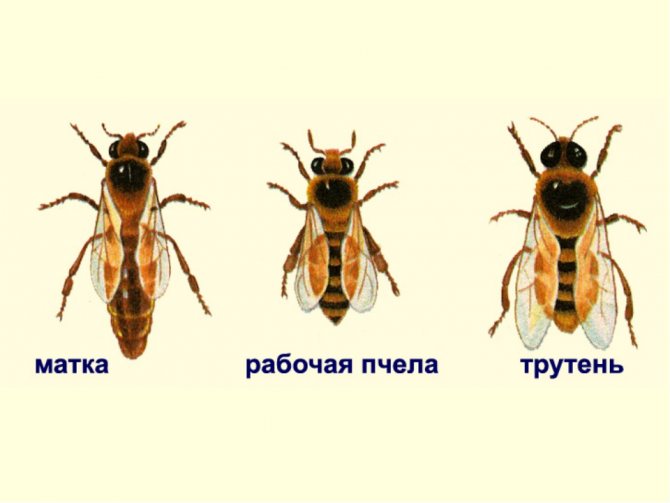
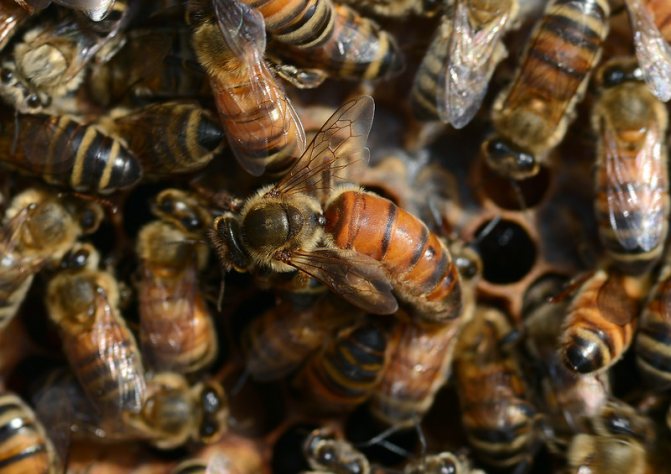
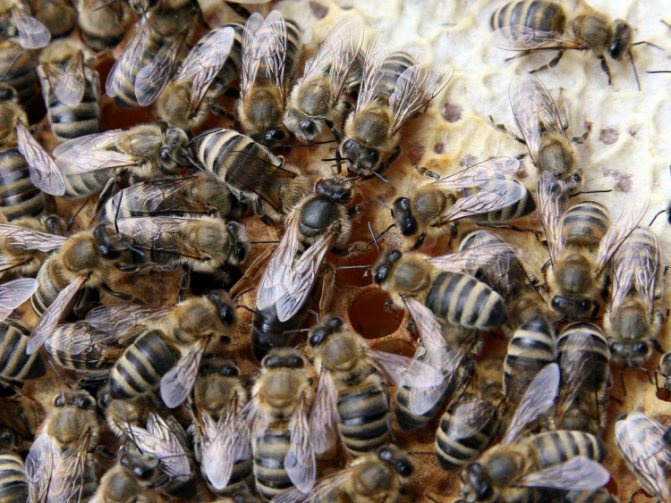
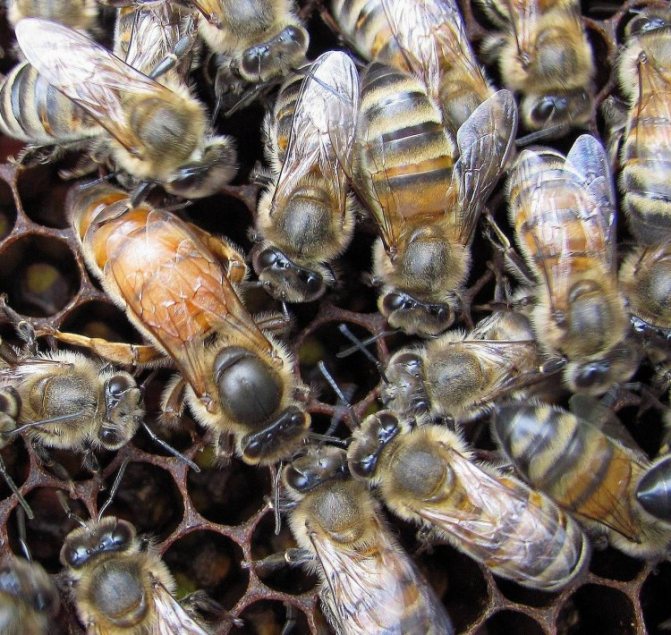
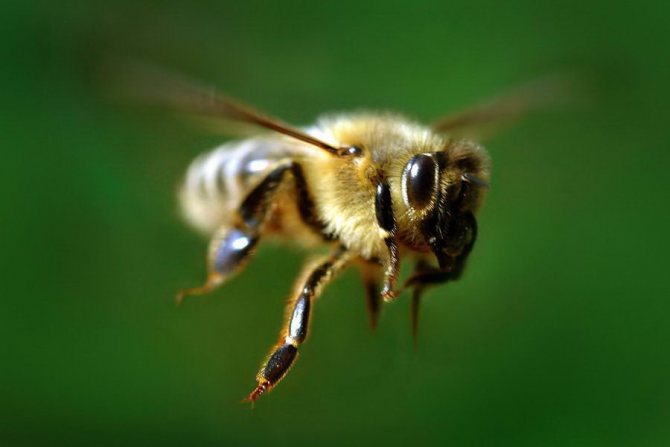
Bees are social insects, with a well-polished way of life and a clear distribution of roles. The life of a family of bees is impossible without a queen - a queen, reproducing more and more generations of little honey workers. Let's take a closer look at what the queen bee does, what a queen bee looks like, and find out if the bees can live without her.
What do bees eat?
Worker bees collect pollen and nectar from flowers of various plants. The pollen adheres directly to the bee's body, to all its hairs, including the inviting ones, the nectar is transferred to the goiter, where it is partially transformed into honey. In the goiter of a toiler, an enzyme called invertase is produced, which separates nectar into cane and fruit sugar, but this product is not final. On the way to the hive, part of the nectar, from 20 to 40%, is spent by the worker bee for recuperation, which is its main food.
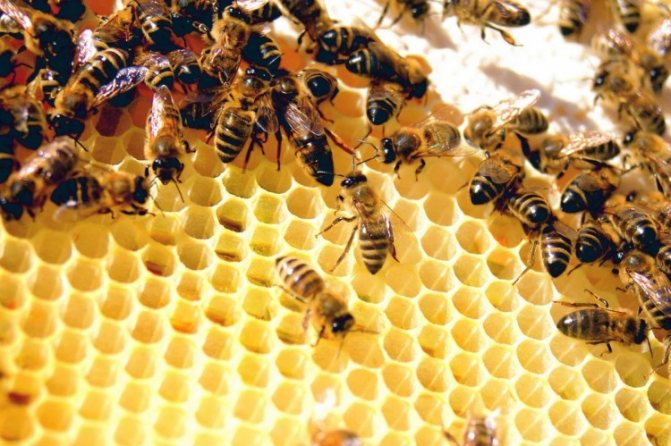
Having reached the hive, the insect hangs a drop of partially processed nectar on the top of the honeycomb cell. If the nectar contains a large amount of water, then it begins to evaporate quickly, which is why the bees have to ventilate their own dwellings well. They do this by actively moving their wings. Fermentation processes continue in the nectar at this time. With a moisture content of 20% in nectar, it is almost ready-made honey.
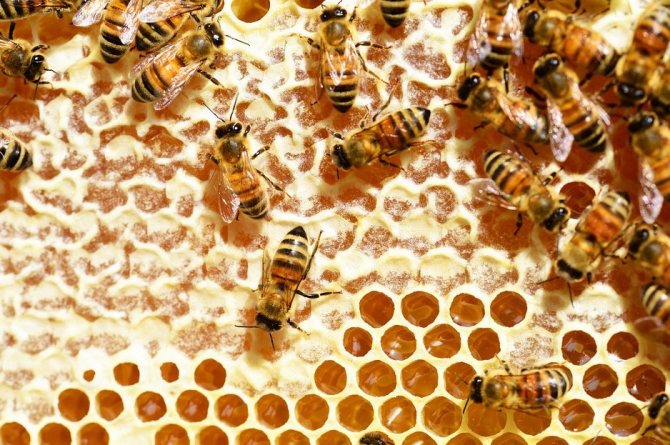

