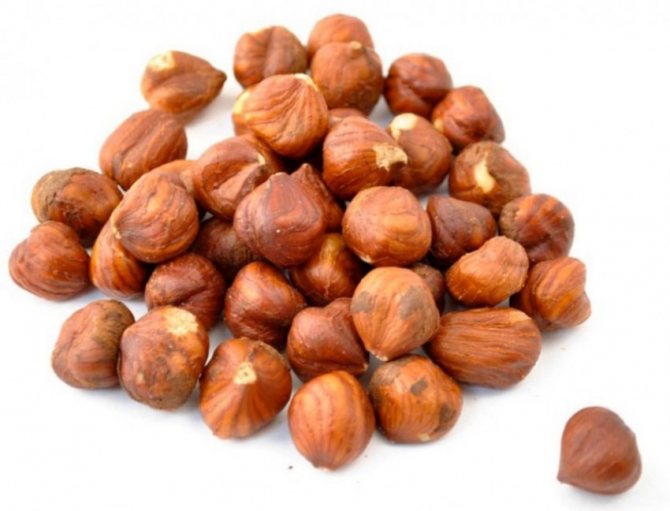
Hazel or hazelnut is a plant of the Hazel family from the birch family. It is a deciduous tree or arboreal shrub. It grows in Europe, the Caucasus, the Middle East and even beyond the Arctic Circle. It is found in mixed, deciduous, coniferous forests, along the banks of rivers and lakes in the form of a bush. The plant is cultivated everywhere. Hazel has been used as a nut plant since ancient times. Its fruits are extremely tasty and contain up to 19% of excellent quality protein. Hazelnut wood is almost white with a brownish tint, heavy, hard and flexible. Furniture, shanks, hoops are made from it, and also used for weaving baskets, chairs, hedges. Hazelnuts are beautiful and are grown for decorative purposes. The most detailed information about hazel is presented on the Agronom.guru portal.
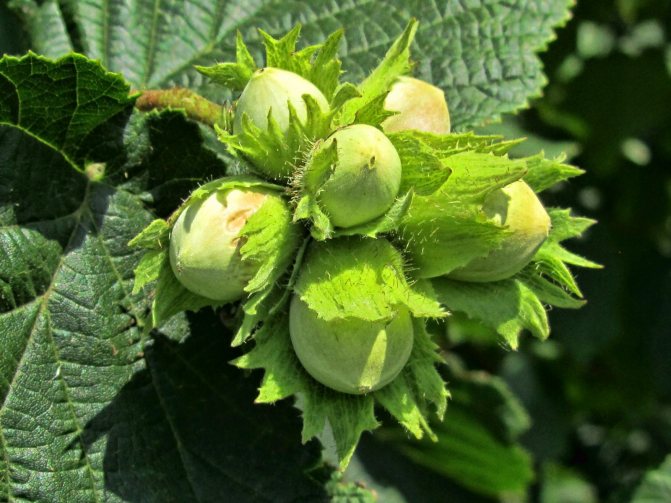

Hazel
Botanical description
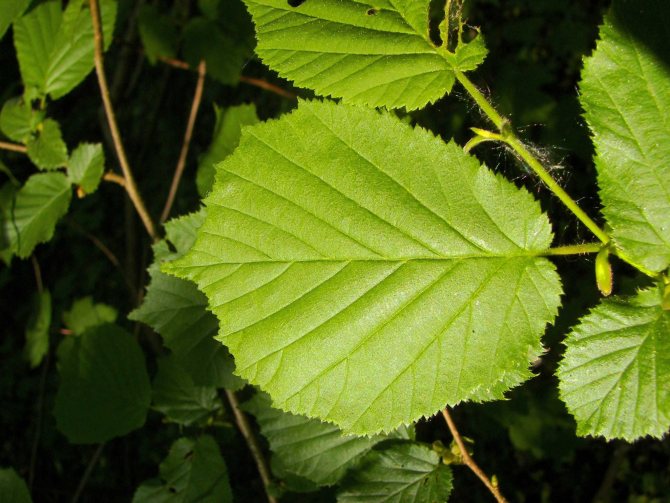
The shrub reaches a height of 5, less often 7 m. The bark of the trunk is gray-brown, light, the wood is almost white. Bushes are round in shape, foliage is abundant.
Until late autumn, the leaf blades remain bright green. In young plants, fluff remains on the leaves, later it disappears.
The root system of hazel is strong, although superficial. One of the lateral roots is usually thicker.
Hazelnut flowers are small and inconspicuous. Male flowers are collected in earrings 5 cm long. Female flowers grow in pairs in the axils of scales. Hazel blooms in April until the leaves open.
The fruits of the plant are of culinary value.
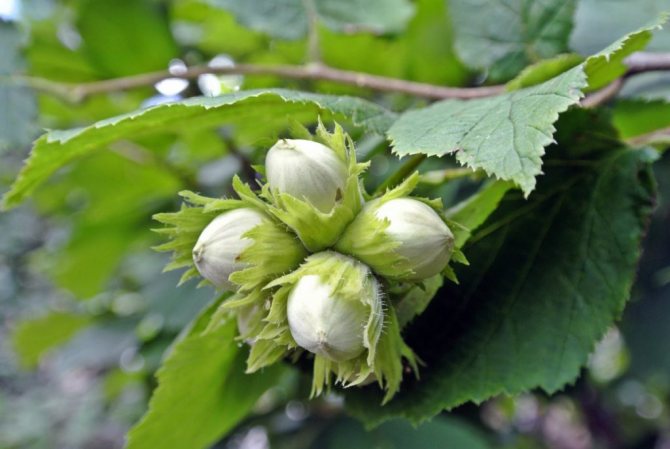
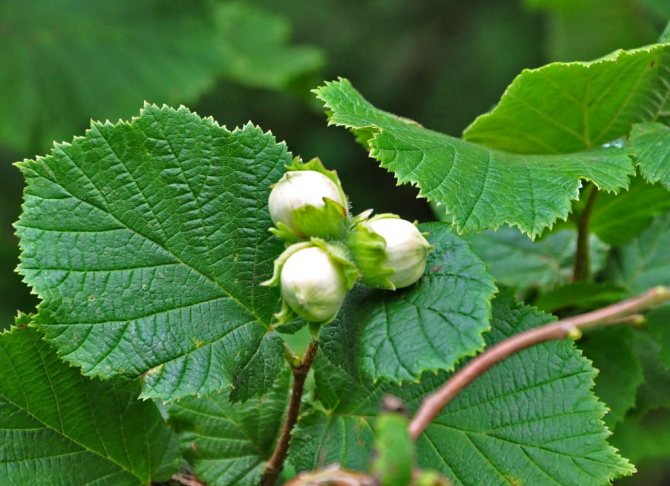
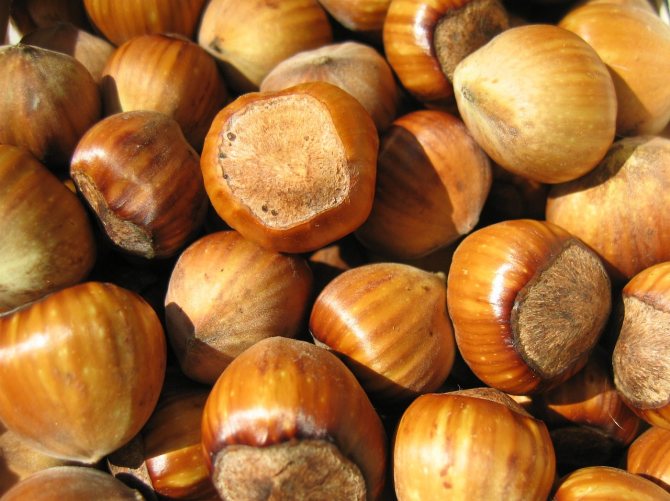
Nuts are almost round or elongated, collected in 2–5 pieces, but there are also single nuts. Fruit color - from light to dark brown.
Shrub bears fruit in August-September. Depending on the year, the harvest can be either plentiful - more than a ton of fruits per 1 hectare, or absent altogether.
Hazel has a unique ability to reproduce by root suckers. The plant quickly takes over forest clearings, hindering the growth of other trees. In forestry, walnut is considered a weed plant.
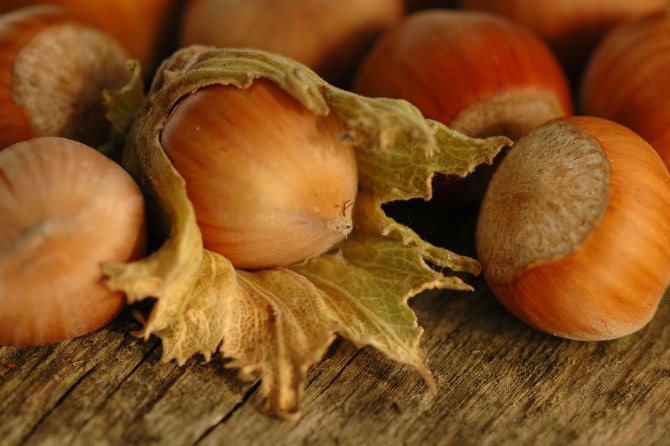


