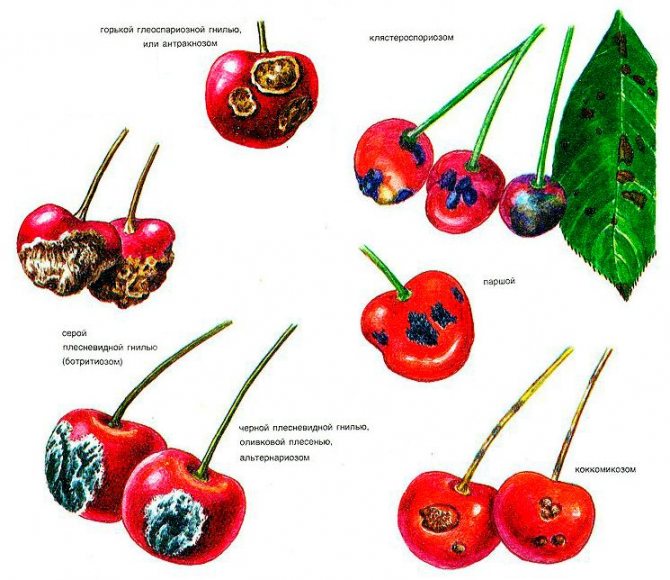
Cherries, like other representatives of stone fruit, exist in parallel with diseases, with which, to our great regret, they periodically intersect. Therefore, in order not to be left without a crop near a dead tree, we will consider diseases that can encroach on the inhabitants of our garden.
I want to note right away that all the sores described below are fungal diseases.

So let's get started.
Cherry diseases and protection against them
All the diseases of this fruit tree subdivided according to their distribution on the:
- Fungal pests form mottling, which leads to the death of leaves, berries, trunk and bark. This is perhaps the most common type of disease. It spreads through spores that are carried by an infected instrument or wind. These include, for example, verticillary wilting of leaves.
- Bacterial diseases are caused by microbial contamination, parasitic insects, wind, or an infected tool.
- Viral ailments are affected by insects that move from one area to another. There are no chemicals that fight this pathology, so the only correct way out of this situation is to remove the tree in order to protect other trees in the garden from the same fate.
- Non-infectious ailments affect the tree as a result of improper care, frost cracks, untimely or improper cutting of the trunk, sealing wet sections with wax, breaking branches as a result of snow or fruit load.
We are sure that the article will be useful to you. with photos of the advantages and disadvantages of the Chizhovskaya pear variety.
Disease protection
It is worth noting that it is impossible to exclude the likelihood of a tree disease, but you can adhere to preventive measures, the essence of which is to pay attention to each damaged leaf.
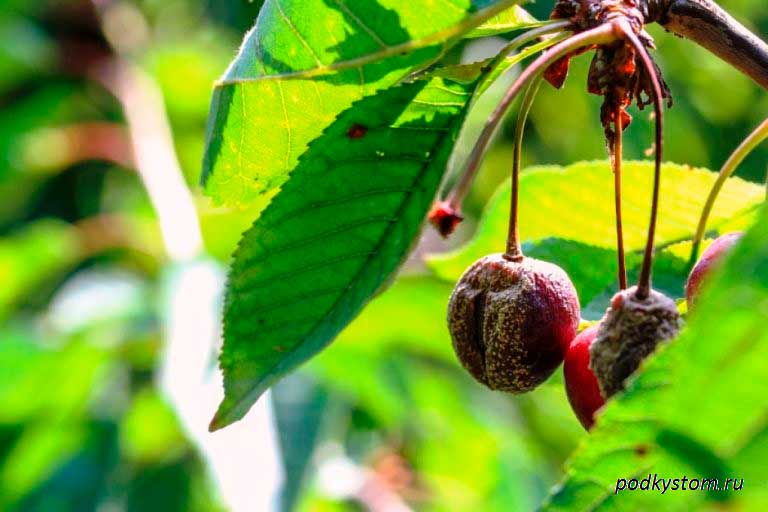
Moniliosis
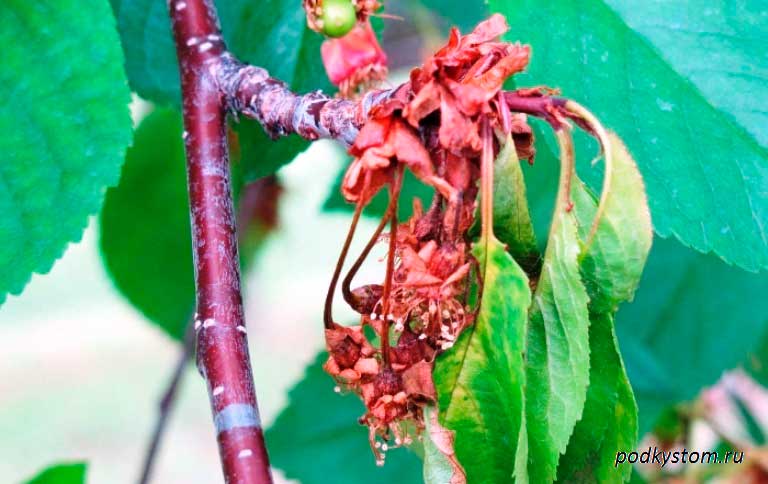
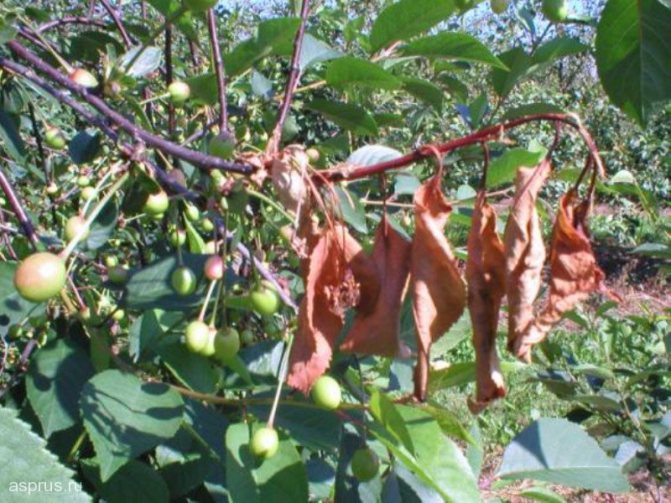
The fungus is the causative agent, which leads to the drying out of fruit buds, shoots, flowers, which outwardly look like the result of burning them with fire. For this reason, another name for the sore is monilial burn. Infected fruits gradually begin to rot, curl up, remaining quite often hanging until spring.
