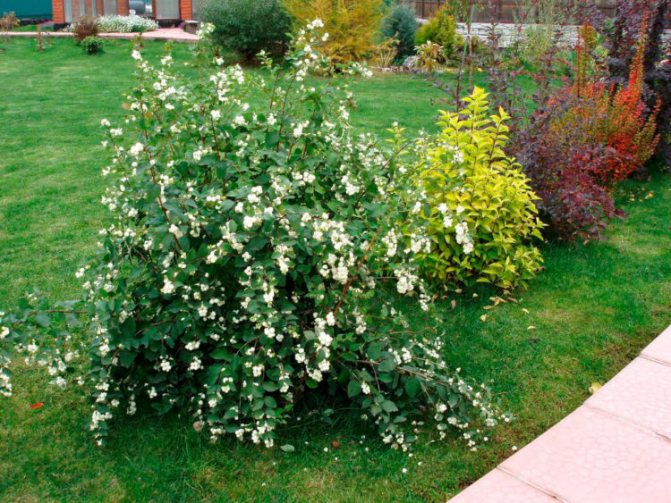
This article describes in detail what a white snowberry is, a photo and description of which are presented below. In addition, you will learn what related varieties of this culture exist, how to properly prepare the soil for planting a shrub with snow berries. We will also jointly try to figure out how to properly plant, care for and prune this crop so that the bush looks spectacular and delights the eyes of everyone who sees it.
Snowberry (Symphoricarpos), or, as it is also called, snow or wolfberry, belongs to the Honeysuckle family and is a spectacular bush with white berries. It is known that this plant has been bred for at least 200 years and is actively used to decorate parks and squares. North America is considered the birthplace of the snowfield, on the territory of which about 15 species of this crop grow.
Main characteristics
Snowball, snow berry, white berry, snow berry, wolf berry ... These are all names of the same plant, which has 15 species. Almost all of them have their homeland - North America, only a single species can be found in China.
The snowberry withstands the extreme conditions of the temperate climate. The plant does not care about frost or heat. It feels comfortable both with medium humidity and with drought, if it is not too long. The shrub grows both outdoors and in the shade.
He has no special requirements for the composition of the soil. It can be seen even in rocky areas, on limestones. But, of course, the plant blooms most magnificently on fertile lands. Especially if they are still fertilized with compost or rotted manure.
The endurance of the species is also manifested in the fact that it is extremely rarely affected by pests. In the fall, the number of insects decreases rapidly as they prepare for wintering. The plant is almost not exposed to diseases, since many of their carriers disappear at this time of the year.
Sometimes disputes arise: is the snowberry bush poisonous or not? Its fruits are dangerous, especially for children. They are sometimes used in very small doses as a medicine. Small lesions of the skin are lubricated with the juice of fresh berries or crushed leaves so that they heal faster. However, it is better not to carry out such experiments, because the medicinal properties of the plant are poorly understood. Moreover, it should not be out of curiosity to taste the fruits, because it is no coincidence that one of the names of the plant is wolfberry. For the same reason, you cannot plant a snowberry near kindergartens, schools.
General view of the shrub
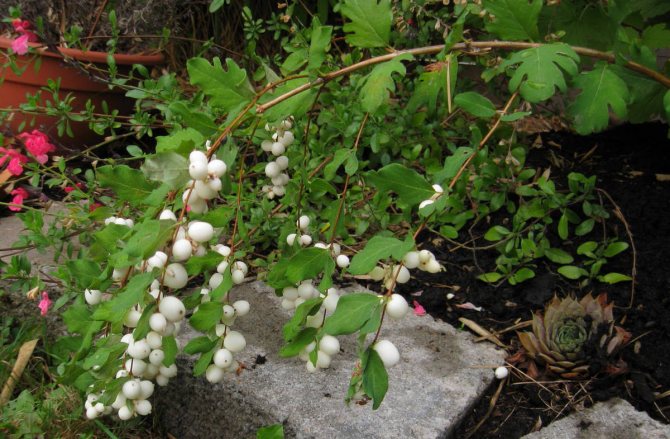
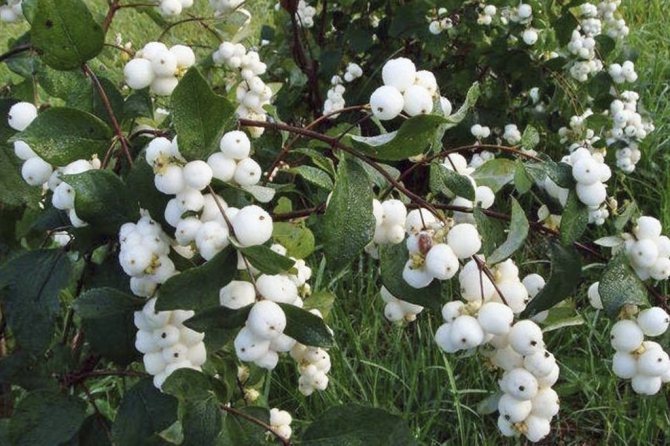
White snowberry (carpal) is a perennial plant from the numerous Honeysuckle family. This is the most popular type. Differs in rapid growth. A dense, deciduous bush reaches a height of 1.5 to 2 m. A trimmed adult plant looks like a huge ball of thin weeping branches.
