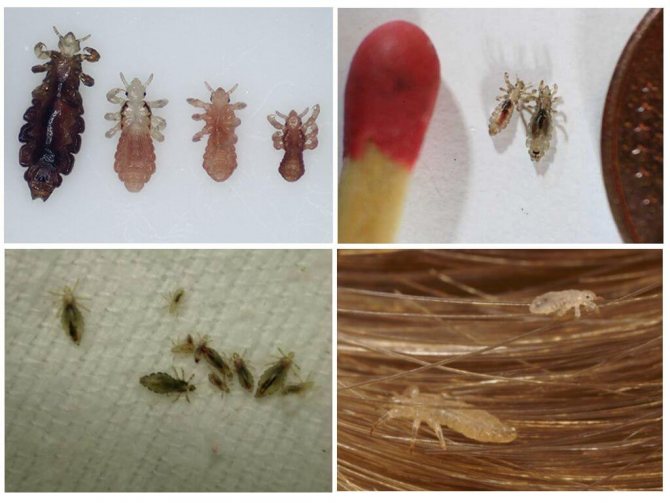
How insects develop

Insect development stages
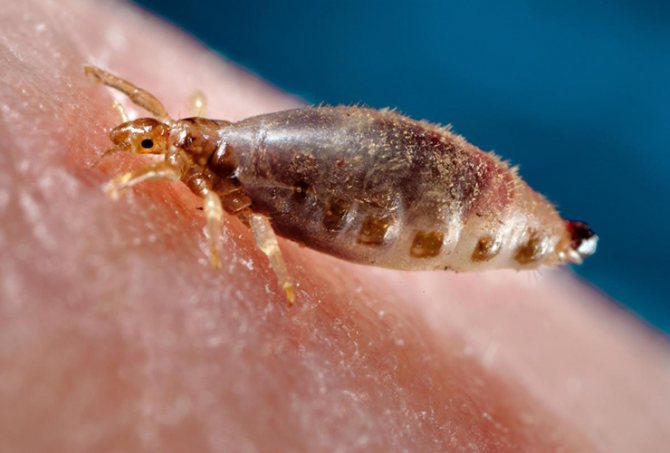
Lice develop with transformation, but incomplete. This means that there is no larval stage in it.
Egg stage
Lice reproduce immediately after molting. After one mating, all the eggs of the female become fertilized. After that, the egg stage starts: the female begins to lay eggs, which she attaches to her hair at different distances (up to 3 cm).
On a note!
Parasites living on the head lay up to 4 eggs, pubic lice up to 3 eggs, pests living in clothes no more than 10 eggs per day.
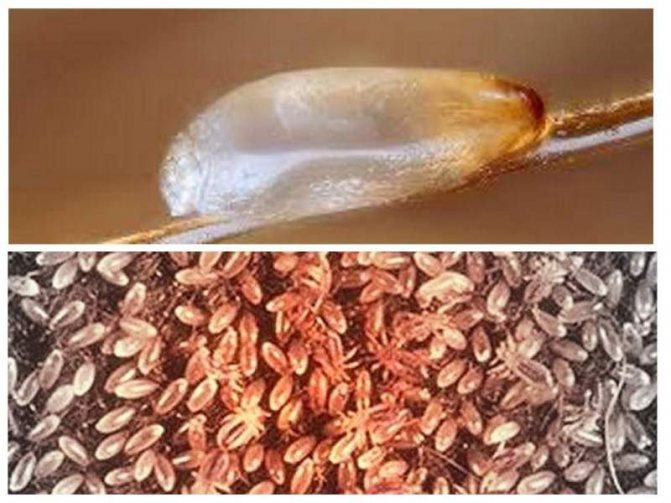
Despite the small size, it is quite easy to notice the nits attached to the hair: they look like white neat bags, which take from 4 to 16 days to form (depending on humidity and ambient temperature). The egg is tightly adhered to the hair with the help of a special sticky secretion, which the female squeezes out of herself when the abdominal wall is strained. This is how a cocoon is formed, which cannot be shaken off or washed off with water due to the sticky composition, which is the main difference between nits and dandruff. In this way, the parasites protect their future offspring.
Larval stage
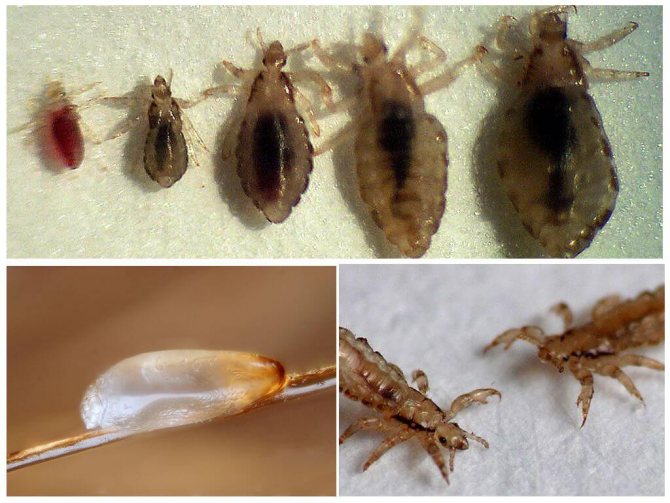
The process of emergence of the larva from the egg is of no less interest. Gnawing through the shell of the cocoon with its jaws, the larva begins to breathe actively, which contributes to the expulsion of air through its anus. The gas accumulated as a result of this contributes to the release of the future bloodsucker outside. Caught in this way on human skin, the larva immediately begins to satisfy hunger.
First instar larvae differ from adults only in smaller size and unformed reproductive system. After the first meal, the tiny bloodsucker is waiting for the molting process, after which he becomes a nymph.
Stage nymph
Due to the fact that the chitinous surface does not grow in accordance with other parts of the body, the bloodsucker at this stage is forced to molt three times. And as the protective cover becomes tight, the nymph throws it off. After this procedure, the nymph turns into an adult insect (imago) capable of reproduction.
Stage imago
An adult insect acquires the ability to fertilize after the first bite. Then insects mate, after which the fertilized female can lay no more than 4 eggs. She is now able to lay such a number of eggs daily.


