Category: Garden Plants
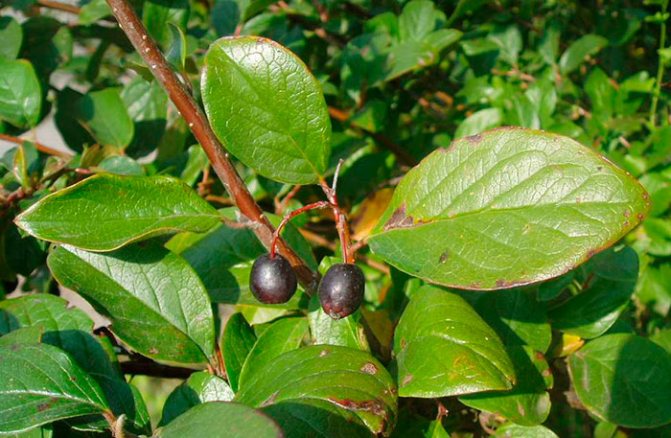
Cotoneaster (lat.Cotoneaster) - a genus of evergreen or deciduous slow-growing shrubs, as well as medium-sized trees of the Pink family. The name of the shrub was compiled by the Swiss botanist Kaspar Baugin from two Greek words: cotonea, which means "quince", and aster - "having a similar appearance." This is explained by the fact that the leaves of one of the cotoneaster species have a strong resemblance to the leaves of quince. The genus Cotoneaster is represented by more than a hundred species, varieties and varieties that grow naturally in North Africa and Eurasia. The poorly informed often believe that the dogwood and the cotoneaster are one and the same plant, and in vain they wait for delicious berries from the cotoneaster. In fact, apart from the consonance in the name, there is nothing in common between these plants - they are generally from different families.
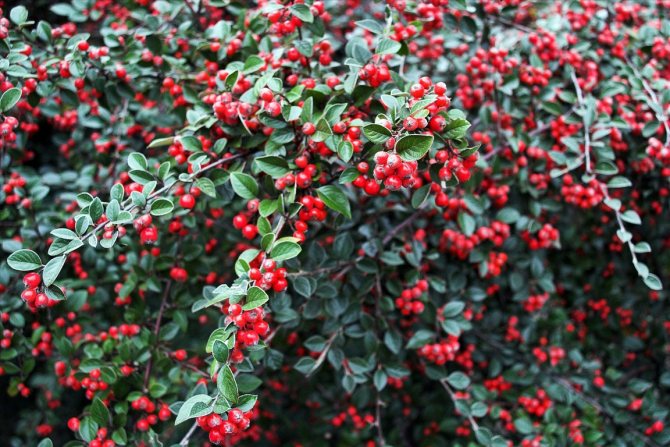
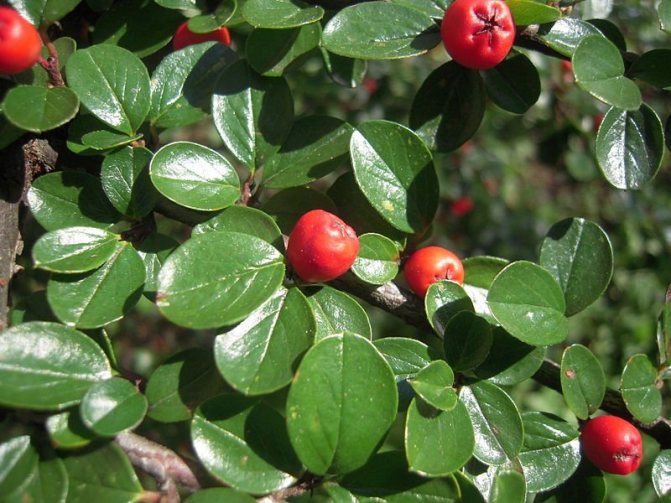
Cotoneaster berries look like a tiny apple and are completely inedible, unlike the juicy dogwood fruits. The value of the cotoneaster is in its decorative qualities, which make it possible to use the plant as a spectacular element of the garden throughout its long life.
