Iron sulfate is a popular remedy used to protect the garden from pests and diseases. Autumn processing of the garden with this tool in the fall is no less active than in the spring. Ferrous sulfate is ferrous sulfate (ferrous sulfate). On sale it can be seen in crystalline form, crystals are odorless. With this fertilizer, you can increase the fertility of young trees, improve the condition of old trees. When processing a garden with iron sulfate in the fall, fertilizer is used in the form of a solution, only for different crops a solution of different consistency is needed.
Iron vitriol: characteristics and purpose
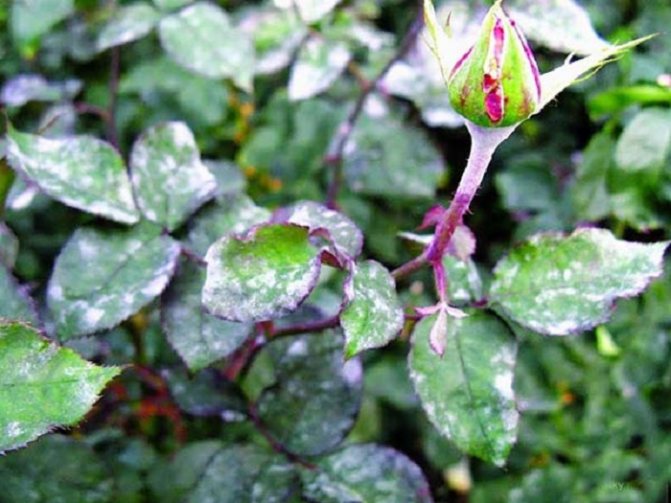
Iron vitriol is active against many fungi, including powdery mildew and peronosporosis.
Chemically, ferrous sulfate is ferrous sulfate, otherwise it is ferrous sulfate. It is a green crystalline salt, readily soluble in water. In horticultural practice, iron sulfate is used specifically for late autumn processing of plots. It is used much less often in early spring.
An aqueous solution of iron sulfate has the following properties:
- is a strong contact fungicide;
- contains up to 53% of active iron, as well as sulfur, and in strong dilution can serve as micronutrient fertilizer;
- in an increased concentration, it exhibits some insecticidal properties and can be used to expel wintering larvae and adults of insect pests;
- scares away rodents from treated plants.
In rose growing, this substance is most often used as an inexpensive fungicide when preparing roses for wintering (
Purpose of application
The scope of application of copper sulfate is extensive. It is widely used in industry and medicine. In amateur gardening, it is often used as a fungicidal agent that provides protection against the development and prevention of the appearance of fungal diseases. In some sources there is information that a working solution of iron of low concentrations can be a fertilizer. After watering, a rapid increase in the aboveground leaf mass is noted. Frequent use in high doses is dangerous for flowering plants, lack of flowering. Concentrated solutions can damage the root system and cause leaf burns, so you need to handle roses carefully.
Stimulation of plant growth appears some time after treatment, therefore this effect should be associated with the general improvement of the rose bush. Immediately after using vitriol, the leaves of the plant may turn yellow and crumble. Spring processing leads to a slight deviation of the growing cycle - 1-2 weeks from the norm.
When feeding garden roses with copper sulfate in the fall, you need to remember that in addition to iron, the plant needs other trace elements and nutrients, therefore it is better to use complex compounds, and copper sulfate should be used for treatment against fungus and pests.
The solution is used in the fight against the following diseases:
- mycoses;
- powdery mildew;
- gray rot;
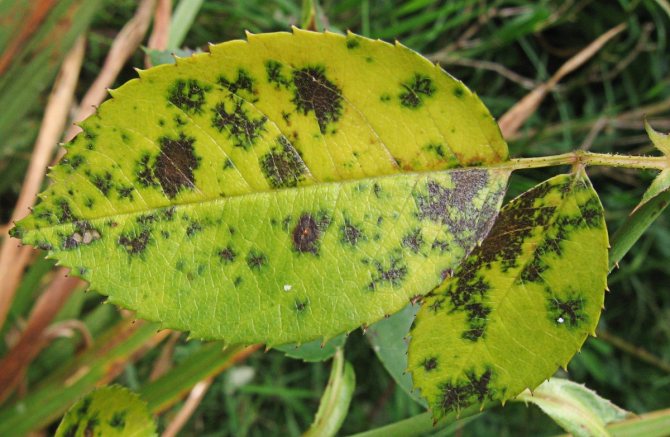
- black spot;
- anthracnose.
Gardeners recommend spilling the rose garden with a weakly concentrated solution before sending the plants to winter.The soil contains spores of various fungi and other pathogens, which, after the construction of the shelter, can be active.

Preparation of a solution of ferrous sulfate for processing roses


Depending on the concentration, the solution of ferrous sulfate has a green color of varying intensity.
For the autumn processing of roses, a solution of 3% or 5% concentration is usually recommended. For inexperienced flower growers, such a formulation may cause confusion. However, here you just need to remember the following: 10 grams of a substance when diluted in 1 liter of water gives a 1% aqueous solution. This applies not only to iron sulfate, but also to any preparations that are produced in dry form.
Thus, a solution of ferrous sulfate for processing roses in the fall is prepared as follows:
- For processing shoots, a 3% concentration is needed. In 10 liters of water, dissolve 300 grams of ferrous sulfate.
- For soil and mulch processing, a 5% solution is required. In 10 liters of water, 500 grams of ferrous sulfate is diluted.
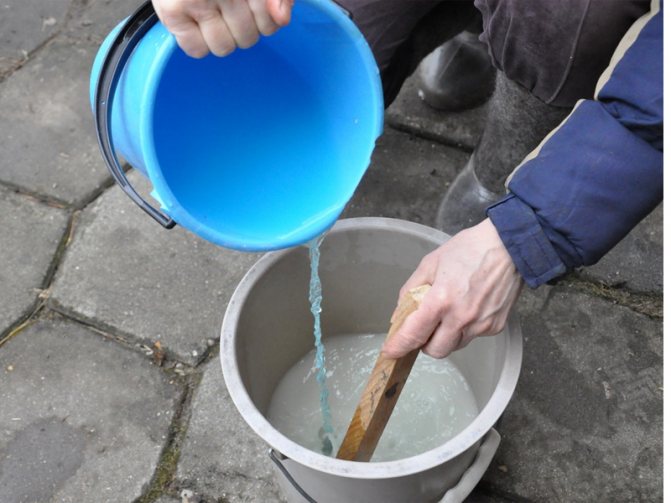
For the preparation of solutions, it is better to take not tap water, but rain or settled water. First, the required amount of powder is measured and diluted in a small amount of water until the crystals are completely dissolved. After that, the resulting mother liquor is poured into the rest of the water in a thin stream.
Features of the drug
The treatment of roses with vitriol can be carried out only in the fall. The use of the drug in springtime is dangerous for the plant, because it provokes the formation of brown spots on the leaves. They do not harm the bush itself, but the leaves cannot be restored. Autumn processing is carried out after the fall or preliminary removal of the green mass. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to process the bush before wintering with a solution of 3% concentration, that is, dissolving 30 g of the drug in 1 liter of water. High concentrations can burn young shoots of a bush, while low concentrations are not effective in combating mycoses.
In emergency cases, solutions with a concentration of 1% can be used after the leaves and rosebuds have dissolved. The buds must be protected from the ingress of liquid, the solution is carefully distributed over the leaves with a spray bottle. Processing is carried out with an interval of 10 days, twice. The activity of the product decreases after rain because the product is washed off the leaves.
When preparing the rose garden for wintering, you need to remember that it is forbidden to cover the flowers until they dry. It takes 2 days for the solution to work, without precipitation. Fallen leaves must be removed and burned. It is not allowed to use vitriol in a mixture with other fungicides or lime.
Treatment options: shoots and soil
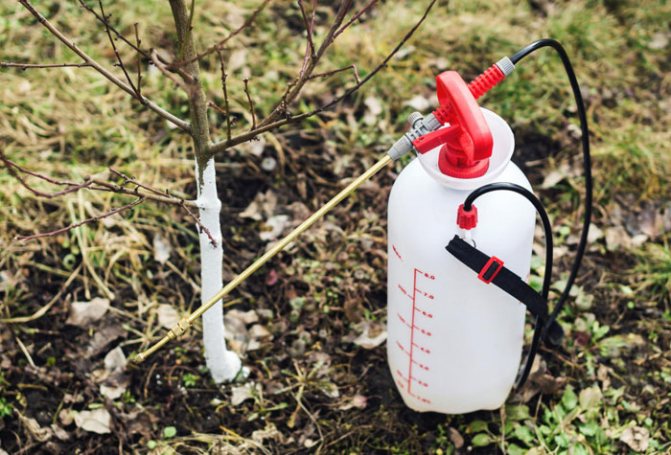
For the treatment of roses with iron vitriol, it is better to use a pump spray, set to the "fog" mode, so that the solution does not settle in large drops.
The treatment of rose shoots with iron vitriol is performed as follows:
- green shoots that did not have time to ripen are pre-cut;
- all remaining peduncles are cut off;
- climbing roses are removed from the support and spread over the covered ground;
- standard roses bend down;
- the sprayer is filled with a prepared 3% solution and the shoots are sprayed from bottom to top.
The soil under the roses can either be watered or sprayed with a 5% ferrous sulfate solution. The procedure is performed after the complete clearing of the near-trunk circle from plant residues, water-charging irrigation and loosening. However, this is done only in cases where the roses during the course were severely affected by infections that could not be completely dealt with.
Tip # 2. The mulch treatment with fungicides, which will cover the roses for the winter, is mandatory. This is done by spraying, after which the mulch is dried.
Why is it so important to stop autumn diseases
Every summer, the queen of the garden is overgrown with new shoots. It is important that they mature before the onset of frost.If the rose is attacked by a disease, then the leaves are affected and fall, and this is fraught with the fact that photosynthesis will be disrupted. As a result, the bush will not receive enough nutrition, the shoots will not become woody and will freeze in winter. In addition, diseased fallen leaves will become a source of infection the next year if not removed.