Nymphs and imago of human lice
- under favorable conditions, this period lasts for 16-20 days;
- with a decrease in temperature, the breeding period of lice can be lengthened;
- with a long-term presence of the carrier of lice in a room with an air temperature below 18 degrees, the eggs cease to develop at all;
- the most favorable temperature for lice is a temperature above 26 degrees - under such conditions, the process of egg development is very fast (within 7 days).
The lice's lifespan also depends on temperature indicators. On average, parasites live for about 30 days, under favorable conditions, the pest's eyelids can lengthen up to 1.5 months. Moreover, the life expectancy of males is 2 times less than that of females. And the volume of blood that females drink in one meal is 3 times more.
On a note!
Specialists who study head lice and the reproduction of lice directly have come to the conclusion that the statement that parasites are more often found in people who do not observe hygiene are incorrect. On contaminated skin, pests may have difficulties when biting through the epidermis, and it is more difficult for insects to move. On a clean head, bloodsuckers feel more comfortable and breed quickly.
Therefore, in order not to infect others with this dangerous disease and not to multiply parasites, if any, it is necessary to urgently treat the head with an anti-pediculosis agent. The pharmaceutical industry produces a wide range of drugs to get rid of lice. Among them are shampoos, sprays, ointments. Also widely used.
Adult lice life
Imago lives for 30-42 days. In a lifetime, it lays about 140 eggs. The short lifespan of lice is due to the constant presence of food, comfortable temperature conditions.
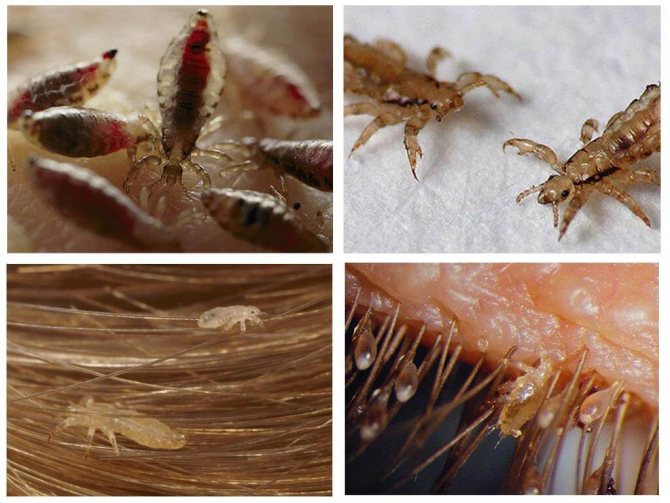


Lice
Lice never starves, there is always an opportunity to drink blood. Time is not wasted looking for a partner. One mating is enough to reproduce offspring for life. Comfortable temperature for existence and development is within 31 ° С. On the human head, the range is always maintained at any time of the year.
The breeding period of lice is adjusted if the louse crawls onto another person's head or is on a pillow or headdress for some time. Outside the human head, an insect can live for 3 days.
The head louse is not able to parasitize on other parts of the body, to infect animals. Pediculosis is transmitted only by a lousy person, his hats, combs. The development of lice and nits occurs imperceptibly to humans. Their existence on the head is betrayed by constant itching, which intensifies in the evening. A strong male is able to reproduce, give offspring, which dies a week after mating.
Interesting!
In ancient times, the appearance of lice was considered an infection. It was assumed that the parasites developed under the skin for a long time, and when exposed to favorable factors, they crawled out. This explains the rapid breeding of lice.
Head lice symptoms, or how to tell if you have lice
- Itching and burning
Crawling over the host's body and constantly feeding, lice irritate the skin. When bitten, the insect secretes saliva, which has toxic properties. It irritates the nerve endings and causes itching. The toxicity of saliva is not the same, and, accordingly, itching may not be felt or, conversely, be very strong.
When a pubic louse is affected, itching is not felt strongly, because there is an addiction to the bites. But the burning sensation in the area of the mucous membranes is a constant concern.
- Rash, redness, blistering, scratching
After bites, blisters may appear, disappearing after 2-3 hours, but sometimes not disappearing for more than a week. Rashes and age spots may appear. In addition, the person begins to scratch the infected areas, and thus scratching appears.
- The presence of nits
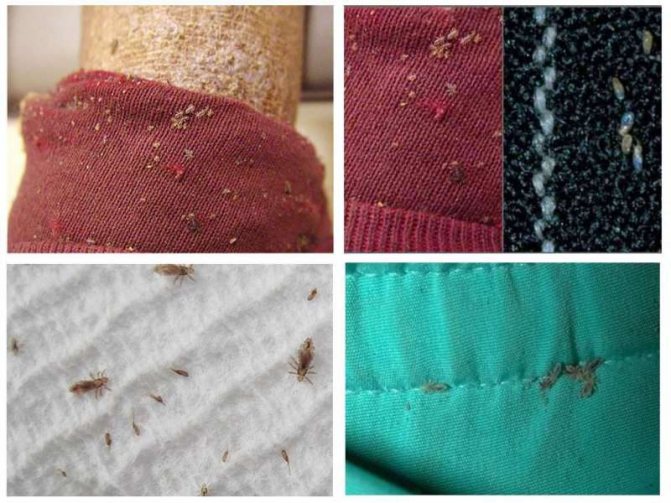
It is not easy to find an adult louse in your hair, it is easier to replace nits (lice eggs). They can be mistaken for dandruff, but unlike it, nits do not fall when shaken, but stick tightly to the hair. If you crush them with your fingernail, you will hear a crack. When infected with body lice, their eggs on the body are difficult to detect, but they can be found in abundance on clothing.


Photo Credit: Deanna Fox
- Lice
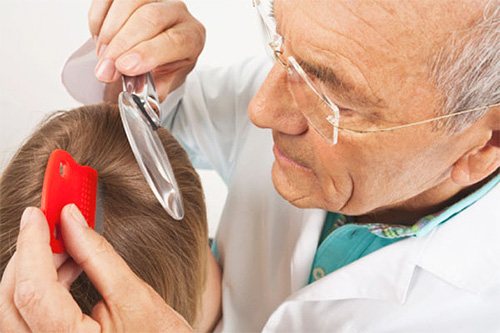
An adult louse can be found by combing the hair with a thick comb over a surface covered with light-colored paper or cloth. On the eyelashes and eyebrows, eggs and lice are easily detected visually.
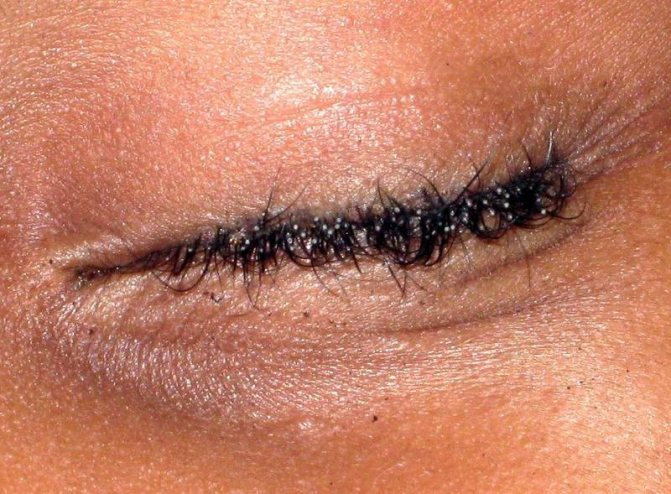