Hazel fruits can be light brown and dark brown.
Hazel or hazel - description
Hazel - tree or shrub
In height, hazel can reach 7 m. It has a spherical or ovoid crown with a conical top. The leaves of the hazel are large, broadly oval or round, with jagged edges. Flowers are unisexual and monoecious: male flowers develop in autumn and form dense cylindrical earrings on short twigs. In the spring, they bloom even before the leaves appear. Female flowers form kidney-shaped inflorescences and are located in pairs in the axils of the bracts. Hazel blooms in late March or early April and produces a huge amount of pollen, which is the main food for bees after wintering. Blooming hazel is decorated with flowers and golden earrings. The fruit of hazel is a small (about 2 cm in diameter) spherical yellow-brown single-seeded nut surrounded by an incised tubular cover (plyuska) and a ligneous pericarp. Nuts ripen in August.
The hazelnut prefers a temperate and subtropical climate. His plantations can be seen in southern Europe, Cyprus, Turkey, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Ukraine and central Russia. Unfortunately, in amateur gardens, hazel can still not be found as often as other fruit shrubs - bird cherry, sea buckthorn, wild rose, hawthorn, actinidia and others.
Chemical composition
Nuts, bark, foliage of the tree are used in folk medicine. The fruits are the most popular because they are very tasty and nutritious.
The chemical composition of nuts is as follows:
- Up to 62% of oils - consist mainly of unsaturated fatty acids. Nut butter improves the taste of breast milk and stimulates its production, so hazel is recommended for young mothers to eat. Nuts contain choline, lecithin, methionine - substances that improve memory and regulate fat metabolism.
- Up to 18% of easily digestible complete protein.
- Carbohydrates - no more than 18%. This is enough to provide a sweet, delicate hazelnut flavor, but not enough to be a danger to the figure.
- Fat-soluble vitamins of groups B, E, PP, and C.
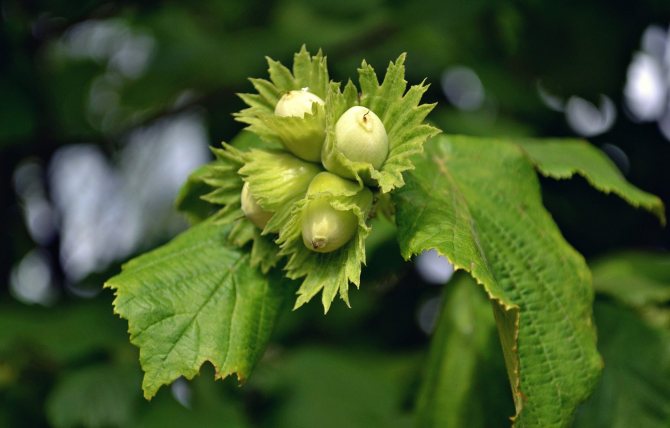


Hazelnuts are not only delicious but also very nutritious.
Hazelnut stimulates the immune system, helps to lower blood sugar, and normalize the blood lipid profile.
For medicinal purposes, tree bark is also used. She also benefits:
- Tannins - flobafens, tannins. They have an astringent and vasoconstrictor effect. Bark decoction is used in the treatment of varicose veins, capillary hemorrhoids, ulcers.
- Betulin is an antilytic and choleretic agent. Betulin reduces the absorption of low density cholesterol and excretes it in the bile. Preparations based on hazel bark are used in the treatment of the liver.
- The bark contains essential oils - they stimulate general immunity, accelerate the healing of wounds and cracks.
Decoctions from hazel bark were used as an anti-dysentery and antimalarial agent.
The phytopreparation knocks down the high temperature.
The leaves of the plant are not so rich in essential oils, but they contain palmitic acid and sucrose. In combination with micro- and macroelements, the substances stimulate hematopoiesis. Due to the high content of tannins, decoctions of the leaves are used to treat intestinal disorders.


