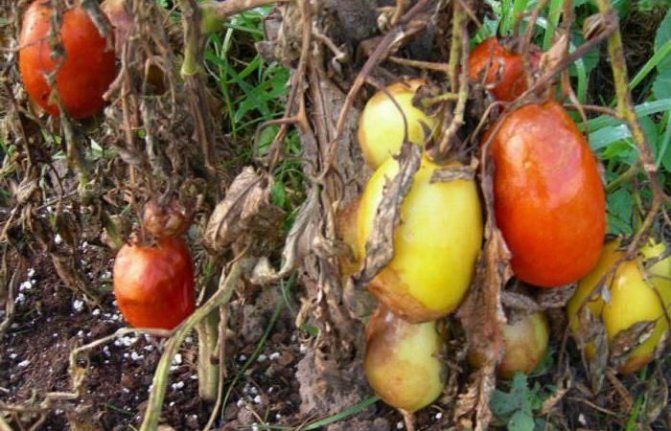
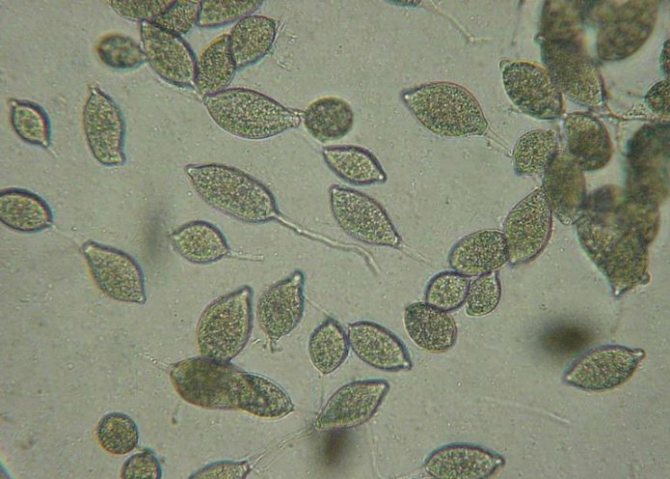
The causative agent of late blight, oomycete Phytophthora infestans Mont. de Bary, very tenacious. In the contaminated soil, oospores of the phytopathogen can wait for favorable conditions for 5–7 years to germinate. Therefore, the simplest way to prevent late blight is to follow the rules of crop rotation. Agronomists advise planting all plants from the nightshade family in the same place no more than once every 3-4 years.
In small areas, this condition is difficult to fulfill. In addition, phytophthora spores are still carried by wind, melt or rainwater. The pathogen multiplies on tops and tubers left over from harvest. It is easier to use means against potato late blight in the fall than to fight a serious epidemic in the next season.
Features of the disease and its signs
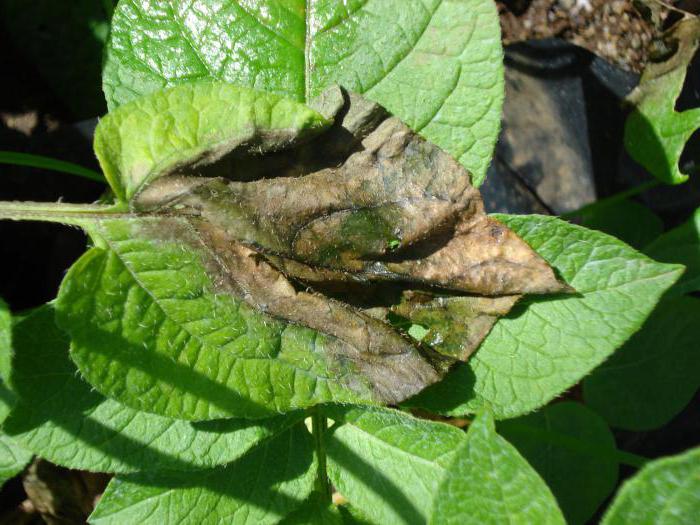
Late blight refers to fungal diseases, pathogens - oomycetes, currently isolated in a special group of parasites. The parasites hibernate without loss on plant residues that were not harvested before the onset of winter - in open beds and in greenhouses, on garden tools. Oomycetes spread at a depressing rate with water, through the air, and upon contact of affected fruits with healthy ones.
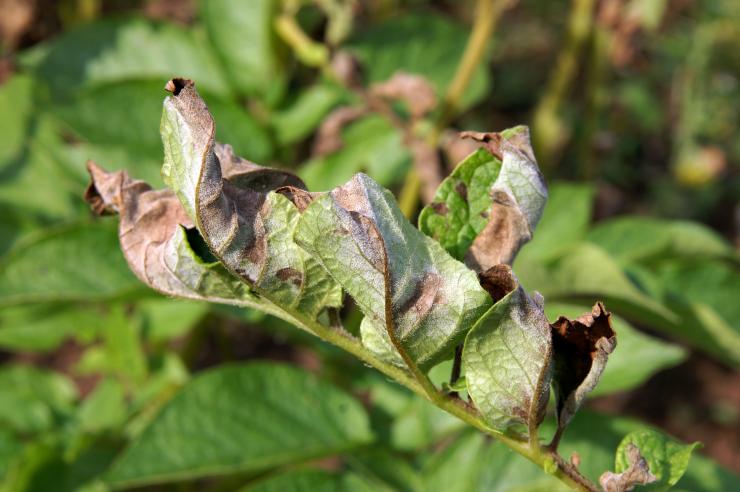
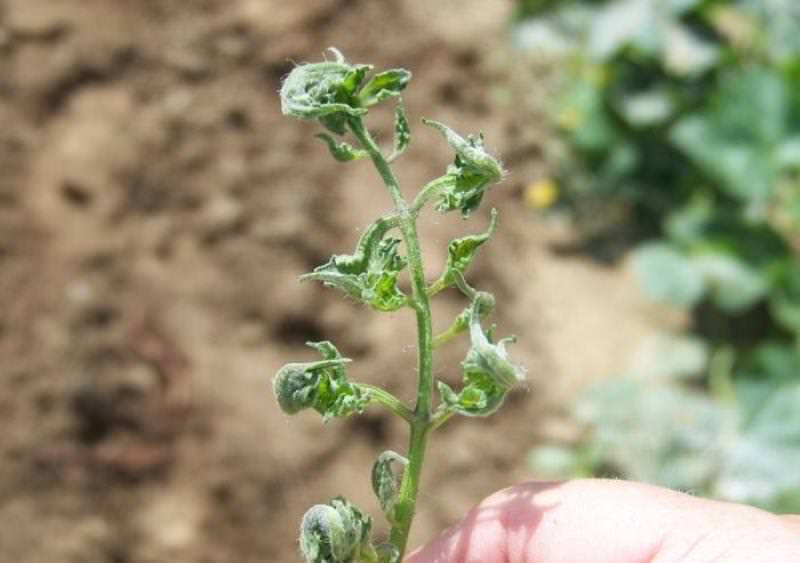
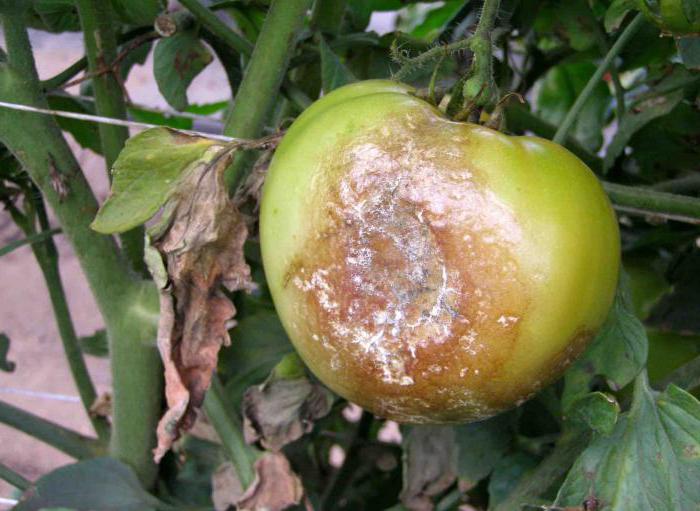
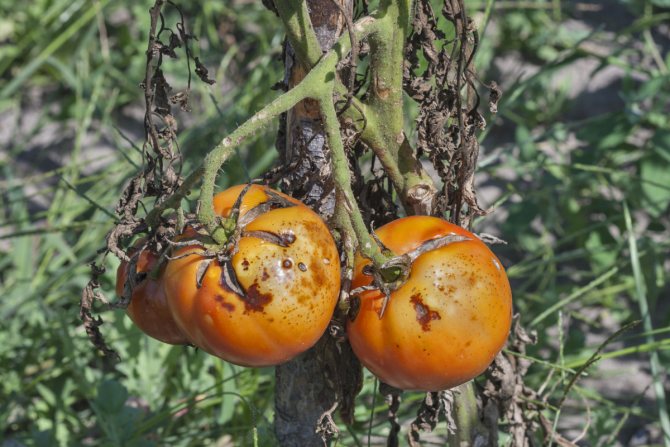
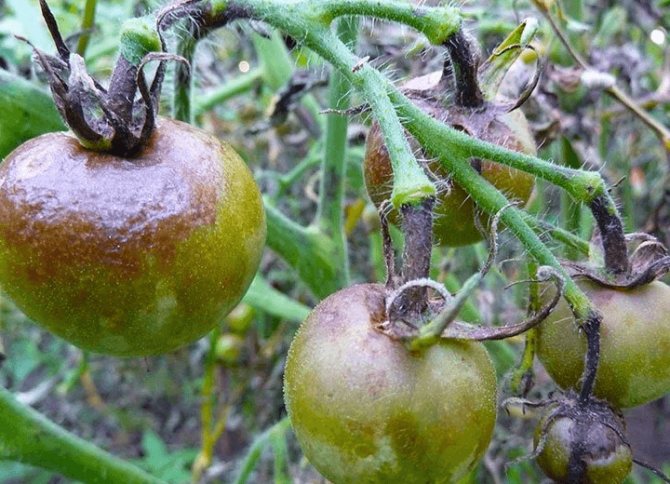
Late blight manifests itself in brown or brown spots on leaf plates, stems, petioles. The underside of the leaves becomes covered with a whitish bloom, similar to a thin web, causing them to deform and dry out. If the phytophthora rampant fell on the period of budding, flowering or fruit setting, there is no chance of harvesting - the disease in a short time destroys delicate flowers, a fragile ovary.
Parasites feel most at ease if the increased humidity of the air is combined with sudden changes in temperature. Prolonged rains, frequent fogs create favorable conditions for the development of late blight.
