeners use them not only for medical purposes, but also in agriculture, which is quite justified. These drugs prevent the development of fungal and bacterial infections, various types of rot. In addition, iodine is one of the essential trace elements involved in the growth and successful development of plants.
Beneficial features
Iodine participates in the processes of photosynthesis, oxygen saturation, metabolism in plant cells, is responsible for the synthesis of proteins, and promotes the assimilation of nitrogen. Nitrogen, in turn, contributes to the growth of vegetative mass, affects the state of the immune system of plants. With a lack of iodine in the nutrition of plants, the following is observed:
- Suspended growth, delayed development;
- weakening of immunity;
- delaying the process of fruit ripening;
- decrease in yield.
⊕ An analogue of iodine as a fertilizer can be used with Pharmayod, which contains 10% iodine → Pharmayod application as a fertilizer for plants.
Complex feeding and iodine-containing agrochemical preparations, including ordinary medical iodine, help to fill the deficiency of a vital element.... As a result:
- growth accelerates, abundant flowering occurs, the number of ovaries increases, the ripening period of the fruits of garden and vegetable crops is reduced;
- the immune system of plants is strengthened;
- the fruits are saturated with iodine, which is important for the prevention of iodine deficiency diseases in humans;
- increases the safety of the crop during long-term storage;
- the quality of products improves - the size, taste, presentation of the fruit;
- the pathogens of gray rot, powdery mildew and late blight in the soil and on the surface of plants are destroyed.
The benefits of iodine for tomatoes
Fertilizing tomato seedlings with iodine is necessary for a good harvest and the beauty of the plant. Due to its antiseptic properties, it effectively fights diseases and parasites. Medical product:
- protects against fungal infections;
- strengthens the immune system to prevent disease;
- performs the functions of fertilizer on a par with nitrate;
- forms large ovaries;
- makes the soil fertile.
Tatiana Orlova (Vasilidchenko) (Candidate of Agricultural Sciences):
The main reasons for iodine deficiency in plants is its lack in the soil of regions remote from the sea coasts.
Application features
Important! Pharmaceutical preparations iodine and brilliant green are, first of all, antiseptic medications intended for disinfection of wounds. Pharmacy preparations based on iodine and brilliant green are, as a rule, 1-5% aqueous-alcoholic solutions, that is, they contain from 95 to 99% water half with ethanol. This concentration of alcohol can be harmful to plants.It is permissible to use medicinal preparations as fertilizer, fertilizing or processing of green spaces only in a diluted form.
In order not to harm the plants instead of being useful, you should follow certain rules for the use of iodine and brilliant green in the garden:
To obtain an iodine solution for feeding and prophylactic treatment of plants, a few drops of the drug are enough for a 10-liter bucket of water.
- Apply the solution only to pre-moistened soil.
- Start treatment with a minimum dose (1-2 drops of the drug per 1 liter of water).
- Carry out foliar processing in cloudy weather, preferably in the evening.
- Do not fertilize perennials during dormancy.
- Process the planted seedlings only after full adaptation to the new soil.
- Do not moisten the root collar with the solution.
- It is permissible to disinfect the ground with an iodine solution no later than 3-5 days before planting.
Tip # 1: Before treating all plantings with a solution of iodine or brilliant green, it is advisable to test the agent on one plant. If after 2-3 days no negative consequences are observed, then the proportion is chosen correctly, the drug can be used on the rest of the area.
Iodine as fertilizer
Vegetable, berry and fruit crops respond positively to iodine feeding. The concentration of the iodine solution used will differ depending on the type of plant and the purpose of the treatment.:
| Culture | Time of feeding | Mode of application | Dosage per 10 l of water |
| Tomatoes | Before the formation of ovaries: in the open field with an interval of 10 days, in the closed field - once every 2 weeks | Foliar dressing | 20 drops |
| Cucumbers | When symptoms of powdery mildew appear | Spraying over the leaves | 10 drops |
| Pepper | Three times until ovaries form, every 10 days | Foliar dressing | 15 drops |
| Cabbage | During the formation of heads of cabbage | Watering at the root | 40 drops |
| Pumpkin, zucchini | 2 weeks after planting, during active flowering or ovary formation | Foliar dressing | 40 drops |
| Strawberry wild-strawberry | Before flowering | Root top dressing | 8 drops |
| Grapes | If symptoms of gray mold infection appear | Foliar dressing on leaves and bunches | 10 drops |
| Fruit trees | Before fruiting | Foliar dressing | 10 drops |
Iodine from pests


Protection from aphids and other small pests living on the leaves is carried out with a composition of 2 tbsp. liquid soap, 2 tbsp. soda ash, 1 tsp. iodine (5%). To destroy the larvae of the May beetle use a solution, which includes 20 ml of iodine and 10 liters of water. For each plant, use 1 liter of the composition. If the plant begins to wilt with normal watering, then most likely there is a pest under its roots. In this case, watering is carried out three times under the roots with the same composition. At least 5 days should pass between waterings. The maximum volume of liquid that can be applied under the plant is 5 liters.
The root zone of plants is treated with a solution of 10 ml of iodine (10%) in 10 liters of water to scare away the larvae of various butterflies and flies that lay eggs in the ground or on the roots and leaves of plants. With the same composition, with the addition of an adhesive, foliar treatments are carried out on the leaf and stems of plants. 2 tbsp can be used as an adhesive. liquid laundry or tar soap. The smell of tar will become an additional agent that repels leaf-eating insects.
Presowing treatment with iodine of planting material
Treatment with an iodine solution (1 drop of a pharmaceutical preparation per 1 liter of water) increases the germination of vegetable seed material, accelerates the emergence of seedlings, while the plants are less susceptible to disease.
Seeds of tomatoes, cabbage, zucchini, peppers, cucumbers are soaked in a weak iodine solution for 3-4 hours before germination and sowing.
To prepare the onion for planting, a few drops of iodine are added to a pink solution of potassium permanganate. In the resulting mixture, the bulbs are soaked just before planting for 2-3 hours.
Seed potatoes are disinfected with iodine solution (2 ml per 10 l) 2-3 days before planting. To do this, the tubers are laid out in 1 layer, abundantly irrigated from a spray bottle, dried, turned over and sprayed again.
Seed and seedling treatment
It is necessary to harden and treat seeds with antiseptics to ensure their viability. In order for the seed to be of good quality, and the seedlings to grow healthy and large, iodine must be used. The preparation is weak - only 1 drop of a trace element per 1 liter of water. The seeds are soaked for 2-3 hours and placed in the refrigerator.
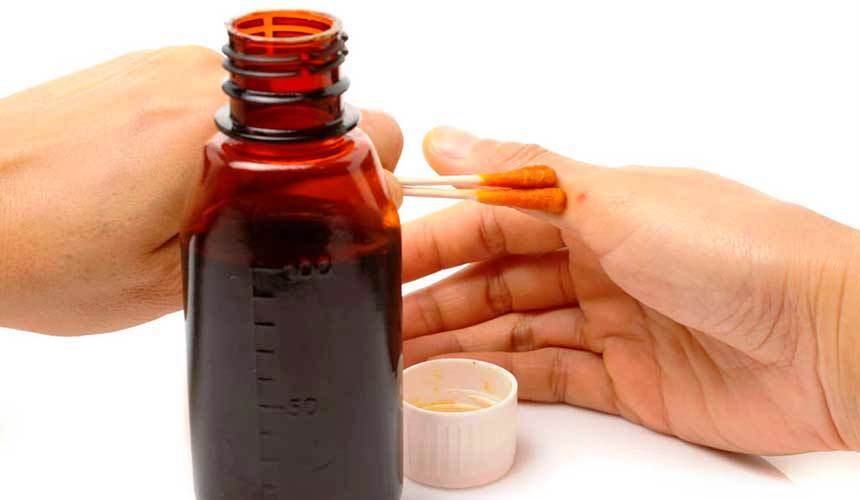