Once this moisture threshold is reached, worker bees seal the combs with a thin layer of wax released from their own little bodies. In sealed combs, honey reaches the required condition. Bees create this material in the summer to provide their families with food for the winter. To feed babies, bees use royal jelly, bee bread or bee bread, as well as liquefied honey. Royal jelly is given to the larvae in the first 3 days of their life after hatching from eggs.
Did you know? It takes 2 minutes for the feeding bee to feed one larva. 15 sec.
Milk is secreted by nurse bees (a separate class of worker bees) from special glands located near the mouth. Each of these bees takes care of several larvae of the same age. Perga is pollen compacted into honeycombs, subjected to lactic acid fermentation with the addition of bee saliva, covered with honey and sealed with wax. The substance contains amino acids, enzymes and protein necessary for the full development of the brood.
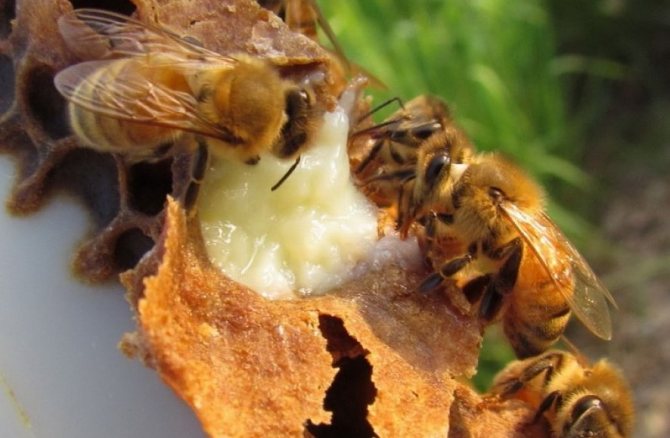


