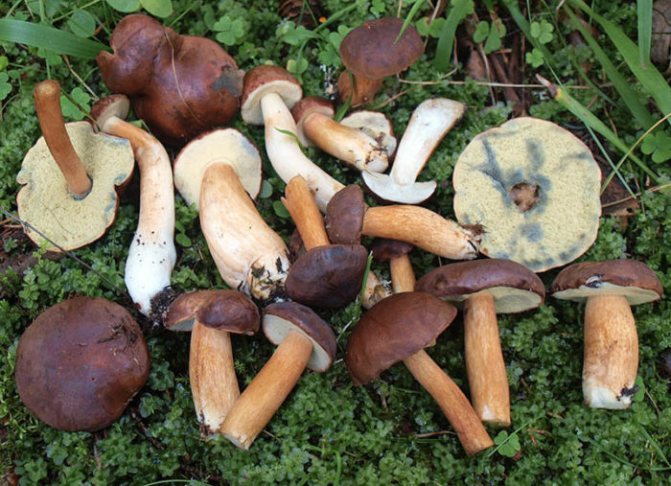
The Polish mushroom is a type of boletus, moss or Imleria. The name of the mushroom comes from the fact that in the past it entered the European markets from Poland. It is also called brown, pansky or chestnut moss. It is considered an edible mushroom, a delicacy that not everyone can afford. Contains a lot of useful microelements. It is not often found in nature. It grows in Europe and the Far East. It is an ingredient in many dishes. It is fried, boiled, dried, pickled.

What a Polish flywheel looks like and its description
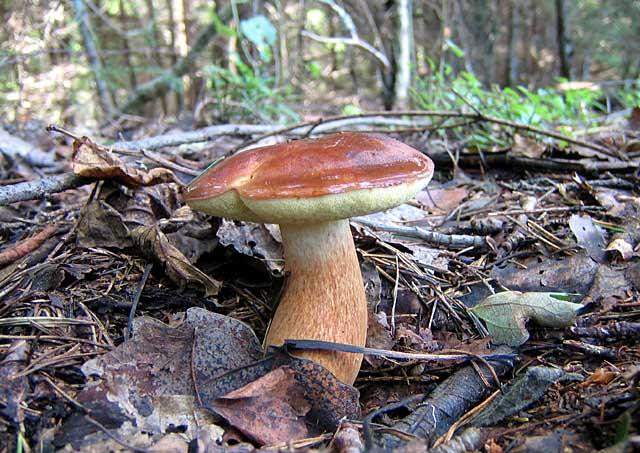
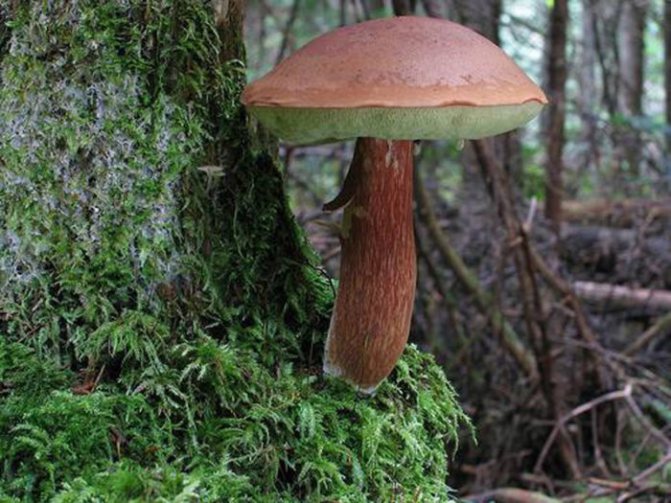
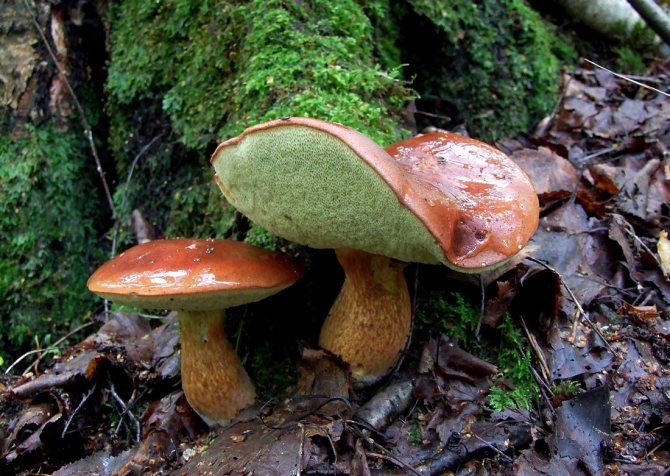
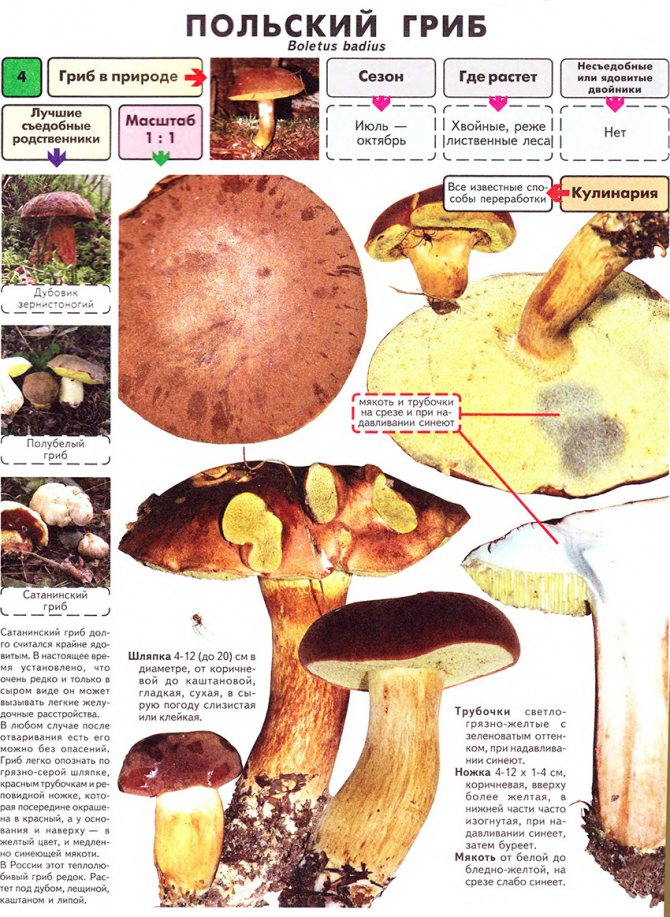
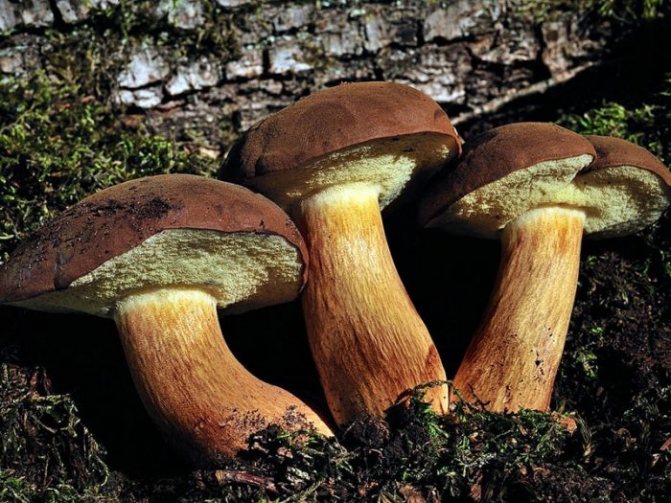
The cap is convex, flatter as it grows and can reach 12 cm in diameter. From below, it has a tubular structure of white or yellowish tint.