Hazel bark is beneficial for vein disease
Benefits of growing bear nuts
Treelike hazel is called bear nut because of its resistance to bad weather conditions. Hazel is not afraid of frost and tolerates the summer heat well. Treelike hazel is a long-lived tree. In its homeland, a tree can live up to 200 years. In addition to climatic endurance, growing this plant has the following advantages:
- like hazelnuts and other relatives of hazelnuts, the fruits of tree hazel are a useful nutritious product;
- the tree bears fruit annually;
- has excellent decorative features.
The fruits of the tree hazel are very tasty both fresh and cooked, but before that you need to get rid of the thick shell. In terms of their taste, bear nuts are not inferior to wild hazelnuts.
Delicate pleasant smell of nut kernels, soft structure of the fruit are appreciated by culinary experts from different countries. Small nuts are added to liver pate, vegetable and meat salads, first courses, etc.
Not only hazel nuts are valuable, but also its wood. Its use for construction purposes has many advantages. Bearnut trunks are hard and durable. Buildings made from such a log house can stand for more than a century. Because of this, tree hazel has been listed in the Red Book for more than half a century and in nature it can be found only on the slopes of the mountains, where it is difficult to reach.
Properties of hazel: harm and benefit
The rich chemical composition is the reason for many of the beneficial properties of the nut.
- Taste and nutritional value are the main advantages of hazel. The fruits are eaten raw and fried. They are added to a variety of dishes, from vegetables to desserts.
- Anti-inflammatory effect - hazelnut oil is an antiseptic and stimulates the immune system, therefore, the fruits and the oil obtained from it are effective for colds, tonsillitis, inflammation. Hazelnut essential oil enhances the effect.
- Astringent - due to the high content of tannins, decoctions from the bark and leaves of hazelnuts restore normal bowel function, promote tissue regeneration and reduce bleeding.
- Vaso-strengthening - active substances reduce the permeability of the walls of blood vessels and strengthen them.
- Choleretic - betulin, contained in the bark of a tree, stimulates the outflow of bile. This helps to restore the functionality of the liver and normalize fat metabolism.
- Antipyretic - a decoction of the bark to some extent replaces aspirin and paracetamol and successfully reduces the temperature for colds and infectious diseases.
- Immunomodulatory - both nuts and decoctions of bark and leaves have an effect. Phytopreparations increase not only general, but also local immunity.
- Healing - tanning compounds in the plant contribute to accelerated regeneration and stop bleeding. So, rinse the mouth with a decoction of the bark during stomatitis and after tooth extraction. Hazel helps to strengthen the walls of blood vessels, the fruits are recommended to eat with varicose veins and thrombophlebitis.
- Diuretic - substances in the composition of hazel dissolve calcium salts and promote the removal of calcium. Walnut is used to dissolve kidney stones, and since calcium is also excreted with calcium, decoctions of the leaves also relieve edema.
Hazel can be included in the diet of patients with endocrine disorders - diabetes, atherosclerosis.
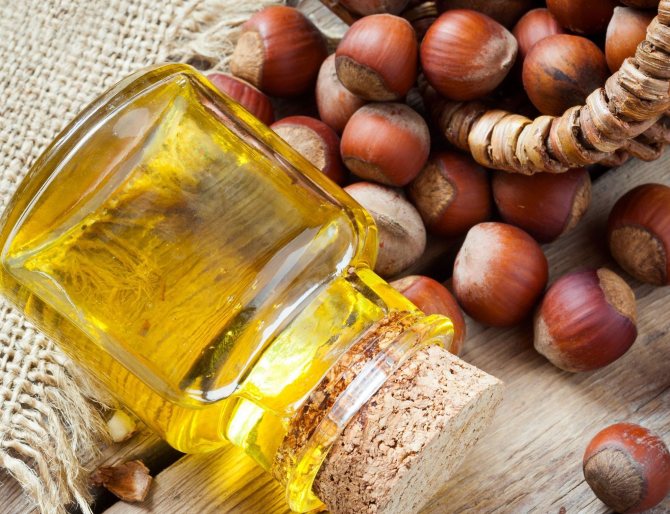


Hazelnut oil is an excellent antiseptic
Application
In cooking
First of all, this nut is incredibly tasty just raw. But to eat it you will have to "tinker", getting rid of the husk. Therefore, it is better to send the nuts to the oven or fry them in a pan. This will allow you to easily remove the dense husk and enjoy the full flavor of the bear nut.
Many believe that it has a richer and more aromatic flavor than wild hazel, as well as a soft texture. That is why it is used in the preparation of the following dishes.
Kovurma
This is an incredibly tasty and beloved dish by many, which first appeared during the time of the Turks.


To prepare it, you need to take the following ingredients:
- Lamb with ribs - 1.5 kg;
- Fresh carrots - 0.75 kg;
- Potatoes - 1.5 kg;
- Sweet peppers (preferably red) - 3 pieces;
- Onions - 3 pieces;
- Oil (vegetable, olive oil) - 3-4 tablespoons;
- Dill - optional and to taste;
- Seasonings (black pepper, cumin, bay leaves, salt, etc.);
- Bear nut - 0.2 kg.
Read also Cabbage kale how to cook
Preparation: Chop the lamb into large pieces. Pour a little into the cauldron to lubricate it. Calcine the zira in a cauldron for 30 seconds, then throw the meat into it. Cook it for 5 minutes, stirring occasionally. Now fill the meat with boiled water (3 liters) and cook. The cooking time largely depends on the meat itself, so watch the degree of its readiness. Then you can add potatoes, carrots, bell peppers and bear nuts. Boil the dish for about 30 minutes (less if the meat is young).


Add salt, pepper and other seasonings and spices just a few minutes before cooking. Kovurma should be infused for about 20 minutes. Be sure to remove the lavrushka from the dish so that it does not spoil the taste in the future. Fresh chopped dill can be added to the plate if desired.


Rabbit pate
Another great dish where bear nuts come in handy. The rabbit and the bear usually get along well in fairy tales and anecdotes. Therefore, it is not surprising that bear nut and rabbit meat are so perfectly combined in one dish.


You will need the following set of products:
- Bear nut - 30 pcs.;
- Eggs - 1 pc.;
- Rabbit or rabbit fillet - 1 kg;
- Chicken liver - 0.5 kg;
- Onions - 2 pcs.;
- Fat - 0.1 kg;
- Greens (at your discretion) - 1 bunch;
- Salt, pepper - to taste;
- Nutmeg - 1 pinch
- Starch - 1 tbsp. the spoon.
Preparation: First, slice the liver and fry it. Process the fried liver with a blender or scroll in a meat grinder. Cut the rabbit meat into small cubes, add salt. Also finely chop the onion and stew it with the rabbit. Chop the greens.