To preserve the shoots of climbing roses, it is necessary to fight diseases, otherwise they will not ripen and freeze
Comparison of ferrous sulfate with other fungicides
Protecting roses from fungal infections for the wintering period is possible not only with the help of iron sulfate. You can replace it with almost any contact fungicide:
| A drug | Active substance | Distinctive characteristic |
| "Abiga Peak" | Copper oxychloride | Unlike ferrous sulfate, it is less phytotoxic and aggressive. It adheres better to the surface of the shoots. |
| Bordeaux mix | Copper sulphate and calcium hydroxide | Safer than ferrous sulfate, it has a mild effect. However, it is more difficult to prepare. |
| "Oxyhom" | Copper oxychloride and oxadixyl | Less phytotoxic than ferrous sulfate, it has not only contact, but also local systemic action. Does not wash off the surface of the shoots. |
| Ridomil Gold | Mancozeb and mefenoxam | Possesses contact and translaminar (local-systemic) action. Does not wash off, gently acts against a wide range of fungi. |
The table shows that modern drugs can serve as a safer, but no less effective substitute for hard iron sulfate. Thus, it is advisable to use ferrous sulfate only as a radical agent.
Preparation of working solution
To effectively combat fungal infections, rose bushes are treated with a 3% solution. You need to spray the bush thoroughly. The manipulation is carried out on dry days, because the solution must dry on the leaves. If it rains, you need to repeat the treatment.
If the processing was not carried out in the autumn, but it is carried out in the spring. For this I use a 1% solution. To prepare a working solution with a concentration of 3% in 10 liters of water, dissolve 30 g. preparation, to obtain 1% - 10 gr. The dry mixture is poured into cold clean water and the composition is vigorously stirred until it is completely dissolved. Do not use the product in conjunction with other fungicides. The finished composition is used immediately; upon contact with air, it loses its activity.
Topical questions about the use of ferrous sulfate
Question number 1. A few days after the treatment with iron vitriol, the shoots and leaves of the rose under the shelter turned black. What to do?
Wait for spring. The beginning of the growing season will show whether the blackening is caused by a chemical burn as a result of exceeding the concentration of the drug. If the shoots die, they will have to be cut back to healthy tissue. However, sometimes black spots after treatment with iron sulfate are not a sign of a burn. The drug can stain insufficiently matured or unhealthy areas of the shoots. Blackening of the leaves is common. Iron vitriol is aggressive towards soft tissues. They will need to be removed in the spring.
Question number 2. Is it possible to process rose cuttings with iron vitriol before storing them?


A softer alternative to iron can be copper sulfate.
It is possible, but it is better to use a 1% solution for this. We must not forget that iron sulfate can slow down the growth of the kidneys, and after treatment with iron vitriol, difficulties may arise with rooting and subsequent germination of cuttings.
Rate the quality of the article. Your opinion is important to us:
Advantages and disadvantages
An antifungal agent has advantages:
- low price;
- high damaging ability against fungi;
- non-toxic to humans;
- does not change the qualities of the potting mix;
- stimulates the growth of crops and increases immunity to diseases;
- acts externally, does not penetrate cells.
- low efficiency as an insecticide;
- limitation of the period of use (before the dissolution of the buds and after the leaves fall);
- destruction of the green mass of the plant;
- difficult to find concentration;
- washed off after precipitation and stops working.
How to prepare roses for winter
Of course, the best covering material for roses in winter is snow. All additional measures are taken in its absence.
If you know from experience that the winter months in your region are frosty, but with little snow, you should definitely cover your roses for the winter.
1. Adjust the feeding regime
How well the roses cope with winter temperatures depends on the maturity of the shoots. Naturally, young branches will die in severe frosts, so it is not worth stimulating their growth at the end of the season.
Stop applying nitrogen fertilizers in August. At the end of the season, roses need potassium-phosphorus feeding, which will strengthen the plant's root system.
You can understand whether the roses are ready for wintering by the color of the branches. The red tint of the shoots indicates active growth. Ripe shoots turn green.
2. Adjust watering
In the summer, roses need regular abundant watering, but in the fall it must be stopped. Otherwise, the bush will be weakened and will not overwinter well.
3. Pinch the shoots
In late August - early September, pinch the tops of all young shoots to stop them growing. When autumn is in full swing, it may be too late to do this.
4. Stop loosening
Beginning in September, stop loosening the soil in the near-trunk circles. This can awaken dormant kidneys. As a result, the plant will be highly vulnerable to severe frosts.
5. Perform the trim
In the second half of September, when the morning frosts begin, you can start pruning roses. First of all, you need to remove all remaining buds, cut out weak, unripe shoots growing in the middle of the bush.
Also in late October - early November, all leaves from the bush are removed and burned. First, it is necessary to prevent black spot and other fungal diseases. Secondly, the leaves under cover can rot and rot the entire plant.
Formative pruning is carried out depending on the type of rose. Hybrid tea and floribunda roses are cut to the middle of the bush. Pruning climbing roses depends on which group the plants belong to - climbers or ramblers. You can find out all about the differences between them in our article: Everything you need to know about climbing roses.
Basic rules for processing rose gardens in spring and autumn
The processing of rose bushes should be carried out exclusively in the fall, preferably after leaf fall. If there are still leaves on the bushes, it doesn't matter, vitriol will speed up the process of foliage falling off. If the autumn treatment has not been carried out, you can spray the roses in the spring, but always before the beginning of the growing season (swelling of the buds). This is due to the fact that the optimal concentration of the solution that destroys fungi and prevents their appearance is 3% (300 g of ferrous sulfate per 10 liters of water). But a solution of such a concentration acts aggressively on young green shoots and leaves, leaving burns on them, so the treatment time with the drug is limited.


It is better to treat roses with a solution of iron sulfate in the fall.
In case of rose disease with black spot or chlorosis it is possible to carry out the treatment with a 1% solution directly on green leaves, 3-4 times with an interval of 7-10 days (taking into account weather conditions).
Before processing the rose gardens, all fallen leaves must be collected and burned, since they are a breeding ground for fungal spores. Spraying is carried out in dry, calm weather, completely covering all branches, shoots and soil around the bushes with a solution. Since ferrous sulfate is very easily washed off with water, the weather for processing should be chosen deliberately not rainy. The drug should have time to dry on the roses, only after that you can start wrapping them with a film.
Autumn processing will allow not only to destroy the spores of fungi of various types, but also serve as an excellent prevention of disease in rose bushes next year, increase the resistance of plants to low temperatures, and facilitate the wintering of roses. Iron and sulfur strengthen the immunity of plants, enhance their vitality.


