You can't do without cabbage in Russian cuisine. Cabbage soup, borscht, pickles, cabbage rolls and just fresh salads are impossible without this popular vegetable. Agrarians have long been using cabbage precisely because of its excellent keeping quality - with proper storage, the culture will lie for the whole winter and will delight with its juicy taste all year round.
On the other hand, novice summer residents and gardeners often face the problem of various cabbage diseases. Sometimes mold or rot may appear on the head of cabbage, dry layers form between the leaves, dark grooves-veins and other manifestations of disease processes in the culture are visible. In the article, we will consider what diseases can affect the heads of cabbage during long-term storage in the cellar, and how to properly store cabbage in order to avoid the development of various vegetable diseases.
Diseases typical of cabbage
Cabbage mainly suffers from disease-causing fungi. It can become infected at any stage of growing and even during storage. If the problem is noticed on time, many diseases can be dealt with with the help of folk remedies. This is even encouraged, because about a month before the planned harvest, the use of any chemicals is prohibited.
"Blackleg"
A dangerous fungal disease that destroys most or all of the cabbage crop already at the stage of growing seedlings. It can develop after it is transplanted into open ground, but this is rarely observed. Contamination is facilitated by regular waterlogging of the substrate, its increased acidity and excessive enthusiasm of the gardener with nitrogen-containing fertilizers. Moreover, the denser the planting, the more seedlings will suffer.
The base of the stem becomes thinner, deformed, and blackens. He is no longer able to withstand the weight of the aboveground part of the plant, the cabbage lays down on the ground. Young seedlings die from the "black leg", adult specimens can survive and even form small heads of cabbage, but the leaves on them dry, wither, and rot.

Often the gardener himself is to blame for the development of the "black leg"
To avoid contamination, the seedling soil must be disinfected. Granules of Trichodermin, Glyokladin or sifted wood ash, crushed chalk are added to it. Seeds are etched in a solution of any fungicide of biological origin (Alirin-B, Maxim, Planriz). Water for irrigation is periodically replaced with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate.
During cultivation, cabbage is sprayed with Fitosporin-M solution every 10-14 days, the soil in the garden is dusted with ash or colloidal sulfur. Fine sand is added to the base of the stems. Treatments with biostimulants - Epin, Immunocytophyte, potassium humate have a positive effect on plant immunity.


Potassium permanganate is one of the most common disinfectants that destroy pathogenic fungi
Having found suspicious symptoms, watering is reduced to the required minimum. Instead of ordinary water, use a solution of Previkur or Fitosporin-M. Cabbage is treated with Bactofit, Fitoflavin. From folk remedies, a pinkish solution of potassium permanganate or an infusion of onion peel is used.
You can try to save cabbage seedlings affected by the "black leg". Having cut off the affected stem, the aerial part is placed in water with the addition of a couple of drops of a biostimulant. It often gives roots.
Video: the fight against the "black leg of seedlings"
Peronosporiosis (downy mildew)
It affects not only any variety of cabbage, but in general all plants from the Cruciferous family. Most often it develops in a heavy acidified substrate. The spores of the fungus overwintering in the soil remain viable for 5–6 years.


The development of peronosporia is promoted by acidification of the soil at the roots of cabbage
Pale yellow spots are blurred on the front side of the sheet. The seamy side is tightened with a continuous layer of pinkish bloom. Gradually, the spots change their shade to reddish, plaque to lilac. Affected leaves turn yellow and die off.
For prophylaxis, the seeds are kept in hot (45-50 ° C) water for 15–20 minutes before planting, then immersed in cold water for 2–3 minutes. Any fungicide is used to combat the disease. The best results were shown by the preparations Ridomil-Gold, Impact, Vectra, Skor.
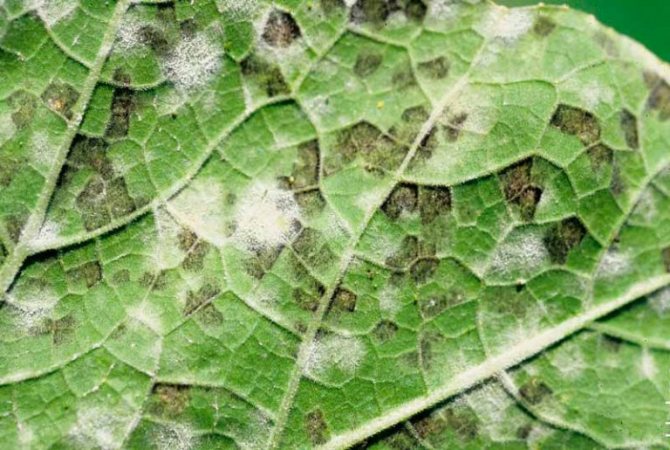


The plaque on the wrong side of the sheet seems to be easily erased, but it is a symptom of a very dangerous disease.
If a pathogenic fungus has infected cabbage seedlings, the plants are dusted with ash or colloidal sulfur 2-3 times with an interval of 4-5 days and planted in the garden as soon as possible. Foliar dressing with potash and phosphorus fertilizers has a positive effect on their immunity.
Alternaria (black spot)
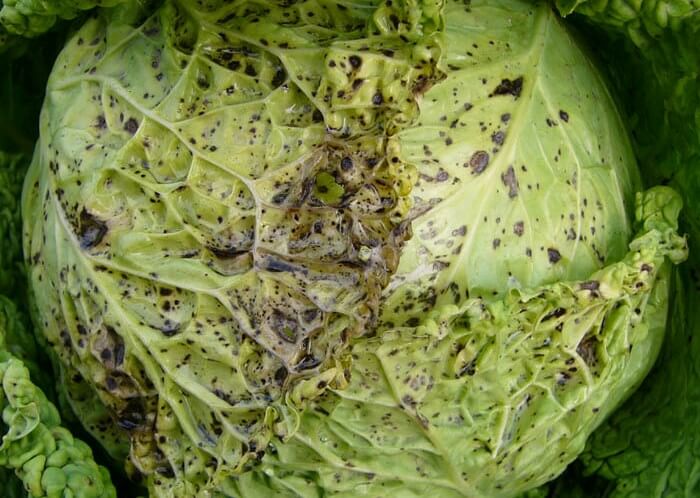
Fungal spores are carried by wind or water droplets. Heat and frequent rainfall contribute to the development of the disease. It can affect cabbage both during growing and during storage. Thin black strokes appear on the leaves, gradually turning into dark green spots with a yellowish border, covered with a layer of "fluffy" bloom. Affected tissues rot.


Alternaria provokes massive decay of cabbage leaves
When planting seedlings in the ground, Trichodermin granules or a little wood ash are placed at the bottom of the hole. Once every 12-15 days, cabbage and soil in the garden are sprayed with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, alternating with Immunocytophyte. To combat the disease, the drugs Abiga-Peak, Bravo, Skor and Quadris are used. Plants are treated every 1.5–2 weeks until the characteristic symptoms disappear.


Copper sulfate is one of the most common fungicides, its effectiveness has been tested by many generations of gardeners.
To avoid the development of Alternaria during storage, the heads of cabbage are provided with optimal or similar conditions (temperature at the level of 2–4 ° С, humidity 70–80%, good ventilation, lack of light). Before laying in a basement or cellar, the room is disinfected by wiping all surfaces with diluted water with slaked lime or burning a small piece of a sulfur block. The heads of cabbage are carefully selected, powdered with wood ash or crushed chalk, laid out or hung so that they do not touch each other.
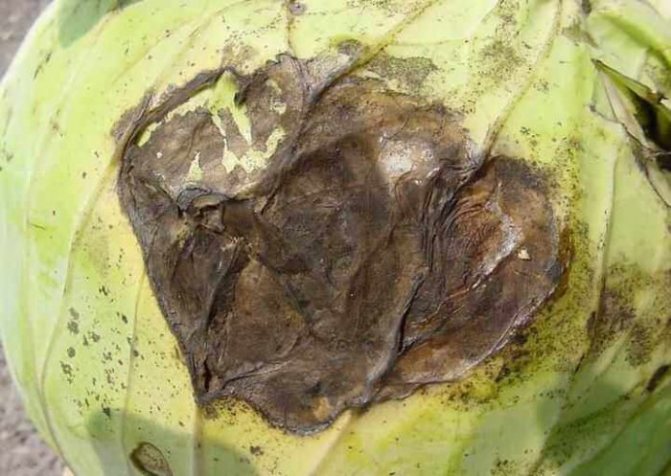
Sclerotinia (white rot)
Most often, cabbage becomes infected during storage, but with high humidity and cool weather, the disease can develop closer to the end of the growing season. The leaves are covered with a thick layer of whitish, cotton-like bloom with small black blotches. The affected tissues “get wet”, become slimy to the touch, the heads of cabbage rot.
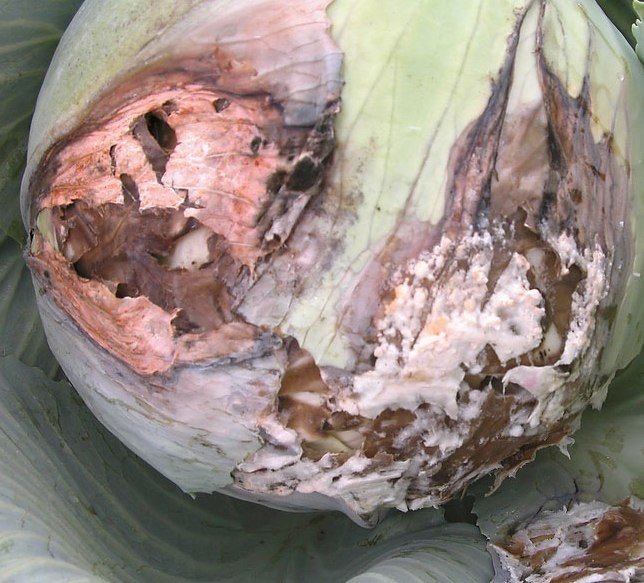