Treatment of seeds and seedlings with iodine
If in your country house the land is infected with late blight or root rot, it will be useful to water the beds abundantly with such a solution before planting, and then plant the seeds.
Zelenka for vegetable crops
The yield of garden crops when treated with brilliant green increases mainly due to an increase in the immunity of plants... This is not so much a top dressing as a cure for bacterial and fungal infections. Methods for introducing brilliant green for the main vegetable crops:
| Culture | Purpose of processing | Mode of application |
| Tomatoes | Fight against late blight | Processing greenhouses and beds after harvesting (50 ml of brilliant green per 10 liters of water; |
spraying seedlings when planting in the ground (45 drops of brilliant green per 10 liters of water)
Zelenka is an excellent remedy for disinfecting the wound surface when pruning the shoots of berry and ornamental shrubs, which is used instead of garden varnish. Orchid roots, dahlia tubers damaged during transplantation or division are treated with brilliant green.
Olga Platonova, host of TV shows "Fazenda", "Country Fairies".
Compatibility with other antiseptics
The effect of the simultaneous use of iodine and brilliant green for processing plants can be unpredictable, since these drugs are incompatible. It is also not recommended to mix brilliant green with any products containing ammonia, chlorine, or alkali.
But with a combination of iodine and potassium permanganate, the disinfecting effect of the resulting product is enhanced without harm to plants. Resistance to diseases also increases when iodine is mixed with boric acid. In a bucket of water, 10 drops of iodine and boric acid are diluted. The resulting product is used for foliar feeding of vegetables by spraying from a spray bottle several times during the growing season: before and during flowering, in the initial phase of fruit formation.
To enhance the antiseptic effect in a bucket of iodine solution, it is permissible to add 1 tbsp. spoon of 3 percent hydrogen peroxide (3%).
Iodine saturation of different types of soil
Soils of any type receive iodine from the atmosphere, where it is transported by air masses after the evaporation of seawater. Naturally, in the coastal regions, the iodine content in the fertile soil is higher than in the interior of the mainland. Thus, vegetables grown far from the sea coast contain ten times less iodine than in coastal regions.
The chernozem and chestnut soils contain almost 2 times more iodine than the soils of the non-chernozem zone (see → how to use chernozem). But in Russia, such fertile land is no more than 7% of the total area. These are mainly the southern regions, where they receive high yields. Peat and manure are also rich in iodine (find out → proper feeding with peat + gardeners' reviews, → manure).
It should be borne in mind that the soil of the same area may contain different amounts of one trace element. For example, mountainous lands are poorer than flat lands, floodplain lands are richer than those on watersheds.
The iodine content is largely influenced by the mechanical composition of the soil.It was found that light sandy loam and sandy soils are significantly poorer than heavy ones - clays and loams. Top dressing with iodine is relevant on gray soils, solonetzes, podzolic, gray forest, poor sandy loam soils, especially in areas with identified iodine deficiency.
Is iodine safe for plants
Iodine for plants as fertilizer. So far, the mechanism of iodine absorption by various representatives of the flora has been little studied. It is well established that algae accumulate iodine because the element dissolved in water is absorbed by plants very well. Iodine, which is contained in the soil in organic form, is practically not absorbed by plants.