Content
- Listen to the article
- Description
- Planting a cotoneaster When to plant
- How to plant
- How to care
- How to propagate
- Preparing for winter
- Cotoneaster brilliant
Sowing cotoneaster seeds

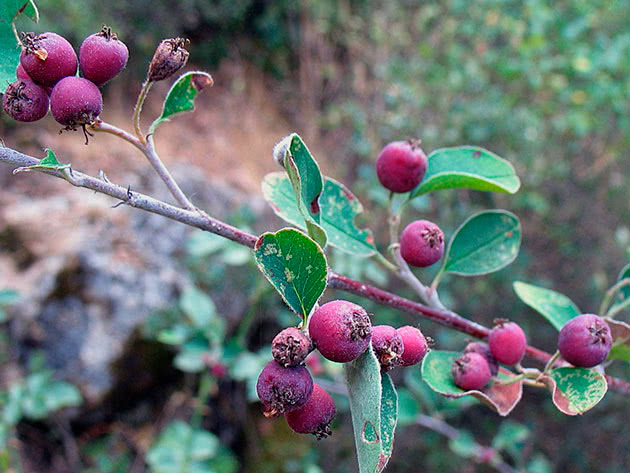
This beautiful shrub bears abundant fruit with red bead berries, in which the seeds are hidden. Cotoneaster can be propagated by sowing them, but this is not the most productive method. The seeds germinate very poorly, a significant part does not germinate, and the sprouts themselves slowly grow in growth. To get a sapling of sufficient size, you will have to be patient and wait 3-4 years. Cotoneaster propagation by seeds is more often practiced by breeders engaged in obtaining new varieties of plants.
If difficulties are not scary and there is a desire to try this method, then you need to follow these tips:
Planting and caring for a cotoneaster
- Landing: in spring, before the buds swell or in autumn, in leaf fall.
- Bloom: in June.
- Lighting: bright sun or partial shade.
- The soil: any: the necessary nutrient mixture is laid directly into the pit when planting.
- Watering: in the season with a normal amount of rain, you can not water at all, and only if there is no rain all summer, the plant is watered once every two weeks, spending 7-8 buckets for each adult bush.
- Cropping: sanitary - at any time, shaping or rejuvenating - in the spring, before the buds swell. Top dressing: in April-May - nitrogen fertilization, before flowering - potassium-phosphorus fertilizer, and in the fall the trunk circle is mulched with peat.
- Reproduction: seeds, cuttings, layering and dividing the bush.
- Pests: apple aphids, scale insects and spider mites.
- Diseases: fusarium, powdery mildew.
Read more about growing a cotoneaster below.
Care
Dogwood is considered an unpretentious horticultural crop, therefore, even after planting young seedlings in open soil, they do not require complex care. The main thing is not to forget to water the seedlings well. In the first year, this is done 2 times a week, the next two - about 1-2 times a week.


Subsequently, watering is carried out as needed, as the substrate dries. The procedure is carried out so as to completely wet the top layer of the soil, about 50 cm deep. In addition, as the bush grows and develops, it is recommended to carefully cut it off.
Pruning dogwood
Shrub pruning consists in creating a tall, high-yielding bole, about 50 cm high. The main basis of such a shrub is about 5 skeletal branches arranged in several tiers. Pruning is often started from the 3rd year, all lateral processes are cut off on the bush, keeping the top with several rudiments of skeletal branches.
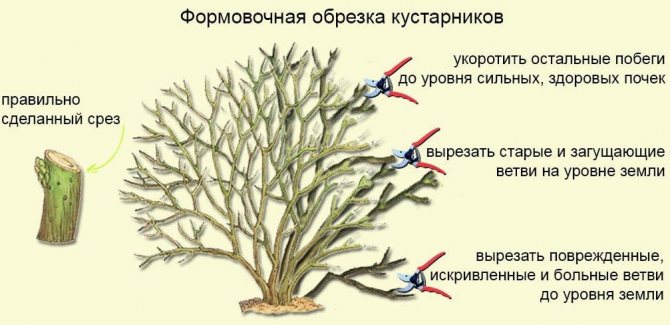

As the plant grows and develops, only the most powerful and active branches are left on it, all other shoots are removed. After several seasons of such care, the bush will acquire a characteristic tiered structure, after which the skeletal branches should be cut to one length and shortened by at least a third.
