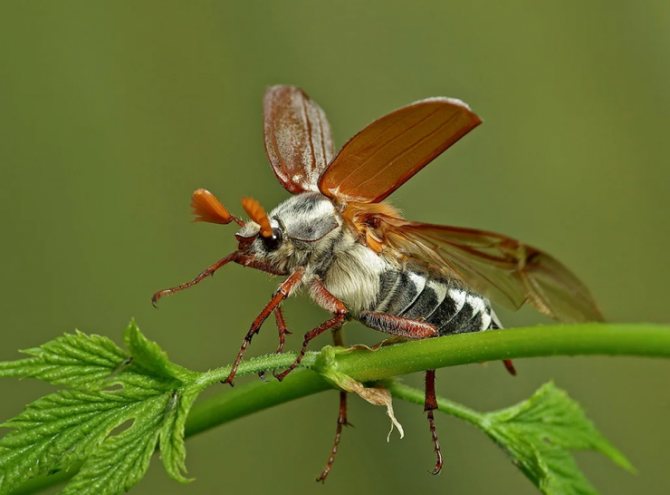
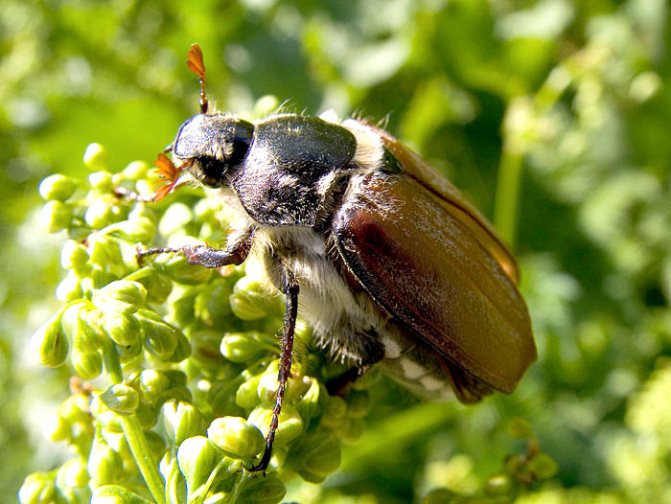
If many have not seen this large insect, then they have heard for sure. With the onset of spring warmth, clouds of beetles with a loud buzzing circle over the flowering trees. One of the most malicious pests, the fight against which is carried out by a variety of methods. Gluttonous insects and their offspring are able to destroy plantings in vast territories in the shortest possible time. The population reproduces rapidly, regardless of region or weather conditions.
The time of May beetles is May and April, this is the most active time for their life, hence the name. During this period, pests actively eat the pulp of flowering buds and soft young leaves, destroying trees, shrubs, and all flowering plants. Large individuals are able to destroy young trees, eating not only leaves, bark and branches.
Chafer
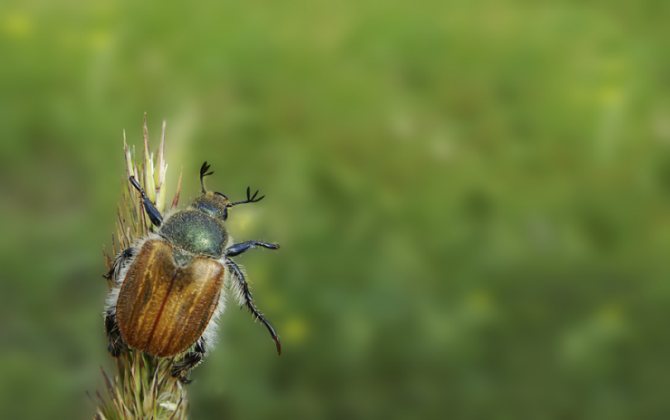
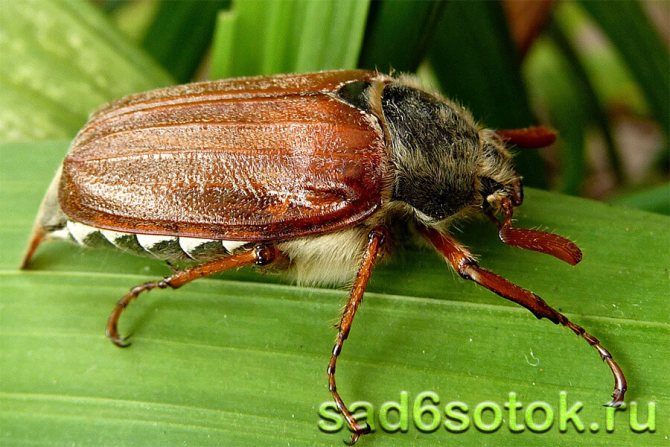
May beetle belongs to the order of coleopteran insects. There are two types: brown and black Most of us are familiar with them by the characteristic glossy shiny brown shell on the back. In another way, a common arthropod insect is called a beetle.