A small part of the bee bread is located in the immediate vicinity of the brood. The bulk of the bee bread is in the lower part of the nesting compartment. If in the spring there is a sufficient amount of bee bread in the nest, the queen begins to worm immediately, which makes it possible to grow a full-fledged new offspring of working bees before the first honey collection. If the bee bread was completely eaten during the winter and in spring it is not in the nest, the uterus does not lay eggs, but waits for the appearance of new pollen.
Important! Top dressing in the spring and summer is carried out in a non-tipping period.
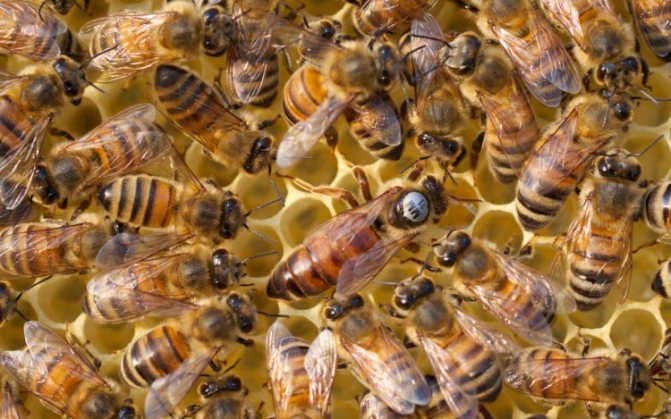
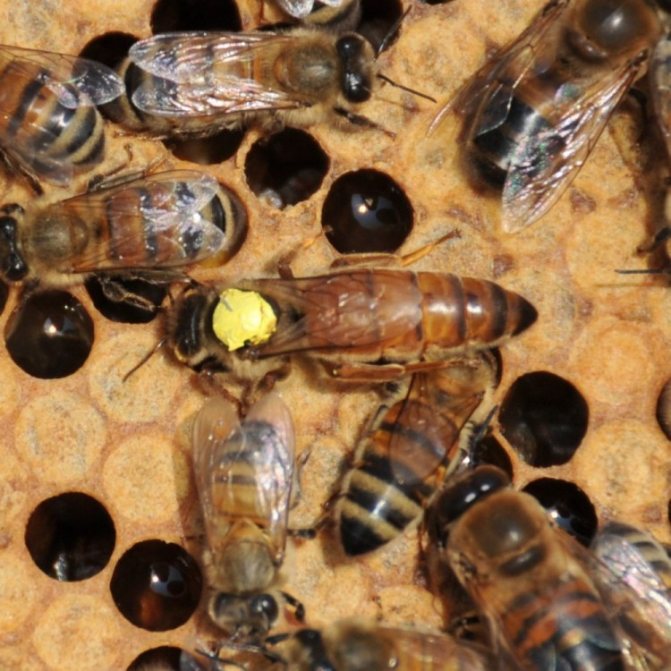
A small number of cells located next to the brood are occupied by water. These stocks are not global, but they are sufficient to maintain optimal humidity in the hive and to liquefy the honey intended for rearing the larvae.The queen is also in the care of worker bees. Initially, she feeds on royal jelly, and a little later she begins to get honey on her own from the sealed honeycombs in the hive. Young drones are fed by worker bees for the first 3 days with royal jelly, then bee bread and honey.
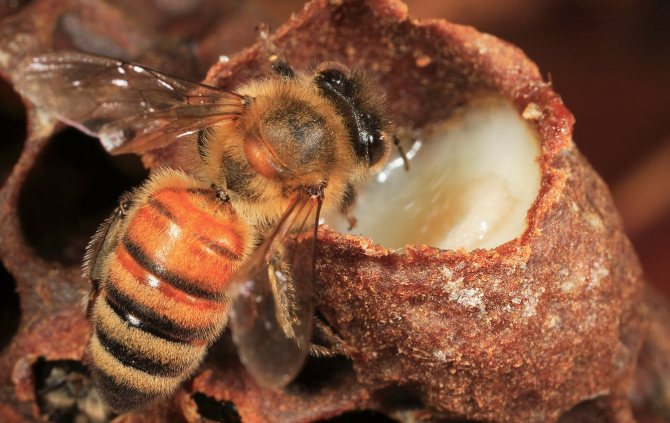


When the male grows up, he begins to independently remove honey from the combs. Gathering honey in the goiter, the male in the summer can make 3-4 flights per day, returning home with a completely devastated goiter. Drones can eat in the summer not only honey harvested by their own bee family, but also fly into other people's hives to eat. Guard bees in the summer launch all the drones into the hive indiscriminately, which gives them the opportunity to feed when they please.
You will be interested to know what royal jelly heals.
Buckfast bees
Families of this breed are also highly productive. They are bred mainly in Ukraine and Belarus. Buckfast queens are capable of laying simply a huge number of eggs, and therefore such colonies never lack working individuals. It is advisable to have bees of this breed, including when the honey harvests are far from the apiary. Working Buckfast individuals can fly very far in search of nectar. The disadvantage of this breed is generally considered only instability to cold. In the northern latitudes and even in central Russia, breeding the buckfast variety is unlikely to be successful.
The uterus of this breed can weigh up to 260 mg. Despite its instability to low temperatures, Buckfast is considered the best bee species today.
Preparatory work before feeding
Before applying top dressing, all frames with low-quality honey (honeydew, quickly crystallizing) must be removed from the nests. Before opening the nest, you need to calm down the bees, for which they use smoke. The main thing is not to overdo it with the "sedative" - a large amount of smoke causes aggression in bees. It is better to choose a sunny, calm day for feeding.
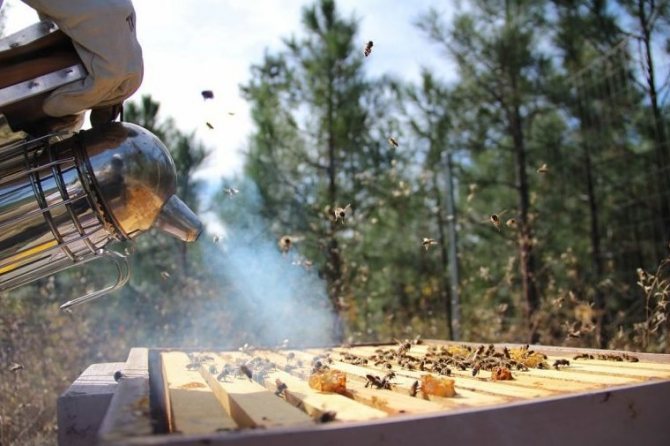


Because in cloudy, windy or rainy weather, even with the help of smoke, it is difficult to restrain insect aggression. First, smoke is allowed into the entrance - literally 2-3 portions, then, when the insects have drunk a little honey, after about 10 minutes, remove the lid and fumigate the hive from above.
Carpathian bees
This breed is bred mainly in Ukraine in the foothills of the Carpathians. The main distinguishing feature of such a species as the Carpathian bee is its adaptability to short summers and frequent rains. These families also endure frosty winters well. The queen of the Carpathian bee lays eggs, including in the fall. And therefore, families leave in the winter rather big. The weight of the uterus of this breed can be up to 205 mg.


Rules and features of bee feeding
Feeding with sugar syrup is perceived with hostility by many domestic beekeepers, while foreign colleagues actively practice feeding with sugar.
Top dressing carried out on time makes it possible to:
- avoid swarming of bees during the period without tipping;
- eliminate problems with lack of food in winter;
- to increase the strength of the bee colony before leaving for the winter;
- to carry out prevention of diseases and parasites dangerous for honey bees.
Important! It is always necessary to clearly track from which plants honey insects collect food and adjust their diet. For example, rose hips, lupines and poppies produce only pollen.
Spring feeding begins to be carried out as soon as the inhabitants of the apiary begin to fly out of the nest and fly around in search of food. In summer, feeding is carried out in mid-July - mid-August, when there is only pollen on the flowers, but no nectar. And this naturally allows the bees to properly prepare the sugar syrup and make themselves stocks for the winter on time. The optimal time for feeding bees with sugar syrup before hibernation is from August 25 to September 5.During this period, the weather is usually still warm, which makes it easier for the bees to process sugar. In winter, feed is added as needed.
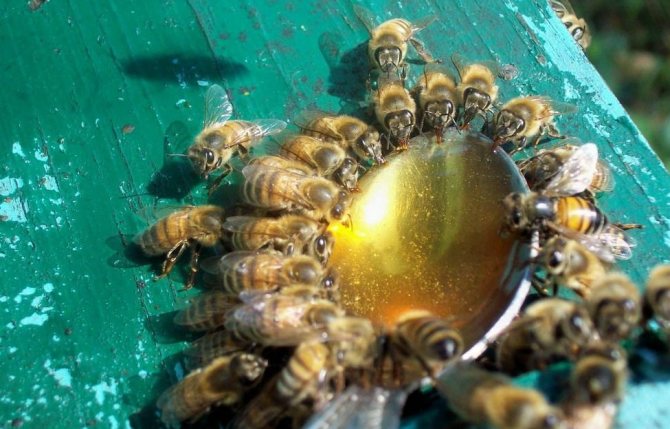