White rot on cabbage heads resembles peeling layers of oil paint
To avoid the development of white rot, cabbage is carefully selected for storage, and suitable conditions are provided for it. Harvested on time - overripe and slightly frozen heads of cabbage are much more likely to suffer from fungus. For prophylaxis during the summer, foliar dressings are carried out every two weeks, spraying cabbage with a solution of zinc sulfate, potassium permanganate, copper sulfate, boric acid, ammonium molybdenum (1-2 g per liter of water).
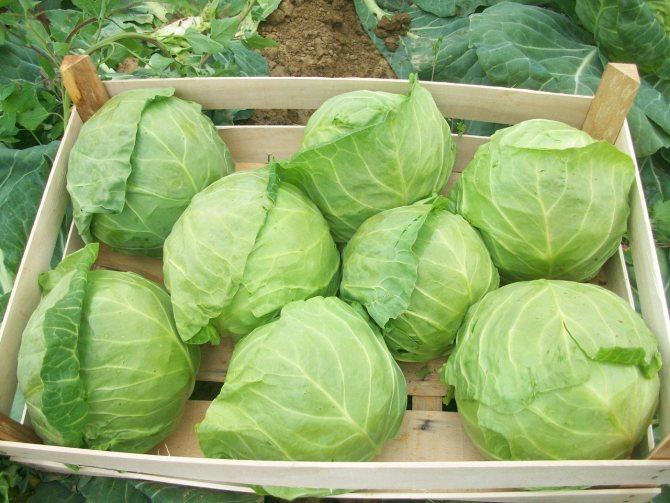


To avoid the development of white rot, cabbage is carefully selected for storage.
It is quite difficult to deal with sclerotinia, because the disease develops very quickly. If, nevertheless, it was possible to notice it at an early stage, the affected tissues are cut out, capturing a little more and those that seem to be healthy in appearance. "Wounds" are sprinkled with a powder of activated carbon, cinnamon or gruel from crushed chalk, diluted with a pink solution of potassium permanganate.
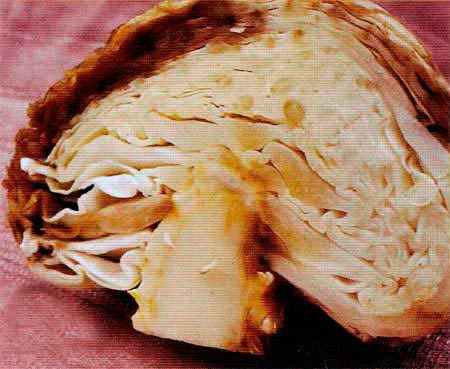
Phomoz (dry rot)
Not only "cultured" but also "wild" cruciferous plants suffer from fomoz. Therefore, special attention must be paid to weed control. Most often, the disease develops in high humidity and moderately warm weather (22-26 ° C). The fungus penetrates into the tissue through mechanical damage. It hibernates in plant debris, retaining its viability for 5-7 years.
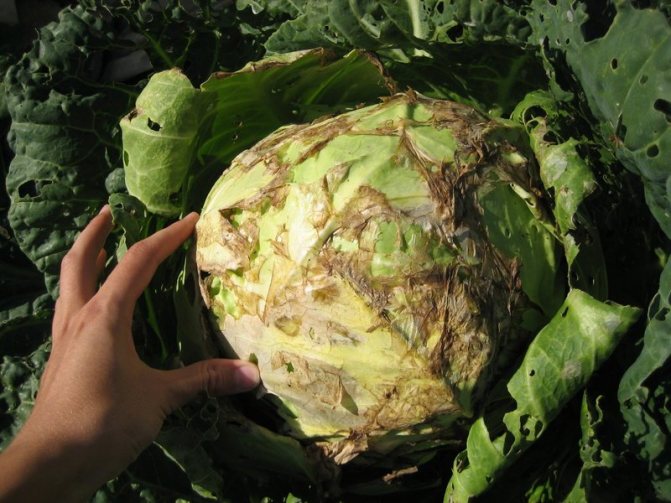


The causative agent of phomosis remains viable for a long time.
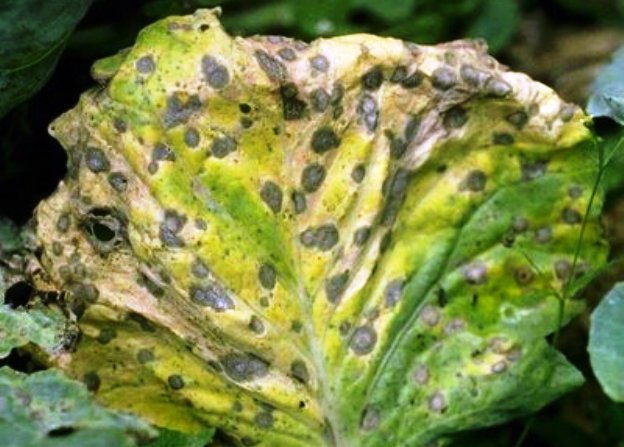
The first sign is an unnatural reddish-purple color of the leaf plates. Then, the leaves affected by the phomosis become thinner, gray, dry, covered with an ashy bloom with small black blotches. Gradually, the spots turn into depressed "ulcers".
For prophylaxis during the vegetative period, plants are treated with a solution of Trichodermin, Phytocide. From folk remedies, an infusion of onion or garlic gruel is used. To make it better "stick" to the heads of cabbage, add a little soap shavings or liquid soap. Any fungicide is used to combat the disease. If it is noticed at an early stage, 2-3 treatments with an interval of 10-12 days are enough.
Botrytis (gray rot)
A very dangerous disease of cabbage that develops during storage. It mainly affects plants with weakened immunity or mechanical damage. Heads of cabbage are covered with slimy dark green spots, then they turn brown and are covered with a layer of "fluffy" ash coating.
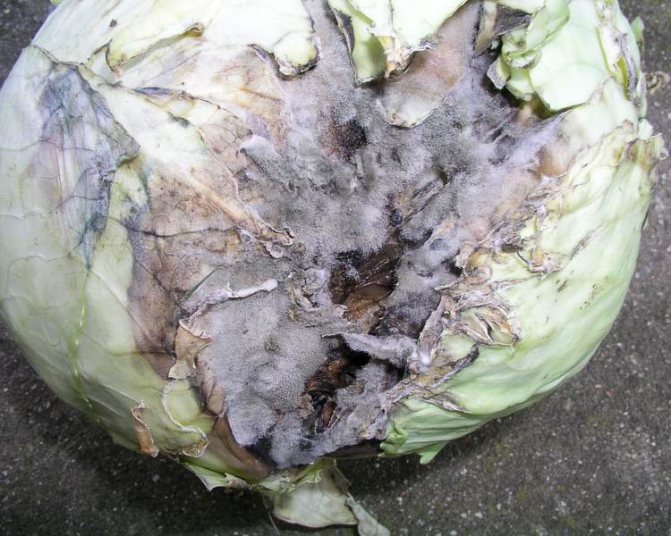


