Climbing rose is a great option for vertical gardening. It is used to decorate arches, walls, arbors, and weeping standard forms are created. There are more than a dozen different varieties. In order for the shrub to please with its continuous flowering for many years, it is necessary to provide it with proper wintering. There are many ways to cover a climbing rose for the winter.
Do I need to cover a climbing rose
Despite their high resistance to low temperatures, climbing roses are also at risk of suffering from cold weather. There is sap inside the plants, which begins to freeze at temperatures below - 2 ° C. As a result, ice forms, which injure the plants. Young bushes are much more susceptible to damage than adults. Injured areas become a hotbed for the spread of diseases and pests.
Having decided whether you need to cover roses for the winter, you should learn how to make a shelter. It must be strong, at the same time it is necessary to ensure that it is of high quality and dense. Since the right material can protect climbing roses in winter, preparing for winter begins with choosing a shelter.
Preparing for shelter
Before covering roses for the winter, a number of measures are taken to prepare them. It depends on their correct implementation and good shelter whether the bushes can survive even a very cold winter.
Top dressing

Preparation of climbing roses for winter begins in August - early September. During this period, when feeding, potassium-phosphorus fertilizers are introduced and nitrogen-containing fertilizers are excluded.
For a greater effect, fertilizers are introduced both under the root and when spraying the bushes from a spray bottle.
Before feeding, the climbing rose is watered abundantly. Moisture-charging irrigation is the final irrigation session for the bushes in the current year. 2 buckets of water are poured onto a small bush, and 3-4 buckets are poured onto an adult, 2-3.5 meters high.
Per one rose bush, 40-60 grams of superphosphate, 15-20 grams of potassium salt or 200 grams of wood ash for a young plant and 400 grams for an adult bush are introduced.
Such dressing accelerates the lignification of wood and prevents the growth of new shoots.
Treatment against pests and diseases


Treatment of bushes from pests and diseases is carried out after the pruning procedure.
After the leaves have been removed from the bushes and the plants have been pruned, the roses are sprayed with prophylactic agents against pests and diseases.
To protect rose bushes from pests, the soil under the bushes is cleared of weeds and debris, and dug to the depth of a shovel.
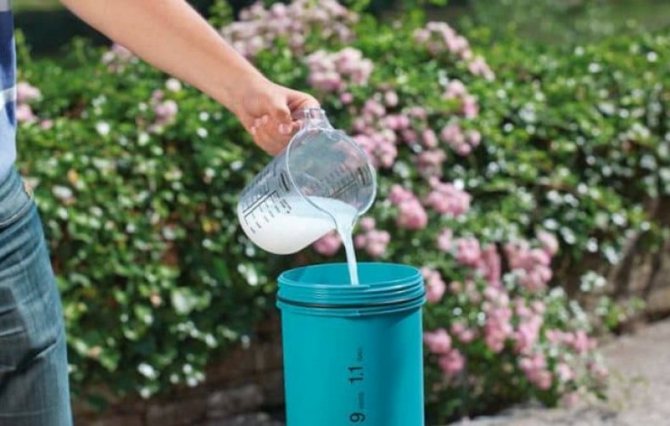
Bushes and soil are treated with a solution of Actellik, Fitoferm, Fufanon.
To protect against diseases, such drugs are used as: Milanit, Paracelsus, Kevlar, Absolut, Carbon, Blok or iron vitriol (300 grams of the drug per bucket of water).
Do I need to trim?
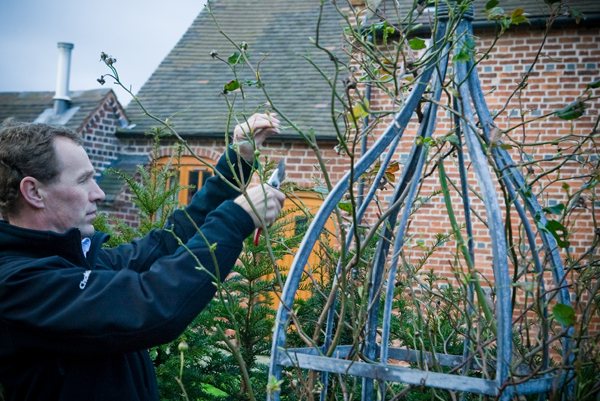


