Common diseases of rhododendrons

Improper agricultural techniques for growing flowers leads to the development of pathogenic microorganisms. In alkaline soil, the plant is quickly depleted, and in wet (clay, sand) it begins to get wet, wither and rot. Moreover, in open sunny areas, the foliage of the culture is covered with burns. Incorrect composition and dosage of fertilizers, as well as sudden changes in temperature, provoke the appearance of debilitating diseases and pests of rhododendrons. Treatment and feeding in such cases should be strictly regulated. In addition, it is necessary to regularly carry out preventive measures in order to increase the plant's resistance to infections.
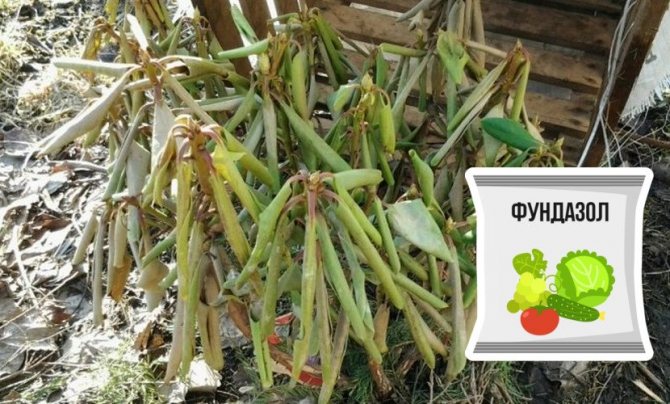
Tracheomycotic wilting or when leaves curl
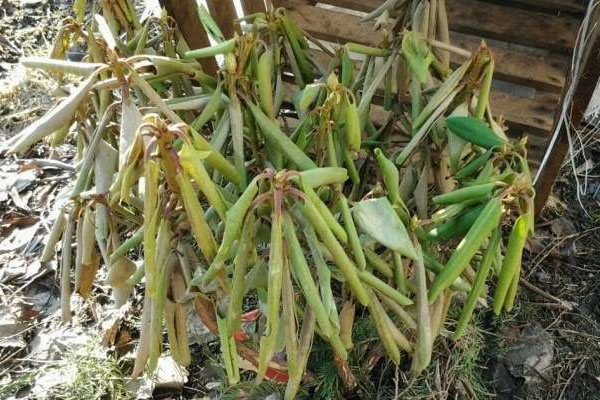


Fungal microorganisms infect the root system of the bush, and the underground part begins to rot at an accelerated rate. In this state, it is unable to deliver nutrients to the culture.
The first signs of this rhododendron disease are:
- white bloom on the stems;
- brown spots;
- fast drying of green mass;
- leaf fall (together with petioles);
- wilting of shoots.
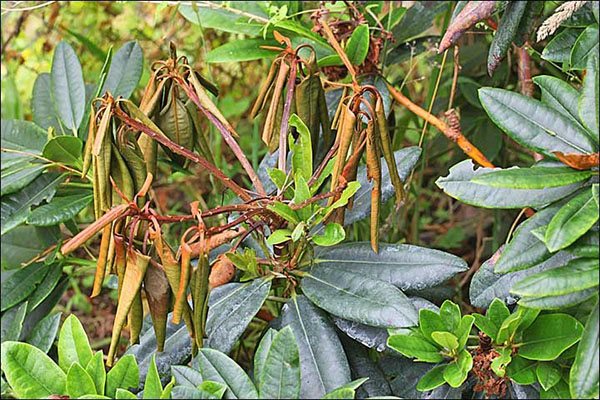


The rhizome is covered with a gray-white mycelium. The process of dying off of living tissues occurs quickly enough. The main reason why the leaves of rhododendrons curl is the blockage of blood vessels by fungal spores.
The infected parts of the bush are removed and disposed of. The remaining stems are treated with a Bordeaux mixture. Prevention - watering and spraying the plant with a solution of Fundazole (0.2%).
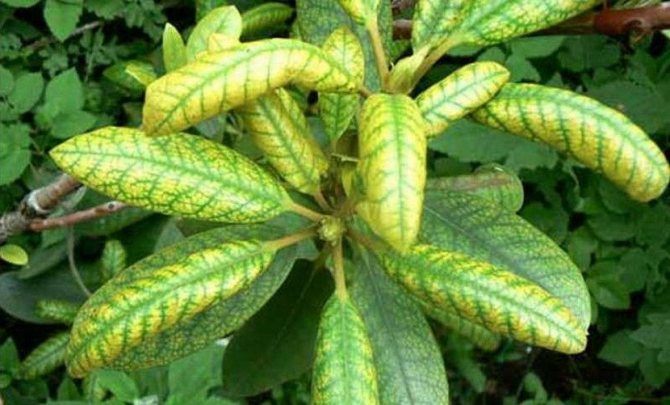
Yellow leaf mosaic


Alpine flower varieties are especially affected by this virus. Insects such as aphids and bedbugs carry the dangerous infection.
A photo of this rhododendron disease clearly demonstrates its manifestation:
- yellow-green tint of foliage;
- swollen, dark-colored calluses;
- thin deciduous plate.
In a short period of time, the bush turns into a terrible sight. If not disposed of, the disease will quickly spread to neighboring crops.
What if the leaves of rhododendrons turn yellow? It is worth knowing that such a bush cannot be treated. It is uprooted and burned. The flower bed is treated with Confidor or another strong insecticide.
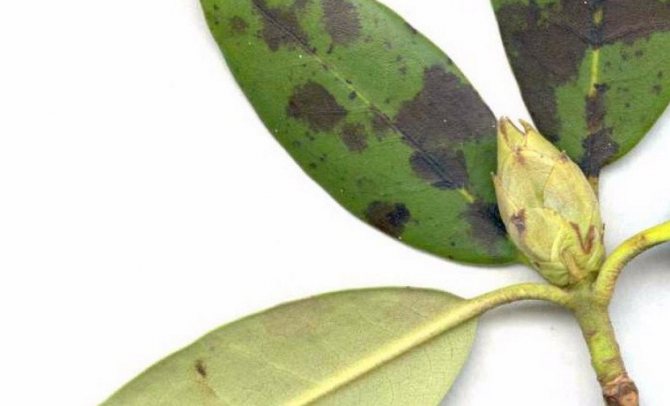
Spotting is not Variegata
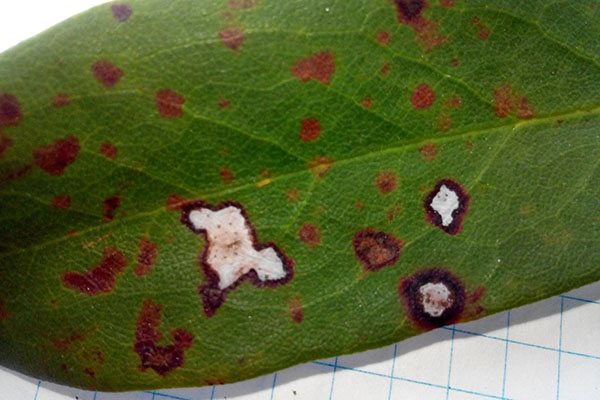

Sometimes the plant sheds its foliage prematurely. However, before that, it begins to turn yellow and becomes covered with brown spots of irregular shape. On the dead areas, massive spore colonies are formed in the form of gray pads.
There are several types of spotting:
- Pestalcium.
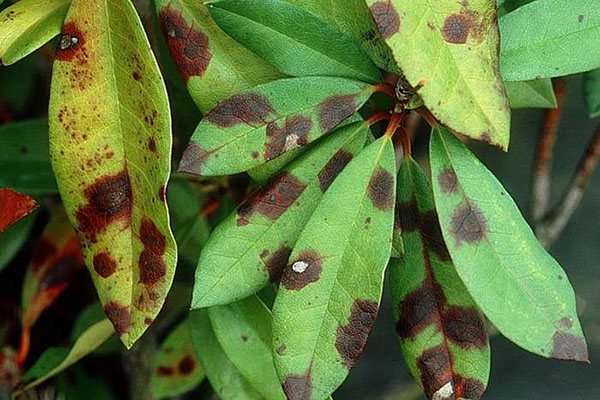


- Phylostictic.