May beetle and its larva: photo and description
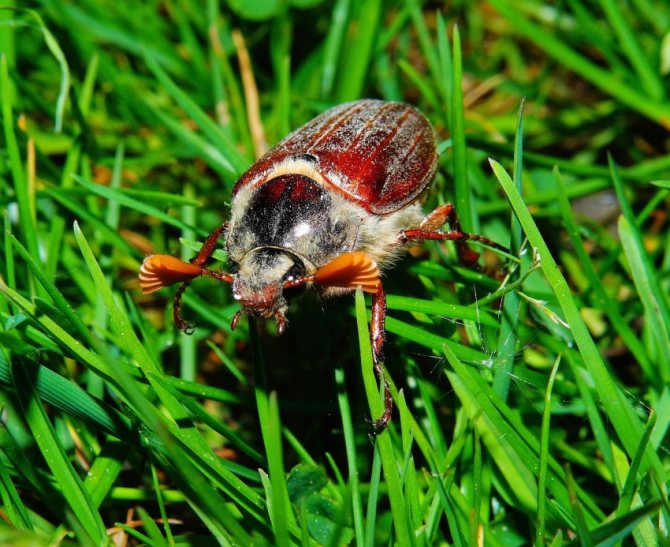
What does the beetle look like? An insect from a large category, sometimes reaching a mark of 3 - 3.5 cm in length. A wide body, with a convex hard shell. Oval, slightly elongated, slightly pubescent.

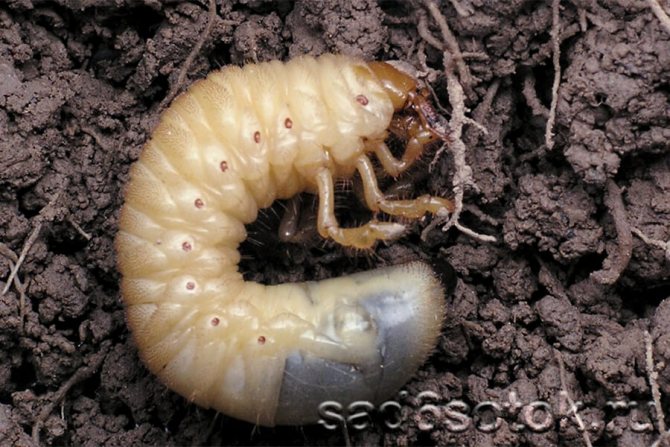
During the spring-summer season, irreparable damage is caused by a rather large larva of the May beetle, it looks unattractive and even menacing. At first glance, these are fat milky-white caterpillars, twisted into a ring, with a small brown head and a slightly pubescent body. After two years, they already reach enormous sizes, up to 6 - 6.5 cm. Three pairs of legs are located on the front, and the head has powerful jaws.