One of the ways to prevent damage to the crop by late blight is the use of varieties resistant to the disease on the site.
The risk of an outbreak at the site increases in the following cases:
- increased content of alkalis in the soil (over-lime content);
- deficiency of potassium, iodine, manganese.
Spring prevention of late blight
Spores of the pathogen begin their activity already at the first signs of heat - a temperature of + 1 ° C is enough for them to start destructive activity. Therefore, the first processing of the soil on the site begins immediately after the snow melts.
- Spilling the soil with hot water. The beds are subject to processing, where nightshades (tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, potatoes), strawberry fields will be planted. Experienced summer residents recommend adding potassium permanganate to the water (1 g per bucket).
- Steaming the soil. Usually the last days of April - early May, when the air warms up enough, are suitable for this procedure. The beds are covered with several layers of dense polyethylene and well fixed at the edges. Under the hot spring sun, the temperature under such a shelter reaches 70-80 ° C. This is enough to drastically reduce the number of phytophthora spores.
Folk remedies
Grandma's secrets are more effective for prevention than for treating a disease. Spores of fungi do not tolerate an acidic environment, therefore, for prevention, the soil is treated with suitable organic matter before planting seedlings:
- fermented kefir (1 liter per 10 liters of water) - 0.5 liters of solution is poured into each well;
- milk whey diluted with water 1: 1, with the addition of 2-3 drops of iodine on a bucket of mixture, abundantly water the soil;
- infusion of rotted hay (or straw) with urea (1 teaspoon per bucket of infusion) spray the soil prepared for planting);
- decoction of needles (half of the container is filled with needles, water is added, brought to a boil and simmered for 15-20 minutes) abundantly moisten the soil;
- the ash infusion prepared according to the standard recipe is poured over the beds.