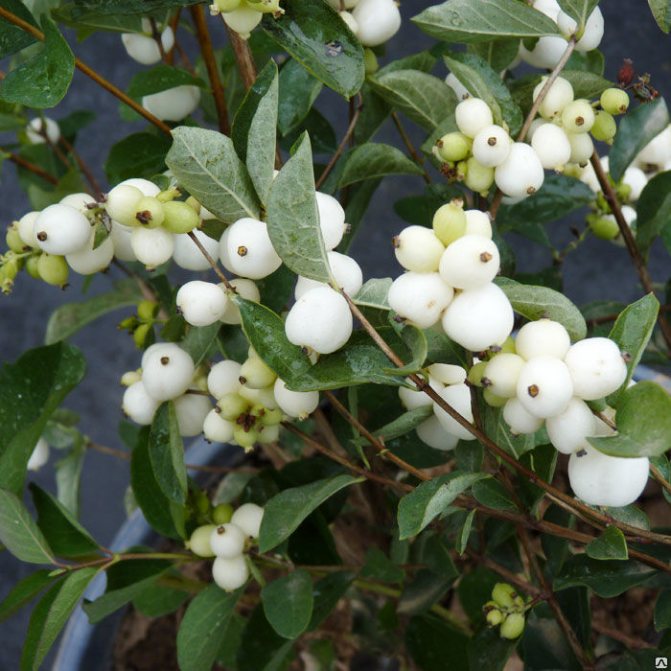

Foliage and flowers
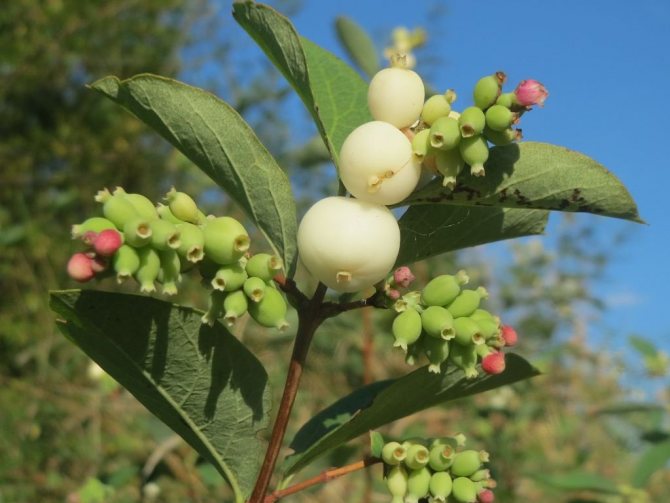
White berry leaves are small, up to 4-5 cm, oval or ovoid, opposite, whole-edged. Their upper side is green, and the lower side is gray, covered with light down. They are attached to the branches with short petioles. In autumn, foliage does not fall off for a long time and does not change color.
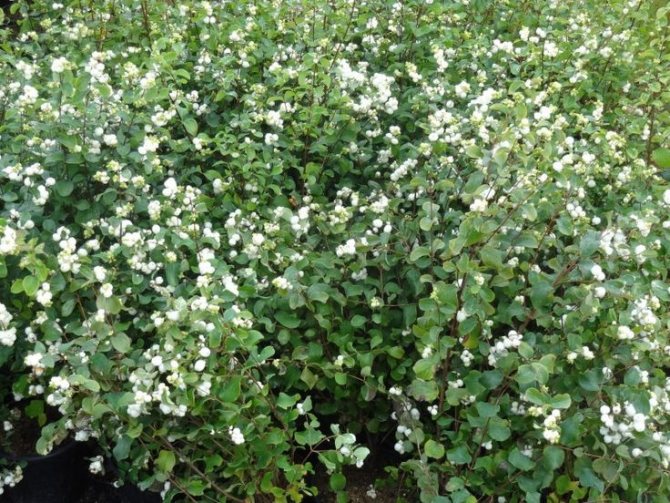
Numerous flowers are small, white with a pink, reddish or greenish tint. The corollas are shaped like bells. Flowers are collected most often in 10-15 pieces in lush racemose inflorescences.The buds of the white snowberry bloom at the end of May - June. The shrub blooms all summer, until early September.
Description of berries
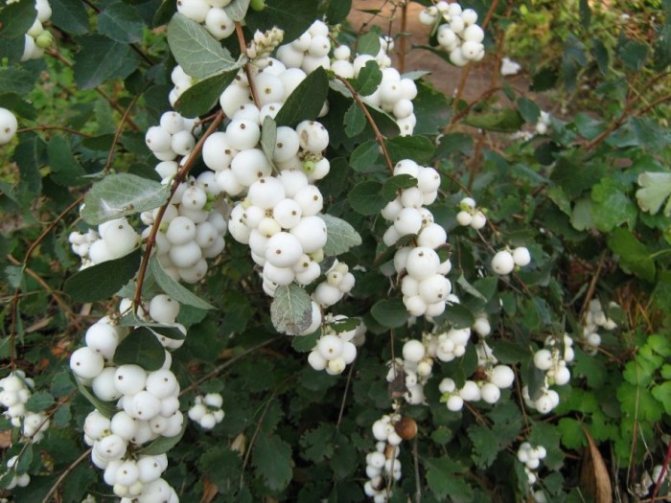
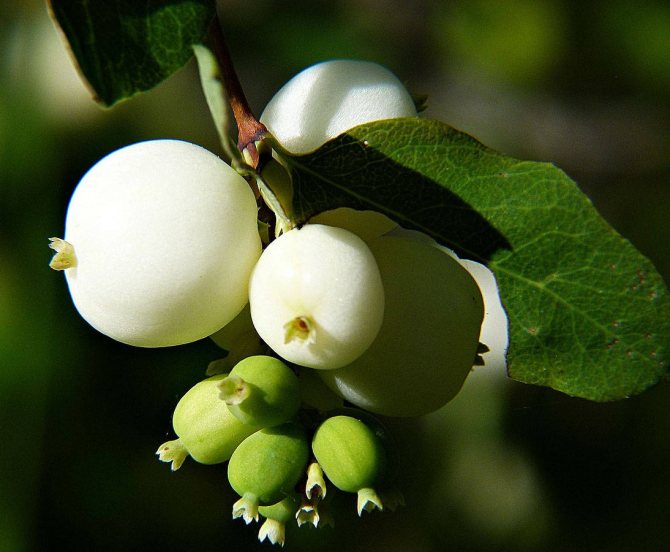
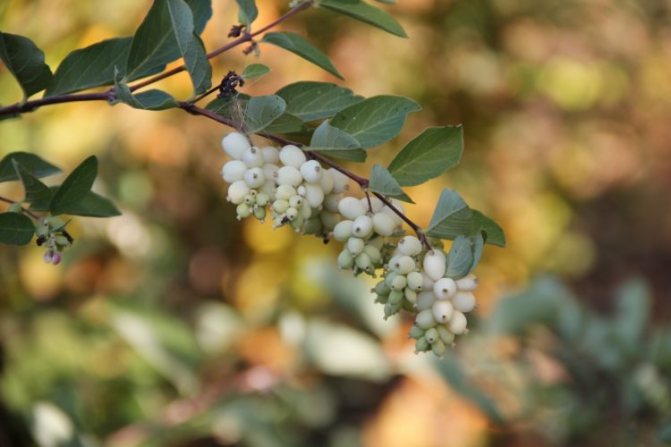
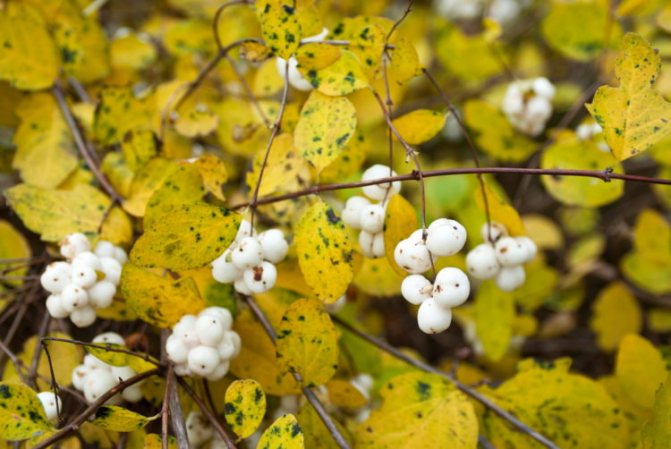
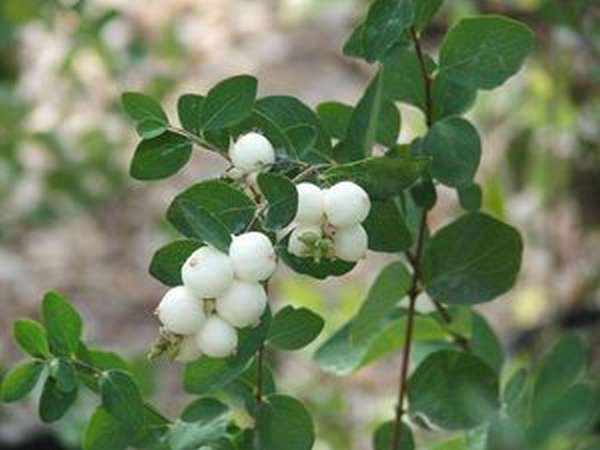
The fruits of the plant are small spherical drupes up to 2 cm in diameter. The color is white, in some varieties it is red or purple. The berries are closely pressed together. Tied in early September. Ripen in turn. When crushed, they emit a characteristic pop. They stay on the branches all winter. Inedible for humans, wolf berries are life-saving food for birds and forest animals in the winter cold.
Healing properties
The chemical composition of the snowberry is poorly understood, so the plant is almost never used in folk medicine.


But in North America, where the shrub is found throughout the territory, the indigenous people have learned to use it for treatment. They know about the antimicrobial and disinfecting properties of the white snowfield and prepare drugs from its berries, bark and leaves to treat wounds.
The shredded leaves of the shrub are used to fight skin ulcers. Compresses made from crushed fruits are used in the treatment of burns, cracks on the skin surface. Infusion of the bark from the plant is good for sore throat, as well as for many other diseases:
- tuberculosis,
- menstrual pain
- venereal diseases,
- stomach pathology,
- cold.
Despite these properties, it is not recommended to self-treat with these poisonous agents without consulting a specialist.
The original berries of the bush are beautiful in appearance, but unpleasant in taste. When poisoning with the fruits of the snowfield, the following symptoms are observed:
- nausea and urge to vomit,
- paroxysmal pain in the stomach,
- burning in the mouth and throat,
- feeling weak and dizzy
- stomach upset,
- lethargy.


If the poisonous substances of the plant get on the skin and mucous membrane, there is swelling, redness and irritation of the skin. The victim experiences painful sensations, the intensity of which will depend on the affected area. The individual characteristics of the organism also matter.