The color of the cap can vary from light brown to chestnut. The skin is difficult to remove. The stem is cylindrical, fibrous, reaching 14 cm in height.
Young specimens have a dense structure that becomes softer over time, and a spore powder of green-brown color.
Another name for the Polish mushroom is pansky, white Polish, brown mushroom or chestnut moss.
Output
The Polish mushroom is a representative of the Mokhovik genus, found on sandy soils and in coniferous forests. It grows throughout the summer until late autumn. It has a fleshy pulp, pleasant taste, and emits a delicate mushroom aroma. Young mushrooms have a matte surface that becomes darker and shinier over time. The Pan mushroom is very useful for humans. Its active biological substances renew nerve cells, increase mental activity, cleanse the body, strengthen the immune system, and improve the condition of the dermis.
Mushrooms contain melanin and ß-glucans, which are powerful antioxidants, fight against malignant formations, strengthen the heart muscle, blood vessel walls, and relieve chronic fatigue.
It is interesting that during heat treatment the chestnut flywheel fully retains all its useful properties. Sauces, soups, gravies, pizza and pie fillings are prepared on the basis of Polish mushrooms. They are great for drying, marinating, frying and braising.
Before cooking, mushrooms are cleaned of "forest debris", pre-boiled.
Cooking: 15 minutes
As I said, the mushroom harvest this year is simply huge. Last week I was given a bucket of fine Polish mushrooms. It was in the evening, so the photo session was carried out with poor lighting, for which I immediately apologize, but the mushrooms were so fresh and beautiful that I could not resist and decided to publish a post about these handsome men. So, I present to you a Polish mushroom.
Polish mushroom
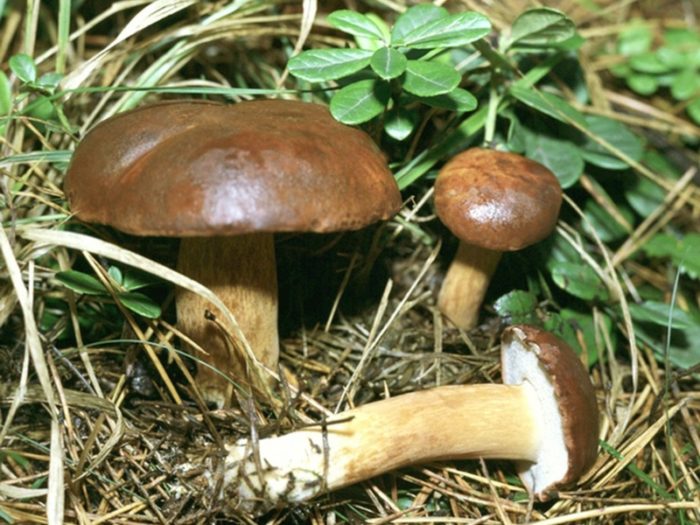
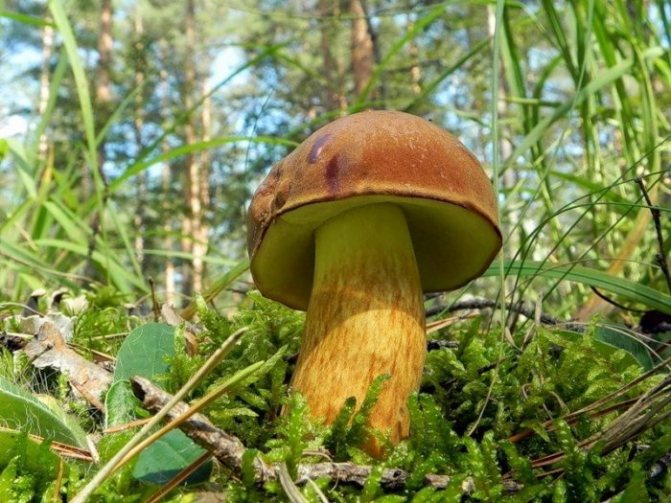
The Polish mushroom belongs to the genus of moss, sometimes the Polish mushroom is called brown mushroom, pan mushroom, chestnut flywheel. The Polish mushroom has a brown or chestnut cap (the shade of the cap may vary depending on the age of the mushroom). In wet, wet weather, the cap of the Polish mushroom becomes slippery and turns dark brown. The bottom of the cap is porous, yellow-white or greenish-yellow in color. When you press the porous bottom of the cap, the flesh turns blue, this is one of the signs by which the Polish mushroom can be distinguished from other similar mushrooms.The leg of a Polish mushroom can be cylindrical, or it can be pot-bellied or, on the contrary, narrow at the bottom, usually it has a light brown or yellowish tint.
The Polish mushroom is valued for its taste and is very similar in taste to the porcini mushroom. Not very experienced mushroom pickers often confuse the Polish mushroom with the porcini, and the experienced mushroom pickers equate the Polish mushroom with the white beauty. So if you are lucky enough to find Polish mushrooms, then you will have a wonderful mushroom dish for dinner.