For the root system, it becomes available after organic residues are decomposed by the action of soil bacteria, and iodine remains in the soil. The concentration of iodine in plant sap will depend on the type and nature of the soil. Moreover, there is more iodine in the ground parts of plants than in the roots. This is due to the fact that iodine is absorbed by sheet plates from the atmosphere.
It has been established that the iodine level in 1 kg of nutrient solution in the amount of 0.1 mg can already have a stimulating effect on the ability of some plants to grow and reproduce. At the same time, studies were carried out on tomatoes and buckwheat, which showed that plants do not react to the introduction of 1.1 kg of iodine per 1 hectare of plantings. But the dose of 11 kg per hectare turned out to be toxic.
Errors when using antiseptics in the garden
- It should be remembered that medical antiseptics are used in the garden mainly as a preventive measure against bacterial and fungal diseases of plants. With an extensive, already onset ailment, these funds will not be able to cope on their own. For serious treatment, special drugs are required, but their effect can be enhanced by adding both iodine and brilliant green. Naturally, this should take into account the compatibility of the main elements.
- You should not be zealous with the use of iodine. Its excess, instead of increased growth, leads to plant oppression. In addition, the consumption of fruits with an increased concentration of iodine in food can provoke in a person malfunctions of the thyroid gland and internal organs, metabolic disorders, and discoloration of the skin. It is not recommended to carry out foliar treatment with brilliant green or iodine during the period of fruit ripening, when the active substance can accumulate in large quantities on the peel.
Answers on questions
Question number 1. Some gardeners recommend preparing a whey-based iodine solution. How effective is it?
Spraying with a solution of iodine based on whey protects tomatoes from late blight, accelerates the ripening process.
A solution of iodine based on milk or fermented milk products is an excellent fungicidal agent. When sprayed, a thin milky film forms on the surface of the leaves, which prevents the fixation of pathogenic bacteria and fungal spores.
To prepare the drug for late blight on tomatoes, 1 liter of milk is diluted with 4 liters of water, 15 drops of iodine (5%) are added. Another option: 1 liter of whey, 40 drops of iodine and 10 ml of hydrogen peroxide (3%) per 10 liters of water. For processing cucumbers, prepare a mixture of 1 liter of milk, 40 drops of iodine and 1 tbsp. tablespoons of peroxide per 10 liters of water. Learn → how to use serum as a top dressing and insecticide, how to breed + reviews.
Question number 2. What plants need to be fed with iodine first?
Cultures react best to iodine feeding:
- cereals;
- legumes (peas, beans, beans);
- nightshade (tomatoes, eggplants);
- cruciferous (cabbage)
- Bell pepper;
- cucumbers, zucchini.
Iodine is necessary for indoor flower plants, especially if the soil in the pots has not changed for several years. Iodine top dressing disinfects the soil, neutralizes accumulated harmful microorganisms, and prevents emerging diseases.Experienced flower growers advise watering indoor plants with iodine solution (1 drop per 3 liters of water) at least 3 times during the summer.
For grapes, cabbage, strawberries and flowers. Why iodine is needed in the garden and vegetable garden?
8:00 04 September 2019


In addition to basic macronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, without which no plant grown on farmland can do without, microelements also play a very important role. In particular, iodine, according to www.interfax.by expert, Candidate of Agricultural Sciences Vladimir Tereshchuk. Moreover,
It can be used almost at any time - both in spring when sowing and soaking seeds, and in autumn - to combat late blight of ripening tomatoes and cabbage pests, as well as for a better harvest.
Basic rules for the use of iodine in the garden and in the garden
You can use iodine as a top dressing, but you should pay attention to the available fertilizers that already contain this element. For example, "Humate + 7 Iodine" contains humic acids and a complex of trace elements, including iodine. Following the instructions, you can soak seeds in a solution of the drug before sowing (soaking time from 1 day - cucumbers to 3 days - tomatoes). Also, seedlings of vegetables, fruit and berry plants are fed (by root and foliar method).
With the help of iodine solution, gardeners are trying to cure plants from diseases and get rid of pests. Such advice from experienced summer residents is based on the well-known antiseptic effect of iodine. However, at the same time, the methods for preparing the working solution vary quite arbitrarily (from 2 drops to 2 ml per 10 liters of water), which at best will not give any effect, and at worst will cause burns in plants. Along the way, we note that the mass of 1 drop of an alcoholic solution of potassium iodide (pharmaceutical preparation) depends on the concentration of the solution, for example, 1 ml of a 5% solution contains 48 drops, and 1 ml of a 10% solution contains 56 drops. We were not able to find exact, scientifically proven recommendations for the use of a pharmacy alcoholic solution of iodine.
Iodine is indeed a strong antiseptic; in agriculture and home gardening, a preparation based on it is used for disinfection. The drug "Pharmayod" is recommended for the treatment of premises (including glass and greenhouse structures), vehicles and equipment. It is effective against a number of bacteria, phytopathogenic viruses, and at high concentrations - against pathogens of fungal diseases. A side effect was also noted - it inhibits the development of certain types of pests (ticks, thrips, nematodes). The premises are treated with 1% -3% working solution.
It should be noted that thod is an antiseptic of continuous action and, destroying harmful organisms, it also destroys microflora, which is important for the nutrition and development of plants
Iodine for plants is used not only to maintain immunity. Apply top dressing with iodine to disinfect the soil, since the substance is an antiseptic and destroys bacteria and fungi.
Plants are treated with iodine in the form of a solution, while the main method is foliar feeding.
Signs of iodine deficiency in plants
Lack of iodine in plants can lead to a decrease in their immunity to various diseases. The reason for iodine deficiency is usually an insufficient amount of this element in the soil (this is especially true for peat and podzolic soils, light sandy loams, as well as substrates with a deficiency of organic matter).
Take a close look at your plants. Signs of a lack of iodine may be:
- poor fruit setting, ovary decay;
- red and yellow fruits of plants (tomatoes, peppers, etc.) are not bright and large enough;
- lack of starch in fruits;
- lack and pallor of the vegetative mass;
- delay in growth, flowering, formation of fruits and seeds;
- reduced resistance to nematodes, wireworms, fungal diseases.
In general, it is quite difficult to visually determine the lack of this trace element in plants, since the signs of its lack are rather arbitrary, and some coincide with signs of various diseases, the action of pests, freezing of plants, etc. Therefore, we recommend at least preventive feeding of plants with iodine - at least it will be useful in any summer cottage and certainly will not harm the plants
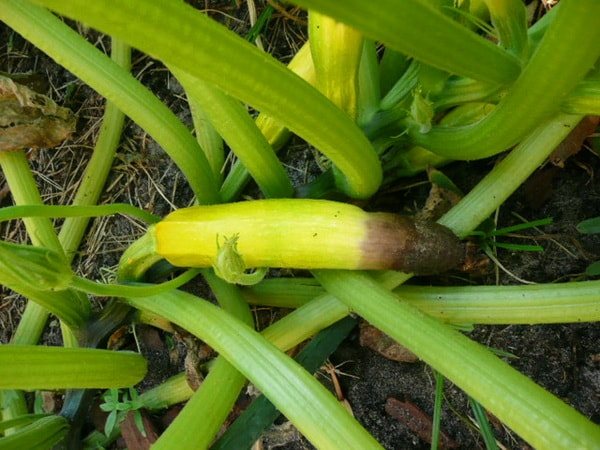