The pathogen itself remains in the organs of culture that have already been infected.
Our help.
We do the same measures as for rust.
Cherry coccomycosis
As a result of prolonged rains near cherries coccomycosis can be provoked... The characteristic features of the course of the disease are: small brownish-red spots on the foliage. The affected areas at the very beginning turn yellow, and then acquire a brown tint and, in the end, crumble. In the first years of the course of the disease, the cherry ceases to bear fruit, and then it dies itself.
Treatment... A preventive measure is the treatment of cherries from coccomycosis during the period of active swelling of the kidneys. It is strongly recommended that the first spraying be carried out with copper sulfate (300 grams per 10 liters of water).
When the time comes and the buds begin to bloom, they need to be abundantly sprayed with the Bordeaux mixture.And also do not neglect the agrotechnical rules for the cultivation of fruit trees, among which are careful attention to the tree, the identification of affected leaves and their timely removal, the autumn digging of the soil under the crown of the tree.
To combat the disease of coccomycosis, you should use the following chemicals:
- Hom;
- Zorus;
- Topaz;
- Horus.
In order for the preparations for coccomycosis not to be washed off soon, laundry soap is added to the solutions.
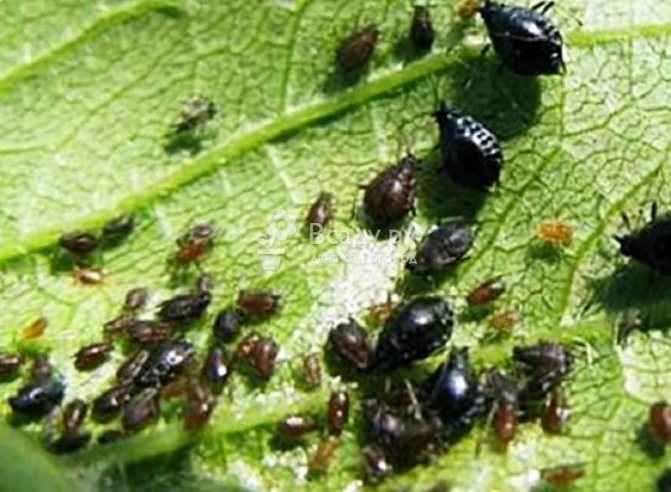
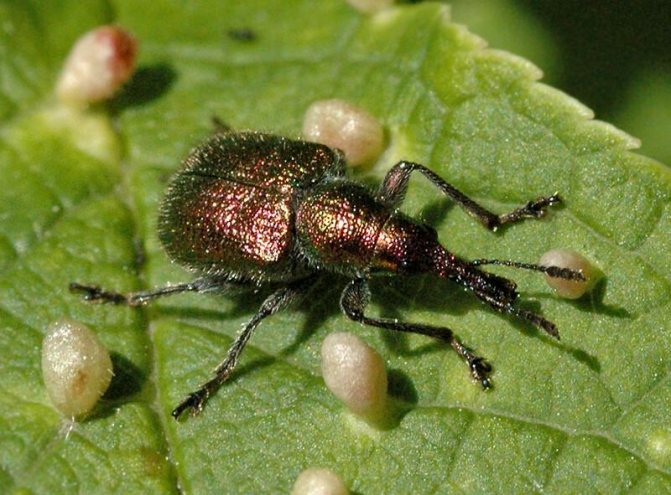
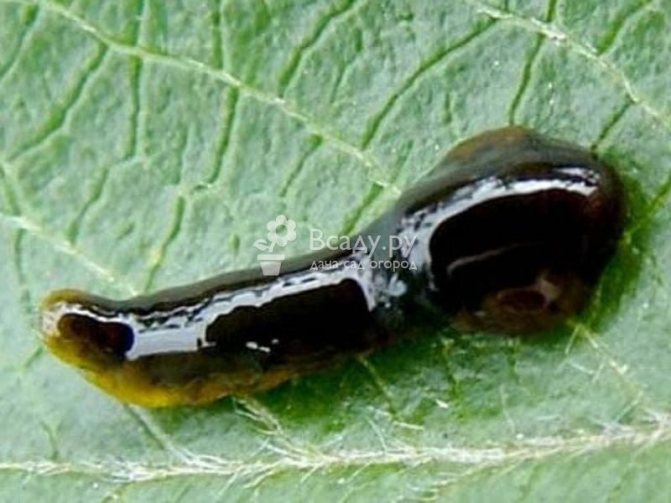
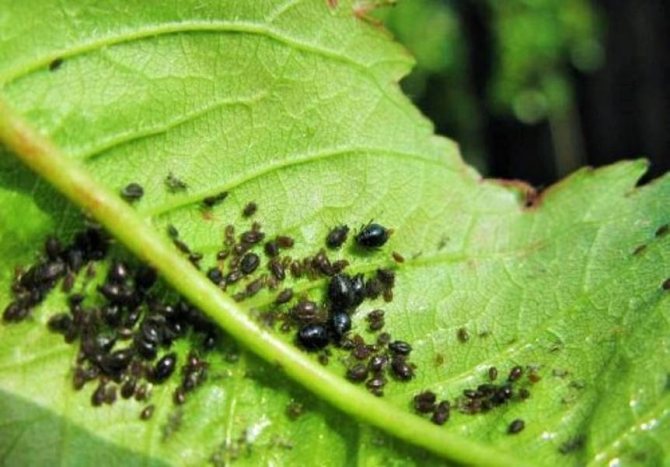
How to deal with pests on cherries
Cherry tree pests damage the crop and generally weaken the fruit plant. Therefore, it is necessary to treat pests at an early stage. You can list the following measures aimed at getting rid of insects:
- With the beginning of spring, cherries should be regularly inspected and checked for the condition of their leaves, shoots and ovaries. In the initial stages, pest infestation may not be conspicuous, but with proper attention, the eggs and larvae of harmful insects on the leaves and bark are not difficult to notice.
- For minor pests, you can use a regular soapy solution for treatment. Natural laundry soap is diluted in warm water in a proportion of 100 g per 1 liter of liquid, and then the crown of the plant is abundantly sprayed in the morning or after sunset.
- In case of serious pest infestation, the fruit plant can be treated with insecticidal solutions, such as Karbofos, Fufanon and Kemifos. Mild chemicals can help eliminate even large populations of aphids and ticks.
