Cucumbers are one of the most common crops found in almost any garden area. However, she has a predisposition to many diseases, especially fungal infection. It is always better to prevent the problem than to eliminate the consequences of the disease, leading to the death of plants and a decrease in yield.
It is important for novice gardeners to know the basic rules of agricultural technology and the parameters of the life support of the crop, than to process cucumbers from diseases, so as not to be left without a crop as a result. There are many known methods of pest control, treatment and prevention of seedlings.
Diseases of cucumbers: treating gray rot

A disease that occurs due to a fungus. And it affects the leaves and stems of the plant. It is transmitted through the air and can affect almost the entire garden. The most favorable environment for the development of rot is very high humidity and low air temperatures. Signs of gray rot: - a very high percentage of wilting of plants in the garden; - shoots begin to rot; - gray spots on fruits, stems and leaves; This disease is dangerous in that it can destroy the entire crop completely, and later spread to nearby crops and trees. Rot hibernates in the ground; therefore, plant damage begins from the bottom. If you notice the appearance of this stroke in the garden, immediately start treatment. Gray rot can be defeated with a solution of copper sulfate, spray all the plants and spill the soil with this solution, then sprinkle the bed with ash. Prevention: - seed treatment; - thorough removal of plant debris; - compliance with the sowing rules.
The main causes of disease and how to avoid them
Temperature
The comfort zone of cucumbers lies in the temperature range from 22 to 28⁰С. A decrease or increase in the temperature of the content, as well as its sharp jumps, will serve as prerequisites for an increase in the incidence: latent fungi sleeping in the soil and on objects surrounding the plantings will begin to activate.
Humidity
The second, but no less important parameter for normal development is humidity. Moreover, both air and soil. Despite many years of selection and breeding of new varieties, the cucumber has retained the memory of its original homeland and comfortable subtropical conditions. Therefore, in the middle lane, its cultivation completely on open ground is still impossible.
For the normal development of cucumber plantings, it is better to stock up on a moisture meter. Maintain a soil moisture level of 80% plus or minus 2-3%. The method for determining humidity by touch, when a rubbed lump of earth does not stain fingers with dirt, but also does not crumble with dust, is available only to experienced gardeners.


Lack or excess of substances
Lack or excess of nutritional components. There should be neither less nor more mineral and organic substances. The exact amount must be found out in accordance with the variety of cucumbers - in this regard, the indicator of the level of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and trace elements can be very different, it is impossible to give general recommendations.
Top dressing is done once for 7-10 days. And the main rule: it is not the plantings that are fed, but the soil bacteria, which will already supply nutrients to the roots of the cucumber in a split and digestible form.
Pathogens
Active pathogens that parasitize crops or related plants, as well as weeds growing in the immediate vicinity. To prevent such sources of infection, you must follow the rules of crop rotation. Select 4 planting zones for cucumbers on the site and practice their cultivation in turn. So that cucumbers grow every 4 years on each site. Moreover: in these areas, zucchini and other crops related to cucumbers should not grow, due to the possibility of infection with their inherent diseases.
It is imperative to treat the soil with aerated compost tincture ("compost tea"), and pickle the seeds with natural fungicides before germinating on seedlings or directly sowing into the ground. And the soil for cucumbers should be densely covered with mulch from sterilized organic residues. An excellent mulching agent for this is the sleeping tea leaves collected by many during the winter: washed all at once in boiling water in spring and dried again, it is an ideal soil mulching agent. Not least because of the presence of residual tannins in it, a natural antiseptic.
Natural infection
If the neighbors of healthy plants are sick. A natural infection occurs, which can be eliminated by removing the diseased parts of the bushes. Additionally, after that, aerosol spraying of all plantings is done, and the soil is disinfected by pouring it with a solution of Fitosporin-M, and with bacterial infection with Pharmayod or Fitolavin.
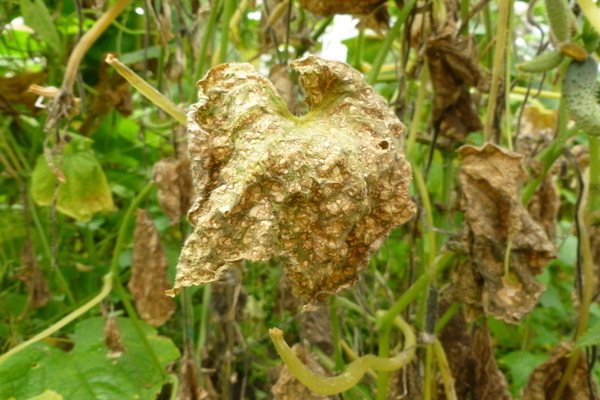
Diseases of cucumbers: prevention of white rot


White rot is the most common fungus; it is carried around the site by wind or insect pests. Growths begin to form on the infected plant. The upper part of the stem begins to suffer first. The leaves turn white and begin to wither, if you do not take action, the plant will die. Most often, the plant occurs due to sudden changes in temperature and high humidity, if the plants are not treated, you risk being left without a crop. In order for your cucumbers not to be struck by white rot, you need to follow the rules of prevention: - cleaning of vegetable debris; - feeding with complex fertilizers; - decrease in humidity in the garden. If white rot has already begun to spread in the garden, it should be treated. The fungus is very afraid of a mixture of activated carbon and potassium permanganate, I advise you to sprinkle the soil with crushed chalk. In order to secure the planting of the next season, sprinkle the bed with ash in the fall.
Pests of cucumber seedlings
Pests of cucumbers in the greenhouse attack and damage not only formed cucumber whips and fruits, but also newly planted seedlings. The bear, the larvae of click beetles feed on young, immature roots. The seedlings dry up and die.
Among the popular methods of dealing with a bear there is this: pour an aqueous mixture of black pepper or a vinegar solution into the passages.
The slugs eat the green mass of the shoots, causing it to dry out. As the main method of dealing with slugs, it is advised to leave cut potato tubers with small indentations in the beds overnight. In the morning, they are thrown out of the greenhouse along with the slugs.
For the operative treatment of diseases of cucumbers in a greenhouse, it is necessary to learn how to identify their pathogens, a photo will help with this.
Experienced gardeners recommend choosing environmentally friendly folk methods of getting rid of pests. If they do not work or the infestation areas are large, you should turn to industrial plant protection products.
For the prevention of diseases, it is important to organize the correct temperature regime and ventilation, maintain an optimal humidity level, and timely replace the soil and disinfect it.
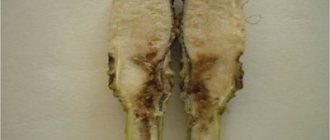
Fighting root rot
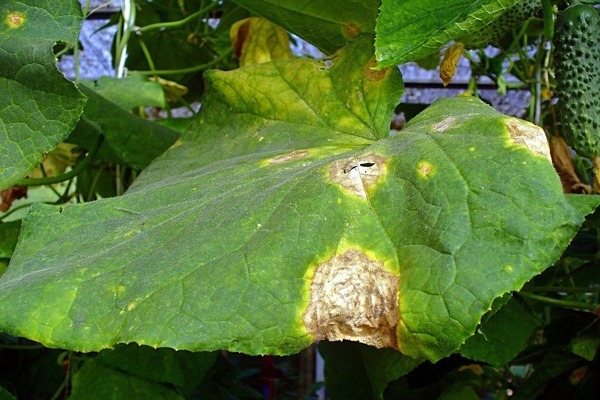