Biological preparations
Their effectiveness is higher than that of folk remedies, but they work at a higher - from + 15 ° C - temperature.
- "Baktofit", a bacterial fungicide, significantly reduces the number of pathogens in the soil during the first days after treatment. For spring processing, use a typical working solution prepared according to the instructions.
- "Trichodermin" ("Glyocladin") is a complex biological product that fights against parasitic fungi and at the same time increases soil fertility. Spill the soil with a solution prepared according to the manufacturer's recommendations, then loosen it. The effectiveness of the drug increases if part of the water in the solution is replaced with kefir or milk whey.
- Planriz is a highly effective preparation containing live bacteria. Soil processing is carried out immediately before planting seedlings with a solution prepared at the rate of 50 ml of the product per 10 liters of water.
- "Alirin B" is a fungicide, the action of which is complemented by an increase in plant immunity. For the prevention of late blight, soil is shed before planting (sowing) the main crops. The suspension solution is prepared from 2 tablets per 10 l of water.
- Fitosporin is a widely used drug. For spring treatment of 1 m2 of soil, the solution is prepared from 6 ml of the product and a bucket of water.
- "Baikal EM-1", "Baikal EM-5" - the means loved by summer residents, capable of anything. In the spring, the soil is watered with 100 ml of the product dissolved in 10 liters of water. Consumption rate - 2.5 l / m2. Processing time - 2 weeks before planting crops.
Use of chemicals
Chemicals are "heavy artillery", they are used in difficult situations.
- Bordeaux liquid is the most common remedy. The soil is cultivated immediately after the snow cover disappears. The working solution is prepared from 250 ml of concentrate and 10 l of water. For soil disinfection, Bordeaux liquid is used no more than once every 5 years.
- Copper sulfate is an equally popular remedy against diseases. For spring (after snow melting) treatment, the working solution is prepared from 2-5 g of the substance dissolved in 10 liters of water.
- Copper oxychloride - the soil is treated with a 4% solution in the first warm days.
- "Oxyhom" - for the soil, a solution is prepared with 2% con is used for planting potatoes. The wells are sprayed with a 0.3% solution, the consumption rate is 10 liters per 100 m2.
- "Farmayod" is intended for soil cultivation before planting seedlings or sowing seeds. Dissolve 100 ml of the preparation in 10 l of water; this amount is used to treat an area of about 5 m2. If in the past season late blight acted especially actively, the concentration can be increased by 3 times. Plants can be planted after 2 days. "Pharmayod" does not have a selective effect - it destroys all microorganisms, therefore, after 7-10 days, the soil is spilled with EM-preparations ("Baikal", "Vostok") according to a typical recipe.
Sometimes summer residents treat the soil with bleach. It is an effective but highly toxic agent. It can be used only before winter, so that there is enough time to neutralize the effects of chlorine on the soil.
When using chemicals, it should be borne in mind that pathogens develop addiction to them, so they must be alternated.
Known methods
Since it is almost impossible to completely get rid of tomato phytophthora, you will have to think about preventive measures.First of all, remove plant residues, and secondly, disinfect, heal the soil on the site.
There are three main methods of soil treatment that gardeners use:
- agrotechnical;
- biological;
- chemical.
Consider how they work and what tools are required.

Compliance with agricultural techniques
Since phytophthora spores can live for several years in the ground, when planting tomatoes you need:
- Observe the crop rotation.
- Do not plant tomatoes next to potatoes.
- You need to plant tomatoes at a distance so that the air can circulate freely. Watering tomatoes should be abundant, but it is impossible to bring the soil to a marshy state - for phytophthora spores, these are ideal conditions. Preventive agrotechnical measures should be taken in the fall after the tomato harvest.
- In the fall, you need to dig up the ridges where the tomatoes were grown in a moldboard way. A clod of earth with spores will be at the top. You need to dig up, deepening the shovel to the entire bayonet. If not completely, but partially, the spores can die.
- In the spring, before planting tomatoes, the soil can be scalded with boiling water by adding potassium permanganate to the water. If the land is cultivated in a greenhouse, then all the vents and doors are closed. The garden bed in the open field is covered with a film on top.
Siderata against late blight
Proponents of organic farming, using green manure to heal the soil and increase its fertility, recommend using their special properties. Plants-disinfectants that help to cope with fungal spores in the soil include oil radish, white mustard, calendula and phacelia. Oil radish is sown in autumn, the rest - in spring.
The sowing time is determined by counting: 30 days - for seed germination and the growth of root and green mass, 10-15 days - for decay of mowed greenery and roots. With an imminent warm spring, the formation of buds in siderates often begins earlier than the expected date, this is closely monitored. At the budding stage, the disinfecting properties of herbs are reduced, therefore, the grass is cut off earlier.
Calendula is a well-known medicinal plant. For its use for medicinal purposes, including for soil, hybrid varieties are not used, since they are of little use.
The fight against late blight should not stop for a minute. From the first warm days of spring to harvest, summer residents need to keep a close eye on the plantings of nightshades and strawberries. It is not enough to cultivate the soil in the spring, because a means has not yet been invented that can kill oomycetes once and for all. Whatever drugs are used, they can only reduce the number of pathogens. Therefore, it is necessary to protect the garden from the disease in a comprehensive manner, using all available means and possibilities - from preventive soil cultivation in spring to pre-winter harvesting of plant residues and their disposal, as well as strictly observing the rules of crop rotation and agrotechnical subtleties of growing crops.
Is it possible to spray plants with phytosporin during fruit ripening
Phytosporin can be sprayed on any plants during fruiting and flowering, including tomatoes, cucumbers, grapes, strawberries and strawberries, raspberries. Berries can be eaten on the same day.
Scientists have proven that Bacillus subtilis strains are not harmful to humans and animals. For those in doubt, reference can be made to the fact that the US Food and Drug Administration has awarded them GRAS (generally regarded as safe) status. Moreover, some strains of Bacillus subtilis Bacillus subtilis (other than in the composition of phytosporin) are the active ingredients of some drugs, for example, Biosporin. It is intended for the treatment of intestinal infections, including in children.Although the strains of bacteria in medicines for humans and plants are different, phytosporin can be considered absolutely safe.