Cut the bacon into strips so that they are thin enough. Dip in starch. Place about half of the bacon in a baking dish. Mix together the egg, herbs, chopped onion, add the bear nut (you must first chop it into large elements). Don't forget to season everything with pepper and salt.
In the form you need to put minced meat (half) on top of the bacon, then put the meat, then the second half of the minced meat and again the bacon. Bake in the oven using a water bath. The mold should be almost completely submerged in water. Cooking takes about an hour and a half. The oven temperature should be around 170 degrees.


Planting hazel in the garden
Hazelnuts are cultivated throughout Russia. The plant is unpretentious, shade-loving, tolerates severe cold well, but does not like heat.
It is necessary to plant hazel in shaded areas, in lowlands, on the banks of reservoirs and rivers.
Hazelnut prefers rich lime-containing soils - moist and even with high humidity, loose brown gray soils, black soil, rich podzolic soils. On acidic soils - peat, or on poor sandy loam, the shrub does not take root.
If the land in the garden does not meet these requirements, it must be modified, and the hazel must be fed abundantly.
The plant is combined with any coniferous and deciduous trees, and shrubs. It is often used for decorative fences. Although its flowers are unattractive, there are varieties in which the nuts and the wrapper are painted in bright, beautiful colors.
Care for hazel
Plant care includes the usual activities: pruning shrubs, feeding, watering, harvesting. Due to the unusual flowering time, events are held at different times.
How to trim
The crown of hazel is spreading and prone to thickening. Pruning is done for different purposes and in 2 ways: to form a tree or to get a bush.
- Post-planting - before planting, the roots of the plant are greatly shortened. To balance the volume of the aboveground and underground parts, shoots are cut off from the planted tree. At the same time, the apical buds are cut, which delays the blooming of the leaves by 6-7 days. This is enough for the hazel to take root.
- Formative pruning is performed for 4–6 years: the main shoots are shortened, lateral branches are cut to 3-4 buds. The height is maintained up to 2 m, the crown is shaped into a bowl. They also remove old, broken branches and growing inward: they thicken the crown, but give almost no fruit. Hazel is pruned in April.
- At the age of 6–7, they perform a "dry": in August, half-strong lateral shoots are broken and left in a drooping position. In the spring, the branches are still shortened by 5-7 cm. This tough stop-growth technique allows the wood at the base of the branches to mature better and also to lighten the crown. Subsequently, fertile strong shoots grow on the broken branches.
Female buds are formed at the ends of overgrown branches. Well-positioned stems cannot be shortened, only old or dried shoots must be cut off.
20 years after planting, a rejuvenating pruning is performed: old trunks are removed, which activates the growth of young ones. Cut out gradually - 1-2 main branches per year.
With proper agricultural technology, hazel grows and bears fruit for up to 90 years.
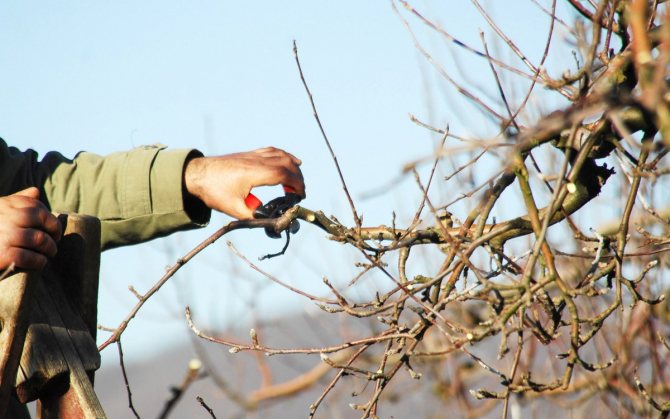


Hazel pruning is done in two ways
How to water
Hazel prefers moist soil and does not like heat or heat.
Watering the plant begins 7 days after planting.
If the hazel does not have enough water, this is bad for flowering. In the fall, the plant is not watered.
On average, a nut needs 1 watering in 4 weeks.
60-80 liters of water are poured under an adult shrub.If the summer is sultry, the amount of watering is increased: hazel loves moisture. In a rainy summer, they do without irrigation.
The volume of water is poured in several steps: puddles should not accumulate under the tree.
Fertilizer
Hazel is unpretentious, so feeding is performed infrequently:
- in spring the plant needs nitrogen. After swelling of the buds, 20–30 g of urea or ammonium nitrate is introduced into the near-stem circle;
- in July, feeding is repeated - this improves the ripening of the fruits;
- in the fall, 20-30 g of potassium salt, 50 g of superphosphate and 3-4 kg of manure are applied under the tree. Fertilized once every 2-3 years;
- young trees are additionally fertilized with rotted manure or compost - 10 kg under a bush once every 2-3 years.
How to care during flowering
Flowers bloom before leaves, as soon as the air temperature rises to +12 C. Earrings grow quickly - up to 30 mm per day.
The drier the air, the faster they grow.
When the earring grows to a length of 10 cm, it becomes loose and throws out pollen. Pollination lasts 4–12 days, and female flowers are open for 14 days. The plant does not require special care at this time.
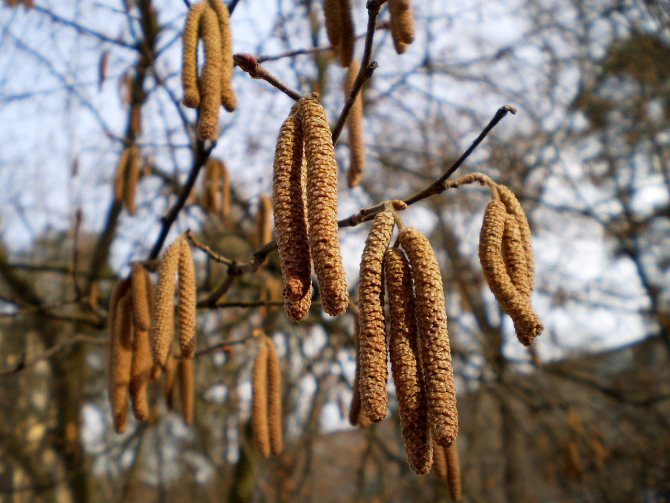