To prevent gray rot from affecting the entire crop, cabbage in the cellar is regularly examined for the timely detection of suspicious signs.
It is almost impossible to fight the disease. For prophylaxis, when harvesting, it is imperative that several integumentary leaves are preserved, and the heads of cabbage are handled carefully so that they do not receive mechanical damage. Cabbage during storage must be regularly examined, all infected heads of cabbage are removed. If the disease is noticed at an early stage, they fight it in the same way as with white rot.
Fusarium
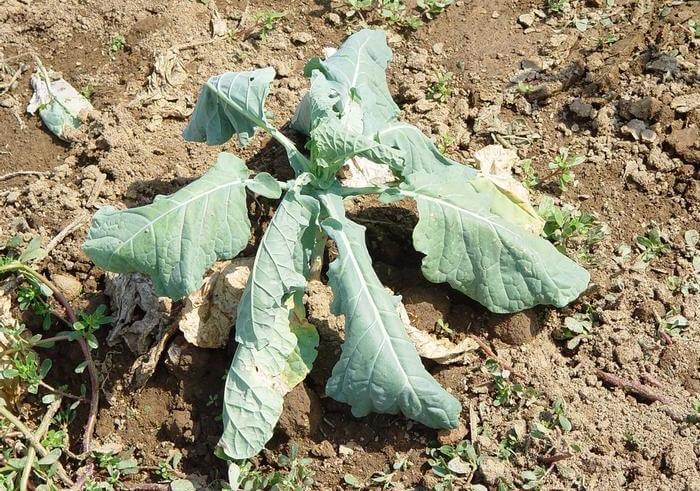
The disease develops very quickly, mainly plants suffer from fusarium within a month and a half after planting in the ground. In just 5-7 days, the cabbage withers. The fungus penetrates the plant tissues through the roots, does not manifest itself for a long time, nothing is noticeable on the aerial part.
The leaves of infected specimens turn yellow, lose their tone. Then they deform and dry out. The head of cabbage stops forming, cracks. If the plant is cut, annular black-brown blotches are noticeable in the stem tissues.
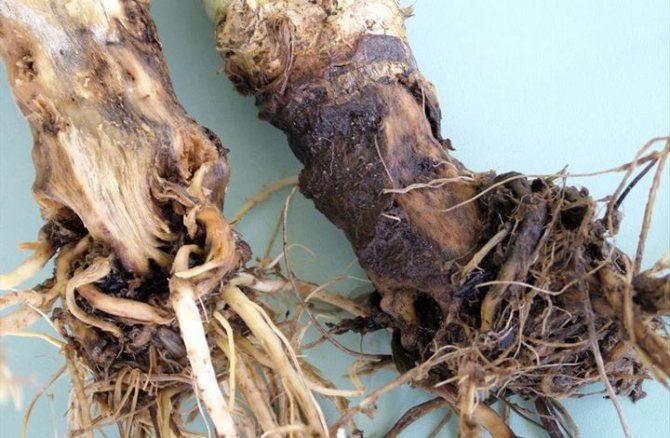


The fungus that causes fusarium has been "quiet" for a long time, the development of the disease can be noticed only if the plants are dug up
There is no way to treat fusarium. Affected plants are immediately pulled out and burned. The substrate in this place is disinfected by spilling 5% copper sulfate, burgundy liquid or a dark raspberry solution of potassium permanganate.
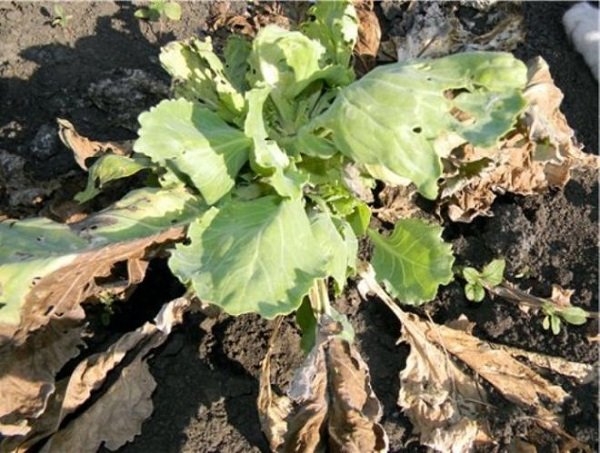


cabbage affected by fusarium withers and dries literally before our eyes
For prevention, the soil in the garden bed is spilled with Fundazol solution. Cabbage is sprayed with Agatom-25K, Immunocytophyte, Heteroauxin, Emistim-M. Healthy plants are less likely to get sick. But the only reliable way to avoid Fusarium infection is to grow varieties and hybrids resistant to it. There are quite a few of them - Fresco, Amazon, Satellite, Kolobok, Paradox, Megaton, Karamba and so on. There are also varieties of red cabbage, leafy cabbage, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, savoy cabbage and kohlrabi with "innate" immunity.
Slimy bacteriosis (black rot)
The disease, the spread of which is promoted by high air humidity, heat, alkaline substrate, deficiency of potassium and phosphorus in the soil and excess nitrogen. Most often, cabbage suffers from it in the second half of summer, towards the end of the growing season.
Leaves starting from the outer ones rot, spreading a pungent unpleasant odor. At first they turn yellowish cream, then turn gray and brown. The base of the stem and veins turn black. The soil is covered with a layer of mold. You can't eat such cabbage.


Cabbage infected with mucous bacteriosis is strongly discouraged from eating.
For prevention, the soil is sprayed with 1% copper sulfate or Planriz every 7-10 days, the cabbage itself is sprayed with Agatom-25K. The soil is powdered with wood ash or crushed chalk. Before planting, the seeds are etched in a solution of Binoram, Previkur, Fitolavin. They can also shed seedling holes. The roots are dipped in a slurry of fresh manure and powdered clay with the addition of Trichodermin, Glyocladin. Fungal spores are tolerated by most cabbage pests, so attention should also be paid to combating them.

Mucous bacteriosis spreads from the periphery of the head of cabbage to its center
It is impossible to cure this disease with modern means. The only way to guarantee crop protection is to plant varieties resistant to bacteriosis. In white cabbage, for example, Valentina, Kolobok, Nadezhda, Slavyanka, Monarch, Lennox, Monterrey.
Keela
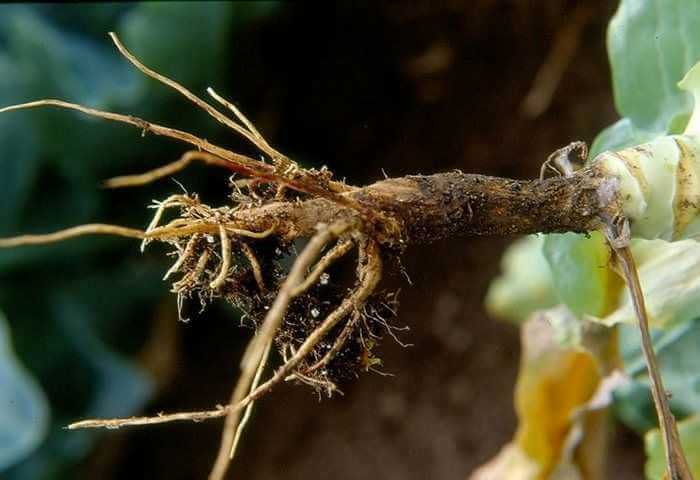
It affects all plants from the Cruciferous family. If keela was found in the garden, cabbage and other crops should not be planted on it for at least 7-8 years. The plant seems to wither for no apparent reason. But if you dig it out of the ground, ugly growths of various sizes, resembling tumors, are clearly visible on the roots. Heads of cabbage on such cabbage either do not tie at all, or they form very loose.
When planting seedlings in the ground, it is imperative to pay attention to the roots and discard all seedlings, even with barely noticeable suspicious growths. Over time, they can grow to the size of a head of cabbage.
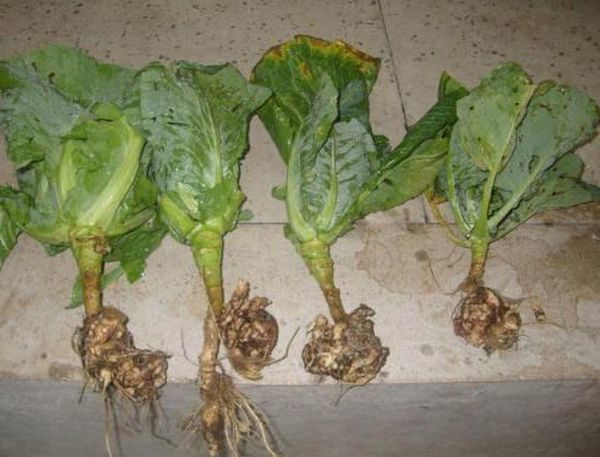


Keela is one of the most dangerous diseases of cabbage
Keela develops in acidic soil. To neutralize it, when preparing the beds, dolomite flour, powdered eggshells, and wood ash are introduced into the soil. At least once a month, cabbage is watered with diluted colloidal sulfur or the same dolomite flour (the so-called milk of lime). A solution of Topaz, Alirin-B is also suitable.