How and what to cultivate the soil in the fall
When late blight develops on plants, soil contamination with spores passes from top to bottom along those natural "funnels" that are formed as a result of swaying plant stems, pulling out weeds, and cracking the earth. Therefore, the soil is cultivated after clearing all vegetation without prior loosening.
In areas where the cultivated layer of land freezes in winter, late blight dies from low temperatures. Soil contamination occurs through newly planted infected plants or seeds. In areas with warm winters, spores of the fungus survive, and autumn cultivation of the land is required.
Before autumn plantings (garlic, bulbous), the holes and grooves are treated with fungicides, even if the treatment is carried out after harvest. True, this reduces the nutrient properties of the soil.
When choosing fungicides, give preference to those that not only fight against late blight, but also feed and strengthen the immunity of plants. All packages have instructions for use and indicate the composition and action. Here are some examples.
Chemical fungicides
This group of drugs generally does not require compliance with the temperature regime of the soil, it acts for several days, does not lose its properties due to rains. But as a rule, it has a high hazard class for people, animals and insects. Since the autumn processing takes place at a time when the pollinating insects no longer fly, care should be taken to ensure that there are no animals on the site and protect the skin and respiratory tract of a person.
- Copper sulfate - a blue crystalline powder - is the most favorite fungicide by gardeners and gardeners. It destroys the spores of the late blight fungus, enhances the immunity and frost resistance of plants, is low-toxic, easy to prepare and apply, and is affordable. 50 g of powder is diluted in 200 ml of warm water until dissolved and diluted in 5 liters of pure water, treated with 1 square meter of area with strong infection and 2 square meters with weak.
- Colloidal sulfur - a yellowish-gray powder - in high concentration is toxic to humans and insects. 30 g is diluted in 10 liters of water, sprayed over an area of 100 square meters, periodically shaking the container with liquid. Spraying is carried out at a soil temperature of at least 20 ° C or the solution itself should have a temperature of 30-35 ° C
- Oxyhom is a white powder that is toxic to humans and insects. 10 g is diluted in 10 liters of water, sprayed over an area of 100 sq. m. Important: chemicals increase the acidity of the soil. Before planting crops that do not tolerate high acidity, the soils are alkalized with chalk, bone meal or ash in the recommended dosages, on average - 1 glass per 1 sq. M.
Biological fungicides
This class of drugs is based on strains of bacteria that need special conditions for action (temperature, humidity, digging). All conditions are indicated on the packages.
- Agate-25K - a fluid paste - created on the basis of bacteria with the addition of macro- and microelements, natural flavonoids and pine extract, low toxicity, promotes plant growth and raising their immunity. 140 mg of the paste is diluted in 3 liters of water and sprayed on 80-100 square meters of area.
- Alirin-B - dry powder or tablets based on beneficial soil microflora, reduces soil acidity. 2 tablets are diluted in 10 liters of water to treat 10 sq.m.
Alternative methods
For processing small areas (beds, flower beds, holes), soil cultivation with high temperatures is used in the plots.
- Pour boiling water over the ground after digging until it gets wet to a depth of 15 cm. When copper sulfate is added to a faint blue or potassium permanganate to a faint pink color, the effectiveness of the fight against late blight increases several times.


When treating the beds with boiling water, the addition of a manganese solution will enhance the antibacterial effect
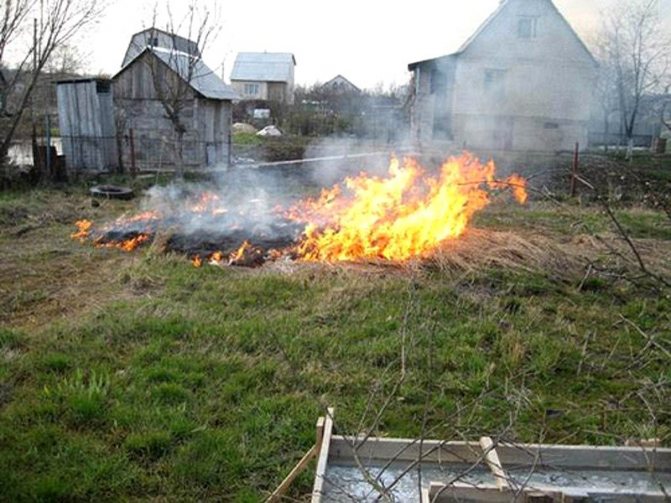
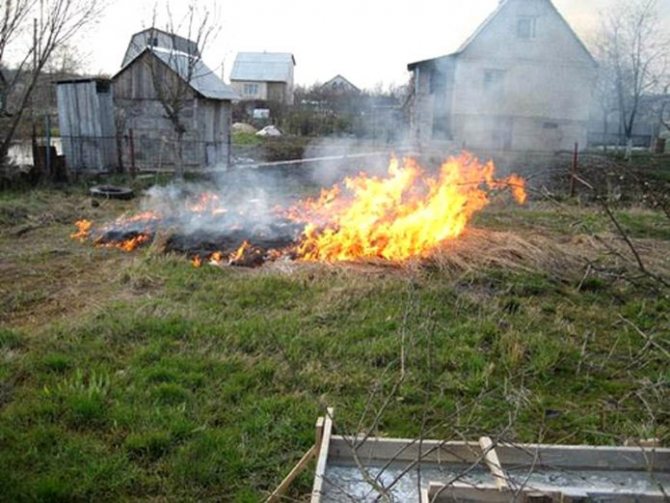
- Dry branches are laid out on the treated area in an even layer, watered with used machine oil or vegetable oil and burned. Ashes with low acidity are removed from the beds, with high acidity they are dug up before planting.


Observe safety precautions when treating the beds with fire.
The first method acidifies the soil, the second partially neutralizes acidity.
Whatever drugs are used to combat late blight, know that they are also harmful to the beneficial microflora of the soil. Therefore, after treatment with fungicides, restore the living beneficial flora with special EM preparations (EM are effective microorganisms), for example: Baikal EM1, BakSib, Stimulin, Shining-2,3, etc.