In total, there are 2 types of dressings that differ in their intended purpose:
- stimulating;
- the main one, replacing food when there is nowhere to get nectar.
Depending on the type of feeding, the thickness of the syrup will differ. For the main feeding, a thicker mixture is used at the rate of 1 liter of water per 2 kg of sugar. Sugar is added to boiling water and stirred until completely dissolved. The mixture is cooled to a temperature of + 35 ° C and then served in the hives. To prepare liquid syrup, a 1: 1 ratio is observed.
Important! All honey should not be left in the hive for the winter. Insects need free space to form a club.
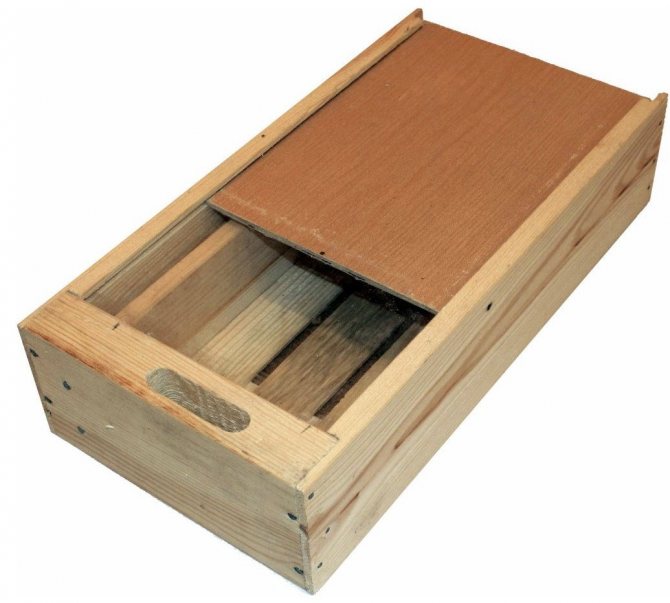


You can dissolve sugar in a similar way, adding it to boiling water, or exposing the mixture for the whole day in a well-lit place, stirring occasionally. The feed is placed in troughs. The most successful option that meets the requirements of quality and safety is a wooden feeder, which looks like a flat box.
Its device assumes the presence of 2 compartments:
- for feed;
- for the penetration of bees into the feeder.
If you put food in deep containers, you can lose most of the swarm, since the bees will drown in the liquid. Before use, a new feeder is poured with linseed oil, and the joints are worked out with wax. The feeder is placed on the frame directly above the bee's nest. The slot, which is the entrance to the feeder, should be located above a place that is freely accessible to insects.
For liquid feed, you can use a regular jar, closed with a plastic lid. Holes with a diameter of 0.8 mm are made in the lid. The jar is placed upside down in the hive. It is better to use a liter container - it will be more convenient to use.
Justified cruelty
In a bee family with a tinderpot queen, only young bees, which have never been flown around, can remain. Since there will be few bees, try to find a tinderpot among them and kill it. After that, young bees can be shaken off into the nucleus, where all their “friends” have flown, without fear that a tinderpot will fall into a full-fledged bee colony, which you have reinforced with bees. But if you keep only one hive - one bee colony, then it will not be possible to save the bees if their queen is lost by the fall, since there will be no one to connect a queenless bee colony with. Therefore, I recommend starting several bee colonies at once: at least three.
TOOL FOR MASTERS AND MASTERS, AND HOUSEHOLD GOODS VERY CHEAP. FREE SHIPPING. RECOMMENDED - CHECKED 100% THERE ARE REVIEWS.
Below are other entries on the topic "How to do it yourself - a householder!"
- Collecting comb honey - directly into the jars (honeycomb body) Modernization of the bee hive to facilitate ...
- How to determine by eye how much a live pig boar weighs Determine the live weight of a pig on ...
- What to do to prevent bees from swarming How to avoid bees swarming? Third decade ...
- Do-it-yourself frameworks with beeswax How to add bee frameworks If in ...
- DIY art stone - photo How to decorate a garden with art stone ...
- How to clean the matrix of a digital camera with your own hands Cleaning the matrix of a digital camera Digital ...
- Do-it-yourself electric heating of a greenhouse - diagram Heating a greenhouse with an electric ...
Subscribe to updates in our groups and share.
Let's be friends!
With your own hands ›News› Queen of bees - photo and what it looks like and why it is needed
The specifics of winter feeding
Any invasions in the winter period are hard for bees and put their lives in jeopardy. In winter, it is quite difficult to carry out a full inspection of the nests and make a complete picture of the quantitative indicators of feed. In this regard, feeding is carried out for all families in which the feed was not enough initially. Winter feeding is carried out only if wintering takes place in relatively warm conditions. The minimum temperature at which it is possible to open the hive is + 2 ... + 4 ° С.
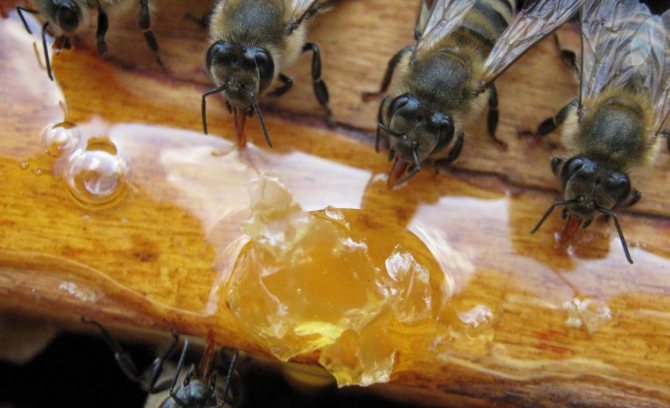