- Anthracotic.
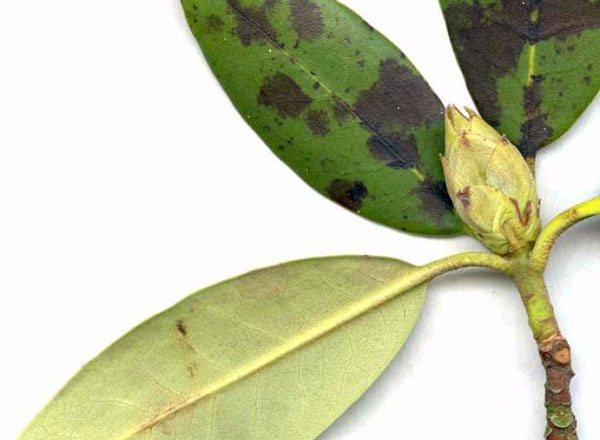


- Septoriasis.


Damaged parts of the flower must be cut off. The remaining greens are sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate, Camulos or Bordeaux liquid.
Most of the leaves are dry brown spots with a red border. As the virus progresses, black sporangia appear on the surface. Having familiarized yourself with the photo of rhododendron diseases and their treatment, it will be much easier to cope with a dangerous enemy.
In order not to harm the culture, all therapeutic measures are carried out at low air humidity. Otherwise, terrible burns will appear on the bush.
Rot in all its forms


The cause of the onset and development of fungal diseases of rhododendrons is the high moisture content of the soil.
As a result, brown spots or necrosis appear on:
- young shoots;
- leaves;
- shoots;
- buds;
- roots;
- flower petals.


With advanced forms of fungal infections, a fluffy coating of a smoky shade forms on the deciduous plates. Sometimes it acquires a filamentous structure, which resembles a web of a web.
The parts of the culture damaged by the fungus are completely destroyed. After that, they carefully monitor the condition of the bush.
The best way to combat rot is through prevention. For this, the plantings are sprayed and watered with a 0.2% solution of Fundazole or other copper-containing preparations. Activities are held every 2 weeks.
Wax disease is a collective responsibility
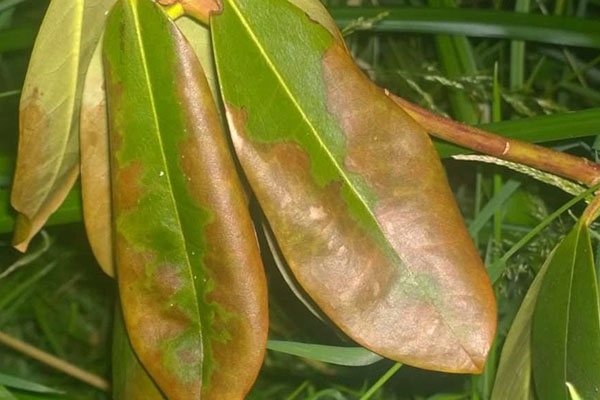


In some cases, the occurrence of infectious diseases can be triggered by several types of fungal spores at once.
The main symptoms of rhododendron wax disease are:
- deformation of foliage;
- thickening of deciduous plates;
- the appearance of yellowness;
- reddish brown spotting;
- the formation of white growths.
At the first signs of damage, the evergreen shrub is cut off. Then the crown is sprayed with a solution of the drug Cumulus. Gardeners recommend performing the procedure in the spring to improve the effect.
While these are just some of the rhododendron diseases and their treatments, it is also worth mentioning:
- late blight;
- rust;
- bacterial cancer;
- chlorosis;
- cercosprosis.


If the tips of the leaves begin to turn yellow, it means that the plant suffers from high acidity of the soil. The bush is sprayed with two types of sulfate: magnesium and iron. The drug is diluted in a ratio of 7 g / l.
According to many growers, rhododendron diseases are the result of improper care of the shrub. All he needs is planting in the right place and monitoring the condition of the plant.
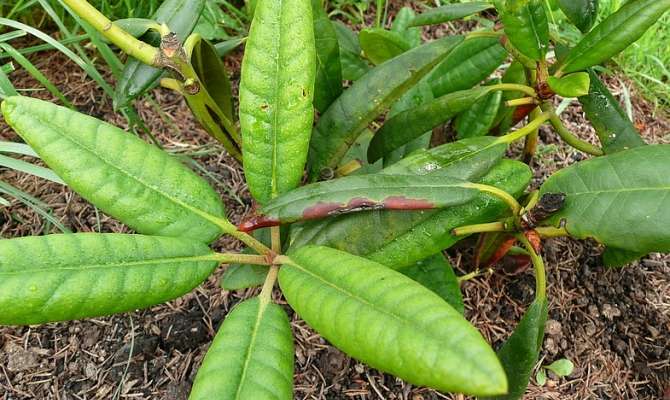
Why did the leaves of the lights rhododendrons turn red?
It's not about nitrogen, it's a lack of phosphorus, we spray it with potassium monophosphate - 5 g per 10 liters of water (preferably rainwater). This year is a very cold and rainy summer (my dacha is in the village of Vaskelovo, about 40 km from St. Petersburg), phosphorus is poorly absorbed by the roots in cold weather and is well washed out by rains. The first signs of a lack of phosphorus appeared in my rhododendrons in June (despite the fact that in early spring I used special prolonged-release fertilizers of a famous German brand, I decided not to use them anymore, they are not suitable for our climate, they are designed for full-fledged spring-summer autumn, in the spring I will use horn-hoof flour (organic nitrogen fertilizers) and liquid fertilizers with microelements (21 microelements) of our production and with a high content of sulfur and magnesium (what rhododendrons love, then 2 dressings with potassium-phosphorus buffer solution (8 g monopotassium phosphate (potassium monophosphate) + 8 g of potassium nitrate per 10 l of water) after flowering and in August) Some leaves turned red (this is normal when this happens in autumn with old leaves 3-4 years old, then they fall off), some turned yellow-red, everywhere on the Internet in topics on rhododendrons they say that this is a lack of nitrogen, along with this, black-purple spots appeared on some plants on the same plants red leaves (type in the search engine "lack of phosphorus in tomatoes photo", the leaves became like in the first photos as a result) in the topics on rhododendrons they write that this is an excess of nitrogen. I was at a dead end, I did not know what to do, there cannot be signs of a lack and an excess of nitrogen on one plant. A week later, the leaves of strawberries, raspberries, apple trees, clematis turned red, even the leaves of the plantain on the lawn turned red, bronze spots appeared on the leaves of Volzhanka, which shimmered in the sun, all this in June.Having shoveled a large amount of information about the signs of a shortage and overabundance of elements on the leaves of different plants, I realized that this is a phosphorus deficiency, in the topics about rhododendrons there is very little information about phosphorus deficiency, and she wanders from one site to another. In such emergency cases, only spraying with potassium monophosphate saves, this is the fastest-acting method, sprayed 2 times with an interval of 2 weeks. It is very difficult to overfeed plants with phosphorus, even if there is a lot of it in the soil, the plants absorb as much as they need, therefore, superphosphate can be used in routine feeding, it is not washed out of the soil and lasts for a long time, some add it every three years. But in acidic soils, superphosphate can turn into compounds that are difficult to assimilate. Potassium monophosphate is well absorbed by all parts of the plants, but it is quickly washed out of the soil, it will not work for future use, 2-3 top dressings are needed per season, in addition, it is desirable to sprinkle after each heavy downpour or prolonged rain with a solution of 2 g of potassium monophosphate per 10 liters of water. And yes, you cannot combine potassium monophosphate with magnesium fertilizers. The potassium-phosphorus buffer solution, which I wrote about above, is suitable only for lovers of acidic soil, it keeps the acidity of the soil within the pH range of 2-7.
Help for the yellowed rhododendron - video
Rhododendrons belong to ornamental plants, therefore they are also attacked by pests and various diseases. Evergreens planted in the sun are more likely to be attacked by ailments than those in partial shade. Correct agricultural technology increases the resistance of the plant, but the threat still remains. In the article, we will consider why the leaves of a rhododendron suddenly dry, the buds darken or the buds die off, as well as the main diseases that these ornamental shrubs are susceptible to.
What can a room rhododendron suffer from?
Plant disease is a negative condition caused by viruses, bacteria, fungi, or improper care. Azaleas react to the lack and excess of nutrients, the degree of soil moisture. Typical symptoms:
- drying of leaves and buds;
- discoloration, the appearance of spots;
- falling leaves and flowers;
- decay of roots;
- growth retardation.
Pests are insects that have settled on a plant. Phytophages feed on azalea juice, causing wilting, yellowing of leaves and deformation of buds. One of the dangers is the spread of viruses and fungal infections by pests.
Tracheomycotic wilting
The first symptom is the beginning of the process of decay of the root system. Mushrooms block the path of nutrients, as a result of which the vascular system of the plant suffers.
Rhododendron turns brown and dries up, petioled leaves fall off, and a gray-white mycelium appears on the bark. The root gradually dies. The remains of the plant continue to store the infection.
If the bush is sick, it is necessary to cut off the infected areas and burn them without delay. Treat the entire plant with Bordeaux liquid. Prevention is carried out by spraying the bushes and watering their root zone with a 0.2% solution of the drug "Fundazol".
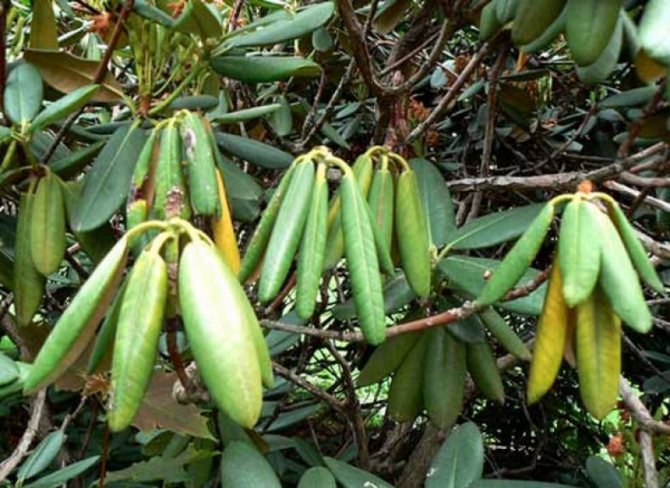


