Do-it-yourself beautiful and productive beds
Home ›Bushes and trees› How to cover roses for the winter in the Moscow region and when to do it
A rare garden or suburban area does without the fact that its owners do not plant a beautiful rose in the most conspicuous place. Given the variety of varieties of garden roses, there is nothing surprising in the fact that you can admire them until late autumn.
Park, climbing, ground cover, floribunda - all varieties cannot be listed, as well as shades of color.
My favorite roses are still climbing roses. They are simply irreplaceable for vertical gardening, very decorative and with proper care, the most common site in the Moscow region can be turned into a piece of the flower kingdom.
However, roses require a mandatory winter shelter. And if in southern latitudes you can limit yourself to light warming of the roots or even neglect this, then sheltering roses for the winter in the Moscow region must be done. Otherwise, even if your beauties survive the winter under the snow, you will still not achieve abundant flowering on the frozen shoots.
Varieties for the Leningrad region
Not always planted roses, even with very good care, survive frosts, one of the reasons may be:
- Inappropriate distillation method. Greenhouse-grown bush and rootstocks are not always frost-resistant.
- Variety. Park or landscape views are least afraid of frost and can survive the winter with minimal protection. Hybrid tea and climbing tea are thermophilic varieties that require the construction of protective devices. Medium-hardy - many-sided floribundas and miniature roses.

What structures are used to shelter plants?
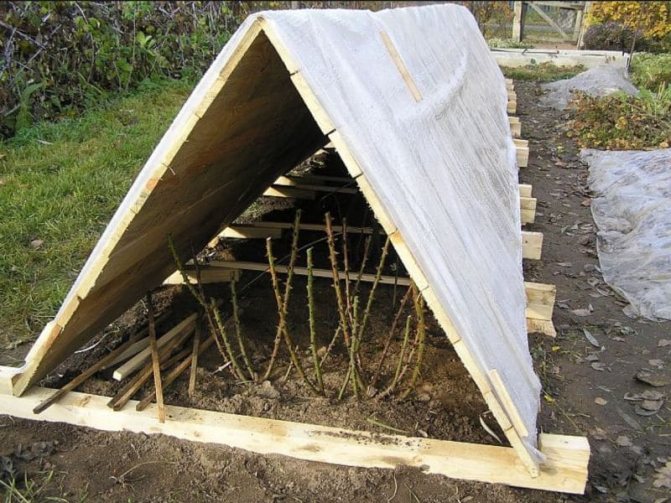


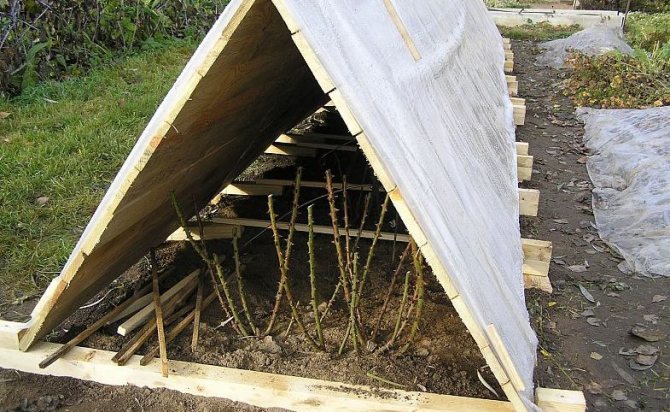
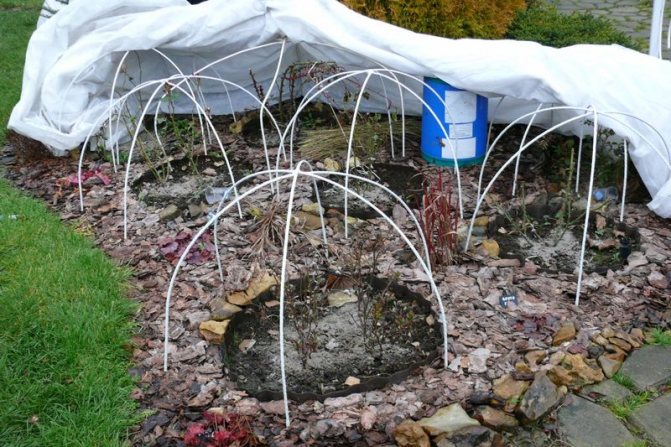
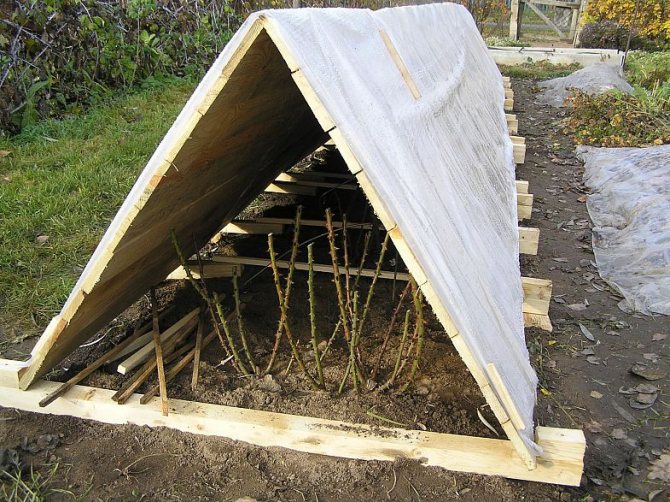
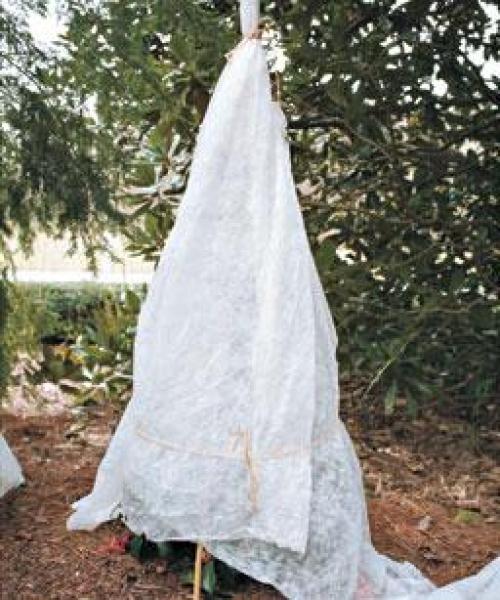
Using a wood frame to shelter roses
Usually, various types of frames are used to cover these perennial shrubs - from iron rods, large plastic vases, wicker baskets, boards, wooden pallets. From above, such structures are covered with non-woven fabric, film, spruce branches, straw or dry leaves.
Main types of work
Shelter roses for the winter in the Leningrad region takes place in several main stages:
- Stop feeding.
- Pruning.
- Cleaning.
- Treatment.
- Hilling.
- Shelter.
Each operation has its own characteristics, depending on the climate of the region and the type of rose. The deadlines are dictated by temperature changes at the time of preparatory work, if the autumn is warm, then you can not sit with a shelter, when sharp frosts below -5 ° C appear, it makes sense to hurry up.
Dates of autumn works
Regardless of the climatic features of the region, the complex of autumn works for a specific group of roses will be almost identical. The only, but very important difference, will be the timing of work on caring for roses in the fall, preparation for winter.
Depending on the region
In the Moscow region and the Middle lane, pruning and feeding of plants is carried out in mid - late September. The bushes are covered in a month.
In the Leningrad region, rose shoots are shortened in September. Flowers are insulated in early October.
In the Urals and Siberia, the harsh climate dictates to start pruning roses at the end of August, and to warm the rose garden at the end of September. In winter, rose bushes are additionally covered with snow.
In the south of our country, in Belarus and Ukraine, the climate allows you to postpone autumn work with the rose garden until early October.It is not required to cover roses here for the winter. It is enough to sprinkle with soil and sprinkle with sawdust.
Lunar calendar
In the fall of 2019, you can take care of the rose garden on the following dates:
- October - 7 and 8, from 10 to 16, from 20 to 23, from 25 to 30;
- November - from 3 to 6, from 8 to 12, from 17 to 20.
Start of preparatory work
Shelter of roses for the winter in the Leningrad region begins in the second half of summer. According to the natural calendar, flowers, preparing for autumn, slow down the process of intensive growth, and at this time it is strictly prohibited:
- End of July - apply fertilizers that stimulate vegetation (nitrogen).
- The beginning of autumn is to cut flowers and pick off wilted buds so as not to interfere with the plant's full flowering cycle.
Any of the above actions can serve as an incentive to create new shoots, which is highly undesirable before the onset of frost.
In the middle of the first month of autumn, it is necessary to fertilize the bush with potassium-magnesium preparations, providing them with a supply of nutrients for better spring growth.
At this time, it is highly undesirable to loosen the ground, as this operation can start the process of flower growth.
By the end of September, the leaves on the bushes begin to dry out, and it’s time to remove the yellowed foliage. It is necessary to start with diseased leaves, at the end of autumn, by the beginning of the shelter, it is advisable to remove all dry leaves, but it is quite possible to limit ourselves to harvesting and burning only diseased shoots.
Why do you need to cover the bushes for the winter
Shelter of roses is undoubtedly the most important component of the high-quality preparation of flower bushes for frost in a country house or a plot of a private house. Naturally, the main purpose of the shelter for the winter is to help the bush survive freezing temperatures, freezing winds, bad weather, in order to start growing normally in the spring and further please with its lush and beautiful flowering.
The correct winter shelter for roses performs 3 essential tasks:
- Protects from cold and dry winter winds. If the plants are left unprotected in the open field, moisture will evaporate from the plant due to dry and strong winds in winter. Competent protection will prevent drying out, it will retain moisture in the plant throughout the winter until the onset of spring.
- Protects flowers from temperature extremes. An optimal air-dry shelter helps to “smooth out corners” by protecting plants in the event of sudden changes in temperature.
- Creates a favorable wintering environment. The shelter maintains its own microclimate, in particular the moisture level normal for the plant.


Note! Despite all the benefits, shelter can be dangerous if done right! Moisture can accumulate under it, which will lead to waterlogging and supporting the plant. In addition, such an environment is very favorable for the development of fungi and pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, it is very important to do everything carefully, according to the rules. This is especially true for novice gardeners.
What types of roses need to be covered for the winter? Climbing roses, hybrid tea, bush, floribunda, standard, and ground cover roses need winter protection (although they are considered winter-hardy, it is better to cover them in cold regions).
Roses that do not require shelter: park roses, hybrids of rugosa, alba, spinosissima, canadian roses, rose hips.
Pruning
Obligatory measures that ensure a good wintering and spring blooming of the rose are shelter for the winter and pruning. The type of work is determined by the plant variety.
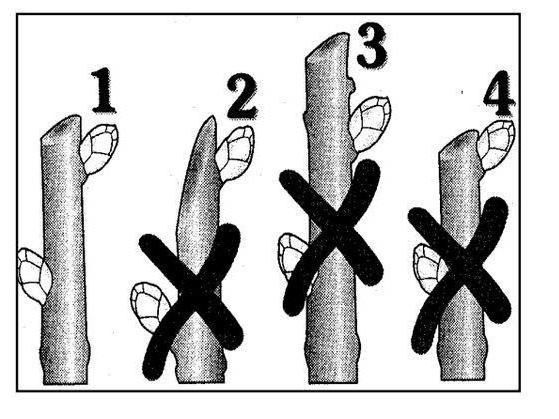

All bushes must be cut, regardless of age. Removed:
- Flowers, buds.
- Sick and weak stems that cannot withstand frost and die, which can lead to infection of the bush.
After pruning, no more than 5 main branches should remain on the bush, depending on its size, all the rest should be removed. All work must be carried out only with a special sharp tool, leaving an oblique cut.
The height of the shoots left for wintering depends on the variety.
- Frost-resistant park varieties practically do not shorten, only preventive cleaning and harvesting of weak branches are carried out.
- In hybrid tea, floribunda and other less resistant varieties, a large percentage of the aboveground part is cut off, leaving no more than 5 buds.
Climbing roses require an individual approach, shelter for the winter and pruning are specific due to the long stems, which are practically not shortened. It is necessary to remove only diseased and dry parts, as well as all the foliage.