Ferrous sulfate solution
A solution of ferrous sulfate must be prepared immediately before use and processing must be done quickly, without delay, since ferrous sulfate oxidizes very quickly when interacting with air and transforms into a form that is inaccessible to plants and less harmful to fungi, i.e. efficiency drops sharply. It will not be difficult to prepare the solution.
Roses "love" iron vitriol very much, react actively to processing and feeding. Timely and competent care will give roses a long healthy life and lush bloom.
Wintering is a rather problematic period for roses. Bushes can not only freeze, but also get wet, which is fraught with the development of fungal infections. Therefore, experienced rose growers practice the treatment of roses with fungicides before sheltering (
How to prune roses in the garden correctly?
We reveal the secrets of the correct pruning of roses of different types.
6. Process the bushes
In order not to give a chance to the fungus, it is advisable to treat the bare bushes with iron vitriol or a ready-made fungicide. Fungicides are diluted according to the instructions on the package. Iron vitriol is used in the proportion of 300 g of the product per 10 liters of water (3% solution).
7. Spud the bush
Make sure the rose grafting site is below ground level. If it is bare, spud the bush. It is advisable to use ready-made peat soil for these purposes.
However, if frequent thaws occur in your climate in winter and sleet and rain are not uncommon, the rose may begin to rot and rot. It is possible to sprinkle roses in such conditions only if they are planted on a slope, and the water near the bush does not stagnate for a long time.
8. Bend down the shoots of climbing roses
For the winter, the stems of climbing roses must be transferred to a horizontal position. Even if in recent years they have wintered vertically, without shelter, you still run the risk of leaving them on a support.
If the shoots are thick, chances are they will break. Such plants bend down gradually, over several weeks. Each week, lower the shoot lower and lower, fixing it until it touches the ground.
Even without further cover, the likelihood that the rose will winter well under the snow is much higher than in the freezing cold and harsh February sun.
Do not place shoots on bare ground. When the snow melts, the plant can rot. Use wood planks or a piece of styrofoam as an interlayer.
9. Don't rush into cover
Without additional insulation, roses can withstand temperatures down to -10 ° C. Growers living in warmer regions only cover their roses in December. As a rule, the most optimal time for sheltering bushes is the end of November, when the thermometer is set at around 0 ° C. The main thing is to catch the moment before a lot of snow falls.
10. Install the arcs
Covering roses for the winter means creating a layer of air between the plant and the environment. The larger the air cushion, the more reliable the protection and the lower the risk of the rose getting rotten. Therefore, it is advisable to install the shelter on the arcs. Accordingly, it is easier to cover roses growing in group plantings than single plants.
Features of work with a solution
Experienced growers recommend treating with fungicide after leaf fall. If the plant has not been sprayed in the fall, this should be done in the spring, but before growth begins. The purposes of using the product are different, as are the methods of application. A solution of vitriol is used for spilling the soil and spraying the aboveground part.
With a fungal infection
Fungal infections often end up in the rose garden with new, acquired varieties, therefore, before planting new bushes in the garden, they must be examined for the presence of fungi and pests.
The list of common fungal infections of roses includes:
- spheroteka;
- peronosporosis;
- gray rot;
- rust;
- infectious burn;
- septoria.
Iron vitriol is used for the prevention and treatment of these diseases in seedlings. A 3% solution is used, which is applied to the shoots with a spray bottle. The leaf mass will be lost. The period of work of the tool is 2 weeks.


Insect control
For treatment against pests, the working solution is used in the fall, before covering the rose garden for the winter. Before irrigation of the aboveground part of the plant, sanitary pruning is carried out and all fallen leaves and removed stems are removed from the front garden. Before spraying, you need to water the soil and feed the rose before wintering.
Additional food
The treatment of the rose garden with vitriol in the fall can be carried out not only for the purpose of healing, but also fertilization. To do this, dissolve 30 g of the composition in 3 liters of soft water. The drug is used at the rate of 10 liters of working solution per 100 squares. Watering is carried out in dry, calm weather. This technique is not used in the summer.


How to process roses in early autumn
For successful wintering, roses are fed in autumn with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers and sprayed with anti-infection agents. Even if the roses look healthy, preventive measures are needed. After all, the disease does not manifest itself instantly, the infection lasts 2-3 weeks, so it is dangerous to count on luck. Roses are healed with purchased fungicides and folk remedies.
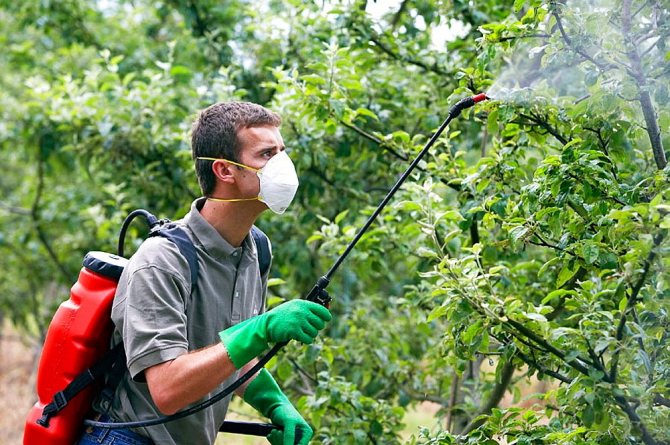


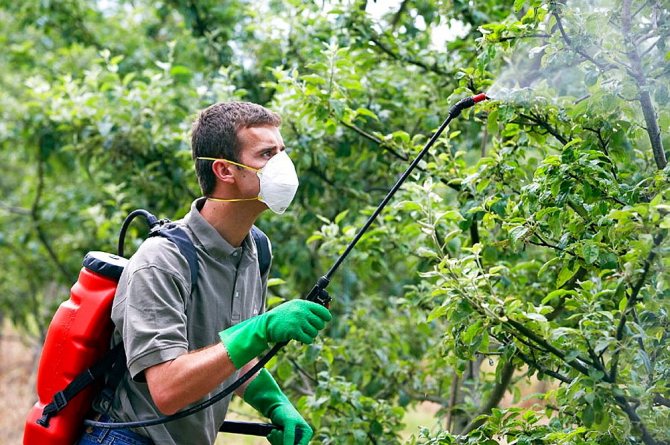
When treating plants, protect the respiratory system with a mask, and hands with gloves, take a shower after spraying
Store drugs
If the roses are not sick: leaves without spots and curling, then preventive spraying with Fitosporin solution is enough. Processing is carried out from August to mid-September: 2-4 times with an interval of 5 days. The signal for action is the onset of cold nights, heavy rains, fogs, dew. Consider an important nuance: both the upper and lower parts of the sheet are always processed.


Fitosporin is an excellent biological product for the prevention of diseases, contains spores of the bacterium hay bacillus
Since August, frequent guests in the rose garden are black spot and powdery mildew. If the disease has just begun - black spots or white bloom have appeared on the lower leaves, the bushes are sprayed with antifungal drugs: Skor (Raek), Topaz or Bayleton. The listed fungicides destroy fungi, but spores must also be fought if they have formed on the lower part of the leaf. In such cases, these chemicals alternate with others: Ridomil Gold, Profit or Quadris. In total, 3-4 treatments are carried out weekly.
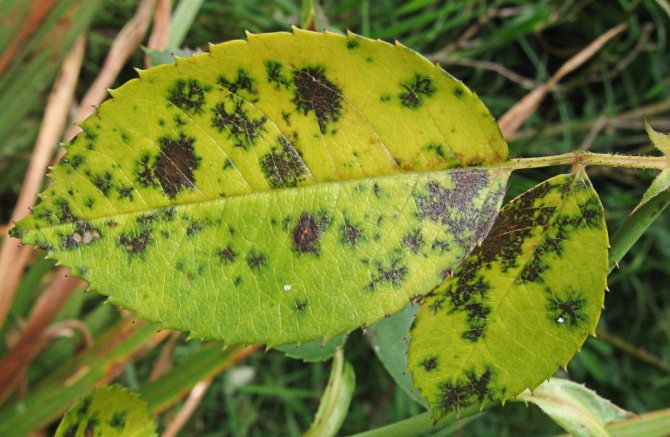


Black spot strongly weakens the rose and can lead to its death.
When the whole bush is affected by the disease, use HOM and Oxyhom. You will need at least 3 treatments once a week in wet weather or once every 2 weeks in dry weather.