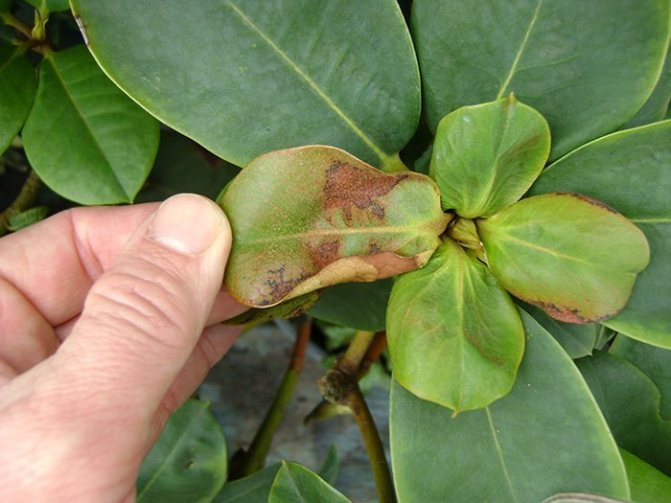
Azalea leaves have dark brown spots, treatment for gleosporia
If dark brown and / or gray spots, as well as traces of blackening, appear on the leaves of the azalea, we can safely diagnose gleosporia. The cause of this ailment may be damage to black thrips, rhododendron tick, fusarium disease.
In the case of black thrips, the plant is reanimated with the help of the Karbofos emulsion, if a rhododendron mite appears on the azalea, the Fundazol solution will help. With fusarium will help the drug "Diazinon".
Important! Azalea reacts negatively to dry air, so keeping the plant close to heating devices is strictly prohibited.
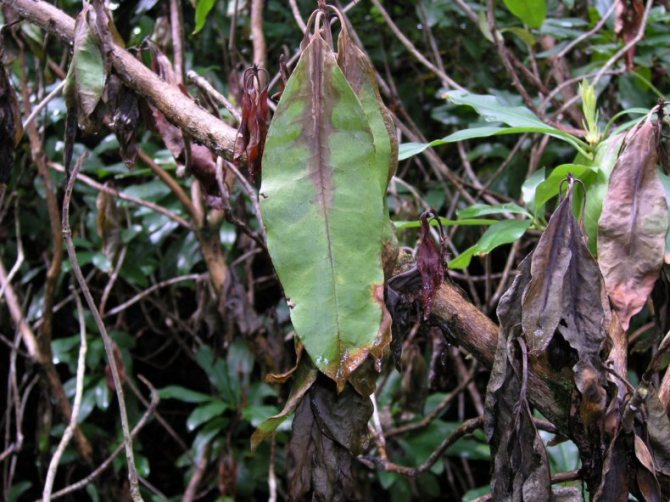
Late blight rot
Late blight rot occurs due to the blockage of the rhododendron or poorly conducted root drainage. In addition, you can bring late blight rot to the garden plot along with the unhealthy shrub purchased from the nursery. The disease begins with wilting of foliage without the possibility of its restoration.
The root turns brown and rots. The branches begin to turn yellow, and then the entire rhododendron. The root collar and base of the stems are covered with brown spots with a purple tint, on which dark gray spores of the fungus develop. The bush withers and dries, but its remains and the soil around it keep the infection.
At the initial stage of the lesion of rhododendron, it is necessary to begin regular treatment with Bordeaux solution, "Quadris" or "Fundazol" 0.2%. Heavier plants should be burned with roots and preventive measures should be taken on healthy bushes.