Climbing roses grow in adulthood and reach quite large sizes and their shelter for the winter causes many inconveniences, especially if the plant is very prickly. In order to simplify the shelter, roses are pruned.
Climbing roses are usually pruned at 1/3 their height. In addition, old, darkened, unripe and broken shoots are removed on the bushes. Thick lignified stems are cut with pruning shears at a height of 1.2 meters above the ground.
Pruning forms the correct growth direction suitable for a support or arch.
When and how to prune roses in autumn
Bending, pruning and sheltering climbing roses for the winter: video
Help the shoots ripen
Gardeners most often pay increased attention to roses in the flowering phase, trying to extend it for as long as possible, until the onset of frost. This should not be done, since such an artificial extension of flowering negatively affects the maturation of the stems. To preserve the plants in winter in the first decade of August, when the roses still continue to bloom, it is necessary to stop feeding them with nitrogen fertilizers.
Particular attention is paid to the climbing rose during the flowering period.
This measure allows you to stop the growth of new stems. Having appeared at the end of summer, they will not have time to mature normally by the onset of cold weather, and they will have to be shortened.
During this period, it is better to feed the roses with the following nutrients:
- superphosphate - 25 g;
- potassium sulfate - 10 g;
- boric acid - 2.5 g
These dressings are dissolved in a 10-liter bucket of water and mixed thoroughly. The resulting fertilizer is enough to process 4-5 m² of climbing rose plantations.
A month later, another top dressing is carried out, but this time 16 g of potassium monophosphate is diluted in a container with water. If it was not possible to apply these fertilizers, it is allowed to replace them with any other fertilizing for flowers in which there is no nitrogen, and phosphorus and potassium are in relation to each other in a ratio of 2: 1. Fertilization is recommended by foliar application.
In the last August decade, further pruning and shaping of the bushes should be completely abandoned. Plants during this period try not to loosen or dig in the soil between the plants. Otherwise, dormant buds placed on roses near the ground may wake up and start growing.
Preparing climbing roses for winter in late summer - early autumn
At the end of summer, you should take some steps to prepare the climbing plant for the coming cold weather. First of all, under the climbing roses, they stop loosening the soil and reduce watering to a minimum, and then completely stop it.
Then the composition of mineral dressings is changed: nitrogen is removed in order to exclude the growth of shoots of climbing roses, which do not have time to ripen before the cold weather and are likely to die. The last dressing, carried out at the end of August, includes superphosphate (25 g), potassium sulfate (10 g), boric acid (2.5 g). All components are diluted in 10 liters of water and watered rose bushes, using 0.5 liters each.


The most effective type of feeding for climbing roses is foliar application. The plant absorbs mineral fertilizers not only with roots, but also with leaves and bark. For foliar dressing, the volume of the proposed fertilizers is reduced by 3 times. After 2 weeks, feeding the plants should be repeated.
Autumn care for climbing roses is aimed at ending the growing season of the plant. Since among the many varieties of climbing roses, there are those that bloom until the very cold.


The next stage in the preparation of climbing roses will begin in mid-October. Plants are trimmed and removed from supports for subsequent shelter. The purpose of pruning is to form the crown of the plants, get abundant flowering in the coming season and keep the climbing roses healthy.
First of all, the broken and affected parts of the climbing branches are cut off, then the upper unripened part of the shoots is cut off. It usually differs in color. There is no point in leaving it, as it will freeze, first of all, and become a threat to the entire bush. Next, cut off all the leaves and the remaining flowers of the plant.
Further pruning will depend on the type of climbing rose in terms of flowering and shoots. There is a group of roses that bloom once a season on the climbing shoots of the previous year. In autumn, such shoots should be removed completely like raspberry shoots. There are young shoots that have grown in the current season (zero) and last year. You can leave 5-10 shoots.