HOM - copper oxychloride, a popular remedy for all diseases of garden and horticultural crops
Fungicide Topsin is alternated with Strobi for the treatment of rose rust. The preparations are diluted according to the instructions and the bushes are sprayed three times every 10 days.
A completely rusty rose will most likely have no cure. It is better to burn it so as not to infect the entire rose garden.


Rust is easily identified by the bright orange pads of the spores.
Folk remedies
Unfortunately, fungi that have settled on the leaves are poorly treated with homemade preparations. They are effective only as a preventive measure or in the early stages of disease development. The best product is prepared with wood ash. It must be infused with water for 2 days: 1 kg of substance per 10-liter bucket. To improve adhesion, add 1 tbsp. l. rubbed soap.It will take 2-3 treatments with a filtered solution once a week. Ash is also sprinkled on the ground around the bushes, and so that it does not scatter from the wind, it is slightly embedded in the soil. This technique allows you to make the environment around the rose more alkaline, and mushrooms prefer acidic and do not grow where they are uncomfortable.
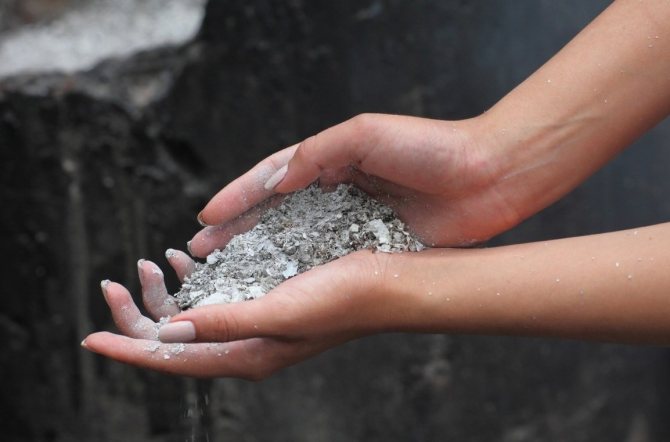


Ash nourishes roses with phosphorus and potassium and protects against diseases
At the first sign of rust, milkweed infusion helps. It is necessary to grind 1.5 kg of stems and insist them in water in a warm place for a day. Usually, two sprays are enough at intervals of a week.
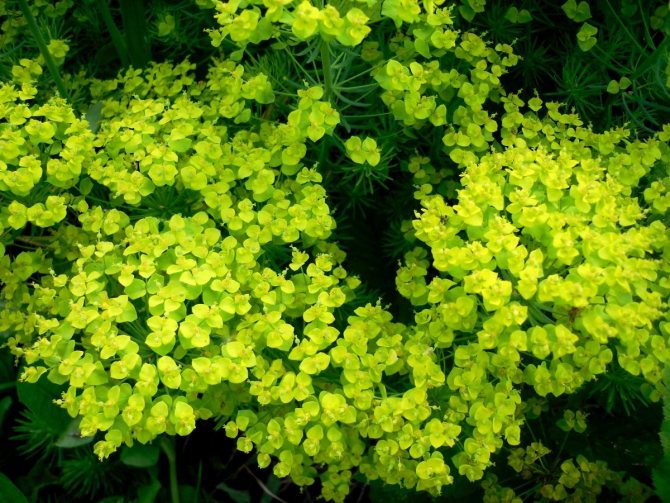


Euphorbia is poisonous, so you have to work with it with gloves.
To prevent black spot, 200 g of onion husks are insisted in 10 liters of water for 8 hours. Roses are processed 2-3 times every 5 days.
Onion hulls contain phytoncides that kill fungi and bacteria
Some rose growers fight powdery mildew like this: dissolve 2 tsp in 1 liter of water. soda ash and 1 tbsp. l. soap shavings. In total, two sprays are carried out 1 time in 7 days.
Soda ash - sodium carbonate is used in the garden and vegetable garden
Eliminate black spot - video
Security measures
Technical iron vitriol in comparison with copper is much less dangerous for the human body. If we talk about the official presentation, then FeSO4 has a 3 toxicity class, non-flammable and non-explosive. However, while working, protect the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose and eyes by wearing a respirator and goggles. Contact with the skin does not entail any consequences - it is enough to wash the contaminated area with soap and water.
Important: iron and copper sulfate are completely different substances. You can distinguish them by color: in the first case, the powder is light green, in the second, light blue (light blue).
Today, the use of ferrous sulfate both in the garden and in the garden is widespread throughout the world. This drug is extremely popular with professionals. But also amateurs can get high yields thanks to the tool. To do this, you just need to carefully study the instructions and properly dilute the solution.
Late autumn processing of roses before shelter
In order not to grieve about the roses that died from an infectious burn and about chlorosis in the summer, it is necessary to treat them with iron sulfate before hilling and sheltering the bushes for the winter.
Chlorosis of roses occurs due to iron deficiency
Preparation of a three percent solution of ferrous sulfate:
- Dissolve 300 g of ferrous sulfate in 1 liter of soft or rain water. Use only non-metallic cookware.
- Pour the solution into a plastic bucket with 9 liters of water in a thin stream, stir.
Note that iron will precipitate in hard water. The bush itself and the ground under it are sprayed. After treatment with this fungicide, the leaves will turn black, this is normal. But it is guaranteed that not a single pathogen will survive until spring. But ideally, all tops should be trimmed and burned before spraying.
Iron vitriol is an old proven remedy that is safe for plants
For rose diseases, I alternately use the fungicides Skor and Ridomil Gold. Thus, it is possible to stop the spread of fungi. For prophylaxis, at the end of June I spray both roses and tomatoes with HOM. It is very convenient if you prepare 10 liters of solution, enough for both.
At first, I covered roses for the winter without treatments with iron vitriol. I noticed that even under a ventilated shelter - lutrasil, the bushes suffer from mold and an infectious burn. Therefore, I believe that it is imperative to spray roses with iron sulfate before frost.
Autumn diseases of roses are suppressed by spraying with fungicides and potassium-phosphorus dressings. If only a few leaves are affected, folk remedies will do. For beginners, so as not to get confused, it is better to use HOM for prevention and treatment. Winter health of thorny pets is guaranteed by treatment with iron vitriol. It burns out any fungi and spores.
Pros and cons of using ferrous sulfate in gardening
Both chemical and organic fungicides, fertilizers can affect the development of certain plants in different ways. Therefore, compliance with the instructions for the use of ferrous sulfate in horticulture and horticulture is a very important condition for obtaining a good harvest. Moreover, the season (spring or autumn) does not affect these rules in any way.
The benefits of ferrous sulfate (FeSO4) include:
- a wide range of applications of the substance;
- very low level of toxicity during external exposure (contact with the skin);
- high efficiency of the agent in the treatment of various plant diseases;
- acid is not absorbed by the culture, but only affects its surface;
- hit of the composition on the ground (drops from branches and stems, a spray cloud) acts as a top dressing, saturating the soil with iron;
- the budgetary cost of the preparation for spraying plants.
The disadvantages of FeSO4 include:
- dependence on weather conditions. If it rains during the day, it will wash off the solution, and all your attempts will be ineffective, or generally useless;
- if it is necessary to destroy pests, additional means have to be used, since vitriol has low efficiency in this direction;
- such treatment can be applied only when there are no leaves on the plants - in early spring or late autumn when the outside temperature is above zero.


Dosage
The choice of the correct dosage of iron sulfate will help to minimize the likelihood of error. The first rule - you need to know that in 1 tablespoon 15-16 g, and in 1 teaspoon - 5 g. The second rule - the required volume of the drug is measured only with a plastic spoon. The material does not react with iron sulfate.
| Concentration level of active substance (%) | Required volume |
| 0,5 | 50 g |
| 1 | 100 g |
| 3 | 300 g |
| 5 | 500 g |
| 10 | 1 kg |
| 15 | 1.5KG |
A solution stronger than 1% is used only after the end of the growing season. Here it is necessary to dwell on two polar points of view of botanists. A low-saturated solution reduces the likelihood of damage to the tree, but does not allow 100% to be 100% sure of the result. The weaker the mixture, the more chances the pathogenic flora has. The second point of view is that they take a 10% more saturated solution than necessary. The "golden mean" has not yet been found. The only recommendation is to rely on the severity of the symptoms.