How and where to pick a Polish mushroom
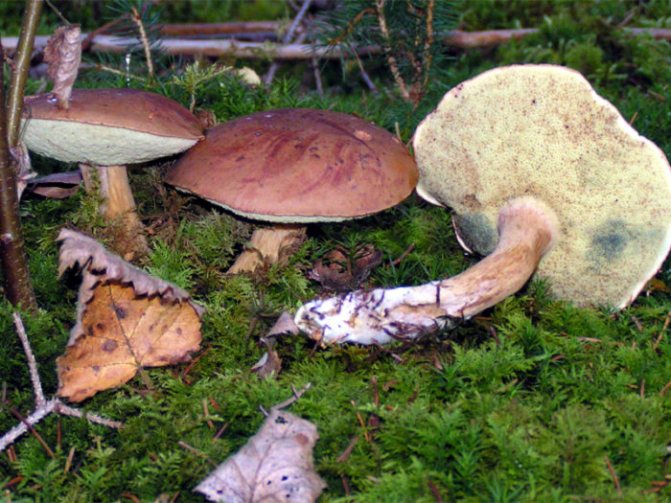
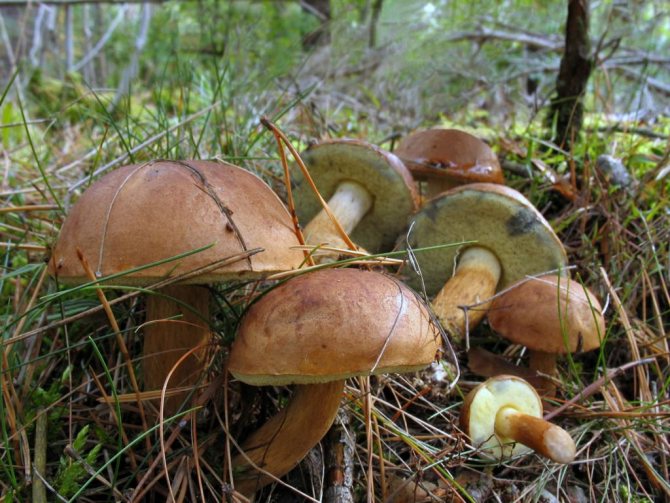
Most often, the Polish mushroom can be found near elderly trees in coniferous, sometimes deciduous, forests. These mushrooms most often grow at the foot of trees and around the stumps in moss, because it is not in vain that they belong to the genus of moss. In general, it is an amazing sight when a dense and proud Polish mushroom rises on a bright green moss mat, so if you are going to hunt for these beauties, be sure to take your camera with you.
Usually the Polish mushroom can be found from August to October, although sometimes, with good weather, these handsome men can be found even in November.
When collecting these mushrooms, you need to remember that when you press on the porous layer of the cap, it acquires a bluish or greenish-blue tint, not instantly, but after 2-5 seconds. The leg on the cut also acquires a bluish tint, then the shade becomes slightly brown, and then the flesh brightens again.
The Polish mushroom has a pronounced pleasant mushroom smell, very reminiscent of a porcini mushroom.
There are two opinions on how to properly cut mushrooms. Some argue that the mushrooms need to be cut at the base of the leg, then you will not damage the mycelium and a new mushroom will grow in this place. Others argue that the mushroom needs to be completely twisted out of the ground, otherwise the remnants of the cut leg will begin to rot and from this the mycelium itself can rot. I haven’t found an unequivocal opinion on how to cut mushrooms correctly, so the right to choose remains with you.
When picking mushrooms, it is best to immediately look at the wormy mushroom or not. It is better not to take wormy, even very noble mushrooms. First, heavily wormy, spoiled and overripe (old) mushrooms can cause eating disorders. And secondly, while you are walking through the woods and driving home, worms can get over to good mushrooms.
If you nevertheless plucked the mushroom, and it turned out to be wormy or old, then it is better not to throw it away, but to prick it on the nearest branch or twig, then the mushroom will dry out, and mature spores will dissipate and next time there will be more mushrooms.
Pickled Polish Mushroom Recipe
A hearty, aromatic appetizer is served with boiled or fried potatoes. It also goes well with hot meat and poultry dishes.
Ingredients:
- Polish mushrooms - 1 kg;
- water - 1 l;
- vinegar - 50 ml;
- olive oil - 50 ml;
- garlic - 5 cloves;
- salt - 30 g;
- sugar - 30 g;
- bay leaf - 4 pcs.;
- cloves - 5 pcs.
Recipe:
- Soak mushrooms for 20 minutes. in cold water, then cut them into chunks.
- Put the blanks in boiling water and cook for 5 minutes.
- Drain the broth, rinse the mushrooms and refill them with water. Add 1 tsp. salt and cook the workpieces for 30 minutes. Skim the foam periodically.
- Discard the mushrooms in a colander.
- Boil 1 liter of water. Add salt, sugar, sliced garlic, bay leaves, and cloves.
- Boil the marinade, pour the vinegar into it and add the mushrooms. Cook them together for another 10 minutes.
- Place the hot mushrooms and marinade in sterilized jars and cover them with olive oil.
- Close the blanks with screw caps, cool them under a blanket.
Store treats in the refrigerator or cellar. You can try the snack after 4-6 weeks.
Selection and preparation of ingredients
Since the Polish mushroom prefers coniferous forests, where sandy soil usually predominates, the mushroom harvest there is often heavily contaminated with sand and needles. To thoroughly wash the product, it is placed in cold water for a couple of hours.
Important! Due to the delayed digestibility of the product, it is recommended to grind it during cooking. Heat treatment in this case will be much faster and more efficient, simplifying the process of further digestion of the gastrointestinal product.
In the process of soaking, the liquid is replaced several times, after which it is drained, and the crop is carefully sorted out. It is necessary to remove the wormy fruits and cut off the tips of the legs.


Description and useful properties
To choose the right one, the mushroom picker needs to know the description of the Polish mushroom. It has a brown cap with a diameter of 3 to 15 cm. The shape of the cap is convex, at the beginning of growth the edges are rolled up, then the cap acquires a flatter appearance.