Photo by: Grook Da Oger, CC BY-SA 4.0
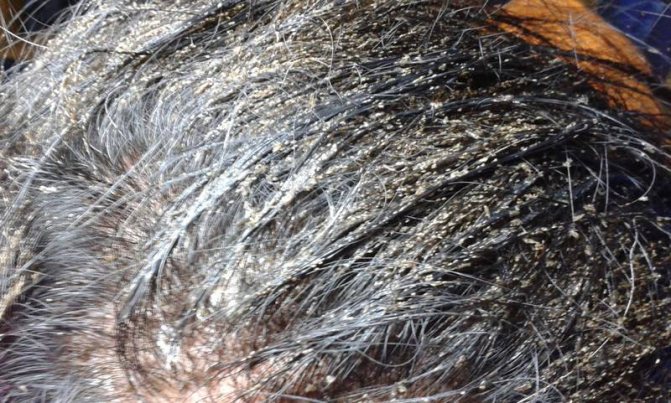

The photo shows very clearly how the lice look on the head. Photo by: Aditya Suseno, CC0


Linen (bed) lice.Taken from the site:
More about head lice
Few people know that lice don't jump. In addition, they cannot fly, so lice are transmitted from person to person either through personal and fairly close contact, or through the general use of clothing, household textiles and personal hygiene items.
If you want to protect yourself from possible infection with head lice, protect yourself from unverified contact with people.
But remember: lice are not always transmitted to another person through direct contact with the skin of an infected person.
If in public transport or in another place in which there are many people next to each other at the same time, you notice a suspiciously itching person - move away from him.
When visiting the pools, wear a rubber bathing hat over your curls. As mentioned earlier, lice do not jump, but they swim beautifully.
Human lice of other species
In addition to head lice, there is a clothing or material, pubic. The latter was named the ploshchita.
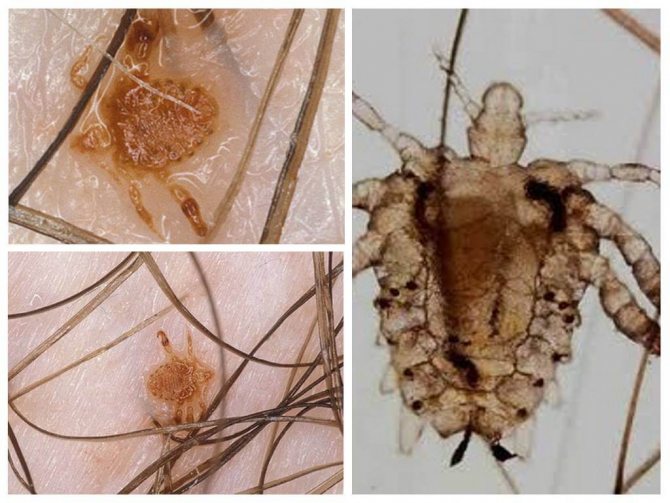

Pubic lice
- Pubic louse differs from the head louse in appearance - it looks more like a small crab. Parasitizes the pubis. With a strong infection, the area is found in the armpits, on the eyebrows, on the eyelashes. The hair on the head does not fit in structure. Infection occurs during sex, contact with towels, personal belongings. Parasites multiply quickly. The female lays about 7 eggs per day. Pubic lice manifests itself within 2 weeks.
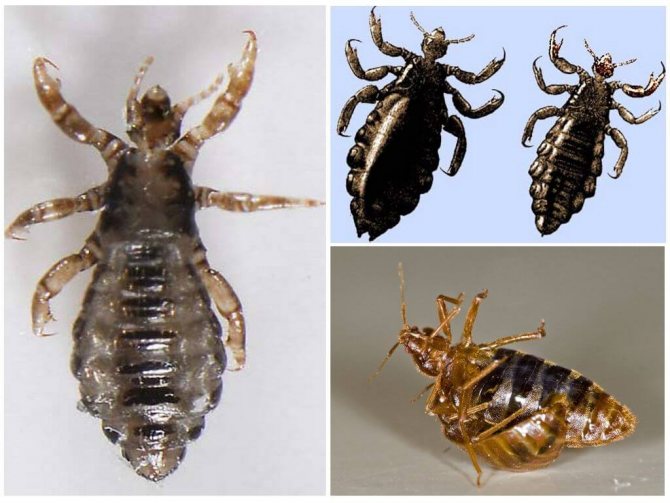
- The body louse is practically no different from the head louse. It repeats the entire life cycle, features of reproduction. The only difference is the habitat - personal belongings of a person, bedding. Parasitizes on the body, except for the pubis, head. It can live without food for about 5 days.


Linen lice
How lice breed has been known for a long time. It is well understood where the parasites come from. all ways of infection. You can get rid of lice in 1-2 procedures. Pediculicidal drugs can be bought at the pharmacy or you can use folk remedies. Children, dysfunctional families, and persons without a fixed abode are at risk. In the absence of treatment, an infection enters the bite wounds, complications develop.
Treatment features
When symptoms appear, treatment should be started immediately. A permanent scalp can cause mechanical damage to the skin surface during scratching.
As a result, there is a risk of getting new infectious infections. After the appearance of lice in a person, the scalp begins to dry and peel off, dandruff appears, and sometimes the lymph nodes in the neck and behind the ears become inflamed.
The patient is nervous, the sores on the head begin to rot, the hair sticks together and smells unpleasant.
Video:
In general, the picture is not the most inspiring, so treatment should not be postponed indefinitely.
Sometimes nits are confused with dandruff as they are small in size and similar in color. For this reason, some people do not start treatment on time.
Only with the help of special equipment can you see that the nits are a cocoon with an attachment at the bottom that allows them to cling to the hair.
If treatment is not carried out for a long time, an empty husk appears on the surface of the head from hatched nits. And getting rid of it is very difficult.
Dry nits are especially noticeable on dark hair, while the lice themselves dig into the scalp and are not visible.
It often happens that nits do not respond to the action of a pharmaceutical agent against head lice and continue to develop on the owner's head.
Therefore, it is recommended to supplement the treatment by combing out the larvae using a special comb.
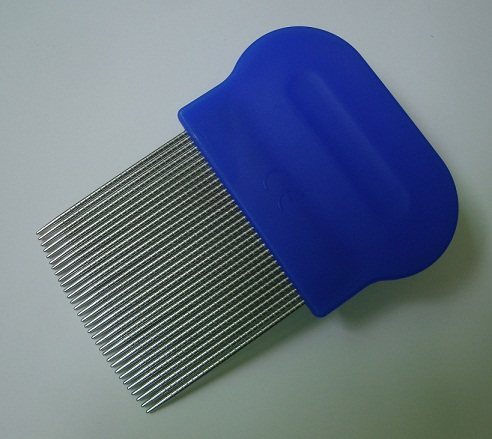