When the plant poison gets on the skin, it is recommended to immediately rinse the affected area with water. When ingested, symptomatic therapy is performed. It is necessary to drink milk, which has the ability to neutralize poison, or activated carbon. If the condition is severe, then you should immediately seek medical help.
Planting a snowberry in open ground
Many flower growers, landscape designers love the white berry and willingly plant it in their backyards, summer cottages, gardens, squares, parks. Since the shrub grows well even in excessively gassed, dusty areas, it is increasingly used in landscaping cities and large villages.
In landscape design, the snowberry is often used:
- when creating decorative spots and floral ornaments, figures, inscriptions in flower beds, on lawns;
- when building alpine slides using dwarf varieties;
- to achieve a spectacular contrast with mountain ash - in late autumn and with conifers - in winter;
- as a ground cover perennial under large trees;
- as a valuable honey plant;
- to strengthen crumbling soil on slopes.
Compositionally, shrubs can be placed in the following options:
- Combined with other ornamental plants when framing paths, alleys.
- Separate bushes standing in the center of a flower garden or a garden plot.
- Long stripes - hedges: monochromatic or contrasting (for example, alternating with red climbing roses).
In order for the snowfields to appear in all their splendor, it is advisable to plant them on slightly alkaline soils. Sufficiently fertile loams are also suitable. First, the soil must be dug deeply. If the soil is heavy, be sure to add a mixture of sand, compost and peat (equally).
Planting material should be sold with a lump of moist soil on the roots.If they are too dry, before planting, they should be dipped in a thick "chatterbox" - a slurry of clay with the addition of "Heteroauxin", a stimulator of the growth of the root system.
What time to plant
Planting a snowy berry can be planned twice a year: at the beginning and at the end of the gardening season. If it is planned to plant bushes in the spring, holes or trenches for seedlings must be prepared in September or October last year. If in the fall - 1-1.5 months before planting. For single specimens, holes are dug 60-70 cm in depth and width. For a hedge, a trench is prepared of the same depth, but 40-50 cm wide.
Landing features
At the bottom of the holes, crushed brick or expanded clay must be laid with a layer of 5-10 cm for drainage. Then a little rotted organic matter (5-10 kg per 1 m2) can be added to each hole. When planting several seedlings side by side, measure 1.5-2 m between them so that the neighbors do not interfere with each other's growth. Their root collars should be visible above the soil!