Climbing roses, which bloom twice a season, form flowers on shoots of different ages from 2 to 5 years. The old age-old shoots of the plant gradually form fewer and fewer buds, therefore, after 5 years of life, they should be removed, leaving the youngest and strongest branches. In total, there should be 4-10 climbing shoots.
It also happens that the plant forms a large number of replacement shoots, which makes it extremely difficult to care for and winter protection of climbing roses. Therefore, the number of shoots should be regulated. It may be necessary to remove many more of them, as their development will pull off a lot of nutrients, which can weaken flowering.
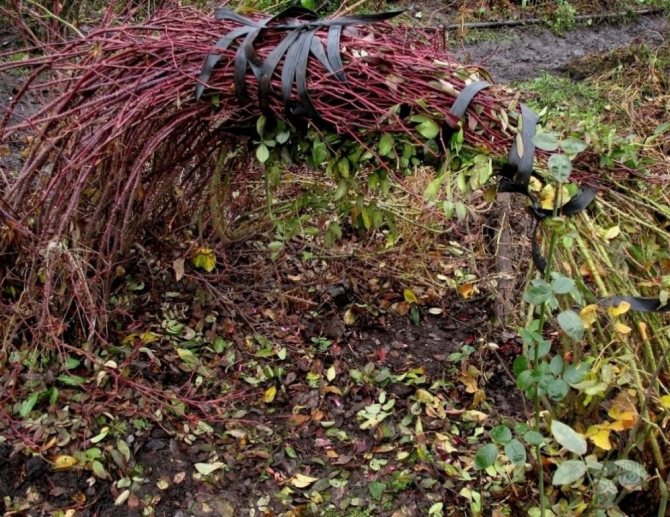
And the most difficult thing remains - to remove the curly stems of the plant from the support. Use gloves to protect your hands from thorns. Then you will not be distracted by annoying interference, and the work will go faster. Curly roses are detached from the support by removing the fastening devices. Lay on the ground, tied together for convenience.
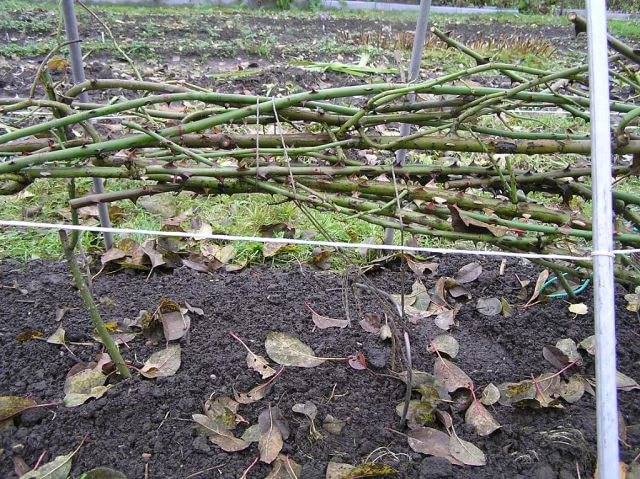


It is not always possible to immediately bend the plants to the ground. The branches of roses are very woody and resilient. Then the shoots in the upper part are tightly tied with a rope and gradually begin to bend. You can tie the other end of the rope to bricks or something heavy. You will simply move the bricks further away, causing the curly rose to tilt. The process can take several days.
At negative temperatures, the wood of a climbing rose becomes too fragile, it can easily break.
There should be no plant debris left in the trunk circle. They are a potential threat. Further, the rose is treated with a solution of Bordeaux liquid, iron vitriol (30 g / 10 l of water), copper sulfate (50 g / 10 l of water). After processing, the trunk circle is either spud, up to 30 cm high, or mulched with peat or compost.
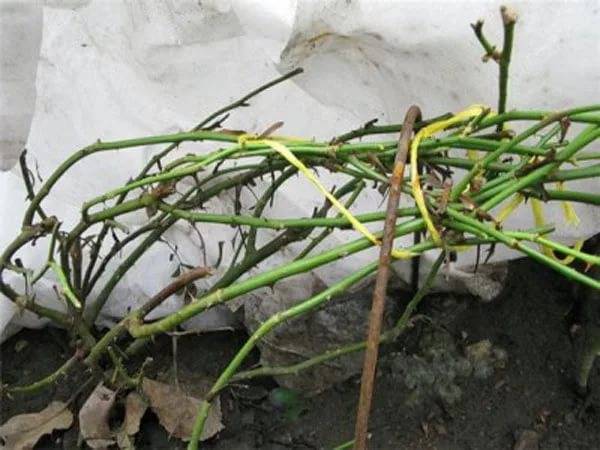