Having solved the issue of pruning, you can start cleaning the land cover. Cleaning should be thorough, nothing should remain under the future canopy that could cause rot.
Protection of roses depending on the species
Before planting roses in the northern part of the country, you need to consider the catalog of varietal seedlings. Roses are divided into three groups: climbing, bush and standard roses. What material to use for covering depends on the type of roses selected. You should not plant plants in separate flower beds throughout the territory, it is better to plant them in groups. This will make the cover job much easier. Protection methods depending on the variety:


Shrub roses. For this group of roses, use an air-dry shelter or spruce branches. The shrub is pruned, and all dry foliage is removed. The area around the trunk is covered with a thick layer of peat, compost or sod. Young plants fall asleep up to half. The remaining upper part is covered with spruce branches. If the plant is thermophilic, then it is additionally covered with an old blanket.- Climbing and semi-climbing roses. The branches of the plant, which are on the supports, are wrapped in a non-woven covering material. It can be lutrasil, geotextile, or spandbond. To prevent the material from untwisting, it is fixed with a stapler or clothespins. You can remove the branches from the support, twist them in a ring and cover them on the ground. The ground is covered with spruce branches and only then the branches of the plant are laid. From above they are covered with geotextiles or spruce branches. To prevent the roots from freezing, the trunk of the plant is spud with a 30-centimeter layer of peat or turf mixture.
- Standard roses. This group of plants has a sturdy trunk that cannot be bent to the ground. Therefore, they are always upright. A thick embankment is made around the trunk. The non-woven material is folded into 4 layers and a bag is sewn from it. Then it is put on the top of the plant and twisted with a rope. The rope is fixed at the bottom of the trunk.
Hybrids obtained by crossing wild roses from Siberia and the Himalayas with cultivated species do not need shelter.
These are roses called Quadra, Bill Reid, John Cabot, Henry Kelsey and Agnes. All these varieties perfectly take root and grow in central Russia. For their cultivation, no additional protective measures are required, they are resistant to fungal diseases. The most winter-hardy rose variety is Agnes. It has double flowers of a bright yellow hue and exudes a bright aroma.
How to properly care for geraniums: home care
Disinfection and hilling
Many gardeners ask the question: "How to process roses before sheltering for the winter?" There are several solutions:
- Classic version: 5% iron vitriol, or Bordeaux mixture. But for a greater guarantee, preventive treatment should be carried out in the summer, for this, many summer residents use Fitosporin, which gives a good disinfecting effect.
- A simpler method and not always an effective method using ash. Sprinkle a piece of land and wet shoots: one can of dry ash per 1m 2.
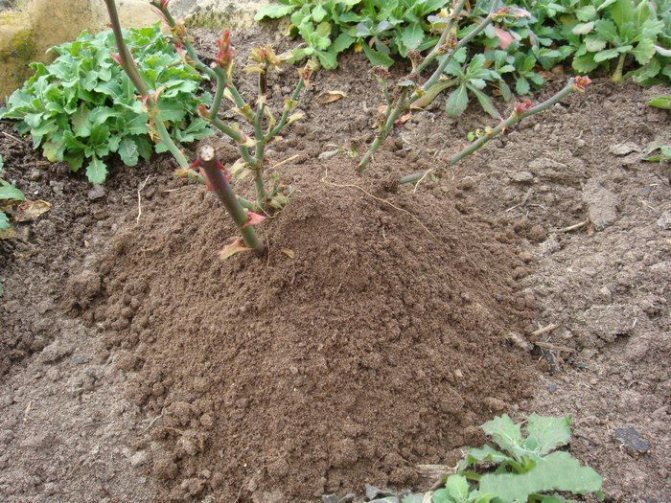
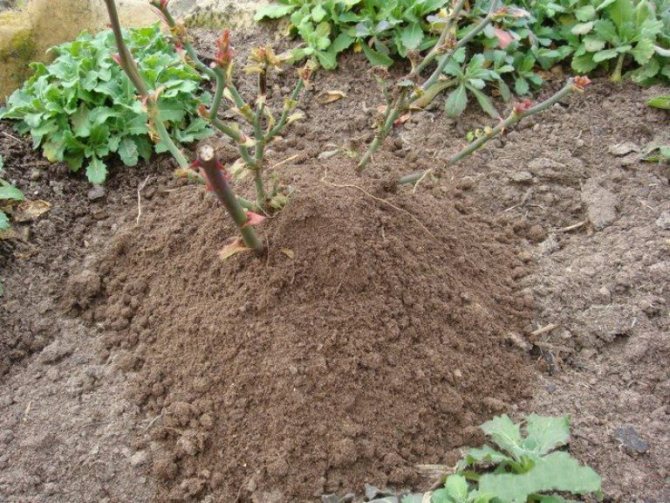
Hilling is a routine procedure for many gardeners, in the case of roses it is advisable to carry out it with sand, after disinfection, since the soil under the bush can contain many different bacteria and fungi.The height of the boulder depends on the size of the bush, on average at least 20 cm. The loose consistency of the sand protects the root system, without forming a crust when freezing, contributing to good ventilation of the underground part of the plant.
Processing roses before shelter for the winter and hilling is carried out on dry ground and shoots. Rain can become a problem during this period, a phenomenon not uncommon, especially in autumn. The solution is simple: the use of polyethylene in the form of an umbrella or a tent. In this case, it is desirable to cover not only the bush, but also the soil.
How to cover flowers for the winter?
To cover these plants before the onset of the winter period, artificial or natural insulation is used. It is permissible to use several types of insulation at the same time. Such materials must have the following qualities:
- they are durable and resistant, do not react to negative climatic conditions;
- moisture permeability to protect perennials from damping off;
- easy to use, easy to purchase;
- have durability so that they can be used repeatedly.
Spunbond (non-woven fabric)
Spunbond has been in recent years the most popular of all nonwovens used to shelter perennial flowers such as roses. This material is breathable, practical and durable, mold resistant, safe and affordable.
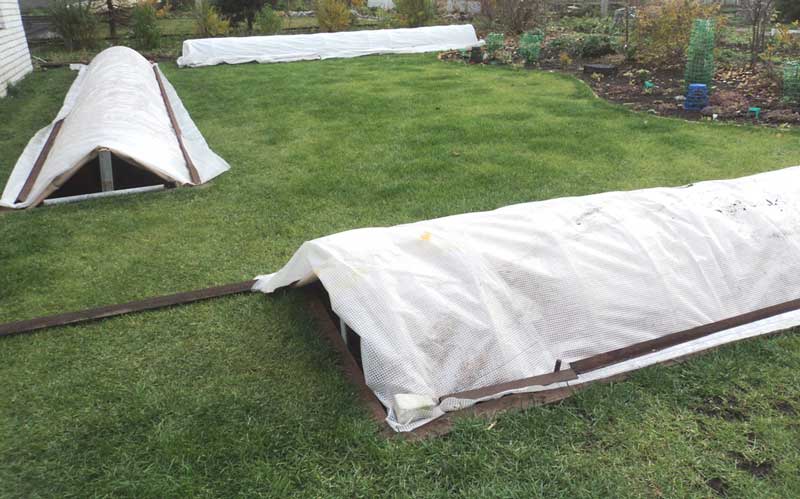


Using Spunbond
It can be fixed on a wooden or metal frame, or cover the bushes in an air-dry way, tying the material at the base of the bushes with twine. Usually, such material is folded in several layers before the procedure.
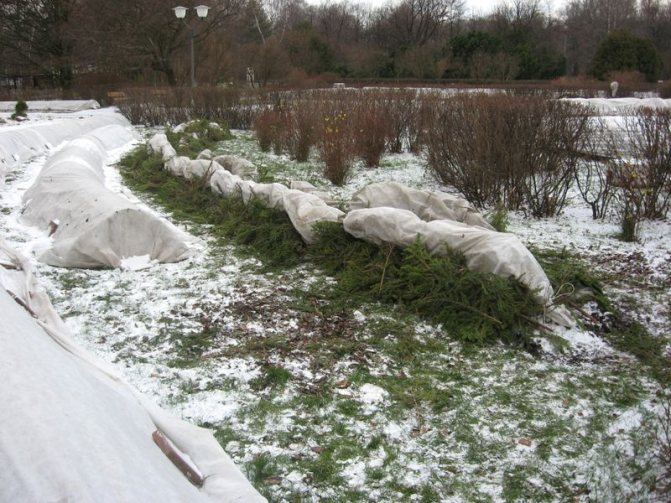
Lapnik
Shelter with spruce branches is most popular with modern flower growers, because they can be found in any forest area, the material is breathable, traps snow during winter, therefore it is used in areas where thaws are often replaced by severe frosts during the winter. You can also use spruce branches as an addition to non-woven insulation or polyethylene.
Spruce branches require drying beforehand. Do not cover plants with damaged branches with traces of diseases.
Using the framework
Such covering structures can be metal or wood.
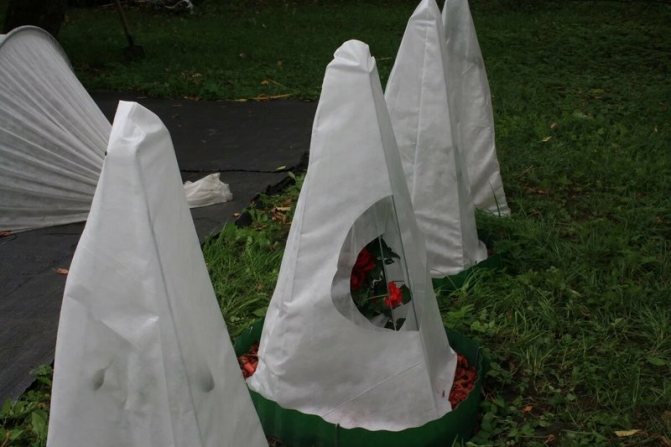