On the aerial part of the plant, the keel does not manifest itself in any way, it seems that the cabbage withers for no reason
It is impossible to cure this disease. The plant can only be pulled out and burned, thus eliminating the source of the spread of the infection. The soil in this place must be disinfected. The varieties of white cabbage that are immune to the keel are Kiloton, Tequila, Nadezhda, Ramkila, Taininskaya.
There are crops that effectively cleanse the soil from keel spores. If you plant any Solanaceae, onions, garlic, beets, spinach, cabbage on this bed for 2-3 years, you can return to its original place faster. Some gardeners recommend planting chopped beet tops in the garden when digging.
Video: keela on cabbage
Mosaic virus
On the leaves, starting from the youngest, yellowish spots appear between the veins. Then, areas of necrotic tissue appear on these tissues, the veins are deformed, the leaves wrinkle. Gradually they dry out, the plant dies.
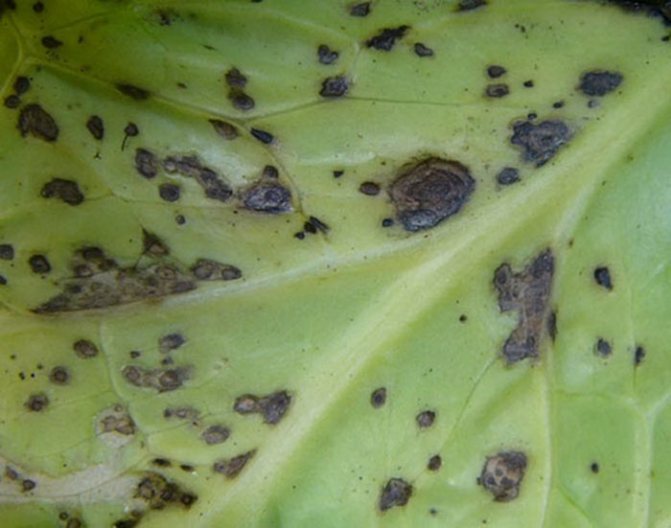


The cabbage mosaic virus cannot be cured by modern means
It is impossible to cure the mosaic, like most viral diseases affecting horticultural crops. Therefore, prevention is imperative. The seeds are soaked in hot water, pickled in a solution of Phytocide, Agata-25K.Spores of the virus are spread by aphids, which also need to be purposefully dealt with.
Gray rot


Gray rot is also caused by fungi, which attack the weakened and dying tissues of cabbage. This disease develops mainly on already harvested heads of cabbage during storage. Symptoms of the disease:
- the appearance of mucous bacteriosis on the leaves:
- development of gray fluffy mold on the lower petioles;
- the presence of black sclerotia.
When the cabbage is severely damaged, it quickly rots and infects neighboring vegetables.
The measures for the prevention of gray rot are the same as in the case of the previous ailment: compliance with crop rotation, timely harvesting, disinfection of the storage facility, rejection of damaged and frost-bitten heads. In addition, cabbage varieties that are resistant to fungal diseases should be chosen for growing.
Dangerous pests
Any variety of cabbage has a lot of pests. Insects are attracted to succulent leaves. They are dangerous not only because they damage plants. Many of them are carriers of spores of pathogenic fungi, viruses, bacteria.
Cabbage aphid
Small pale green insects literally dot the inside of the leaves. Aphids feed on plant sap. Multiple discolored dots appear on the affected tissues, clearly visible in the light. Then the leaves are deformed, thinning, as if decaying.
Recent Entries
5 of my favorite tomato varieties that are great for pickling 7 super early and delicious potatoes to plant in 2020 6 rare 2020 tomato varieties that will bring you a decent harvest
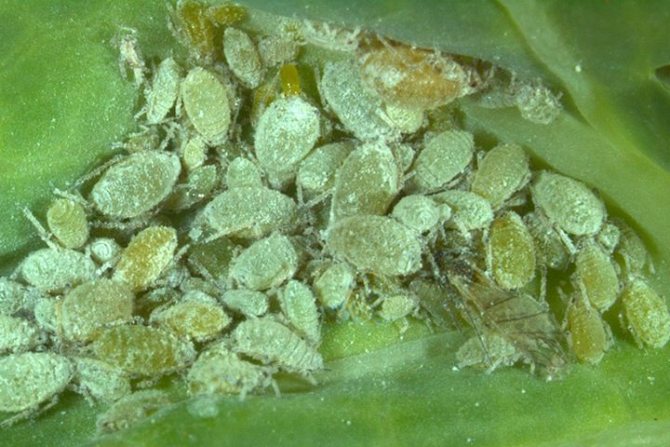


Aphids are one of the most "omnivorous" garden pests; it is also dangerous for cabbage of all varieties.
Aphids do not like strong odors. She is frightened off by marigolds, calendula, rosemary, lavender, sage, basil, and other spicy herbs planted around the perimeter of the cabbage bed. The most pronounced effect is given by carrots, garlic, fennel, dill, parsley. The same plants can be used as raw materials for the preparation of infusions, which are sprayed with cabbage every 10-12 days. Also suitable are tomato tops, mustard powder, onion and garlic arrows, hot peppers, dry tobacco leaves.
Natural enemies of aphids are birds (sparrows, tits) and earwigs. For the former, feeders can be placed on the site, the latter are attracted with the help of containers filled with wood chips.


Discolored areas on cabbage leaves - dead tissue
Having found aphids, while there is still a little of it, the cabbage is sprayed with soapy foam, a solution of soda ash. They also use infusions designed to scare it away. Only the intervals between procedures are reduced to 6-8 hours.
If there is no expected effect, any general action insecticides are used, for example, Commander, Corado, Inta-Vir, Iskra-Bio, Fitoverm. Usually 2-3 treatments are enough with an interval of 7-12 days.
Video: aphids on cabbage and methods of dealing with it
Cruciferous bug
Adults and larvae suck the juice from the cabbage leaves. They turn yellow and dry up, the plant stops developing. Early varieties suffer less from bedbugs. Until the moment it is activated, they form rather powerful plants that are more difficult to harm.
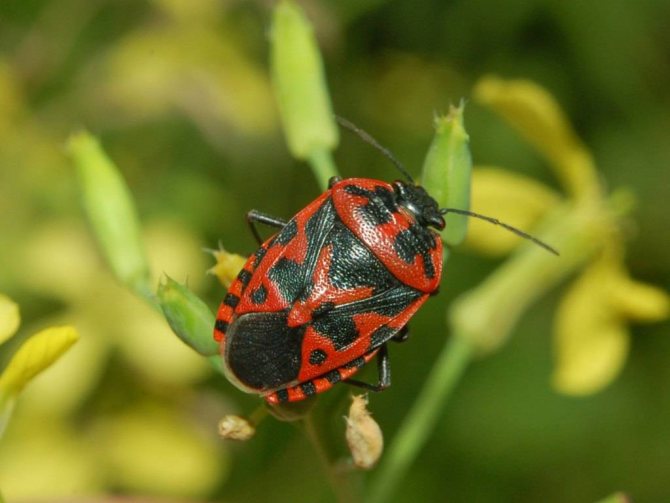


The cruciferous bug is a cute bug, but it does significant harm to cabbage beds
To scare off the pest, the cabbage bed is surrounded around the perimeter with wormwood, tansy, and calendula. Rags moistened with kerosene or turpentine are laid out in the aisles. Sprinkle the soil with mothballs mixed with wood ash (1: 5).


Early varieties of cabbage suffer from cruciferous bugs much less often, the leaves of plants have time to "coarse" before it begins to be active
Prevention - spraying cabbage with infusions of chamomile pharmacy, tomato or potato tops. When pests appear, plants and soil are treated with Belofos, Fosbecid, Engio, Aktellik. If the bugs have multiplied en masse, the concentration of the chemical is doubled compared to that recommended by the manufacturer.
Cruciferous flea
A specific pest of plants from the family of the same name. Small bugs can turn leaves into a sieve in a matter of days. They generally destroy cabbage seedlings literally in hours. The most active pests are in the spring, when the air temperature rises to 15 ° C and above.