Nobody wants to get such "tenants" as lice and nits on their heads. If this happens, you need to systematically undergo a course of treatment and comb out the remaining nits with a special comb.
To prevent the disease, you just need to follow the simple rules of prevention, then the problem will not arise again.
Description of the parasite


Human louse
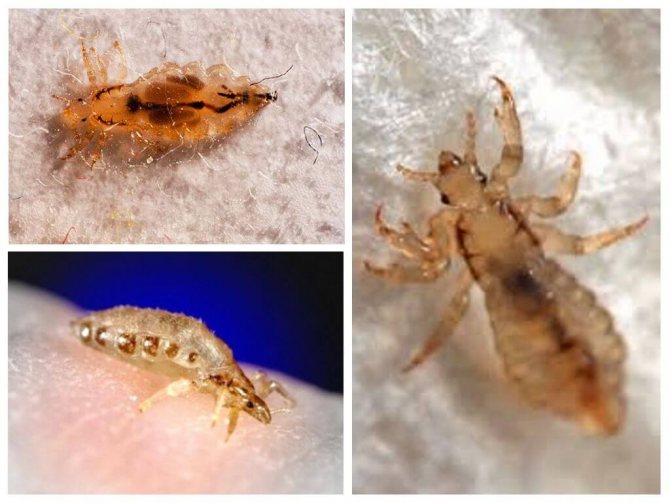
The human louse is a small insect that leads a parasitic lifestyle and feeds on its blood. The body of the parasite reaches 1.5-2 mm and has a grayish color. A satiated pest takes on a dark brown hue.
Insects of this species are dioecious. Females differ in both internal structure and appearance:
- females are much larger than males, have a bifurcated abdomen at the end and a special spur on their hind legs;
- males are distinguished by a rounded abdomen and the presence of a claw-like outgrowth, due to which males hold their partners during mating;
- in the almost transparent abdomen of the female, spherical nits can be seen, in males, the copulatory organ is noticeable;
- the internal structure of the female and male genital organs is discernible only under a microscope.
Types of lice in humans
Scientifically, there are only two types of lice that parasitize the human body. Lice are considered picky bloodsuckers regarding the choice of their host, unlike many other insects, for example, fleas. Representatives of all species of the suborder of lice live exclusively on one specific species of animal: human - on humans, canine - on dogs, etc.
Therefore, if we talk about what lice are in humans, then infection is possible with only two species - human (Pdeiculushumanus) and pubic lice (Pthiruspubis). It is quite simple to distinguish them from each other in appearance.
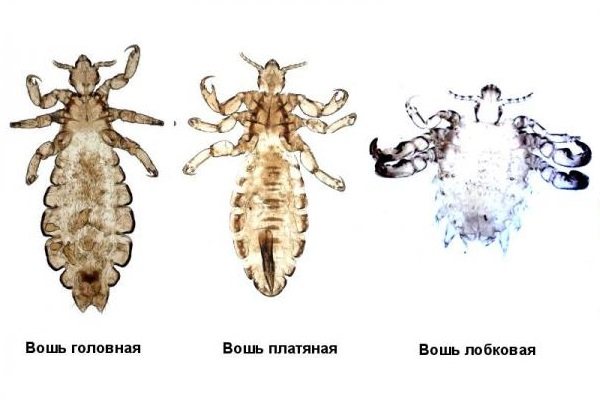

Human lice are of two subspecies - head lice and body lice. The former live in the hair of the head, the latter live in clothes. Since subspecies have their own habitat, the fight against them also has its own characteristics. This is the reason that there are three types of head lice:
- head;
- wardrobe;
- pubic.
How many lice live outside the head of a person
Based on the lifestyle and body structure of lice, we can say that, evolving, they are fully adapted to life on the human body. Modifications of the legs of insects led to the fact that with their help they can only deftly cling to the hair during movement. The mouth apparatus of insects is only able to suck blood. Lice are not able to eat other food.
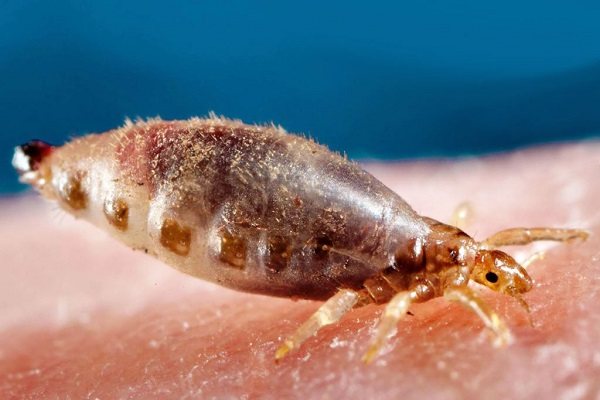


However, the most noticeable is the adaptation of the reproductive organs to the human body and hair: the female is able to lay nits in a sticky shell, and she does this, moving along the hair. As a result, after the egg is attached, it immediately finds itself on the scalp, where it has the opportunity to eat.
Another type of lice - clothes - do not live on the head, but they feel great living on clothes. On it, they mate and lay eggs. Body lice feed on, periodically crawling to the surface of the human body. Their legs are slightly different from those of head and pubic lice. With their help, they adhere well to any fabric surfaces.
How long do they live
The lice have a maximum lifespan of 2 months. Insect lifespan:
- head lice - 4 weeks;
- body lice - 46 days (female) and 32 days (male);
- pubic lice - 20 days (females), 22 days (males).
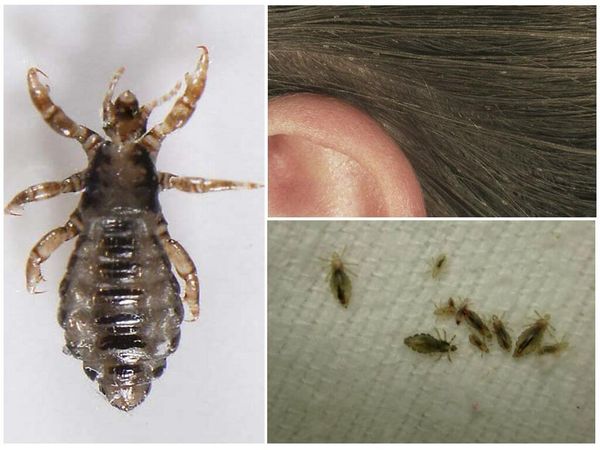