Using wireframe shelters
The iron rod is bent in the form of an arc, the ends are buried in the soil and after the beginning of the winter period, insulation is pulled. If necessary, the material near the ground is strengthened with stones.
A similar structure is also being prepared from wooden blocks.
Straw
Straw is also used to cover these flowering perennials with the onset of winter. It serves as an excellent thermal insulator, however, it has a number of negative qualities:
during thaws, the straw gets wet, cakes, begins to rot and mold;
this material practically does not let the sun's rays through, so in the spring the soil warms up more slowly, as a result, the vegetation is delayed;
in winter, rodents often hide in this shelter, which can feed on the roots of the bush. As a result, plants are severely damaged and may die.
Burlap
Burlap is one of the most affordable covering materials, although the natural version of such a shelter is becoming less and less common. In recent years, flower growers increasingly use synthetic burlap, which protects plants from frost, but does not allow air to pass through.
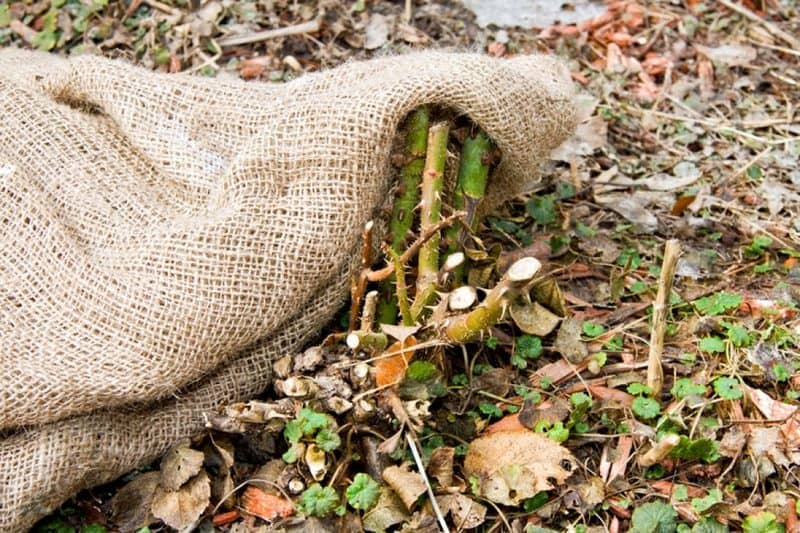


Using burlap
But natural burlap is also not ideal: it absorbs moisture well, and freezes during the frosty period. As a result, such insulation will not save the rose bushes from the cold. Old burlap from under vegetables, used as insulation, can cause mold or fungal diseases on the vegetative part of the flowers.
Plastic bottles
If there are no other covering materials at hand, rose bushes can be covered with five-liter bottles.They are cut in half, holes are made in the walls for ventilation, and high-moor peat should be poured inside.
Preparing a shelter
It is not recommended to start a full-scale warming procedure before reaching -5 C ° (critical temperature for varieties with low frost-resistant qualities), since wrapping too early can weaken the bush. Most often, the shelter period is late October-early November.
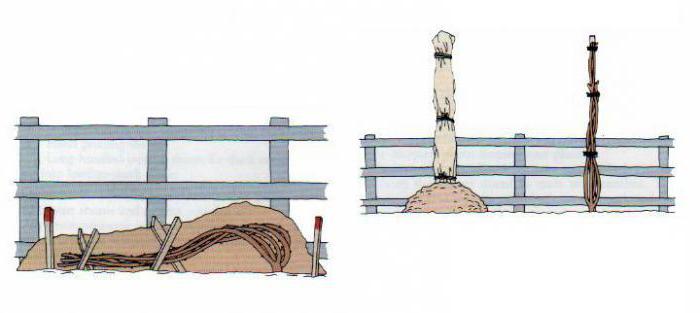
Labor intensity depends on the variety, climbing roses are especially laborious, shelter for the winter and pruning takes place with a lot of time and resources, since the branches of the bushes are not cut off before wintering, they must be bent correctly. This must be done slowly, if necessary, slightly loosen the ground under the bush. The branches are tied, laid on a surface previously covered with straw, spruce branches or shields and fixed with holders.
At what temperature do cut roses freeze. What kind of frost can roses withstand?


Roses react differently to frost with the onset of winter and spring, when the temperature regime changes almost instantly. The region in which the bushes are grown also plays a significant role.
Roses and winter frosts
Average temperatures that roses can withstand in winter without shelter are from -6 to -10 degrees. Most varieties tolerate a short-term drop in temperature to -15 without significant losses.
It is worth noting that different parts of the bush react differently to the first winter frosts - if -10 and even -12 degrees are not terrible for the ground part, then the root collar freezes already at -3.5 degrees.
For this reason, a minimal shelter is always organized for roses, sprinkling the necks with dry peat, sand or garden soil. In regions with warm winters, when the temperature rarely drops below -3 degrees, the culture perfectly tolerates the cold without shelter.
Overwintering with shelter is recommended when the thermometer drops below -8-10 degrees. Complete freezing occurs at -30 - this mark is critical for most varieties.
When the specified temperature is reached, the juices in the shoots of the plant freeze, turning into ice and tearing the tissue. This leads to the formation of microcracks, through which pathogenic bacteria subsequently penetrate.
What kind of frost can they withstand in spring?
Spring frosts are dangerous for roses, which in some regions can occur in April. Roses without shelter can withstand low temperatures from -1 to -3 degrees - such a cold snap passes unnoticed and harmlessly for them.
The frost resistance of covered and huddled bushes is higher, since a protective layer of spruce branches or an air gap guarantees successful transfer of low temperatures down to -7.
You should not rush to remove the shelter in the spring - it is advisable to wait until a stable heat is established.
Unprotected roses can suffer from strong and prolonged frosts from -7 degrees and below - not only branches will freeze on the bushes, but also opened leaves with buds.
Although this will not do much harm to the plant, it will postpone the flowering, since the budding will occur anew.
When to cover roses, taking into account the regional climate?
In order for the wintering of roses to pass without loss, it is important to choose the right time to organize a shelter. It should be cool enough for the bushes to slow down their activity - this will prevent active vegetation and subsequent damping.
It is recommended to build a shelter for roses at the following times for different regions:
- The middle zone and the Moscow region - the first or second decade of November. It is better to choose a dry, clear and windless day, when the temperature settles in the range of -5-7 degrees.
- Ural - end of October. The optimal conditions are considered to be a temperature of about -5 degrees and the presence of a layer of dry snow.
- Siberia - the last days of October - early November.The shelter process begins when the temperatures settle within -5, and ends after the soil freezes by a couple of centimeters.
For the southern regions of Russia, simple hilling is enough - an earthen hill will protect the root collar from freezing. Since winters in this region are most often warm and humid, it is better to use covering materials, under which the plantings will not be wiped out.
Protection for thermophilic varieties
The climbing rose also requires special care, shelter for the winter can be implemented in different ways, the choice depends on the region of disembarkation and the capabilities of the owners:


Shield. A reliable and time-consuming option that provides a high percentage of flower survival even in severe frosts.
- It will require two wooden boards fastened with nails, the length depends on the height of the flower, the width is up to 90 cm.
- Place the structure on top of the fixed branches.
- Drive wedges into the ground to keep the roof from moving.
- Place moisture protection on top: film, spruce branches. Very often there is a recommendation to cover the film with earth, but not all summer residents go for this, fearing the appearance of excessive condensation.
The shield is made of wooden boards, it is not necessary to knock them down tightly, the presence of cracks is permissible. The main criterion is reliability, abundant snow drifts can break the structure by damaging the whip of the rose.
The frame method and strapping are also used.
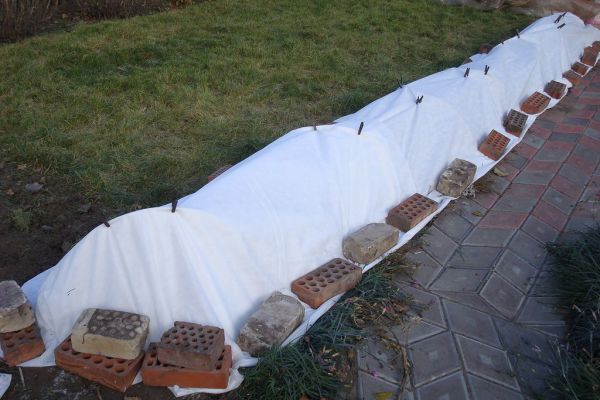
In the second case, the associated shoots are covered with spruce branches and lutrasil, pressing down to the ground with bricks, boards and tarpaulins.
A frequent occurrence is a greenhouse with different varieties of bushes, among which a climbing rose rises, a shelter for the winter in this case will have its own characteristics.
The branches cannot be lowered to the ground, they must be fixed to the hammered support posts, and then the roof must be made.

Correct bending of the bush
Some spray roses are bent to the ground in front of the shelter. So that during bending the stems of the plant do not break, they are gradually tilted. The stems are laid on special supports, and then gradually lowered below. The procedure begins 3-4 weeks before the shelter. Bending rules:
- Rods or construction pins are used as supports. They are flexible and well into the ground.
- Thick stems that do not bend are tilted gradually and in stages.
- If you dig in the root, the stem will bend easily. For this, three incomplete undermines are made with a pitchfork or a shovel. The stalk is not dug out, it is enough that it moves a little.
- In order not to break the graft site, the stem is bent towards the graft.
How to transplant a violet at home step by step
Shelter floribunda varieties, hybrid tea
Most often, the shelter of roses for the winter in the Leningrad region of medium frost-resistant varieties is carried out by the air-dry method.
Advantage: good ventilation, ease of manufacture
- The basis is the frame. Metal rods or wooden bars and slats will do. The height depends on the bush, usually just over 50 cm.
- The fence should evenly encircle the entire plant.
- Cover the structure with insulation, fixing it to the frame. Many experts recommend using lutrasil with maximum density, its feature is a breathable structure that does not impede air circulation and absorbs excess moisture well. Also, spruce branches or improvised materials in the form of cardboard, woven rugs, paths are very often used.
- Insulate the outer part from rain with polyethylene folded in several layers. At the same time, the ends must remain open.
Prevailing natural soils, their optimization to increase the winter hardiness of roses
With a high groundwater table, a terrace with a retaining wall is built for planting roses.
Most of the territory is dominated by podzolic peaty soils formed by historically swampy areas. Many areas are characterized by a high groundwater table.To determine to what height the water rises, in the spring after the snow melts or in the fall, when seasonal rains have passed, they dig a hole with a depth
1.5 m and monitor the level for two or three weeks. If during this time the water has not disappeared at the bottom of the pit, then it is necessary to drain the site.
There are 2 options:
- Drainage construction.
- Increasing the level of planting, adding fertile soil.
Therefore, before planning roses on your site, you need to make sure that the water level does not rise above 1.5 m.For large climbing varieties and scrubs - 2 m.
The root system of roses does not tolerate even short-term flooding.
An important property of the soil for roses is its qualitative composition. Optimal performance:
| Structure (mechanical composition) | Light loam or medium loam |
| Acidity | Neutral |
| Fertility | High |
Dolomite flour is not only a soil deoxidizer, it contains magnesium compounds that roses need to strengthen their immunity.
Sour peat bogs prevail in the Leningrad region. In order to bring them to the state necessary for roses, such improving additives are introduced:
- Black earth or clay for moisture retention - 20 - 30 kg / m2 (depth 25 - 30 cm),
- Calcium-containing substances to neutralize acidity:
- Slaked lime, or
- Chalk, or
- Dolomite flour, or
- Eggshells.
A good remedy is ash from birch logs. While the product of coal combustion does not affect acidity, but acts as a baking powder.
Tip # 2. Pay attention! Neutralization of natural soil is carried out with preliminary control of acidity in order to correctly determine the rate of addition of the additive. The recommendation is as follows:
- 200 g / m2 substances increase the pH value by one unit of the acid-base balance scale.
- Organic fertilizers to improve fertility. Rotted cow dung is considered the best remedy. It is brought in at the rate of 4 - 6 kg / m2. If there is none, humus from other rural animals or compost from plant residues - 3 - 4 kg / m2 will do.
If the basic soil preparation is carried out correctly, roses can not be fed for the next 2 to 3 years. Adequate nutrition of roses will ensure good growth, strong immunity, and therefore high winter hardiness.
ROSE SHELTER FOR WINTER


In autumn, many are tormented by the question: "What will happen first, severe frost or snow?" Renowned rose connoisseur, forum host "Rose Garden-online" on the site of the "Gardener Bulletin" Alexey STEPANOV is sure that you should not worry unnecessarily: properly covered roses are not afraid of any frosts.
Scarlet rose bush again
Filled the morning with scent
In winter he froze in anguish
of tired dreams, calling for spring.