It is recommended to treat cherries from pests several times per season. Since some pests have time to lay eggs several times over the summer, re-treatment increases the effectiveness of the treatment. It should be remembered that spraying with insecticides should be carried out no later than 3-4 weeks before harvest, otherwise chemicals can penetrate into the tissues of the fruit.
During the preparation of the fruit plant for winter, you need to remove all fallen leaves from the trunk circle and dig up the soil. Many pests hibernate in plant remains or the upper layer of the earth, therefore, cherry trees can again attack on a neglected area with the onset of spring.
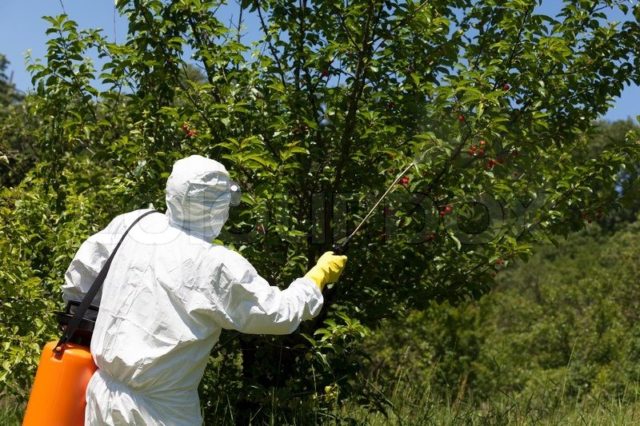


The most effective way to control parasites is with insecticide treatment
Cherry gum flow
One of the most common diseases is cherry gum flow... Gum flow is formed on the bark of the trunk as a result of damage to the integrity from frost or defeat by moniliosis, clasterosporium, or other viruses, infections or bacteria.
The disease is manifested by abundant secretions on the tree trunk of gum (glue), which, when solidified, forms transparent glassy formations. But why do they start to form on the bark of a tree? What does the release of gum lead to?
Treatment... To prevent, and not cure, the disease, it is recommended to increase the winter hardiness of sweet cherries by proper fertilization and watering. Frostbite should be disposed of by cleaning it; wounds on the bark should be disinfected by covering them with garden varnish or nigrol putty. In places where the gum is released, it is recommended to carry out a slight furrowing of the bark.
The main diseases of cherry in the Moscow region and their treatment:
Moniliosis
Cherry varieties for Siberia
A very common fungal disease of cherry. The spores of the fungus Monilia cinerea are carried by the wind.
A favorable environment for the development of moniliosis is dampness and coolness. Most often, outbreaks of the disease are observed during the period of rains and cold snaps. The high risk period is spring and late summer. Spores are able to successfully overwinter in diseased parts of the trunk, bark and fallen leaves.
Young shoots are the first to suffer from moniliosis. The infection spreads rapidly through the tree.
Signs:
- The branches begin to dry, as if scorched by the sun.
- In a flowering tree, flowers and buds dry out and fall, in a fruiting tree, berries.
- The bark begins to crack, and ugly outgrowths appear on the trunk.
- Stem cracks rot, become stained, and gum flow may begin.