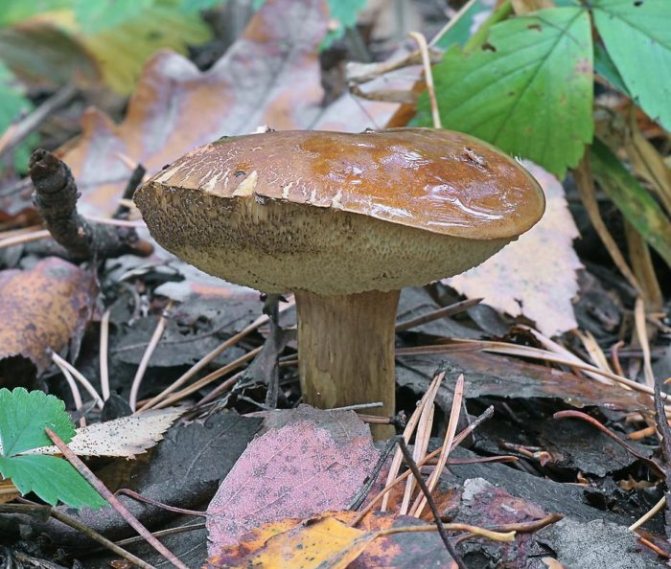
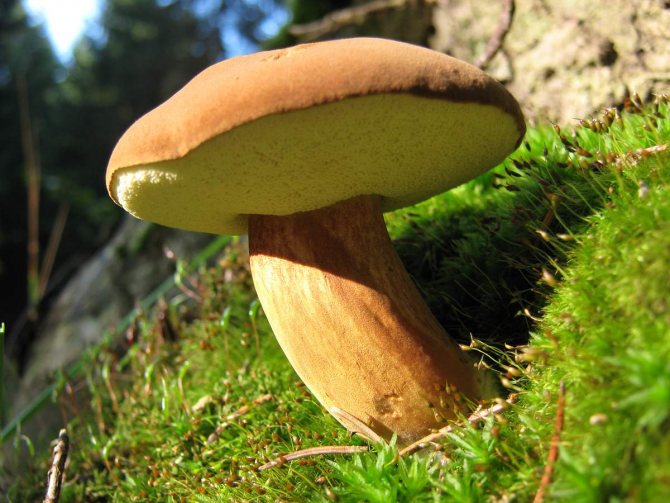
The surface is velvety, in dry weather it remains dry, and in wet weather it becomes slimy and slippery, while it has the property of being difficult to separate. Color from bright red-brown to dark chestnut-brown. The tubular layer initially has a light yellowish tint, and becomes greenish as it grows. The pulp is white and dense, slightly blue on the cut. The smell is light, the taste is pleasant, sweetish.
The leg reaches 14 cm in height, up to 4 cm in diameter, cylindrical, slightly swollen at the bottom, can have a curved shape. The color is always lighter than the hat, in brown tones. When pressed, it first turns brown, then slightly blue.
Botanical characteristic
According to the description, the Polish mushroom is very similar to the white boletus.
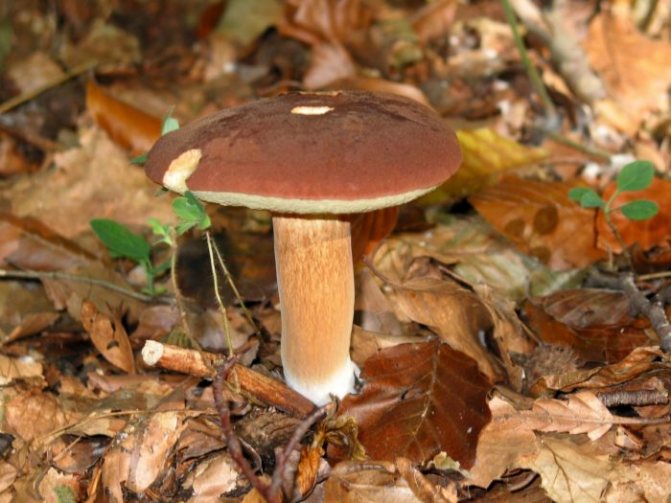
- Hat: diameter - up to 15 cm, the shape at the initial stage of development is semicircular, later it looks like a convex one, in old specimens it becomes flat. The surface layer is tightly attached to the pulp and cannot be removed; it is smooth in structure. It is dry and becomes sticky in humid conditions. In young mushrooms, the surface of the cap is dull, with time it becomes shiny. The color is brown, dark brown or chocolate chestnut.
- Pulp: in structure, it is fleshy, dense. The color is white or cream with a yellow tint. On the cut, it turns more or less blue. The smell of mushroom, the taste is soft, there is no pungency. In the pulp, worms are very rare.
- Hymenophore: tubular, can be loose or adherent to the mushroom leg. Has a slight notch. Formed by tubules up to 2 cm long, having a yellowish color at first, then golden yellow or with a green tint. The pores are small, rounded. When you press on it, it turns blue.
- Mushroom leg: cylindrical shape, height - 4-10 cm, thickness - up to 5 cm. The structure is fibrous. The color is light brown, brown or yellow. The fibers are brown. The upper part of the leg and the base are lighter than the middle.
Collection features
Like any mushroom, Belopolsky is capable of accumulating harmful substances from the environment. Refrain from collecting along roads and near industrial sites
If the wormy areas are small, they can be trimmed neatly. It is desirable to choose young individuals: they are better in taste. Old and overripe can cause eating disorders.
After returning from the forest, the collected mushrooms are processed within 24 hours. With longer storage, they overheat, cake and deteriorate.
Recipes and cooking features
After a thorough heat treatment, the Polish mushroom can be pickled, frozen, dried, fried. In terms of its taste, this mushroom resembles a white one, so it is most popular in the preparation of various dishes.
Processing rules
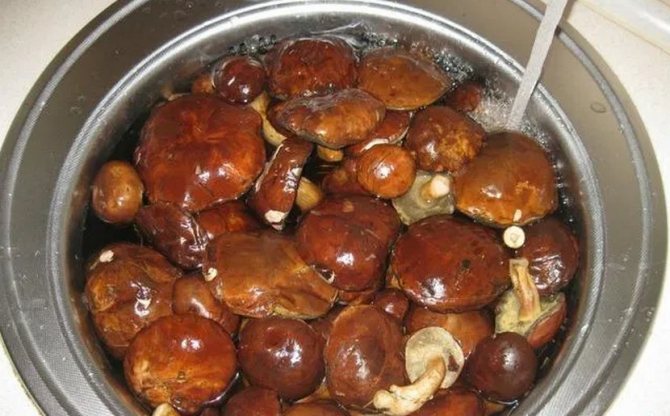
The washed and carefully peeled Polish mushrooms are boiled in small batches.It should be borne in mind that during the heat treatment, foam is released, which must be removed. Therefore, you should choose a large capacity.


Polish mushroom processing
Large specimens are cut into several parts, and small ones are laid intact in the container. Mushrooms are dipped in boiling water and, after boiling, boil for 10 to 20 minutes. This time is enough for the mushrooms to boil. The water is drained after processing. When draining the liquid, the mushrooms darken quickly. Therefore, before cooking, the mushrooms are left for a short time in the cooking water.