Hazel earrings without pollen
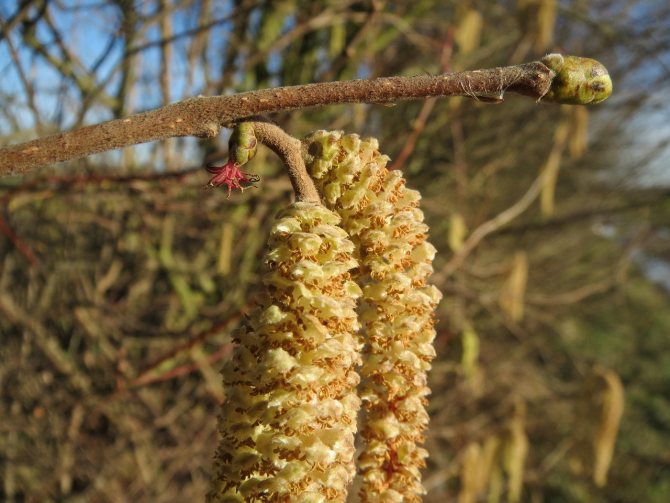


Hazel earrings with pollen
Growing
Landing
It is necessary to plant a nut in the fall. To do this, you need to make a hole of about 0.5 by 0.5 meters, fill it with 10 kg of humus, 200 grams of mineral fertilizers and 50 grams of potassium salt. Also, you can not do without fertile soil.
Prepared or purchased seedlings must be pruned before being placed in the ground. It is advisable to dip the roots in a mash made from manure and clay. If you are not making a hedge, then keep the distance between the seedlings about 5 meters, otherwise the planting is denser. It is important to water the tree abundantly.


They take care of the bear nut by constantly loosening the soil to a shallow depth. Also, don't forget to mulch. If the weather is dry, you can water the tree occasionally. Apply mineral fertilizers every year, and organic fertilizers only once every 2 or 3 years.
Growing a bear nut on your own is not difficult.
The easiest way, of course, is to purchase ready-made seedlings. But you need to make sure that they are of high quality and will give the desired result. Therefore, purchase in trusted places.
As a result, you will receive not only nuts that you, your children and grandchildren can enjoy, but also a very beautiful tree that can decorate any part of a summer cottage or private house.
| Tree hazel | |
| Treelike hazel leaves and nuts | |
| Scientific classification |
| Domain: | Eukaryotes |
| Kingdom: | Plants |
Read also Grated garlic with salt for the winter
| Subkingdom: | Green plants |
| The Department: | Flowering |
| Class: | Dicotyledons [1] |
| Superorder: | Rosanae |
| Order: | Beech flowers |
| Family: | Birch |
| Subfamily: | Hazel |
| View: | Tree hazel |
Wintering hazel
Hazelnut is able to withstand very severe cold: in natural conditions, it grows even beyond the Arctic Circle. However, young trees are more sensitive to cold weather, so the shrub is covered with spunbond in the first 2-3 winters.
Another way: to bend the hazel to the ground, cover it with spruce branches and snow.
In the middle lane, both young and adult hazel tolerate winter equally well.
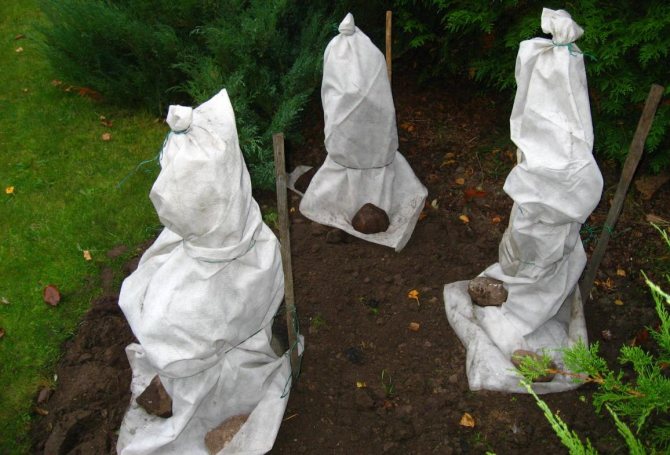


Proper wintering of young hazel
Appearance
In many ways, bear walnut is valued for its excellent decorative properties. In addition, it is the only plant of the genus hazel that has a life-form in the form of a tree. The height can reach 20 meters, however, in the conditions of the Russian climate, trees higher than 8 meters are rarely found. This nut lives for about 200 years.


The trunk is even, covered with light bark. The leaves are broadly ovate, large, the petiole can be up to 5 cm long. Fruits are small, covered with a thick shell. There is a nut hidden inside, but getting to it is not so easy. So do not try to split the shell with your teeth.
Interestingly, although the fruit is larger than that of a hazelnut, the edible part, that is, the seed, is still smaller. Plus, it is covered with thick husks. Their main advantage is that they taste better than hazelnuts.


Pests and diseases of hazel
Hazelnut is insensitive to many diseases and pests. But in the garden, he encounters insects and diseases more often, since mostly garden crops have lower immunity and are prone to infection.
Hazel pests
Most of all, hazel is damaged by a kidney mite, weevil, leaf beetle:
- A bud mite is a tiny insect only 0.3 mm long. The mite hibernates in hazel fruits and lays eggs in them in the spring. Affected kidneys swell greatly, increase to the size of a pea. They do not open, but dry and fall off. The yield is greatly reduced.
- Aphid - affects foliage. It sucks out the cell juice: the leaves curl up, the flowers dry up. Due to the lack of foliage, fruits are formed less, they ripen longer. However, the main danger is different: aphids - a carrier of viral ailments.
- The hazel barbel is a black little bug. Its larvae eat the core of young shoots. The stems dry up, the foliage curls and falls off on them. The affected parts of the plant must be removed immediately.
- Weevil - The beetle lays eggs in nuts. The weevil larva feeds on the pulp of the fruit. If you do not take action, you can lose half of the crop.
- The leaf beetle is the most dangerous pest. Due to the masking color, it is lost against the background of foliage. It can only be detected by damage: the beetle eats foliage, young shoots.
They are fighting with believers both manually and with the help of insecticides.