Lice can live in water for up to two days, and their eggs can live for 3 days. And without food, lice have a short lifespan - about 2 days. The hatched larvae, which do not have access to food, die after 12-48 hours.
The main
Pediculosis - what is it? This is a skin disease, the causative agent of which is a small insect (louse) that lives on clothes and skin. How the head parasites look can be seen in the picture.
The most common species is head lice. Their habitat is the scalp. Their life cycle is not long, but due to the fact that the parasite feeds on human blood and is able to lay eggs, the body can be significantly damaged. In addition, there is pubic lice.
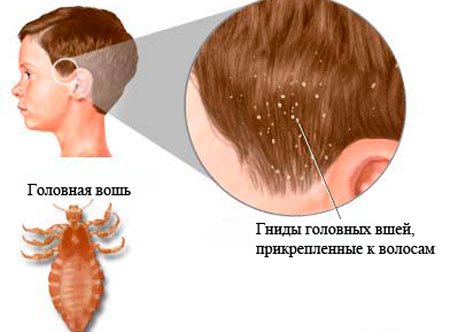

Pediculosis is characterized by an epidemiological form of spread. This is explained by the fact that the insect easily changes its owner and multiplies quickly. It should be noted that adult individuals move exclusively by crawling, while younger parasites are able to fly and jump, which simplifies the process of their spread.The infection routes are simple. It is enough to violate the rules of hygiene or to be in close contact with an infected person.
Life cycle
The head louse can live no more than a month. During its life, the insect lays about 300 eggs. The life cycle of a head lice includes:
- fertilization;
- laying eggs.
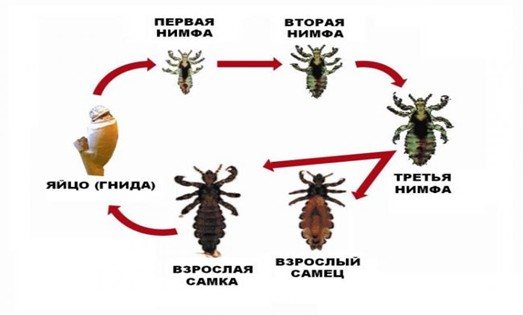
Lice development stages:
- nits;
- larvae;
- nymphs;
- adults.


Development of special
Insect eggs are called nits. An adult lays nits, which are attached to the hair with the help of a substance - chitin. Nits ripen to larvae. The development cycle lasts for four to thirteen days. After that, the head lice are ready to breed. However, more often the nits of the larvae are empty.
The developmental cycle at the stage between the larva and the adult of head lice is a kind of molt. After the third change of the chitinous cover, the microorganism becomes an adult and is capable of full reproduction. Read more in the article "The incubation period of head lice."
What a head louse looks like can be seen in the photo.

Development cycle
Absolutely everything about head lice is unknown even to scientists, since it is an ancient disease that has been observed in mankind for many centuries. But in the modern world, due to the increase in the level of hygiene, pathology is much less common than in ancient times.
Conditions under which lice breed
Reproduction of head lice occurs in fairly limited temperature ranges. Their nits stop developing at temperatures below 22 ° C and above 45 ° C. The optimum temperature for the rapid development of the life cycle of the head lice is 30-31 ° C.
Head lice reproduce as quickly as possible with a large number of them on the head, when females and males do not have to search for each other for a long time. These parasites are species-specific, that is, they cannot infect a host other than humans and some species of monkeys very close to it.

It is believed that lice breed with the greatest speed in places where a large number of people live together. They were a huge disaster during the wars and people living in barracks.
From larva to breeding
When the nit is ready for independent life, it opens and the larva of the first stage emerges from it. After she makes the first independent nutrition in her life, molt will come. After molting, the larva will turn into a nymph. Nymph is a condition of a newborn pest in which there are no visible differences from an adult. Nymphs are inherent in only a few species of insects, most of them are absent. Sexually mature lice are called adults. The nymph louse is the same adult, but in a smaller size. The cycle of development and life of the parasite is so short that it contains 3 transformations of nymphs.
Parasites molt for the reason that their shell cannot grow together with soft tissues. Not being able to fit into her "shell", the nymph gets rid of it.
When the louse molts for the third time, it is ready to breed. Every day 2-3 eggs are produced and up to 150 eggs are produced for the entire life cycle.
The process of hatching of the larva is peculiar. When she is ready to "go out into the world", she pierces the lid of the nits with her sharp jaws. But she is not able to get out of the case on her own. During this period, she has a process of active breathing. The larva inhales air through the mouth opening and exhales through the anal opening. Thus, air accumulates in the back of the bag. When there is a lot of him, he simply pushes the newborn out of it. Once in free space, the parasite immediately begins to feed.
The cycle of rebirth of each louse is conventionally divided into periods. The first is the development of nits, which takes 5 to 8 days. It takes up to three days to transform into an early nymph. The development of an early nymph takes place over 5 days. The next 8 days, an older nymph develops.A sexually mature louse lives for a month (in the record case, one and a half). During this time, the insect constantly reproduces with a stable offspring daily. This is due to the favorable conditions with constant food.