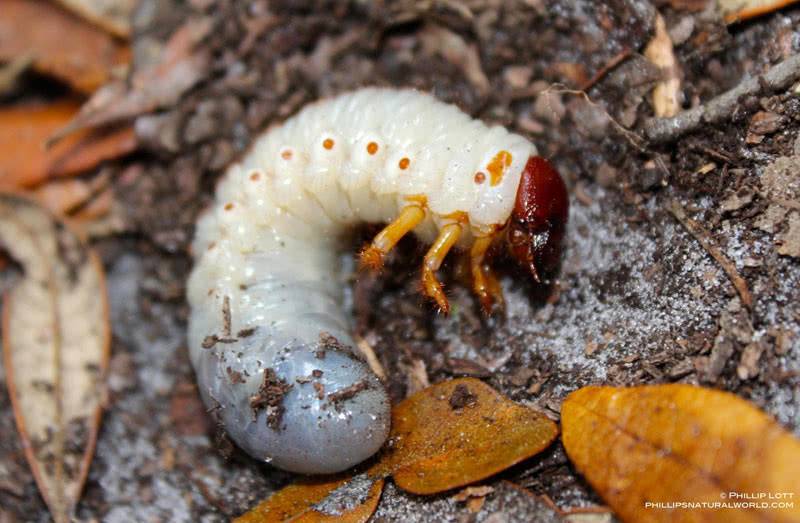


May beetle larva
In the garden, they develop from the larval stage to adult insects and cause irreparable harm to plantings. The main diet is the measles system of any vegetables, berry bushes, cereals. Due to their unique gluttony, the larvae destroy a huge cultivated area in a short time.
Passing into the pupa phase, they become similar to adults. Located at great depths, up to 30-50 cm, they can thrive safely. It hatches in the spring when the ground is fully warmed up. The description of the beetle larva changes throughout life. 3-4 years is the period for which they are fully formed.
Differences
In order to protect your site from a pest, you need to know the differences between the larvae of these two insects.
It is quite easy to distinguish between their larvae. The beetle larva looks like a white caterpillar, the size of which is 2 cm and the thickness is up to 8 mm. The offspring live from 3 to 4 years. Fisheries are carried out underground, and during this time they can do great harm to your plantings. The larvae make their way into the soil by 60 cm. When you dig up the ground, you may not notice them.
In front of the beetle's offspring, there are 3 pairs of legs, which are covered with fine hairs. The peculiar oral cavity is endowed with strong jaws. They can even gnaw through the thick roots of trees.
Still, the larvae prefer something tastier: the roots of any vegetables or strawberries.On the sides of the body of the insect there are small brown dots.
Unlike the beetle, the development of the bear proceeds somewhat differently. With each molt, small newborns take on their characteristic shape. They are not very mobile and differ in color from future May beetles. The coloring of the newly appeared larvae is close to red... Throughout the entire time, until it turns into a pupa, the color can only darken slightly.
Medvedka, beetle and their larvae are dangerous for the future harvest. They breed quickly, so the fight against their destruction must be thoughtful and precise. So you can save the long-awaited fruits and protect the green part of the garden from damage.
Characteristics of the May beetle
Visually, all views look the same.
