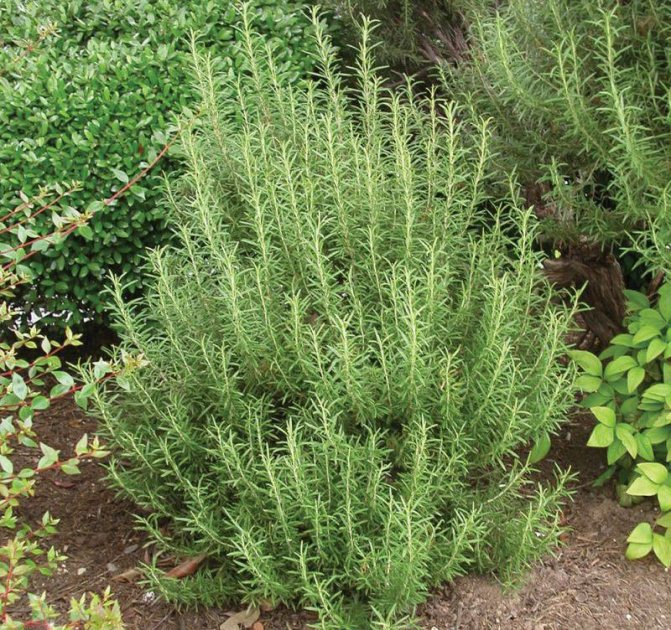
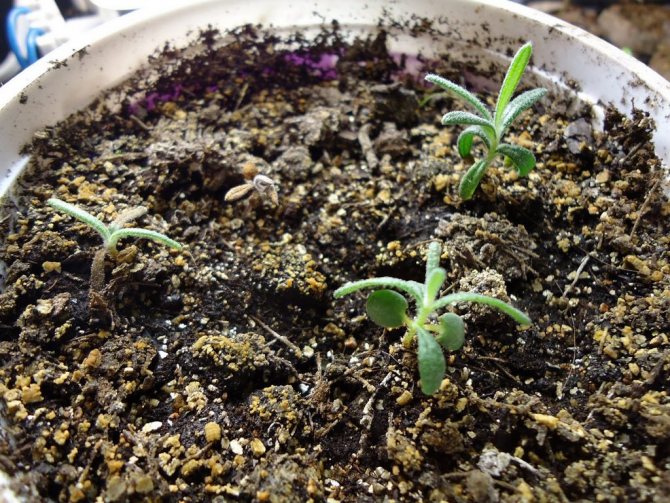
Planting rosemary at home: basic rules
Before we move on to the farming techniques of this overseas shrub, check out the basic characteristics of the plant.
- Rosemary came to us from southern countries, he loves warmth and sun very much.
- The plant prefers neutral or slightly alkaline loose, light soils.
- Best of all, the shrub propagates by cuttings and division.
- The easiest way to grow in our area is medicinal rosemary (ordinary).
- He needs moderate watering, he is resistant to dryness, but he feels better when the soil is constantly moistened by 40-50%.
- Rosemary does not grow well in drafts and shady places.
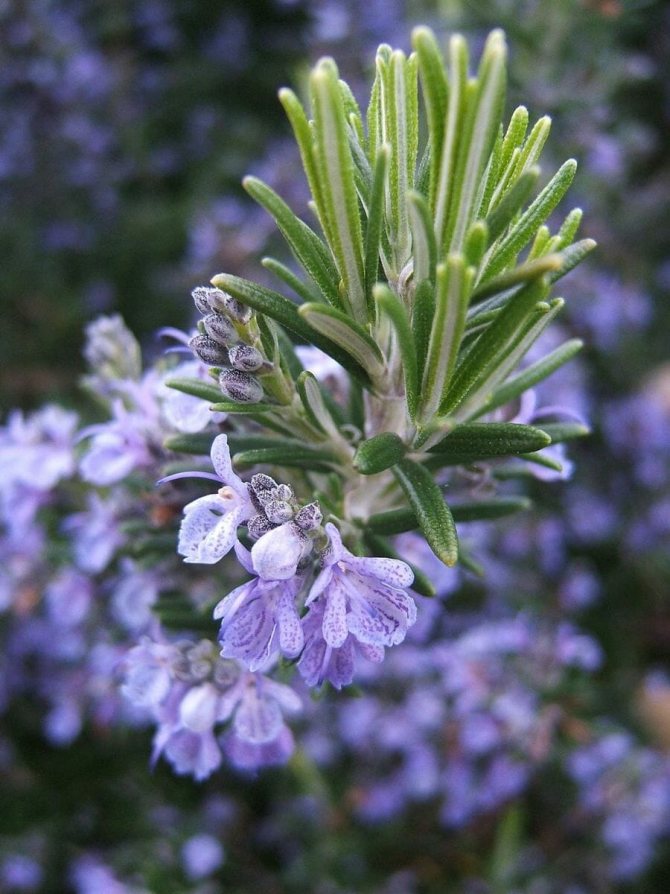
- He does not like the neighborhood with a rose and rarely blooms in her presence.
- Due to the high content of ethers, the bush is resistant to pests.
- At temperatures below -8-10 ºC, the grass dies, in cold regions it is covered with greenhouses for the winter.
- The bushes are planted in the beds, at a distance of 40-50 cm from each other, otherwise they will be cramped.
- If you water the rosemary frequently, it can begin to shed the leaves - this is a signal that it is time to reduce moisture.
- With insufficient watering, the leaves begin to turn yellow.
- Planting greens is best in late spring or summer.