Cruciferous fleas become active towards the end of spring.
For prevention, cabbage is placed away from the beds with radish, radish, daikon. Plants are sprayed weekly with diluted water in a 1:10 ratio with vinegar essence. The bed is dusted with a mixture of wood ash, tobacco chips and red pepper. The plants themselves - with crushed chalk or colloidal sulfur. To water for irrigation add an infusion of valerian, an essential oil with a pine aroma (8-10 drops per bucket of water).
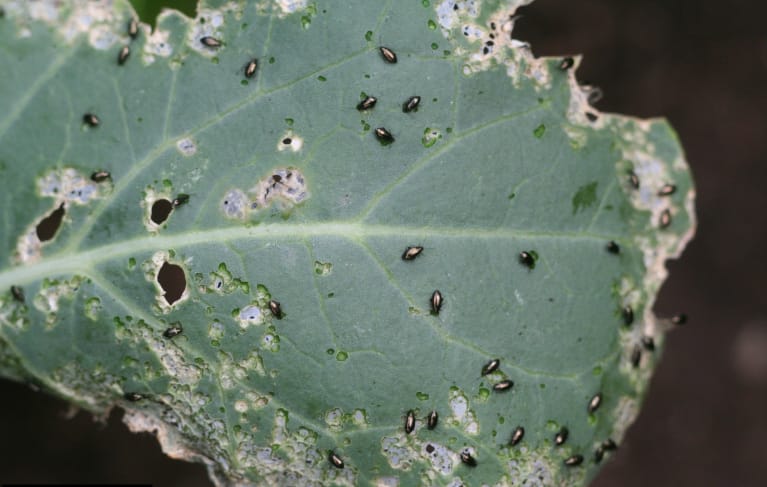


From cabbage leaves after the invasion of the cruciferous flea, a real sieve remains
When a pest is detected, the drugs Decis, Karate, Bankol, Aktara are used. The flea shampoo intended for animals (50 ml per 5 liters of water) also has a good effect.
Slugs
The shell-less mollusks feed on cabbage leaves, eating large holes in them. A sticky shiny coating remains on the surface, shimmering silver. The keeping quality of such heads of cabbage decreases sharply, and so does presentability. I don't want to eat such cabbage at all.
Slugs can be collected manually, since they do not differ in movement speed and camouflage abilities. Traps also have a good effect. Deep containers are dug into the ground and filled with beer, sugar syrup, kvass, fermented jam, cabbage pieces or grapefruit pulp.
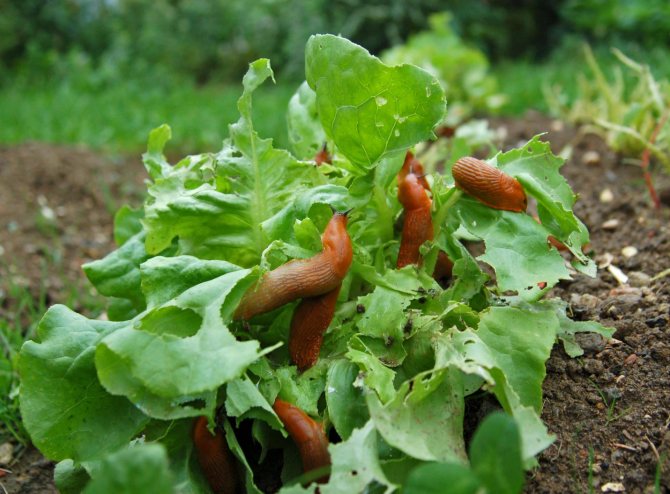


Most often, folk remedies are enough to fight slugs.
To scare away slugs, the garden bed is surrounded by any spicy herbs - mint, sage, wormwood, parsley. Nettle stalks are laid out in the aisles. Their natural enemies are hedgehogs, toads, starlings. Attracting them to the site is not that difficult.
A good effect is given by spraying with strong coffee, diluted with water with ammonia (1: 6), salt solution (a teaspoon per 3 liters). You should not get carried away with the latter, otherwise the heads of cabbage will turn yellow and dry out. At the base of the stems, a "barrier" is built of needles, ground eggshells or nuts, sand, hot pepper, ash, and fine gravel.


Cabbage heads damaged by slugs are unsuitable for long-term storage
Chemicals are used only in the event of a massive invasion of slugs, which is extremely rare. They use drugs Thunderstorm, Slizneed, Meta, other insecticides, which contain metaldehyde.
Video: how to get rid of slugs on cabbage
Cabbage moth
Small grayish-brown butterflies lay eggs 5–6 times per summer. The larvae emerging from them feed on leaf tissues. Caterpillars are especially rampant if it is extremely hot outside. Affected plants stop developing, dry out, and do not set heads of cabbage.
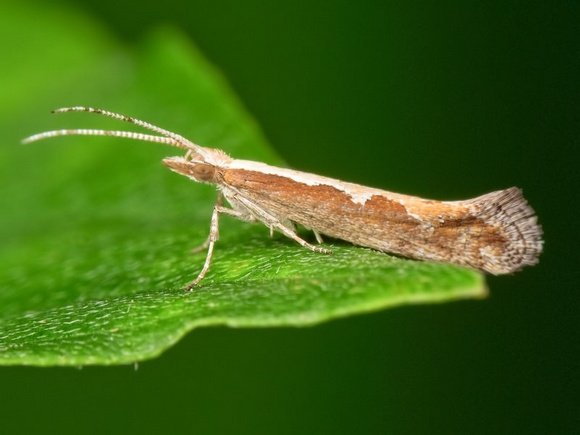


The main harm to plantings is caused by the caterpillars of the cabbage moth, but this does not mean that there is no need to fight with adults.
From folk remedies to scare away cabbage moths, a decoction of tomato tops, dandelion leaves, an infusion of mustard powder, ground pepper, and tobacco crumbs are used. Several tobacco bushes can be planted around the perimeter of the garden. A good effect is given by the "barrier" of clover, parsley, cilantro, mustard, carrots. They attract the natural enemies of the cabbage moth.
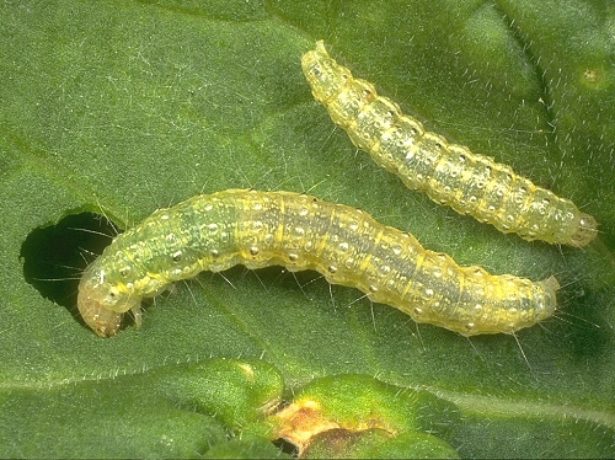


Cabbage moth breeds en masse if the weather is hot and dry.
To protect against adults, sticky tape for catching flies or pieces of cardboard smeared with resin, petroleum jelly, honey, and long-drying glue are hung next to the garden bed. Cabbage is sprayed with Entobacterin, Gomelin, Dendrobacillin.Treatments with Aktellik, Ambush, Nurell-D, Kinmiks are effective against caterpillars.
Cabbage white
The pest is better known to gardeners as a cabbage butterfly. If you do not fight it, you can completely lose the crop. Each butterfly lays 200 or more eggs, the caterpillars hatching from them devour the leaves in a few days, leaving only veins of them.
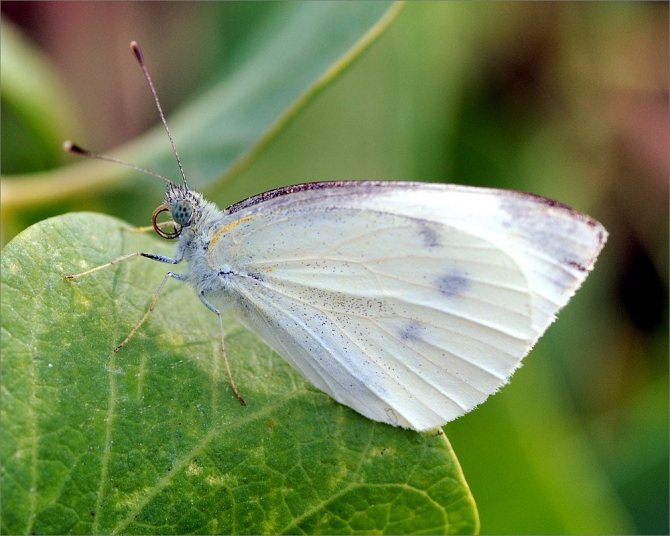


Every gardener has seen a cabbage butterfly at least once in his life
For prevention, the leaves must be regularly examined, especially from the inside out. Eggs found are immediately destroyed. If there are many of them, sprinkle the bed with tobacco crumbs. Adults are scared away in the same way as the cabbage moth. You can also use an infusion of burdock rhizomes, wormwood. Fitoverm, Kemifos, Kinmiks are used to destroy caterpillars.
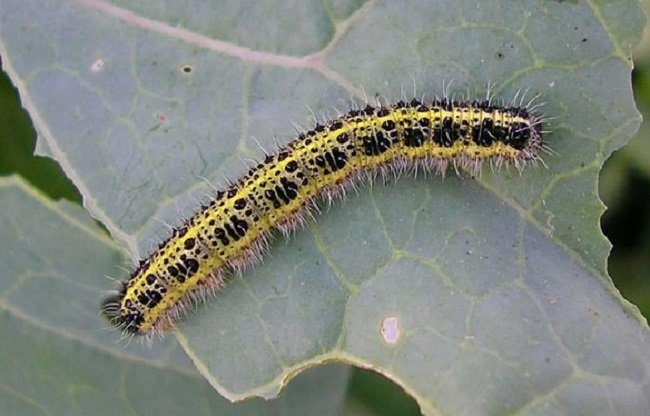