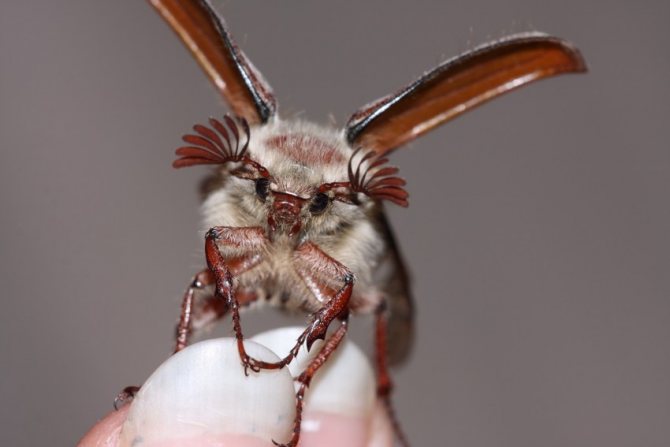
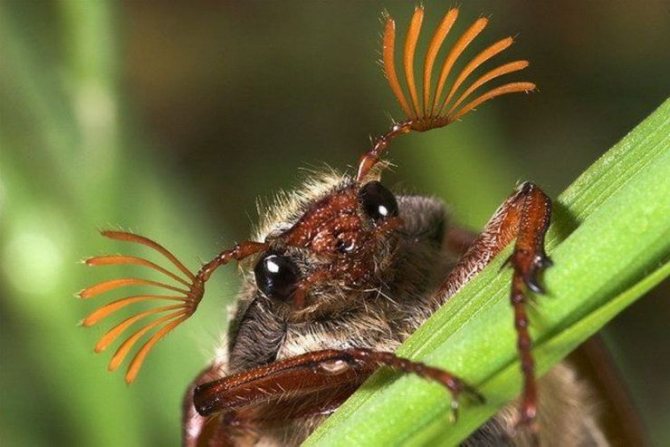
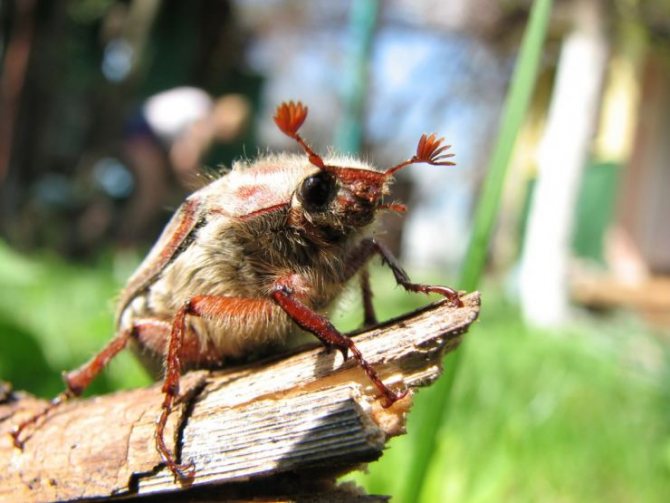
- Head. Complex eyes are composed of many simple eyes. In front there is a lamellar mustache resembling a fan. They are more pronounced in males than in females. The insect can only tilt its head, but cannot turn it.
- Chest. Each part has a pair of legs. The fenders are placed on the front and back.
- Abdomen. Connects to the thoracic region. The flaps cover the top completely.
Reference! On European territory, there are two types of beetles: eastern and western.
The dimensions of the beetle change as it grows and sometimes reach a mark of 3.2 - 3.8 cm, the shape is oval, resembles an acorn in color.
The color of body parts depends on the species. Black beetles live in dense forests, in places with insufficient sunlight. Redheads prefer areas with limited vegetation.
The weight of the May beetle reaches 10 g. Despite their overall dimensions, they are able to fly over rather long distances, they overcome 30 meters in a minute. Usually their vigorous activity is noticeable in the evening.


The size of the beetle larva varies with age. When they hatch, they resemble small small worms. After 3 years, they are huge and fat white caterpillars. In the last stages of life, they reach a size of 6-6.5 cm. This is the most active period when pests can cause significant harm to plantings.
Internal structure
The internal life support systems of the May beetle include:
- digestive system;
- respiratory system;
- excretory system;
- reproductive organs;
- primitive circulatory system;
- primitive nervous system.
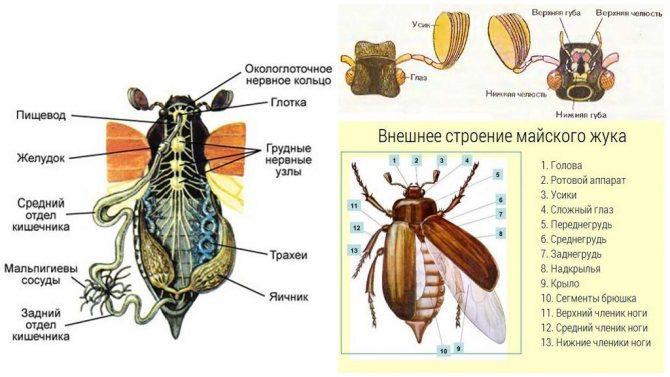

May beetle structure
The circulatory system consists only of a dorsal vessel passing along the central axis of the beetle and "suspended" from the upper part of the chitinous skeleton. 3 primitive hearts are located in the belly of the insect.