How to "banish" phytophthora from the site forever - a successful experience of our reader
Adding an article to a new collection
At the mention of phytophthora, many gardeners and truck farmers sadly look towards their plantings, followed by a heavy sigh. Do not despair! Let's give a worthy rebuff to an insidious disease that is already "looking closely" to your potatoes and tomatoes.
Our reader from Nizhny Novgorod shared her personal experience of successful fight against late blight.
A bit of background. In the first year of gardening in a new place, I simply did not know about the high background of soil contamination with late blight. Therefore, of course, I was not ready and used only Fitosporin, which was familiar to me at that time. The result, which is natural, was deplorable - the bushes of my tomatoes "burned out" at the end of July. As it turned out, this picture was familiar to our village. Having sobbed over my tomatoes, I decided not to put up with it, as my neighbors did.
The winter was fruitful - tons of sources were studied. By the spring, a plan for prevention and control was ready. I met the second season fully armed, and it was quite successful. My tomatoes got sick anyway, of course, but I was able to "stretch" them in the greenhouse until October and they looked pretty decent. The harvest was also pleasing, and not a single tomato went to the landfill. In the next couple of years, my plan underwent a slight correction, and now I am no longer afraid that one day, having come to the greenhouse, I will see black bushes of tomatoes.
I want to share my plan for dealing with late blight, I think that this can be useful to many of us. The article is devoted to the methods of soil and greenhouse processing, as well as the methods and frequency of processing tomatoes.
Take measures against late blight
The late blight problem does not go away on its own. An epidemic begins without our intervention. Fungal spores are tenacious, do not die in the cold and will last 7 years. With the onset of spring, they begin to develop and lead to the repeated death of the crop.
The earth is infected with late blight, what should I do? You can defeat the disease on the site by creating unbearable conditions for the development of the disease. The main actions are to disinfect the ground. You can cure the infected area in different ways:
- plant siderates;
- fumigate greenhouses with sulfur bombs;
- spill the soil with bactericidal solutions.
Inaction is unacceptable. Particular attention should be paid to infected tops and tubers, as this is a source of infection. They need to be carried out of the territory, or doused with kerosene to burn.


Rotten tubers and harvested tops must be immediately removed from the site or burned, otherwise the pathogen will develop further when the heat comes
Do not bury diseased stems - this is a breeding ground for pathogens. Once opened, the infection will spread through the air and the problem will remain.
Folk ways
Phytophthora is not a new disease, our ancestors knew about it. In those days, there was no chemistry. Our grandparents invented their own methods of combating late blight of tomatoes, which gardeners still use today. If the disease is not very spiteful on the site, then they will be effective.You can use folk methods as a preventive measure - there will be no harm, since the products are fertilizers.
- One liter of fermented kefir is poured into a bucket of water. They are sprayed with tomatoes and the soil under them.
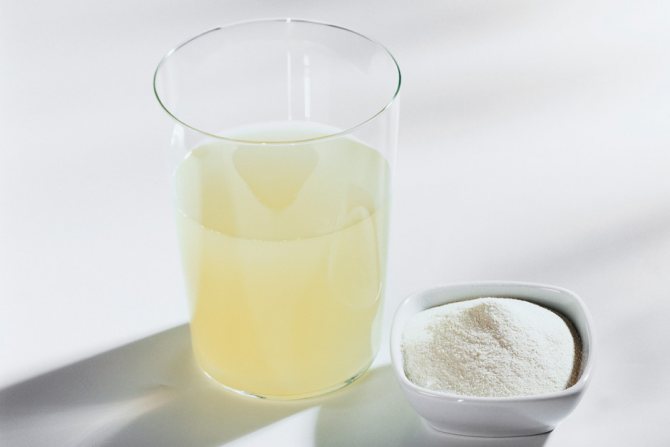
- In the fight against late blight of tomatoes, whey helps. Take an equal amount of serum and water to spray the soil and plants. You can add a few drops of an antiseptic such as iodine.


- Pour over spilled straw or hay with a bucket of water, adding a little urea. The infusion is kept for up to 5 days. Water the soil under the tomatoes every 10 days.
- Our grandmothers used wood ash for dry or wet treatment against late blight. To prepare a solution, 500 grams of ash, 40 grams of laundry soap (grate) are placed in a three-liter jar and poured with water. After the soap has dissolved, spray the tomatoes and the garden bed. Row spacing between tomato plantings can be sprinkled with a layer of ash on pre-moistened soil.
- It is good to use a solution of skim milk (skim milk) for treating soil and tomatoes. One liter of skim milk is poured into a ten-liter watering can, iodine is added (15 drops). Bring to 10 liters and water the soil under two tomatoes.
- Sow green manure in the beds.
Why are folk methods interesting? It is not necessary to wait some time between treatments. Such funds can be combined, alternate processing of tomatoes and soil from late blight.
Biological methods
If late blight was not too rampant on the site, biological preparations can be dispensed with. They are safe for cultivated land, animals and humans. Among the most effective drugs used to treat soil against late blight are:
They must be brought into the soil two weeks before the onset of frost before digging the soil.
Gardeners consider biologically active fungicides no less valuable for cultivating the land from late blight:
- Baktofit and Trichodermin;
- Planzir and Alirin B;
- Fitosporin, Phytocide M and a number of others.
These preparations are applied in accordance with the instructions in the autumn after the soil has been dug up. In early spring, immediately after the snow melts, the treatment must be repeated.
How the land is treated with fungicides: dissolve the required amount of the substance in water and shed the soil to a depth of 10 cm.
Consider working with some drugs:
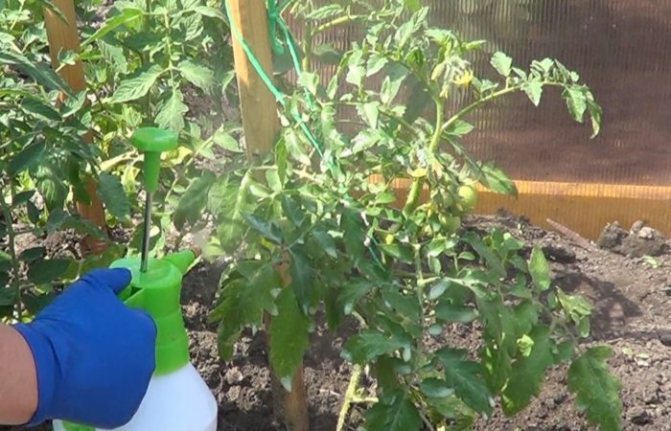
- Phytosporin is used for autumn and spring treatment of the site from phytophthora. 6 ml of the substance is added to 10 liters of water. This solution is enough for one square. Watering can be repeated during plant growth.