A fungus that attacks the roots of a plant. Affected roots rot and the plant dies.This disease is very difficult to determine, since the focus of infection is underground, you can only navigate by the state of the plant.
1) Even after watering, the plant looks sluggish.
2) Leaves dry massively.
3) Flowers fall, which means that the ovary is not formed.
4) The leaves are covered with a dark bloom.
5) The bush slows down growth.
It is not just fungus that can lead to root rot development. Root rot can be brought in with a garden tool, when watering seedlings with cold water and when planting very deeply. In order to defeat root rot, you need to use a solution of honey, ash and chalk, mix everything in equal proportions and fill it with a liter of water (I take 1 tablespoon of each component). We process the ridged areas. In order to exclude the appearance of this disease in your garden, you should follow the rules: - in very hot weather, weeding is prohibited; - we water the plants only with warm water; - we water the plants only at the root.
Traditional methods
Homemade fungicides


Folk remedies for processing are safe for humans
Manufactured fungicides can be hazardous to plants, insects, animals and humans. The use of pharmaceutical preparations and "home" remedies is becoming more and more popular.
Folk remedies
How to treat cucumbers for diseases:
- mullein infusion (1 kg per 3 liters of water, hold for 3 days, strain, add another 3 liters of water);
- sour milk (mixed with water 1: 1);
- baking soda with laundry soap (50 g are diluted in 10 liters of warm water).
Processing is carried out at least 2-3 times with an interval of 1 week.
Gardeners share their experience of preventive and therapeutic spraying with furacilin. An inexpensive drug that is used to gargle, treat wounds, will help to cope with powdery mildew. To do this, cucumbers must be treated with a solution prepared from 10 tablets and 2 liters of hot water (the tablets dissolve poorly in cold water). For prophylaxis, you can take 10 liters of water for such a number of tablets.
Metronidazole
In the fight against different types of bacterial and fungal diseases of cucumbers, spraying with Metronidazole (analogue of Trichopolum) will help. Preventive treatments are carried out with a preparation prepared from 1 g of trichopolum (4 tablets) and 10 liters of warm water (some gardeners add a bottle of brilliant green). For treatment, the concentration is tripled: 3 g (12 tablets). It is necessary to process so that the liquid penetrates into the affected areas. For root watering, a less concentrated solution is also suitable.
Many owners, instead of insecticides, use folk remedies for pest control. Cucumbers are processed with garlic. The tincture is prepared as follows:
- the cloves are crushed;
- pour water in a ratio of 1: 1;
- I insist in a dark place for 7-10 days.
To spray cucumbers, take 50 ml of tincture per bucket of water. For better adhesion, add laundry soap or detergent. Treating cucumber beds with garlic will also help against fungal diseases.
Connoisseurs recommend spraying with tar soap, which itself has deterrent properties.
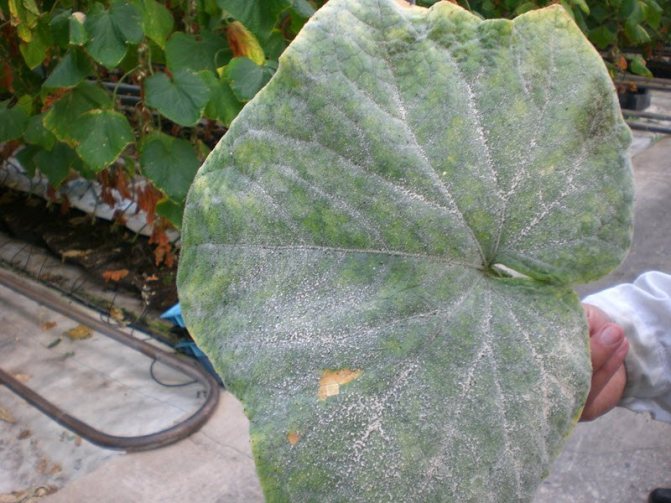
Powdery mildew
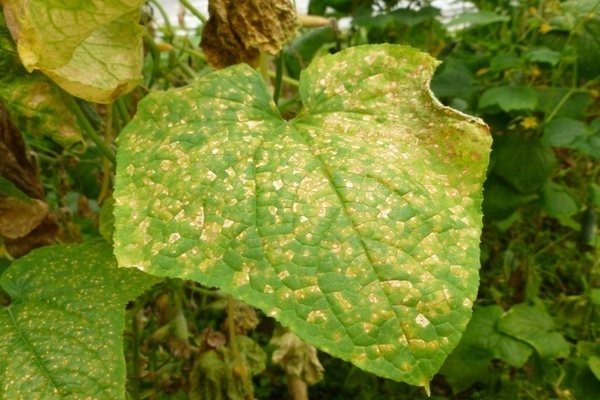


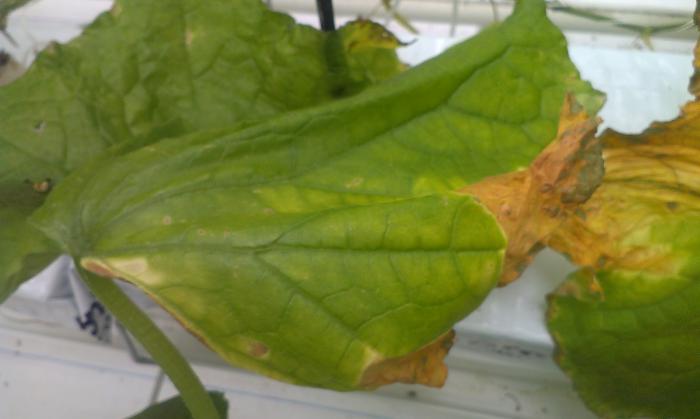
This disease is provoked by a spore parasite. They can be seen on the leaves of cucumbers as they cause a white bloom. The fungus infects the plant completely. The white bloom formed on the plant gradually begins to darken. The leaves turn black and die. High humidity and frequent temperature changes are very favorable for the development of this infection. Also, the appearance of a fungus can cause an excess of nitrogen fertilizers and not a residual amount of light. In order to cure your plantings, you will need 5 grams of soda and liquid soap, diluted with a liter of water. We carefully spray the bushes with this solution. Another effective measure is to spray the garden with whey.Prevention of the onset of the disease: - water the cucumbers only at the root; - we regularly fertilize the soil with phosphorus; - we remove all plant residues.
Content
- Listen to the article
- Cucumber leaf diseases (symptoms) Why cucumbers dry
- Why do cucumbers turn yellow
- Why do leaves dry
- Why do cucumbers rot
- Why do the leaves turn black
- Why do cucumbers fall
- Cucumber leaves wither
- Why do the leaves turn white
- Plaque on cucumber leaves
- Causes of diseases
- Powdery mildew on open field cucumbers
Downy mildew treatment
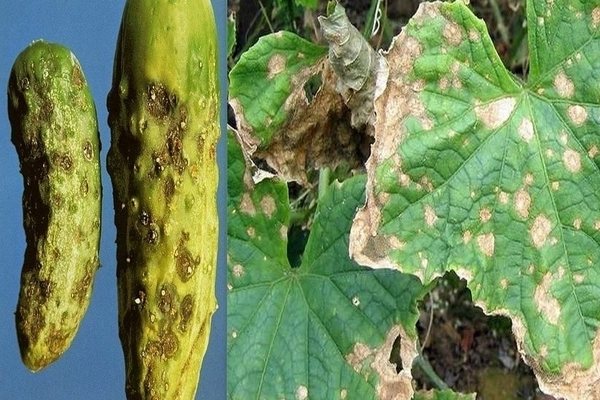