Cabbage larvae are incredibly gluttonous
An interesting method of dealing with a butterfly is placing sticks with pieces of eggshell glued to them on the garden bed. Apparently, they take them for "relatives" and fly on, believing that the territory is already occupied.
Cabbage scoop
Caterpillars, hatching from eggs laid by a brownish-gray butterfly, first eat the integumentary leaves of the head of cabbage, then penetrate inside, making long "tunnels".
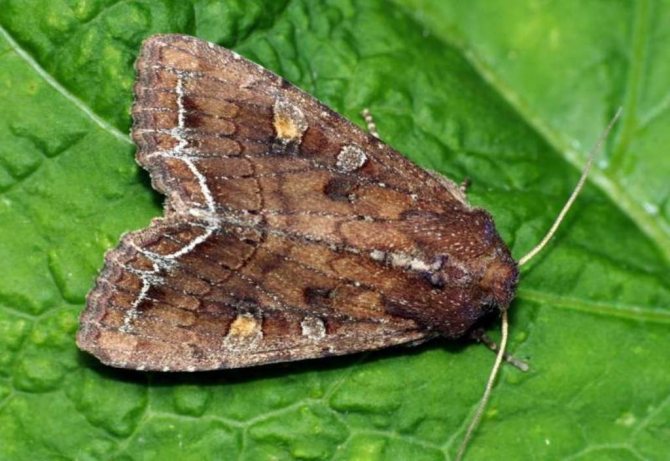


The cabbage scoop is a rather inconspicuous butterfly
Caterpillars and eggs are harvested by hand. Butterflies are scared off by spraying cabbage with infusion of chili peppers or baking soda diluted with water (10 l glass). A good effect is also given by the traps described above, the drugs Lepidocid, Bitoxibacillin, Zolon. In the event of a mass invasion of caterpillars, Inta-Vir, Fury, Sherpa, Karate are used.
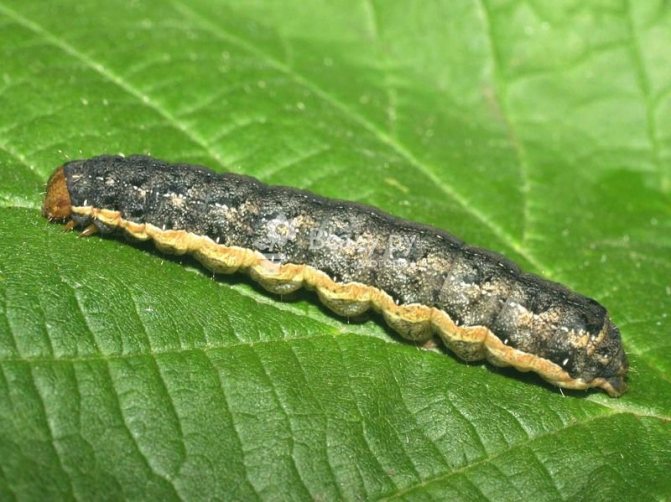


Mass invasions of cabbage moth caterpillars are quite rare.
Video: butterflies on cabbage and how to deal with them
Rapeseed sawfly
Female beetles lay their eggs in plant tissues. They "seal" the place of masonry with their own excrement. The larvae that emerged from them eat the stems and leaves from the inside, gradually coming out. In addition to cabbage and its "relatives", the pest also affects plants from the Celery family (carrots, parsley, parsnips, coriander), so it is better to plant them away from each other.
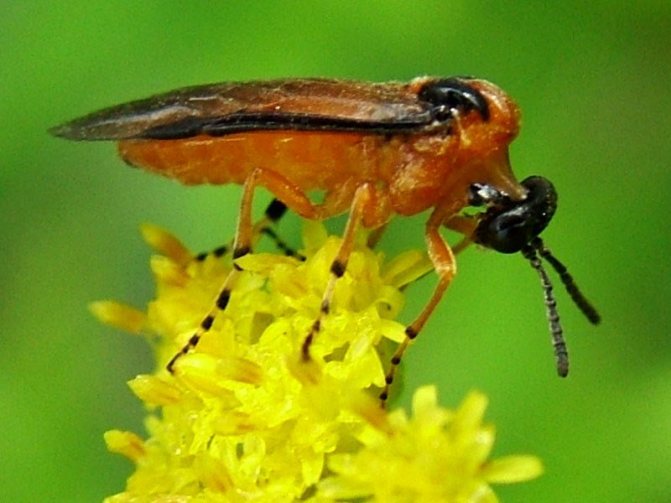


The "sphere of interest" of the rape sawfly includes not only Cruciferous, but also plants from other families
For prevention, cabbage is sprayed with infusion of wormwood, chamomile, tansy, aconite (the latter is very poisonous). Another option is a solution of soda ash (70 g per 10 liters of water). The larvae are destroyed by treating plants and soil with Metaphos, Phosphamide, Arrivo, Aktara, Confidor-Maxi.
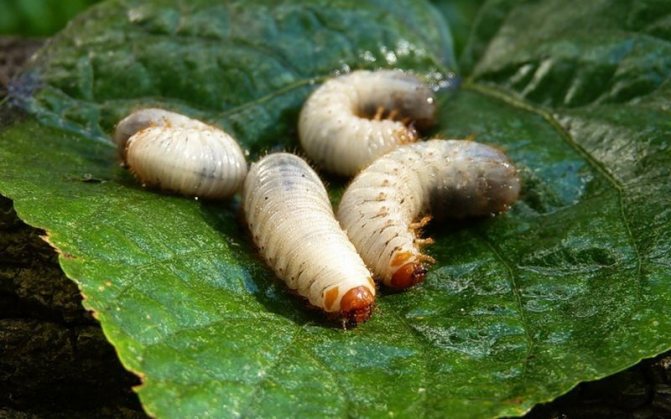


Rape sawfly larvae feed on leaf tissue
Cabbage fly
Adults lay their eggs in the soil. The larvae penetrate the roots and gradually move up the stem without going outside. They make long tunnels in the tissues. The plant slows down in development, dry up.
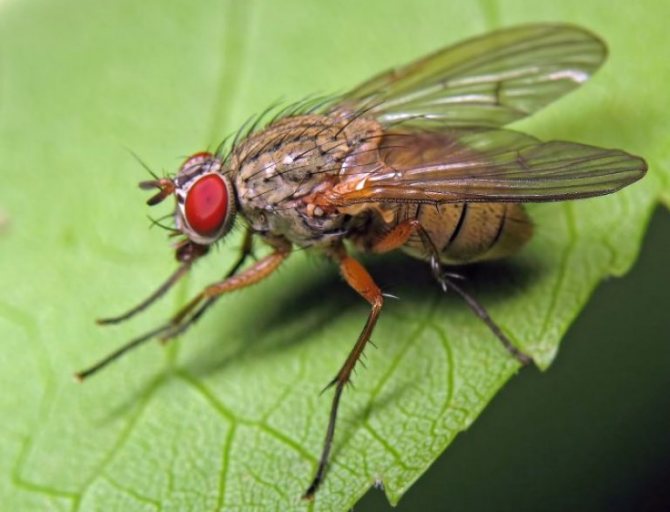


The peak activity of the cabbage fly is in May.
Adults are scared away by surrounding the garden with dill, calendula, marigolds, caraway seeds, coriander, celery. They also cannot stand the smell of valerian. The soil is sprinkled with ash, the cabbage is sprayed with infusion of dandelion or burdock leaves, saline (a glass per bucket of water) or ammonia diluted with water (10 ml per 10 l). When planting seedlings in the holes, granules of Bazudin, Pochina, Zemlin are introduced into the soil. At the time of peak activity of flies (you can focus on the beginning of lilac flowering), cabbage is covered with lutrasil, spunbond, and other similar white material.
It is very difficult to see the cabbage fly larvae, even by regularly and carefully examining the cabbage.
When loosening, the soil is powdered with a mixture of mustard powder and ground pepper or wood ash with naphthalene or camphor. Having found the larvae, they use Rovikurt, Trichlormetaphos.
Whitefly
Pest detection is easy.Small moth-like whitish butterflies fly into the air even at the lightest touch of the plant. Both they themselves and the larvae feed on cabbage juice, yellowish spots spread on the leaves. This crop especially often suffers from whitefly when grown in a greenhouse. She is very comfortable with heat, high humidity and stale air.
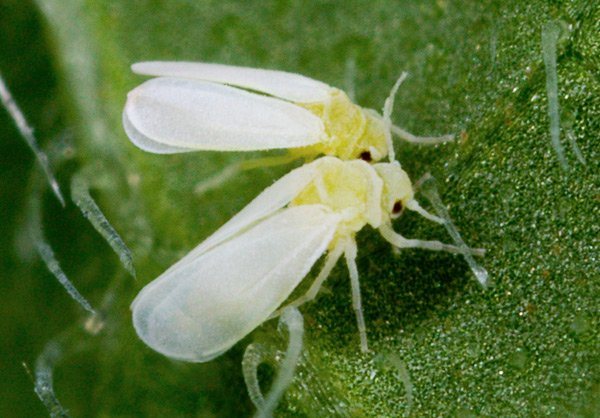