Further life cycle
Development process details
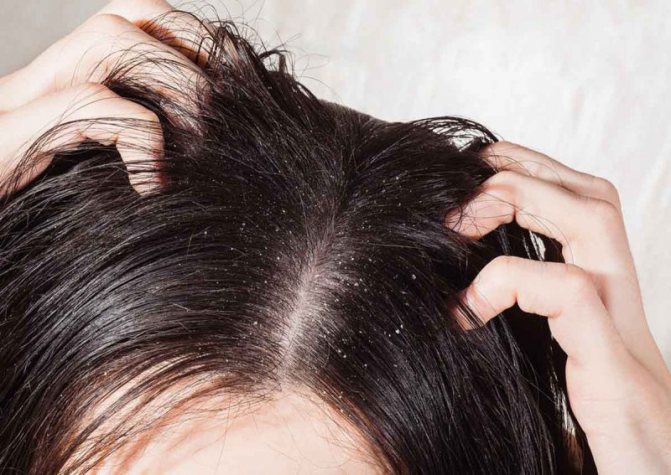


The nit is unable to immediately leave its egg. With the help of her jaws, she makes punctures in the lid, but she will not be able to get out in this way. In order to leave the shell, the nit begins to breathe actively. The resulting air exits through the anus of the insect, accumulating at the bottom of the egg. When there is enough of it, it simply pushes the nit out.
Once on the skin, the larva can begin feeding, followed by molting and transition to the nymph stage.
How quickly lice on a person's head can multiply:
- Nits are formed in 5-8 days.
- After hatching, the larva becomes a nymph in 2-3 days, and sometimes even in a day.
- 5 days pass before the transition to a nymph of the second age.
- The nymph of the third age appears after another 8 days.
After that, the louse becomes a full-fledged adult. It usually dies in about a month, but the longest recorded lifespan for a mature louse is 46 days. Mating with males occurs already in the very first hours from the moment of transition from the nymph stage to the adult.
How to get rid of lice and nits
At home, you can easily get rid of lice and nits. At the moment, there are many modern chemicals and medicines, as well as all kinds of folk remedies for fighting lice.
- External pediculicidal agents Medicines for the treatment of pediculosis are produced in the form of: shampoos (Sumitrin, Pedilin, Paranit, Parasidosis, Veda 2, tar shampoo, Nit fries, Nix, Nok, Khigia),
- emulsions and suspensions, (Medifox, D 95, Medilis-Super),
- aerosols and sprays (Nyuda, Paranit, Para Plus, Lavinal, Pedikulen Ultra),
- solutions (Full Marks),
- creams (Nyx, Nittifor),
- ointments (Nittifor, boric ointment),
- lotions (Medilis bio, Fenotrin, Nittifor, Parasidosis, Paranit, Paranit Sensitiv),
- hellebore water, which is an alcoholic tincture of the roots and rhizomes of hellebore Lobel.
Many effective remedies are toxic. In addition, after treating hair with anti-lice products, it is necessary to comb out the remaining nits with a frequent, preferably metal comb, using oil for ease of combing and healing of wounds on the skin, if any.
- Head lice pills
To get rid of head lice, you can use tablets that are sold at a pharmacy. Insects die by sucking on the blood of a person taking the medicine. With drug treatment, you need to know that many drugs have contraindications, such as pregnancy, lactation, childhood, allergies, respiratory diseases, etc.
- Folk remedies for lice
There is a wide range of folk remedies for lice: from shaving the head to the use of kerosene, tar and laundry soap, dichlorvos, vinegar, cranberry and lemon juice. In recent times, even DDT powder (dust) was used, which is currently prohibited due to its exceptional harm to humans. When using these funds, you need to remember about allergic reactions and the possibility of burns with kerosene, vinegar and dichlorvos.
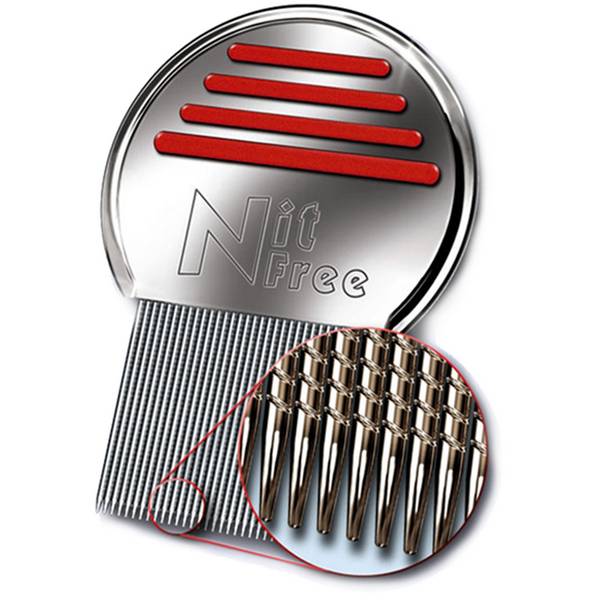


The methods of dealing with different types of lice also differ:
- Head lice
The head is carefully treated with a drug, and then the lice and nits are combed out of the hair.
- Pubic lice
Nit control methods
It is quite possible and even necessary to destroy and poison the nits at any stage of their development. For this, special shampoos with effective insecticides are usually used - Pedilin, Parasidosis, Nittifor, Pedex, Khigia.Earlier, even kerosene was used against lice, but in terms of efficiency and ease of use, of course, it is significantly inferior to modern shampoos.