Pickled Polish Mushroom Recipe
To prepare 2 kg of pickled mushrooms you will need:
- 1 liter of water
- 1 teaspoon of sugar;
- 2 tbsp. tablespoons of salt;
- 3 tbsp. tablespoons of vinegar (9%);
- 3 pcs. allspice;
- 1 PC. carnations;
- 3 pcs. black peppercorns;
- one bay leaf.
First you need to cook a marinade from the indicated ingredients: add salt, sugar, all spices to boiling water, boil for 3-5 minutes and pour in vinegar. Put the pre-cooked mushrooms in the marinade and boil. After that, the mushrooms are laid out in cleanly washed, sterilized jars and sealed with lids.
Fusofacts
- Polish mushroom is growing
in coniferous forests, less often in deciduous ones. Often grows on stumps and in moss on the bases of the trunks of elderly pines, spruces, oaks, beeches. Loves dryness, so it is almost never found in deciduous forests. In Russia, the Polish mushroom is widespread in the European part, in Siberia, in the Far East and in the North Caucasus. - In different places the Polish mushroom has different
titles
... In the common people it is called a pansky mushroom, a chestnut flywheel, a brown mushroom. -
Gathering season
Polish mushroom - from June to November. - The Polish mushroom has brown
hat
up to 15 centimeters in diameter, becomes sticky in wet weather. The bottom of the cap is yellow-white, porous. The leg of the mushroom has a light brown or yellow hue, up to 12 centimeters high, 1 - 4 centimeters thick. It can be cylindrical, narrowed or swollen from below. The pulp is firm, white or yellowish in color. - In the place of the cut, the cap of the Polish mushroom
turns blue
- this is its distinctive feature, it does not in any way affect the taste and quality of the mushroom. If you are in doubt about which mushroom you collected, white or Polish, after a couple of minutes the Polish mushroom will give a blue one. - Polish mushroom
rich
essential oils, sugars, minerals. In terms of protein content, it can replace meat in the diet. - Fresh Polish mushroom has a pleasant mushroom
smell
, boiled mushroom has a mild taste, according to its taste, it belongs to category 2 out of 4 (for comparison, porcini mushroom is category 1, and ryadovka is category 4. - Polish mushrooms are better
to process
immediately after collection. To do this, they need to be laid out in one layer on the surface, remove debris, dirt, cut off the lower part of the leg from each mushroom and cut out the wormy areas. For an old mushroom, you need to cut off the spongy part of the cap. Pour the mushrooms with cold water for 10 minutes so that the earth moves away from them, rinse thoroughly. If the mushrooms are old and there is a risk that the mushrooms are wormy, it is recommended to soak the mushrooms in salted water. - Fresh Polish mushrooms
keep
in the refrigerator in the vegetable compartment for no more than 12 hours, store boiled Polish mushrooms in mushroom broth, covered with a lid, for 3-4 days. -
Calorie content
Polish mushroom - 19 kcal / 100 grams.
Growing at home


Today, avid amateur mushroom pickers began to grow many types of mushrooms at home on their own, turning this business from a favorite hobby into a rather profitable business. Polish mushrooms can also be classified as such "domestic" mushrooms, which, with good and proper care, will delight their owners with a generous harvest more than once a year.
Land requirements
For growing Polish mushrooms, a small plot of land about 2-3 square meters in a dark place or semi-dark room is best suited. First, you need to dig a shallow ditch up to 30 cm and fill it with a nutrient mixture.At the very bottom, you need to place a 10 cm layer of wood dust, fallen leaves, bark or grass, and then another 10 cm - dung humus or soil from under the trees. After preparing such a nutrient base, the mycelium of the mushrooms is evenly distributed over the entire surface of the "pit". From above again 3 cm of plant residues, and in the end - 3-5 cm of good soil from the garden.
Temperature and watering
Immediately after sowing and thereafter, as necessary, the mushrooms must be constantly moistened, especially if the yard is hot and dry. The most favorable temperature for their good growth is 12-26 ° C.
Since mushrooms do not have a growing season, they can be grown all year round, only for this, first transplant from open ground into boxes.
Ripening period
If everything is done correctly and in a timely manner, then in 1.5-2 months after sowing, the first mushrooms will appear, which, in the future, will delight their owners every week and a half with new shoots.
Benefit and harm
Chestnut moss is a low-calorie product, 100 g of which contains 19 kcal, 1.7 g of protein, 0.7 g of fat and 1.5 g of carbohydrates. The mushroom contains 15 amino acids, vitamins B, PP, manganese, selenium, sodium, phosphorus, potassium, copper. Tannin gives the representative of pain relief medicinal properties that green tea possesses.
Chemical composition of the Polish mushroom Name Nutrient content in 100 g of product, mg Vitamins Macroelements Microelements
| Choline (B4) | 38,7 | |
| Niacin (PP) | 7,956 | |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) | 3,294 | |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 0,359 | |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | 0,21 | |
| Thiamin (B1) | 0,145 | |
| Folic acid (B9) | 0,021 | |
| Potassium | 320 | |
| Phosphorus | 151 | |
| Sodium | 19 | |
| Copper | 144 | |
| Manganese | 0,21 | |
| Selenium | 0,0036 | |
The water capacity in the mushroom reaches 90%.
Advantages of the chestnut flywheel:
- cleanses the body of toxins;
- improves wrinkle, condition of hair, nails, nervous system;
- increases mental alertness, anti-cancer immunity;
- inhibits the negative effect of caffeine;
- lowers blood pressure, the risk of developing atherosclerosis;
- normalizes digestion processes;
- relieves swelling with bruises, abrasions, renal failure (has a diuretic property);
- promotes weight loss, relaxation and calming;
- accelerates the resorption of adipose tissue, warts, hematomas, activates metabolism;
- balances the nutrition of the body.
A properly processed Pan mushroom does not harm human health, but, on the contrary, improves its functioning. It is recommended to collect fruit bodies away from factories and highways. Contraindicated in people with chronic diseases of the liver, stomach and individual intolerance to mushrooms.
Healing properties


The fungus is able to remove toxins from the body
The healing properties of the Polish porcini mushroom are due to the beneficial elements included in its composition:
- amino acids: have a calming effect, stabilize blood pressure, serve as a prophylaxis for cancer, increase brain activity;
- B vitamins: improve the functioning of nerve cells, activating the regeneration (restoration) of neurons; have a rejuvenating effect on the skin, have a beneficial effect on the condition of hair and nails;
- chitin: cleanses the body of toxins and removes toxins.