How to use iodine for vegetable seedlings?
Most often, such dressings are used for growing tomatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, and other Solanaceae. Plant seeds are placed in a pre-prepared liquid for 7 hours. For 500 milliliters of water, 1 milliliter of iodine. Before planting in the ground, shoots or sprouts are watered only once so as not to damage the roots. The solution is different, the concentration in it is less, 1 milliliter of iodine is stirred in 3 liters of water. Concentration increases over time. If you water the bushes, then for each plant you need to use one liter of liquid, and water should be watered evenly around the plant.
Watering the seedlings with iodine helps it to rise faster and more amicably, and also accelerates growth. In the early stages of development, the use of this trace element also serves as a guarantee of the formation of high resistance to unfavorable environmental factors and various diseases. Top dressing with iodine solution is indicated for seedlings of tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, eggplants, cabbage. To create a working solution, 1 drop of iodine is diluted in 3 liters of water. After thoroughly mixing, the seedlings are poured under the root with the solution. To enrich the seedlings with iodine, such a single watering will be enough.
An alcoholic solution, even in such a low concentration, can burn a plant, especially a young one. Therefore, for all manipulations with iodine preparations, carefully monitor that the solution does not fall on the stems and leaves. If this is spraying, carefully observe the dosage of iodine preparations.
Later, during transplanting young seedlings into closed or open ground, the prepared soil can be spilled with an iodine solution at the rate of 3 drops of iodine preparation per 10 liters of water.
Iodine against late blight
For grown seedlings, it will be useful to prevent fungal diseases and stimulate further growth by spraying with the same iodine solution. This is especially true for plants prone to late blight - tomatoes, eggplants, peppers. About three weeks after germination, gently spray the young plants with a solution of 15 drops of iodine, 10 liters of water and 1 liter of skim milk. This treatment can be repeated 2-3 more times with an interval between spraying of at least two weeks.
Iodine solution is successfully used not only for the prevention of diseases, but also for the treatment of plants at the initial stage of infection. There is another popular way of processing tomatoes and potatoes with iodine from late blight. 4 drops of the iodine preparation are diluted in 10 liters of water and the plants are watered under the root with this solution at the rate of no more than 2 liters of solution per bush. To combat late blight, instead of an alcoholic solution of iodine, you can also use a 0.02% solution of potassium iodide at the rate of 2 g per 10 liters of water, as well as water-soluble iodine preparations (for example, Iodopiron) according to the instructions.
Iodine against powdery mildew
The iodine solution has also proven itself in the fight against powdery mildew, which in inclement weather is most often picked up by zucchini and cucumbers. These cultures should be abundantly sprayed with a solution of 1 ml of iodine and 1 liter of skim milk or whey per 9 liters of water (1 tablespoon of liquid soap can be added to the solution). Spraying can be repeated every two weeks until the disease disappears completely. A bright green vegetative mass and increased fruiting will also become a "side" effect of such treatments with iodine, so that even without the presence of powdery mildew, after the first wave of fruiting, cucumbers and zucchini can be sprayed with the above solution with an interval of 10-14 days.Iodine will help fight powdery mildew and ornamental shrubs. True, in this case, the concentration of the solution should be increased and 5 ml of iodine should be taken for 10 liters of water.
Iodine against plant rot
Plants treated with iodine solution also successfully fight various types of rot. So, all berry crops (and especially strawberries and grapes) will be grateful to you for your help in resisting gray rot. For this, a solution of 10 ml of the drug per 10 l of water is used to spray the plants in the spring, during the formation of the ovary and buds. The treatment is repeated twice more, with an interval of 10 days. Iodine will also help in the prevention of root rot in cucumbers and cabbage keels. The composition of the solution and the spraying schedule are the same as described above.
For fruit trees, iodine is an excellent prevention of apical and fruit rot. 10 ml of the drug is diluted in 10 liters of water and the trees are abundantly sprayed with this solution about a month before the expected harvest (if we are talking about young seedlings, such spraying is carried out in the spring). The procedure can be repeated again after 3-4 days.
And a solution of 10 ml of iodine in 10 liters of milk is an excellent remedy for aphids on fruit trees.
Iodine as a top dressing and fertilizer for plants
Iodine is successfully used for plants not only as an antiseptic and bactericidal agent, but also as an additional universal feeding. Cabbage, cucumbers, tomatoes, peppers, and garden strawberries gratefully respond to such dressings. For feeding tomatoes, cucumbers and peppers with iodine (both in the greenhouse and in the open field), use a solution of 40 drops of the drug per 10 liters of water. 0.5 l of this solution is applied under each plant after the first flowers appear. Feeding with iodine is repeated no earlier than after three to four weeks. The same solution is watered with cabbage during the very beginning of the formation of heads of cabbage at the rate of 1 liter for each plant (feeding is carried out after abundant watering).
For foliar feeding of strawberries with iodine, the solution is made less concentrated - 10 drops per 10 liters of water. Spraying is carried out three times per season, with an interval of 10 days.
To prevent rotting of young ovaries in squash and pumpkin, also use the above-described iodine solution. They are fed plants two weeks after planting, as well as during the formation of fruits.
How to treat trees or shrubs with iodine from fungi?
In case of plant damage by fungal diseases, the plant is fertilized with a 1% solution of Farmayod.
How to get rid of parasites with iodine?
All insects are afraid of this substance. To get rid of the larvae or the insects themselves, the plants are treated with a composition in which 15 milliliters of pharmaceutical iodine are dissolved in 10 liters of water. Pour 1 liter of the prepared mixture under each plant. The more pests are on the plant, the more you will have to water. This solution must not get on the leaves of the plant. To get rid of the weevil, this composition must be applied early, after the snow has melted. To get rid of aphids, you need to apply ten percent Pharmayod.
How to use iodine in the garden and vegetable garden?
A few tips for gardeners Any living organism, both animals and plants, needs iodine. If there is not enough iodine in the plant, then the root system and other plant organs rot. Fruits lose their properties, they are getting smaller. In order to prevent this process, feed with iodine is used, following certain rules, in compliance with dosages. Gardeners and summer residents use iodine to prevent rotting. Also, iodine counteracts insects, protects against infections and bacteria. The action of parasites on the plant is prevented. If you water the plant with iodine solution, the earth will become more favorable and fertile, and at the same time will strengthen the plant.
How to use iodine?
Iodine should not be used in the passive stage of plant growth.
A 5% mixture with alcohol is used in extremely small dosages. The concentration is 1 milliliter of the mixture in 2 liters of water. In case of an overdose, the roots of the plant are burned. Also, bacteria necessary for growth are destroyed in the soil.
Shoots, young plants should not be treated with a solution immediately. You need to wait for the plant to take root and hold firmly in the soil.
Water the plant so that the solution does not fall on the lower part of the root. Watering can only be carried out on already wet soil; it is better to use a warm solution.
If possible, you can use wood ash in the solution. The ash should be no more than 10% of the solution; in this ratio, the efficiency of irrigation will be greatest.
The solution can be used through a sprayer if the plant is small. So iodine will be much better absorbed in plant tissue.
Iodine in the garden:
plant nutrition, pest and disease control The improvised means that are in every home can come to the rescue in the fight against pests and diseases of plants in the garden. They may be simple medications. Antiseptic drugs are used not only in the treatment of people, but also come to the rescue with bacterial diseases of plants and the appearance of pests. One of these means is a simple alcoholic solution of iodine 5%. Thanks to its disinfecting properties, it is possible to simplify the care of indoor plants, crops in the garden or vegetable garden.
The use of iodine in the garden.
Iodine is suitable for processing areas with peat and ash soil. For plants, iodine is necessary in small doses for diseases such as gray mold and powdery mildew, as well as for prevention. The alcohol solution is also useful after winter to stimulate plant growth. It is also used for growing seedlings. The use of iodine in the garden enhances the taste of vegetables and increases yields.
Iodine treatment will be beneficial for tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, strawberries and strawberries. The most effective alcohol solution for berry, vegetable and fruit crops. The use of iodine against pests is also effective. The drug is readily available and does not require special preparation before irrigation.
The use of iodine in vineyards
- For the prevention of diseases. The product is used to prevent gray rot as one of the most dangerous diseases in the vineyard. Rot affects both fruits and vines, therefore destroying the crop for several years in a row. Spraying is carried out with diluted iodine.
- During the fight against powdery mildew. The iodine-based preparation helps to cope with powdery mildew and prevent its further development. The solution is used during the ripening of the berries.
- As a comprehensive tool. To combat various fungal diseases, a mixture of boric acid or iodine solution is used. The substance is diluted with water and used as a root dressing.
Spraying with iodine is most effective:
In the spring.
If the leaves on the vine are covered with brown spots, they are processed. To do this, use an iodine-based remedy. Plaque or dry leaf edges are additional reasons to spray the vineyard. In the spring, it can suffer from plaque, which indicates the development of a fungal disease (the leaves smell unpleasant).
In summer.
If the bunches that are still developing begin to fade in the summer, they must be urgently processed. Natural ingredients will get rid of the problem and will not affect the development of the bunches. Another reason for additional spraying is that the berries rot or crack.
Pharmayod or any other type of iodine is a powerful disinfectant that not only protects the plant, but also helps it grow.
After spraying the grapes with iodine, the following occurs:
- berries are enriched with iodine - when consumed raw, a person consumes an important component for the proper functioning of the thyroid gland;
- the sugar content of the berries increases;
- improves the quality of the peel, which does not crack even during heavy rains.
The grapes grow faster after processing. If prevention is carried out in the spring, the vineyard does not suffer from diseases of neighboring horticultural crops. Such events are suitable for both young vines and adult plants.
Method of using iodine
If preventive treatment does not help, iodine is used to combat the first signs of the disease. To strengthen the grapes, use a freshly prepared solution. Additionally, the vineyard is moistened (leaves and bunches are sprayed). The root part of the plant is temporarily not watered.
The treatment is carried out after sunset (at high temperatures, burns may form on the green part of the plant). The grapes are additionally processed: the infected branches and leaves are removed to stop the disease. All tools for pruning the vineyard are pre-disinfected: this is how the gardener protects other garden crops from dangerous diseases.
Fighting gray mold
Gray rot affects grapes. If 1 drop of iodine per liter of water is used to prevent rot, then the dosage of the natural component is increased to combat the first signs of the disease.
A good time for processing is when the berries are larger than a pea, otherwise they may dry out. If the disease progresses rapidly, the bunches are treated with a solution of a lower concentration. Spraying is carried out with a complex solution. To do this, use natural serum (1 l) and 1 drop of iodine. Processing is carried out after watering. For prevention, such a solution is sprayed once a week, at the first symptoms of gray rot - every day for 7 days.
Fighting mildew
To combat mildew, a complex solution is used. To prepare it you will need:
- 1 liter of milk (fresh or sour);
- 20 ml of iodine;
- 10 tablets of Trichopolum;
- a bucket of water.
It is better to process the vineyard in several approaches: the solution should completely cover all visible parts of the plant. The culture is sprayed with iodine with milk no more than once every 11 days.
In recent years, new generation products "BTF-Jodis" with a balanced composition have been used in planting grapes. They contain a large number of useful substances, among which iodine plays the leading role. Valuable components help to improve yields and protect plants from diseases. Therefore, the technology of using iodine in agriculture and vineyards is becoming more popular every year. With its help, many indicators are improved:
- increasing the mass of grapes;
- an increase in the size of berries;
- activation of regeneration processes after grafting of grapes;
- increasing plant resistance to various diseases;
- improving the growth of seedlings.
Iodine for cabbage: to increase the yield
With improper care, cabbage is often exposed to fungal diseases - keela, white and gray rot, black leg and others. It is difficult to resist the fungus, since the spores are carried by the wind, birds, insects. The only way to preserve the plant and prevent the death of the crop is to use non-aggressive methods of control. For example - watering the soil with iodine solution to destroy the fungus.