When wintering outside, before feeding, the hives are transferred to rooms where the air temperature is above 0 ° C. The most correct option is feeding with sugar syrup. Prepare it thick enough for 1 liter of water add 2 kg of sugar. Brown honeycombs are filled with syrup; for weak families, only one half of the honeycombs are filled. Prepared honeycombs are placed directly to the bee club. The procedure is best done together.
Step-by-step instructions for feeding bees in winter:
- Remove the hive cover.
- Unfold the canvas until you can see the bees in the extreme street. At this time, an assistant will be required to illuminate all frames with a lantern with a red light.
- Move all frames with quick precise movements to the extreme street to make room for the frame with syrup.
- Place the frame directly next to the club and slide everything as it was.
Learn about the peculiarities of wintering bees in a barn.
With a good dense filling, 1.5-2 kg of feed can fit in the honeycomb, which will be enough for a month. After this period of time, feeding is again carried out if the heat has not yet come. If the humidity in the hive is high enough, then feeding is carried out with the help of candi. It is made from honey and sugar. The consistency of the kandy should resemble a thick plastic dough. This feed will need 1 kg for a month. The kandy is pre-wrapped with gauze in 1 layer.
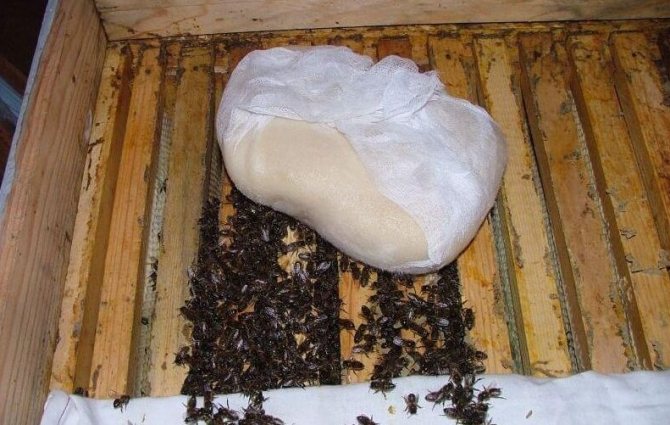


It is also placed directly next to the swarm. Frames with food for the winter are placed in the upper part of the hive. In winter, bees eat harvested products and move up. If frames with poorly filled combs are located in the central part, then in winter the club will begin to separate, scattering into different combs, which will lead to hypothermia of the hive. In winter, it is very important to add food frames on time.
Conclusion of queen bees
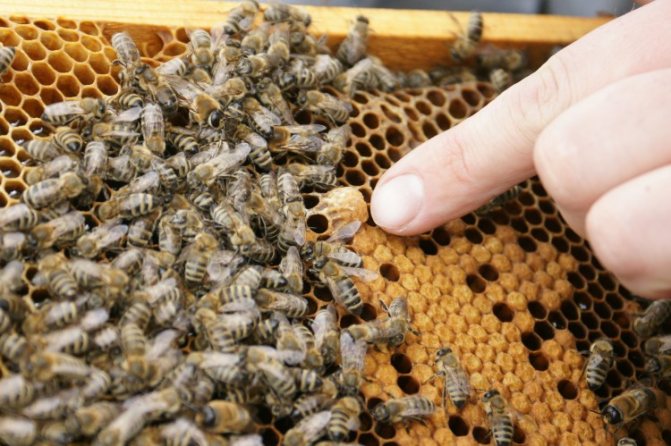
Beekeepers use 2 methods of hatching bee queens: natural and artificial. With natural hatching, bees build a queen cell in which an egg is laid. In order for an individual with reproductive abilities to appear from it, it is intensively fed with royal milk containing special hormones.
Artificial withdrawal uses 2 technologies. Most often, a method is used in which:
- open brood and the queen are removed from the hive, leaving only larvae and freshly laid eggs;
- the combs are cut from below (only in this case, individuals with reproductive abilities will hatch from the eggs);
- the queen cells are cut out and placed in the hives, and the queen bee is returned back.
The second technology is complex and rarely used: the larvae are transferred into wax bags and artificially fed with royal milk. However, thanks to her, it is possible to get very high quality and most prolific queens.
When removing queen bees, several rules must be observed:
- use only strong bee colonies;
- maintain optimal conditions for development (temperature at 32 degrees, and humidity - 75-90%);
- evenly distribute queen cells throughout the family in order to provide complete feeding;
- take into account the time frame using the queen bee hatch calendar.
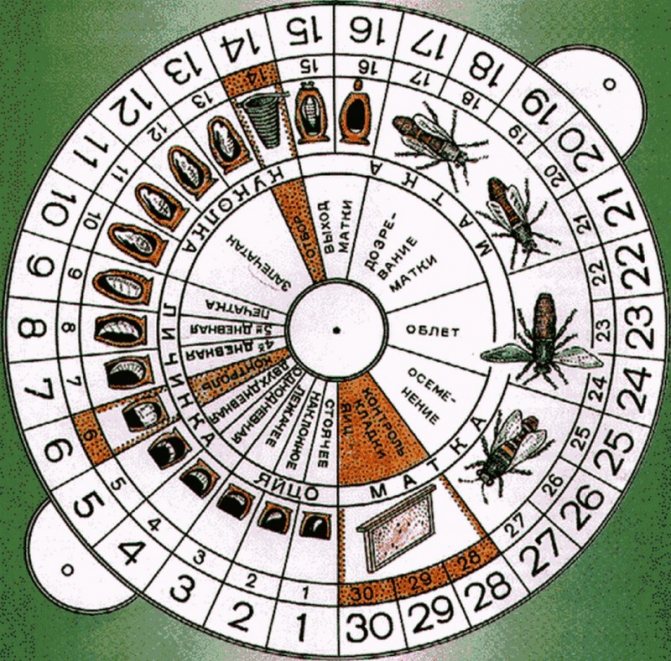