Important! Shrub formation is best done in spring, the most suitable time for sanitary cleaning is the second half of autumn.
In the future, the dogwood retains the acquired crown shape, therefore, only sanitary cleaning is carried out for adult bushes. In this case, all unproductive, damaged or withered shoots, as well as all unwanted growth, are subject to removal. Around the 20th year after planting, the shrub should be rejuvenated. During the procedure, it is recommended to cut off all branches that are about 4-6 years old, this will stimulate the bush to form many young shoots.
Shrub cotoneaster - description
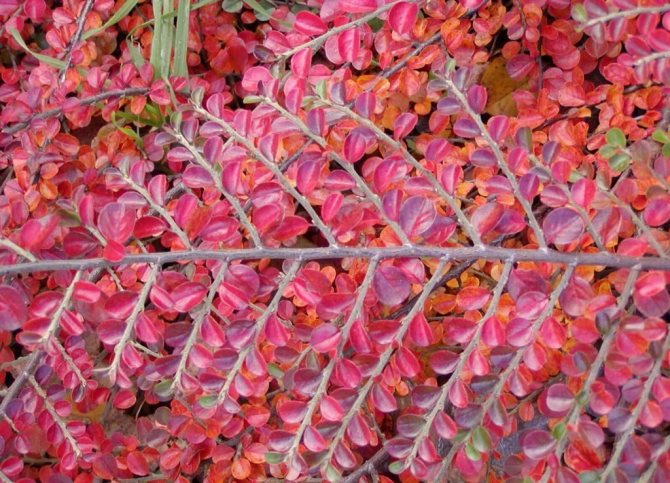
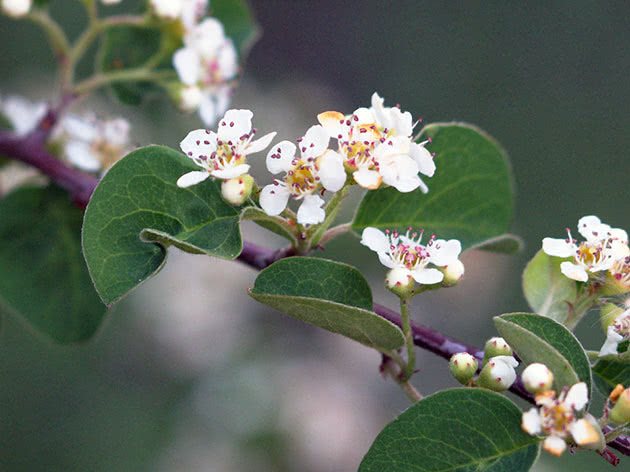
Cotoneaster bushes can be deciduous or evergreen depending on which species you are growing. Most of the cotoneaster is a densely branched shrub used for landscaping streets. A hedge from a cotoneaster is a fairly common picture in our cities. The leaves of this plant are small, simple, alternate, ovoid, whole-edged, in the summer of a dark green hue, in the fall they acquire shades of red. The cotoneaster blooms with small pink or white flowers - single or collected in corymbose or racemose inflorescences.
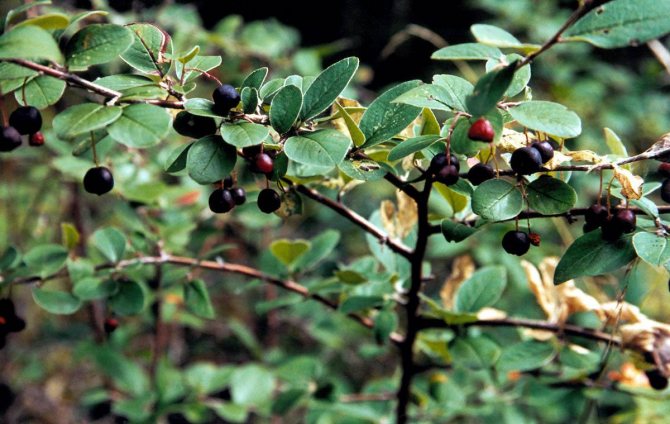
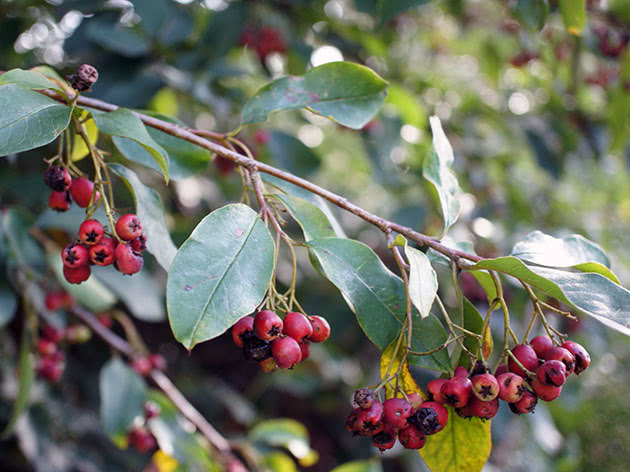
Small fruits of the cotoneaster are black or red. For better or worse, the cotoneaster grows very slowly and lives in one place for up to fifty years, or even longer. There are about forty types of cotoneaster in culture, however, in addition to species of plants, various forms and varieties of shrubs are widely used in garden design. Among the most popular species are brilliant cotoneaster, whole-edged and black-fruited cotoneaster, which have high winter hardiness.