- Trichodermin contains active spores and mycelium of the fungus Trichoderma lignorum. Thanks to him, late blight spores die. For watering plants and soil, 100 ml is enough for a ten-liter bucket of water.
Chemistry in the arsenal of gardeners
In the case when agrotechnical methods, folk remedies and biological preparations did not help get rid of late blight, you will have to use chemistry. For this, drugs with a 3 or 4 hazard class are suitable. Before treating tomatoes with chemicals, you need to carefully read the instructions.
After digging the soil in the fall of the harvest, the land is treated with Bordeaux liquid. This procedure is repeated in the spring.
The liquid contains copper sulfate, it disinfects the soil and replenishes the need for sulfur and copper. Bordeaux liquid can be sprayed on tomatoes and treated soil. If the spraying of plants can be carried out annually, then the soil is only once every 5 years.


You can also use 4% copper oxychloride solution, or 2% Oxychom solution.
During the planting of tomatoes, each hole is spilled with Quadris, Bravo, Hom. Any chemical product must be used strictly according to the instructions.
Only complex measures can rid the soil of phytophthora.Remember to do soil cultivation systematically every fall and spring.
It is in this layer that phytophthora spores parasitize.
How to treat the soil against late blight:
Autumn processing
If an infection appears on the site, then the treatment of the land is carried out immediately after harvesting. In autumn, soil cultivation after phytophthora can be carried out with various preparations. All of them are divided into two groups: chemical and microbiological.
Chemicals
The most effective preparations for disinfection are copper sulfate and Bordeaux liquid:
| Copper sulfate A 0.5–1% working solution is made from the powder. For 10 liters of water - 50-100 g of copper sulfate. Copper accumulates in the ground, so it is recommended to use it no more than once every 5 years. For prevention, a less saturated concentration is made - 0.3% |
| Bordeaux mix To prepare the solution - 200 g of Bordeaux mixture per 10 liters. For 2 m², 1–1.5 liters should be used. |
| Hom The preparation containing copper belongs to the group of fungicides. Analogs: Bordeaux mixture, Oxykhom, Polykhom. It is used as a surface spraying and for soil treatment. Soil spill solution: 40 g + 10 l, consumption of this volume per 1 m². |
Various preparations are used to treat affected plants and soil:
- Bravo;
- Profit Gold;
- Fundazol;
- Consento;
- Tattu;
- Cuproxat;
- Quadris;
- Ordan;
- Previkur;
- Topaz;
- Infinito.
Chemicals are harmful not only for pathogenic bacteria, but also for cultivated plants!
Microbiological preparations
The work of these drugs is based on the activity of fungi and stems of beneficial bacteria that suppress the infection. Biological agents are not dangerous for insects and microflora, do not accumulate in the soil, and meet the requirements of organic farming.
Maintained high ratings:
| Fitosporin It is used for the prevention and treatment of various bacterial and fungal diseases. Does not negatively affect the environment and fertility. The dynamics of action is based on the activation and reproduction of the hay bacillus, the stem of which is the basis of the drug. Sold in different forms: paste, powder, liquid. The cost is low. Detailed instructions for breeding and processing are on each package. |
| Baikal EM-1 It is used to fight infections and as a microbiological fertilizer. Available in the form of concentrates. It contains a complex of living microorganisms: photosynthetic and lactic acid bacteria. To combat late blight, Baikal is used in the form of spraying and watering the soil. Autumn treatments are carried out 20-30 days before frost, so that bacteria have time to activate and acquire frost resistance | |
| Gamair Gamair contains beneficial microbes that inhibit the development of fungal bacterial infections. Available in powder and tablet form, instructions on each package. Does not accumulate in fruits and leaves. Not dangerous for animals, fish, insects and vegetation | |
| Trichophyte The composition is based on the fungal culture Trichoderm. It parasitizes phytophthora spores, completely destroying them. Trichoderma multiply in an acidic environment, therefore, treatment with the drug cannot be combined with the use of lime and ash. Improves soil condition, harmless insect repellent. Produced as a liquid concentrate Trichodermin and Trichophyte |
If you do not have drugs, and you do not know how to process the affected plantings of tomatoes and potatoes, there are grandmother's methods. I'll tell you about the most popular, safe and effective methods:
To destroy phytophthora spores in the fall after harvesting, you can spill the earth with boiling water, this neutralizes the pathogen
Toxicity
Fitosporin has a hazard class 4 for humans (it can cause slight irritation of the mucous membrane when in contact with a drug or solution) and a hazard class 3 for bees (border protection zone for bees 4-5 km). Not phytotoxic, harmless to beneficial insects.
Security measures
Use gloves, avoid smoking, drinking and eating during work. In case of contact with the skin or mucous membranes, rinse with water, if it enters the digestive tract, drink 3-4 glasses of water, induce vomiting, take several tablets of activated carbon.
Store the drug in a dry room, optimally from -20 to + 30 ° C, separately from food and medicine, out of the reach of children and pets. Shelf life is 4 years. Storage of the working solution is permissible in moderate temperatures, protected from the sun.
Processing a polycarbonate greenhouse in the fall from late blight is a prerequisite for getting rid of this disease, as well as a means of prevention and a guarantee of a good harvest next year.
What is late blight and how is it dangerous for plants and humans? How to treat a greenhouse from late blight in autumn and during the vegetative period of plant growth, folk and modern means of combating the disease. Plant processing methods and how to disinfect the soil in the greenhouse from late blight? You will find answers to these and some other questions that are so interested in summer residents in this article.