Useful properties of the drug


Iron sulfate is known to many as a remedy for the protection and destruction of pests and diseases on trees, shrubs. However, the drug has a wider range of actions. It is possible and even necessary to use iron sulfate in the garden in the fall to complete the following tasks:
- Fertilize the soil with iron.
- Cure rose spot, leaf chlorosis (processing is carried out on the foliage before leaf fall).
- To carry out the prevention of diseases of grapes and other plants in the garden.
- Protect fruit bushes and trees from pests.
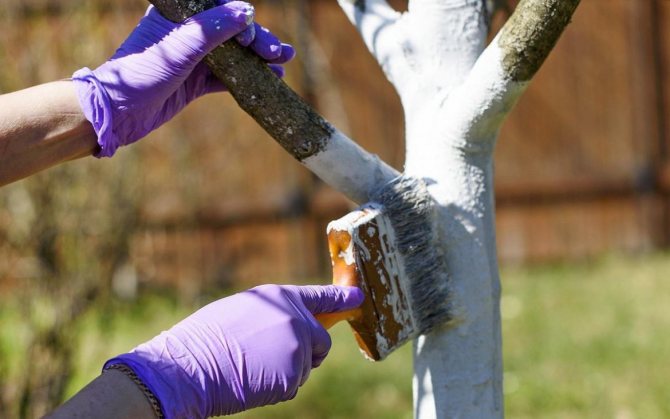
- Add to whitewash to kill pests in the bark and remove moss and lichen from trees.
- Restore old trees.
- In vegetable stores, spray surfaces to remove fungus.
- Protect mechanical damage to the trunks from the penetration of fungi, viruses, larvae of harmful insects.
It is important! A highly concentrated solution of ferrous sulfate is used to destroy pests and diseases. Therefore, the processing of the garden is carried out after leaf fall in autumn or early spring. Only to get rid of chlorosis, plants are sprayed over the foliage, for which a weak 1% solution is made (recipe below).
Toxicity
Iron vitriol has a 3rd class of danger to humans, the danger to bees is not assessed, since no leaf and color treatments are carried out. Copper sulfate is phytotoxic in concentrations of more than 1%, since the strongly acidic reaction of the solution eats up the thin epidermis, the denser covers of the branches and trunk can withstand a concentration of no more than 6%.
Iron sulfate is a popular remedy used to protect the garden from pests and diseases. Autumn processing of the garden with this tool in the fall is no less active than in the spring. Ferrous sulfate is ferrous sulfate (ferrous sulfate). On sale it can be seen in crystalline form, crystals are odorless. With this fertilizer, you can increase the fertility of young trees, improve the condition of old trees. When processing a garden with iron sulfate in the fall, fertilizer is used in the form of a solution, only for different crops a solution of different consistency is needed.
Consumption rates
Typically, the following concentrations are used:
- 3% solution for stone fruit crops (plums, cherries, apricots, peaches, sweet cherries, cherry plums) - 300 g of ferrous sulfate powder per 10 liters of water. Spraying in front of shelter on bare branches or vines.
- 4-5% solution for pome fruits (apple, pear, quince, chokeberry, grapes): 400-500 g of ferrous sulfate powder per 10 liters of water, with a consumption rate of about 10-15 liters per 100 m2.
- 5-6% solution - for the destruction of mosses and lichens on trees and garden tiles, as well as a basement or cellar against mold: 500-600 g of ferrous sulfate powder per 10 liters of water.
If you do not have scales, measure by eye a 2% solution: half a tablespoon of ferrous sulfate per 1 liter of water, you get a bright orange color of the liquid.
Iron vitriol delays bud opening (for about a week), therefore, treatment with a 3-4% solution before the start of the growing season helps to survive the period of spring frosts. Especially true for crops such as grapes, if processed about a week after removing the winter shelter, exclusively on bare vine with unopened buds.
Instructions for use
The aqueous solution is used for various purposes. Therefore, the correct concentration of the drug and the time for processing are important.
Against pests
Ferrous sulfate destroys many pests. To prepare the working mixture, take 0.5 kg of the drug per 10 liters of water. Spraying of plants and near-stem circles is carried out in early spring before bud break or after autumn leaf fall. The maximum number of treatments is 2 times per season. Spraying of young trees with thin bark is carried out 1 time in the spring.
During the first treatment, the insects woke up, and the plants are still dormant. A high concentration of the drug will not harm plants, but will destroy insects. The tool is not universal for the fight against all types of pests, so they are not limited to it only.
Fight against mosses and lichens
Trees on which mosses and lichens have settled do not grow well, yield decreases, and branches may dry out. Harmful insects settle in the growths. Most trees are sprayed with a 3% solution, pomes - with a 5% solution. Processing is carried out in early spring before bud break. At a later date, the plants are burned with the drug, they may die.
Autumn processing is carried out after harvesting, when the trees have shed their leaves. They and dry grass are pre-raked and burned. Spraying is carried out twice with an interval of 2 weeks. Spray the drug along the trunk and branches, soon the growths will disappear.
Another method is used - a composition is prepared from an ash extract. Take 1 glass of ash, pour 3 liters of boiling water, insist for 3 days. Add water to 10 liters, dissolve 0.5 kg of ferrous sulfate. The affected branches and trunk are whitewashed with the tool.
Treatment of fungal diseases
Ferrous sulfate can fight the fungus. It has the properties of a contact fungicide, so the duration of action is limited to 2 weeks - the drug is washed off with rain and dew. Processing is carried out 2-3 times with an interval of 1 week.
The drug is not able to completely destroy the fungus, spores persist in places where the surface action solution does not penetrate. Gardeners use copper sulfate in the spring, and iron sulfate in the fall. Concentration - 3%.
Chlorosis
The disease occurs when there is a lack of iron and other trace elements. There are several types of the disease, but all are characterized by common symptoms:
- leaves shrink, turn yellow, curl, then fall off;
- the development of plants stops;
- flowers and fruits develop or dry out incorrectly;
- the bark and young shoots die off.
Iron vitriol copes with the disease. A 0.5% solution is being prepared, which does not burn the leaves. They are sprayed with it every 5 days until the green color of the leaves is restored. To prevent the disease, 10 g of the drug (0.1%) is taken in a bucket of water, the treatment is carried out every week.
Spraying the vine
The grapes are sensitive to temperature changes. After the first warm sunny days come in the spring, the growing season begins on the vine. Recurrent frosts can cause significant damage to the formed kidneys. They freeze, sometimes the plant dies.
To slow down development, grapes are treated with iron vitriol. When the warm days come, the shelter is removed and the plants are sprayed. A film forms on the vine, which inhibits the development of the buds for half a month. Grapes tolerate temperature fluctuations without significant losses. The concentration of the drug is 0.5-1%.
The second treatment with a 3-5% solution is carried out in the fall, when the leaves fall off. They are removed, the vine and the ground around the bushes are sprayed. This is a preventive measure aimed at preventing disease, while pests are destroyed. Both seasonal treatments enrich the plants with iron.
Foliar processing
Plants can suffer from iron deficiency. This trace element in an accessible form is contained in iron vitriol. Foliar dressing is carried out 2 times. In the spring, a solution is prepared from 50-100 g of the drug per 10 liters of water. For young trees and those with thin bark (peaches, pears), the concentration is less - 50 g. Sprayed before bud break, so as not to burn.
Read also: Why aloe is useful for men
Autumn processing time - after leaf fall. The dose of vitriol is increased to a proportion of 300-500 g per 10 liters. Trees are sprayed or coated on trunks and skeletal branches with a brush.
The vine is sprayed with a solution, the concentration of which depends on the time and disease. Chlorosis is treated with a 0.05% drug. Mildew, oidium, spotting - 3-5%. The same dosage for pest control.
Root dressing
Sulfate is not only sprayed with plants, but also introduced into the soil next to them. Iron root feeding is combined with watering. For fertilization, small doses are needed - 15 g per bucket of water.
The least amount of iron is found in alkaline soils, but in other types of soils it may not be enough. The following signs indicate a lack of a trace element:
- young shoots, thin vine grows poorly;
- smaller leaves, change color, fall off;
- fruits ripen poorly, late harvest.
These signs also indicate illness, but root feeding will not hurt.
Root dressing
Grape seedlings processing
In planted shanks, roots form more slowly than buds open. The task is to slow down the development of the aboveground part of the plant. The problem is solved by soaking the cuttings in a sulfate solution and processing the tops. Concentration - 0.5%. This slows down the development of the kidneys, during the specified time roots are formed. Treated cuttings, planted in spring, take root and grow better.
Soaking in a solution of ferric sulfate is also carried out for the purpose of disinfection. Eggs and phylloxera larvae, which can be brought with purchased seedlings, are destroyed. At the same time, the development of fungi and lichens is inhibited. Such processing of seedlings is an effective technique for cultivating grapes.
Spraying berry bushes and trees
Spraying with iron sulfate is carried out 2 times, when the buds have not yet blossomed on the plants or the leaves have already fallen off. Young trees are treated only in spring with a 3% solution.Adults also in the fall - 7%. The concentration is harmless to the bark, and while young leaves appear, the ferrous sulfate will wash off. Currants, gooseberries, felted cherries and other crops can be sprayed when they have leaves, but the limit is 1%.
The garden is preliminarily cleaned in order to deprive insects and fungal spores of wintering sites:
- remove fallen leaves, dry grass and dried branches;
- remove shoots with mechanical damage;
- digging up the soil.
Treatment of cuts and wounds on tree branches
Wounds and cuts in trees are open windows through which infectious and putrefactive microflora can enter. It is carried by mice, insects, snow, rain, air. Unwashed hands and dirty tools can also cause plant diseases. Fresh sections are treated with a 1% solution.
Wounds and cuts in trees
Wounds on tree branches are treated differently. Rotten wood is removed from the hollows, disinfected with a 10% preparation. After treating each wound, the instrument and hands are wiped with vodka, cologne or washed with soap.
During disinfection, living cells partially die, wounds heal worse. But such treatment is necessary if the tree is sick. This eliminates existing infections, prevents new diseases that can penetrate through the slices.
Application as fertilizer
Easily soluble iron is well absorbed by plants. For different crops, top dressing is carried out by application to the soil or by spraying. If the root method is used, compost and ferrous sulfate are scattered around a tree or bush, and the earth is dug up. Proportion of components: 10 kg of organic fertilizer and 100 g of vitriol. For foliar feeding, plants are sprayed with a mixture of 10 g of the drug per 10 l of liquid.
To stimulate photosynthesis, a chelate is used - a highly efficient fertilizer. It is sold at unusually high prices, or you can cook it yourself. The recipe is simple: in 3 liters of boiled water, which is cooled, 1 tbsp is poured. l. citric acid, add 1 tbsp. l. iron sulfate. The fertilizer is light orange in color.
They are used for 1-2 hours, since useful properties are quickly lost. They are fed by spraying or applied at the root along with watering, repeating several times during the season.
Chelate - high efficiency fertilizer
Basement and vegetable storage processing
Iron vitriol stops the development of fungi and mold. A film forms on the surface, the microflora is deprived of oxygen and dies. A 10% solution is applied, which is applied by spraying. You can add a little white clay to get a viscous composition. The surfaces are traversed twice with a brush, covering all areas. The most suitable time is autumn.
It is used to prevent the development of pathogenic organisms and to destroy them. Used in basements, cellars, granaries. They handle plastered and wooden surfaces, concrete, asphalt. Effectively used to protect outbuildings from harmful microflora - gazebos, greenhouses, wooden fences. To combat the house fungus, a solution of increased concentration is prepared - 15%.
Punctuality is the key to success
There are no universal spraying times. The summer resident builds on the climatic features of the region. Residents of the middle lane perform the manipulation 2 weeks before the onset of cold weather. The second condition is to wait until all the leaves fall off. There are no restrictions in the southern regions. In the fall, preventive treatment is performed at the end of November, and in the spring - after the temperature background has stabilized.