For some reason, adults of the whitefly are very partial to yellow, and the larvae to blue, this feature is used in the manufacture of homemade traps
Scare away butterflies by spraying plantings with infusion of yarrow, garlic arrows, foam of laundry or tar soap. Adhesive tape for catching flies and special pheromone traps help in the fight against whitefly. They are also made independently from pieces of cardboard, greased with petroleum jelly, honey, glue. Any fumigator plate can be burned in the greenhouse from time to time. Inta-Vir, Talstar, Mospilan, Fitoverm are used to combat the pest.
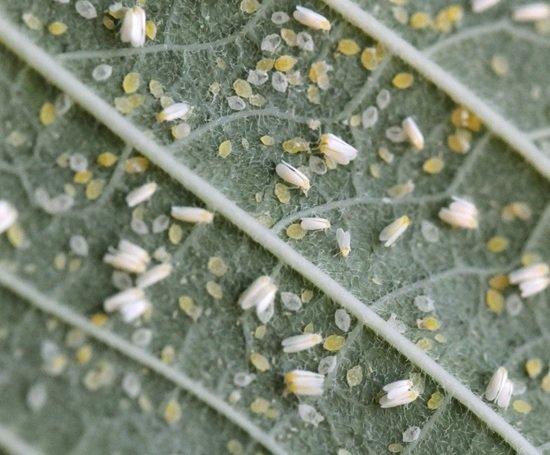


Most often, cabbage grown in a greenhouse suffers from whitefly, for open ground it is a rather rare pest
Gardener Tips
Additional recommendations are useful for both beginners and experienced vegetable growers. A few simple tips will help prevent cabbage diseases and their unwanted consequences.
Recommendations of experienced gardeners:
- Before planting seedlings, wood ash should be added to the soil.
- Lime must be added to the contaminated soil around the plants.
- You should not fertilize cabbage with organic matter during the active growing season.
- For a good harvest, disease-resistant hybrid varieties should be chosen.
- On the site, you need to regularly remove weeds.
- It is necessary to protect cabbage from slugs and snails, as well as harmful insects that spread infection.
- Potassium nitrate is the best fertilizer.
- You need to water the cabbage with settled water, preferably not cold.
- Diseased plants removed from the soil cannot be used to make compost or humus.
Any antifungal and antibacterial agents must be used in strict accordance with the instructions. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the varietal characteristics of cabbage and the climatic specifics of the region.
How to prevent cabbage infestation and pest attacks
Preventing a problem is much easier than dealing with the consequences later. Properly cared for cabbage is much less likely to suffer from diseases and pests.
The garden bed must be dug deeply in the fall. This helps to kill eggs and larvae of pests. For the same purpose, it is cleared of weeds and other plant debris. In the spring, fresh manure is prohibited. Many pests hibernate in it. During the summer, the bed is regularly weeded and loosened.
You should always remember about crop rotation. Ideally, the cabbage is moved to a new location every year. If there is no such possibility - at least once every 2-3 years. Good predecessors for her are beets, herbs, any Solanaceae. Unwanted - other cultures from the Cruciferous family.
Seeds and seedlings are planted in a garden bed, maintaining the recommended distance between plants. With "crowding" in the garden, especially if cabbage is cultivated in a greenhouse, diseases and pests spread much faster.
For seeds, pre-planting preparation is carried out by heating them in hot water or pickling in a solution of a fungicide of biological origin or potassium permanganate. Seedlings should not be poured, otherwise you can lose the crop even before the cabbage is planted in the ground. You should not hesitate in planting cabbage in the ground - such plants have much worse immunity.
For long-term storage, only those heads of cabbage are selected that do not have the slightest suspicious traces and mechanical damage. They are provided with optimal or close to them conditions. They are laid out on the shelves so that they do not touch each other.Slices must be processed; in the process of harvesting, they use only sharply sharpened and disinfected tools. Cabbage in the basement or cellar is regularly examined, infected heads of cabbage are immediately removed.
Do not feel sorry for the plants if you did not notice the development of the disease on time. When the process has gone far, the only thing that remains is to pull them out and burn them, stopping the spread of the infection. To be on the safe side, the place in the garden bed is disinfected.
Jaundice
Fusarium wilting, or jaundice. This disease affects both seedlings and cauliflower seedlings planted in open ground. The fungus, the causative agent of the disease, penetrates into the vascular system of plants and spreads into the stem, preventing the movement of nutrients and moisture. The infection persists in the soil for many years and is especially dangerous when cabbage is grown for a long time in the same area.
On yellowed leaves, a small dark speck appears, a noticeably weak darkening of the veins is noticeable.
On the cross section of the stem and leaf stalks, even with a weak development of the disease, a light brown ring of blood vessels can be seen. Sick leaves fall off, the head becomes ugly.
Other problems arising when growing a crop
Often, the gardener himself is to blame for the fact that the cabbage does not feel very well. Unintentional mistakes in care can provoke a deterioration in the condition of the plant. As a rule, this is not culturally critical. You just need to "correct" in time and everything will return to normal.
- Thin, almost lanceolate leaves. Broccoli and cauliflower very small or none at all. The reason is a deficiency of molybdenum in the soil and / or an overly acidic substrate.
- Yellow spots between veins, gradually changing color to orange-red or burgundy. Caused by a lack of magnesium.
- Dry leaf edges curling inward. Provoked by a deficiency of manganese.
- Deformed young leaves, shrinking heads of cabbage, bitter aftertaste of cabbage. Due to the lack of boron.
- Blue leaves. Indicate a phosphorus deficiency. Perhaps the cabbage was planted in the soil that has not yet warmed up. This affects the ability of the roots to assimilate this macronutrient.
- The heads of cabbage are not tied at all or are very loose. Cabbage is planted in the wrong place (even partial shade does not suit it) or in an overly light soil that is not nutritious. Either the prolonged drought is "to blame" for this. Another possible reason is that cabbage seedlings of medium late and late ripening were planted in the last decade of May. That is, the heads of cabbage simply did not have time to form.
- Cracking heads of cabbage. Improper watering - first, the cabbage is not "watered" for a long time, then the soil is moistened very abundantly.
- Several small heads of cabbage are formed instead of one large one. Most likely, the cabbage fell under return frosts in spring, as a result, the apical growth point suffered. Similar damage can be caused by mechanical injury or "burns" with fertilizers in high concentration.
Cabbage is a horticultural crop that often suffers from diseases and pests. But any problem is easier to prevent than to deal with the consequences later, especially if the process has gone far enough. Simple preventive measures and competent planting care help to minimize the risk of infection, respectively, the gardener can count on a good harvest.
To eat or not to eat - that is the question
Eating infected Chinese cabbage leaves is not recommended. They will not bring benefit to the human digestive system. Those gardeners who feel sorry for the effort spent can wash cabbage from their garden well, cut out dark spots and then use it for food. The taste of the vegetable is not lost. It is not worth buying such a head of cabbage with black "marks".
Leaves with holes are also best avoided.It happens that the black dots of Alternaria in the center turn yellow-brown and fall out, forming holes. In this case, "lumbago" on the leaves of Peking cabbage may also indicate a disease.
Mosaic
Cabbage mosaic is one of the most serious viral diseases that can occur in this plant. Infection is facilitated by improper processing of bushes or infected crops that are nearby. Quite often, a mosaic appears after a pick of young seedlings. Also, the disease is transmitted by various insects, which include thrips, ticks, bugs and aphids.
There are several main signs of the manifestation of this disease:
- The leaves are deformed and covered with spots of different colors. They can be purple or even have a lilac whitish tint.
- The development of the bushes slows down several times due to metabolic problems. As a result, young shoots begin to dry out and die completely.
- The bushes are covered with brown markings, which gradually begin to rot.
Many people think about how to treat cabbage from diseases. Treating infected bushes will do nothing, as this disease cannot be cured. It is recommended to engage in prevention, which consists in the timely destruction of weeds in the beds and various harmful insects.
A viral disease, the first signs of which appear 4-5 weeks after planting seedlings in a permanent place. Optimal conditions for the development of mosaic are temperatures of 16-18 ° C. At higher temperatures, the symptoms of the disease are masked. With the onset of cold weather, the disease resumes. On the leaves of diseased plants, lightening of the veins is first observed, then a dark green border appears around them.
Infected mother plants and cruciferous weeds can also be a source of infection.
Mucous bacteriosis
The disease gets its name because infected bushes begin to become covered with mucus. This bacterial disease can appear on cabbage during storage or growing. Quite often, it appears in conditions of elevated ambient temperatures. The main reasons for the appearance of bacteriosis include:
- increased air humidity;
- overuse of nitrogen fertilizers;
- violation of crop rotation.
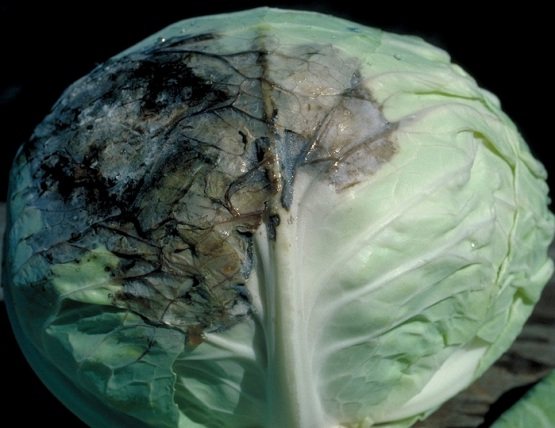