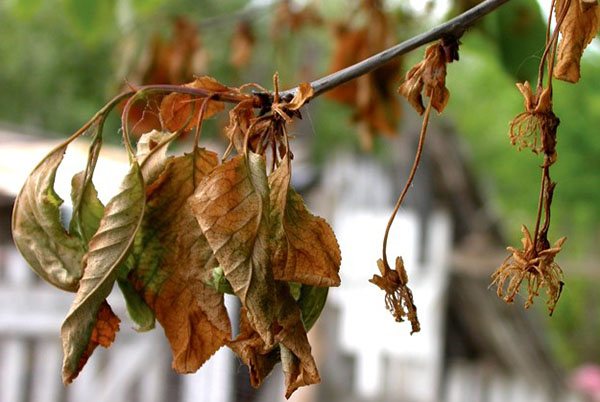


Moniliosis on cherry
Control methods:
- Planting varieties with high disease resistance.
- Sanitary pruning of the crown, burning of fallen leaves, whitewashing of the trunk.
- Removal of all dying branches (cut or sawn to living tissue).
- Cherry treatment with fungicides (Gamair, Horus, Rovral), copper preparations (copper sulfate).
If the disease manifests itself on one plant, all stone fruit crops in the garden (apple, pear, plum) are at risk. Treatment with copper-containing preparations should affect all fruit trees and be not one-time, but systematic.
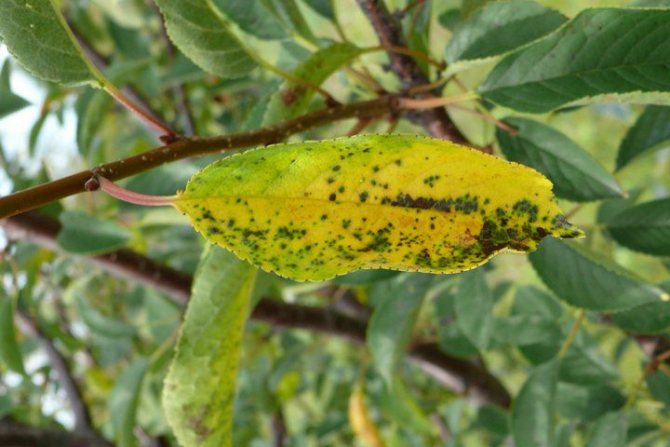
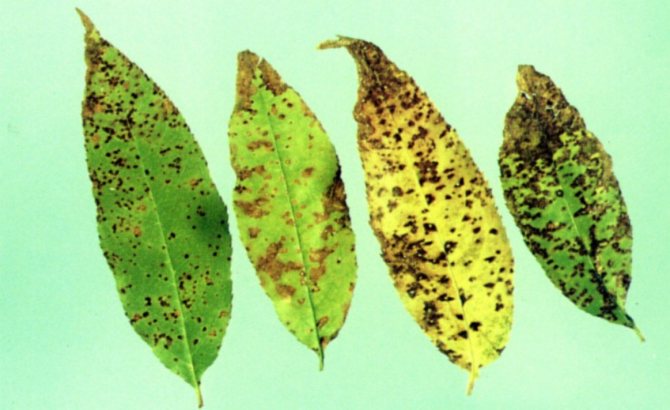
Coccomycosis
Along with moniliosis, one of the largest diseases of stone fruit crops in the Middle Lane. All the fault of the microspores of the fungus Blumeriella jaapii, carried by the wind during the spring thaw. The pathogen slumbers in the upper layers of the soil under last year's foliage, waiting for an opportunity.
During the growing season in the garden, up to 6-8 generations of coccomycosis fungi mature and scatter. Warm weather and high humidity stimulate the breeding process. The disease moves along the tree from bottom to top, quickly occupying new areas, being transmitted from diseased leaves to healthy shoots.
Signs:
- In the initial stage, the lesion does not attract much attention. There is a slight mottling of individual leaves.
- Red dots on the leaves gradually spread, increasing in size. The core of the blotch turns brown, the back side is covered with gray growths, and spores ripen on cherry leaves.
- Sick leaves turn yellow and crumble prematurely. By the end of summer, the infected plant completely discards its leaves and fruits.


Coccomycosis on cherries
The infected plant does not have time to accumulate a sufficient supply of nutrients by winter. It becomes vulnerable to defeat by other ailments. Winter hardiness decreases and the fruit crop dies.
Control methods:
- Planting varieties of young selection resistant to fungal spores.
- Autumn collection and destruction of volunteers and the remains of foliage.
- Digging the upper layers of the soil under the trees in spring and autumn.
- Before opening the flower buds and after setting the fruit, the fruit plantings are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid.
- After harvesting, the tree is sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate.
If you do not start the treatment of the disease in a timely manner, then it will not only leave the gardener without a good harvest, but in a few years it will completely destroy the entire garden.
Note! The Blumeriella jaapii fungus was introduced to the country in the mid-60s of the 20th century, therefore, none of the old-breeding cherry varieties and their heirs are immune to this disease.