Common indoor flower diseases
- Desiccation - arises for many reasons, in particular, due to incorrect temperature conditions, incorrectly selected substrate, lack of timely fertilizing and insufficient lighting, direct sunlight on the plant or various diseases of the root system. When dry, it is worth taking a closer look at the plant to determine its causes.
Attention! If, when examining the azalea, you did not see living buds, then the plant will no longer be able to reanimate. - Yellowing of the leaves. There may also be several reasons:
- The development of chlorosis. In this case, the water for irrigation must be acidified (with citric acid or other acids).
- Damage by the scabbard. To get rid of it, you need to treat the leaves with soapy water or chemicals.
- Blackening of the leaves can occur as a result of being hit by black thrips. The pest lives on the inside of the leaf plate, where black or grayish spots are formed. In such cases, the azalea must be treated with chemicals.
- Shedding. If the leaves fall off in winter, then in this case we are talking about the dormant period of the plant after flowering. If the leaves fall off despite the fact that the plant has not yet bloomed, then this indicates improper care of the flower.
- Brown and brown spots on the leaves. The reason is inappropriate conditions of detention.
- Brown spots on the leaves - the reason is waterlogging of the soil.
Why azalea leaves grow very light and undergo other changes is described here.Azalea is very demanding on temperature and many problems in growing arise due to the high temperatures of its content. The optimum temperature for an azalea is 17 degrees Celsius.
- Buds fall due to dry soil, high temperature or dry air.
- If moss has formed in the pot - this indicates excessive moisture, which is a favorable environment for different types of rot.
How to determine the cause of rhododendron disease?
If you notice a deterioration in the condition of a houseplant, then you should carefully consider it. If pests are found, it is, of course, worth fighting with them. In other cases, it is necessary to revise agrotechnical care and study the symptoms of the disease. Then it will be clear what the plant is infected with.
What is the danger for the plant?
Any disease threatens azaleas with gradual death, if treatment is not started on time. The sooner you start to reanimate the plant, the more chances you have to save it.
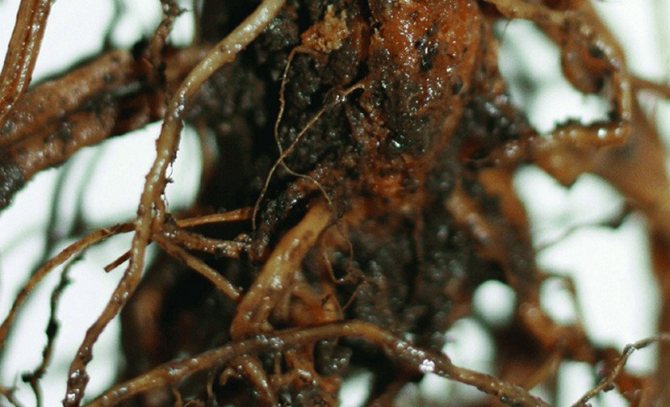
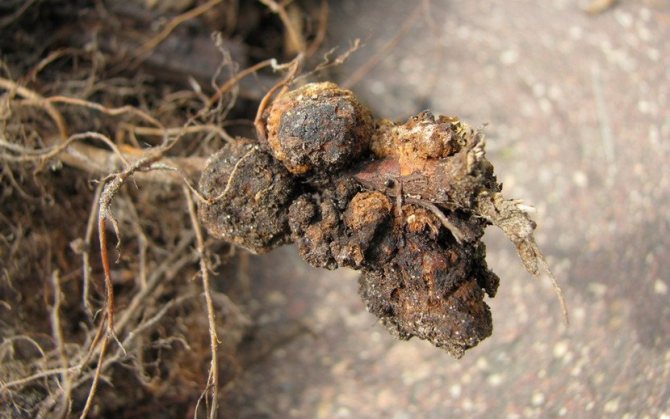
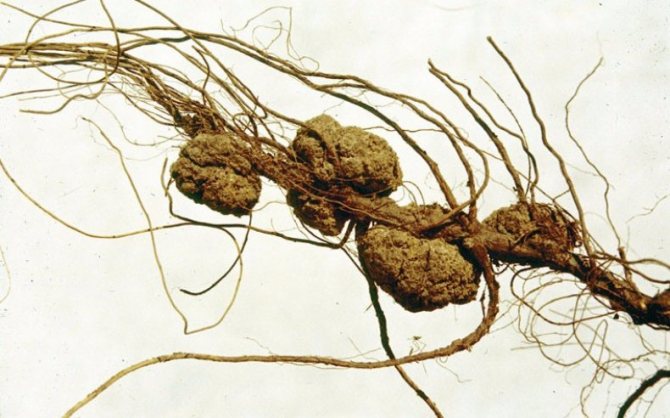
Bacterial cancer
Bacterial cancer is manifested by the formation of rounded growths of significant size on the roots and root collar. These formations become darker and harder over time.
The bush slows down in growth and loses its flowering power. Further, the growths, together with the root collar, begin to rot, the plant dies, but its remnants continue to keep the infection.
As with late blight rot, bushes showing initial symptoms should be regularly treated with Bordeaux liquid or another similar drug.If the damage is severe, burn the plant along with the root system.


Gray and other rot
Rhododendron can affect a variety of rot:
- gray;
- seedlings and young seedlings;
- buds;
- root;
- dry white;
- dying off of shoots.
Gray rot appears on the foliage, stems, buds and petals of the plant in the form of blurry brown spots without a border.
The surface coating dries gradually and begins to crack. With high humidity, the parts of the bush that have suffered from necrosis are covered with a fluffy smoky gray spore bloom. After a while, the drying mycelium is filled with brown, rounded sclerotia.
The only way to deal with rot is by cutting off the affected areas of the rhododendron. For preventive treatment, spray the plant with a 0.2% solution of the drug "Fundazol", and also pour it over the root zone.
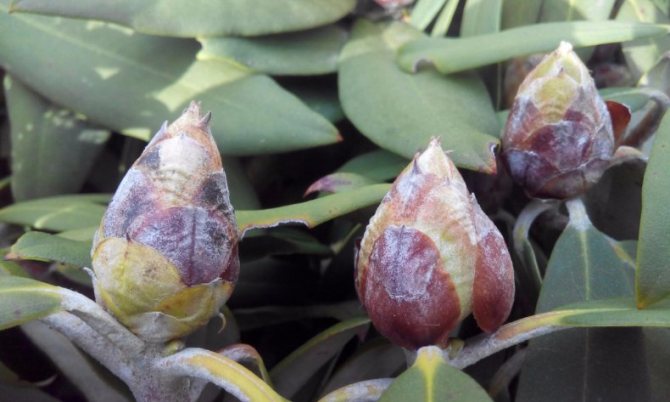


Rot of seedlings and young seedlings for a rhododendron, it begins with wilting and ends with death. On its leaves, white fungal spores or brown mold form, and the surface is covered with threads resembling cobwebs.
Sprinkle seedlings that have begun to die with chopped charcoal or powder of the drug "Fundazol". In addition, for the purpose of prophylaxis, you can treat with a 0.2% solution of the drug "Fundazol".
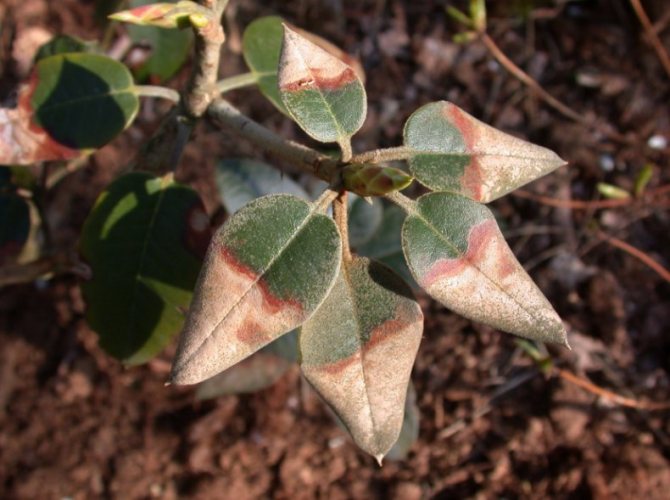


Rot of buds. The buds turn brown and die off, after which the mycelium grows into the branches. You can limit the development of the disease by removing dark buds and dry shoots. While the plant is living the growing season, spray it with preparations containing copper every two weeks.


Dying off of shoots threatens shrubs growing in the shade. The buds at the top of the bush will not bloom. Instead, their color will turn brown and the process of withering away will begin. Following them, the leaves will begin to curl up, acquire a brown color and dry. If severely damaged, the plant will die. The disease can also begin with the drilling of leaves on some shoots. Then they will begin to dry, after which the entire shoot will die off.
You can cope with the death of shoots by burning affected foliage and shoots. As soon as the rhododendron has faded, it should be treated regularly (every two weeks) with copper-based preparations.


Root rot affects roots and stems at the base. But first, the foliage withers and dries for no reason. Further, the buds acquire a brown color and die off. Just before the death of the rhododendron, the root system becomes brown and rotten.
To cope with the disease, it is necessary to burn the affected areas of the plant or completely the entire diseased bush. It is possible to protect the rhododendron from root rot. Maintain the acidity of the soil at the level that your particular variety needs, and follow the rules for watering.
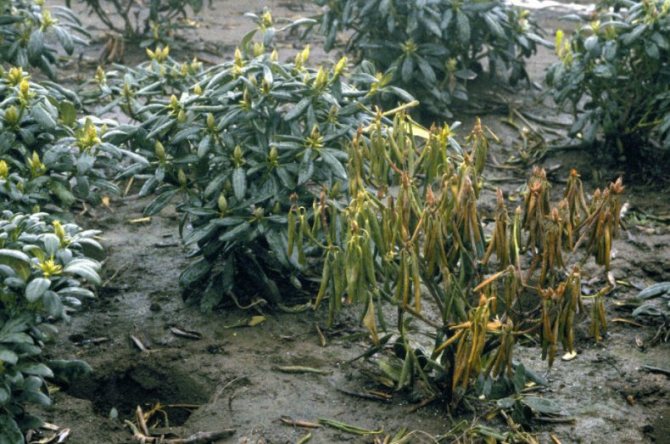


Dry white rot twists around the root collar of the plant and looks like a gray-white ring. The defeat is caused by a well-known mushroom - a real honey fungus, it is his mycelium that grows in weakened rhododendrons. As a result, the bush dies. Strongly growing rhododendrons do not suffer from this disease.
The affected plant must be dug up and burned, and the bushes near it must be transplanted.