Under the shelter, roses can withstand prolonged temperature drops even to -30 without snow, and without it they freeze even at -12, especially hybrid tea. So when is the best time to cover? Even professionals often give the wrong answer to this question of beginners.
Accepted
consider that the roses should be covered when the temperature is set at –5… –7 o.
Many people still firmly believe that frosts will not only not damage the roses, but, on the contrary, will harden them before wintering. These tips were born when there were no non-woven breathable materials and they covered in the old fashioned way - a hillock plus spruce branches. With this method, early-packed roses could simply ripen at positive temperatures, but now there is no need to wait for frost. Lutrasil transmits light, air and retains heat, smoothing the difference between day and night temperatures. The weather in late autumn is unpredictable, you can't guess what will happen: a small minus (-5 o), in which open roses will not suffer, or suddenly -12 o - and they immediately freeze.
Therefore, I start pruning and covering the bushes early, from October 15th. By this time, in the Moscow region, the growing season of roses stops, they begin to enter a state of dormancy.But it is quite possible to start this business earlier, for example, from October 1. Practice has shown that early hiding does not harm in any way. On the contrary, roses ripen in greater comfort.
I start by removing the leaves
... People often ask if this is an extra job? I think such an event is mandatory, although there are roses with a large number of shoots (climbing, ground cover), and, therefore, leaves, which are simply unrealistic to remove. Well, you can leave them. Having lost their clothes, roses understand that winter is coming, it's time to stop growing and store nutrients, in addition, the main source of fungal diseases is leaving the foliage. It is better to carefully tear off the leaf, twitching in different directions, and not cut off with pruning shears, otherwise a petiole remains, which can rot in winter and the disease will spread to the stem. Experienced rose growers pick off the leaves with a “light movement of one hand”. In no case should diseased leaves be left on or under bushes. The spores of the fungi overwinter well and go into the soil, and a new infection will begin at the beginning of summer. The autumn treatment with iron sulfate will reduce the damage to the stems by an infectious burn in the spring and reduce the spread of other diseases, such as gray rot, under cover.
Many, without regard to the variety, advise before hiding. remove and unripe shoots (did not have time to bloom). I think this opinion is erroneous. Rose and rose are different, and if in h / g and floribunda successful overwintering of such shoots is reduced to zero, then in bush (especially English) and climbing it is quite probable. It is only necessary to cover the rose early, before the first frost, because temperatures down to -6 will destroy the unripe shoots.
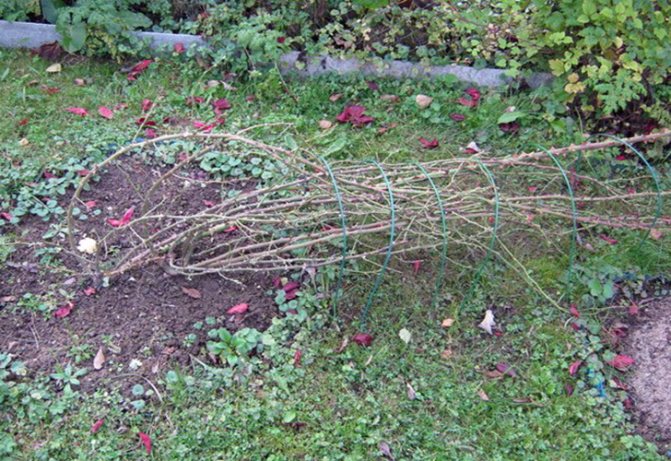
The next stage of preparing roses for shelter is the most difficult. Determined that it is better to hibernate not cut under a shelter, but bent bushes.
But not all roses can be bent, the shoots of adult h / g and floribundas do not bend, so they have to be cut to the height of the shelter, leaving about 30-40 cm. Usually, in the year of planting, all roses bend down without effort, after the second, some produce strong, rigid, erect, stubborn shoots. Then the bending is stretched for 2-3 receptions. The bush must be tied with a rope. Having bent the rose at an angle, for example, at 45 degrees, you can leave it in this position for a day or more, then lower it by another 20 degrees. and, finally, bend down completely. You can fix the shoots in a semi-recumbent state with the help of a skewer stuck in the ground and a rope, periodically shortening it or winding it on a skewer.


Bending the rose with a skewer.
It is advisable to bend the entire bush at once and certainly in one direction, so as not to break it in half. It is not necessary to lower the branches to the very ground, but the lower they fall, the better for wintering. Shoots must be fixed near the ground. Many people use metal staples or hooks for this. It's bad if the cold metal will come into contact with the shoots all winter, and I use wooden slingshots. The part of the slingshot that sticks in should be long so that it does not break out of the ground, and the second one should be short, just to catch the shoot (or several).


Bending down spray roses and fixing them with slingshots.
It happens that varieties with especially rigid branches do not want to bend, then it is better to dig the rose from the side in which it itself seeks. Further, the bush is gradually tilted, while bending not the stems, but the root. It is more elastic. Sprinkle it with earth on top so that it does not freeze. It is advisable to lay lashes not on bare ground, but on spruce or pine spruce branches, foam. You can put empty plastic bottles under the fold so that in winter the snow does not crush the shelter and does not break the branches. Standard roses are laid in the same way of digging, tilting the stem to one side, onto the lower graft.
Preparing roses for winter


Gradual preparation is due to the fact that often during Indian summer, roses form new buds in response to warming. New shoots are released.And a sharp deterioration in the weather - a drop in temperature up to frost - catches by surprise the bushes that are ready to bloom.
The increased sap flow is stopped by subzero temperatures, and not by a natural transition to a state of rest. The frozen moisture in the tissues of the stem tears it apart. The result is injury. At the slightest thaw, infectious agents get into the cracked skin of the shoots. But before stable cold weather, warming during the day is often replaced by night frosts. And all this against the background of active vegetation, depleting the root system, which will have a long winter.
Therefore, it takes a lot of effort from the grower to suspend the growing season, adjust the feeding, which allows you to accumulate reserves of nutrients for a safe wintering. This is the task of the August events. And only after a stable decrease in temperature to zero, prepare the bushes for a dormant period.
Top dressing of roses in autumn
The rose menu has been revised since August. Bushes no longer need nitrogen: it provokes vegetation. And phosphorus and potassium are essential. The first macronutrient strengthens the root system, the second is important for future flowering, and both help the roses to bloom and complete the growing season. Therefore, prepare the following mixture:
- superphosphate - 20-25 g;
- boric acid - 2-2.5 g;
- potassium sulfate - 10 g;
The components are stirred in a bucket of water. A near-trunk circle, framed with an earthen roller, is abundantly spilled so that the solution does not spread. The proportions are indicated for areas up to 4 sq. M. If the concentration is reduced by three times, then spraying is carried out on the leaf. Foliar feeding is the shortest route of nutrients to the cells.
Important! Flowers planted in the current year (subject to high-quality filling of the seats) do not need top dressing. The supply of nutrients is sufficient for a year. If the method of feeding is watering, pre-moisten the earth. Mineral fertilizers are never applied to dry soil: this is fraught with root burns.
Instead of potassium sulfate, potassium magnesium is used: in the composition of the magnesium necessary for this period. Both components are included in potassium monophosphate. The dosages are the same. Other complexes of RK (phosphorus-potassium) or ready-made fertilizer for autumn are effective:
- for roses in autumn, Fertika produces Kristalon;
- from the same special composition for rose bushes;
- Gloria - granules from Fasco.
Each fertilizer company has an autumn rose complex in its product line.
Adherents of organics for autumn feeding of roses use:
- ash - dusting the bushes or watering with infusion (200 g + 10 l);
- bone meal - sprinkle the soil around the bushes;
- fishmeal - also left on the surface of the trunk circle;
- banana peel (source of potassium) - dried and crushed - on the ground near roses.
It is difficult to harm plants with organics, but the process of assimilation of nutrition is longer, and the necessary concentration is difficult to calculate.
Moisture charging irrigation
The watering regime changes when September comes. Excess moisture stimulates the development of new shoots, which weakens the plant. Therefore, in a dry warm autumn, ornamental bushes are watered every 7-10 days, in the second half of the month - once every 2 weeks.
Important! September is a landmark for gardeners in central and central Russia. The farther south the region is, the more time is shifted. In the Crimea and the Caucasus - until mid-November. And in Siberia, by mid-September, watering is reduced to a minimum. They moisten the earth only under drought conditions, which happens very rarely beyond the Urals in autumn.
The traditional for perennial crops, water-charging watering of roses is not required.
If autumn is rainy, then roses, on the contrary, protect against excess moisture by draining water from the trunk circle or covering the flower beds with a canopy.
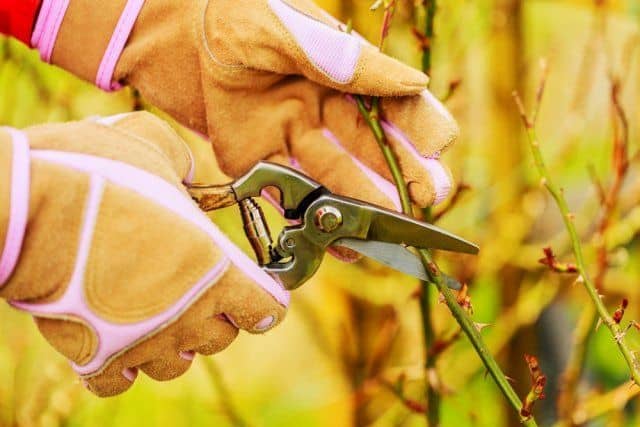
Pruning roses in autumn, when and how to prune
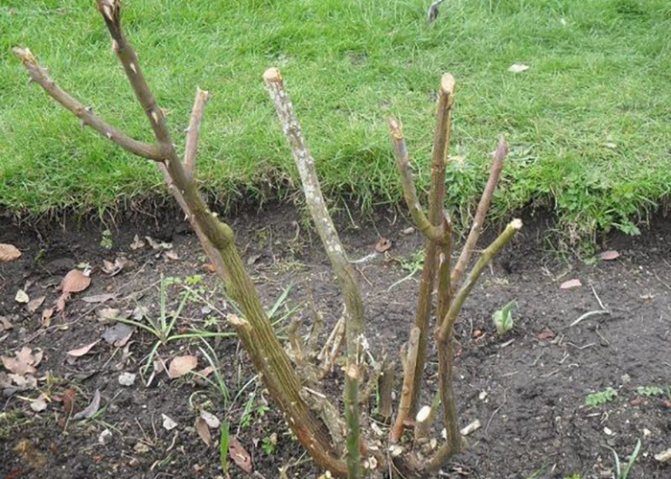