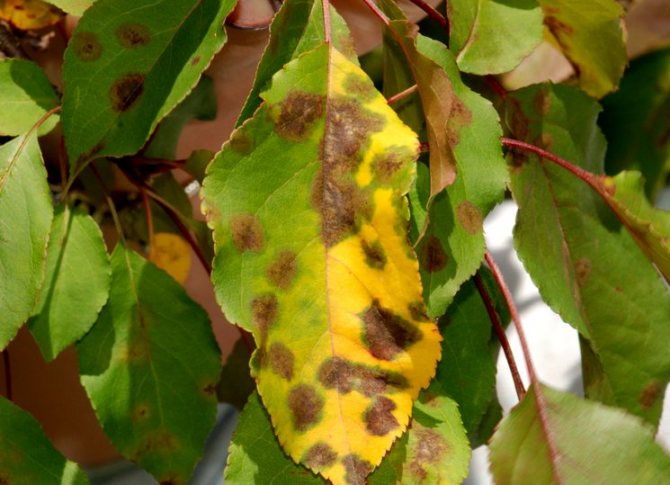
Clasterosporium disease (Hole spot)
Cherry clasterosporium disease is caused by the harmful fungus Clasterosporium carpophilum. Its spores find refuge in crevices in tree bark and under fallen leaves. The optimum temperature for the growth of the fungus is + 20 ° C in combination with high humidity. Spores are carried by the wind and rain drops flowing from infected leaves.
Signs:
- The leaf blades are crumbled with tiny reddish-brown dots that grow in diameter. For 2 weeks, holes form in the affected areas.
- In the later stages of the disease, cracking of individual sections of the bark (the formation of growths) occurs.
- Sore wounds leak with tree sap, gum leakage from some kidneys is observed. Flowers fall.
- In case of a serious injury, foliage falls off the tree.
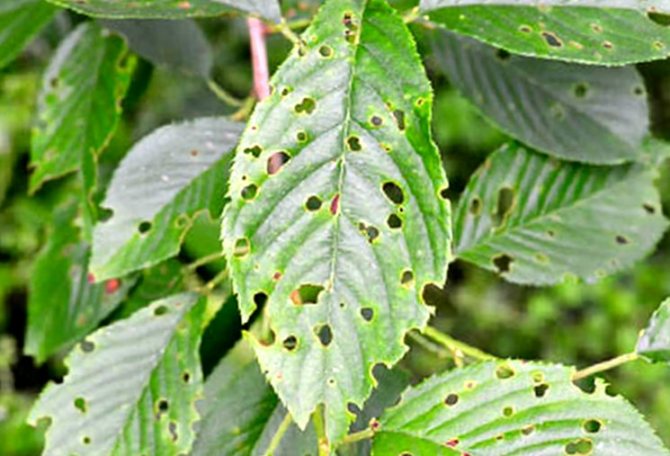


Clasterosporium disease (Hole spot)
Control measures:
- Compliance with agricultural techniques.
- As a treatment, measures similar to those used to combat other fungal diseases of cherries are used.
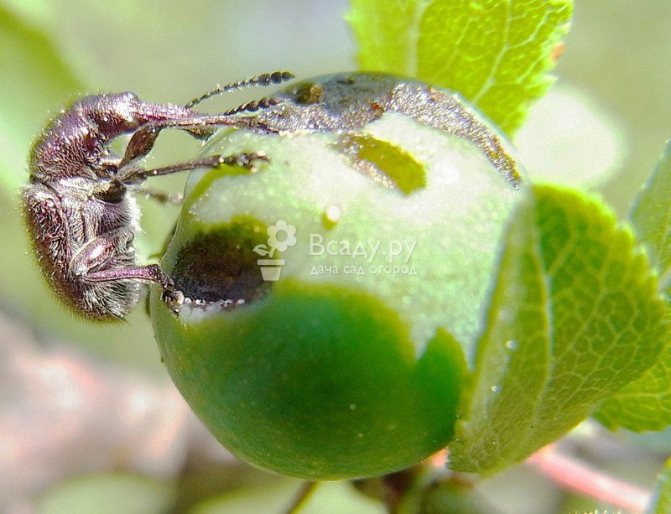
Anthracnose
A disease carried by spores of the fungus Gloeosporium ampelophagum. Distributed everywhere, thrives on many vegetable and fruit crops. Cherries are characterized by berry damage.
Signs:
- Pigmentation on fruits with their subsequent decay.
- Light specks appear on the berries. The spots increase in diameter, become dark and hard. The fruit dries up, covered with a bloom of ripe fungal spores.
Control measures:
- Destruction of infected fruits and carrion.
- Autumn treatment with urea solution (0.5 kg per bucket of water) or Bordeaux liquid solution.
- Spraying with a solution of the preparation Polyram (1 sachet per bucket of water) or other fungicides containing it before the buds dissolve and after the formation of ovaries. With obvious signs of the disease, a third treatment is carried out, 2 weeks after the second.
Cherry anthracnose actively devours the crop, and the fight against it is simply necessary. If it was not possible to preserve the fruits in the current year, then it is important to carry out all the treatments on time - to save the harvests of future years.
Gum therapy
Gum removal, or gommosis, is a resinous discharge on the trunk and branches of stone fruit trees. Hommosis precedes the death of the part of the plant where it appeared.
Signs: Drops of sticky translucent resin on the trunk of the cherry.
Important! If gum flow has begun in cherries, treatment should be started as soon as possible, since the resinous gum of gummose (gommose) attracts parasites, weakens the plant, and provokes the occurrence of fungal diseases.
Cherry fumigation can be prevented by observing the rules of agricultural cultivation. There can be many reasons, the main one being deep injuries (cracks, cuts, breaks) of the trunk. Sticky tree sap (gum) flows out of the damaged area. It is recommended to cover up all the "problem" places with garden pitch.