Precautions
The drug belongs to the 3rd class of hazardous substances, it is characterized by the following: low toxicity, fireproof, does not explode. To prevent it from causing harm, they adhere to safety rules: they work in gloves and a respirator. If a highly concentrated solution comes into contact with the skin or eyes, burns are possible.Rinse immediately with water and consult a doctor.
If the drug has entered the body in large quantities, the person suffers from general toxic effects, indigestion, irritation of the mucous membranes and skin. Doctors need an ambulance.
Autumn has come, which means that it is time to prepare the garden for winter. One of the most important activities is the autumn processing of trees and shrubs against all kinds of pests and diseases. For this, there are different drugs, one of them is iron vitriol. He will be discussed today.
Read also: How many flowers can not be given
Protecting trees
Iron vitriol is a 53% salt of iron and sulfuric acid (ferrous sulfate) in the form of crystals or greenish powder, from which a solution for irrigation and spraying is prepared.
Ferrous sulfate is used in the following cases:
- Fight against fungal diseases of many garden plants (raspberry anthracnose, cherry coccomycosis, scab, downy mildew and powdery mildew, oidium on grapes, gray rot).
- Prevention and treatment of chlorosis.
- Insect pest control.
- Fight against lichens that have settled on tree trunks.
- Treatment of wounds and hollows of trees.
- Basement walls processing.
- Destruction of the tree fungus.
Iron vitriol packaging. Photo from the site
Let's consider in detail the main situations.
How to breed iron sulfate for spraying trees in autumn
Initially, gardeners buy the drug in packaged form. Crystals are packaged in bags and should not stick together. On top of the package there is an instruction on how to prepare the solution, its proportions, spraying with iron vitriol within the specified time frame. In an open package, crystalline powder is stored for a certain time without losing its properties. The expiration date is indicated by the manufacturer.
The solution is prepared immediately before use. The concentration is maintained depending on the task:
- For surface treatment of wood from mosses, lichens, fungi, 3% of the active agent is enough (30 g per 10 l of water);
- The destruction of insects living under the bark and in the hollows requires an increase in concentration up to 5 percent (50 g per 10 l of water);
- Disinfection of cracks formed by hollows is performed with a saturated 10% solution (100 g per 10 l of water). This liquid is used to whitewash the trunks of old trees.


If the garden is old, you don't have to worry about the bark of the trees. Young seedlings are treated with only a 3% solution so as not to burn the branches and buds laid for the next year.
Gardeners consider the type of fruit tree before spraying:
- For stone fruits (plums, peaches, cherries, apricots, cherries, etc.), prepare a 3% liquid;
- For seed plantations (apple trees, pears, etc.), the concentration of the solution is increased to 5%.
A thoughtful and balanced approach to the use of a solution based on ferrous sulfate brings only benefits to the garden, protecting it from the attack of parasitic insects and plants.


Compatibility with other drugs


Mixing ferrous sulfate and solution with laundry soap
In general solutions with phosphate insecticides, other agents that decompose in an alkaline environment, ferrous sulfate cannot be used. It is not mixed with lime, preparations of magnesium, zinc, copper, boron, calcium. When added to the solution of laundry soap (for better adhesion to the surface), its reaction should be neutral.
What is ferrous sulfate: composition, formula, release form
FeSO₄ - this compound plays an important role in plant development.
Important! It participates in the oxidative and energetic process, contributes to the creation of chlorophyll, and also helps in the formation of the correct respiratory system of the plant.
So, the use of ferrous sulfate is mandatory for areas with calcareous and saline soils.In these places, where the pH values are more than 7 units, and calcium, magnesium and phosphorus exceed all norms, plants absorb iron with difficulty. In this case, ferrous sulfate is the best option to provide any garden crop with the necessary trace element.
The drug can be purchased at any garden store, as well as in construction centers. Iron vitriol packaging can be 200, 250 g or 300 grams. It is very rare to find a pack of 500 grams. The remedy is of two types:
- sulfate content not less than 53%;
- sulfate - 47%.
Interesting! Gardeners and gardeners most often use the 1st grade drug.
It is a powder in the form of crystals, greenish in color. It has many functions and capabilities in the farm. Basically, a solution for root and foliar feeding is prepared from it. Also, ferrous sulfate is added to the compost.
Watch the video! Why do you need Iron Vitriol in the country
How to properly dilute the drug
To obtain a solution, you can use only plastic or ceramic containers, but not metal containers. There should be no traces of any substances on its walls. To properly dilute the iron sulfate, first pour it into warm water, mix. Then, after 20 minutes, when it is infused, mix again.
The concentration will depend on the purpose of the application. It is convenient to measure the amount with a matchbox, a tablespoon or a teaspoon. A matchbox contains 22 g of the substance, 16 grams in a tablespoon, 5 g in a teaspoon.
For treatments, a 5 and 3 percent solution is prepared (take 500 g and 300 g per 10 l, respectively).
Preparation for processing
It should be noted that before the very action of protecting the garden with special means, careful preparation is necessary. First of all, it is essential to prepare materials and tools:
- Sprayer - gasoline models are distinguished by their high power, which makes it possible to cover a large area in one day. In addition, gasoline units can be refueled anywhere, however, they are more weighty and larger than battery ones. Battery models differ in the least level of hum during operation, but at the same time their performance is less than gasoline ones.
- Protective respirator or gauze bandage.
- Latex gloves.
- Spraying preparations (selected in any particular case).
- Protective glasses.
Popular: The main ways of grafting pears for a large harvest