Planting rosemary at home
Features of the care and cultivation of rosemary on the windowsill
You can grow rosemary from seeds. Although the method is lengthy and not always successful, the hostesses grow it.
Below are some basic guidelines for landing:
- Place the seeds in wet cheesecloth. They must lie in it for two days.
- Next, the swollen seeds are spread on moist soil, consisting of peat and sand. It is not necessary to deepen, just press down slightly. Wrap the container with cling film. To access oxygen, pierce holes in the film with a needle.
- After the seedlings appear, open the film and spray the sprouts.
- In a month, the sprouts should grow up to 10 cm. Up to 4 leaves should form.
- Then the seedlings are dived into separate containers. They are transplanted very carefully.
Seeds are sown in early March or October. After sowing in autumn, you can get fresh rosemary greens already in winter.
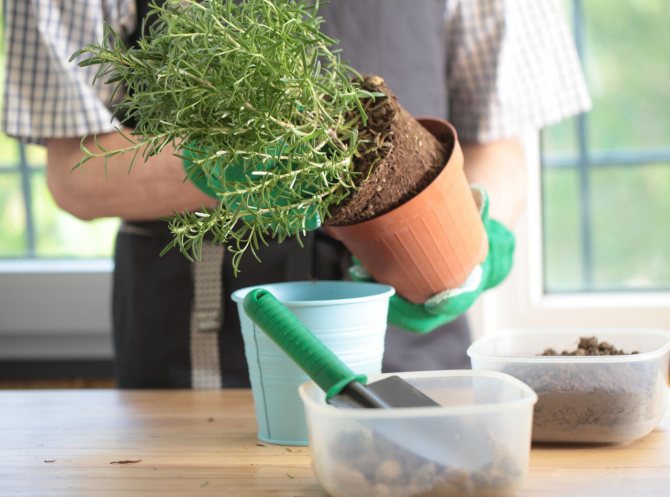
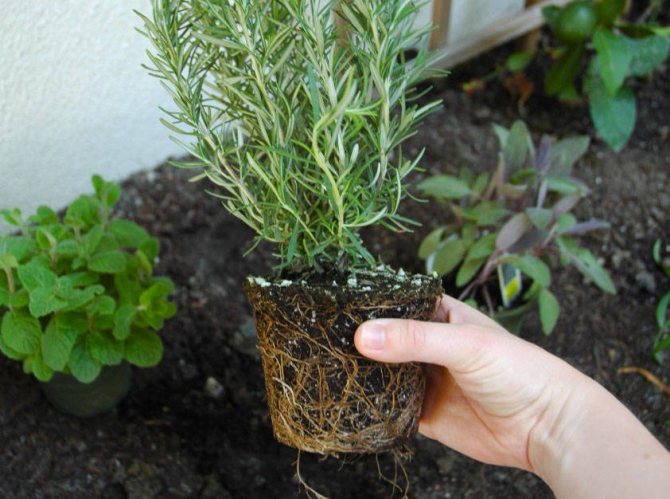
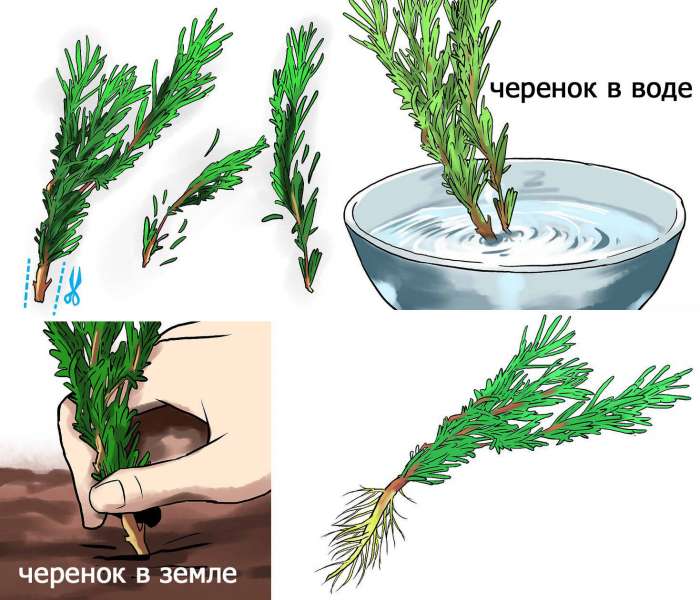
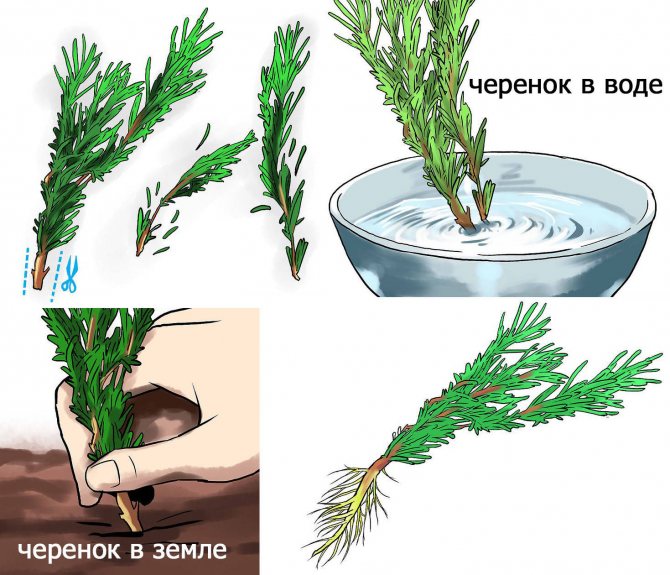
You can still grow by planting cuttings. From an adult bush, shoots are cut, which are lignified. The lower leaves are cut off. The cutting is rooted in moist soil, consisting of peat soil and sand. When the roots grow, the cuttings are planted in new containers.