The central nervous system includes:
- the brain, consisting of two nodes of the supraopharyngeal ganglion;
- periopharyngeal connectives;
- abdominal nerve chain.
The first two nodes are in the head, the rest in the torso.
The digestive system consists of the anterior, middle, and posterior intestines. In the first two sections, the insect assimilates food, the latter is responsible for excretion and water exchange.
On a note!
The respiratory system consists of 18 trachea, the spiracles of which extend to the lower parts of the chest and abdomen. A large number of spiracles provide the May beetle with good air exchange when it burrows into the ground or is in flight.
The female reproductive system includes:
- 2 ovaries;
- 2 oviducts;
- 1 "external" oviduct through which eggs enter the external environment;
- seminal receptacle;
- accessory gonads.
The male has:
- 2 testicles;
- 2 seed tubes;
- the vas deferens;
- copulatory organ;
- accessory gonads.
What do May beetles eat
The most delicious delicacies are young leaves of fruit trees and berry bushes. The adult May beetle also feeds on barren trees.


In the first year of life, the larvae are practically harmless, they eat only plant waste - humus. By the second and third years, they are significantly gaining strength, their appetites increase.
Advice! For effective control, it is enough to sow the area with white clover. The plant produces nitrogen, which is fatal to the beetle offspring.
May beetle larva feeds on the roots of vegetables, strawberries, raspberries, flowers. A special treat for them is potato tubers. They are able to eat the flesh of potatoes over large areas, destroy young trees and shrubs. Three-year-old larvae can eat the roots of a two-year-old tree in a day.
Rider.
Females, following strictly in the direction of a field, meadow or densely grassy hill, get to the place of laying eggs. They hatch larvae that live in the ground. They are whitish yellow or reddish in color. The body is soft, tender, thick, divided into several segments. Their food is the roots of woody and herbaceous plants. Larvae, like beetles, interfere with the normal development of plants or lead to their death.In Asia, they feed on needles, greens of willows, poplars, and various shrubs. Only ash and lilac leaves are not eaten. As soon as the foliage in one area is eaten, the beetles fly over to another, leaving behind plants with eaten leaves. They try to stay near the edges and fly less into the depths of the forest. They feed most often in the twilight evening or at night.
The benefits and harms of the May beetle
Insects are capable of causing irreparable damage to plantings in a short time. Moreover, if adults eat up the aerial part: leaves, buds, catkins on conifers, then the harm from the larva is much larger. They completely destroy the root system, the plants have practically no chance of recovery.
Reference! It is very common to use beetles and larvae in fishing as bait.
There are also some benefits. In folk medicine, recipes with their use for treatment are quite popular:
- purulent processes;
- tuberculosis;
- injuries;
- radiculitis;
- scrofula;
- impotence.
There are known cases of a positive reaction after the use of such drugs for cancer.
Consequences and complications of treatment with witch doctors
During the therapeutic course, provocative signs of the body's reaction (fever, fever, fatigue) may appear, for which you should be prepared and do not stop taking. This condition indicates the activation of defense mechanisms and the beginning of the resistance to the disease. If these signs last more than 3 days or the state of health has deteriorated greatly, it is necessary to stop treatment with beetles and consult a doctor.
Chitosan contained in the hard shell of insects can provoke an allergic reaction, which is the reason for refusing to use healer beetles. The mild treatment regimen is designed for early detection of the first signs of a negative effect on the body in case of intolerance to biological organisms and substances secreted by them. If the healer beetle for some reason is not perceived by the patient and leads to the appearance of undesirable symptoms, it is necessary to look for other methods of treatment.
How to deal with the May beetle
It is recommended to apply preparations against the May beetle in the early morning or in the evening. Do not process in direct sunlight. In dry weather, with insufficient soil moisture, after processing, the soil is watered abundantly.