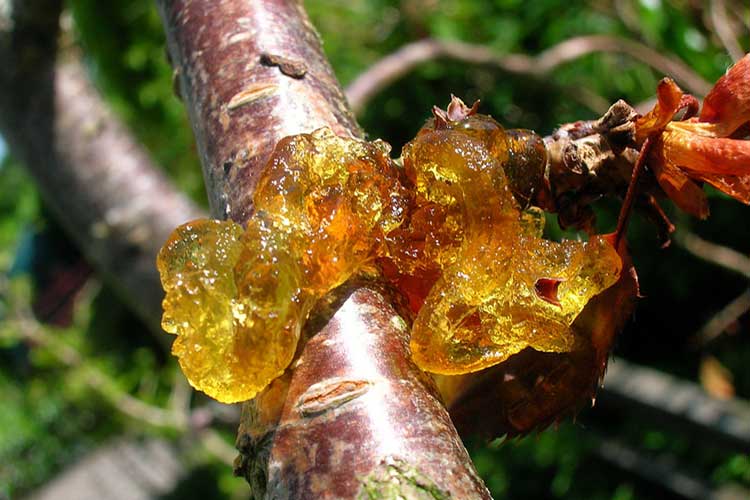


Cherry gum flow
It is advisable to clean the affected areas of the trunk, removing all tissues to healthy wood, disinfect and process with garden varnish. The procedure is performed after the completion of the spring sap flow.
Rust
Rust on plants in the garden is the spread of the harmful fungus Thekopsora padi. Conifers are most intensively affected. Rye quickly spreads throughout the orchard.
Disease manifestations: rusty red-orange spots appear on the leaves. Spores of the fungus mature on the affected areas. Leaves die off and fall off.


Rust on cherry
How to cure cherries: all diseased shoots and leaves are removed and the plantings are treated with copper-containing preparations or a solution of colloidal sulfur (according to the instructions). Effective fungicides for cherry processing: topaz, Bordeaux liquid, falcon, super alto.
False tinder
False tinder fungus is a pest fungusthat affects the trunk of the sweet cherry. The main symptom of the disease is the formation of white rot in the wood. As a rule, it affects the crack (crack) in the lower part of the trunk. In that place, a growth of yellow, dark brown or brown is formed.
Spores of the pest fungus live on the wounds of the bark of the tree, formed as a result of sunburn, direct exposure to frost or the negative effects of insects. A diseased tree loses its power, becoming soft and breaking at the slightest gust of wind.
Treatment... For the most effective pest control, it is necessary to remove and burn the cherries. But, if you do not want to do this, then it is necessary to remove regularly formed growths in a timely manner.
The wounds that will appear as a result of the removal of growths must be carefully cleaned and copiously treated with copper sulfate and covered with garden varnish.For preventive measures, and not control, it is recommended to carry out all the necessary measures aimed at avoiding the occurrence of mechanical damage to the bark. We strongly recommend that you whitewash the trunks and skeletal branches of the tree annually.
Tips for protecting your cherry orchard after treatment
After successfully combating cherry diseases, the level of correct agricultural techniques for working with this tree must not be reduced in order to preserve its productive potential;
- Fruits from a treated tree must be thoroughly washed under running water before use;
- In modern specialized stores today you will be offered the safest for humans and drugs that are effective against infections and pests;
- We remind you about the high toxicity of copper sulfate. If it is impossible to replace it with another means of protection, then at least use the best personal protective equipment: glasses, masks, clothing, shoes, do not smoke or eat while processing trees. Less dangerous, for example, is the drug "foundazol", especially during cherry blossoms;
- It is necessary to strive to preserve as lush a crown as possible so that the tree is more resistant to frost.
Described in this article cherry fungal diseases can threaten almost all fruit trees in the garden, not just stone fruits, cause damage to the crop, distract the energy and time of the gardener and cause some damage to the budget. In this regard, all the indicated preventive measures and direct control of the emerging disease of the cherry orchard should be combined with a full set of agricultural techniques for caring for fruit trees.
Bacteriosis (cherry cancer or ulcer)
Based on the name of the disease, it is immediately clear that the disease has bacterial origin... This pest is susceptible to diseases at the age of 3 to 8 years. Bacteria spread by wind and rain. In the winter season, bacteria reside in the buds and blood vessels of trees.
The humid and cold climate in spring promotes the mass reproduction of pathogenic bacteria that affect all plant organs.
Branches of the affected tree covered with ulcersfrom which gum flows abundantly. On the foliage and fruits of the cherry, brown or black spots with a pronounced yellow border are formed. The peduncles are abundantly covered with brown ulcers.
The wood on the infected trees dies off, and so does the leaves. Sometimes, the cherry dies completely. Bacteriosis visually may not manifest itself in any way if the weather is hot and dry in summer.
Treatment... To date, there are no effective methods of dealing with this ailment, because it is not for nothing that it was also nicknamed cherry cancer. Each of the existing types of cherries has an individual susceptibility to bacterial attack.
It is worth noting that trees that receive adequate nitrogen nutrition and moderate watering are practically not susceptible to this disease.
Cherry tree - description
Cherry is a deciduous tree or shrub 3-4 meters high with oblong, oval, pointed, serrated or serrate leaves along the edge of a dark green color on top and lighter on the lower side of the plate. The length of the leaves is 5-7 cm, the width is up to five cm, the leaves are arranged on the branches in the next order. White or pink cherry blossoms have a pleasant smell and form umbrella-shaped inflorescences.