In a trench for a hedge, bushes no older than 2-3 years are planted closely, 4-5 copies per 1 m. To keep the line straight, twine or rope is pulled. The soil around the seedlings must be compacted and thoroughly moistened. Then they should be watered every day for 1 week.
Specialized treatment
The victim is sent to the nearest toxicology department. There is no antidote for the poisonous substances found in wolf berries. Therefore, symptomatic treatment is prescribed:
- antispasmodics;
- means for restoring blood clotting;
- intravenous infusion of saline;
- anticonvulsants.

If breathing is difficult, the victim is connected to a ventilator. Severe internal bleeding requires the use of hemostatic drugs and blood transfusion.
Caring for a snowberry in the garden
Shrub maintenance requires minimal effort. In the hot, dry period of summer, it is enough to moisten the plants every 5-6 days: 1-1.5 buckets of water for a seedling and 3-4 for an adult plant. In rainy weeks, watering is not necessary at all.
Weeds adjacent to the seedlings should be weed out regularly. They grow much less if the soil in the near-trunk circle is mulched with hay. This technique is also good in that it helps to retain moisture in the depths of the soil longer.
Transfer
When moving a snowberry to a new location, special care is required. The most important thing is not to damage its extensive roots during this operation. They are located within a radius of 0.7-1.5 m, so you need to dig out the bushes very carefully. The process of replanting itself is no different from the algorithm for the initial planting of a seedling.
Pruning and shaping the crown
It is necessary to put in order the bush in early spring, before the start of sap flow. Should be trimmed with pruning shears:
- broken off branches - completely, viable - 1/4 or 1/2 of the length;
- dried knots;
- extra shoots, too thickening the crown;
- branches that interfere with creating a beautiful spherical shape of the plant.
It is advisable to lubricate large sections with garden pitch, copper sulfate solution or clay putty. Young plantings need more frequent pruning to create a spectacular crown. Snezhnik easily tolerates this surgery. If you do not carry it out, then not a bush will grow, but a tree. Plants over 7-8 years old need rejuvenation. To do this, they are cut off much more, leaving shoots 40-50 cm long.
Necessary feeding
For the whole season it is enough to water the plants with Agricola: 50 g of the preparation per 10 liters of water. Or feed the snowberries with liquid organic matter: 500 g of rotted manure and 4-5 tbsp. l. ash for 7-8 liters of water. When digging near-trunk circles in the autumn, it is useful to close them up to 80-100 g of complex fertilizer.
Diseases and pests
When the summer is too rainy, the snowfield can get sick with fungal infections.It is easy to get rid of powdery mildew, gray rot with the preparations "Quadris", "Topaz" or "Fundazol". Even better - in the spring, prophylactically spray the bushes with dormant buds with Bordeaux liquid.
Young shoots of a snowfield can attract aphids. They destroy pests by dusting the branches with wood ash. If there are too many insects, you will need an insecticide: Aktara, Confidor, Aktelik or Fufanon. But there is no chemical protection from sawflies, the branches affected by them must be cut off and burned.
Necessary first aid
Any poisoning with a wolfberry requires the intervention of qualified specialists. But while waiting for the doctor, you should provide the victim with first aid yourself. This can alleviate his condition and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Need to:
- Empty the stomach. This must be done through vomiting, which will remove from the body the remnants of berries that have not had time to be digested. To provoke a reflex, you should press on the root of the tongue.
- Rinse. The poisoned person must drink at least half a liter of warm water, saline or a weak solution of potassium permanganate. After vomiting is caused. Repeat until the vomit is clear.
- Until the doctor arrives, you can only drink non-carbonated mineral water or milk at room temperature.
- You can remove pain syndrome with Almagel A, jelly or fresh rice water.
If the plant comes into contact with the skin, the problem area must be rinsed with running water or soda solution. A solution of lidocaine will help to remove the burning sensation and pain. Further manipulations should be carried out by doctors.
It is strictly forbidden to give the victim non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or Aspirin. Such drugs help to thin the blood, which will increase the symptoms and accelerate the spread of the poison throughout the body.
Snowberry breeding
You can get new plants yourself. When choosing a method, it is necessary to take into account the composition of the soil, the presence of groundwater, the climate of the area. Shrub breeding options:
- seeds;
- undergrowth;
- dividing the bush;
- layering;
- cuttings.
How to grow from seeds
It is recommended to plan sowing in autumn, then in winter the seeds will be stratified in natural conditions. Sow them in a flat box. If you immediately place very small seeds of a snowfield in the ground, then when it thaws, they can go deep and not sprout. It is better to transplant the emerging plants into the soil at the very end of May.
Sowing can be done in early spring. The seeds are preliminarily subjected to stratification artificially. In autumn, they are poured into a bag with a wet mixture of peat and sand, mixed and placed in the refrigerator for the whole winter. The seeded box is kept in a greenhouse. Seedlings are transplanted into the ground in June. However, both options are quite troublesome. In addition, a snowberry from seeds blooms only in the third year.
How to propagate by root shoots
The bush has a lot of growth. This is a good starting material for its propagation. You need to carefully dig out the bush and carefully separate the required number of shoots. The rules for planting them are the same as for seedlings.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
An adult snowfield can be easily divided into several small bushes. Each of them will become an independent plant. After dividing the bush extracted from the ground, the wounds are treated with charcoal. The wells for the separated parts are prepared in advance. But this method of reproduction is not very popular, since digging up an adult plant is not an easy procedure.
How to propagate by layering
This method is based on the use of bush branches. A young branch is selected from the lower shoots, bent to the ground, pinned and covered with a layer of soil. After 1.5-2 months, the roots will form at the layer. All that remains is to cut it off, carefully dig it up and plant it.
Cuttings
At the end of summer or in autumn, pieces of mature branches from 10 to 20 cm long are harvested. The cuttings are placed in a box with moistened sand and stored in a cool place throughout the winter. The sand should not be allowed to dry out.In early spring, cuttings are planted in the ground.
Another option: mature shoots are stored in the summer, after the end of the flowering of the snowfield. The workpieces are placed in wet sand with peat and placed in a warm place. Rooted cuttings are planted in the ground in the fall. With the onset of cold weather, immature plants are covered for the winter with a thick "blanket" of fallen leaves.