- How to store bulbs in winter
Amateur gardeners love the cotoneaster for its unpretentious care and undemanding growing conditions. As for professionals, the cotoneaster in landscape design is most often used by them as a hedge.


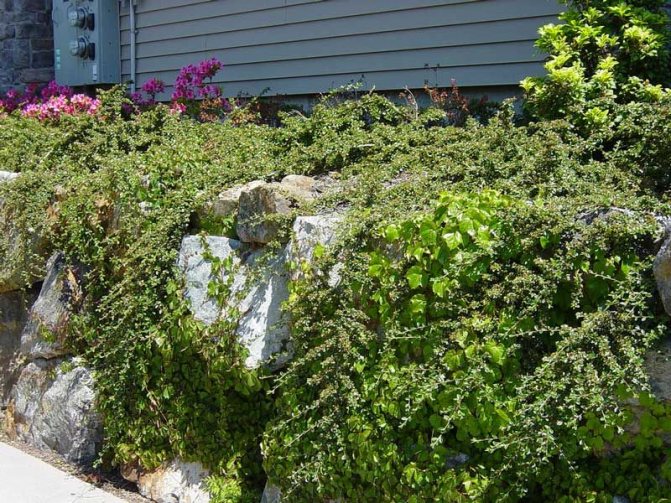
Horizontal cotoneaster in landscape design
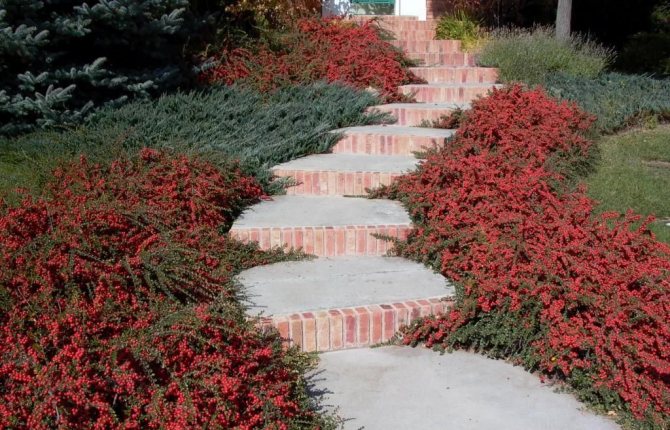
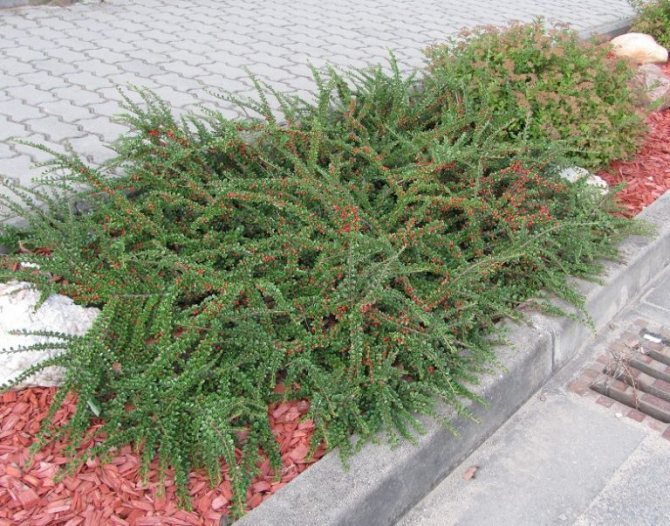
In gardening, it is the horizontal cotoneaster that is very much appreciated as an ornamental plant. The horizontal cotoneaster in landscape design can be seen in various photos. These are most often hedges and various structures. And you can also often use small varieties in the form of curb structures that adorn garden paths.