Calendar for the withdrawal of queen bees.
It is also important to follow a specific algorithm:
- Find strong, highest quality maternal and paternal families. The productivity of the offspring will depend on them.
- Select family educators and organize work with them.
- Control the appearance of layers, the process of fertilization of the female and evaluate the result.
How to calculate feed consumption
For a bee colony for the winter, you need to leave 20-30 kg of honey. Based on these calculations, it is decided whether to introduce additional feeding. In the hive, all 20-30 kg of honey products are not left - just as many frames are placed as there are honeycombs with bees.
We advise you to learn more about honey bees.
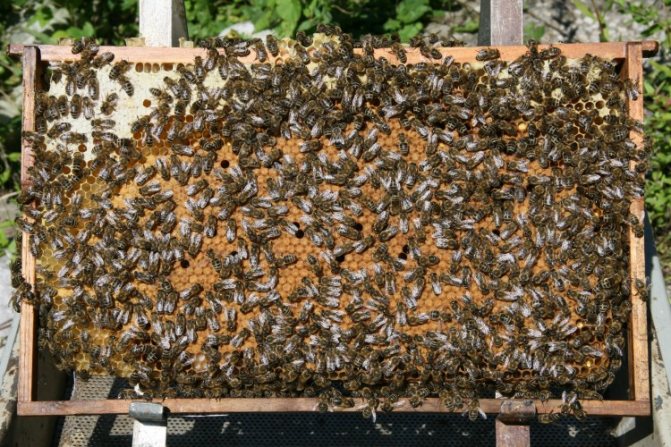
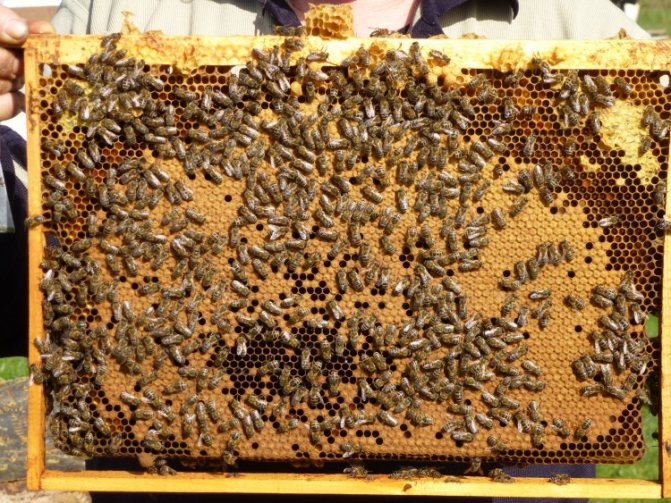
The number of food frames directly depends on the strength of the bee colony:
- strong - 8-10 cells;
- medium - 6 hundred;
- cores - 3-4 cells.
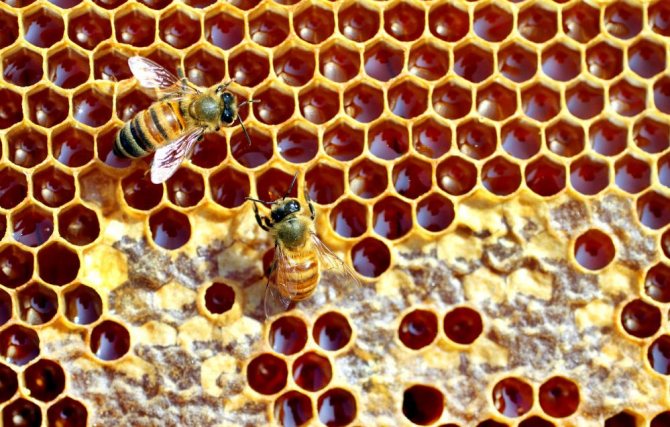