It is easier for thermophilic plants to overwinter after pruning, and for the gardener to hide the shoots from frost.In regions with mild winters, park varieties, wrinkled varieties, ground cover are not cut. These roses only need a sanitary cut: dried, damaged or clearly diseased shoots are cut out. Dry buds and foliage are removed.
And where severe frosts are not uncommon in winter, pruning is needed for all varieties and varieties. But everyone has their own approach. The goal is the same. Forming a bush is a gardener's task in the spring. And in the fall - prevention of the spread of infections, preparation for winter.
Roses are usually pruned immediately before being covered. Cutting too early will give the bush an incentive to grow, which should not be allowed. The timing depends on the climatic zone and weather in the current season. The general criterion is regular frosts at night and a small plus during the day. But by the average daily minuses, the roses should be completely ready for winter, i.e. cut and covered.
So that the plant does not exhaust itself, resuming flowering in the second half of September, small, less than a centimeter, the buds are removed, and large inflorescences are cut off. Sometimes, so that pests do not settle in the wounds for the winter, the stem under the flowers sags, without breaking.
Experts advise how to prune a rose in order to keep it outdoors in winter:
- All bushes are subject to pruning, even those planted in the current year.
- Shoots that did not have time to turn green (red is a sign of immature stems) are cut out. They will not survive frost and become sources of disease or prey for pests.
- Shoots older than 5 years are cut completely.
- Remove everything that grows inward to thin out the bush.
- The cut is oblique, at 45 ° from the vertical of the stem.
- The cut point is above the kidney, not closer than 5 mm and not higher than 10 mm. If this is a lateral shoot, then an external bud is chosen.
- Roses, except for climbing ones, are cut so that up to half a meter of the length of the shoots remains. Or they are calculated so that the stems become shorter by a third.
Important! The instrument is well sharpened so as not to tear the tissue: any excess wound is a source of future problems.
What roses require shelter in winter?
There are several types of shelter for roses in winter: dry type of shelter, digging, incomplete shelter, etc. The choice of wintering option for this plant will depend on its winter hardiness and other characteristics of the variety.
Cold-resistant varieties do not need to be covered?
Park, species varieties and some hybrids are considered the most cold-resistant. The opinion that frost-resistant roses can winter without preparation is wrong. Even the most hardy species need special preparation for subzero temperatures.
In the middle lane and in the south of Russia, frost-resistant varieties can winter without shelter, but it is still better to spud the root system with sod soil, spruce or dry foliage. All feeding and pinching stops by September. Before winter, the bushes are treated with an antiseptic, cut off and covered (in whole or in part). Full cover is necessary for bushes that hibernate in especially harsh conditions - if the thermometer in winter drops below -30 degrees.
The most cold-tolerant varieties are: Ritausma, Golden Celebration, Pink Grothendorst, Leonardo da Vinci, Konrad Ferdinand Meyer, Hansa, Adelaide Hootles, Lavinia, Scabroza, Snow Pavel, Jens Munch, John Davis, Hansa, Peace, New Dawn, Black Magic, Black Magic William Shakespeare 2000, etc.
Wintering conditions for thermophilic roses
Climbing roses, miniature, hybrid tea and exotic varieties are sensitive to cold weather. Such varieties require special protection in the winter: they must be insulated from above, spudded, and some even completely buried in the ground.
Caring for roses at the end of summer
Preparation of roses for winter in the middle lane begins at the end of summer. Nitrogen-containing fertilizers are excluded from top dressing, they activate the growth of leaves and shoots. In August, fertilizing with potassium and phosphorus is carried out, which strengthen the root system and contribute to the ripening of rose shoots.Superphosphate (25 g), potassium sulfate (10 g), boric acid (2.5 g) are dissolved in a bucket of water and watered rose bushes.


In September, feeding is carried out again. Superphosphate and potassium sulfate, taken 15 g each, are dissolved in a bucket of water. Foliar dressing in the form of spraying with a solution of fertilizers effectively affects plants, the dosage of which is reduced by 3 times.
With the beginning of autumn, in the middle lane under a rose bush, they do not loosen the soil so as not to cause the development of young weak roots and the development of shoots. From the second half of September, all buds that appear should be removed.
When is it time to cover the roses?
It is not possible to cover rose bushes until the end of October. Otherwise, the temperature in the shelter may rise, provoking the development of roots and shoots. In addition, soil moisture rises in early autumn. This condition will lead to excess moisture and plant decay. Experts advise hiding flowers in winter, when the temperature has dropped to -5 degrees for more than a week.
Light frost - is it good?
Roses are not afraid of the first frost down to -7 degrees. Experts even advise to specifically wait for such a temperature, without covering the bushes. This contributes to the correct introduction of flowers into a state of dormancy, the hardening of the stems and the root system.
Expert opinion: everything must be dry!
Experienced growers warn that the main condition for the successful wintering of rose bushes is a dry shelter. Do not add roses with wet soil, damp foliage or covering material. Both the bushes themselves and all means of shelter must be dry. This protects roses from pests, rot and mold.
The choice of covering material
Thanks to the covering material, the plant is protected not only from severe frosts, but also from other adverse influences. The material perfectly transmits moisture, air and light, and also creates a favorable climate inside the structure. It is environmentally friendly and completely harmless to plants.
Insulation for roses can be purchased at the store or use scrap materials.
Gardeners prefer to use:
- Geotextile or plastic wrap.
- Lutrasil.
- Spandball.
- Lapnik or dry foliage.
A step-by-step guide to sheltering roses for the winter
Stage 1: preparing roses for wintering correctly
1. At the end of summer, you need to stop nitrogen fertilizing, which provoke the growth of shoots. Before autumn, you can occasionally fertilize flowers with potash mixtures, which contribute to the stiffness of the stem. The last feeding should take place no later than September (in warm climates - the end of September). The most successful composition for pre-winter fertilization is potassium-magnesia. Such a simple care of roses in the fall will bear fruit.


2. Before the shelter, the roses must be allowed to ripen. To do this, you must stop cutting flowers into bouquets 3-4 weeks before hiding. This also applies to young roses of the first year, the buds of which you have cut all summer. Before winter, they must be allowed to bloom in order to end the growing season naturally.


3. Almost all garden varieties of roses do not have a natural period of foliage. Therefore, all leaves must be cut or torn off. This will not only put the plant into a dormant state, but also rid it of potential foci of infection.
4. Directly before the shelter, the bushes should be treated with a fungicide or a solution of ferrous sulfate in order to disinfect all aerial parts of the plant. The soil under the roses should be cleared of fallen leaves, weeds and any other debris.
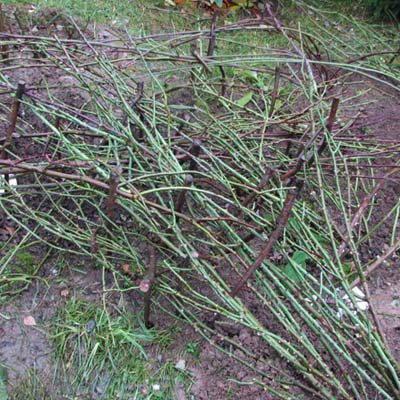
Stage 2: Bending or Trimming
You can not cut off park and weaving varieties. Climbing roses and some shrub varieties that are sensitive to cold should begin to be bent to the ground in advance, as laying on the ground can immediately damage or break the stiff stems. So, 3-4 weeks before the shelter of the rose, you need to start putting it on the supports, which gradually sink lower and lower.
Curl or trim park roses?
Many growers like to cover roses without cutting, citing the fact that this way the plant tolerates winter better. In addition, the risk of throwing out new shoots is significantly reduced, and the bush itself wakes up and blooms earlier in the spring. However, opinions are not unambiguous, because in conditions of harsh winters the plant winters the better, the smaller its aboveground part. There is one more thing - the upper part of the stems can contain bacteria and rot, which is dangerous for the plant as a whole. Therefore, we are for pruning!
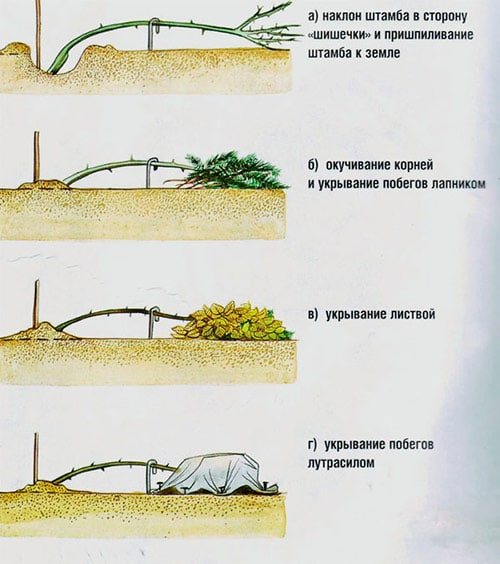

How to bend the bushes correctly?
- If the stems are dense and not flexible, then they need to be bent in several stages, as mentioned above. Old construction rods or rods can be used to bend the branches. They easily enter the ground, bend well and serve for many years.
- In order for the stem to bend without damage to the plant, you can dig the root of the rose with a pitchfork. It is not necessary to dig up the bush too much, make 2-3 incomplete digging so that the stem becomes mobile. Now he will better lie on the support for shelter.
- The bush must be bent towards the side of the graft in order to avoid the breaking load on the stem in this place.
Standard and all climbing roses are removed from the support and laid on the ground.
Stage 3: Covering
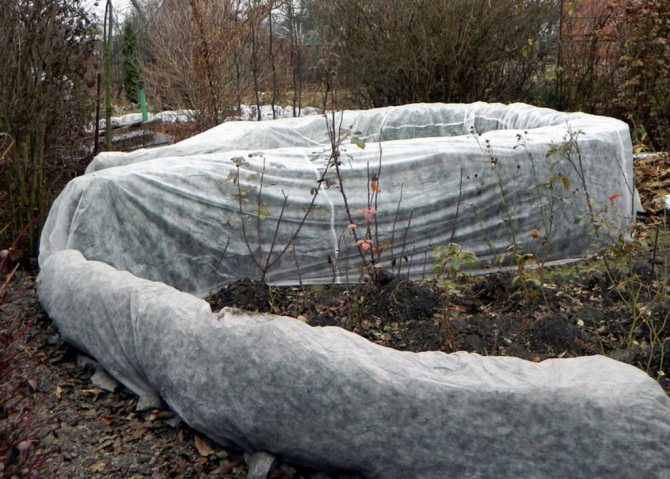
How to properly cover roses for the winter? This can be a ditch, an air-dry type of shelter, or a wrap.
- The bushes are dug in as follows: we sprinkle the roots of the prepared rose with earth by 20-40 cm of the height of the stems; the upper shoots of the bush are covered with dry foliage or covered with spruce branches. You can completely bury roses in the ground;
- The air type of shelter provides for the insulation of the root with foliage or needles and the construction of an air dome over the rose made of plywood, plastic or other suitable materials;
- Some growers use a method of wrapping roses with geotextile fabric or other thermal insulation material.
How to prune roses in the fall
Preparing roses for winter in the middle lane includes an important agricultural technique - pruning. Pruning not only makes it possible to simplify the shelter process, but also stimulates the growth of new shoots with a large number of buds in the coming season. Many shoots will not shade each other, the crown will receive the maximum amount of light and heat, ventilation will improve, which will not allow diseases to attack the plant. Cut bushes are much easier to tolerate the winter cold of the middle lane.