It is important that even after cutting, the head must be washed with shampoo and held under a plastic bag, since nits and lice themselves can remain on the skin and near the hair follicles. And when using a shampoo that does not have the ability to kill lice eggs, you need to rinse your head with it again after 5-6 days.
And of course, always and everywhere it is necessary to observe the rules of hygiene: do not dry yourself with someone else's towel, do not use someone else's comb. It is known that head lice can survive in water for up to two days, so even swimming in public places can be fraught with danger.
Be carefull!
What is important to know about lice in order to successfully get rid of them
Lice control
Pharmacies now sell a large number of shampoos that use insecticidal ingredients.
They actively affect the lice, leading to their weakening and death. In addition, there are a number of folk remedies. Some of them are more effective, some are less effective.
However, no matter what means you use ("grandmother's" or pharmacy), most likely, a single treatment will not help you. Lice are very resistant even to special poison.
After thoroughly washing your hair with an insecticidal shampoo, experts recommend using a conditioner or balm.
That is, moisturize the hair as much as possible and make it smooth, so that the process of combing out the lice is easier.
Unfortunately, only mechanical action will help get rid of lice eggs. If you are not ready to shave your head, you will have to get a special comb.
There are also some nuances here. Some people try to use conventional combs with fine, fine teeth. However, they are not suitable.
Video:
The fact is that a serif system is used on the teeth of special combs, which allow you to comb out everything without damaging the hair itself.
To make combing easier, experts recommend using a vinegar solution first.
For him, the table version of vinegar is diluted in a ratio of one to two with water. Thus, the concentration should be 4.5 percent.
Vinegar is able to dissolve the very layer of glue that allows the lice to anchor the egg.
It is enough to moisten the hair with the solution and hold it for about forty minutes. After that, you can start combing.
How to comb out nits correctly is shown in the video below.
By the way, if you had the courage to shave your head, or if we are talking about a small child who does not care too much about his image, do not forget to rinse your head with the same insecticidal shampoo after a haircut.
This will save you from a possible relapse, probably destroying all the lice and their waste products.
Pediculosis is classified by specialists as an infectious type of disease. There are a number of measures available to prevent the infestation and spread of lice.
Video:
Today there are a large number of remedies that are able to eliminate lice, but it is best to start treatment as soon as you notice the parasites on yourself.
Do not forget that if lice are on your head for a long time, you can become the owner of allergies or dermatitis.
For the treatment of such diseases, much more serious drug therapy will be required.
Egg cycle
Louse belongs to insects with incomplete transformation. In her life, there is no stage of the larva, which differs in appearance, nutritional characteristics.
Patients are always interested in the question of how many eggs one louse lays, since the infection occurs very quickly. An adult begins to produce offspring a few hours after mating. From 2 to 4 eggs appear daily.
Breeding lice is a fun process.The seminal fluid of the male fertilizes all the eggs of the female. One mating is enough for the female to lay eggs for her entire short life. The female no longer needs a partner to produce offspring continuously, which is why females lay so many eggs.
The louse fixes the eggs - nits at the base of the hair roots. At a distance of 1 cm, by the location of nits on a hair, you can determine how long ago the eggs were laid. Initially, sticky mucus comes out of the lice's genitals, followed by an egg. The substance hardens, provides reliable fixation to nits. It cannot be removed when combing with a regular comb, washed off with shampoo, other hair care products, which greatly distinguishes nits from dandruff.
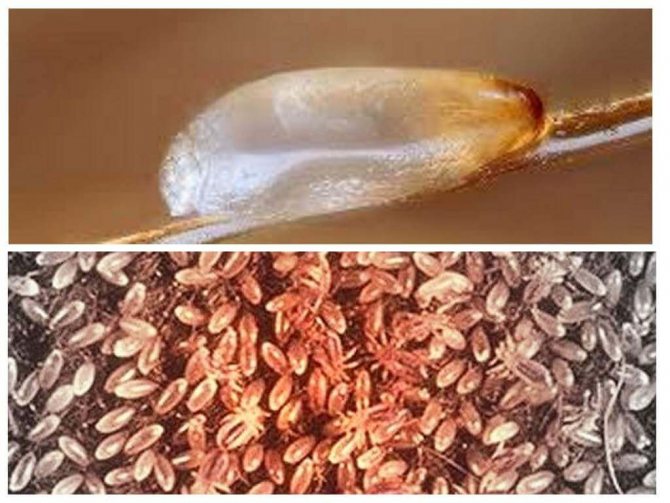

Nits
Interesting!
The shell of nits is so dense that no insecticide passes through. The larva develops safely after a “heavy attack”. The only method of dealing with the larvae in the shell is by combing out the nits. For these purposes, use a comb with a fine step or a special lice comb.
Symptoms
Head lice make themselves felt as early as the first day after infection. Insects are fed through a bite, from which the first signs of the disease appear. The symptoms of head lice in an adult and a child differ only in the intensity of their manifestation.
To know how to identify head lice, you need to study the signs of its occurrence. It manifests itself as follows.
- Itching. After the head louse hits the skin, it begins to move and feed, by biting, such actions provoke itching and irritation of the skin. In addition, in the process of feeding and emptying, parasites secrete substances that also cause severe itching. The patient constantly scratches his head, causing additional damage to the epithelium and creating conditions for the development of infection.
- Rash. If head lice accumulate in one area, then the skin is much more injured. This leads to increased itching, red spots and induration. In the case of an additional action of the infection, erosion or a purulent process occurs.
- Pigmentation. Similar signs are observed if chronic head lice progresses. With the constant presence of parasites on the skin, small blue pigment spots form. They then merge and can cover a large area.
- Detection of nits and individuals. A clear symptom is the identification of eggs of parasites and their individuals. Nits can be found along the entire length of the hair. They are grayish in color. Adult insects also move along the surface of the hairline. Sometimes you can see the head lice jumping over.
- Psychological condition. The patient, under the influence of constant itching, begins to develop insomnia, irritability, depression and weakness.
If signs of head lice are observed, then it is better not to start treatment on your own, but to consult a pediatrician who will establish methods on how to determine head lice. Only after confirming the diagnosis can therapy be started.
Modes of infection and signs of lice
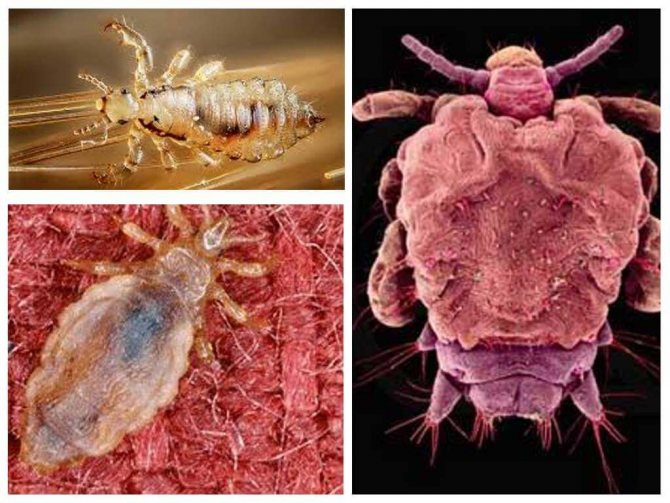