Distribution area
In natural conditions, a wild-growing snowberry prefers river banks, mountainous forest areas, slopes, ravines. The main distribution area is North, Central America.
Snowberry white is widespread in Canada and the northern part of the United States. In Russia, it grows well in the middle lane, in the Urals, in Siberia, withstanding frosts down to -30 ° C. Young plants can freeze slightly, so it is better to cover them with spruce branches, straw, pinning the branches to the ground.
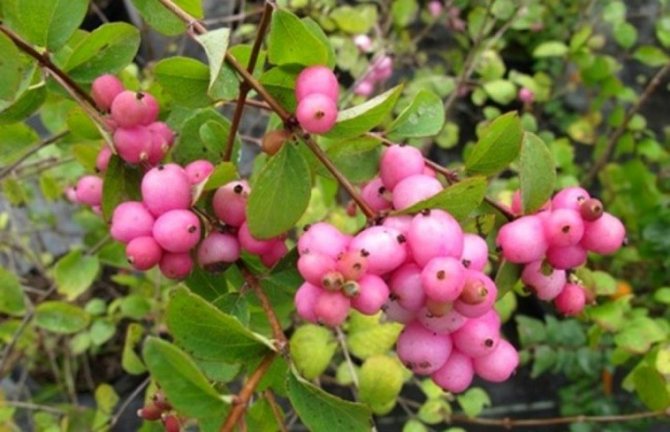
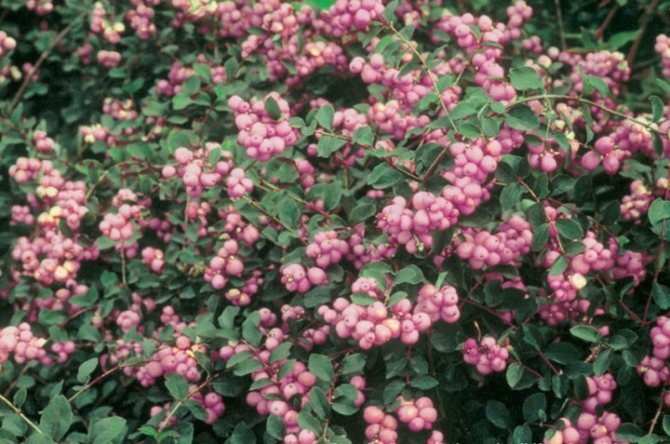
Snowberry pink is common in the southern part of America. In Russia, southern regions are more suitable for him due to prolonged heat and less humidity. Although, with the right cover in winter, this variety can be grown even in the middle lane. But during a cold and rainy summer, the bush does not reveal its capabilities, it may even stop developing. It is widely used for decoration of parks and streets.
A hybrid of pink snowberry - Chenot snowberry has an average frost resistance, but due to its small size, it is popular with gardeners. This variety is an excellent honey plant.


Most Dorenbose hybrids require shelter for the winter, keep temperatures only up to -8-10 ° C degrees of frost, and can freeze out. In addition, in the middle lane there is often a cool summer, as well as a small number of sunny days, then the bush does not have time to ripen. Also, snowless winters are dangerous for him.
These varieties are most popular with Russian gardeners, but the variety of types of snowberry is not limited to them.
The western snowberry is widespread in the eastern, central, western regions of North America. The mountain-loving snowberry is found in the mountain forests of western North America at an altitude of 2700 m above sea level. Small-leaved or Mexican snowberry is the southernmost species of the variety, found