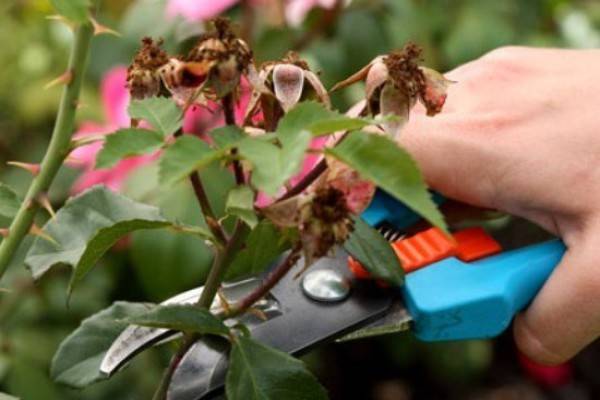
The secateurs must be well sharpened and disinfected. The cut should be flat. Old lignified shoots are removed with a hacksaw.
Pruning of roses in the middle lane is carried out in late autumn, in late October or early November, shortly before the hiding place of the roses.
First of all, dried, broken, diseased branches are removed. Then all leaves and buds are removed, after which green shoots are cut out that have not ripened and will be the first contenders for frost damage.


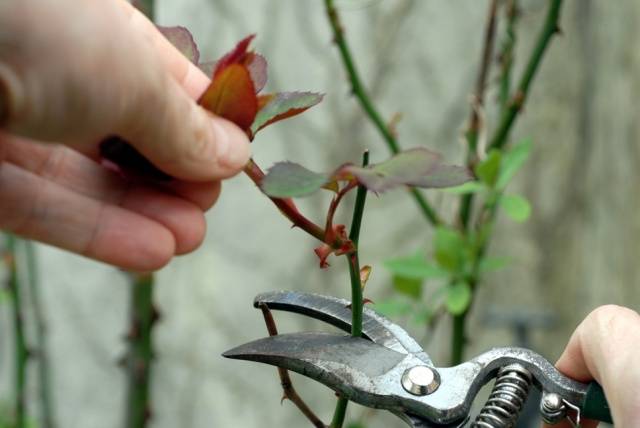
Pay attention to the features of pruning roses:
- Green shoots are cut to a white core;
- The cuts are made at an angle, then water will not stagnate in them;
- The cut passes over the kidney at a distance of 1.5 cm;
- The bud should be directed to the outside of the rose bush so that the future shoot does not grow inward;
- A dry, windless day is suitable for pruning.
In no case should you leave trimmed parts of plants on the site, usually spores of fungi and bacteria hibernate in them.


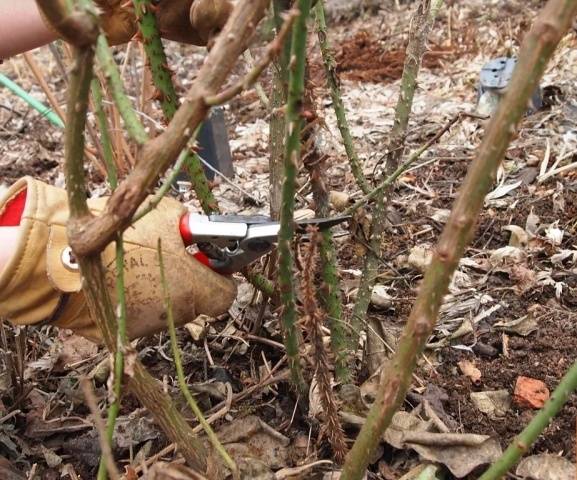
There are 3 types of rose pruning:
- Very short when the entire bush is cut to the base, leaving 2-3 buds. This type of pruning is suitable for hybrid tea roses and floribunda varieties. Prune other varieties if they are damaged by diseases or insect pests;
- Medium pruning is most often applied to Old English and hybrid tea roses, the shoots are shortened by half, leaving their length by 30 cm, the buds remain 4-5. By shortening old shoots, they make it possible for the young and strong to develop;
- Long or light pruning is applied to rare varieties of roses, a gentle pruning type allows flowers to appear earlier, but over time the bushes lose their shape.
In climbing roses, sanitary pruning is carried out, removing dried, broken and damaged branches, healthy shoots are barely shortened, 2 old lashes are shortened by 5 buds in order to stimulate the growth of shoots from replacement buds.
Correctly carried out pruning rejuvenates the bush, maintains its neat shape, health, and makes it easier to cover roses.


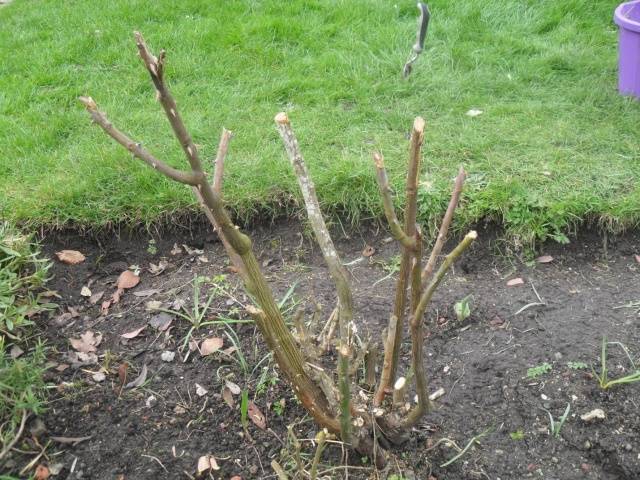
Three best designs for hiding roses
For those who cover climbing, standard and spray roses with only the roots in place, we present the three most popular types of shelter.
I. Skeleton method


Finished hilled bushes can be covered with a frame on top. Material that can be used: metal rods, plastic sheets, large plastic flowerpots, old wicker baskets, wooden pallets, boards, etc. We build the frame as follows:
- We mark a place around a trimmed bush or bent rose;
- We form a dome or roof-shaped shelter from two plates above the rose;
- If the winter is especially frosty, the dome can be covered with a covering material, and the plant itself can be additionally sprinkled with needles or foliage;
- The edges of the insulation are pressed with bricks from all sides, in order to sometimes ventilate the covered roses.


Frame shelters are of different types:


II. Fence with embankment
The essence of the method is the dry filling of the rose according to the shape established around it. As a fence, you can use a stainless steel mesh, thin plywood or cardboard boxes. From the selected material, a fence is made according to the height and width of the bush. Insulation is poured inside: dry sawdust, foliage, hay, etc. If the fence is made of a metal mesh, then it can be additionally wrapped with polyethylene from the sides so that the bulk material does not spill out.
III. Lutrasil cocoon
Some tall varieties, especially standard ones, are covered by winding insulation material on the crown, leaving the stem on the support. At the same time, the root is also insulated by hilling. To insulate the leafy part of the rose, it is wrapped with lutrasil or other insulating material. From below, the cocoon is tied up so that cold air does not pass through the insulation.
Summing up, we can note the following: even if your roses live in warm winters (-5, -10 degrees), they should be insulated before frost. Covering roses is not only protection from the cold, but also a means of preventing many diseases (rot, late blight, etc.). Choose the type of shelter according to your rose variety and the climatic conditions in your region. We wish you beautiful and healthy rose gardens!
How to properly cover roses
After your roses are ready, you can proceed directly to the shelter. Roses can be covered in different ways, but the most common are three:
- dropping. After you have covered the roots and covered them with a layer of warming mulch, the upper ground part of the bush can be covered with spruce branches or covered with foliage. When snow falls on top, the rose will be securely closed. The main thing is to do this not too early so that the shelter does not get wet with rain. It must be dry. You can simply completely bury the flower, covering it with loose dry earth;
- dry shelter. Above the ground part of the bush, a plywood protection or pegs are installed on which the covering material is stretched. As a result, a kind of dome appears above the plant, which will then also be covered with snow;
- some growers simply wrap the stems of roses with fabric material that insulates the rose and prevents it from freezing. But this method is rarely used.


Take your time with cover. Spudded roses will easily endure frost of 8-10 degrees.
When to shelter
The question is correct, if only because no one wants to take care of "vines" several meters long.This is normal, only in the case of roses instead of the word - I want, should be used - necessary. Moreover, in relation to all types and varieties, without exception.
Why is it so categorical? If we take, for example, undersized and medium-sized roses, they all feel the approach of winter and at a certain period of time go into "hibernation". Then the weather and temperature will change or not, they do not care, sleep means sleep. Climbing at the lowest subzero temperatures also "freeze", but if it gets warmer outside at least to plus 1 ° C, the plant will grow again. If this happens in winter, the planting will not survive until spring. The shelter is designed to create a constant cool microclimate for the bushes.
The climate of the Moscow region is quite unpredictable. A warm, sunny autumn can unexpectedly end with a September snowfall. That is why the preparation of roses for shelter for the winter begins here earlier than in the southern regions, and, accordingly, they also cover earlier.
Usually, the time of work on the shelter of garden beauties refers to the end of October - beginning of November. But you need to carefully monitor changes in daily temperature. Roses are covered at a stable average daily temperature of -5-7˚С.
This temperature is the main signal to start covering work. You can do this earlier, but another problem will arise - excess moisture will accumulate under the shelter, which can lead to mold and decay of the bushes, especially if warm days are delayed.
In most regions of Russia, climbing roses without shelter cannot survive the vagaries of the weather themselves and freeze out. They practically do not enter a dormant period. Even in late autumn, you can see buds, flowers and shoots with leaves on them. At the same time, the sap flow continues.
When the air temperature drops below 0 degrees, the sap in the plants freezes and leads to tissue rupture. Frost cracks appear on the plants. Ice forms in these cracks. The juice thaws with slight warming and flows out of the stems of the roses. Diseases penetrate through the damaged areas and begin to multiply actively. By the spring, with such damage, the upper part of the plant dries up, and if the root system is frozen, then the bush simply dies.
To protect roses from cold and disease, a number of activities are carried out, the quality of which determines whether they will delight their owners with flowering next year.