There are several options for the course of this disease. Slimy bacteriosis of cabbage can infect the outer leaves. They undergo deformation and acquire a not very pleasant smell. After a while, the disease spreads to the head of cabbage and the bush gradually dies. During infection of cabbage, the disease immediately spreads to the head of the plant.
In the second option, rotting begins with the stump. The bacterium enters it from the soil or is carried by harmful insects. Then the disease spreads to the inner leaves, which change their color and become softer.
There are different ways to prevent the disease:
- store heads of cabbage correctly;
- fight pests throughout the year;
- grow only those varieties that are resistant to mucous bacteriosis;
- disinfect planting material before sowing;
- the storage for cabbage is being processed.
Blackleg
Not everyone knows why plants have a black leg. There are several reasons for this cabbage disease. These include:
- Fungi. These pathogens most often enter the ground from cabbage plants that suffered from black leg a year ago.
- High humidity and acidity. In humid air, the disease develops much faster than under normal conditions.
- Incorrect fit. If cabbage seedlings were planted too densely and overfed with fertilizers with nitrogen, then the likelihood of the appearance of a black leg increases several times.
In terms of its manifestation, the disease resembles cabbage Alternaria.The main symptoms include the fact that the decay process begins on the leaves of cabbage and on its stems. Blackleg is very dangerous as it spreads quickly between plants.
It is recommended to figure out in advance how to deal with it in order to protect healthy seedlings. First you need to get rid of pathogens in the soil. For this, the soil with plants is treated with copper sulfate and poured over with heated water. You can also get rid of the black leg with the help of Fundazol or Planriz. If the treated plants do not recover over time, they will have to be removed from the garden and burned.
Black leg seedlings. Causative agents: Olpidium brassicae, Department of Chytridiomycot, Pythium debaryanum, Department of Oomycot, Rhizoctonia solani, Department of Basidiomycot.
Symptoms: Olpidium and Pythium attack plants early in development (from seed germination to the phase of two to three true leaves). With this disease of cabbage, the root part of the stem becomes watery, turns brown and rots. The plant lodges and dies. Adult seedlings are affected by the Rhizoctonia solani mushroom: the affected part of the stem darkens and dries up.
Sources of infection: cysts (Olpidium), oospores (Pythium) or sclerotia (Rhizoctonia) in the soil.
Keela
Many consider the kilu to be the main enemy of all varieties of cabbage. Most often, it occurs in the ground with a high level of humidity. This disease can appear after transplanting plant seedlings into open ground. In this case, the first symptoms begin to appear very slowly. First, the wilting of the leaves, which are located below, occurs. Later they are deformed, die off and the cabbage stops developing further.
The roots of the bushes also suffer from the keel. Over time, small growths appear on them, which gradually increase. Because of this, a malnutrition occurs and the plant completely dies. If you do not get rid of the dead bushes in a timely manner, the pathogens will enter the soil.
This cabbage disease affects bushes at any age, but most often it appears in young seedlings.
Every gardener should know how to deal with a keel. When the first symptoms appear, you should immediately get rid of all affected bushes. To do this, they should be dried in the sun and burned away from the garden. Healthy cabbage is watered with not too cold water and spud. It is also recommended to dig up the soil and place the beet tops in it. Work should be performed with separate pre-disinfected equipment.
To get rid of this disease, other measures are taken to combat it. Some gardeners carry out soil disinfection for this. The essence of this method is to plant crops on the site that destroy pathogens. To do this, you can plant garlic, onions, eggplants, peppers, tomatoes and spinach.
After the site is rehabilitated, it is recommended to check the soil for the presence of a disease. The plot is planted with early cabbage. If, during cultivation, growths do not appear on its roots, then we can assume that there is no keel on the site.
Downy mildew
Peronosporosis of cabbage actively develops at temperatures above 20 degrees Celsius. After planting seedlings in the garden, the disease slows down. However, this does not prevent the fungus from continuing to maintain its viability.
The first symptoms begin to appear with the onset of warm weather. Light leaves and leaf veins are covered with scab. Also, specks of a reddish hue appear on their surface. Over time, a gray coating and yellow or white spots appeared on them. Affected bushes begin to fade gradually. To learn more about the symptoms of downy mildew on cabbage, below is a photo of infected bushes.
There are no effective treatments for peronosporosis. The fight against him is to timely harvest the bushes and create the best growing conditions.
Effective prevention methods
Prevention of cabbage diseases includes a set of the following procedures:
- observance of crop rotation - do not plant cabbage on the same bed for 2 years in a row, and do not return it to its previous place earlier than after 3 years;
- planting varieties and hybrids that are resistant to certain diseases;
- timely removal of weeds;
- harvesting plant residues at the end of the season;
- protection of plantings from pests;
- disinfection of soil and seeds before sowing;
- preventive treatments in the early stages.
Advice. In order not to have to process ripening cabbage with pesticides, take care of protection in advance. At the stage of planting seedlings, add 50 g of ash to the holes - the fertilizer will protect the roots from microbes and accelerate plant growth.
Cabbage is a juicy vegetable. Its tissues contain a lot of water, and moisture, as you know, is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria and microbes. But, knowing the symptoms of diseases, you can successfully fight them and harvest good crops.
White-headed
Interested farmers try to learn everything about cabbage, about the features of the most common varieties, so that it is easier to navigate among the varieties of this amazing and healthy crop on the market. So, white cabbage has a high degree of cold resistance, it can withstand temperatures down to -3-4 degrees. To obtain a high-quality harvest, you should choose well-lit areas with fertile soil; heavy and loamy soils enriched with humus are also suitable. It is best to plant it in place of tomatoes, potatoes, beans, cucumbers.
Of the late varieties, the most popular are Stone Head, Amager, Kharkovskaya, which can be stored until spring, are suitable for fermentation. Of the early and middle varieties, June, Slava, Transfer, Golden hectare are celebrated, they are used fresh and in cooking.
Fusarium
Fusarium wilting of cabbage occurs due to fungi that are in the soil. Most often, this disease occurs in young seedlings of cauliflower or cabbage growing at very low temperatures.
It is very easy to notice the disease, as it manifests itself almost immediately. First, the cabbage leaves cover yellow spots, which eventually lead to the complete wilting of the leaves. Due to infection, new heads of cabbage do not set and the plant stops developing.
Fusarium cabbage is not amenable to treatment, so there are no effective methods of dealing with them. The only thing a person can do is to remove all infected bushes so that the infection does not spread further. You can also treat the area with copper sulfate for prevention.
Causes of vegetable infection
Crop development can be hampered by various factors, the main of which are unfavorable environmental conditions and soil quality. If we consider these global reasons in more detail, the list will be as follows:
- lack or excess of fertilizers;
- excessive amount of nitrogen in the soil;
- prolonged increase in air humidity (rain, morning dew);
- combination of low temperatures with high humidity;
- dry soil, insufficient watering;
- non-compliance with crop rotation;
- violation of the rules of agricultural technology and crop care.


Cabbage is often affected by various diseases.
The reason for the spoilage of the finished product is non-observance of the temperature and humidity conditions in the room where the crop is stored.