in Mexico, Guatemala, can grow up to 3000 m above sea level. The mild snowberry prefers open, sunny places with a subtropical climate on the coast of California, in the north of the Mexican Highlands. It is part of the chaparral ecosystem, which is defined as an ecosystem with rainy winters and dry summers.


Types and varieties of snowberry with photos and names
The height of snowfields of almost all varieties is the same: from 1 to 1.5 m. The branches are gracefully bent. Leaves in the form of an oval or ellipse are also similar. Their colors are different: the top is green, and the bottom is gray-bluish, sometimes pubescent. The bright, large clusters that dot the shoots are made up of countless miniature flowers.
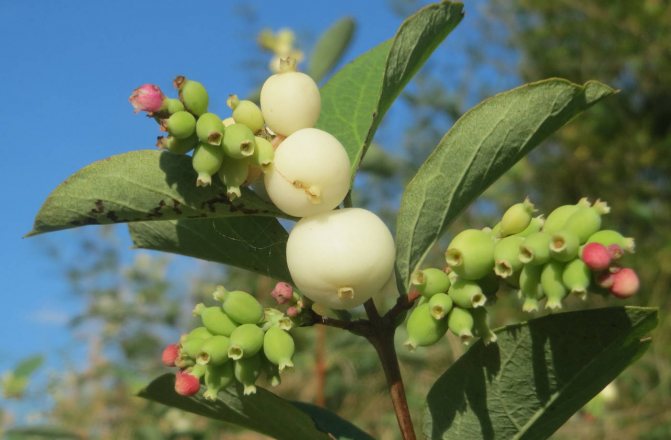
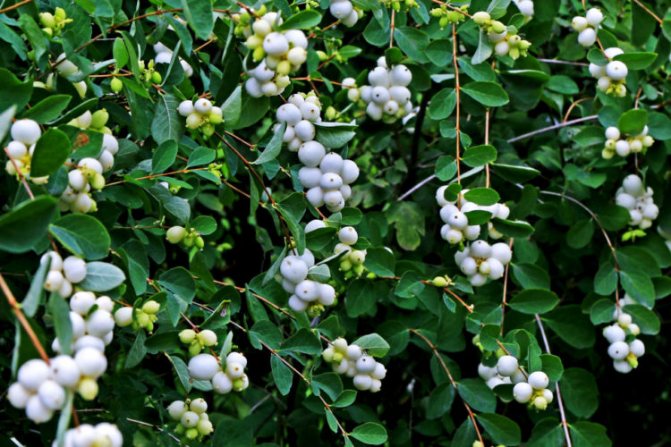
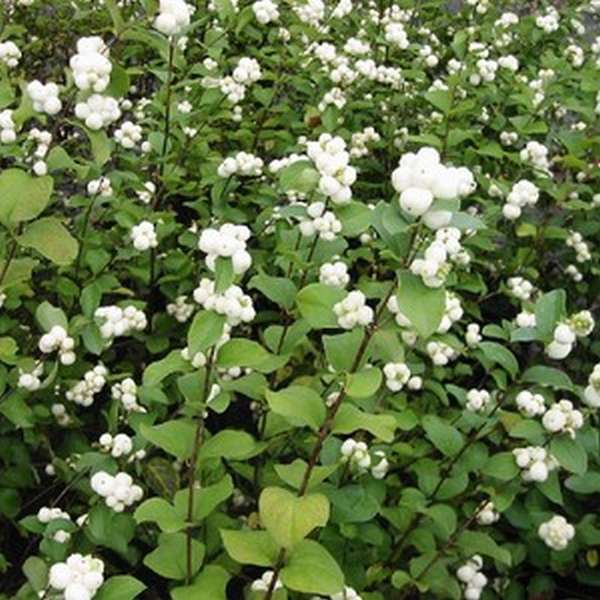
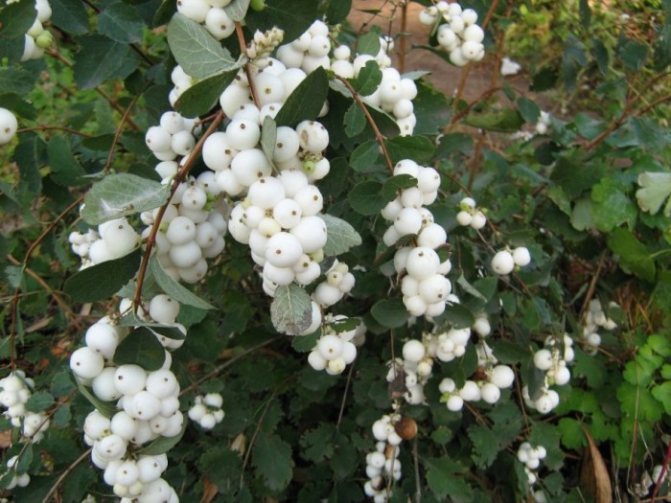
Snowberry white (Symphoricarpos albus)
The plant is valued for its high decorative effect. The spectacle of a lush ball with a huge variety of delicate pinkish flowers is mesmerizing. The flowering period of the species is long. There are just as many fruits that turn white all winter long. Moreover, flowers and berries decorate the bush at the same time. This is one of the most frost-resistant species. The most popular variety is the White Snezhnoyagodnik (Symphoricarpos albus laevigatus).


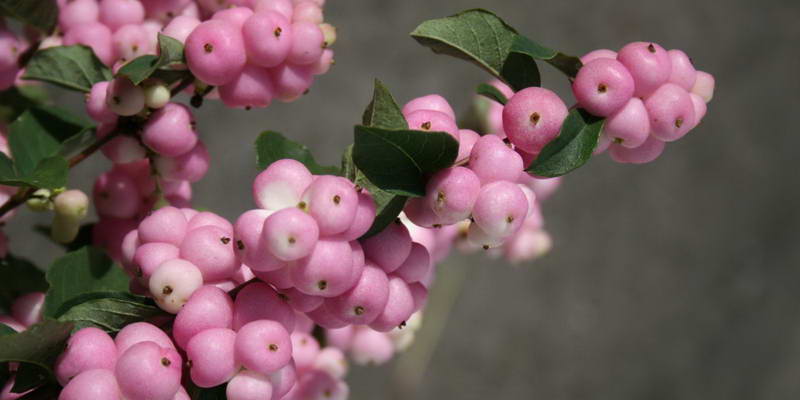
Common snowberry (Symphoricarpos orbiculatus)
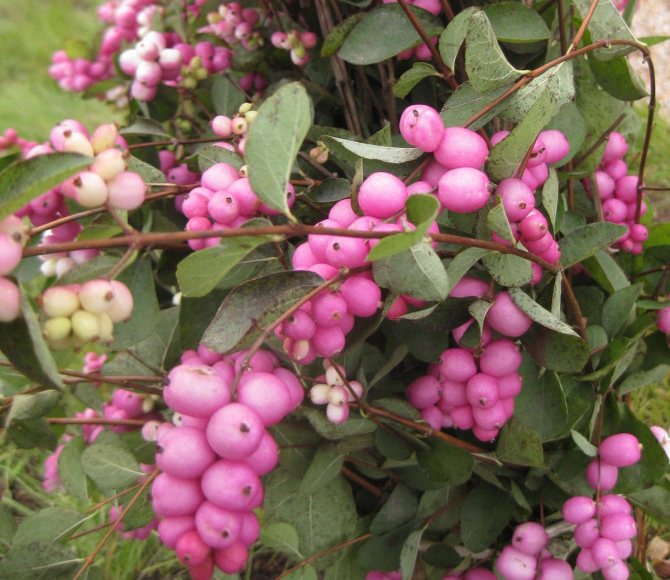
Coralberry, pink, rounded snowberry, Indian currant - this is also the name of the varieties of this species. It is a large shrub with a hemispherical crown. It is decorated with flowers of pale pink shades. The berries ripen dark purple with a bluish tint. In the fall, the foliage turns crimson. The frost resistance of this species is medium. The most common are 2 varieties: Variegatus and Taffs Silver Age.