Hazel leaves often affect aphids


The weevil loves hazel
Hazel disease
Hazelnuts are resistant to disease, but are affected by powdery mildew and rust.
- Powdery mildew is an extremely common fungal disease. It begins with the appearance of small whitish spots on the foliage. Their number increases until the whole bush seems to be doused with lime water. The spots turn brown, the foliage turns yellow, but premature leaf fall does not begin. The dew-causing fungus is alive as long as the plant on which it parasitizes lives. Powdery mildew does not kill the plant.
- Rust - The fungus causes dark red bumps to form on the outside of the foliage. Pustules appear on the seamy side of the plate. The spots merge into stripes, the foliage turns yellow and falls off. So you can lose not only the crop, but also the plant itself.
- White rot - affects all parts of the hazel. The foliage loses its color and becomes covered with a white bloom, the stems rot in the root area, the tops of the shoots wither. The disease is very dangerous, difficult to treat and can lead to the death of the garden.
Procurement of raw materials
Nuts are harvested as they ripen. Ripe fruit acquires a rich color, and the wrapper dries up. The walnut peels off easily. Fruits ripen by the end of August - early September, ripen by October.
The fruits are collected, laid out on paper and dried in the air.
Then the nuts are freed from the wrapper and dried for another 2-3 weeks. You can use a dryer or oven, but not desirable.
For medicinal purposes, the bark and leaves of the plant are harvested.
The bark is harvested in September-October or early spring. Dry in a special dryer at + 60–70 C. Store in linen bags for 2 years.
Only young leaves are suitable. They are harvested in May and dried in the fresh air. Direct sunlight should be avoided. The shelf life of raw materials is 1 year.


Nuts must be dried before storage.
Planting rules and requirements for seedlings
Hazelnut, even when it became a cultural form, retained the need for group planting. From this, several seedlings should be bought for planting in one area at once. Self-pollinated hybrids are rare. This is required for high-quality pollination, without which the harvest cannot be obtained. The distance between plants should be 4 to 6 meters.At a closer location, overgrown bushes will interfere with each other. Hazel must be at least 5 meters away from other large trees and bushes, otherwise it will not have enough nutrients.
Pick-up location
The place for the nut is selected without drafts, sunny, but without direct sunlight. The plant does not tolerate shadow. You should not place the plant where water from the roof will drain onto it. A good solution is to plant seedlings along the fence on the west side. It is impossible to place hazel in an area where there is melt water in the spring, as it will be destructive for the hazel. Groundwater should be no higher than 1.5 meters from the surface. With their closer location, the shrub will die as soon as the main root reaches the aquifer. A drainage system won't help.
The soil for common hazel is optimal loose, light, rich in humus. Its acidity should be negligible or neutral. If a group of plants is planted at once, then it is first recommended to dig up the entire area to a considerable depth and only then dig holes for each seedling.
When to plant
March and November are considered the best months for planting in open ground (in the fall, seedlings should be planted 15-20 days before persistent frosts begin). At this time, the plant is easier to tolerate the stress of transplantation, since sap flow is still / no longer. If it is possible to choose the planting season, then preference should be given to the autumn period. This will prevent damage to the hazel in the summer heat, it will more easily survive the winter, and in the spring it will quickly grow.
Landing
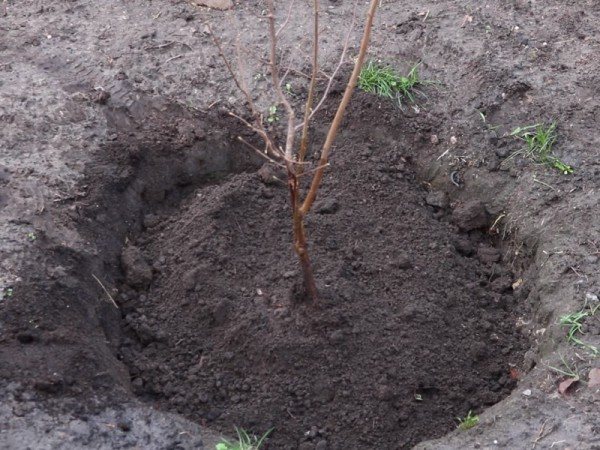


A good viable seedling should have 3-4 powerful stems up to 15 mm in diameter and a developed root system with a root length of at least 50 cm.However, before planting, the roots should be shortened to 25 cm.
Plant pits are prepared 30 days before planting, and for spring planting - from autumn. In areas with nutrient soil, the depth and width of the pit is needed at 50 cm. If there are few nutrients, then the dimensions increase to 80 cm. The pit is left to stand for 3.5 weeks. Before planting, a mound must be poured to the bottom, on which the plant will be placed. It should be composed of nutrient soil. With poor soil, the same soil is poured into the pit in an even layer to a height of 30 cm. You can buy nutrient soil, or you can improve it and use the one that was taken out when digging holes. To do this, it is mixed in a 1: 1 ratio with compost and 200 g of wood ash is also poured into each seedling. If possible, it is a good idea to add a few handfuls of forest soil from wild hazel areas.
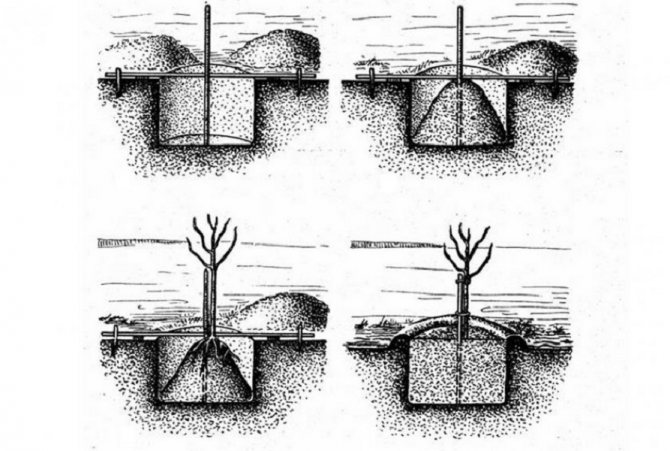