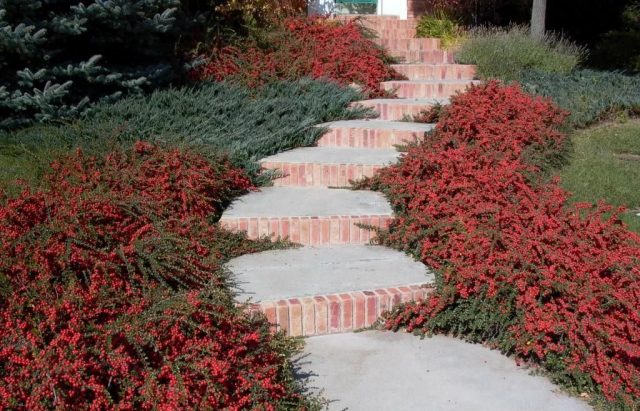


In group plantings, the dogwood shrub goes well with various conifers.
Used in landscaping parks, as well as sidewalks and recreation areas around the world. If you use a cotoneaster in rock gardens, then the middle tier is chosen for it.
It also looks great against the background of stones and rocky hills, and therefore is used in various combinations.
Planting a cotoneaster
When to plant a cotoneaster
In open ground, cotoneaster seedlings of almost all types are planted in spring, when the ground thaws, but the buds on the trees have not yet had time to open. It is permissible to plant a cotoneaster in the fall, in the time interval between the beginning of massive leaf fall until the first frost - this time is most suitable for planting brilliant and black cotoneaster cotoneaster.
Cotoneaster shade-tolerant, you can grow them in partial shade, and this will not negatively affect the decorative qualities of the plant, but the cotoneaster reaches its best shape in open sunny areas. The plant is undemanding to the quality of the soil, especially since the composition of the soil optimal for the growth of the cotoneaster can be introduced directly into the pit for planting.


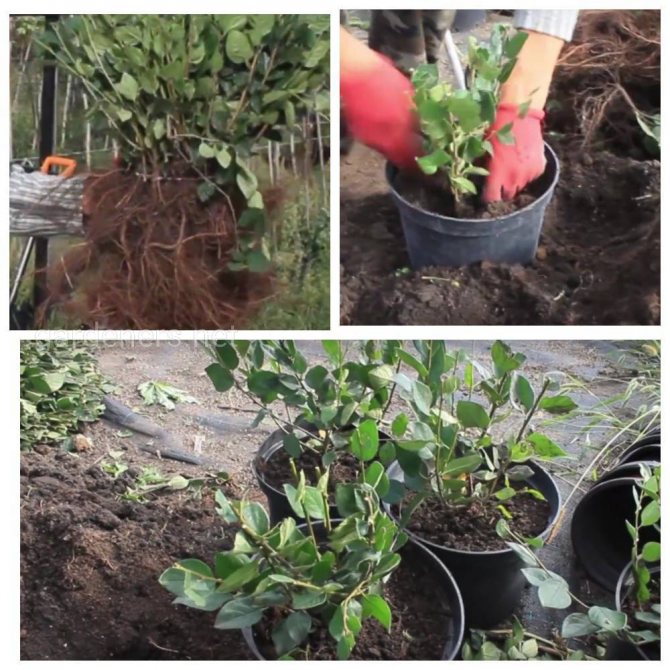
How to plant a cotoneaster
The size of the pit for the cotoneaster should be approximately 50x50x50 cm, and it is necessary to fill the pit on top of the obligatory twenty-centimeter layer of broken brick or gravel with a soil mixture of the following composition: one part of peat, sand and humus and two parts of sod land. It will be nice if you add 200-300 grams of lime to the soil mixture. The distance between the cotoneaster bush and any other plant or structure should be between 50 cm and 2 m, depending on the expected crown size of an adult plant. When burying a seedling, make sure that its root collar is strictly flush with the surface.