Care activities
Soil for rosemary
In order for rosemary to develop well, you need to pick up the soil. The soil mixture should be nutritious, well-drained, and neutral in acidity. It is not allowed to use soil with acidic soil. The following soil composition is recommended: two parts of turf, one part of peat, two parts of humus, one part of refined sand.
Landing
The planting capacity needs a spacious one. At the bottom of the container, be sure to lay out a drainage layer of fine building material. Planting rosemary in a clay pots will be beautiful.
Lighting rosemary
The plant is very fond of sunlight. Therefore, you can safely place rosemary by the south-facing window. No high temperature required. In spring and summer, a temperature of 18-22 degrees will be sufficient. In autumn and winter, the temperature should be lowered.Especially in the winter months: up to 15 degrees. If rosemary is kept at high temperatures in winter, it may not bloom.
Humidity
High humidity is not required. But, you need to spray the plant. Spray with warm water.
Watering rosemary
Consider how often you need to water the rosemary. Watering is needed regularly: waterlogged soil is harmful to the plant as well as dry soil. Therefore, water the rosemary when the topsoil dries up. Watered only with soft water. Standing water or rainwater will do. In winter, watered with warm water.


Transfer
The plant needs to be replanted once every two years. They transplant in early spring, around the beginning of March. Transplant if the roots have filled the entire pot.
Earlier we talked about the description of Lofofora.
Top dressing
When rosemary begins to grow actively after hibernation, you need to make top dressing. Therefore, from March to October, every two weeks, organic and mineral fertilizers are applied. Fertilizers can be alternated.
Those who live in a private house can tolerate the plant and sunbathe. Only in the evening do not forget to take the plant home.
Pests, diseases of rosemary
- The plant is not afraid of diseases or pests. It happens when a spider mite settles due to dry air. It is recommended not to use chemicals immediately, but to wash the leaves with soapy water. Only when neglected are insecticidal agents used.
- If the watering is incorrect, then the leaves located below may turn yellow. This rosemary lacks water in the soil. But if the leaves began to fall off, then this is a clear excess of moisture in the soil.
- If brown spots are found on the leaves, spraying with copper sulfate will help.


Propagating rosemary in the garden
There are three main ways this plant propagates:
- division of bushes,
- grafting,
- growing from seeds.
The latter method requires patience and diligence. The fastest and easiest option is to divide an adult bush into small sprouts with roots and plant them. But cuttings also germinate quite successfully. You can buy any seedlings or seeds at a nursery or gardening store.
Cuttings can be obtained in an easier way: cut the tops of the shoots from any rosemary bush. Today it is not uncommon and grows in many gardens, parks, gardeners in the country. If you have your own plot, you will probably find rosemary from some of the neighbors and can ask for several shoots for breeding.


Propagating rosemary in the garden
How to grow rosemary outdoors
Spicy greens should not be planted in lowlands, places with stagnant groundwater, flooded areas. It should be a flat, draft-free surface. What is the shrub most afraid of? - acidic soils and clay sticky earth.
It is advisable to prepare such a substrate for rosemary: mix black soil with dry leaves, neutral peat and coarse river sand in equal parts. For 10 buckets of substrate, it is recommended to add 100 g of crushed lime.
The beds are prepared 8-10 days before planting rosemary, they are moistened in advance. In about 3-4 days, you can fertilize the soil with mineral fertilizing.
If you intend to grow rosemary as a perennial, then take care of the greenhouse right away. In the open air, the plant will not survive the winter. Although, if in your area the frosts do not fall below -10ºC, then it will be enough to remove the shoots and cover the roots with sawdust, hay or other natural insulation.
Many people grow rosemary in their dacha or plot as an annual, that is, they plant new bushes every spring, and in the fall they harvest the entire crop at the root.
Now let's take a closer look at all types of spice propagation.
Harvesting
Leaves are harvested only from plants that have reached the age of 3-5 years.It has been proven that it is at this age that rosemary leaves contain the largest amount of essential oils. The collection of young leaves is carried out during active flowering.