Insects - pests of azaleas
The struggle for existence concerns all living beings without exception, regardless of their beauty and charm, size, level of organization and environment. This rule also applies to indoor, seemingly protected, plants. There is a group of the smallest animals that can sleep up the vigilance of flower growers and use the azalea as a source of food, causing damage to it, or even irreparable harm. Each of the parasites has its own handwriting and the competent owner of the rhododendron will be able to recognize the villain from the very first strokes.
If on the lower part of the leaf, more often along the perimeter, tiny moving light dots are visible, it can be assumed that the flower is attacking a spider mite. After a short time, the leaves will acquire a light marble color, they are densely entwined with thin threads of cobwebs. Parasites are hiding under this protective mesh. When the sun is low, they get out of an ambush, pierce the cell membranes and suck out the cell sap. Leaves, deprived of vitality, first lose their elasticity, and then completely fall off. Infection is facilitated by dry air, high temperatures and a thick layer of dust on the leaves.
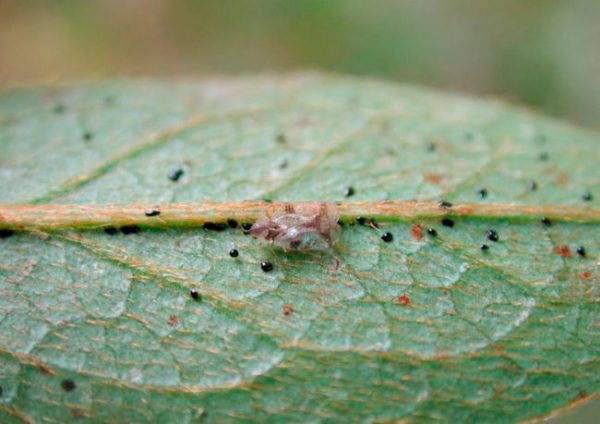


A particular danger for azaleas is a relative of the described pest - strawberry mite... He loves to feast on flowers and young shoots. Thanks to his efforts, many small, practically unviable buds are laid, the flowers, if they are formed, are ugly. If the ticks have settled belatedly on a blooming azalea, they will show their cunning, changing the inflorescences themselves beyond recognition: the light ones turn brown, the dark-colored ones discolor. Both those and others dry up.
Another lover to live off rhododendrons - mealybug... Selectivity does not differ: it affects all the succulent parts of the plant - shoots, flowers, leaves. They lose symmetry, dry, fall off. Insects hide in the axils of leaves, flower scales, cover them with cobweb, cotton-like secretions. And they themselves look like quickly moving powdered lumps. The damaged organs stop growing and blooming. The plant weakens, exposing itself to new misfortunes, in particular, sooty fungi.
Azalea moth - a representative of flying pests. It feeds on the thickness of the leaves, they begin to crumble. The matured larvae crawl onto healthy leaves, transform them into a cozy tube, and pupate in it. Leaflets do not tolerate such abuse and fall off.


The furrowed weevil is perhaps the largest eater of rhododendrons. The beetle is atrocious at night. He is able to destroy not only delicate leaves, shoots, flowers, but even bark. The larvae resemble furrows, they live in the ground, feeding on the roots. The plant withers, and since adults can fly, they hide well during the day, it is not always possible to notice their presence and it is difficult to establish the cause of the death of the plant. One of the most common pests of azaleas is the rhododendron bug. It attacks the underside of the leaves, laying eggs on it, and leaves discolored spots on the top.
Long black, as if varnished, very mobile insects, called thrips - avid enemies of azaleas. Their yellow larvae readily group with adult forms. The consequence of their insatiability is the perforated leaves. In this case, the hole is noticeable by the inhomogeneity of color: the top is lighter, and the bottom of the hole is blackish. At first, the leaves take on a silvery gray color, then turn yellow and fall off. The plant completely loses its attractiveness.
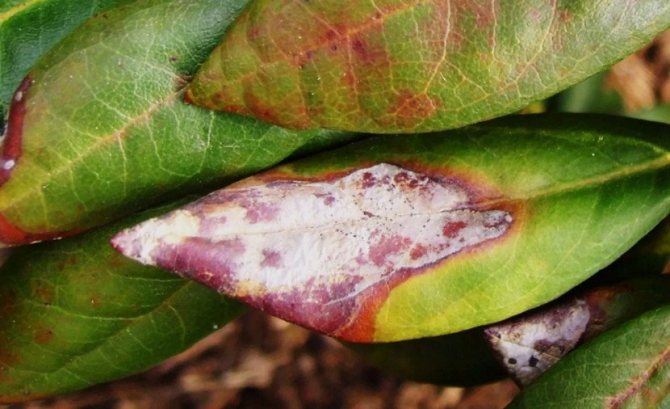
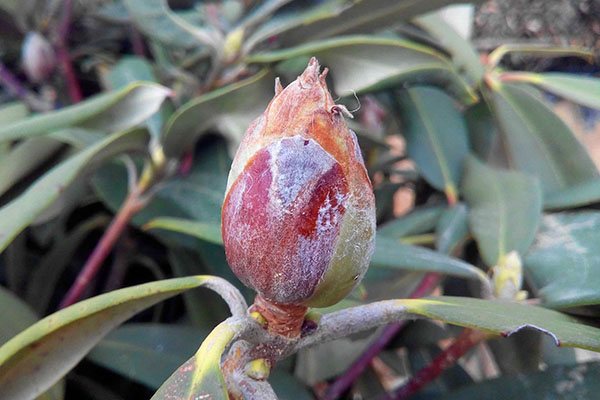
Wax disease
Several types of mushrooms can provoke wax disease, which:
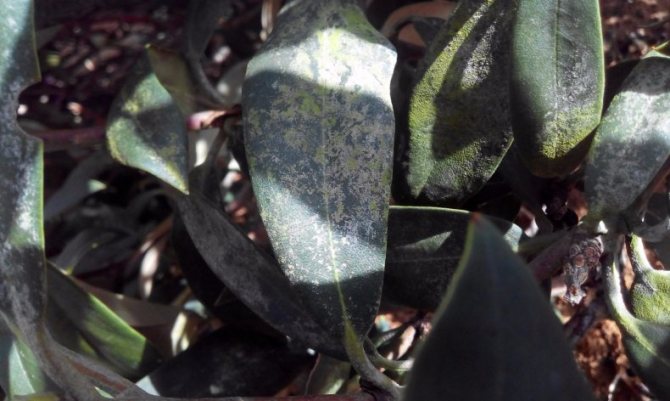