After planting, the soil is tamped tightly, watered, and the trunk circle is mulched with a peat layer 8 cm thick. Planting a cotoneaster shining as a hedge for greater convenience is not done in pits, but in a trench.


Cotoneaster pests
As mentioned above, cotoneaster is one of the most resistant plants and in the rarest cases can be sick or suppressed by insects. But at the same time, sometimes you can find green apple aphids on young shoots and on the lower part of the leaves. It is not difficult to notice this, since when damaged, the leaves wrinkle, the shoots are bent, and often dry up. There is also a white moth - it mines the leaves, then thin narrow passages appear on them. Some damage can lead to drying out not only of the leaves, but also of the branches, often this is a consequence of the scale insect, mite or plum sawer.
Caring for the cotoneaster
How to care for a cotoneaster
Planting and caring for a cotoneaster is very simple, and even if you don't know how to grow a cotoneaster, your intuition will tell you what to do in a difficult situation. Fortunately, such situations may not arise at all. The main thing that you need to know about this plant is that it does not tolerate excess water in the roots, the cotoneaster will survive all other natural phenomena with dignity. Based on this, in principle, there is no need to water the cotoneaster, since even in dry summers it can do without water for a long time. If it is dry all summer, water the plant every two weeks, water consumption for an adult plant is 7-8 buckets.
After watering or rain, you need to remove weeds from the site and shallowly, by 10-15 cm, loosen the soil on the site. Caring for a brilliant cotoneaster does not involve watering as regularly as washing the plant from dust under running water, especially if the hedge from the brilliant cotoneaster replaces the fence facing the street.


Fertilizing cotoneaster
In the very first warm spring days, the cotoneaster is fed with nitrogen fertilizer. It can be urea, diluted in an amount of 25 g in a bucket of water, or granules of prolonged action of Kemira-universal. Even before the plant blooms, it is fed with 15 g of potassium and 60 g of superphosphate per m². At the end of the season, the soil around the bush is mulched with peat.
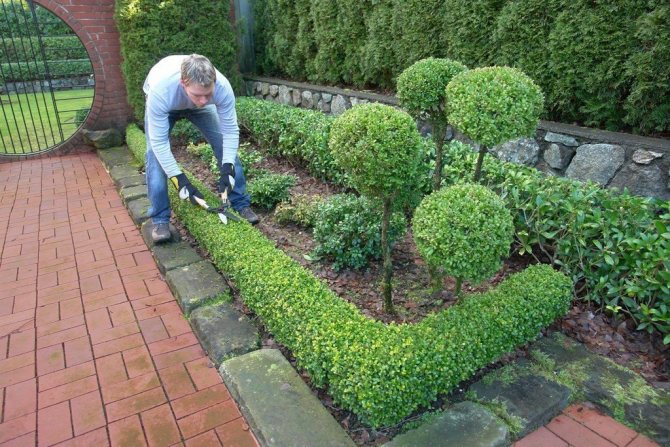
Cotoneaster pruning
The cotoneaster responds well to pruning, being just the plant from which designers form bushes of all sorts of shapes - cones, prisms, hemispheres and more complex shapes. It is allowed to trim the annual shoot by a third of the growth.Such curly trimming requires certain skills and special tools. After formative pruning, the shoots grow back, keeping the shape given to the bushes.
Cutting a cotoneaster can also have a sanitary function, because sooner or later old, sick, broken or thickening branches appear on any bush. In the end, with age, you have to do a rejuvenating pruning of the cotoneaster. Sanitary pruning can be done at any time, and rejuvenating and shaping pruning in the spring, until the buds open.


Cotoneaster pests and diseases
The cotoneaster has a stable immunity to diseases and harmful insects, but sometimes an apple aphid appears on the lower side of the leaf plate of the plant, which causes the leaves to wrinkle, and the shoots bend and dry out. From time to time, the cotoneaster gets from the tick and scale insects. You can destroy harmful insects by processing herbal decoctions - makhorka, tobacco, yarrow. Or a stronger remedy - insecticides sold in specialized stores. Of the diseases, the plant is most often affected by Fusarium, which is treated with fungicides, after cutting out the diseased areas to healthy tissue.