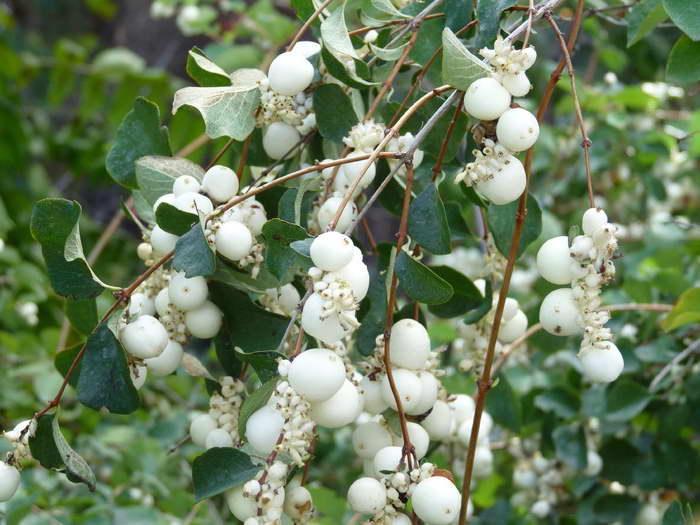
Western snowberry (Symphoricarpos occidentalis)
Plants of this variety of wolfberry often form dense growths. They have tougher, leathery leaves.White or slightly pink bells open on the branches. The shrub blooms profusely almost all summer. The color of the berries is pink. Frost resistance of plants is average, in severe winters they partially freeze.


Mountain-loving snowberry (Symphoricarpos oreophilus or utahensis)
This is an erect, less often creeping bush. He has white or pink flowers both single and paired. The fruits are distinguished by their impeccable snow-whiteness. The frost resistance of the species is medium, due to severe frosts, the shrub can freeze slightly.
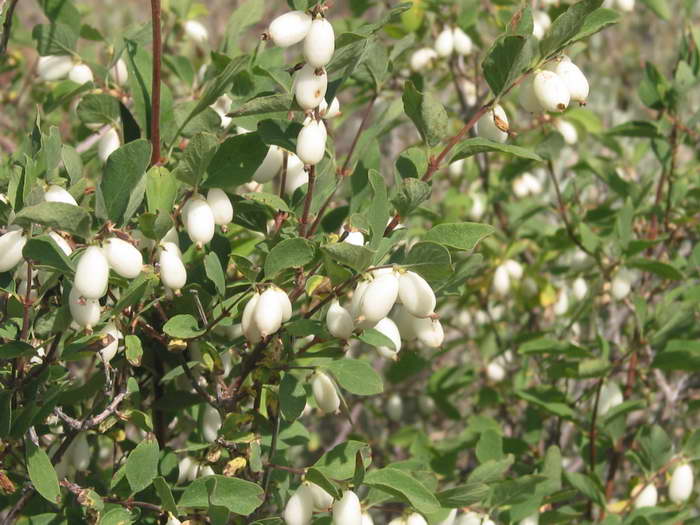


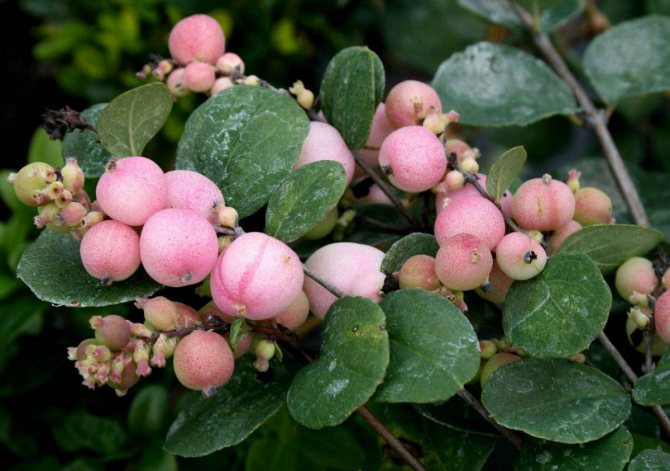
Snowberry Chenot or Henault (Symphoricarpos x chenaultii)
This beautiful hybrid was created in the Chenot nursery near Orleans, France. A new species was obtained by crossing two snowy berries: small-leaved and ordinary. The flowers of the shrub are pink, and the berries grow in white, pink and purple. The frost resistance of the hybrid is low, therefore the plant is a covering plant. The most spectacular variety that has become very popular is Hancock.
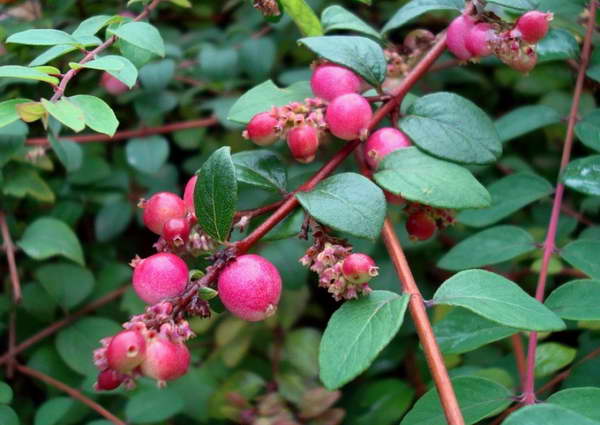


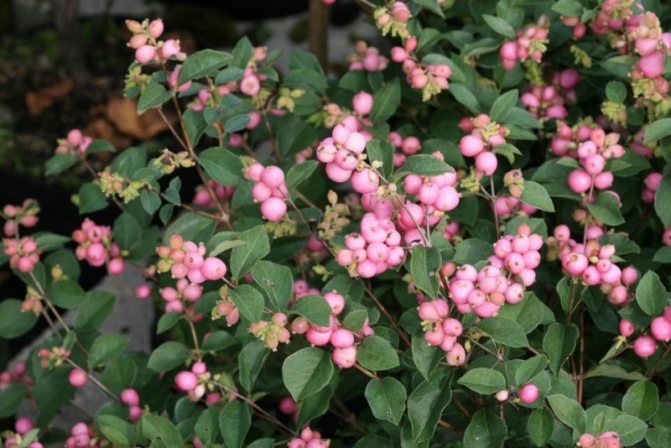
Dorenboz's Snowberry (Symphoricarpos doorenbosii)
Botanist Doorenbos (Holland) obtained a series of these hybrids by breeding white and rounded snowberries. Compact bushes have a spreading crown, consisting of shoots growing in a horizontal direction. The colorful flowers have different colors: from white to red with a lilac tint. The berries grow in different sizes. The most beautiful varieties are Amethyst, White Hage, Mather of Pearl, Magic Berry. Dorenboz hybrids are distinguished by good frost resistance, but severe snowless winters are dangerous for them. For this reason, young plants must be covered securely.