The shelter time of climbing roses in different regions is different, since they have different climatic conditions. In warmer regions, roses take refuge at the approaches of the calendar winter, and in colder regions, roses require earlier protection.
Shelter of garden beauties in the Moscow region and Central Russia is held in late October - early November. Roses take refuge in dry weather, with a stable average daily air temperature of –3–5 degrees. A more precise time of shelter is determined depending on the weather conditions this year.
In the Urals
Shelter of climbing roses in the Urals is carried out in the second - third decade of October. By this time, the bushes must go through all the stages of preparation and be fully prepared for the coming cold weather.
It is impossible to cover the bushes at temperatures below -7 degrees, as the plants become brittle and easily vulnerable at the same time. If possible, you need to clarify the upcoming weather for several days ahead and take protective measures on time.
In Siberia
In Siberia, rose bushes take refuge in late September - early October. The main thing is that the plants are fully protected by the beginning of stable cold weather.
Shelter of roses in the Leningrad region is carried out until the beginning of November. When severe frosts are approaching, protective measures must be carried out a week before their onset.
The rose is considered the most beautiful flower. She is the queen of any garden. Despite the capriciousness and demanding care, these flowers are popular among gardeners.
The question of the need to protect the rose for the winter arises before many growers. The answer depends on the climate. In the southern regions, where winter is not particularly cold, climbing roses do not need to be covered. There are frost-resistant varieties that can withstand quite severe cold without any problems. For them, after the autumn pruning, it is enough to pour sawdust or branches under the root.
But for the northern regions, sheltering a rose for the winter becomes a necessity. Even the most frost-resistant variety will not be able to withstand severe cold. The bushes just freeze over. The sap inside the bush freezes at a temperature of - 2 ° C, and the trunk begins to crack. Then pests and microbes get into the cracks, the plant begins to hurt and eventually dies.
In order to avoid the death of a climbing rose in winter, it is necessary to construct special devices that will protect the bushes from frost, but retain the ability of the plants to breathe.
There are several ways to cover climbing roses for the winter. Each of the methods is good in its own way. When choosing, it is worth considering the location of the plants on the site and the distance between neighboring plants. For bushes that are close to each other, the wireframe method is best. For climbing roses that wrap around pillars or arches, frameless structures are best suited.
This type of shelter is the simplest. It is suitable both for old bushes that are difficult to bend down, and for young ones that bend well.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with: How to properly grow grapes in the Moscow region
The sequence of actions for frameless shelter:
- Bend the branches in the direction where they bend better (if the bush is old with a thick stem, then you can not bend it).
- Put spruce branches on top of the bush or at the roots.
- Cover with covering material.
- On the sides, fix the covering material with stones or boards (on the old bush, the covering material is fixed by tying it with a rope).
Important! When bending, you need to act carefully and try not to break the branches.
The second common way to cover a climbing rose for the winter is a frame device. This method does not require bending the plants and allows them to breathe better.
Shelter stages:
- Rose bushes can be cut to the height of the intended frame or bent to the ground.
- It is necessary to make a frame in the form of a hut from metal arcs, pegs or boards.
- From above, the frame is covered with material (spunbond, film, roofing material, and so on).
- At the edges of the frame, it is necessary to fix the covering material so that it is not blown away by the wind (sprinkle with earth, stones or boards).
At what air temperature to start covering the rose garden


Covering work cannot be started too early. In case of light frosts (-1-3 ° C), it is better to leave the rose without shelter, otherwise the death of the bushes may occur. Under the material, the shoots will continue to develop, they will release buds, which, under the influence of heat and moisture, vomit out - as a result, the plant will no longer bloom in the spring.
Before starting the covering work, you should wait until the average daily temperature reaches -5-7 ° C, wait another week, and only then build "houses" for roses.
On a note! It is necessary to do the insulation of the rose garden in dry weather. If work is carried out in high humidity, the risk of developing fungal diseases increases.
Features of the shelter of standard roses
To hide standard roses, use one of two methods. Either the plant is tilted to the ground, fixed and covered with a film, or the covering materials are wrapped around the upright plant. The second method is not considered reliable in regions where winter temperatures drop below -20 ° C. Residents of the Moscow region are better off choosing the first method.
In order to make it easier to lay rose bushes with a high trunk on the ground, they are undermined on one side. Then the stem is gently tilted. This operation must be carried out slowly in order to prevent cracking of the barrel.
After the trunk has reached a horizontal position, it is fixed with staples or tied to a heavy stone. A cover made of spruce branches and non-woven material is installed on top.
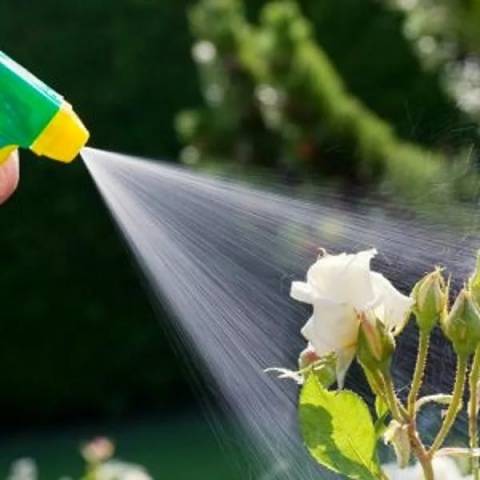
Autumn processing of roses
Since many varieties of roses are susceptible to various diseases and pests, it is recommended to treat the shoots and the near-stem circle with copper-containing preparations in the fall. This will help protect the seedlings from dying in the spring. On our site you can find an article on preparations for autumn plant prevention, and it will help you decide how to process roses before sheltering.


How to prepare roses for shelter
Top dressing
During the summer months, during which, with good care, roses bloom almost continuously, the soil, even if summer fertilizers are applied to it, is depleted. Therefore, before sheltering, the rose needs protective and preparatory measures. And cropping is just one of them.
Around the beginning to mid-September, roses must be fed with special autumn fertilizers. Precisely in the autumn, because if you add a standard summer complex to the soil, the rose will begin to release new shoots, and it simply will not have time to properly prepare for winter. Therefore, for example, it is not necessary to introduce organic matter into the soil in the fall.
In the fall, you need to feed the rose with potassium, calcium and phosphorus. You can prepare the fertilizer yourself by diluting the ingredients in a bucket of water and watering the bushes (about 10 liters of water add 15 g of fertilizer), or you can simply buy a ready-made mixture in the store.
In addition, you can add ash under the roots of the rose and spill it with water on top - the ash contains exactly those components that the rose needs in the fall.


Pruning
The next thing to do when preparing roses for winter is pruning them. Pruning roses for the winter is one of the main components of caring for them; without this procedure, your roses will not only not bloom normally next year, but they will not overwinter either.
Be sure to prune your roses or your efforts will get you nowhere. Pruning makes roses more resistant to winter cold.
Of course, both the pruning of the rose and their winter shelter depend on the variety of your beauties. Therefore, we will consider the most popular pruning and covering methods that will suit all roses in one variation or another.
Around the middle of September, it is advisable to remove all the leaves from the roses, which are already beginning to fade slowly. This should be done so that the rose, firstly, does not evaporate moisture, and secondly, so that the leaves do not begin to rot in the winter shelter. In addition, there are often infections on the leaves that are not immediately visible, but will quickly spread in shelter.


When the temperature begins to fluctuate around zero, the roses can already be pruned. Tall bushes should be cut off by at least two-thirds, cutting off the shoots with a sharp pruner about 1 cm above the last bud.
The bud should be located on the inside of the shoot if you want to form a bush with vertical shoots, and on the outside if you want a lush, spreading bush. The cut itself should always look inside the bush.
Do not worry if you inadvertently cut the rose too short, there is nothing wrong with that. The main thing is to preserve the root system, and it will bloom on new shoots, which the bush will begin to grow in the spring.
Deep pruning, on the other hand, is useful in that it rejuvenates the old bush, which begins to actively release new shoots.


If you grow undersized varieties, then on your roses you just need to cut off dry inflorescences and slightly shorten the shoots, by 10-15 centimeters, this will be quite enough.
Sometimes in autumn, shoots with buds appear on park roses, which begin to bloom. You do not need to cut them, because the rose will begin to release new shoots - any early pruning leads just to the formation of new side branches.Cut these shoots later when it gets cool.
If new stems appear on the roses in the fall, you just need to pinch them slightly, preventing them from growing. Then lateral shoots will not appear on your rose, late buds will not form on them, and your rose will not weaken by winter.


Spraying
Be sure to spray your rose bushes with a pest repellent - roses are very prone to disease and attract a variety of food lovers - from slugs to spider mites.
When to cover roses. At what temperature to cover roses for the winter: tips and tricks
There is an opinion that roses are capricious plants. But this is not at all the case. A rose requires care, dressing and watering no more often than its other cousin in a flower bed. It is important to properly cover these flowers for the winter so that the roots and stems are not too hot or cold.
Rose is not as delicate as she seems. After reading about the temperature at which to cover roses for the winter, many may be surprised. After all, not everyone knows that a bush with ripe stems will calmly endure frost down to -8 ° C. Excessive overheating and humidity during wintering are much more dangerous for a plant, because of which they can simply rip off. Therefore, it is important to know how to properly cover the roses.


Firstly, there is no need to be frightened if it is -1 ... -3 ° outside, and the plants are not yet covered. Let them pass hardening in this way.
Secondly, in order for the bushes to winter well, they are not fed in the fall and watering is stopped.
Thirdly, if prolonged rains are expected in October, then the ground under the bushes should be covered with dense cellophane. Then the plant will not be afraid of excessive moisture during wintering.
Easy shelter for roses
They begin to warm roses for the winter when the weather has settled at 0 ... -1 ° С. Here is at what temperature experienced florists recommend to cover roses for the winter. Usually in the middle lane this corresponds to the beginning of November. But they should be bent to the ground until frost, at + 2– + 6 ° С, then the whips are more pliable.


After the theoretical knowledge about the temperature at which roses are covered has been obtained, they should be prepared for winter. First, all unripe shoots are cut out. Low varieties of plants (floribunda, hybrid tea, ground cover) can be cut in such a way that the stems rise 10-15 cm from the ground. Climbing roses are bent to the ground using arcs, large hooks, hairpins. It is better to lay branches on spruce branches. For the prevention of diseases, the lashes are sprayed with a solution of copper sulfate in a ratio of 1:20 to water. Now you can pour 5-7 cm of high-moor light peat under the trunk and around it. The plants are covered with cellophane on top. In this form, they will stay until mid-late November.
It is important to know at what temperature to cover roses for the winter if their seedlings are brought from warmer regions. For example, standard plants are covered a little earlier, without waiting for severe frosts to come. Approximately at the end of October, when the night temperature reaches + 1 ... -1 ° С, they begin to heat insulation. A special cover made of spunbond, high-density lutrasil is put on top of the plant. The cape should be well secured so that it is not blown away by the wind and the plant is warm. In order for standard roses to winter better, they should be very carefully bent to the ground and also secured with arcs and hairpins.


Capital Shelter of Roses
After the frosts have established (approximately at the end of November), a layer of spruce branches is placed on top of the plant, and then covered with tar paper or roofing material. This will help the roses to winter well and not be affected by rains, thaws, which can lead to their drying out.
Speaking about the temperature at which to cover roses for the winter, it should be summed up that the first light warming of plants is carried out at 0 ... -2 ° С, and in a more global way, they are wrapped up when the temperature overcomes the mark of -5 ° С.
Shelter of common varieties of roses in the Moscow region


The main conditions for wintering roses:
- go under cover with removed leaves and a shortened crown, without dry, damaged and unnecessary shoots
- for insulation, use a material that does not accumulate condensation
- provide periodic ventilation
- a sufficient amount of snow, which is an additional and important insulation.
Rarely does a manor near Moscow manage without planting these enchanting beauty and aroma of plants. Many owners have rosaries of many varieties. These gifts from God on earth fascinate with their fiery flowering. The specificity of preparing beauties of any kind for the winter cold is practically the same.
Thaws often occur in the Moscow region in winter. During this period, it is necessary to ventilate the shelter to dry and circulate air. In such cases, it is advisable to additionally provide the shelter with plastic wrap so that the melted snow does not create moisture for wintering plants. Dwarf bushes can get by with a cardboard box, in which holes are made, and a tall rose needs a larger structure.
Shelter terms in the Moscow region
So that the flowers do not die from severe frosts, which are inherent in the Moscow region, rose bushes must be covered. If the temperature is below freezing, it can significantly damage the young stems and the root system of the plant. This can cause the death of the rose. Adequate shelter will help the shrubbery gain strength and ensure a quiet winter.
The event itself for sheltering the plant is not particularly difficult, but you should still pay attention to some points. First, you need to understand that you cannot cover a rose bush in the Moscow region ahead of time, otherwise it will rot and die. The event should be held when the temperature reaches -5… -8 ° C and remains at this level for 7 days.
Shelter types
For the Moscow region, it is optimal to use two types of rose cover: frame and frameless.
Wireframe method
This method is for climbing roses. These plant species tend to retain their greenery even in winter. When a stable cold comes, and the previous preparatory measures have been completed, the following steps must be performed:
- Purchase two Wooden Shields. Their width should be about a meter, and their length should be the height of the shrub.
- Place shields over the plant. They should be in a house position. Fasten the wooden boards with pegs driven into the ground. This step must be performed without fail, otherwise the shelter will slide down due to the thick snow layer.
- Cover the resulting structure with polyethylene material. It is necessary to ensure that the ends are well rolled. The bottom of the polyethylene must be covered with soil.
Frameless way
To insulate standard and climbing rose varieties, you can use a frameless design. For this, the plant bent to the soil must be covered with spruce branches, tree foliage and film material.
Shine and chic on top