It is necessary to carefully examine the constituent parts of trees (branches and trunks) for the presence of lichens and moss. If found, remove it with a wire brush. You need to inspect the attachment with which you will spray.
Treat trees completely, as a partial procedure may not give the expected result and harm the plant. Consider the consistency of the solution - it should be extremely homogeneous. Before pouring the solution into the apparatus, stir it thoroughly with water. If this rule is not met, there is a possibility of heterogeneity, which will lead to uneven processing - some of the trees are sprayed with plain water, and some will be exposed to the influence of an undiluted substance.
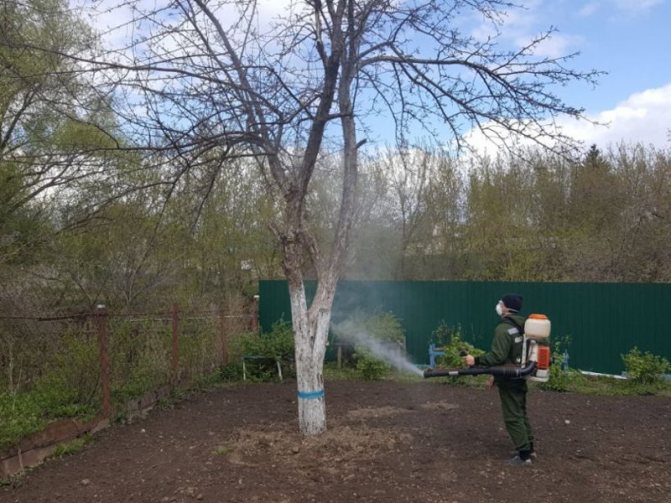
Spraying trees in autumn
Garden cultivation aims to remove diseases and parasites. Insects hide under the bark, in the soil, on the branches. As a result of disinfecting the garden in the fall, you can get a positive effect:
- the moss will fall off the bark;
- plants receive a dose of iron - prevention of chlorosis;
- the growth and development of plants will increase.
It is better to spray the garden twice a week apart. When working with chemicals, you need to protect yourself from harmful influences.


Antifungal protection of roses in spring
In spring, copper sulfate (copper sulfate, CuSO4) is often used to combat pathogenic fungi. When dry, it is small, bright blue crystals. Copper sulfate has pronounced antiseptic and fungicidal properties.It also fertilizes the soil, positively affecting plants and stabilizing metabolic processes.
The advantages and disadvantages of copper sulfate differ little from its "iron" counterpart. It is low-toxic, cheap, easy to use and prevents the development of pathogenic microflora, especially powdery mildew or septoria. The treatment of roses with copper sulfate in spring is carried out in the "green cone phase", that is, immediately before bud break. The average air temperature is about 5 ° C.


The rules are the same as when working with sulphate iron: only in dry weather with the "capture" of earth and mulch. Spraying with copper sulfate is carried out for preventive purposes, it will not cure already infected plants. For the treatment of rose bushes, they choose the second half of the day, towards the evening, then tender young shoots and hatching leaves will not receive a thermal burn.
For the processing of blossoming greenery and flowers, not pure copper sulfate is used, but its mixture with milk of lime. The fungicide was named "Bordeaux liquid".
How to make a working solution of copper sulfate
It is recommended to prepare a 10% masterbatch in advance, which is then stored in a dark place (up to 1 year) and diluted as needed. Copper crystals are dissolved in warm water so that the process goes faster, and the liquid turns out to be homogeneous. The working solution is made immediately before use in a glass container.
The optimum concentration of copper sulphate is 1%. If the rose garden was previously infected with a fungus - 2%, but no more. Having prepared the solution, it is immediately used, having previously filtered from the sediment.
Recipe for 1% Bordeaux liquid:
Mix 100 g of copper sulfate with 150 g of slaked lime. Dilute 10 liters of clean well water at room temperature. It makes no sense to store the learned fungicide, it will lose its disinfecting properties.
Warning: Spraying with copper or iron preparations is carried out in rubber gloves and a respirator; it is better to protect your eyes with special glasses.
Iron vitriol for non-infectious chlorosis
Sometimes plants can suffer from a lack of iron in the soil or an inability to absorb it. Non-infectious chlorosis occurs, which is expressed in yellowing of leaves and a general weakening of plants.
Hydrangea chlorosis
Iron sulfate will help to cope with this disease. To do this, prepare a solution at the rate of 30-50 g of the drug per 10 l of water and spray the plants several times in 5-6 days until the green color is completely restored. For preventive purposes, use 10 g per 10 liters of water.
In the next video, you will see how to prepare a solution and process plants if they get sick with chlorosis.
Pest Control Applications
Iron vitriol is fatal to many insects and their larvae, as well as eggs laid under the bark of trees. In early spring, when the buds have not yet woken up, you need to carry out the first treatment.
Caterpillars on a flowering tree
For this, a 5% solution is prepared (500 g of the substance is diluted in 10 liters of water) and the plants are abundantly sprayed or doused. You can also process fruit trees and shrubs in late autumn, after leaf fall.
This drug is very effective against apple sucker - the enemy of most fruit trees. With early spring spraying with a 3% solution (300 g of the drug per 10 l of water), almost half of the eggs laid by females die. It is necessary to spray both the trunks and branches of the tree and the soil under it.
When processing, it is important to correctly calculate the time.
When processing, it is important to timing correctly. Usually they are carried out in the middle of April - at this time the insects have already woken up and laid eggs, and the buds on the trees have not yet begun to bloom. It is important to understand that ferrous sulfate cannot destroy absolutely all pests, so you should not limit yourself only to its use.
Result from use
This powder is cheap.Despite this, it is very effective. The use of ferrous sulfate leads to an improvement in the condition of the tree bark, which becomes softer and more flexible - the leaves become larger, acquire an intense dark green tone, the color of flowers improves, the fruits significantly increase in volume, and the number of processes grows.
This is due to the fact that iron vitriol is a trace element that eliminates the lack of plant nutrition. The composition contains a lot of iron, which can be quickly dissolved in water. With a reduced concentration of the component in the soil, premature yellowing occurs, the disappearance of young tree shoots.
Extermination of pests
Ferrous sulfate is known for its anti-parasite properties. It instantly and permanently destroys parasites and their eggs with larvae. So, with a painstaking one-time processing, up to 50% of the eggs of apple sucker - the worst enemies of fruit trees - can disappear on the trunk.
For pest control, 5% is prepared. Branches, trunks, tree trunks are sprayed with the substance. A suitable period is considered to be the period of 1 half of April. If the treatment is carried out earlier, then the effect should not be expected, because the pests have not yet had time to lay eggs.


Preparation of solutions of different concentrations
We will not be able to give a single instruction for the preparation of a solution of ferrous sulfate. It simply does not exist; a solution of different concentrations is required to process different cultures. This can be seen from the table.