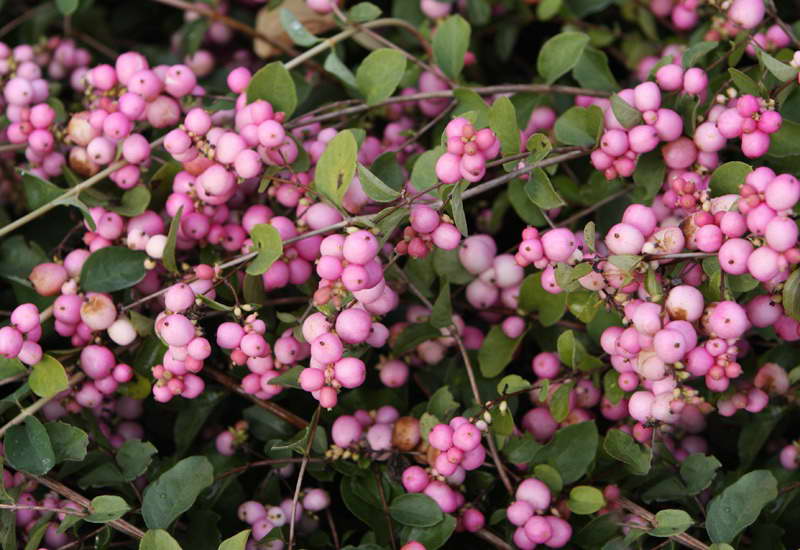


What is wolfberry
Wolfberry is a poisonous plant. The following dangerous shrubs can be called so by the people:
- snowberry;
- belladonna ordinary;
- brittle buckthorn;
- raven eye;
- daphne;
- common honeysuckle.
But most often the wolfberry shrub is common privet. Another popular name - "wolf's eye" - is obtained due to the appearance of the fruits - they are small, round, bluish-black in color.
In spring, privet begins to bloom violently, the first berry of a wolf's eye appears by the beginning of autumn. During this time, children or inexperienced adults begin to pluck the attractive fruits and consume them or try to use the leaves to brew herbal teas. This is prohibited.
Berries of the white snowfield
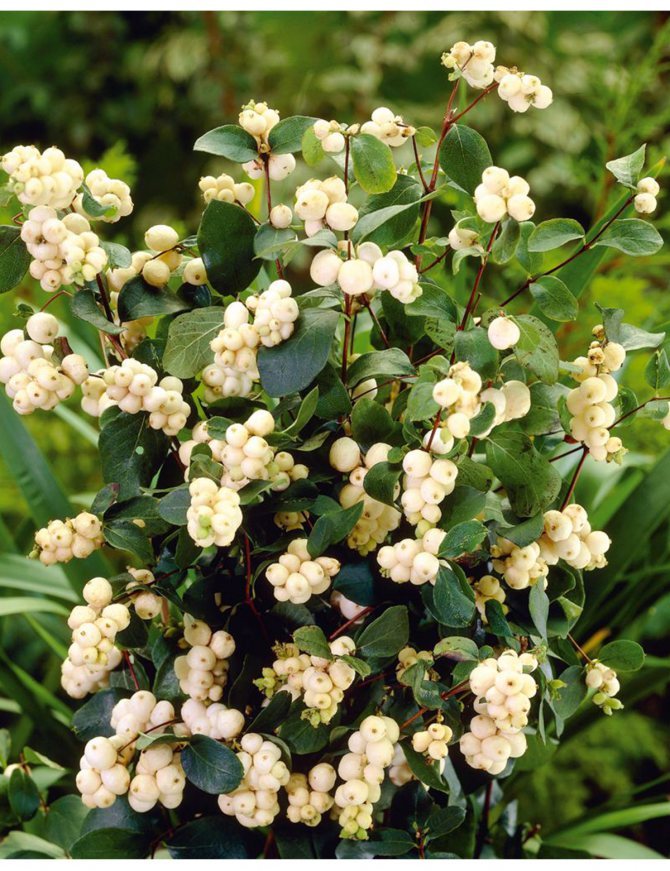


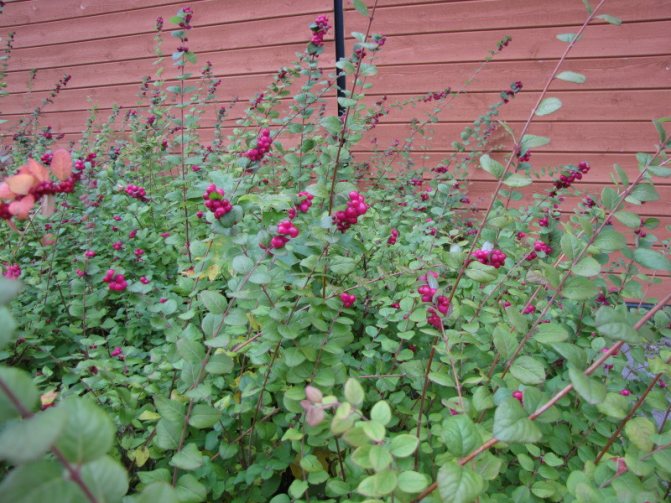
Thanks to its original white fruit, the shrub got its name. Small round waxy berries are soft to the touch, adhere tightly to each other, forming beautiful and original bunches. Branches with red berries are not often seen, but the rarest is the inky purple color.
Read also Managa: harm to the body and the consequences of use
In late autumn, the berries are already fully ripe, but with the onset of frost, the balls do not fall off. They stick well to flexible branches, sinking to the ground. In winter, the fruits often serve as food for many birds. In autumn, they can be mistaken for lumps of snow that adorn the graceful shrub.
Very often, a bush with white berries that snap attracts children. Kids play with balls, breaking them on the asphalt with their shoes. At the same time, the berries emit a click, which delights the children.
Most people don't know if a snowberry is edible or not. In fact, berries are not suitable for human consumption, since they are poisonous. If eaten in small quantities, they will not cause terrible harm to health. A large portion of the fruit will lead to poisoning of the body. The fruit contains a poisonous substance called corned beef and another toxin, which is still unknown to scientists.






