The most common disease of the cucumber garden, which is caused by a group of fungi. The fungus manifests itself on shoots and leaves, with a massive spread, the plant dies. Infected plants can be identified by the brown color of the leaves. There are different ways to treat this disease. Ten drops of iodine must be mixed with a liter of skim milk and diluted with 9 liters of water. We spray plants in dry, calm weather. The second method, we dilute 2 grams of manganese in 10 liters of water and process the cucumber bed. If the fungus has spread throughout the entire area, then chemicals should be applied, there is no other way to destroy the fungus. Prevention: - 2 weeks after planting in the soil, treat the cucumbers with a solution of Bordeaux liquid; - we carefully remove organic waste; - if plants grow in a greenhouse, provide regular ventilation.
Conditions for growing cucumbers in a greenhouse and open field
Parameters for growing greenhouse cucumbers, which must be observed:
- temperature regime,
- humidity of air and soil,
- feeding,
- loosening,
- mulching.
Temperature
The root system of cucumbers is vulnerable, it cannot stand even short-term frosts. Low temperatures can lead to poor growth, morbidity of the roots and root collar, up to the complete death of seedlings. The minimum value for the period of planting seeds is +16 grams, although cucumbers will quite survive a short-term decrease to +8 grams.
Important! When planting plants in open ground, the temperature of the top layer of the soil should be + 16 + 18g. Closer to June, the level should be lowered to +15 degrees.
Watering
The optimum air humidity for the greenhouse is 80%, it must be maintained to protect the soil from drying out. When growing cucumbers in a greenhouse, the soil should be constantly moist, so you need to water it more often with warm water (especially during the growing season), preferably in the morning. Ideally, it is worth watering for the rooting of seedlings - 3 times a week, for the formation of flowers - 1 time in 4 days, pouring 2.5 liters of water under each bush, for the formation of an ovary - 2-3 times a week (up to 9 liters of water 2-3 bushes).
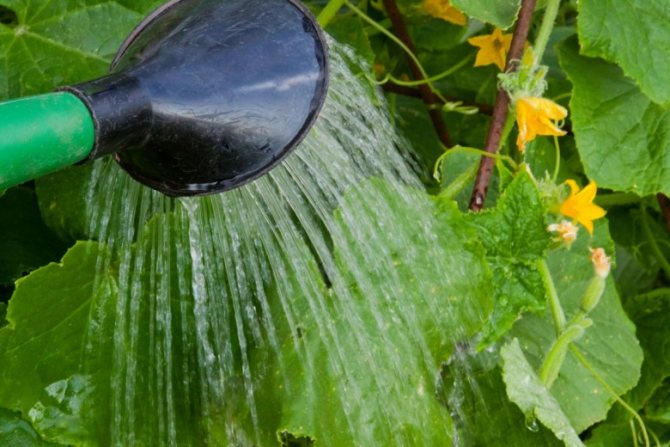


Water supply
Loosening the soil
To provide oxygen access to the plant roots, it is important to loosen the soil under the bushes before and after watering. This will help prevent root rot, assimilate nutrients, and normalize breathing.
Advice. You need to loosen the soil carefully, to a depth of 7-8 cm.
It is also worth mulching it in order to avoid evaporation of moisture from the soil and the formation of a crust on the soil surface, add humus (peat) to preserve heat when planting cucumbers in the winter.
Top dressing
Foliar feeding of cucumbers (potassium chloride, ammonium nitrate, mullein, manganese sulfate, double superphosphate, urea, boric acid) should be done regularly, 5-6 times per season.Inorganic, organic components are introduced during irrigation or the lower surface of the leaves is sprayed with solutions.
Hilling and pruning
Hilling is carried out after the garter of immature young seedlings to stimulate the growth of the root system.
Pruning is carried out as the 4th bottom sheet grows. The excess ones are removed together with the shoots from the axils, the lateral shoots above 7 internodes are thinned out in order to avoid a decrease in yield due to the large number of branches.
Reference! It is better to water cucumbers from a watering can, so as not to accidentally damage the delicate roots and stems with the pressure of water. You can freshen up wilted leaves by spraying warm water from a hose.
If excessive humidity is observed in the greenhouse, it is imperative to ventilate after each watering.
Cucumber Diseases: Anthracnose
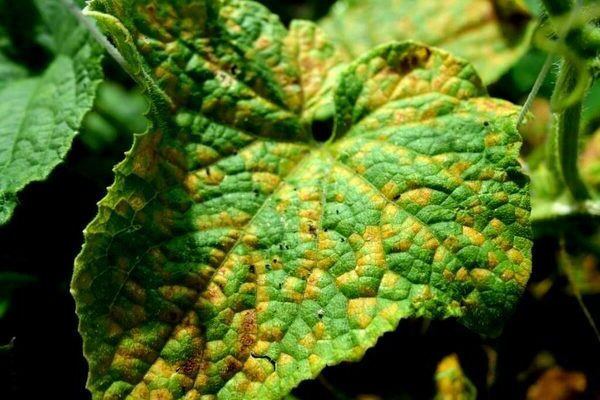