Each honeycomb contains on average 1.5 kg of honey or syrup.Accordingly, if there are 8–10 honeycombs left, 12–15 kg of honey remains in the hive. In this case, winter feeding is most likely not required. It will be possible to add combs with stored honey in early spring (late February - early March) in order to start the egg-laying process at the uterus. For brood rearing and their own nutrition in spring, bees will need 10–12 honeycombs, 2 of which should be with bee bread. At the time of the first spring bribe, 4 kg of honey should remain in the hive.
Constitutional monarchy in bees
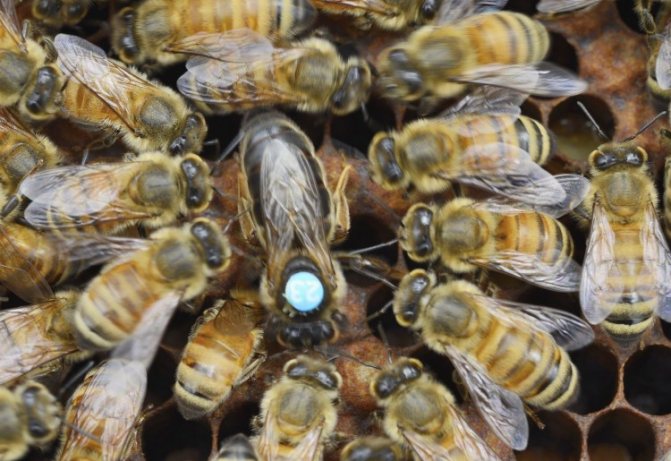
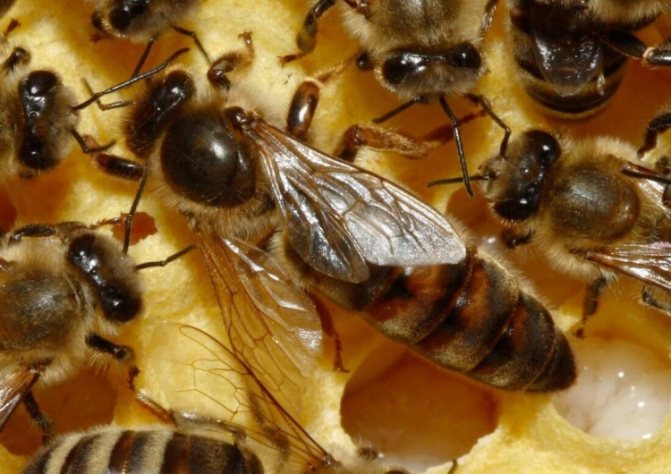
If we compare a bee colony with any enterprise where ordinary employees not only choose a leader themselves, but can also "re-elect" (get rid of) him at any time, then a queen bee is a leader in a bee colony who is controlled by the immediate environment.
If the queen is doing her job well before the "bee collective", then she will be surrounded by the attention of winged workers all her life. A retinue of bees will be “assigned” to it, which will take care of it: guard, clean it, if necessary, clean it up, feed it with high quality and render all kinds of honor to its “overlord”.
But even with such attention and care, the life of a queen bee cannot be called simple.
When is top dressing not needed?
Top dressing is not needed if the insects managed to stock up on a sufficient amount of high-quality honey - not crystallizing, not honeydew. In summer, if there are plants in the neighborhood that have bloomed for a long period, feeding with syrup will also not be needed. If there is enough nectar, then by the fall the workers store honey in surplus.
You will be interested in learning about the lifespan of a bee.
Then feeding is carried out only at the beginning of September in order to increase the fertility of the queen and form a large strong family with new working bees. To properly organize the care of the apiary, you must first of all know what bees eat in the wild. Accurate feed calculations and quality control can significantly reduce insect losses in winter.
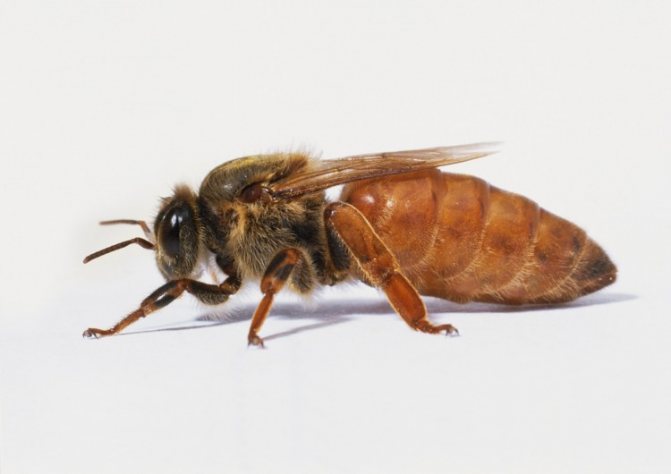
Flight of the queens
After the queen of the hive has reached puberty, she goes to perform the mating ritual. Often, the queen bee does not leave the apiary during the flight. After 7 days, the uterus flies around for mating. If mating for some reason does not occur during the week, then the queen remains infertile.
The drone that managed to catch up with the queen participates in mating; the whole process takes place in the air, in warm weather. If fertilization is successful, then the bee pulls out the genitals from the drone and returns with them to the hive to prove that mating was successful.
Attention! As a rule, mating is carried out only in warm, calm weather, in some cases it is possible to fly over the queens in September.
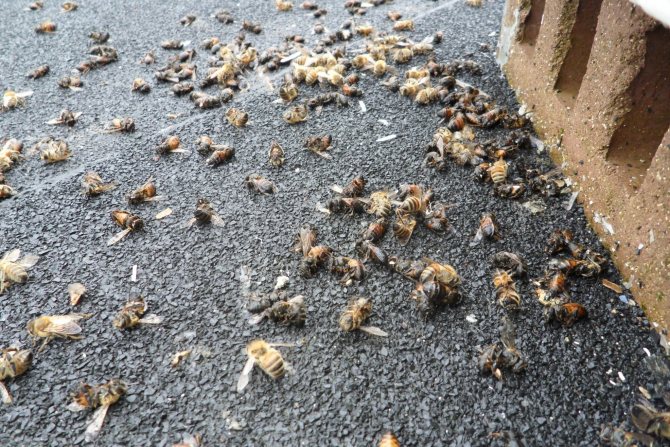
Colony collapse syndrome


0


0
Colony collapse syndrome was first described in 2006 in the United States. According to the World Bee Protection Fund, every winter in the United States, 30-35% of bee colonies die out. Since 1961, the number of American bees has halved, and the number of bees per hectare has dropped by 90%. Subsequently, the same began to be observed in several European countries: in Belgium, Bulgaria, France, the Netherlands, Greece, Italy, Portugal and Spain, and to a lesser extent in Switzerland and Germany. In Northern Ireland, a double decline in bee populations was reported in 2009. In Europe as a whole, 20% of bee families are lost every year, a similar trend is beginning to be traced in Latin America and Asia (possible cases of the syndrome are reported in Taiwan). The reasons for this phenomenon have not yet been fully elucidated, but there are opinions that it can be caused by a number of biotic factors, such as varroatosis and other diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms. In Europe, Varroa mites are blamed for the death of bees, which, having invaded the hive, infect the bees and their offspring.Scientists brought the tick to Europe from China and India, together with the wild Indian bee Apis cerana indica, on which the tick parasitizes. Since the 1980s, each of the apiaries of Eurasia can a priori be considered infected with the Varroa mite. The tick very quickly adapted to the chemicals used to kill it. After the treatment of the hives with insecticides, honey cannot be sold, and to replace the bee, which lives only 35-40 days, a new one will not grow out of the larva - the mite parasitizes on the larvae, destroying them (bee's milk is a great help in this - the saliva of a working bee which feed the larvae, allowing them to survive). Other reasons include changing environmental conditions, lack of food, and pest control using pesticides (eg imidacloprid). Since most of the dead bees are found in the fields (only a few of them are able to fly to the hive and already die there), there are good reasons to suspect that the bees were poisoned with chemicals used by unscrupulous agricultural producers to process fields (especially rapeseed). Kills bees and nosematosis, European foulbrood, American foulbrood, 19 strains of viruses that have not yet learned to cure, and hypothermia (especially in winter, in cold weather). It has been suggested that a combination of several factors may be the cause. The suggestions that the cause of the phenomenon may be the radiation of cell phones are groundless - in Japan, where the highest mobile network density, the syndrome is not observed. A viral infection may also be the cause. Today it is impossible to start an apiary near rapeseed crops - it is sprayed 2-3 times per season. The bees cannot stand this: at first they become angry, and after a month or two they leave the hive. However, the more typical harm from the neighborhood of bees with rapeseed crops is the unsuitability of rapeseed honey for wintering. A bee colony left for the winter with such honey dies in most cases.
Evolution of bees