The seedling is placed on a mound, distributing the roots along its slopes so that they do not tuck, and then they fall asleep, keeping the plant in an even position. The soil around is compacted by trampling. It is impossible to fill up the root collar. If a tree hazel is planted, then it is tied to a peg. Next, the plant is watered using 20 liters of settled warm water per seedling. Then the trunk circle is mulched with sawdust to prevent excessively rapid evaporation of water, as well as hypothermia of wet soil.
Types and varieties of hazel with photos and names
There are 20 types of hazel that grow in natural conditions. On their basis, various varieties are obtained, including decorative ones.
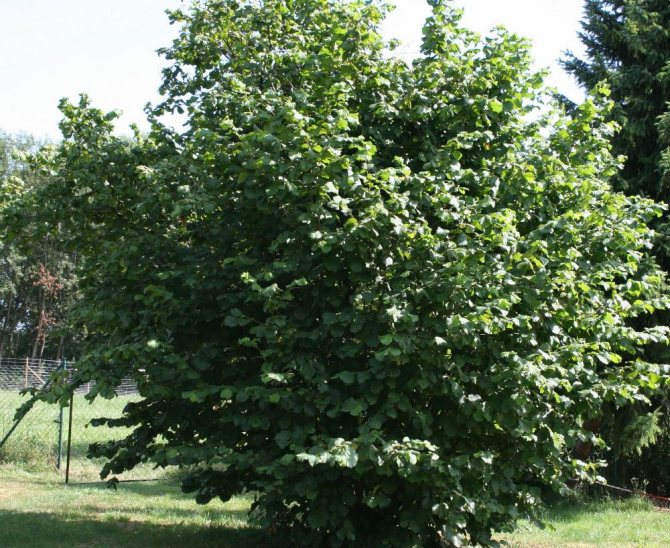
Common hazel
A multi-stemmed shrub, reaches a height of 4 m. The crown is spherical, spreading - up to 6 m in diameter.
It is the most widespread variety in Russia and Western Europe.
Hazel fruits are spherical or slightly elongated, up to 18 mm in length. Nuts are twisted in 2-5 pieces. Juveniles are light green in color, bell-shaped wrapper of the same shade. The color of a ripe nut is bright brown. The taste can be considered classic: soft, sweetish, delicate.


Common hazel
Treelike hazel, or bear nut
A tall tree reaches a height of 25-30 m.Crown width from 6 to 8 m, regular pyramidal shape. The foliage is abundant, bright green, in the fall it acquires a green-yellow tint.
The fruits ripen by September, their shells are thick, the wrapper is cut into sharp slices.
The taste is less pronounced. Bear nut is readily used as a stock, as it does not give offspring.
Treelike hazel is a long-liver. There are specimens over 200 years old.
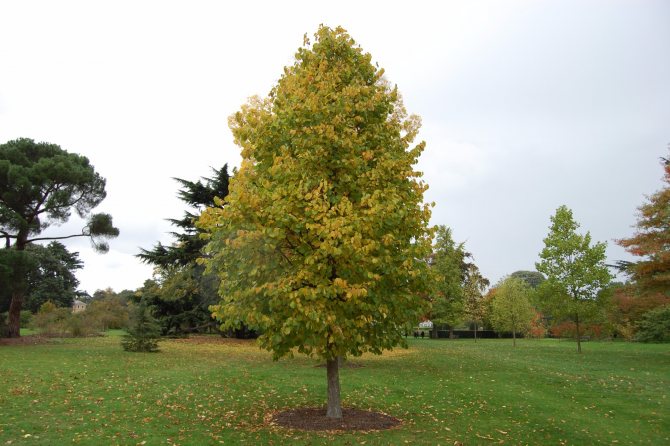


Tree hazel
Manchurian hazel
The compact shrub grows up to 2.5–3 m tall. Leaves are oblong with a pointed tip, young foliage and shoots are strongly pubescent. Elongated nuts, collected in 4-5 pieces. Although their shells are thin, it is difficult to extract the nuts.
Fruit wrapper is prickly, which makes picking difficult.
Manchurian hazel is grown for landscaping parks, hills, ravines, forest clearings.


Manchurian hazel
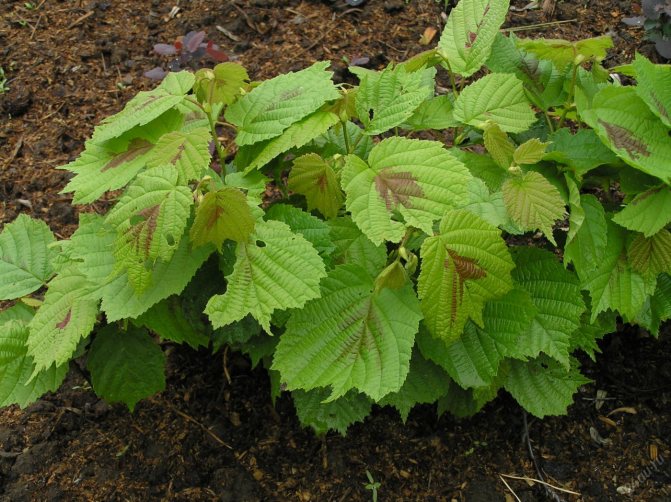
Various-leaved hazel
A small bush - up to 3 m, but with a very spreading wide crown. In spring, young leaves have a reddish tint. They turn dark green in summer and golden orange in autumn.
For this feature, the plant got its name.
Hazel fruits are flattened, usually solitary.
Nuts contain only slightly less oils and proteins than common hazel and have an excellent, delicate taste.
The plant is drought-resistant, tolerates extreme heat and frost well.


Various-leaved hazel
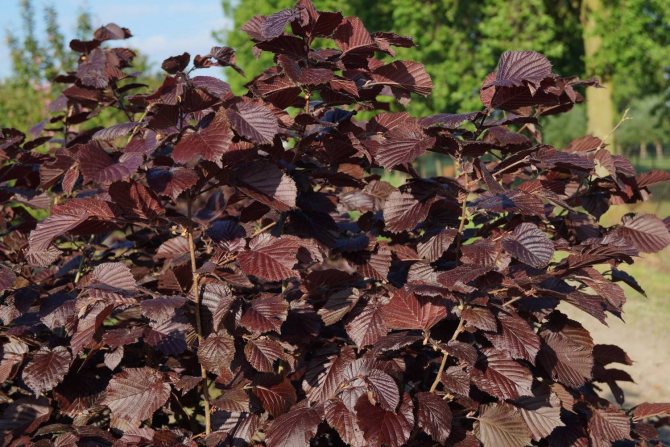
Red-leaved hazel
A very decorative variety. Its foliage is dark purple and only turns green by autumn. The buds and earrings also have an unusual maroon hue.
On the basis of red-leaved hazel, new crop hybrids are obtained.
The shrub is high - up to 4-6 m, the crown is round and wide. The fruits ripen by mid-August. Up to 8 kg of nuts are removed from 1 bush.