Popular methods of protection against May beetles are:
- mechanical digging of soil onto a shovel bayonet;
- turfing (planting green manure);
- processing with onion and garlic infusion;
- sowing lupine.
Advice! For prevention, plant garlic in the habitat of the beetle and its offspring. The smell repels insects.
A remedy with ammonia, tested in the garden, helps well. Add 100 g to a bucket of water.table salt and 2 tablespoons of alcohol. The soil is spilled during the flowering period of potatoes and for preventive purposes.
On strawberries, in raspberries, for the purpose of prophylaxis in spring, a solution of water and ammonia (10 liters of water and 20 ml of ammonia) is spilled between the rows. Treatment with insecticides, folk methods is also effective: each bush is carefully spilled with infusions from onion peels.
Advice! Traps are prepared for adult beetles. On a well-lit area at night, containers with kerosene are placed.
To reduce the population of insects from trees and bushes, they are manually shaken off in the evening and burned. Khrushches are afraid of the smell of elderberry, flowering cruciferous plants: turnips, turnips. Having planted the site with these plants, you can be sure that pests will not fly into this area.
How to get rid of beetle larvae
The fight against beetle larvae is an integrated approach. From autumn and throughout the entire growing season, it is necessary to carefully dig up and loosen the soil deeply. Eggs, larvae and cocoons, exposed to regular mechanical stress, are injured and die.
It is guaranteed to get rid of the larvae with the help of chemicals. There are many remedies for beetle larvae. Among the most popular insecticides are Bazudin, Zemlin, Aktara. Biological agent Nemabakt guarantees the destruction of larvae in the ground within several days without harm to health and plantings. The popular effective remedy offered by the industry Antichrusch is characterized as an effective way of fighting in a short time.
Sow the affected areas with lupine. Weeds do not germinate in such an area. The larvae in the ground, forced to feed on lupine roots, die. The soil is treated with chlorine solution: 0.5 l. water add 100 g of chlorine. Watered as carefully as possible, in the aisles, so as not to damage the roots of plants.
Ammonia from larvae is effective when used regularly. Places where traces of damage are seen are abundantly spilled with a solution of ammonia. The procedure is carried out with the onset of heat and just before the onset of frost, trying to avoid getting the composition on the plants.
It is effective to use iodine (10-15 drops of iodine are added to 10 liters of water), spill the affected areas with such a solution throughout the summer period. After watering, the soil must be loosened deeply. In the spring, they make deep, up to 40-50 cm, grooves in the beds and water them with a solution of Karbofos or Decis. The larvae die within a few days.
Advice! The use of preparations containing chlorine for soil cultivation is effective. So in practice they use the familiar Whiteness.
You can fight without the use of aggressive chemicals, folk remedies. For this, garlic and onion husks are traditionally used for infusion. A concentrated solution is prepared in a bucket, kept for 3-5 days. Dilute with water 1: 1 and add 1 liter each. under each bush.
You can bring out the larvae of the May beetle by burying rotten fish or herring in the ground, not far from the affected areas.
Practical proven method: manure traps. Since autumn, they dig deep, up to 1 m holes in the garden and fill them with fresh manure. The larvae will definitely choose this cozy place for wintering. It remains only to dig up everything in the spring and destroy.
If gardeners do not want to poison pests with chemicals, they are collected by hand when digging. This method does not guarantee the result.
It is not recommended to leave old stumps and thickets of herbaceous plants in the country. By uprooting them, you can find whole colonies of larvae. Of the effective drugs, Prestige is noted, it is used to process the roots of seedlings and potato tubers before planting.
To combat the larvae, ammonia is used in the soil under raspberries and roses: 10 ml per 10 liters of water.The soil is watered abundantly twice during the spring and summer period.
You can process strawberries, a special treat for larvae, in any suitable way. If folk remedies do not help, it should be transplanted to another site, having previously processed the soil and making sure that there are no pests there. Dig up the previous place and sprinkle with bleach.
In areas where pest colonies are seen, the land is cultivated especially carefully. If there is an opportunity for next year not to sow the site, it is better to carry out complex treatment for preventive purposes.