How to feed cabbage with iodine:
- Prevention is done at the stage of growing seedlings - the roots are put into an iodine solution for 5 - 7 minutes. 10 drops in a bucket of water.
- After planting in open ground, watered with a solution of 40 drops per 10 liters of water.
Iodine in the cruciferous garden is a safe way to deal with root-damaging keels.
Iodine for tomatoes and cucumbers: as fertilizer
Iodine for tomatoes and cucumbers is a growth stimulant. The most useful additives on podzolic and peaty soils, where there is a deficiency of this microelement.They begin to use at the very beginning of the process of growing vegetables: when germinating seeds; with a disease with powdery mildew; to rejuvenate shoots, to harvest longer in the fall; for fertilizing on soils where there is a deficiency of a trace element.
Iodine for vegetable plants is used in the following dosages:
- For seed germination - 1 drop per 1 liter of warm rainwater. Soak for 6 - 7 hours.
- For watering tomato seedlings by the root method –1 drop per 3 liters of water. This increases the productivity of the crop, enables all plants to rise and bloom. After transplanting into open ground, after two weeks, you can water with a more concentrated solution - 3 drops per 10 liters of water.
- For cucumbers they are used by root and foliar method. Water the seedlings for soil disinfection with a solution of 1 drop / bucket. Mature plants - 3 drops / bucket. With late blight - 1 liter of milk, 40 drops of potassium iodide, 15 ml of hydrogen peroxide, 10 liters of water. Powdery mildew - 1 liter of milk, 15 drops of potassium iodide, 10 liters of water.
Feeding plants with iodine is carried out in combination with other trace elements - boron, manganese, brilliant green, ammonia.
If you combine ammonia and iodine, you can get a good harvest that is not damaged by garden insects. Lack of nitrogen has a bad effect on plants - they turn pale, weaken, stop growing, pests and fungi start on them.
How to feed cucumbers with iodine? To get rid of or prevent the multiplication of common fungal diseases on cucumbers, it is necessary to spray the bushes with the following solution: 1 liter of milk, 9 liters of water and 8 milliliters of a five percent iodine solution. Cucumbers not only spray with this liquid, but also fertilize the soil. Watering should be carried out once a week until the plant acquires a healthy appearance.
You need to mix 40 ml of ammonia, 3 drops of iodine and 10 liters of water. Water the solution at the root 3 times per season. The method helps to get rid of nematodes, beetles, aphids, fungal infections.
Important! The use of iodine in the garden heals the soil for the next season
How to feed tomatoes with iodine? More mature plants need watering with iodine most of all. In order to protect tomatoes from viruses, iodine and milk must be used. Per 10 liters, take 1 liter of milk, 9 liters of water, 35-45 milliliters of iodine and 20 milliliters of hydrogen peroxide. Tomatoes are treated with this solution once a week for one month. Watering is carried out in the evening.
There is another type of solution that can be used just as effectively. To do this, take two tablespoons of ash, dissolve them with two liters of water. The solution should be infused for about 5 days. Then you need to add 6 liters of hot water to it, mix and cool. 8 milliliters of pharmaceutical iodine, 8 milliliters of boric acid are poured into the cooled liquid. This mixture should be infused for 10 hours.
Iodine for strawberries
The use of iodine in the garden and vegetable garden is not limited to vegetable crops. Spraying berry bushes with a solution helps - they protect plants from fungus, which multiplies especially strongly in cool rainy weather on weakened bushes.
For plants such as strawberries and strawberries, iodine is essential for plant development. It is especially needed for bushes after wintering. Therefore, when the snow melts completely, the bushes are immediately treated with a mixture of 10 milliliters of pharmaceutical iodine in 10 liters of water. Such feeding should be carried out no more than three times at intervals of a week. This treatment will not only strengthen the plant, but also protect it from pathogenic bacteria. Iodine as a fertilizer for strawberries is useful for spring stimulation of bushes that wake up and prepare for fruiting.
The first watering can be done with a solution of 1 drop per bucket. The second is more concentrated.The third top dressing must be done foliarly in order to destroy possible pests and fungal spores before setting the berries.
If the berries are not on special agrofibre, but come into contact with the soil, this can cause massive infection of strawberries with fungal spores. In this case, a solution of 5 drops / bucket of water is made and the soil is spilled under the strawberry bushes at the rate of 1 liter per plant.
A common pest of strawberries is the weevil beetle.
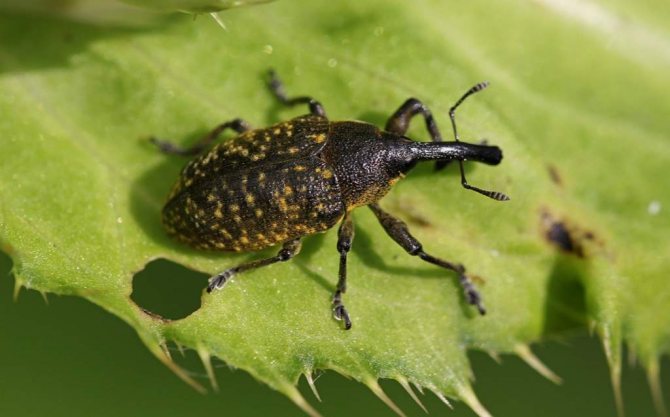