In addition, eating the mushroom has a diuretic effect. Thanks to this, swelling is reduced and the benefits of the product for the kidneys are noticeable.
Low calorie content (up to 10 kcal per 100 g) allows you to include dishes with Polish mushrooms in your diet menu. Fried and pickled foods can be harmful for people with indigestion.
How to recognize poisoning?
The first symptoms of damage to the body by poisonous mushrooms are:
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea;
- stomach ache;
- gastroenteritis or gastroenterocolitis;
- convulsions;
- increased body temperature;
- clouding of consciousness, hallucinations;
- cold sweat.
In case of mushroom poisoning of hepatonephrotoxic action, the first symptoms are gastroenterological in nature, develop within 6 hours after consumption, and gradually worsen as the liver hepatocytes are damaged.
Chestnut moss twins:
- Variegated: Has a yellow-brown cap that cracks with age, exposing the reddish-pink fabric.
- Green: has a brownish-green cap and a tubular layer, a light stem. When cracked, it exposes a yellowish tissue.
- Brown: The specimen features a brownish hat, through the cracks in which you can see the whitish fabric.
- Satanic (parasitic). Visually resembles a Polish mushroom. The pulp is white. On the cut, it turns red or blue, poisonous.
In order to avoid mushroom poisoning, each cut specimen is subject to visual inspection again. It is important to check all traits in the collected species. Often, mushrooms are confused with gall or pepper mushrooms, which have a bitter taste that intensifies during heat treatment. The use of such a product is hazardous to health.
Remember, picking mushrooms should not be taken carelessly, otherwise the price of a mistake can be a person's life. The mortality rate of forest bread poisoning is scary. Every year this figure increases by 1% worldwide.
Practical use
This species is edible. Polish porcini mushrooms have high gastronomic qualities, belong to the 2nd category of nutritional value, therefore, they are massively harvested.
It is widely used in cooking. It is used for cooking in different ways: in the first and second courses, for drying, salting, they can be fried, closed for the winter in the form of pickles and canned.
Polish pansky moss is a competitor for white boletus, but it is inferior to the latter in its richness of taste.
Before cooking, the mushrooms are cleaned of dirt, spoiled fragments are removed, the top layer of the hymenophore with spores is cut off, washed under running water and soaked for ¼ h in salted water.
First, they are boiled for 10-15 minutes, after which the water is drained. After preliminary cooking, it is used for further cooking, canning, or left for storage.
Attention! Although it is believed that raw mushrooms can be stored in the refrigerator for up to a day, however, many chefs are sure that after 15 hours a huge number of worms appear in the fruit bodies of the mushrooms and it will not be possible to save the harvest.
Advice. If for some reason you cannot start cooking mushrooms immediately after boiling, leave them for a while in the water where they were cooked - then they will not change color and remain light.
The Polish mushroom is a striking representative of numerous types of porcini mushrooms.
Characteristics of the Polish porcini mushroom
Poisonous and false counterparts of the Polish mushroom
The Belopolsky species can only be confused with boletus mushrooms only by a novice mushroom picker. But the mistakes associated with some false mushrooms like him are not always harmless.
Bilious
Sometimes it can be mistaken for a chestnut flywheel not poisonous, but extremely bitter gall mushroom. In order not to be mistaken, you should be aware of the differences between these forest gifts:
- On its leg there is a mesh, brown pattern.
- The cut flesh is soft and pink, not white and hard.
- When pressed, it does not turn blue.
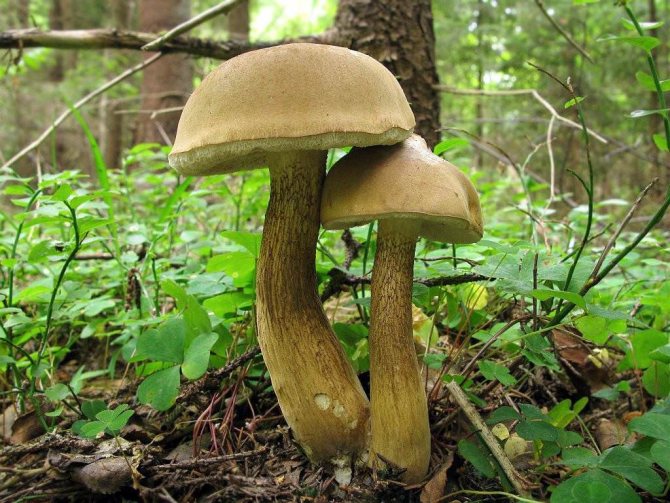


Gall mushroom
Satanic
In the southern regions of Russia, you can find a poisonous satanic mushroom. A distinctive feature of this pan mushroom counterpart is a clear mesh pattern on the reddish stalk. And his hat is off-white.
Description of taste
The nutritional value of the pan mushroom can successfully compete with the white one, although the taste of the white counterpart is still brighter. Prepare it in the same way as any other forest spore food.
It is pickled, boiled, salted, fried, dried and frozen. Since this is a difficult-to-digest food, the product must be crushed during cooking.These mushrooms are good for preparing first courses, side dishes, snacks, pancake and pastry fillings, sauces. They are combined with spices, herbs, vegetables, cereals.


The nutritional value of the pan mushroom can compete successfully with white
Delicious recipes
The most common recipes with Polish mushroom as the main ingredient:
- Fried Polish mushrooms with onions and sour cream. After the initial preparation, the mushrooms are chopped and fried in vegetable oil with the addition of sour cream and onions. Cooking time is about 7 minutes.
- Pickled Polish mushrooms. The washed mushrooms are boiled for 15 minutes. Be sure to remove the foam. The readiness of the broth is determined by the color. It should turn golden. At this time, the marinade is being prepared. Based on a liter of water, take 2 tablespoons of sugar, 4 teaspoons of salt, 5 tablespoons of vinegar and spices to taste. Allspice, garlic, bay leaves, black pepper and cloves are suitable for this recipe. The marinade is boiled for several minutes. All spices are added at once. Garlic is added at the very end. Pour over boiling marinade and cook for about 10 minutes. Then add vinegar and lay out in jars. Roll up immediately.
- Mushroom soup. Dice the mushrooms, potatoes and onions. Boil water, add mushrooms and cook for about 5 minutes. Then add vegetables. Let it simmer for about fifteen minutes. Add semolina and vegetable oil for two to three minutes. Sprinkle with herbs and serve with sour cream.