A 3% solution is suitable for processing stone fruit crops (apricot, cherry, sweet cherry, plum, peach). To prepare it, you need to take 300 g of crystalline fertilizer, dissolve it in a 10 liter bucket of water. Before the onset of cold weather, this solution should be sprayed on the trunk and bare branches of plants, trees and shrubs.
For the processing of fruit pome crops (grapes, pears, apple trees), a 4% solution is needed. In some cases, a 5 or 6% solution may be used. The solution is prepared according to the same recipe, only the amount of the fertilizer itself is increased - they take respectively 400-500-600 grams per 10 liters of liquid. Spraying trees with a solution from insect pests should be carried out in late autumn. The solution will help get rid of those insects that are hiding in the bark of trees.
Against lichen and moss rot, an autumn spraying is used with a 3% solution for stone fruit trees, and 5% for pome fruit trees. As a preventive measure, treatment with a 1% solution is sufficient. It is held in the autumn. It is enough to spray the damaged parts of the plant with the solution.
Trees are treated with iron vitriol as a top dressing. It is necessary for crops that suffer from a lack of iron in the soil. The fact that there is little iron in the soil is indicated by the chlorosis of young leaves, while the old leaves retain their color. You can spray trees in spring and autumn.
Gardeners who grow apple, grape, raspberry and plum trees often find that their crops suffer from iron deficiency. How to dilute the mixture? To feed the plants, you need to take 50 g of ferrous sulfate per 10 liters of water. It is necessary to process the soil and trunk every five days until the leaves turn green.
Iron vitriol can delay bud opening. For example, after processing with a 3-6% solution, the delay will be 7-10 days. During the spring frost, you can take advantage of this circumstance to delay development until it is warm.
Is it possible to do without chemistry?
Whether to treat the garden with chemicals is up to each gardener personally. Someone chooses organic principles of gardening and refuses any chemical spraying. In addition, this activity is quite laborious, considering that such treatments are recommended in autumn, spring, and during the summer.
| Therefore, resort to chemical treatments as a last resort and pay more attention to proper agricultural technology and the creation of a low-maintenance garden. |
Biological products are not suitable for the autumn processing of the garden. They should be applied in warm weather. They operate at positive temperatures of 12 ° C and above. Therefore, they will not be effective in autumn, and it is recommended to use them in spring and summer.
Fungal infections of the "queen of the garden"
You need to understand that it will not be possible to help whimsical beauties only by spraying with fungicides. A set of measures is needed to strengthen the immunity of plants, to enhance their ability to resist infections. The development of diseases is facilitated by unfavorable climatic factors - hot weather, excessive air humidity. Or improper care of rose bushes: shading of the site, thickening of plantings, excessive nitrogen fertilization or lack of calcium, lack of mulch.
The "neighbors" of the rose garden are also very important. Some representatives of the garden flora, by their mere presence, are able to scare away potential pests, acting better than any chemicals. Among them are marigolds, calendula, basil, clematis and daisies.


Often the fungus enters the garden with new purchased plants. Therefore, it is important to recognize the signs of infection in time and separate the affected specimens. The following table will help you to correctly diagnose.
| Types of fungal infections | Manifestation on roses |
| Powdery mildew (spheroteka) | Forms a whitish bloom on the leaves, which grows rapidly, capturing young shoots and peduncles. The greenery dries up, the rose bush as a whole looks pale, does not grow and bloom well. |
| Downy mildew (downy mildew) | This disease is difficult to recognize in its early stages. A mealy plaque appears on the underside of the leaf plates, and spots of different shades can be seen on the visible surface: reddish, black with a white center, yellow. Buds and young leaves darken at the edges, wrinkle and crumble. |
| Gray rot | Leaves and stems are covered with brown spots with a smoky fluff. Plaque grows rapidly, which leads to decay of the flower. |
| Rust | The bright orange spores of the fungi that cause the disease appear first on the stems and then on the leaves and buds. Stains that resemble real rust are visible from afar and cannot be overlooked. On the reverse side of the leaf, characteristic brownish tubercles appear. |
| Infectious burn | Otherwise, the disease is called stem cancer. The fungus develops only on the stems, forming transverse rings of red-brown color. Then the colored areas brighten, the bark cracks on them, ulcers appear. Affected plants die off. |
| Septoria | The leaves are abundantly covered with small dark brown spots that grow larger and brighter in the center over time. As the disease progresses, the stem is also covered. The eaten leaves fall off, the flower stops growing and gradually withers away. |


Even healthy-looking rose bushes must be treated with copper sulfate immediately after purchase.
Iron or copper sulfate: What to choose?
Both substances are classified as fungicides and have a similar effect. However, in the list of diseases against which these funds are used, there are differences:
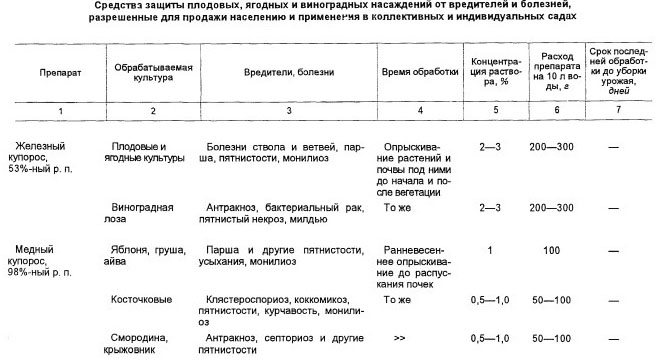

Fragment from the book "Handbook on gardening" (authors BD and LI Zhdanovich).
As you can see, the spectrum of action and the list of processed crops coincide. You can use either copper or iron sulfate. Dosages differ.
Main disadvantages
It is useful for a gardener to know about the shortcomings of the drug, so as not to be mistaken in the application:
- When stored in an open container, the drug is oxidized, and useful properties are lost. After spraying, the effectiveness lasts no more than 2 weeks.
- Solutions up to 1% concentration are ineffective. Higher levels of the drug can cause burns to the buds and leaves.Treatment with highly concentrated solutions is carried out in the spring, until the plants wake up, or in the fall, when the leaves have fallen off.
- Ferrous sulfate is useless against infectious diseases. It does not destroy pests that hide in the soil or bark for the winter.
- Vitriol is easily washed off with water. The treatment is carried out in stable dry weather when rain is not expected.
Precautions for use
Ferrous sulfate is relatively safe, but it is imperative to follow the rules for working with this substance:
- Read the instructions carefully before use.
- To dilute the product, use enamel, glass, plastic dishes.
- When spraying, wear rubber gloves on your hands, protect the respiratory system with a respirator, wear a hat and overalls.
- In case of contact with the eyes, the mucous membranes should be rinsed with clean, running water.
- After treatment, wash the skin with soap.
- Avoid contact with pets.
- Spraying should be carried out in calm weather.
Applications
The drug is used in the garden in the fall for the treatment and prevention of diseases. Green crystals or powder dissolves quickly in water. The resulting solution is used immediately after preparation, otherwise the concentration level of the active substance decreases. Botanists recommend doing 1-3 sprays of green spaces to solve the following tasks:
- whitewashing the trunk;
- elimination of spotting;
- prevention of the appearance of pests;
- prevention of grape diseases;
- introduction of missing iron into the soil;
- treatment of diseases: scab, powdery mildew, anthracnose, gray rot and so on;
- elimination of mechanical damage;
- restoration of bark on old trees;
- elimination of fungus in a greenhouse or at home;
- getting rid of the fungus in the storage of vegetables.
Processing is carried out after the leaves have fallen or have not yet appeared. Iron sulfate is a substance with a high acidity level. During processing, make sure that it does not get on the leaves.
On a note! Iron sulfate does not affect diseases that are caused by a bacterial pathogen.
Application
Iron sulfate is used in the garden to protect plants from a number of diseases:
- alternaria
- anthracnose
- coccomycosis
- clusterosoporia
- gray rot
- apple and pear scab
- downy mildew
- powdery mildew
- oidium grapes
Ferrous sulfate does not protect against bacterial infections. Practically not used in indoor floriculture.
You can spray trees and shrubs only in spring or autumn - strictly before bud break or after leaf fall and bare branches. Iron vitriol is not used as a fertilizer and for the treatment of infections on the green leaf - it causes burns of the leaf tissues - the acidity of a 3-5% solution is about pH 3-5 (very acidic reaction).


















