It settles in flowers and gradually destroys the entire crop. You can cope by diluting ammonia and potassium iodide:
- 10 liters of water;
- 3 tablespoons of ammonia;
- 3 drops of potassium iodide.
This feed is a good nitrogen supplement and also protects against insects.
Iodine for flowers
Iodine for indoor plants as a top dressing is used when watering or spraying. The lack of trace elements can be eliminated by combining simple pharmaceutical antiseptic preparations - brilliant green, manganese, iodine.
For indoor flowers that are constantly in the room, with a lack of sunlight, you can use a solution to protect the leaves from the invasion of aphids and other pests.
What indoor flowers can be fertilized with iodine?
ficuses; dieffenbachia; geranium; indoor roses; pelargonium; violets; gloxinia; orchids.
How to water indoor flowers with iodine? It is important not to let the solution get on the roots, make sure that water flows to the walls of the pot. The concentration must not be exceeded - 1 - 2 drops are needed for 3 liters of water. Another important rule: the soil is first watered with plain water, then with an iodine solution.
To combat the fungus, feeding flowers with iodine is carried out with a more concentrated composition - 30 drops per liter of water.
interfax.by
The effectiveness of brilliant green in the opinion of gardeners
Svetlana: On the advice of a friend, I tried a simple, economical, but very effective way of processing strawberries. Before flowering, I watered the beds twice with a weak solution of brilliant green (5 ml per bucket of water). The result was surprising: the growth of the mustache slowed down, useful substances were used to form the ovaries. As a result, the berries are large, juicy and very tasty. I advise everyone to try it - you will not regret it!
Iodine is a trace element that is found in every living organism and which everyone needs. The use of iodine is not limited to medical purposes, it can also be used as a top dressing for indoor plants and in the garden - for seedlings of tomatoes, cucumbers, cabbage and other vegetable and berry crops. This is what will be discussed in our article.
Geranium
Geranium attracts lovers of indoor plants with abundant and beautiful flowering for a long time. However, this unpretentious indoor flower does not always please the eye with bright colors. In this case, a simple bottle of pharmaceutical iodine will help out, which will work a miracle with your plant. It will not only ensure the rapid growth of geraniums, but also accelerate the budding period, prolong flowering and make the color of the petals themselves more saturated. As a rule, iodine feeding for geranium flowering is carried out in the form of a solution that even a novice grower can prepare.
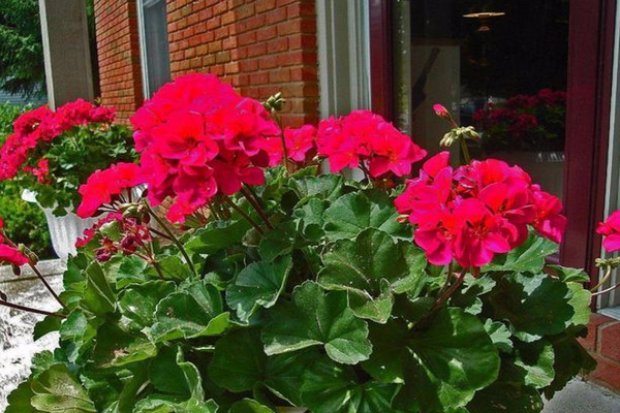