- They cause slight deformation with thickening of the leaves. They are covered with large spots of red or red-brown color, round or elongated. In the area of necrosis, a waxy coating of spores appears. As a result, the stains dry and crack.
- Form white cushion-like growths on the young foliage of an evergreen bush.
- Cover the leaves with round spots. On the back of them, you can observe the development of white spores.
- Change the color of the foliage to yellow-brown. A mealy bloom appears on the back of the leaf, after which the process of dying off begins.
- Leaves and shoots are affected. Huge pale green leaves of abnormal thickness begin to grow on the rhododendron. They are covered with a white coating. The sheet begins to wrinkle, mold and dry out.
Prevention of azalea diseases
Often the causes of azalea disease are a complex of disorders in care. It is important to observe the temperature regime, timely watering, spraying, and also to feed the azalea with organic fertilizers. For prophylaxis, treatment with copper chloride fungicide can be carried out. Fundazole is also used, since it does not have phytotoxicity.
Hello readers of my blog. Imagine, my beloved Azalea, which for a long time delighted me with its magnificent color, fell ill. It is my fault. I had to leave for a while, and the household looked after the flowers and, apparently, it was wrong. I studied the Internet and realized that such a problem with a flower is not only mine, which means there is a need to find out what Azalea's diseases are, their treatment with a photo will be posted on the pages of my resource.
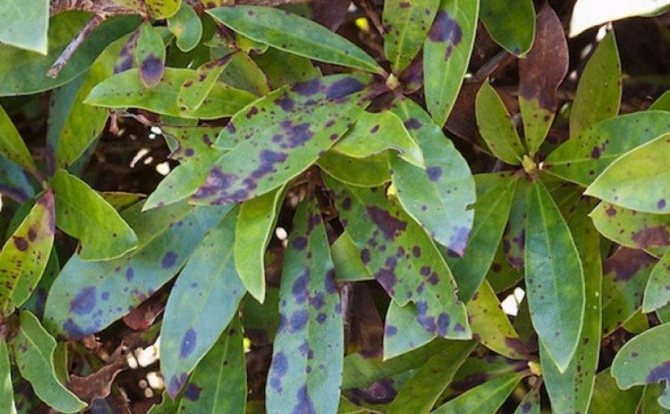
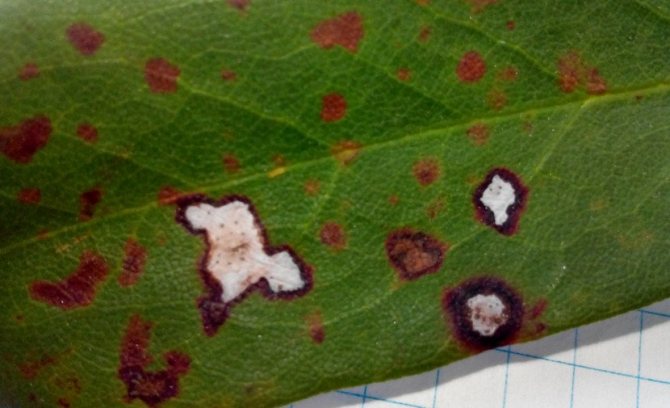
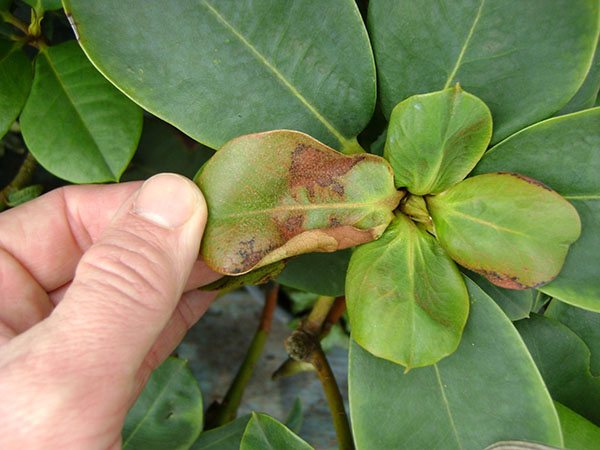
Different spots
Pestalocium spotting affects foliage and stems. Irregular brownish spots appear on them. They are framed by a thin brown border. The spots on the leaves are smaller than on the stems. Gray pads with spores appear on top of the spots.
Treatment of anthractosis spotting is based on cutting off lesions and spraying with Bordeaux liquid.
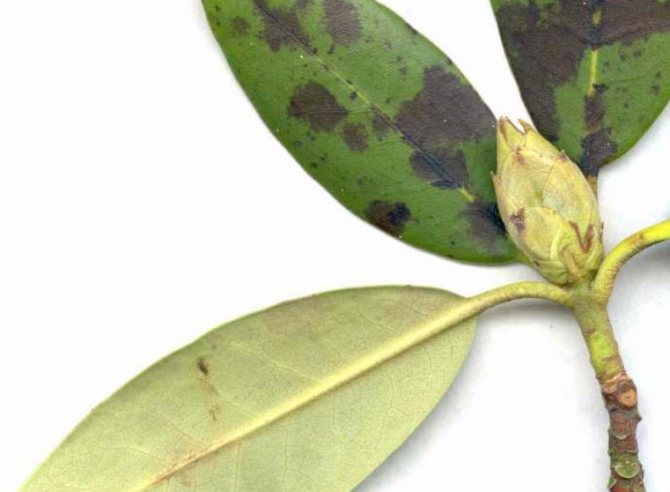


Septoria spot affects the foliage of rhododendron. It is covered with rounded red spots. After a certain period of time, black dotted fruits of the fungus appear on the spots. After this, the foliage turns yellow and dries.
The disease of rhododendron, which is shown in the photo, is characterized by the formation of black fruiting bodies of the fungus on the surface of the spots, therefore, its treatment is carried out by cutting off the affected areas and treating the shrub with Bordeaux solution or Camulus.


The framing of the spot can be brown, depending on the type of pathogen. Over time, the lesion brightens, cracks and crumbles. In this case, it is necessary to cut off the affected parts and treat the bush with Bordeaux liquid or Camulus.


Pest control measures
To destroy harmful insects that suppress the azalea with their vital activity, it is necessary to use the appropriate drugs:
- Decis, Fury against the rhododendron bug.
- Actellic shows its effectiveness against mealybugs, ticks.
- Bazudin, Aktar is recommended for use against a weevil, whitefly.
- Diazinon is effective against crunchy.
- Mesurol, special traps help to get rid of slugs.
- Karbofos can fight aphids well at home, as well as thrips.
- Spraying with sulfur allows you to destroy the moth on the bush.
- Nicotine sulfate has proven to be excellent in the fight against flies.


Decis


Actellik


Aktara


Bazudin
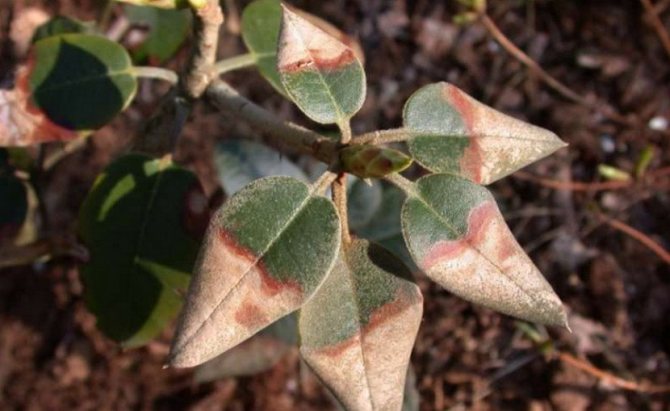
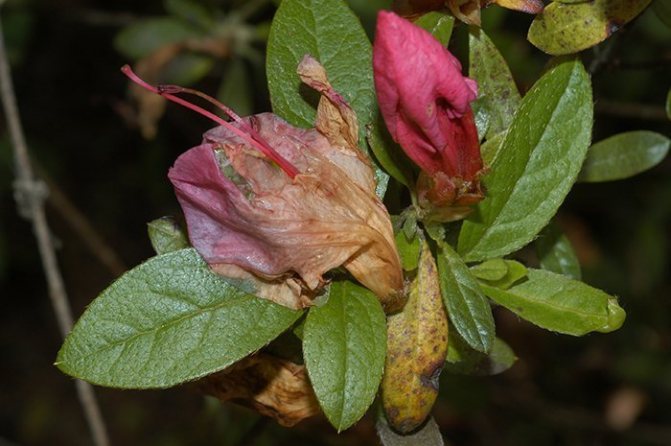
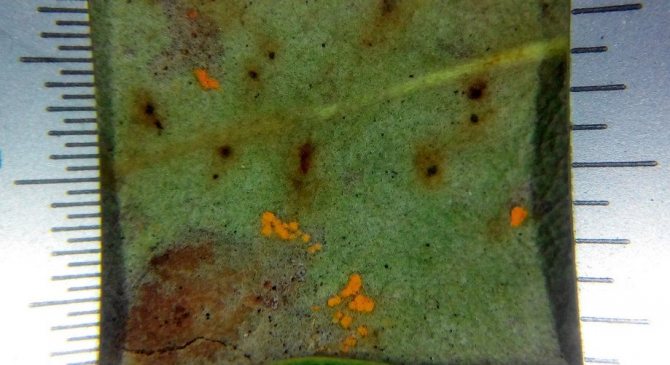
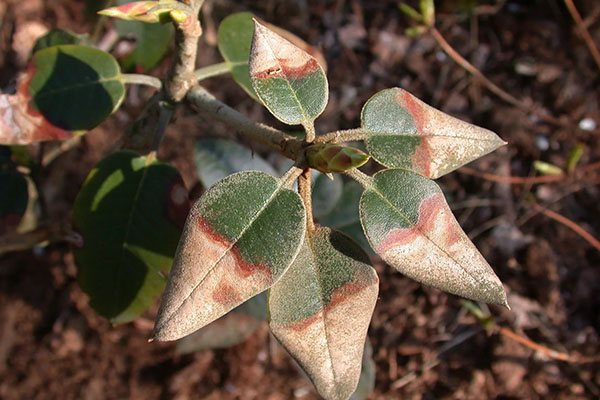
Rust
Rhododendron rust is sick in the autumn period. On the back of the foliage, dusty swellings of red, yellow or brown appear. The plant starts shedding leaves too early. In spring, pads with dark red spores can be seen on the leaves.
Rhododendron disease from the photo appears only on foliage, so the first step in its treatment is to collect and burn the leaves. Next, they are treated with drugs that contain copper. In the initial stages of the disease, the bush is sprayed with Bordeaux solution.