- How to grow strawberries from seeds
Fruits are juicy drupes of red or black color with one seed, which have valuable nutritional qualities. Common cherry is a relative of stone fruit trees such as sakura, plum, apricot, bird cherry and sweet cherry. Actually, there are suggestions that it was from the crossing of the sweet cherry, or bird cherry, with the steppe cherry that the common cherry appeared. Today the species has about 150 varieties. Common cherry is frost-hardy, drought-resistant and unpretentious. Begins to bear fruit at the age of 3-4 years.


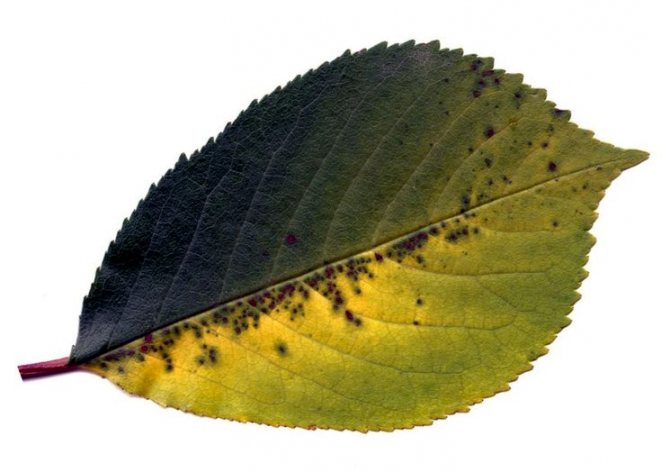
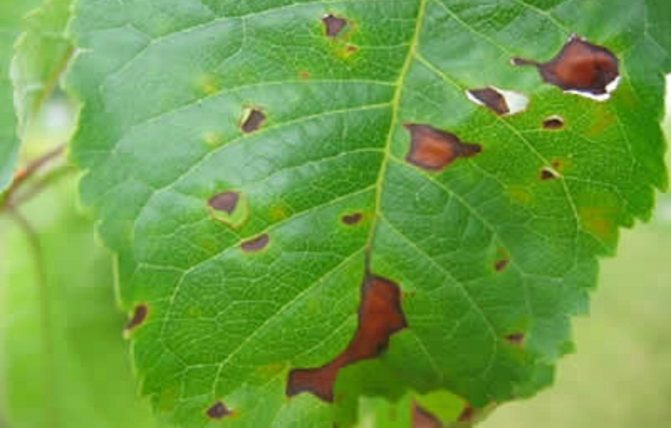
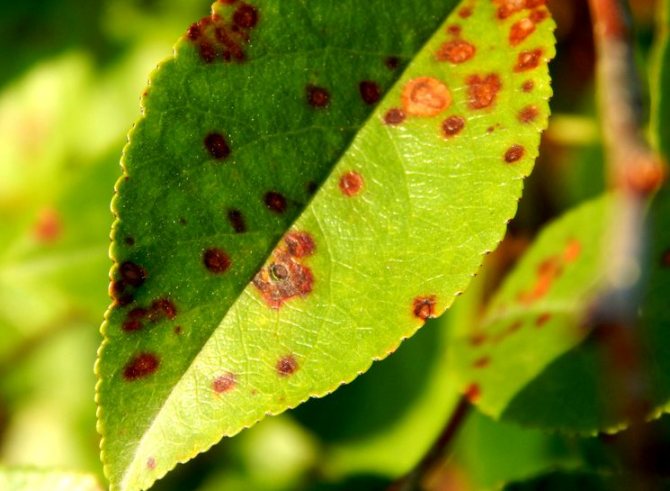
Brown spot (phyllostictosis)
You can calculate whether your tree is doing well with the leaves, which should be carefully examined. It is they who, first of all, give out the affected fruit trees.
If, upon examination, you noticed the presence of small spots of brown color on the foliage, then the diagnosis will be far from comforting - your fruit tree is affected phyllostictosis or brown spot.
This disease is of fungal origin, which manifests itself as black dots on the leaves. Over time, the leaves of an infected tree wither, dry out and fall off.
Treatment... Affected foliage should be collected and burned in a timely manner. Before budding begins, it is strongly recommended to treat the tree with 1% Bordeaux liquid, 1% copper sulfate, nitrafen. Subsequent processing is carried out after flowering with Bordeaux liquid, after 2-3 weeks.
After a few more weeks, it is recommended to treat the tree with the Hom fungicide. If the tree is heavily affected, it is recommended to carry out another treatment in the fall.
Cherry feeding
How to feed cherries
The first spring treatment of cherries and tree trunks with urea is complex. It is both protection against pests and diseases, and feeding with nitrates at the same time. During flowering, you can fertilize the cherries with liquid chicken droppings, but this is not necessary. After flowering, manure is introduced into the trunk circle for digging or in the form of a solution. Organic nutritional dry mixes can also be used according to the manufacturer's instructions. If during this period there is no rain, then it is better to carry out liquid fertilizing.
In the summer, foliar spraying of cherries with nitrogen-containing preparations is carried out two or three times: the first is in mid-July, and then not earlier than three weeks later. If you find that the cherries are lacking in any element, apply a foliar dressing with a preparation containing it. After fruiting, fertilize the trunk circle with compost, rotted manure or other organic matter.


Autumn feeding should include mineral compositions of calcium, potassium and phosphorus. In the same period, insufficiently acidic soil is liming. After the first frost, add potassium-phosphorus fertilizers to the trunk circle for digging to a depth of 8 cm.