To obtain an iodine "mixture", you need to dissolve just a drop of this microelement in a liter of well-settled or rainwater. But if you have a stunted flower, then the number of drops can be increased to three in order to also heal the plant.
You should not water the geranium with the entire amount of the solution at once - it is enough to add up to 50 ml of iodine water, and even then closer to the walls. It is advisable that before this procedure the soil itself is slightly moistened in order to protect the roots from burns.
Such top dressing can be applied already from spring, right up to the dormant period, which begins in the fall. However, do not get carried away with frequent watering with iodine - take breaks for up to three weeks so as not to harm the indoor flower.
How to water indoor plants
Feeding with an iodine solution for indoor flowers should be done either at the root, watering closer to the walls of the vessel, or on the sheet. It is forbidden to introduce the nutrient composition into dry soil; it must first be watered with settled water. If you exceed the dosage, then instead of benefit, green spaces will receive harm in the form of a violent flowering of the bush and the absence of buds. The use of a basic iodine solution for watering home crops will allow both to saturate them with nutrients and protect them from pests and diseases.


Violet
The violet, popular among flower growers, also needs the close attention of its owners. To ensure continuous flowering without harming the appearance, it is advised to feed the plant not only with complex fertilizers, but also separately use iodine. For this purpose, a pharmacy preparation is perfect, the concentration of which, however, should be reduced. To create a weak solution, you need to stir a drop of iodine in three liters of soft water. It is advised to apply such fertilizer only a few times (maximum four) with an interval of ten days. The next stage of feeding is carried out after transplanting violets, and even then not earlier than three months later.


When using top dressing with iodine, be careful not to fill the plant with it, as an excess of iodine in the soil can affect the color of the leaves and the decorative effect of the flowers.
In general, a capricious violet reacts positively to iodine, you just need to monitor its dosage and frequency of introduction.
For vegetable crops
During the cultivation of seedlings of many vegetable crops, feeding with the addition of iodine helps to increase yields. But in order for you to get a rich harvest, and not burnt plants, you need to adhere to some rules.
Cabbage
For cabbage, iodine is used as a means of preventing various diseases. As a rule, it is used as a root fertilizer, but spraying is also recommended in some forums. The required solution is prepared very easily: about 40 droplets are used for 10 liters of water. Direct feeding of cabbage is carried out during the formation of heads of cabbage, 1 liter of fertilizer for one plant.
Cucumbers
This culture is often subject to a disease such as powdery mildew. And in order to get rid of this dangerous disease for the plant and prevent its occurrence, the seedlings of cucumbers and the soil around them are treated with a special solution. You can prepare it without any effort: you need to mix 3 liters of water, about 0.4 liters of milk and 3-5 drops of iodine. Treatment with such a medicine must be carried out once at the root. After a week or a week and a half, the cucumbers must be sprayed - for this, a mixture is used prepared as follows: 10 liters of water, one liter of milk and 10 drops of iodine. Spraying should be repeated every one and a half weeks. This remedy can be used not only as a medicine for powdery mildew and other diseases, but it also promotes the growth of the climbing part of the cucumber.
Did you know? From one ton of algae, you can get 2.5 g of pure iodine.
Tomatoes
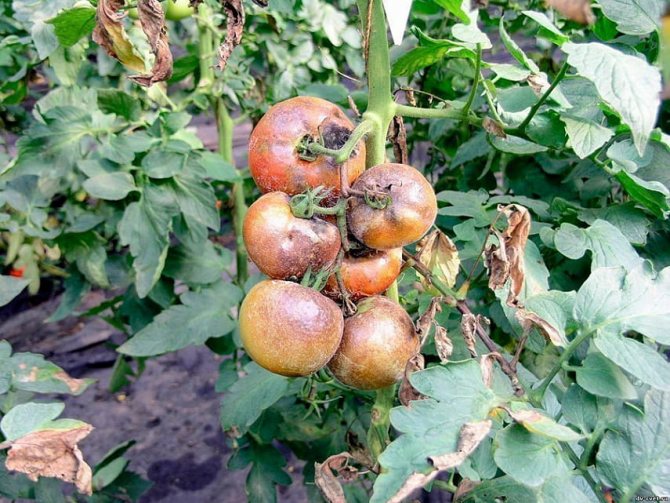
Experienced vegetable growers are very familiar with such a disease as late blight and how dangerous it is for tomatoes. In order to prevent the appearance of this fungal disease or to slow down the rate of its development, the majority use, as a rule, copper sulfate. However, this substance is very toxic and dangerous for humans, so recently people have begun to use an alternative to copper sulfate - this is foliar feeding with iodine solution.