Fungal lesions and infections
Excessive watering, lack of drainage, disturbed temperature conditions provoke fungal infections. Fungus infestation often occurs through the soil. If you have symptoms of fungal infections, be sure to isolate the azalea from other indoor plants. It is best to disinfect the windowsill and plant pots.
Alternaria
A characteristic sign of azalea alternaria is the appearance of dark red spots of various sizes and shapes. To combat this type of defeat, a solution of Bordeaux liquid is used as a fungicide.
Botrytis, gray mold or mildew
Gray rot caused by fungi of the genus Botrytis develops on the leaves, stems and buds of an azalea. Vague brownish-brown spots are a symptom of the disease. Damaged plant tissues dry out in a short time. Poor air circulation in the room may be the cause. As a control measure, a soap solution is used and treated with insecticides.
Root rot
Late blight spreads to the stem and leaves of the azalea, which contributes to the complete decay of the plant. Signs: kidney death and leaf rolling. High humidity and high temperatures may be the cause. Bordeaux liquid and Fitoverm are used as a control measure at the initial stages.
Anthracnose or rust
The disease is more common in tropical climates, since anthracnose develops at temperatures above 23 ° C. Red, brown or yellow swellings are characteristic. The leaves of the affected plant fall off. For treatment, spraying with preparations containing copper is recommended. For example, Bordeaux liquid.
Cercospora
In cercosporosis, angular brown spots with a dark red rim can be seen on the underside of the leaves. A gray coating forms on the top of the leaf plate. The leaves of the lower tiers are more affected. Treatment consists in the alternate use of Ditan M-45 and Fundazol.
Powdery mildew
The main reasons for the appearance of this azalea disease are poorly circulating moist air and sudden changes in temperature. A white or reddish powdery coating forms on the affected parts. Infection begins in the lower tiers of leaves and gradually spreads to the entire plant. For treatment, you can use a soda solution, as well as fungicides (dosage according to the instructions).
Sooty mushroom
It mainly affects weakened and young plants. Often a sooty mushroom settles on the sticky secretion of azalea pests - whitefly, aphids. Colonies of sooty fungus contribute to the death of the affected parts of the azalea. The leaves are covered with a dark gray bloom. For prophylaxis, regular ventilation is necessary, for treatment - a soap solution and treatment with fungicides.
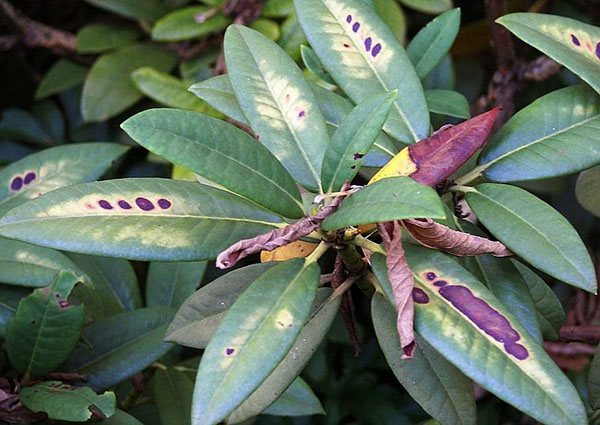
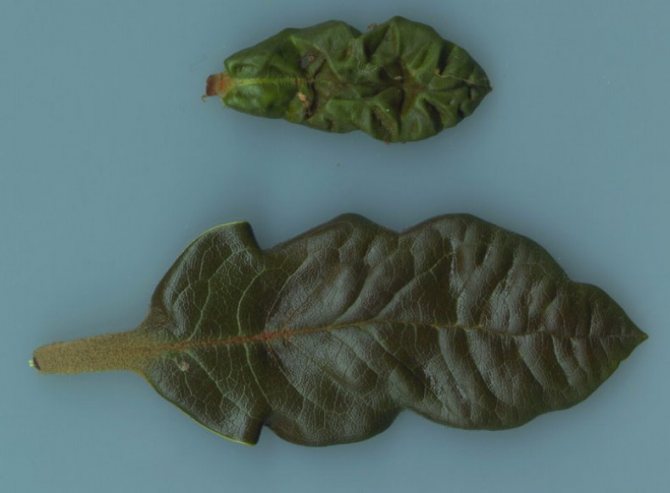
Mosaic
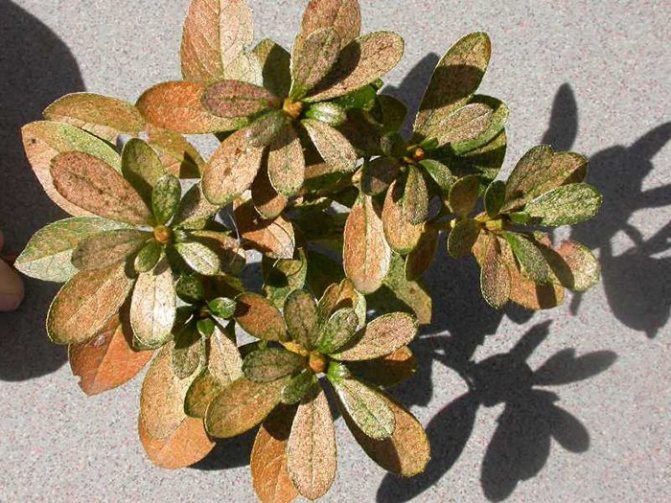
Consider the danger of rhododendron mosaic disease and how to treat it. The mosaic virus very disfigures the leaves of the bush. They become rough and calloused. The color of the leaf turns yellow-green, and the calluses remain green.
To cope with the disease, cut off the branches and leaves of the affected bush. If the plant is too damaged by the virus, remove it.


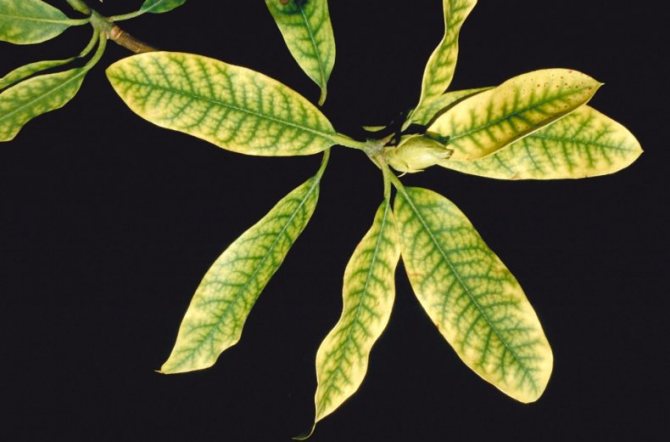
Chlorosis
Chlorosis is diagnosed by yellow spots along the edges of the leaf. Rhododendron gets sick due to the increased acidity of the soil or a lack of nutrients and trace elements in it.
You can cope with the problem by spraying the shrub with magnesium sulfate and ferrous sulfate. The preparations are diluted in water. The dosage is 7 g / l.