Diseases and pests
Cotoneaster practically do not get sick and are not attacked by various insect pests.
Of the diseases that appear on the bushes of this culture, it can be noted fusarium... When this disease occurs, the affected parts of the plant are cut out to healthy tissue and burned. Can be additionally treated with fungicides. Prevention of fusarium is the correct choice of planting site and care technology.
Of the pests on the cotoneaster can be found apple aphid, shield and ticks... Combined insecticidal agents are used against all these pests: Actellik, Akarin and Bankop. You can also carry out treatment with insecticides of systemic action: Aktara, Tanrek, Biotlin.
Reproduction of cotoneaster
How to propagate a cotoneaster
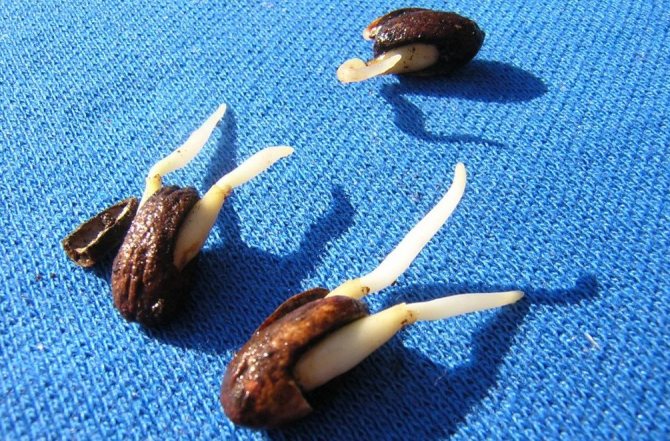
Different types of cotoneaster reproduce in different ways, however, those who decide to choose the cultivation of cotoneaster by seed should be aware that cotoneaster seeds have a low germination capacity, so they need to be sown with a margin. They do this before winter, so that the seeds undergo natural stratification in the cold soil, and the cotoneaster seedlings will appear only next spring. We will tell you about another method of stratification in the section on seed reproduction. Cotoneaster reproduces vegetatively - cuttings, layering, dividing the bush.


Seed propagation of cotoneaster
The cotoneaster fruits are harvested and slightly dried to make the flesh easier to separate. Then the seeds are removed from the berries and washed with water. The washed seeds are immersed in a glass jar with water: those suitable for sowing will sink to the bottom, and the seeds floating on the surface are completely useless. After that, the seed is mixed with sand and peat, moistened, placed in boxes and stored until spring at a temperature of about 0 ºC. During this time, the seeds will undergo stratification, and they can be planted in the ground.
- How to store bulbs in winter
However, there are no guarantees that even stratified seeds will sprout and give seedlings, so it is better to resort to a more reliable method of reproduction of the cotoneaster - vegetative.