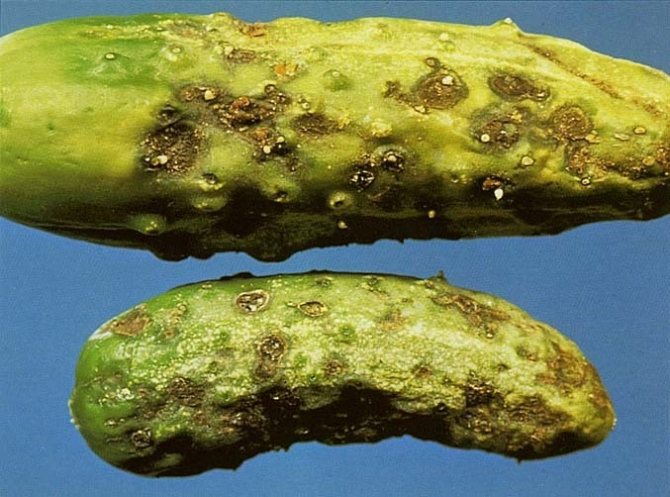
A fungus that can appear on many horticultural crops. You can understand that the plant is sick by the brown spots on the leaves. The spots become larger and gradually take over the entire plant. The bushes dry out and gradually die. The outbreak most often occurs in mid-May. The main causes of this fungus are: - high acidity of the soil; - insufficiently fertilized soil; - high humidity. You can fight this disease with Bordeaux liquid or 1% colloidal sulfur solution. Also, the bushes can be sprayed with soluble copper sulfate. Prevention for this disease is very simple, feed the soil regularly and water it strictly on schedule.
How to protect cucumbers from disease
The variety of different diseases in cucumbers requires the use of appropriate means to combat them.
Biological preparations
Biological products are created on the basis of strains of beneficial bacteria or fungi or their metabolic products. Depending on your needs, you can choose a drug with insecticidal, fungicidal, stimulating properties. The preparations are used both by spraying the plants and by root dressing.


Fungicides are used to combat fungal diseases
Fungicides
Fungicides are drugs used to fight fungal diseases. They can be mineral or organic. It is important to remember that in concentrated form, fungicides can be dangerous to people and the environment, and in the form of a working solution, they must be handled with care.
Treatment of bacteriosis
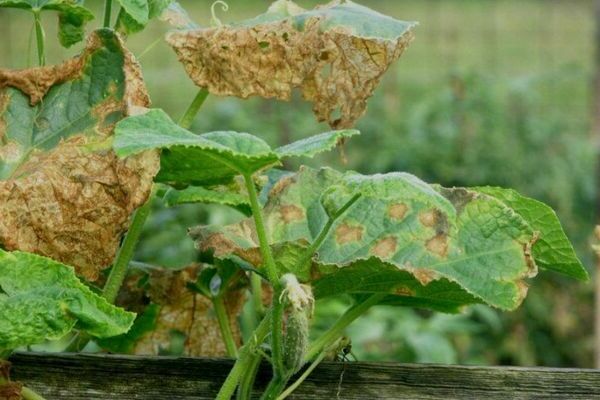


A disease caused by three types of fungi. This infection only appears and spreads in hot weather and high humidity. Bacteria enter the soil with poorly processed seeds or with the help of insect pests. The disease is very dangerous and can lead to the loss of a significant part of the crop. You can understand that plants are infected by small yellow spots on the leaves and watery spots on the stem. In this case, the fruits begin to deform.
In order for an outbreak of this infection to occur in your garden, you must carefully follow the rules of agricultural technology.
1) Remove all plant residues from the area.
2) Re-plant seeds and soil.
3) Dig deep into the soil.
4) Do not allow excess water to accumulate in the garden.
How to process seeds
When planting cucumbers, it is very important to properly prepare the planting material. For this, the seeds are placed in a special solution, but in which one, we will consider further.
In order for the seedlings to be healthy and strong, it is worth performing pre-sowing soaking. This method is considered the most effective because it stimulates the growth of seedlings. To answer the question of how to properly soak the seeds, you need to keep in mind that several options can be used to prepare the solution, including:
- 300 ml of methylene blue and 1 liter of water;
- 1 liter of water, 20 ml of boric acid;
- 1 liter of water and 2 g of zinc sulfate;
- 1 liter of water and 5 g of soda.
The material used for planting must be sent to the prepared solution and kept there for a day. Then remove the seeds and use for sowing. It will also be useful to learn about how cucumbers with corn are planted in open ground.
On the video - how to treat cucumber seeds for diseases:
In addition to soaking, you can pickle grains. This is done in order to protect the planting material from pests and diseases. For such a procedure, all varieties are suitable, such as gherkin cucumbers and others; for this, Fentiuram is used - 3 g of the product is used for 1 kg of grains.
Diseases of cucumbers: Rhizoctonia
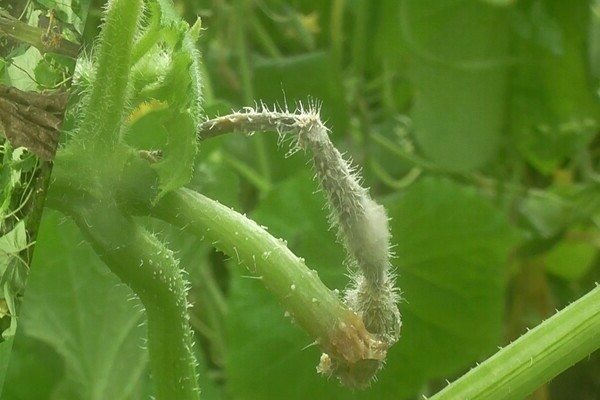


This fungus spreads not only on the cucumber garden, but also on potatoes and cabbage. Signs of the disease - dry leaves and fruits covered with ulcers, it is impossible to eat and store such fruits. This fungus is excreted only by preparations containing chemicals.
In order for the disease not to appear in your garden, you need to follow the rules.
1) Monitor soil moisture.
2) Mulching regularly.
3) Remove all plant debris from the site.
4) Very often loosen the soil and huddle cucumbers.
The main diseases of cucumbers
A sudden illness of a cucumber can deprive a summer resident of the entire harvest. Therefore, cultures not only fight diseases when they have already appeared, but also carry out mandatory prophylaxis to help prevent them. Cucumbers are susceptible to the following diseases:
- Gribkov;
- Bacterial and viral.
Fungal diseases of cucumbers: causes, treatment, prevention
Cucumber is a vegetable more susceptible to fungal diseases or infections than others. Most often, they can be caused by temperature differences or insufficient / excessive soil moisture. There are these types of fungal infections:
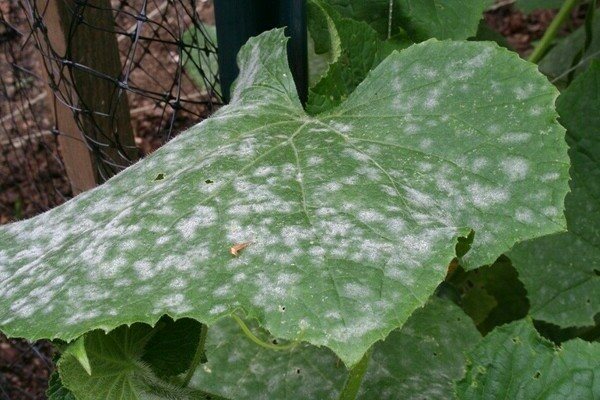
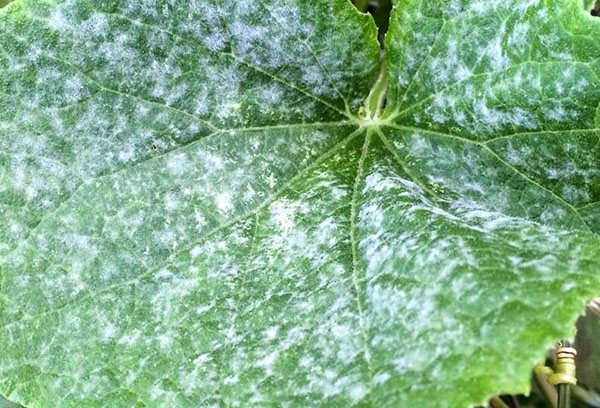
Powdery mildew
Its name speaks for itself - it is this kind of white, powdery bloom that it gets on cucumbers. Plaque is most often rounded, appears mainly on the leaves, but can occasionally be observed on the petioles and stems. In the future, the cucumber begins to shed the affected, yellowed leaves.
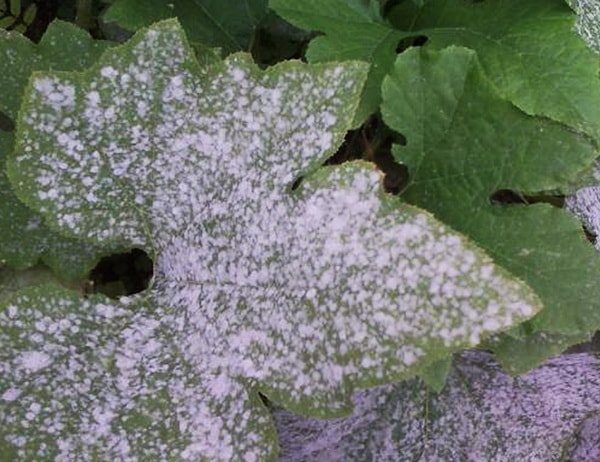