Each of the rhododendron species is prone to a particular disease. Many diseases have a number of similar symptoms and only a couple of differences. Timely, correct treatment can preserve the affected shrub and protect healthy rhododendrons from infection. To prolong the life of the bush, pay attention to any changes in it.


Rhododendrons have been popular with gardeners around the world for many years. Amazing flowering, delicate greenery make you fall in love with these plants at first sight. But unfortunately, rhododendrons, like any other crops, are susceptible to various diseases and pests. That is why beginners need to study rhododendron diseases and their treatment methods with a visual photo. This will allow you to determine the nature of the trouble and select the appropriate drugs.
The reasons
If the soil for rhododendrons is deprived of any nutrients, the leaves of the plant become discolored. Potassium deficiency signals brown spots around the edges of the leaves and yellowing of fabrics. Brown or reddish spots indicate a small amount of boron in the soil. Iron deficiency manifests itself yellowing of tissues between the veins... When the soil of rhododendrons is overloaded with nutrients, the leaves appear chlorosiscaused primarily by an excess of lime in the soil. The leaf blades become yellowish, white or light green, the veins remain dark green. Treat chlorosis by spraying rhododendron with iron chelate. Use a multicomponent fertilizer to strengthen your plants. Supporters of homemade methods are advised to add chopped tree bark, natural fertilizers or untreated peat to the base.
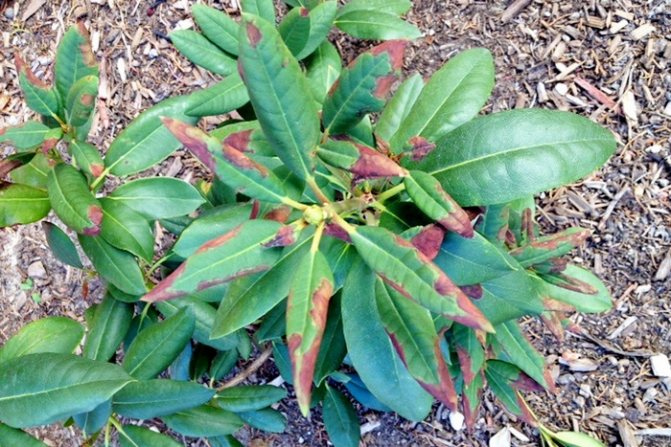


Factors that lead to disease
Professionals unanimously argue that the problems arising in the process of growing a flowering shrub are associated with a violation of agricultural technology.


Adverse factors are:
- Low acidity of the soil, which leads to the depletion of the plant.
- Increased soil moisture and water stagnation at the roots.
- Planting a bush in an area where sunlight burns delicate foliage.
- The use of inappropriate nutritional formulations and the violation of fertilizer dosage.
- Dryness of the soil, particularly in winter.
- Sudden changes in temperature, refusal to shelter roots in winter.
- Poor or depleted soil.
- Illiterately selected soil composition on which the plant will simply get wet.


In order to grow a healthy rhododendron, and not to subsequently study diseases and pests from the photo, you should strictly adhere to the rules of agricultural technology of the variety. Following simple tips, you can enjoy the abundant flowering of rhododendrons for many years in a row.
General requirements for the care of an azalea
An exotic plant lives well and develops with frequent and abundant watering. The earthen coma should not be allowed to dry out: it is useful to moisten the soil with water once a month with the addition of a few drops of lemon juice. This technique allows you to maintain an optimal level of acidity in the soil substrate. The method of immersing the pot in a container of water at room temperature has a beneficial effect on the azalea.
To maintain the recommended humidity in the room (from 70%), it is necessary to regularly spray the plant with a spray bottle
Alternatively, you can place a container of water near the bush. In spring and summer, the azalea should be fed with a nutritious ready-made formula. The frequency of feeding procedures is 4 times a month.
To maintain the shape of an evergreen shrub, it is necessary to prune regularly, every year, shortening last year's branches and removing diseased parts of the plant. Such events also ensure an abundant and lush bloom of the azalea. The optimal time for pruning early varieties is March, and late ones - May. In addition, at the end of spring, you need to pinch young shoots of rhododendrons, leaving only 5 leaves. And already towards the end of summer you can see flower buds on their tops. Pruning the bush is done even before the dormant period begins.
List of diseases to which rhododendron is exposed and plant treatment
How and how to treat rhododendron - it is necessary to determine as accurately as possible, since some diseases kill the bush almost instantly.
Tracheomycotic wilting
Fungal disease caused by Fusarium fungi. The first signs of the disease are considered to be the appearance of a gray bloom on the shoots, the rapid drying and falling of leaves, and the wilting of the stems. The fungus affects the vascular system of the plant and manifests itself when it has already spread throughout the bush. The root is the first to suffer, it simply rots in the ground.To save the bush, it is necessary to take drastic measures: all damaged shoots are cut off and burned. Healthy parts are generously sprayed with Bordeaux mixture.


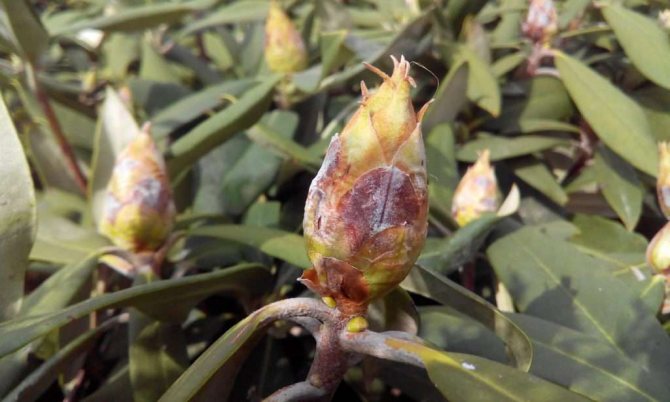
Late blight rot
The disease is caused by the fungus Phytophthora. The first signs are the appearance of dark crimson spots on leaf plates and shoots. If measures are not taken, then the root begins to rot and the plant does not receive the necessary nutrition. It is depleted and stops growing. Treatment - regulation of watering in the direction of reduction and the use of special fungicides.


Bacterial cancer
A fatal disease, which is manifested by the formation of specific growths on the roots and root collar. The affected bush stops growing, sheds its buds and eventually dies. The disease is also terrible because it continues to develop on a dead bush and in the place of its growth. At the beginning of the development of the disease, it is advisable to apply Bordeaux mixture. If the plant cannot be saved, it should be uprooted and burned, and the site should be treated with a fungicide.
Prevention and protection of plants
In order to prevent the development of ailments dangerous for azaleas and the invasion of harmful insects, the following recommendations should be adhered to:
- It is necessary to place flowering shrubs in a bright, but protected from direct sunlight place.
- Water the plant with boiled or melt water.
- Do not overdo it with soil moisture.
- Maintain air temperature readings in the range of 12-15 degrees.
- It is necessary to feed the azalea in the summer with ammonium sulfate, and in the winter with superphosphate.
- Timely pruning and pinching allows the plant not to waste its energy.
- For transplanting a bush, use only disinfected soil, containers and tools.
Growing azaleas is a rather complicated process that requires both knowledge of all the intricacies of planting and the features of care. If you adhere to the correct agricultural technology, then the risk of infection of an evergreen shrub with fungal diseases and pests is reduced to zero. Only a favorable microclimate in the room and adherence to all recommendations for the maintenance of azaleas can achieve the desired results.