In a bent position, a curling rose can be left for 1 to 2 weeks, fixing it with hooks. To do the preparation of the shelter ourselves.
Shelter terms for the winter
Inexperienced gardeners often seek to cover the rose bushes as early as possible, believing that even a slight cold snap will have a detrimental effect on the condition of the plants. The overwhelming majority of old varieties of roses belong to the category of winter-hardy and feel fine at temperatures down to -10 ° C and below. Recently bred varieties often do not have a dormant period. They continue to bloom and grow actively even in cold weather.


What time is it necessary to snatch a climbing rose?
Weak and short frosts not only do not harm the roses, but also harden them, preparing them for winter. Frost forms on plants during light frosts, which does not even need to be removed, since it protects the plantings from sudden thawing when a thaw occurs. In this regard, the laying of plants and the construction of shelters begin not earlier than the first half of October.
Since the onset of persistent cold weather in certain regions of Russia occurs at different times, one should focus on the time when the average daily air temperature will constantly drop below -5 ° C. In September, gardeners should continue caring for the climbing rose in the fall, aimed at overwintering it as best as possible.
Instead of bending plants to the ground, some gardeners practice pruning. The stem is shortened based on the height of the intended shelter. In this case, the height of the remaining shoots should be approximately 15-25 cm. This reserve is enough in order not to injure the vaccination site.
Causes of death
During the summer season, the climbing rose produces powerful shoots 2-3 meters long. In the first year, they do not bloom. By the end of the season, these shoots should ripen well, and the next year, after a successful wintering, there will be abundant flowering. If the plant is frozen or wiped out, it will not bloom.
Gardeners often have a question whether it is necessary to cover climbing roses for the winter. It all depends on the climatic conditions. In the middle zone, where the air temperature is below 15 degrees, shelter is simply necessary. In the southern regions, additional protection is not required.
If the plant is not properly prepared for wintering, disappointment cannot be avoided in the spring. Therefore, many gardeners do not risk growing such beauty on their plots.
The main causes of plant death:
- very coldy;
- alternation of thaw and frost;
- damage to the cortex by mice.
Removing debris and strengthening immunity
In early autumn, the rose garden should be cleaned. From under each bush, dry grass, fallen leaves and flowers, and all other organic debris must be removed. Most often, these plant residues are a winter shelter for the larvae of harmful insects and spores of fungal diseases.
Overwintering climbing roses will be much easier if the plants are resistant to diseases caused by increased humidity. To increase immunity, the plantings should be treated with Bordeaux liquid, iron vitriol or another suitable fungicide.
Biological preparations are highly effective in this case, for example:
- glyocladin;
- alirin-B;
- phytosporin, etc.
After the first spraying with pesticides, the plants begin to gradually remove from the supports and tilt them to the ground. So that neither the gardener nor the plants are injured, it is necessary to tie up the plants in spring so that it is easier to remove them later. If the bushes are already old and overgrown, then they must be removed especially carefully.
Even so, it is not always possible to successfully remove the plant from the supports. In such situations, they practice covering the whips for the winter with a dense non-woven material folded in several layers. You can also use burlap or any other compacted fabric instead.
Wintering standard roses
Standard roses also need shelter. However, the process itself is slightly different. The fact is that they are practically not cut off. Basically, they are subjected to only a sanitary type of pruning, removing only dry and damaged shoots. The shelter itself is carried out as follows:
- If the stem is still young, then it must be bent to the ground and the stem should be fixed. In this case, you can use metal pins or staples. Sand, spruce needles or foliage are poured at the base of the tree, and spruce branches are laid on top. Next, the structure is covered with a film or waterproofing material.
- Stems of adult plants cannot be covered in this way. Their trunk is already stiff and can be easily broken. Therefore, first a wire frame is made around the tree, like a hut. Inside it, needles, sawdust or foliage are poured, and a polyethylene bag is put on top, which is fixed with twine. Or they wrap the rose with roofing material.
- Another more complex method is the Minnesota method. This method can be very dangerous and harm the plant. It consists in tilting the bush and digging it in. Therefore, it is necessary first to remove a little earth from the side to which the plant will lean. One person carefully takes the tree by the trunk and slowly tilts it in the chosen direction. The second person at this time pokes one part of the root system with a shovel. In this case, the roots on one side remain slightly outside. The barrel is laid on the ground and secured with staples or studs. The plant itself, along with protruding roots, trunk and crown, is sprinkled with needles, sand or spruce branches.
Pruning and hilling
In climbing plants, pruning in preparation for wintering is characterized by a number of features. So, as the stems are removed from the supports, only the youngest green stems at the top of the shrubs, which have not had time to ripen, are cut off. All buds and flowers are removed immediately before the start of the shelter.
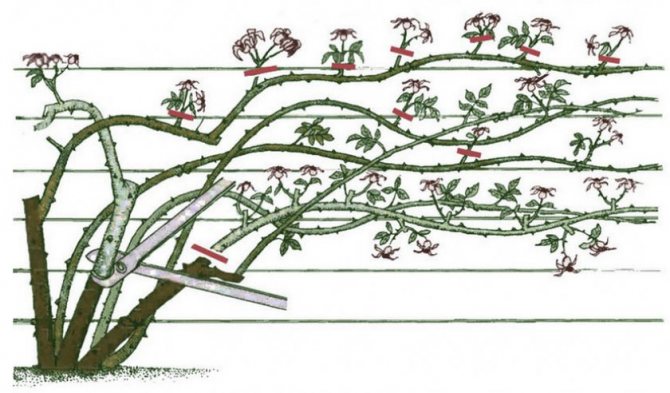