0


0
Bees, like ants, are essentially a specialized form of wasps. The ancestors of bees were predatory wasps from the Crabronidae family. The transition from an insectivorous lifestyle to feeding on pollen was, most likely, the result of eating pollinating insects sprinkled with pollen. A similar evolutionary scenario is observed in the Vespoidea superfamily, one of the groups of which, known as the Flower Wasps or Masarinae, is now pollinated, but originally descended from a predatory ancestor. Today the oldest undoubted fossil of a bee is a find in Burmese amber "Hukawng Valley" (Myanmar) (described in 2006). The age of the find is about 100 million years (early Cretaceous period), the found species of bee is named Melittosphex burmensis and is a clear transitional form from predatory wasps to pollinating bees. The shape of the hind legs of M. burmensis is characteristic of carnivorous wasps, but the thick hairline is characteristic of the pollinating insect.
Swarming


0


0


0
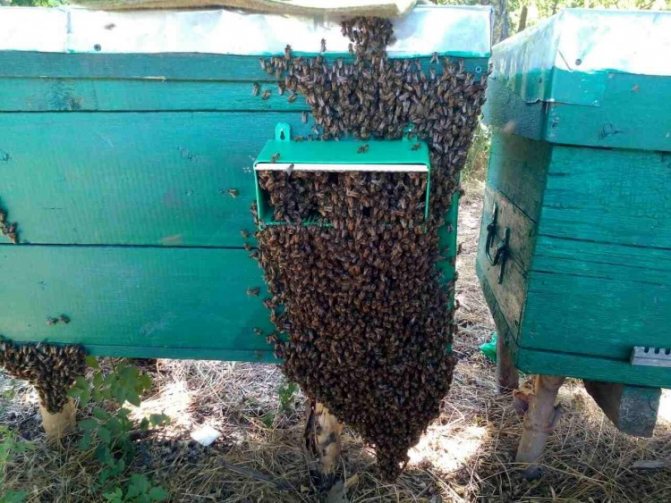
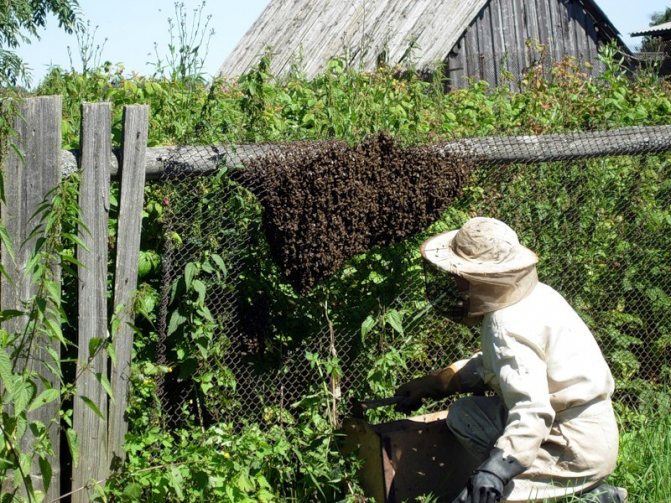
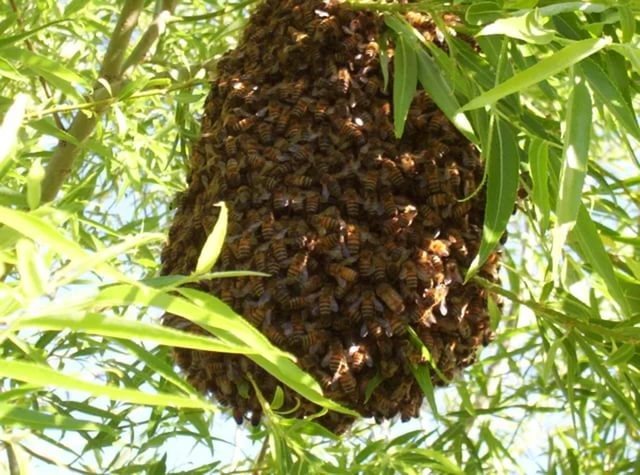
The bee swarm is a new family of honey bees, separated from the old family, which is called the mother. Each bee swarm consists of a queen (sometimes several queens), several hundred drones and tens of thousands of worker bees. A swarm of bees can fly 20 kilometers or more away from the mother's family. Swarming is a natural form of bee breeding. When swarming, the bees of the swarming colony quickly leave the hive, rise into the air with the attached queen, whirl for some time and "graft" somewhere on a tree branch. A bee swarm can weigh up to 7-8 kg, it consists of 50-60 thousand bees with 2-3 kg of honey in their goiter. In inclement weather, bees can feed on honey stock for 8 days.
Description
Bees are a superfamily of flying insects of the suborder Stem-bellied of the Hymenoptera order, related to wasps and ants. The science of bees is called apiology. There are about 20 thousand species of bees. The family of bees has more than 520 genera, the most important of which are: halictids, andrenides, melittids, real bees, stenotritis, colletids, megachylids. They can be found on all continents except Antarctica. Bees have adapted to feed on nectar and pollen, using nectar primarily as an energy source and pollen for proteins and other nutrients. Bees have a long proboscis, which they use to suck out plant nectar. They also have antennae, each of which consists of 13 segments in males and 12 segments in females. All bees have two pairs of wings, the back pair is smaller in size than the front; only a few species of the same sex or caste have very short wings, which makes the flight of the bee difficult or impossible. Many types of bees are poorly understood. The size of the bees ranges from 2.1 mm in the dwarf bee (Trigona minima) to 39 mm in the species Megachile pluto, which lives in Indonesia.
Getting honey


0
To get a spoonful of honey (30 g), 200 bees must collect nectar during the day during the honey flow. Approximately the same number of bees should be engaged in receiving nectar and processing it in the hive. At the same time, some of the bees intensively ventilate the nest so that excess water evaporates from the nectar faster. And to seal the honey in 75 bee cells, the bees need to allocate one gram of wax.















