- Bigos. Bigos is a masterpiece of Polish cuisine. In this country, the Polish boletus is very popular. For its preparation, take sauerkraut, boiled mushrooms, hunting sausages, onions, tomato sauce, spices and red wine. The cabbage is washed and stewed on lard. Then add mushrooms, finely chopped onion, tomato sauce and some wine. Sprinkle with spices two minutes before cooking.
- Mushroom salad. For a half-liter jar of mushrooms, one processed cheese, a couple of pickled cucumbers and three boiled potatoes are taken. Cut everything into cubes and add mayonnaise to taste. Decorate with parsley. It tastes like boletus. It is cooked with vegetables and cereals. Greens are added to the finished dish.
False and true boletus: the main differences
Other names for Polish mushroom
The Polish mushroom is so called because it is widespread in Poland and is even exported from there to Western Europe under the name Pansky. Russian lovers of quiet hunting, because of the characteristic color of the cap and shade of the leg, also call it the chestnut flywheel.
This majestic mushroom is also called the king of the moss. And he received the popular nickname "bruise" due to the fact that when you press on it, a bluish spot is formed in this place, which then turns black.
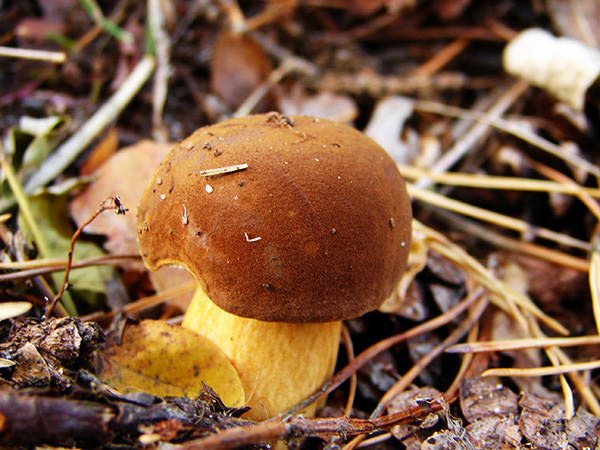


The Polish mushroom is so called because it is widespread in Poland.
Answers to common questions
Cleaning the Polish mushroom is not difficult, however, this process should be started immediately after arriving home. To do this, cut off the lower part of the leg, remove adhering debris, dirt and wormy parts. It is not necessary to remove the skin from the cap. It is better not to eat old specimens at all. After that, the mushrooms are soaked in salted water and kept for up to 20 minutes, then washed with cold clean water and heat treated.
The name "Polish" mushroom got its name from the wide export from Europe, mainly from Poland. And also has the following names:
Knowing the properties of the Polish mushroom, many mushroom pickers say that it is not necessary to boil them, but you can immediately fry, stew, bake. This statement is false. Indeed, due to the porous structure, mushrooms tend to absorb harmful impurities from the environment and soil.
Therefore, if you do not subject the flywheel to proper heat treatment in the form of boiling, then it can become inedible and adversely affect health. Only after boiling, various dishes are prepared from the mushrooms.
The best place for collecting mushrooms is the edges of the coniferous forest in ecologically clean areas, far from hazardous production.The best time is August-September, when there are fine days. Since they grow in small clusters, in order not to disturb the mycelium, it is necessary to carefully move the coniferous litter with a long stick.
When cutting the mushroom, the lower part of the stem is left in the ground to form a new mushroom, promoting a new harvest. For collection, a wicker basket with a dose for natural air circulation is optimal.
The Polish mushroom is rightfully considered a delicacy because of its taste, the content of nutrients, and its positive effect on the body as a dietary product. By adhering to the rules of collection, processing and preparation, you can get an excellent nutritional addition to various dishes.
Polish porcini, or pansky, mycologists refer alternately to the Bolet genus, then to the Mokhovik genus from the Boletov family. And sometimes they even distinguish Pseudoboleth into a special kind. It has a wide range of practical uses in cooking.


How to cook Polish porcini mushroom
Before you start creating a culinary masterpiece from Polish mushrooms, they need to be processed. It is better to do this right away so that worms do not start in them. Mushrooms are laid out on paper and peeled, cutting off the lower part of the leg and the places spoiled by worms. In older specimens, it is better to also remove the "sponge" with spores. You do not need to cut off the skin from the cap.
What do boletus mushrooms look like and where do they grow?
After that, you need to thoroughly rinse the forest gifts with a sponge in running water. It is good after that to soak them for a couple of tens of minutes in salted water, so that the dirt and sand from the spongy part of the mushroom, and at the same time the worms remaining after cleaning, go away.
Then you need to cut the mushrooms and boil them in salted water for ten minutes, removing the resulting foam. Drain the water after cooking, and the mushroom semi-finished product (if it is not planned to immediately prepare it) put in jars. As such, you can store it in the refrigerator for several days. It doesn't matter that the mushrooms darken after cooking. With subsequent processing, they will become lighter.
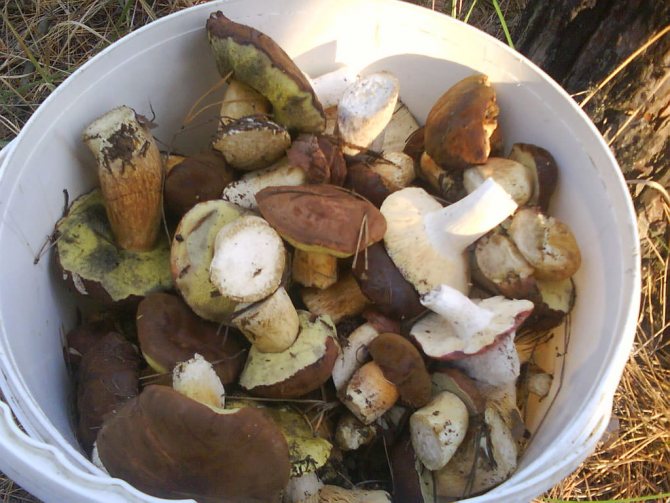


Before you start creating a culinary masterpiece from Polish mushrooms, they need to be processed
Salting chestnut mushrooms
Put the prepared mushrooms in layers in jars, filling them with salt so that it takes two tablespoons per kilogram of product. Place some dill and garlic between them.
All this must be kept under pressure for a day, and then closed with plastic lids and removed to a cellar or refrigerator. Add vegetable oil before serving.
Marinating White Polish mushrooms
For a marinade, designed for a kilogram of forest gifts, you need: a liter of water, a quarter of a glass of vegetable oil and vinegar, a spoonful of salt and sugar, a few cloves of garlic, bay leaves and cloves. Cooking sequence:
- Put the mushrooms in the boiled marinade, cook for several minutes.