Sulfur - yellow tinder fungus
Another fungal infection that affects cherries is sulfur - yellow tinder fungus... Due to the course of the disease, core brown rot is abundantly formed, in which cracks with mycelium are formed.
As a result of the influence of the fungus, the wood becomes quite fragile and breaks down into small pieces. Pronounced symptoms of the course of the disease are mushrooms with wavy hats, colored orange or light orange, formed in cracks in the bark.
Treatment... To prevent the development of sweet cherry disease, it is necessary to carry out measures that will prevent the formation of frosts in the bark. To do this, it is necessary to whitewash the trunks and skeletal branches in the fall. In the spring, you should definitely carry out top dressing after the winter cold.
If frost and sunburn could not be avoided, then the affected areas should be thoroughly cleaned, disinfected and covered.
The main causes of cherry disease
The health of cherries primarily depends on proper care of them. Compliance with all the rules of agricultural technology (timely watering, feeding, pruning) significantly increases the immunity of trees, and reduces to a minimum the likelihood of damage to their diseases.
There are other factors that affect the degree of disease damage to cherries:
- Climatic conditions of the region;
- Weather conditions (temperature drops, dry summers or high humidity, frosty and snowless winters);
- Mechanical injury to branches or bark surface;
- Pests that carry bacteria;
- Diseases of other trees growing nearby.
Having established the causes of the disease of cherries and cherries and eliminating them, if this is in the power of the gardener, it will be much easier to fight the disease.
Sweet cherry mosaic disease
Mosaic disease - This is an ailment of viral origin, which contributes to the suppression of the tree's immunity. Symptoms of the disease are: the formation of yellow stripes on the leaves along the veins, twisting of the affected foliage, staining in a brown tint and death.
The virus is spread by insects, as a result of grafting infected cuttings and pruning infected and healthy trees with an infected tool.
Treatment... There is currently no cure. You can only carry out regular preventive measures, treating trees from insects, observing all the rules of quarantine measures, using processed and sterile planting material. To our deepest regret, we will have to get rid of infected cherries.
Mosaic ringing
Symptoms of mosaic ringing are the appearance of pale green or whitish rings on the cherry leaves, which, after a while, crumble, and voids form in the same place.
Cherry necrotic ring spot virus (PNRSV)
Signs of cherry necrotic ring spotting depend on the virus strain and the susceptibility of the cherry tree variety. In the spring, rings or spots of a chlorotic color form on the leaves of cherry, this is the main sign of damage to the garden. Certain strains of PNRSV can cause very severe crop losses in cherries.


The necrotic ring spot virus can stop the growth of trees in the garden, lead to the death of buds and shoots on cherries. Such viral infections severely impair the growth of cherry trees while reducing resistance to other diseases.
Prevention of necrotic ring spot virus
- Use only healthy seedlings.
- Grubbing and destruction of affected cherry trees.
- Spatial isolation between trees.
Particularly severe damage from the PNRSV virus can be observed from May to June - during the growing season of cherry trees. Treatment for necrotic ring spot virus involves cutting and killing infected shoots, and sometimes uprooting entire trees. No chemical treatment is used against this virus.
Disease care
Cherry care in the Moscow region should be carried out regularly to avoid the development of mold and other infectious diseases provoked by moisture and harmful insects.
Mandatory spring preventive care for cherries is carried out, which consists in spraying with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid in a proportion of 300 g per bucket of water. The procedure will help to avoid the development of fungal diseases. Forming pruning is carried out to prevent the appearance of brown spotting.
In the summer, comprehensive care should be carried out:
- the fight against shoots that provoke depletion of the plant;
- harvesting wild-growing grass that attracts insects;
- correct and timely watering, which is applied during the dry season;
- digging up the soil after rain or watering will saturate the root system with oxygen and avoid fungal infections.
In the fall, they carry out sanitary pruning, removing dried, broken and moldy branches. The trunk is whitewashed to prevent mold.
Signs of Hole Spot
All parts of the plant fall into the affected area. The spots are similar to those that cause brown spotting, the color of the border is different - it is darker, almost black. If there are fruits on the tree, then they dry out very quickly, the foliage is prone to falling off, and the shoots to death.
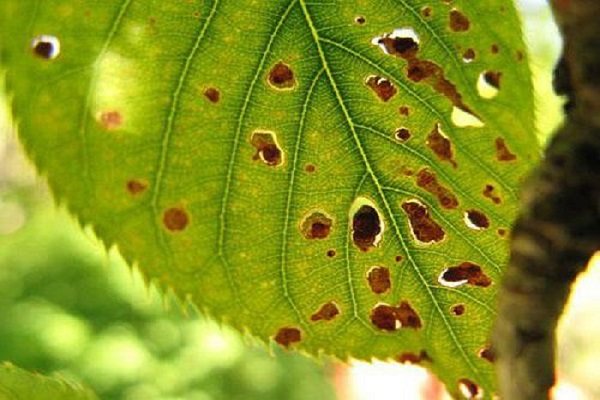


When a disease attacks a part of the shoot, it must be removed, the cuts are treated with a solution of copper sulfate, according to the above recipe. Carry out activities similar to the treatment of brown spot. All fallen leaves are removed from the site, because it can be a carrier of fungal spores. The soil is dug deeply, and the affected leaves remaining on the branches break off.