A vegetable can most likely "catch" such a disease within a few days after heavy cold precipitation, when the thermometer's thermometer tends to + 15 °, and the air humidity rises sharply. It is these conditions that are favorable for the development of the mycelium of the fungus.
But the further development of the disease is facilitated by the already dry and hot weather - the spores spread most actively in the bright sun. The process of spreading the disease is additionally "helped" by the lack of moisture in the soil and the temperature drop, when day gives way to night. The spores of the fungus lead a rather active process of absorption of biologically active substances of the culture, which leads to a violation of the photosynthesis of the cucumber. Accordingly, this leads not only to a slowdown in growth and inhibition of plant development, but can cause the complete death of the crop.
If the cucumber leaves have caught powdery mildew, you need to take active measures to save the plant, otherwise it will have a detrimental effect on the quality and quantity of the crop, and even the death of whole cucumber branches is possible, since such a disease develops very rapidly. In addition, powdery mildew can also be transferred to neighboring beds - to pumpkins, zucchini, melons, or, accordingly, from them to a cucumber.
It is quite difficult to get rid of powdery mildew, therefore it is necessary, firstly, to apply a number of measures aimed at protecting cucumbers from diseases:
- do not plant cucumbers in the same place every year, but periodically change its location;
- remove at the end of the season all the tops, especially the affected ones, since the bodies of the fungus can winter on these remnants in order to infect new crops in the new season;
- monitor the level of potassium and nitrogen in the soil: avoid a deficiency of the first and an overabundance of the second.
The risk of cucumber disease rises most in the second half of summer, when the pathogenic fungus is actively spread by wind and insects. The easiest way to handle infested cucumbers is with colloidal sulfur.
You should also be aware that there are varieties of cucumbers that are most resistant to powdery mildew infection. Such hybrids are derived taking into account the weather conditions of a particular region. They should be preferred, if possible.
Anthracnose or copperhead
This is perhaps one of the most dangerous diseases. Gherkins grown in greenhouses or under film material are especially susceptible to this disease. Both leaves and fruits are affected. The appearance of the lesion appears as yellow or brown round spots on the leaves of cucumber plants.
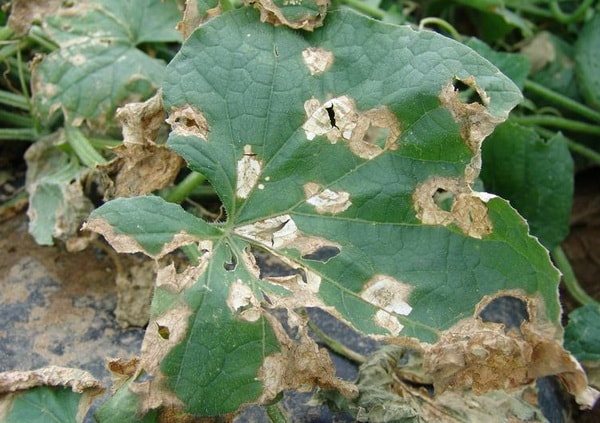


As for the fruit, you can find dents on them, of a fairly large size, which over time are covered with pinkish moss. All this leads to drying out or rotting of the fruit. The first signs of disease in greenhouse plants can be detected already at seedlings.
A cucumber can get sick with copperhead in the following cases:
- Seeds of cucumbers for seedlings already contain the causative agent of the disease. This is because the seeds were taken from an infected crop.
- Contact with cucumber tops, not harvested from the last season, on which spores can hibernate, activating with the new season.
- Increased rainfall in hot weather. This is due to the humidity of the air, because in a dry climate, anthracnose is almost impossible.
Cladosporium
In another way, this disease is called olive spot, because this is what it looks like in reality. On the fruits themselves, small water spots first appear, turning into olive-colored sores. These ulcers then begin to collapse. If the air humidity is high, then the spots also begin to be covered with a brown bloom. Also, the manifestations of this infection can be seen on the stems of the cucumber - exactly the same specks of olive color appear on them. As for the leaves, they simply begin to dry out, leaving only streaks.
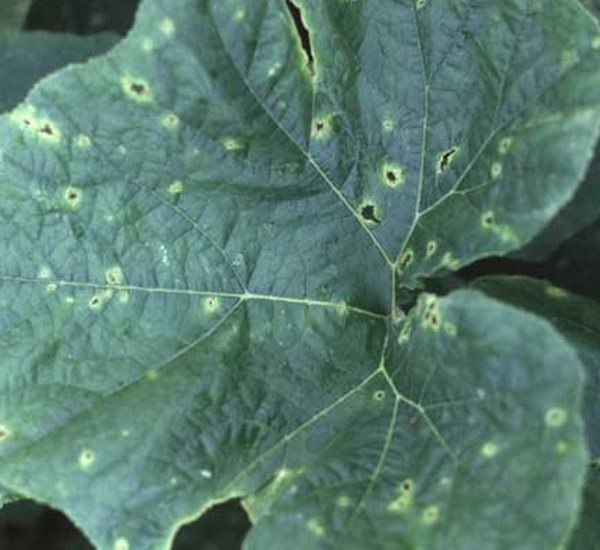