Cultivation of the land from late blight: effective means for the prevention and destruction of the fungus
Late blight is one of the most dangerous diseases, which is very difficult to cure if it has already appeared on plants. Cultivation of the land from late blight is a must, be it open ground or a greenhouse. The fungus overwinters well in the soil, as well as in plant debris. A rainy spring only contributes to its rapid spread. At a temperature of only a couple of degrees Celsius, the pathogen begins to actively develop. Phytophthora can completely deprive you of your harvest, so it is better to carry out prevention. It can be done using folk remedies or special preparations.
After harvesting, it is imperative to harvest and burn the tops, which can serve as a source of infection. In regions with cold winters, where the soil layer in which crops grow freezes, spores most often die. But if the winter is warm, the fungus hibernates well and survives. In any case, it is better to carry out preventive soil treatment than to unsuccessfully fight the disease already on the plants.
Remember
- Carry out prevention... Phytophthora on plants develops and spreads very quickly, and can deprive crops, therefore, preventive treatment of plants is carried out.
- Remove tops... If the affected plant remains are not removed from the site, the infection will continue to actively destroy the plants in the new season. Burn infected stems and fruits.
- Use biologicals... Give preference to effective and harmless remedies based on the work of beneficial bacteria.
Phytophthora is a dangerous enemy of the garden. Use whatever means you can and your crop will not be affected by infection.
From what appears
Plants with late blight are inflicted by oomycetes, which until recently were classified as fungi, and now they have been isolated as a separate group of special mycelial organisms. Phytophtora specializes in representatives of the nightshade, so potatoes, eggplants, tomatoes, peppers and physalis become their victims in the beds.
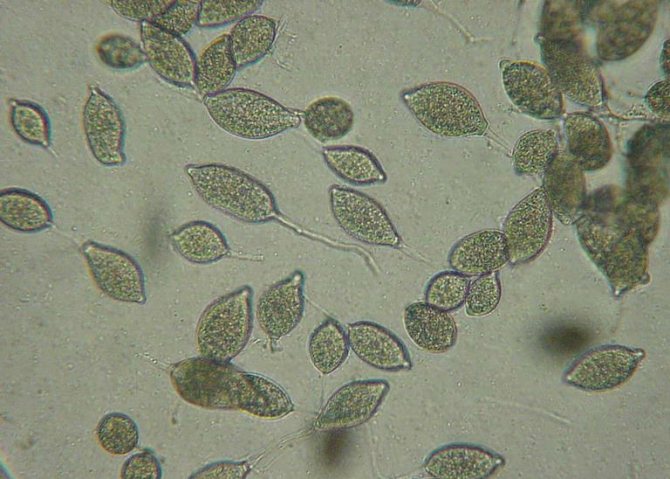
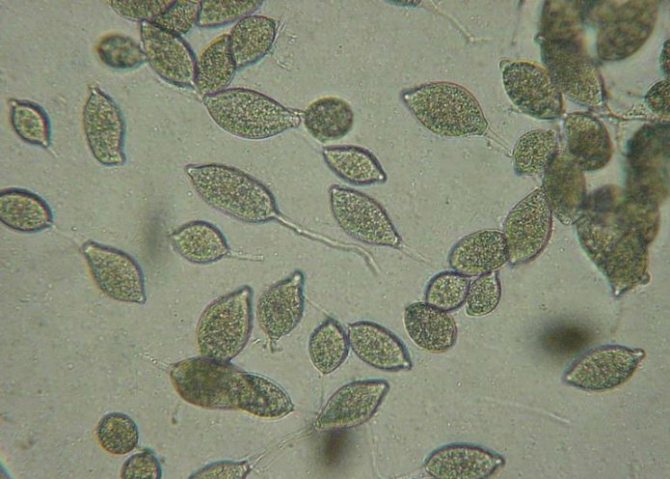
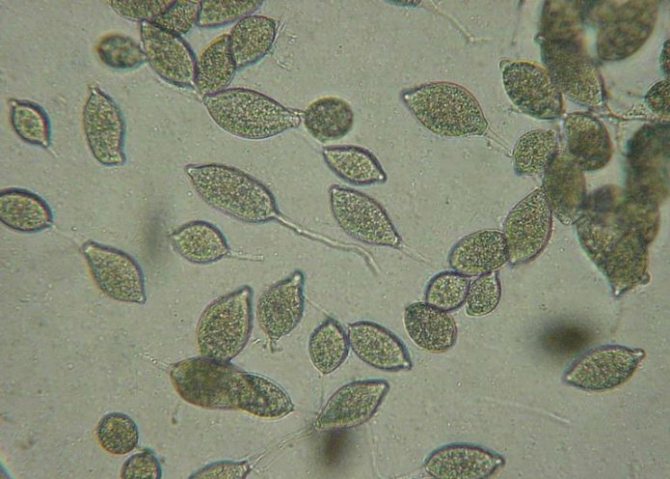
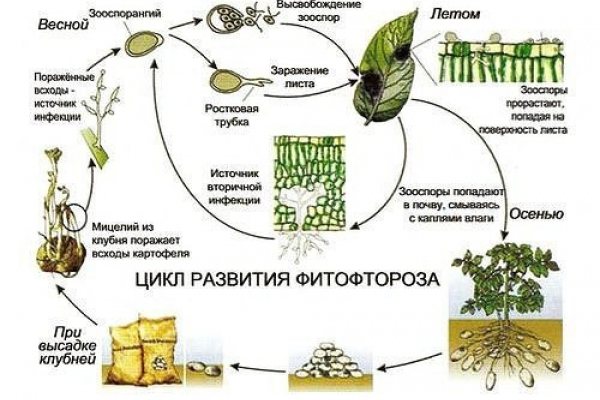
Oomycetes spend most of their life cycle in the phase of spores in the soil and in the remains of diseased plants. Only with the onset of favorable conditions do they move on to active life, the purpose of which is to leave offspring. When the air is warmed up to a temperature of +25 - +30 ° C, spores in dew drops are able to germinate and infect the plant within an hour.
Phytophthora is especially active during sudden changes in daily temperature, when the daytime heat is replaced by rather cool nights, which contributes to frequent fogs and abundant dew. Frequent rains in late July and early August also contribute to its spread. But dry weather, as well as heat above +30 ° C or cooling to +10 ° C and below, lead to almost complete fading of the pest's vital processes.