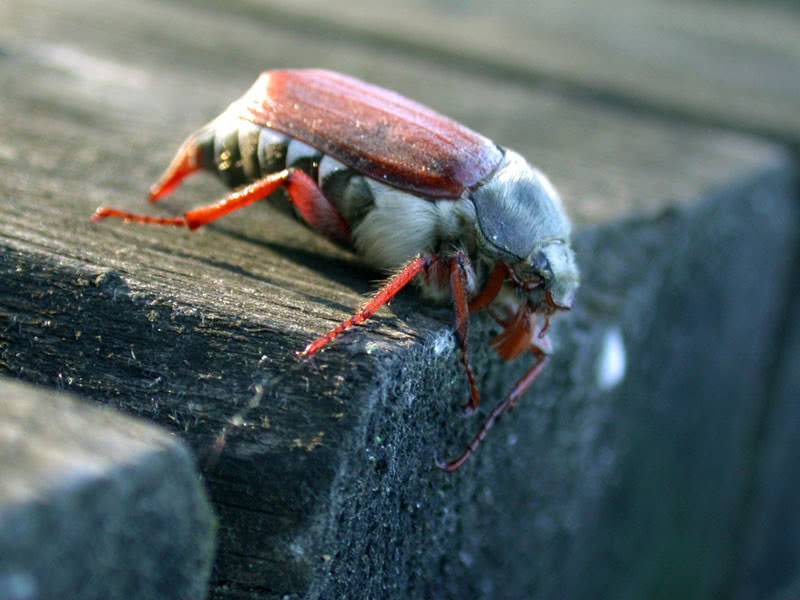


June beetle
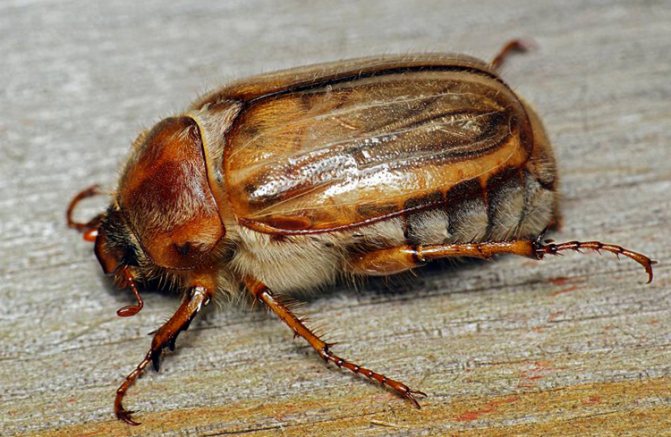


June beetle
This beetle itself is brown in color with a dark shade, and its elytra are pale, pinkish-yellow, shiny. They have small dots and slightly pronounced longitudinal ribs. Legs and antennae are reddish, with a shade of yellow. The chest, like the abdomen, is densely covered with long fluffy whitish hairs that form lateral spots in the form of triangles. Length 14-18 millimeters.
It eats leaves, roots and other parts of poplar, pine, beech, fruit trees. And also young shoots of cereals, flowers - especially lilacs, chrysanthemums, dahlias. The larvae sometimes eat their congeners.
Larvae
In sand or loam, as well as under cow cakes, to a depth of about 10 centimeters, females lay from 20 to 30 eggs. The larvae, although similar to those of the May beetles, are much shorter - 4-5 millimeters. They have thin legs and elongated claws on their paws. Throughout the summer period, they live in the soil layers close to the surface and eat the roots of plants.


June beetle larva
Generation and resettlement
The flight of the June beetle lasts from June to August in the evening. There are two opinions regarding its generation. One of them testifies in favor of the fact that the period of development of the larva is 10 months, others consider it to be two years.
This beetle is very common throughout Europe and in the Russian part of Asia. In the north, the area of his presence reaches the borders of Finland. He is often met in the Crimea and the Caucasus.