Lice types
There are several types of lice:
- head lice;
- pubic ploshchiki;
- body lice.
By themselves, they cannot appear, since the parasites lack wings. Therefore, the only way of infection is contact. Pediculosis can be contracted in various situations, the most common are the following:
- a trip in a crowded city transport;
- visiting public places: swimming pool, sauna, hairdresser, gym and other organizations;
- in a kindergarten, school, hospital or hotel;
- direct contact with a person infected with lice or household items.
These factors indicate that unsanitary conditions are not always the cause of infestation with lice and nits. Insects prefer to live on healthy, clean hair.
The incubation period of head lice is not a pronounced course of the disease without typical symptoms. It largely depends on the degree of infection and ranges from 6 to 12 days. If the number of lice is small and the sensitivity of the skin is weak, then the patient may not feel discomfort for a long time. However, the primary insensible infection is dangerous because the lice have the ability to reproduce quickly, releasing nits incessantly.
The main symptoms of head lice include the following phenomena:
- intense, debilitating itching of the scalp;
- small spots of a grayish-bluish color on the skin;
- multiple scratching, contributing to the development of acute dermatitis;
- the appearance of inflammatory papules at the bite sites;
- the presence of nits in the hair.
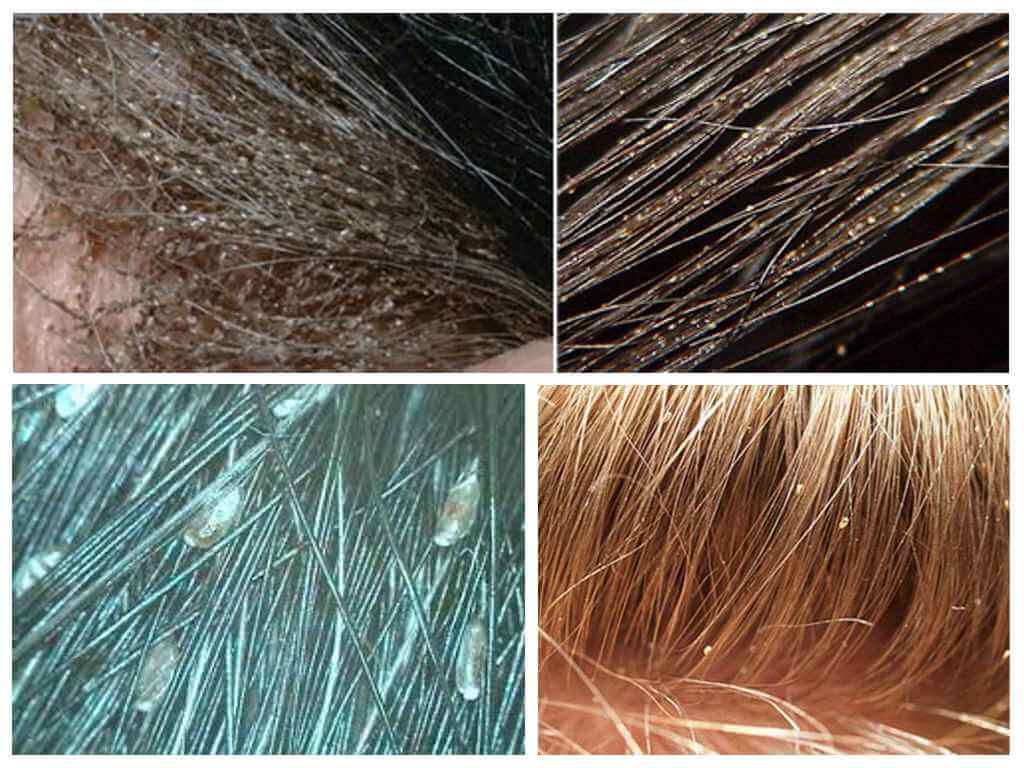


Lice in hair
With advanced forms of the disease, signs of anemia can be recorded in a person, the hair takes on an untidy sticky appearance with a specific putrid odor. How lice and nits look in the hair is shown in the photo.
Important!
During one meal, the parasite absorbs up to 5 mg of blood, injecting saliva with a special enzyme into the wound, which prevents its clotting, with a slight infection at first, lice bites remain unnoticed.
Parents often ask the question - where do lice come from in children. The answer is quite simple - babies often exchange clothes or hats, use other people's hairbrushes, as well as other personal belongings. Children are almost constantly in contact with a large number of people in kindergarten, school, summer health camps or just in the yard. In order to avoid the spread of parasites, it is necessary to examine the child's head as often as possible, and when the first signs of the presence of lice and nits are detected, a comprehensive treatment of head lice should be carried out for all family members.
Treatment
There are many popular methods for getting rid of lice quickly. But head lice in children and adults has some differences, in this regard, not all "grandmother's" methods can be used to eliminate parasites from the head of a child.
The symptoms and treatment of lice infestation are related. After the destruction of insects, the symptoms gradually disappear. But to restore the skin, a number of procedures are required.
How to treat the disease can only be determined by a pediatrician (therapist). You can not start self-medication without his consent. Folk remedies for head lice can have a side effect or exacerbate existing pathologies. So, for example, the well-known "grandmother's" remedy - dust, destroys insects, but can cause toxic poisoning of a child. Therefore, when diagnosing head lice, it is better to trust a specialist.
Incubation period
Nits
The incubation period for nits is usually around eight days, depending on the ambient temperature and the availability of food. In winter, the development of nits is suspended, and the entire breeding cycle takes months..
Under optimal conditions, the number of lice grows exponentially, reaching hundreds a few weeks after infection. It takes 15 days for a nit larva to become an adult capable of breeding.
Lice
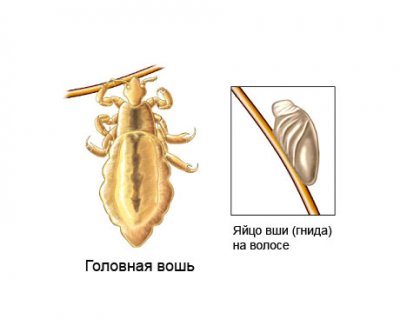

You can only get lice from another person. Lice cannot fly and jump, but they crawl very quickly. The speed of movement of the insect is 23 cm per minute.
Learn more about the types of lice in our article.
Therefore, being at a great distance from the patient with head lice, it is impossible to get infected, but it is enough to approach the infected person just for a moment, as an agile louse will jump over to a new owner.
Most often, infection occurs in crowded places. Also you can get infected through clothing and personal belongings... There is an opinion that all diseases are caused by nerves, and head lice is no exception.
Of course, a nervous breakdown cannot be the cause of lice, but a person under stress is more prone to developing head lice.It has been speculated that the smell generated by the adrenaline rush attracts insects.
Lice are spreading especially rapidly in children's groups. IN kindergartens and schools often experience head lice epidemics... Children in the process of playing very often come into close contact and use each other's things.
In addition, about head lice in children, read our articles:
There is no incubation period for head lice. An insect cannot live more than one day without food. and therefore immediately begins to bite the newly found victim. A person may not feel the bites of one or two parasites. Immediately after infection, it is quite difficult to detect head lice.
It will take about a month, as there will be severe itching, irritation, a feeling of tightness of the skin, since by this time the lice will already have offspring. Thus, head lice symptoms appear several weeks after infection.
Understanding the characteristics of the reproduction of lice in humans on the head helps to realize the need for immediate treatment of head lice.