Naturally, the fruits that the disease caught at an early stage of development remain underdeveloped and twisted.
The percentage of development of cladosporiosis increases sharply with increased precipitation, high humidity, etc. It is water that carries pathogens throughout the culture - this can happen even during watering. But in a drier and hotter summer, outbreaks of this disease are not observed.
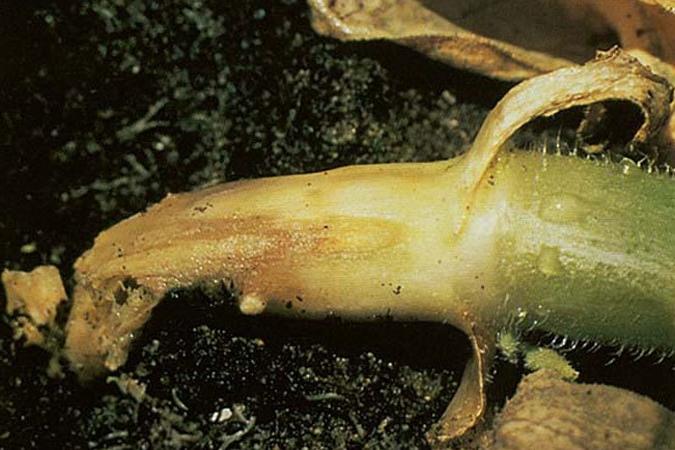
Fusarium wilting
The causative agents of infection are various types of soil fungi. A very harmful disease that affects plants at any age. Fungi from the soil penetrate the root system of cucumber plants and grow in conducting vessels. Depending on the age of the seedling, as a result, the cotyledons wither on the seedlings, the lower part of the stems decays. Often there is a massive death of seedlings, in which the roots completely rot away or dry out. It happens that plants die before they appear on the soil surface.
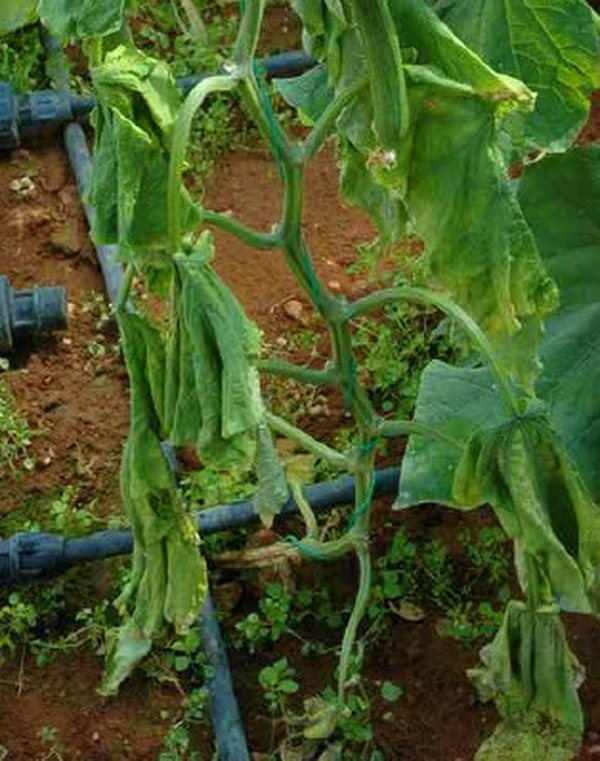


On fully developed plants, the lesions cause wilting of the tops of the whips. The edges of the leaves of the lower tiers are marked with spots, the leaf tissue between the veins dies off; the upper leaves lose their turgor (hang like rags), chlorosis of the leaves appears.
After a short time, the entire plant wilts. On the cut of the stem, the brown vessels are clearly visible, in the lower part the stem becomes brittle. The disease is strongly manifested in dry years. Fusarium affects cucumber plantings in cases of soil salinity or oversaturation with fertilizers. To prevent infection next year, change the planting site, and "treat" this bed with siderates: white mustard and oil radish are successfully coping with parasitic fungi of root rot.
White rot or sclerotinosis
This disease occurs quite often in cucumbers. Outwardly, this is expressed in the appearance of white moss or cotton wool at the base of the stem or in those places where the process originates from the stem. Due to the fact that the tissues of the culture are infected with an infection, they cannot, as expected, feed the fruits, since the stem of the culture flabs, withers, becomes loose, the necessary substances do not enter the cucumber fruit through it in full. But also directly on the fruits you can see signs of white rot - after which it also withers.
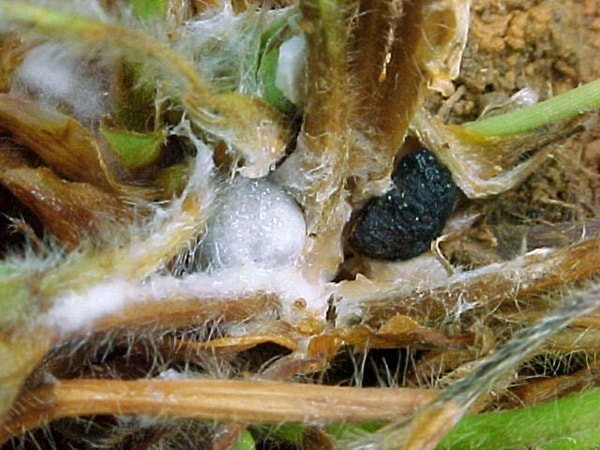


Most often, the disease occurs when the following conditions are met:
- aridity or poverty of the soil on which the cucumber grows.
- drafts in the greenhouse.
- watering the plant with cold water.
- cool summer.
It should be noted that the causative agents of sclerotinosis live either in the plant remains of the previous year, or in the soil itself. Therefore, appropriate preventive measures should be taken to increase soil fertility, since protecting cucumbers from diseases is much more effective than treating them.
Ascochitosis
Ascochitosis on cucumbers usually does not develop as rapidly as downy mildew, so summer residents have time to crunch greens. At later stages, the disease also affects the fruits - they darken, begin to rot. Often, beginners do not recognize the signs of ascochitosis, and assume that the deterioration in yield is caused by aphids. Of course, at the end of summer, sucking insects are harmful, but they attack already weakened plants.
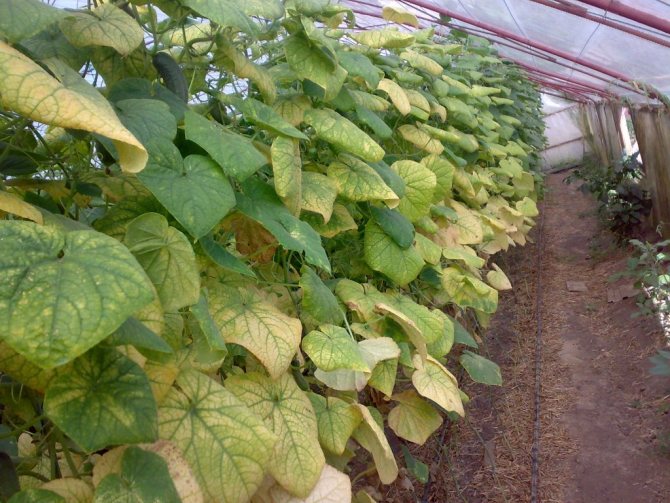