Red-leaved hazel
Large hazel, or Lombard nut
Grows up to 10 m tall. Spreading shrub with abundant foliage - dark green or, more often, dark red. Plants bloom in March, fruits ripen by September.
Lombard nuts are large - 2.5 cm long and 1.5 cm in diameter.
They grow 3-6, sometimes one at a time. The wrapper completely wraps around the nut and goes into a tapering tube. Color - dark green or red-green... Lombard nut not only looks beautiful, but also extremely tasty and looks more like almonds than hazelnuts.
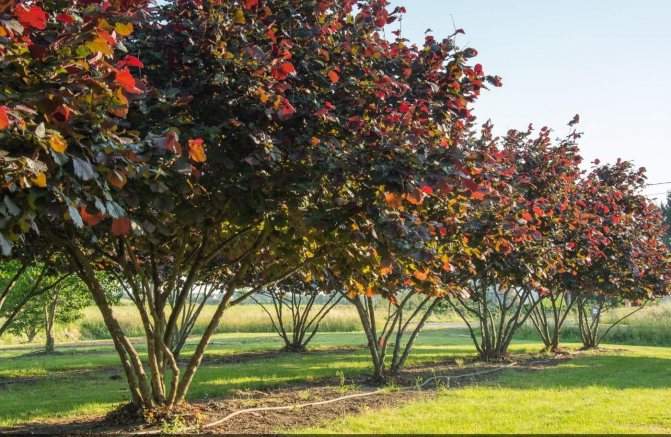


Large hazel
Reproduction
Hazel breeding is possible in several ways. In the auxiliary area, if necessary, use the simplest one - by root suckers. Growing shrubs from seeds is rarely practiced.
- Root offspring. The shoots are located next to the bush. The first young plants appear within 2 years after planting the culture. At the age of 2-3 years, the offspring are dug up, separated from the parent plant and then planted in a new place. The wound on the maternal root and on young hazel is sprinkled with crushed coal.
- Layers. This breeding method is also popular. It produces plants that fully retain the properties of the parent hazel. Tree hazel is not suitable for this method. In late autumn or early spring, low-growing annual branches are chosen. Grooves with a depth of up to 15 cm are dug under them. The branches are placed in them and fixed. They do not need to be covered with soil from above. Over time, vertical shoots will appear on the branch, which will give roots. They are regularly spud up to the middle. Layers can be deposited after 2 years. The shoots are dug up and separated with the part of the branch on which they were formed.
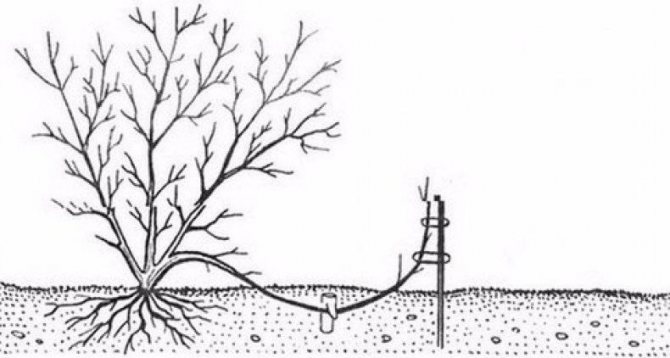

Reproduction by layering. - Graft. For rootstock, seedlings from wild walnut or bear nut are used (the best option, which does not give root shoots). In the spring, the cultivated hazel cuttings are inserted under the bark of the rootstock and fixed end-to-end. Cuttings are cooked in winter and stored in a refrigerator or snowdrift.
- Bush division. A simple method applied to bushes from the age of 10.The bush is dug up and divided into parts so that roots of at least 20 cm in length remain on each. After the place of the cuts, they are covered with crushed coal. Then the bushes are planted in a permanent place.
Trying to grow hazel from a nut is not worth it. This process is very long, and the likelihood that the new bush will retain the qualities of the parent is low.
Hazelnut oil
The fruits of the plant contain up to 65% oils. Get it cold pressed. The substance retains all nutrients and vitamins, with the exception of proteins.
Salads are seasoned with oil and added to ready-made meat dishes to enhance and highlight the taste.
Used in medicine - it stimulates the digestive system, enhances the outflow of bile, and activates hematopoiesis. The oil is used to treat skin conditions and to get rid of acne. Walnut oil is a frequent ingredient in anti-aging creams as it accelerates skin regeneration.
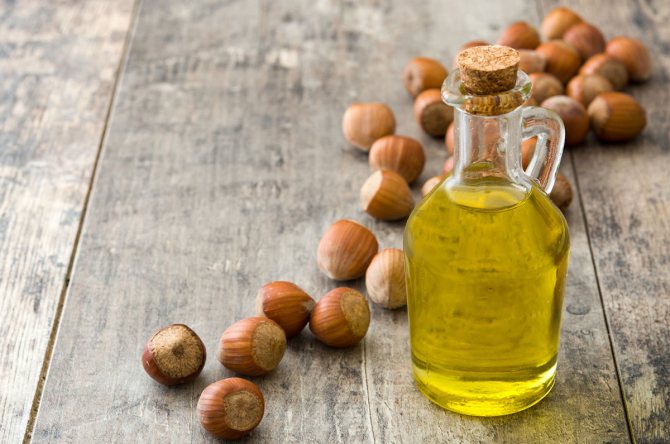


Healthy hazelnut oil
Peanut butter
One of the health benefits of hazelnut is oil, which has properties very similar to almond oil.
Hazelnut oil is indicated for use in epilepsy and ascariasis. Very effective as a hair loss remedy.
The following main beneficial properties of hazelnut oil can be distinguished:
- as an antihelminthic;
- tonic;
- wound healing;
- regenerating;
- anti-inflammatory.
The oil is actively used by cosmetologists and dermatologists both in pure form and in the form of constituent creams, ointments, hair and face care products, in aromatherapy.
Walnut oil is recommended for oily skin care. It is great for toning skin, getting rid of acne, shrinking pores, improving complexion and reducing wrinkles.
A mixture of oils: hazelnut, sesame, calendula and St. John's wort will help relieve fatigue from the legs. The mixture is prepared in a ratio of 4: 2: 1: 1, respectively.
Thus, it turns out that between nuts: hazelnut and hazelnut, the difference is small and the main difference is in the culture of the plant.
Watch the video of how walnuts are harvested in the south of Russia
Contraindications
There are few bans:
- Hazel should not be eaten with severe diseases of the gallbladder and liver. Due to its high fat content, it is poorly digested in such diseases.
- Nuts can exacerbate some skin conditions. So, with psoriasis, hazel is excluded from the diet. It is also unsafe to eat it with neurodermatitis.
- Infusions from the bark and leaves of the plant should not be drunk for hypertensive patients. Since herbal medicines increase blood pressure.
Hazel is grown in gardens for its delicious fruits. The plant is unpretentious, not afraid of even severe frosts, multiplies easily, gives a good harvest. The nut fruit has a high nutritional value, and the bark and leaves are used for medicinal purposes. Some varieties of hazel are very decorative.





