Rules for pruning a climbing rose.
The foliage of roses most often crumbles on its own as the period of light frost begins. If this does not happen, then the leaves will have to be removed on their own.
This is especially important for the lower part of the plant, where small branches and cuttings are located. Pathogens and pests often hide in these areas.
An infection can penetrate the plant through unhealed sections. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary, immediately after removing the stems, to process the cuts with brilliant green or charcoal.
On some varieties of climbing roses, manual foliage removal can be problematic. This is due to the excessive number of thorns on the stems. In such cases, you should resort to using special preparations to remove the leaves. Among them, the most effective are those that belong to the sulfur group.
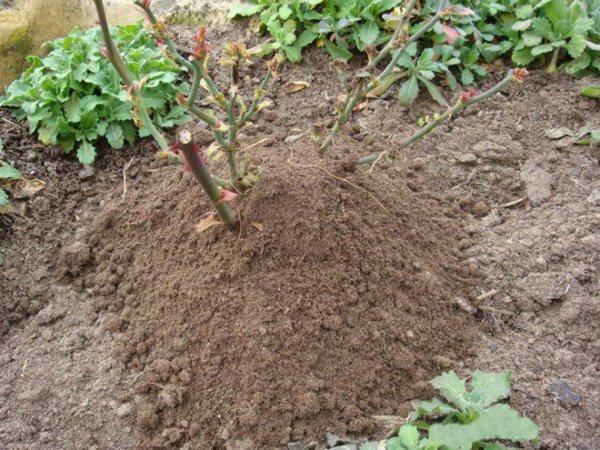
Before starting to shelter a plant, it is imperative to spud its root collar... This procedure allows you to save and protect the plant even under the most unfavorable weather conditions in winter.
For hilling, it is recommended to use soil collected between rows. The land must be dried with high quality, which is why it is recommended to prepare it first and dry it, sprinkling it under a canopy. 1 bucket per bush will be enough for young plants, 2-3 buckets of soil will have to be spent on old specimens. The earth is poured directly to the central part of the plant, forming a cone-shaped mound. The height of the earth layer should vary from 20 to 30 cm.
Dry sand is a good alternative to earth. Humus, peat and sawdust are not suitable for use in this case, as these materials strongly accumulate moisture. In some cases, it is allowed to use a torus, but it is necessary to mix it with sand so that the material does not cake and can normally let air through. Plants can be overlaid with spruce branches or wooden planks in a circle so that the wind does not destroy the embankment.
Shelters for climbing roses
A florist should know how to lay a climbing rose for the winter. At the same time, he should pay attention to the location of the plants on the site. If the rose bushes are planted in oblong rows, then it is best to cover the roses with shields. If the plants grow close to each other, it will be preferable to build a frame that covers the entire rose garden.
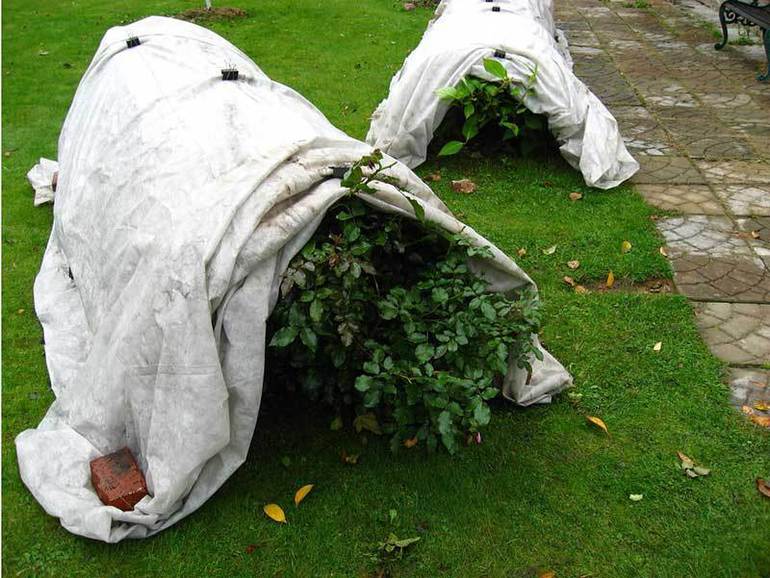