It is unlikely that it will be possible to cure the affected plants, and to contain the fungus, it is necessary to regularly tear off diseased leaves. Plant debris must be destroyed, and the planting site must be changed next year. In addition, it is better to choose varieties and hybrids that are resistant to fungus.
Gray rot
This disease is typical for cucumbers in a greenhouse - it is there that a microclimate is created that is suitable for the spread of gray mold spores. The period from the introduction of the fungus to the culture and the onset of signs of infection is about 5 days. Outwardly, gray rot is expressed in the appearance of dirty brown spots on the green tissue of the plant, a dense gray bloom on the fruit itself.
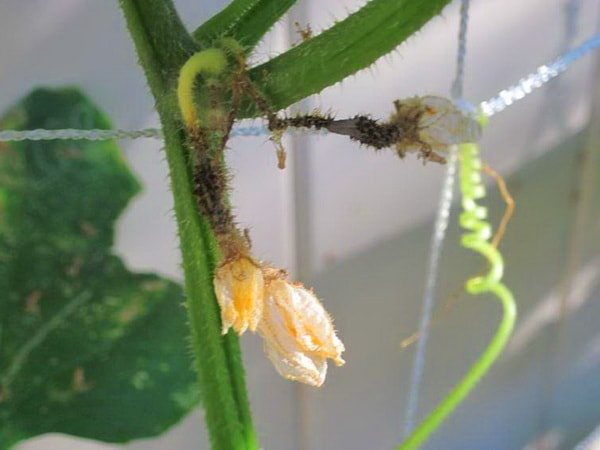


Intense spread of infection occurs in cool weather. Bees and other pollinators facilitate the transfer of fungal spores from diseased flowers to healthy ones during the entire growing season, causing massive damage to plants.
At the first signs of gray rot disease, it is necessary to stop watering for a while (to reduce the percentage of moisture in the air and on the soil) and air the greenhouse. It is also best to treat the beds with EM preparations and sow siderates. If it is not possible to replace the contaminated soil in the greenhouse, then the cucumbers are returned to their original place after 2-3 years.
Peronosporosis
This disease is also called downy mildew. Common among cucumbers and zucchini. Outwardly, the disease manifests itself in the appearance on the outside of the leaf of various sizes of greenish-yellow specks of oily origin, which then dry out, drying out the entire leaf as a whole, after which it falls off. On the reverse side of the leaf, peronosporosis is characterized by the appearance of a gray bloom.
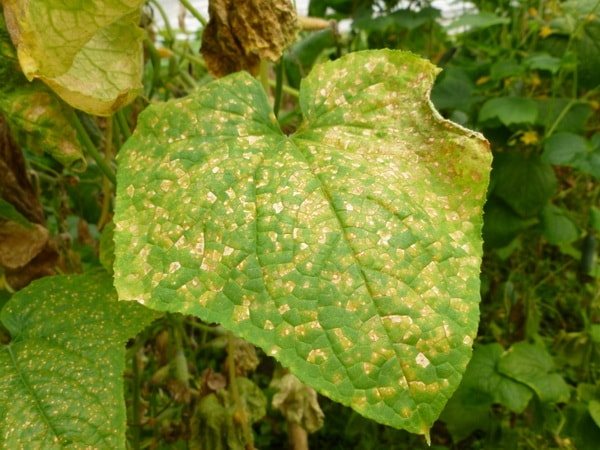


The causative agent of the infection is a fungus that has already infected the seeds of a cucumber, or that remained on the plant tops of the last year. The impetus for the development of downy mildew is given by increased humidity at a temperature of 20 degrees, as well as the constant presence of droplet moisture (dew) on the leaves.
Bacterial and viral diseases of cucumbers: causes, treatment, prevention
Viral and bacterial diseases of cucumbers occur through direct contact of a healthy crop with a sick one or are introduced by seeds. Such contact is observed during harvesting, when pruning plants, etc.Most likely, a cucumber can catch such a disease from weeds that breed in clouds around it - for example, sow thistle or bindweed. The most significant diseases of this origin are:
English cucumber (or green speckled) mosaic
It is especially dangerous for a cucumber in greenhouse conditions, and the likelihood of its occurrence increases several times in hot summer, when the thermometer tends to reach the 30 mark. The disease appears most often about a month after the cucumber seedlings are planted in the greenhouse. The virus is found in last year's plant debris, in the seeds themselves, in the soils on which the culture is planted.
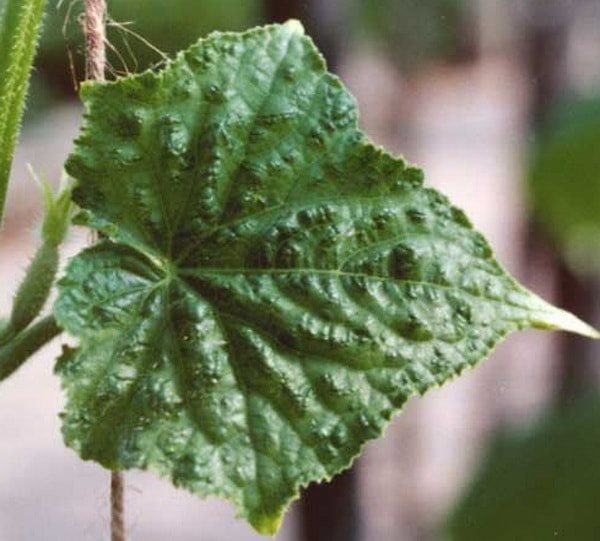


Signs of the disease of the cucumber with the English cucumber mosaic is the appearance of yellow stars on the leaf. Then they cover the entire leaf, after which it shrinks, dries out. As for the fruit itself, they acquire white stripes that tighten its tissues. Slow growth of culture is also a sign of green speckled mosaic. Treatment for viral diseases has not yet been produced, the affected plants must be carefully removed from the soil and burned.
Ordinary mosaic
This viral disease can affect not only greenhouse but also street cucumber. The external signs of the manifestation of the disease are in many ways similar to the English mosaic - the same slow growth that will be noticeable at an early stage, light green areas on the plant tissue, thinning of the stem at the very base, tissue death.
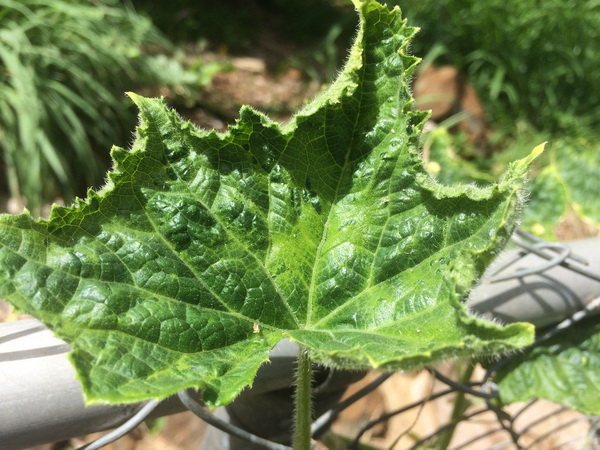