There are several options for how to feed tomatoes with iodine. The first option is applied before the ovary appears, and the second after, but before the fruits begin to form.
First recipe: add two drops to one liter of water. In greenhouses, spraying with such a solution is carried out once every two weeks. If the bushes are in the open field, then once every one and a half weeks.Before the appearance of fruits, along with spraying, root feeding can be carried out in proportions of 5 drops. on a bucket of water.
Second recipe: add about 20 drops to a bucket of water. substances and one liter of ordinary milk whey. It is recommended to add one scoop of hydrogen peroxide to improve bacterial resistance. Spraying should be done every 10 days. Also, this solution is able to accelerate the ripening of fruits.
Pepper
Vegetable growers also use iodine in the cultivation of pepper. Processing can be carried out even before planting. To do this, take a 0.1% solution and place seeds in it for about 6 hours. After this initial treatment, the seeds germinate faster, and the sprouts themselves look stronger and healthier. After the appearance of two true leaves, it is advisable to treat the roots of the seedlings with 5% iodine tincture at the rate of one drop per three liters of water.


It will not be superfluous to fertilize the pepper after planting it in the open ground. To do this, dissolve 3 drops in 10-12 liters of water and pour about a liter per bush under the roots of the seedlings. Such feeding of pepper promotes the rapid formation of ovaries and favorably affects the formation of the fruit itself. A fed plant becomes more resistant to various diseases, the maturation of sweet pepper is accelerated, and its quality is much higher than that of untreated plants.
Do not forget to use the solution in order to prevent late blight disease, especially if you have all the prerequisites. In a 10-liter bucket, you need to stir 15 ml of the pharmaceutical preparation and spray the peppers just a few times at intervals of 10 days.


Important! Peppers are sprayed outdoors only in cloudy weather.
Effective recipes
For watering and spraying, they take a standard alcoholic solution of iodine, which is sold in any pharmacy. It is strictly forbidden to use the drug in concentrated form. It is necessary to prepare an aqueous solution, the content of the active substance in which is not the same for different plants.
Use a pure formulation. Or they add various useful components to it.
From late blight
To combat infectious pathology, a solution is prepared from 1 liter of milk whey, 9 liters of water, 40 drops of iodine. Spraying for therapeutic purposes is carried out every 2 weeks. It is advisable to do three treatments, even if the symptoms of infection have disappeared after the first application. All parts of the diseased plant are processed, including the fruits. They also moisten the soil on the site.
Phytophthora most often develops in a greenhouse, where, in warm and humid conditions, the fungus rapidly captures neighboring plants. The peculiarity of iodine is its ability to evaporate. This property allows it to be used as a prophylactic antiseptic.
It is enough to leave several bottles of iodine without lids in different places of the greenhouse in order to forget about the fungal infection for the entire growing season. But for a person to breathe air saturated with iodine vapors is harmful. Therefore, if you are going to work in the greenhouse, you should ventilate it and close the bottles.

Fighting root rot
To make a remedy, take 1 liter of serum, 10 ml of iodine, a small amount of laundry soap in a bucket of water. Processing is carried out every two weeks. The tool normalizes the condition of the plant, prevents the spread of fungal infection.
With kefir or milk
This remedy is effective against powdery mildew. Take 1 liter of milk or kefir, 9 liters of water, 10 drops of iodine. A sick plant is treated with a solution, the soil under it is moistened. The procedure is carried out once a week until the symptoms of pathology disappear.
With bread
An excellent remedy for the prevention of peronosporosis, prolongation of the growing season, prevention of early yellowing and wilting of cucumbers. For cooking, take a loaf of wheat bread, pour 1 liter of water, leave for 12 hours. The crumbled bread is kneaded, the whole bottle of iodine is poured in. The resulting composition is dissolved in a large bucket of water.Processing is carried out every 2 weeks.


For berry crops
Regarding berry crops, we can say that this microelement is a good strengthening and prophylactic agent against gray rot and other fungi. Its addition accelerates the flowering and ripening of berries, improves the palatability, and increases the size of the fruit.
A common berry plant such as strawberry is fertilized with iodine in the spring to improve vegetation and fruit quality. Also, the substance is used as a prophylactic agent against weevils and fungal diseases. Before flowering, you need to spray the bushes with a solution at the rate of 8 or 10 drops per bucket of water. It is also believed that this element can provoke a second flowering and the appearance of fruits. To do this, you need to make root dressing with a solution of 20 drops per bucket of water.


Grapes are no less popular berries than strawberries, and they also need additional care. Therefore, for the prevention and treatment of fungal diseases, grapes are sprayed with an iodine solution: in 10 liters of water, you need to add a liter of milk and about 20 drops of iodine. Spraying should be done every one and a half weeks.


Did you know? Iodine is a very toxic trace element: 3 g of pure substance can cause damage to the heart and kidneys in a person, as well as lead to death.
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize that although this element is very important for all vegetable and berry crops, it must be used responsibly, otherwise you will only harm the plants.
| Berries (strawberries, strawberries) | Prevention of powdery mildew, gray mold and other bacterial diseases | Watering twice at the root with an interval of 2 weeks during flowering and ovary formation (5 ml per 10 l of water) |
| Cucumbers | Preventing root rot and powdery mildew | Weekly watering of the soil under the root and spraying of the stems (10 drops per 10 liters of water) |
| Onion garlic | Disinfection of the seat | Soil processing 3-5 days before planting (5-7 ml per 10 liters of water) |
Signs of iodine deficiency in tomato seedlings
The main sign will be external manifestations:
- Decreased yield. For example, you planted a proven tomato variety in its usual conditions. When you notice a decrease in the number of ovaries or the size of the fruits, then iodine feeding for tomatoes is necessary.
- Delay in the onset of the fruiting phase in an adult plant. If during this period they are not fed, the yield will be low, and the fruits will be small.
- Weak immunity of tomato seedlings. If the seedlings grow poorly, get sick, are affected by diseases, iodine is needed.
- When tomatoes are affected by mosaics, root rot, brown spot or late blight, spraying with an iodine solution is used.
- The appearance of characteristic signs of iodine deficiency in tomatoes - thin stems, pale and sluggish leaves - also signals the need for feeding.
Tomatoes are known to be able to absorb iodine compounds from the surrounding atmosphere. But how much element is needed for good development of the bush? Tomatoes do not have the most obvious characteristic sign of iodine deficiency, so you need to carefully monitor the plants from the first days of life. This will help you notice in time that it is time to feed the tomatoes with iodine. It is best to carry out pre-sowing processing of tomatoes.










