Shelter of climbing roses
A climbing rose is looking up at its fellow tribesmen. Cascades of gorgeous flowers give the site a fabulous charm. The plant beautifully decorates unsightly walls and fences, turning any corner into a flower kingdom.
Covering roses with lashes up to three meters in length is not so easy. The weight of lashes, leaves and flowers of such a beauty will not pull one kg. It is necessary to remove all this wealth from a solid structure fixed in the ground or on a wall. Tie together several shoots and lay them neatly on the prepared spruce branches. This must be done very carefully, trying not to damage the lignified branches of a tall rose. Pin to the ground with wire or metal staples. Over this fading luxury, it is necessary to install arcs or build a tent of thin boards or plywood.Lay the covering material on top and fix it at the bottom. In such conditions, the cold-resistant goddess will winter well and next year she will again delight her with her unusually beautiful flowering. You need to know that the leaves of this type of plant do not fly around by themselves, they must be removed. You need to start cleaning the shoots from the foliage from the bottom.
An arch or a structure in the form of a column can be ennobled by a climbing rose. Flexible, pliable, easily bendable shoots, framed by inflorescences of various shapes and colors, will create an extraordinary miracle on the site. They, as if performing a fiery dance, will give odds to any exotic liana.
You will have to cover a rose of wondrous beauty for the winter right on the spot, without removing it from the supports, with the help of textiles or other warming cloth, wrapping it around the wayward beauty. If the rose is young, and the support is removable, then you need to remove the plant along with the support and hoist it on a prepared site, and then make a cover with non-woven material. This will be the best wintering option.
During the summer season, lashes at a blooming liana with an unbending character can add up to two meters in length, so a shelter in Moscow gardens is a must for such a plant. In the spring, prune frozen or podoprevny lashes, as well as the ends of the shoots with a strong outer bud. A climbing rose requires autumn pruning if the bush is heavily thickened.
Delusions
The procedure for preparing roses for the winter season arouses interest and anxiety among flower growers. Even experienced plant breeders are often at the mercy of delusions and make the same mistakes from year to year when preparing bushes for wintering. These delusions are not always harmless and quite often become the reason for the inhibition of plant development, the lack of flowering, and sometimes the death of the specimen.


You may be interested in:
Opening roses after winter in the suburbs Growers know that outdoor rose bushes can be particularly problematic. Time is important ... Read more ...
The more thorough the better
The main protection of the bush from the cold is not an insulating material, but an air gap between the shoots of the plant and the matter. For this reason, the warmest shelter option is a strong frame, which creates a large warm air gap, and a layer of snow on top of the structure. But, when the air temperature is not too low, it becomes hot and humid under the insulation. In such circumstances, such a shelter can lead to the beginning of the debate of the plant, and then to its death.


Phosphorus and potassium are the only things you need for a successful wintering
The plant needs feeding in the fall, but in order to increase the durability of the flower, the rose needs not only phosphorus and potassium preparations, but also other fertilizing containing calcium, magnesium and other elements. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the autumn fertilizer does not contain nitrogen. Top dressing in the fall is only a supportive and immunity-enhancing measure; without shelter in severe frosts, roses will not survive.
All roses are cut short for the winter
Bushes of an ornamental flowering culture need pruning and this procedure is mandatory in the case of preparing a plant for wintering. But, there are several length options - medium, short and long. The short version rejuvenates the flower, but negatively affects frost resistance. Long, with annual repetition, leads to a decrease in flowering intensity. There are certain rules that a grower must follow:
- Pruning is carried out on a windless day when there is no precipitation and the air humidity is low.
- Shoots are cut off only with a sharpened tool - this will minimize damage to the bush. When the pruner is blunt, it pinches the shoot, which can lead to death of a particular plant specimen.
- Shoots are removed only at an acute angle, and the cut is directed to the center of the bush.
- The place of the cut from the extreme kidney must be located at least 1.5 cm.
- The bud, which will give rise to new stems, must look outside the bush. This position will expand and give splendor to the rose. But, when it is necessary that the shoots are directed vertically, and the lateral shoots are absent, it is necessary to leave the bud facing the inside of the bush.
Attention!
When the grower does not remember which variety is growing, it is recommended to choose the middle type of pruning. But, sometimes it is better to completely abandon this procedure. In this option, it is necessary to remove all buds, inflorescences and foliage from the plant, and then bend the shoots to the ground and fix in this position. They make a shelter on the bent shoots from above.
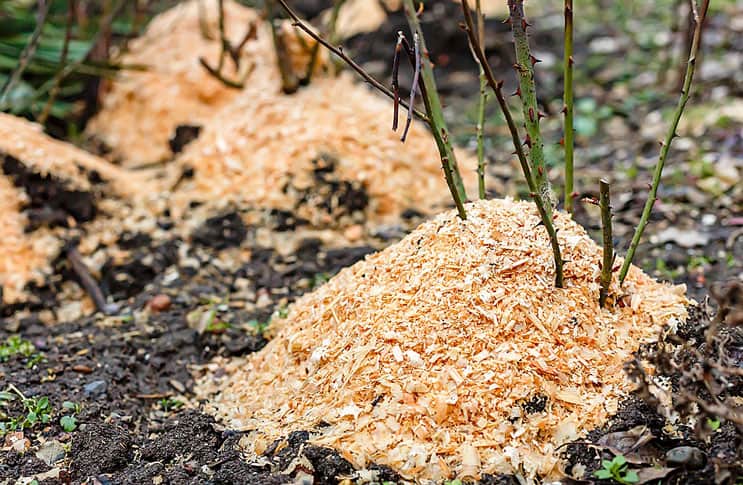
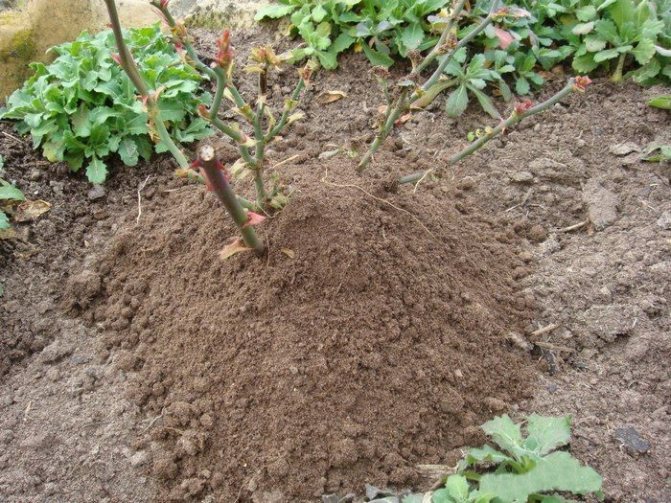
Before wintering, you need to spud flowers.
It is recommended to sprinkle roses for the winter, but this procedure does not always only benefit the plant. During the thaw period, the bush can heat up, and with the subsequent cold snap, this will result in cracking of the bark. The obligatory hilling procedure is only for self-rooted roses that were grown from cuttings. Only their root system is so vulnerable to frost.
Nurseries often sell plants that have been grafted onto rose hips. Such specimens are more frost-resistant and do not have to be hilled. But, with insufficient deepening of the root system into the ground and the grafting site, located above the ground, this procedure is also necessary. Peat, sand and other dry substrate are used as material. When the grafting site is deepened 4 cm or more under the soil, there is no benefit from hilling.


Shoots are elastic and easily bend to the ground
Instances with thick branches are difficult to bend to the ground. For this reason, it is not recommended to delay this until November. Starting from the last September days, it is necessary to gradually bend the shoots so that the stems can reach the ground by the frost. At the same time, the stems acquire the greatest elasticity on warm days, and with the onset of cold weather they become more coarse - the likelihood of accidentally damaging the shoots increases with late bending.
Lapnik is the best material
Lapnik is a good material for sheltering rose bushes, but it is difficult to get enough of it, especially with large rose gardens. The grower faces difficulties - in order not to receive a fine, it is necessary to contact the leshoz and find out about the planned felling, ask to pick up the remaining spruce branches and the like. As an equivalent alternative, it is possible to use non-woven material - spunbond, or roofing felt. But, it is better to refuse polyethylene, since this material disrupts moisture exchange and air circulation in the shelter.
The best materials for sheltering bushes
As insulation, it is possible to use purchased materials and improvised means. The most affordable purchased material is plastic wrap. Such insulation is recommended for those varieties that do not tolerate frost well. But, the film is wrapped loosely - they preserve the air gap. Spunbond is also used, sold in rolls or packs of 10 linear meters. There are several types:
- agrospan;
- agil;
- lutrasil;
- agrotex;
- agroSUF.
For reference!
Spunbond has many advantages - it does not interfere with air exchange, protects against gusts of wind, increases the internal temperature in the shelter, and guarantees aeration. In addition, the material has a long service life and decent strength indicators.
Some breeders do not buy covering material, but use improvised means for this purpose. The best options are rags, spruce branches, burlap, leaf litter, peat and sand. It is possible to cover the roses with wood sawdust for the winter. These are not ideal materials for shelter - the service life of such funds is only 1 winter. In addition, such materials at hand also create difficulties during transportation.
What temperature roses can withstand without shelter. What roses can winter without shelter
Roses that winter safely and do not require shelter at the same time are a real dream of a florist.And this dream is not so unrealizable. In parks, these very roses are often planted, which perfectly tolerate winter and bloom every year, while requiring minimal maintenance.
Rose varieties that can successfully winter without shelter in the middle lane are most often hybrids of Alba, Rugosa, Spinozissima roses. Also, winter-hardy varieties of American and Canadian selection can be added to this list.
Winter-hardy roses can be divided into 3 groups:
- Absolutely winter-hardy (withstand frost down to -40 ° C, hibernate in an upright position);
- winter-hardy (withstand frost down to -34 ° C, hibernate in an upright position);
- moderately winter-resistant (withstand frost down to -28 ° C, it is recommended to bend to the ground).
Creating an air dry winter shelter for roses


Covering a rose with a film for the winter.
The best results in regions with cold winters are provided by an air-dry shelter. It involves the creation of a frame of wood or metal rods over the rose plant in the fall.
With the onset of stable cold weather, lutrasil or spandbond is laid on the rods.
The frame is created in such a way that the edges of branches and shoots do not touch the surface of the film. The air gap formed between the film and the plant provides protection from frost, and the condensate that appears on the nonwoven fabric is freely drained out through the pores.
Thus, the plant receives protection from both frost and damping off. Wintering roses are closed only after the onset of the first frost. Autumn pruning of roses should already be completed by this time.