It is noteworthy that the mosaic virus is usually not found in cucumber seeds - it can only be transmitted from weeds (common sow thistle), from flowers (gladiolus, dahlia, phlox) or from sucking insects (for example, aphids).
It was once believed that in order to reduce the likelihood of disease, in no case should weeds spread near the crop closer than 10 m, it was recommended to maintain the same distance between the plantings of cucumbers and flower beds. But in natural farming, weeds and compacted plantings are treated differently - forbs improves the ecological environment on the site. Therefore, if you identify affected plants, simply carefully remove them from the ground and burn them.
Wet rot
This disease is rampant on cucumbers planted in open ground. The bacterium lives in seeds and on compost. The external signs of the disease are dark spots covering all leaves of the plant, collecting mainly near its center, and an oily bloom can be observed on the back of the leaves. It is spread by sap-sucking insects - after their bite, a watery circle of pale tissue appears.
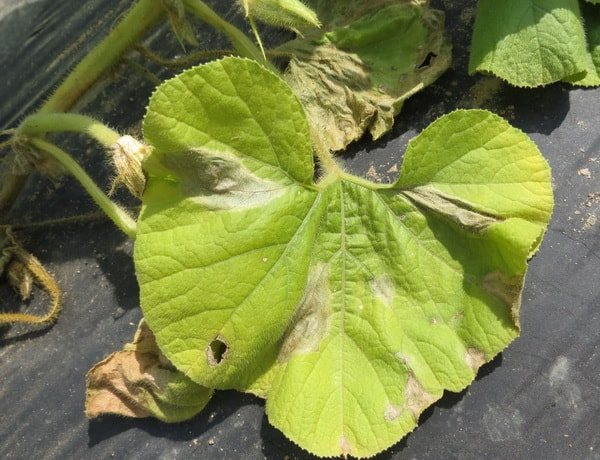


In this case, the cucumber bush dies almost immediately - when only a few leaves (from 2 to 8) are formed on the plant. You can try to save them by processing Fitolavin, but it is better to get rid of the affected plants so that all leafhoppers do not spread the bacteria further.
Displaying the mosaic


With a mosaic disease, the leaves turn brown and begin to roll up, both leaves and fruits suffer from this disease. This fungus overwinters very well in the soil. This disease usually affects damaged or weak seedlings. It is worth noting that this virus cannot be cured; therefore, infected plants must be immediately eliminated. But if you follow agricultural practices, then the outbreak of this virus can be avoided.
1) Thorough disinfection of garden tools.
2) Treatment of seeds by replanting.
3) Timely weeding.
4) Destruction of insect pests.
In autumn, the soil must be treated against fungi and viruses.
Processing cucumbers before sowing
Even a novice gardener can grow cucumbers. However, this culture is quite demanding on the observance of agricultural techniques and, despite its resistance to most diseases, it is prone to rapid defeat by them.
The first problems can arise even at the stage of growing seedlings.Therefore, experienced gardeners pre-prepare seed and land. In addition to hardening and soaking, the seeds are treated with one of the disinfectants.
- Potassium permanganate. The seeds are kept in a bright purple saturated solution for 20-30 minutes, then washed and prepared for planting.
- Bacterial preparations - Baxis, Fitosporin and others. The seed of a cucumber is soaked in a solution for 1.5 hours, then dried.
All these products destroy harmful fungi and bacteria from the surface of the seeds. Such a measure will help prevent many diseases.
The soil is pre-frozen, calcined in the oven, or watered with disinfecting solutions:
- insecticides - "Aktara", "Thunder", "Iskra" (one month before sowing);
- fungicides - "Fitosporin", "Barrier", "Extrasol", etc .;
- a pale solution of manganese (2 weeks before planting).
Further adherence to agricultural technology will contribute to obtaining healthy seedlings. Strong plants are much more resistant to disease and parasites.
But diseases can affect a plant at any stage - in a glass on a windowsill, in a greenhouse or in an open field.


Prevention of olive spot
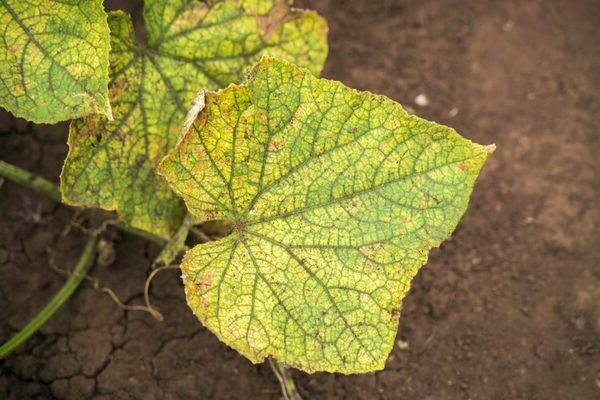


It is possible to understand that the plant is infected by the brown spots on the leaves, which eventually become covered with a white bloom. This virus infects the entire plant completely; the harvest from the infected bushes cannot be expected. Infection of the plant usually occurs through the soil or through poorly treated seeds. To treat this fungus, you can use a weak iodine solution or milk whey. If you apply fertilizers and weed the beds on time, the disease can be prevented. Now by knowing the precautions you can prevent diseases and infections of cucumber and treat them correctly.
Garden bed preparation
The most common problems in the cultivation of cucumbers arise precisely due to the fact that plastic fences for the beds were not installed and the soil was poorly processed. There are several options for this, each of which is effective in its own way:
- Calcination... Send the soil to the oven for 15-20 minutes. Keep it there at a temperature of 90-100 degrees. For uniform calcination of the earth, it is worth spreading it on a baking sheet with a layer of 5 cm thick. You cannot exceed the temperature, otherwise the soil will deteriorate and will not be suitable for growing vegetables.


Calcining the soil - Steaming... This method of soil preparation must be used a month before the upcoming planting. Place the earth in a container, cover tightly with a lid, and then place in a water bath. The duration of the procedure is 2 hours.


Calcining the soil - Freezing... This method is used for soil that was harvested in the fall. Place the earth on the balcony so that it is there all winter. Pick it up 30 days before planting and keep it at room temperature.
- Processing with potassium permanganate. This method is one of the most effective and simplest. Moisten the earth with a fresh hot solution of potassium permanganate. To obtain a solution, you need to take 5 g of potassium permanganate and 1 liter of water.
But how the garter of cucumbers and tomatoes in the greenhouse takes place is described here with a photo.