The harvest peaks in early July - mid-August. The crop is dried in the shade, and after completely drying it is stored in a dark, dry place.
Growing rosemary from seeds at home
The seeds are germinated indoors in early spring. This will require flower pots, boxes, or any other convenient container.
You can sow seeds directly into open ground, but, firstly, the air temperature must be warm and stable, and secondly, the shrub will only grow closer to autumn. If you want to harvest already in mid-summer, then sow the seed indoors at the end of February, and then transplant the seedlings into the beds in mid-April.
Rules for planting rosemary seeds
- Prepare a clean gauze, fold it several times so that you put the seeds on one part, and cover them with the other.
- Moisten the gauze with water and spread the seeds over it with a thin layer, cover them with the second side of the damp gauze.
- Use a spray bottle to moisten the gauze every day. The room where the seeds are located should be warm (+ 18-22 ºC).
- Prepare the soil for your rosemary planting in advance.
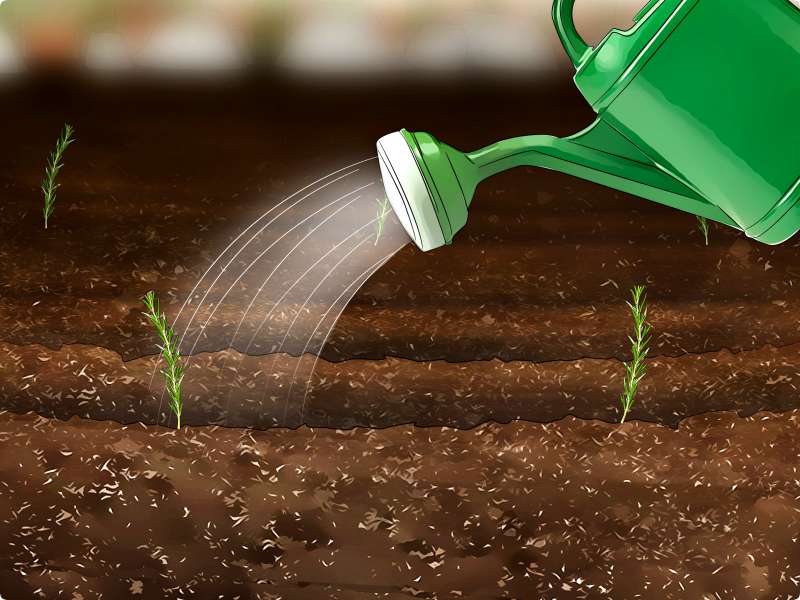
- After 3-4 days, carefully collect the seeds and sow them in a thin layer into the soil. Sprinkle with earth on top, then no more than half a centimeter layer. Moisten the soil through a spray bottle, cover the container with plastic, punching several holes in it, and remove to a warm place.
- Water the soil every other day, preferably always using a spray bottle to avoid blurring the thin surface layer of the soil.
- After about a couple of weeks, you should notice the sprouts breaking through. When seedlings emerge from the ground, remove the film and expose the boxes (pots) to sunlight.
- After about one and a half, two months, the sprouts will get stronger and will be ready for transfer to open ground. They are simply carefully dug up and transplanted into the beds.
- After transplanting, the soil is also immediately moistened.


Growing rosemary from seeds at home
Further, the standard care of rosemary is supported, which we will discuss in more detail below.
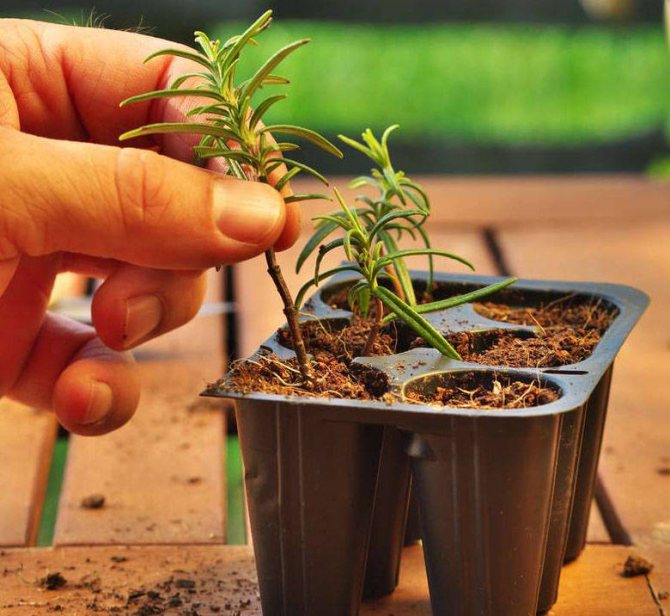
Growing rosemary at home using cuttings
Cutting rosemary is an easier way to grow a Mediterranean shrub. The tops of the shoots cut from an adult shrub will serve as cuttings. You can even use regular bunches of herbs purchased from the market as a spice.
Cuttings are carried out in April and early May.