Shelter material for climbing roses.
With a separate arrangement of plants, it is necessary to take into account the weather and climatic conditions of the region. If there is a light frost outside and there is an excess of snow, then plants can be sprinkled on them; how to do it correctly - lay spruce branches on top of the snow. This material will not only warm the roots well, but also reduce the risk of mice and other rodents in the plantings. In all other cases, it is recommended to organize a frame of any size with an air layer.
It is not recommended to lay the stem too low. In low areas, moisture will accumulate, which will cause the development of diseases and rotting of the stems.
Shields for roses
After the plant has been cut for the winter and removed from the supports, it must be carefully but tightly tied in the form of a bundle and, if possible, bent to the ground as much as possible. The ground is lined with spruce branches. To keep the plant better, the branches of the roses are fixed to the soil in several places with a tough and strong wire.
After that, you need to make 2 shields from wood. Their width should be 80 cm, and the length should be equal to the length of the row of plants.Shields are located along the plants at an angle in the form of houses. From the outer sides, it is necessary to fix them with pegs. It is allowed to leave several small gaps and slots in the shields.
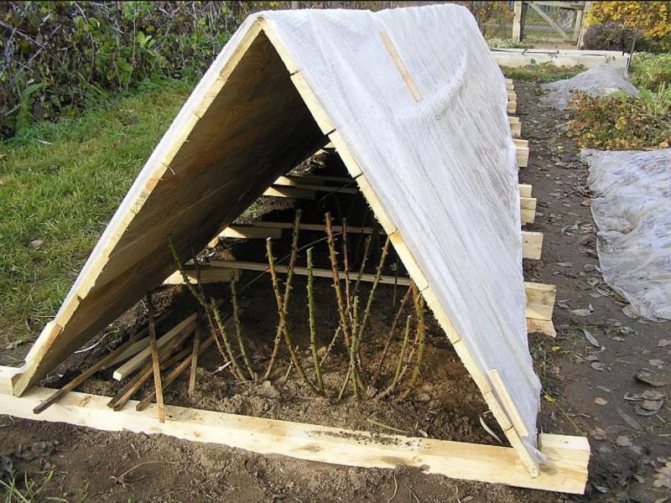