- Put the finished product in jars, pour a little oil on top.
- Close with sterile lids, keep the jars upside down under a blanket until they cool.
- Then send to a cool place.
Recipe: Fried Porcini Polish Mushrooms (Video)
Rules for processing and storing mushrooms after picking
It is advisable to carry out the processing immediately after returning home. If this is not possible, then it is necessary to transfer the boletus to the refrigerator, in which they can be stored for up to 3 hours without losing quality. If you store it longer, then there is a risk of losing some part of the product. Since the processing will also take time, it is recommended to spread the flywheels in one layer on the prepared surface. This way, they won't overheat and stay fresh.
Primary processing consists of removing debris. It is necessary to clean both the cap and the areas on the lower part of the leg.It is undesirable to collect old specimens, but if they have already ended up in the basket, then when cleaning, you should remove the spongy part on the cap, since there are spores in it.
The next step is soaking. You can use clean water or slightly salted water. The second option is preferable, as it will destroy the worms if they find themselves somewhere. Soaking time is different and varies from 20 minutes to 5 hours, after which you should rinse the mushrooms well in running water. When the product has been removed from the water, it is advisable to start cooking as soon as possible.
Small mushrooms can be cooked whole, and large ones can be cut into 2-4 pieces. The average cooking time is 10-15 minutes after the start of boiling. The first water is always drained. When choosing a saucepan, you need to take into account the fact that a lot of foam is formed during cooking. Therefore, it is best to cook in portions in a free container. Boiled boletus mushrooms are ready for further cooking or preparation.
Mushroom soup with Polish mushrooms
Products
per 4 liter saucepan Polish mushrooms - 300 grams Potatoes - 2 tubers Tomatoes - 2 pieces Carrots - 1 piece Green onions - 5 shooters Bulgarian pepper - 1 piece Olive oil - 30 milliliters Black ground pepper - half a teaspoon Salt - half a teaspoon
How to make soup with Polish mushrooms
1. Clean Polish mushrooms from debris and soil, cut off the lower part of the leg, remove darkened and wormy places, wash in cool water. 2. Cut the Polish mushrooms into 1-inch cubes. 3. Wash, peel and chop the potatoes and carrots into cubes 3 centimeters long and 0.5 centimeters thick. 4. Pour 2.5 liters of cold water into a saucepan, add the Polish mushrooms, place on the burner, bring to a boil over medium heat. 5. Remove the resulting foam, put potatoes, salt, pepper in the same pan, cook for 10 minutes. 6. Wash the bell pepper, remove the seeds, the stalk, cut into squares centimeter wide. 7. Pour oil into a frying pan, put on medium heat, heat up. 8. Fry carrots and bell peppers in oil for 5 minutes. 9. Pour the tomatoes with boiling water for 2 minutes, remove from the boiling water, remove the skin, cut into squares two centimeters thick. 10. Put the tomatoes in a skillet with vegetables, fry for 5 minutes until the moisture evaporates. 11. Add fried carrots, bell peppers, tomatoes to a saucepan with mushrooms and potatoes, cook for 10-15 minutes. 12. Wash and chop green onions. 13. Pour soup into bowls, add sour cream, sprinkle with green onions.
Preparation for the winter
If you are lucky enough to collect a large harvest of forest delicacies, you can provide yourself with aromatic and tasty dishes for the whole winter. It is important to know how to make the blanks correctly.
Pickled
Marinating can be started immediately after boiling the mushrooms. To do this, in parallel with the processing process, it is necessary to start preparing the marinade. To prepare it, per liter of water, dilute two tablespoons of salt, one tablespoon of 9% vinegar, put three peas of allspice and black pepper and 1 each of cloves and bay leaves. Put on fire and boil.
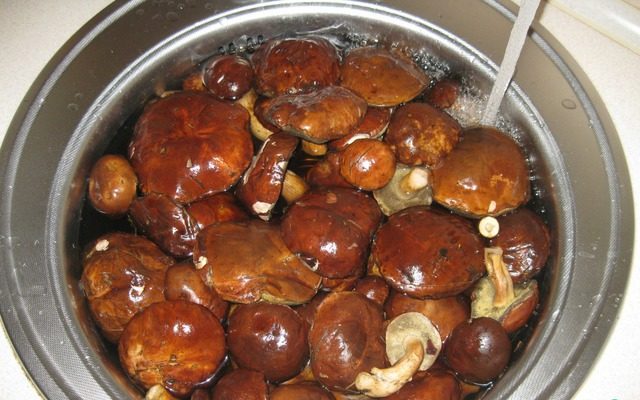


Pickled Polish mushrooms
In order to roll up mushrooms for the winter, it is necessary to prepare lids and jars by any sterilization method. Boiled mushrooms are laid out in banks, tamping slightly. Do not reach the top, it is better to stop in the place where the bank begins to narrow. Without removing the marinade from the stove, carefully pour into the containers to the very top. Close with lids, turn over and wrap with a blanket.
Pickled blanks are infused for about 40 days. To prepare them for use, it will be enough to season the product with oil and garlic / onions.
Where does the Polish mushroom grow
The name of the Polish mushroom was due to the place of greatest distribution. In Poland, the Polish porcini mushroom is the leader in terms of harvest. In Russia, it is often called chestnut moss, pansky or brown. It grows in the European part and in the Far East.In Europe it is considered a delicacy due to its rich taste and nutrient content.
Polish mushrooms prefer mixed or coniferous forests with acidic soils in the northern temperate zone. The collection time for this species is from June to October. Under favorable weather conditions, the peak yield occurs in September.
The fungus grows at the bases of old trees: firs, oaks, beeches - either next to stumps, in groups, or one at a time. Belongs to the Boletov family from the Borovik family.
Distribution area
Most often, the white Polish mushroom is found in the northern temperate zone. It is characterized by the formation of mycorrhiza with pines and spruces. Quite often, mycorrhiza forms with trees such as beech, oak and European chestnut. Most often, mushrooms of this species are found in conifers. Somewhat less often, they grow in deciduous forest belts.
The optimal condition for the life of the Polish fungus is the presence of sandy soil, but sometimes it grows on the base of the trunk of a tree or on stumps. Fruiting is separate or in small groups. The peak of fruiting occurs in the period from June to November.
One of the poisonous mushrooms - satanic - is close to the white Polish mushroom in its genus and main external characteristics. This false porcini mushroom is also widespread in our country, it is distinguished by a reddish leg and a characteristic coloration of the pulp. Some similarity is observed with porcini mushrooms, as well as variegated flyworm.