Growing rosemary at home using cuttings
- Remove the lower leaves from the branches, exposing part of the stem.
- You can put them in water and wait for root formation, or plant them directly in the soil. But this must be done indoors, the seedlings will be ready for open ground only when they take root.
- If using water, change it every 3-4 days. After "sticking" the cuttings into the substrate, water them every other day, but not too abundantly.
- After about 3 weeks, the branches should form roots. As it happened, transfer them to the beds, pulling out the hole to the length of the roots. Water the soil and continue with your normal care.
Planting rosemary in this way produces more successful results, and the death rate of the plant is significantly reduced.
Features of growing in the Urals
In the middle lane, the plant can be covered with spruce branches, after mulching with sawdust. However, when growing rosemary outdoors in the Urals, it will have to be dug up when the temperature drops to 5 degrees above zero.


In winter, it is better to transfer the bushes to warmth.
Due to the fact that the flower has to be moved into the house every year, many doubt whether rosemary is a perennial or annual. But this should be done only at subzero temperatures in winter. It must be placed in a cool room and watered occasionally so that the earthy ball does not dry out.
Also, in the Urals, the soil warms up later than in the middle lane, so planting a plant in open ground should be planned for June, whereas in warmer climates, this can be done in May.
Planting rosemary by dividing
Unlike growing from seeds or cuttings, dividing is the easiest way to propagate rosemary in the garden. You can plant the twigs directly into the open ground.
The best time for dividing seedlings is June.


Planting rosemary in the garden by dividing
- Prepare the soil in advance in the beds as described above.
- Find or shop for an adult, lush rosemary bush with many shoots.
- Gently remove the roots from the ground, shake them off.
- Separate the shoots from each other along with the roots.
- Before deepening the sprouts into the soil, it is advisable to dip them in a growth-promoting mixture (available in stores).
- Dig holes in the soil to the length of the roots and plant the shoots.
- Moisten the soil and continue leaving.
How to grow rosemary from a twig
It is best to grow rosemary from cuttings. They can be purchased from a nursery or cut from a bush. This is done in late spring or early autumn.
Each cutting is planted in a pot of soil mixed with coarse sand and peat moss. The pot is placed in a sunny place, watered regularly.
Once the roots have formed, the rosemary can be transplanted outdoors. In colder climates, it is grown in containers. When planting in soil, choose land with good drainage. If the soil is damp, the rosemary roots can rot.
Rosemary: plant care at home
Its health depends on the proper care of this slightly capricious plant. Many people wonder how much to water rosemary, because opinions are often contradictory - some say that the bush loves moisture, others deny it. Let's figure out all the rules for caring for a shrub.
Watering
So, the most important question is: how to water the rosemary? Moisturizing greens growing in a garden or vegetable garden should be done often, but in moderation. Much depends on the climate.
On hot days, watering can be regular every other day, on cooler days - once every 3-4 days. The most important thing is that the soil does not retain moisture and has good drainage properties, for this it must be weeded periodically.
Loosening, weeding
Weed the soil under the bushes in the summer about once a month; by autumn, the frequency of loosening can be reduced. This must be done carefully, not too deep, so as not to damage the root system.
Weeds around the greenery must be removed.
Top dressing
Reinforced top dressing (once a month) of rosemary begins closer to the period of its flowering - at the end of April and continues until August. Mineral fertilizers alternate with organic ones.
With the beginning of autumn and all winter, the spice is fertilized once every 2 months.


Rosemary: growing conditions at home
Pruning
To make the shrub lush, in the spring, the upper stems can be cut, then it will take on a beautiful, spherical shape.
Once every few years, shoots are cut at the root in the fall to renew the greenery.
Diseases and pests
Rosemary, whether planted outdoors or grown indoors, successfully resists pests and diseases because of its antibacterial properties.
However, under certain circumstances, the bush can be affected:
- powdery mildew;
- spider mite;
- aphids;
- shield;
- whitefly.
If the plant has already undergone a disease, it is recommended to cut off all affected parts. After sanitary pruning, fungicide treatments are beneficial.