Wooden boards for wintering roses.
The upper part of the shields is covered with a polyethylene film so that it can cover them on both sides. The shelter is sprinkled with soil and attached with planks to the shields. Before the onset of frost at -10 ° C and below, the film can be left slightly open, but with the onset of a strong cold snap, the ends should be repaired. With the onset of spring, you need to slightly open the film to prevent the plants from drying out.
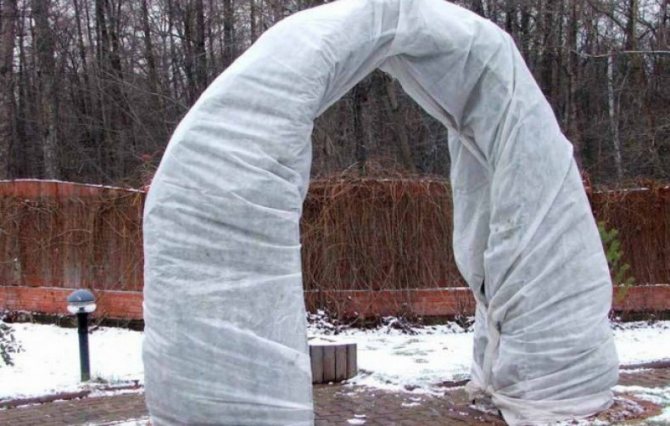
Frame shelters
You need to know how to insulate roses with a frame. Such a shelter for a climbing rose for the winter involves the construction of homemade frames in the country. For this, you can use wooden slats or metal wire. Climbing roses are looked after in the same way.
Such a shelter for the winter contains additional supports, to which the branches of plants are tied with a rope. However, they should not come into contact with the frame. When asked how to cover plants, they answer that in this case, fiberglass will be the best material for the frame. It provides good ventilation, but at the same time does not allow the climbing rose to suffer from the accumulation of fluid.
If glass cloth cannot be applied, nonwoven densified material can be used as an alternative. Its upper part can be combined with plastic wrap, which will allow the plants to be covered as best as possible from snow and other precipitation.
It is not necessary to remove the shelter from the plants immediately, but step by step by raising its individual sections in order to ventilate the plants. It is best to start this procedure when the buds on the plant are from 3-4 cm. It is necessary to completely remove the shelter in cloudy weather. This will reduce the risk of sunburn.
After removing the shelter, it is required to inspect the plantings for the presence of sick, injured, shrunken stems. If found, they must be cut, which is what the flower growers do. The bushes should not be straightened right away, they should lie bent to the ground for about 2 more days, otherwise there is a risk that they will break.
Excavation
Before covering the climbing roses for the winter, it is necessary to clear the area of weeds and other debris. These activities will help prevent the emergence of pests and the development of diseases in the coming year.
To do this, the gardener needs to do the following:
- remove all broken off twigs, scraps, fallen flowers and leaves from the soil, weeds and other vegetation are also removed, that is, after work, the soil should be perfectly clean;
- if annuals grow next to the shrub or there are wilted plants, then you also need to get rid of them;
- It is most convenient to remove plant debris and foliage with a rake.


Faded buds should not be left on the site, as spores of fungi or other infections, such as black fungus, can be localized in them. They can become a breeding ground for insect larvae and other pathogenic microbes, which, after wintering, will simply move to the rose.
Therefore, all vegetation and debris must be removed from the site without fail, moreover, it is important not only to remove it, but to burn it. It is strictly forbidden to use this raw material as compost, as this material can spread diseases and harmful insects in the garden.


