Phytophthora affects almost all parts of plants: gray-brown spots appear on leaves, fruits or stems.At the same time, in rainy weather, diseased plants rot, and in dry weather, they dry out and break. From them, the spores are washed off into the ground, and are also actively carried around by drops of water and gusts of wind.
Penetrating quite deeply into the soil, phytophthora spores successfully endure winter frosts and in summer they again begin to attack nightshade crops. They can also overwinter quite safely in the remains of infected plants abandoned in the garden.
How to treat
Unfortunately, at the moment there are no such effective chemical or biological preparations with which it would be possible to completely disinfect the territory from phytophthora.
The proposed substances can significantly suppress the development of pathogenic microorganisms, but the soil will not get rid of them completely. Also, there is no way to cure a plant after being affected by a disease.

In the fight against the pest, chemical preparations containing copper have proven themselves quite well. The easiest way is to shed the soil for planting nightshade crops with a 1 - 3% solution of copper sulfate, after which the site should be dug up and additionally treated with such a microbiological preparation as Fitosporin-M. You can also use the copper-containing fungicide Ordan.
It is quite common among gardeners that the introduction of chlorine is an effective way to combat this pest. However, it is unlikely that it will be possible to destroy the spores with this substance, but it will definitely be possible to harm the humus. Neither soil nor plants will benefit from this.
Chemicals not only suppress pathogenic microorganisms, but also harm the beneficial fungi found in the soil. In contrast to them, microbiological preparations act more selectively, since in their composition they contain colonies of microorganisms for which the pest spores serve as food. At the same time, the earth is not exposed to harmful influences.
To prevent late blight outbreaks, the use of such microbiological preparations as Fitosporin-M, Mikosan or "Shining" is effective. They should be applied three times throughout the summer. For the soil in those places where it is planned to plant flowers or strawberries, you can use Alirin, which is similar in composition and effect to Fitosporin. If these preparations are not available, then the soil can be treated with Bordeaux liquid.


Distribution mechanism
Initially, scientists believed that such an infection spreads over land plots along with potato tubers. However, as the results of recent studies show, late blight is transmitted by seedlings and seeds of a wide variety of cultivated plants. Fungal spores are able to remain active when exposed to a wide range of negative environmental factors. They are not afraid of low and high temperatures. The disease is resistant to certain chemicals. All this significantly complicates the fight against late blight.
To understand how to get rid of phytophthora in the ground in the fall after tomatoes or potatoes, vegetable growers go for a variety of tricks. Often it is not possible to overcome the fungal pathogen due to the use of high-quality seed material, as well as proper soil preparation. In the presence of favorable conditions, the land plot can even become infected with several spores that were brought by the wind.
Prophylaxis
It is very difficult to get rid of the phytophthora that has appeared on the site. However, carrying out preventive measures allows you to minimize its spread and harvest an excellent harvest. Since the main source of infection is the land, then the lion's share of the efforts is directed to it.
Fungicides and microbiological preparations are used to destroy the spores in the soil. Since chemicals take a long time to decompose, after they are added, vegetables can be used in food only after a month.Therefore, the treatment with copper-containing substances is carried out in early spring. The introduction of microbiological preparations into the soil is allowed at any time, except for the flowering period, when they can harm the bees collecting nectar.
From the soil, phytophthora spores enter the plants by means of moist air currents rising from the heated ground. In order to effectively prevent this process, mulching is used. Covering the ground with a layer of mulch several centimeters thick in spring becomes a reliable barrier against many diseases, the sources of which are the spores of pathogenic fungi wintering in the soil.
It is also important not to plant nightshade crops in the ground. In addition to the fact that the plants in this case lack light and are poorly ventilated, late blight will easily move through the beds and affect large areas.
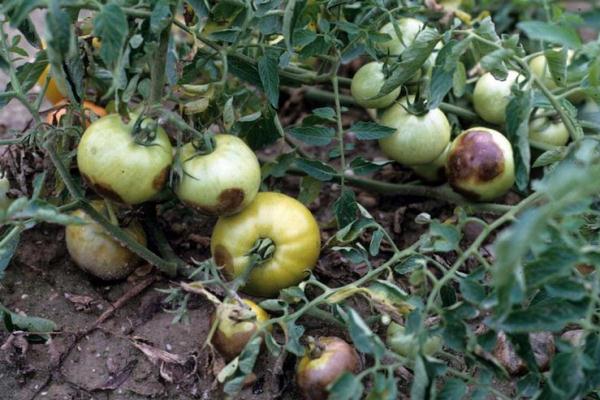


Autumn harvesting and off-site incineration of all waste effectively helps to get rid of the spores remaining in the ground parts of the plants. After that, the soil should be dug deep.
A good result is the use of a drip irrigation system for plants. At the same time, the soil is not waterlogged, and the plants receive the optimal amount of moisture for their growth and development. A good way of prevention is the use of crop rotation. Solanaceous plants in the same soil areas should be planted at intervals of three to four years.
Another option to avoid damage to plants by late blight is the cultivation of certain varieties of nightshade. These can be varieties that are especially resistant to the pest or early ripening, the ripening of which occurs at the time when the late blight begins to actively multiply.
Testimonials
I am still an adherent of traditional methods of prevention and treatment. Moreover, you can always switch to fungicides, or you can try different methods. I was interested in the method of my friend - she first sows mustard, and then sows potatoes and tomatoes. He assures that it is an excellent remedy for the prevention of late blight. The use of systemic fungicides is mandatory before the disease, because if the disease has already appeared, the fungus can adapt.
Melenkavskaya
And regarding the cultivation of the land, I advise you to spill it with a strong Bordeaux solution, then you need this solution to dry on the surface of the earth, so it will start working. After it dries, dig it up. But it is necessary to let it dry, this is very important. In general, I prefer to use Bordeaux everywhere, this is the most effective remedy.
egorov
I am very careful about treating the land with different chemicals. Where is the guarantee that they will spare beneficial microorganisms?
Uman tura
In the fight against late blight, preventive measures are the most effective. The main stage of prevention is the autumn cultivation of the land.