Growing rosemary at home will be possible for everyone who plant properly and organizes proper care. Using these simple guidelines, there should be no problems with growing. If in doubt, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the training video.
Sergey
Winter rosemary care
Winter is a difficult period for a heat-loving plant. In order for him to successfully survive the cold, it is advisable to build a plastic greenhouse for him, and cover the roots with sawdust, tyrsa, straw or hay.
Some dig up the bushes, transplant them into pots and bring them indoors for the winter. This is also an option for taking care of the spice.
Read more about growing rosemary on a windowsill here. Watering in winter is reduced to 1 time per week. If the plant is brought home, then you can water it a little more often - 2 times a week, in moderation.
Growing conditions for rosemary during the winter months depend a lot on the climate. In the southern regions, where winters are short and not frosty, the shrub does not need any special care and winters well on its own in the garden or vegetable garden.
So we examined everything about the propagation of rosemary, about planting and care in the open field. Now you can independently practice the cultivation of this spicy, aromatic shrub, which contains a huge amount of useful substances and is used not only in cooking, but also in folk medicine. If this plant "starts" on your beds - consider that you are growing a green first-aid kit.
How rosemary reproduces
Zinnia - outdoor cultivation and care
Rosemary reproduces in several ways. Germination of seeds and rooting of cuttings are especially popular with gardeners. Reproduction methods are also used by air layering and dividing the bush.
Germinating seeds
How to plant rosemary in the country using seeds:
- Prepare containers for planting with loose soil.
- The seeds are soaked in warm water a few hours before the procedure. They should swell.
- The soil is moistened in advance.
- Seeds are placed in prepared pots to a depth of no more than 4 centimeters.
- The container is taken to a warm and dry place. It is important to keep the temperature within 25 degrees and avoid drafts.
After planting, you periodically need to spray the ground when the top layer dries out.
With proper care, seedlings will become visible in 2-3 months. You can transplant to a permanent place when they get stronger. Usually their length is about 6 centimeters.
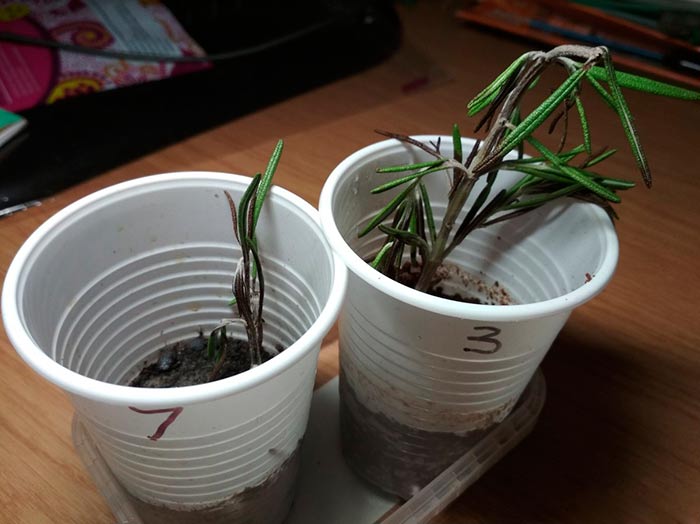
Rooting cuttings
Cuttings for planting are cut at the end of September. In this case, they take small branches and divide them into parts so that the length of each does not exceed 10 centimeters. They must have at least three internodes.


Cuttings
Cut cuttings are treated with an agent that stimulates root growth and placed in a nutrient soil. The soil must be periodically moistened, not to dry out, but also to avoid excessive watering. After new leaves appear, young plants are planted in separate pots.
Note! You do not need to take large containers, the diameter should not exceed 10 centimeters. 1-2 weeks after transplanting, it is better to remove the tops of the plant so that they give new shoots and a branchy shrub forms.
Air layering
It is very easy to propagate with air layers. You just need to bend the branch to the ground and sprinkle it with soil, fixing it in place. If this is not enough, you can put a stone on top. The soil around you must be moistened.
When roots appear, the plant is ready for independent life. You can carefully cut it off and transplant it to a permanent place. Usually, the roots become visible in 1.5-2 months. Depending on weather conditions, the date may change.
Dividing the bush
Dividing the bush is more suitable for indoor plants. Rosemary must be removed from the container, damaged areas removed. Carefully divide it into 2 or 3 parts, make sure that both shoots and roots remain on each. Treat the cut sites with coal powder, this will exclude the penetration of infection, disinfect. After that, new plants can be planted in separate containers or a place on the site, if it grows in the garden.