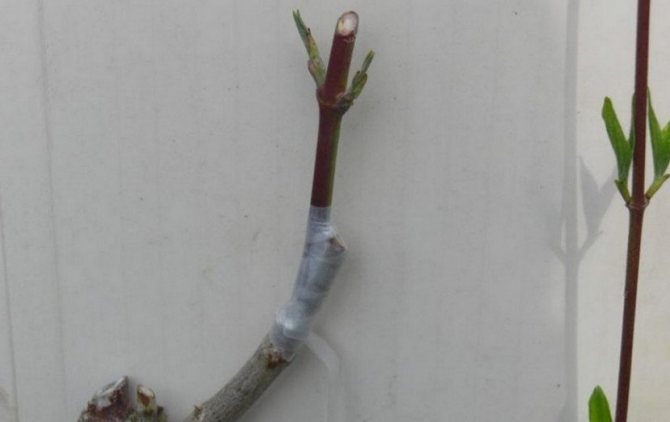
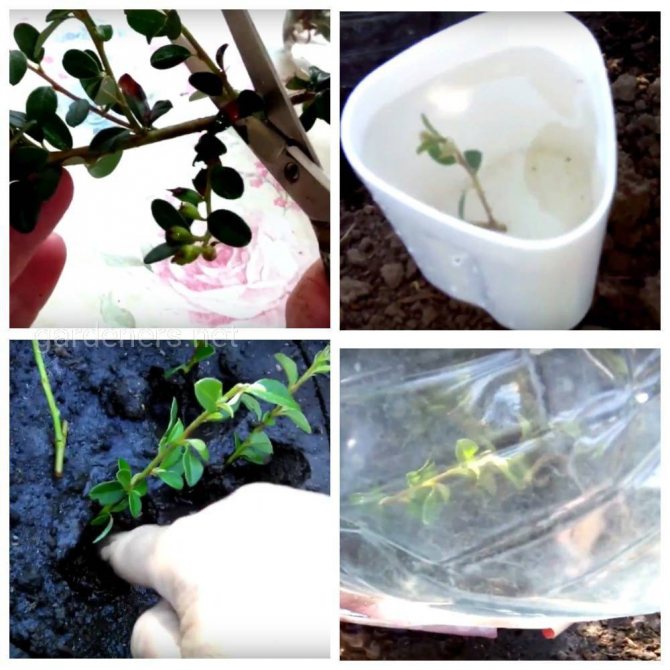
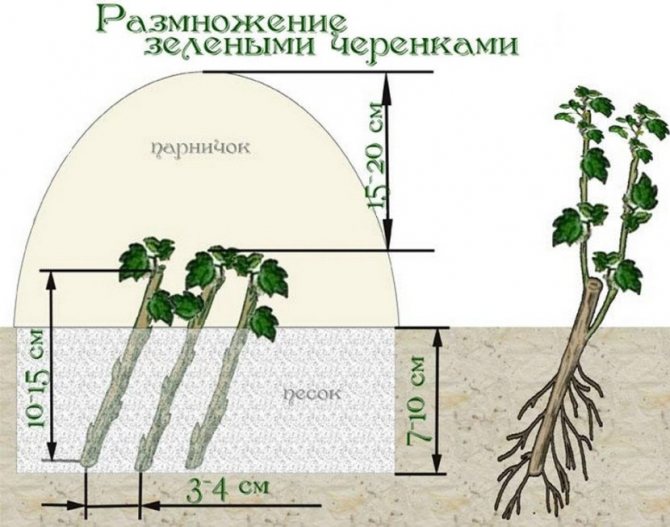
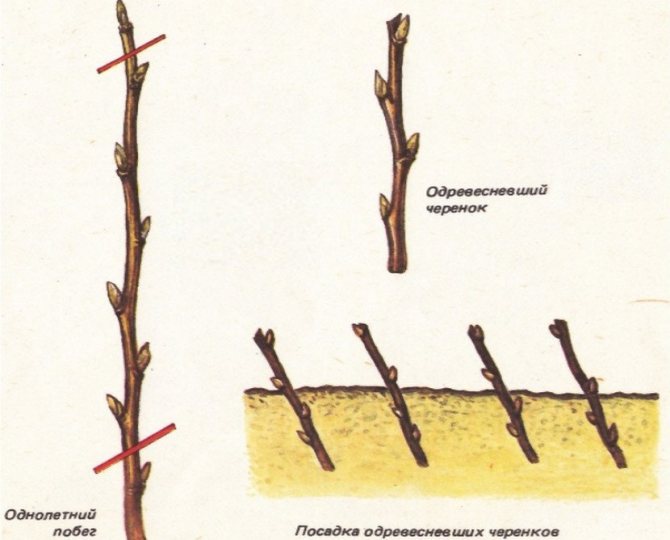
Reproduction of cotoneaster by cuttings
After cutting the bush, there are segments that can be used to reproduce the brilliant cotoneaster, but it is still better to cut the cuttings for rooting in June. First, they need to be cut into water for a day with a growth stimulant dissolved in it, after which they are planted at an angle of 45 ° on a garden bed in a light loose soil consisting of sand and peat, watered with warm water and covered with a large plastic bottle with a cut neck. On hot days, the bottle is removed so that the plants do not spill out. You can water the cuttings without removing the bottle.
The following spring, rooted cuttings can be planted in a permanent place.
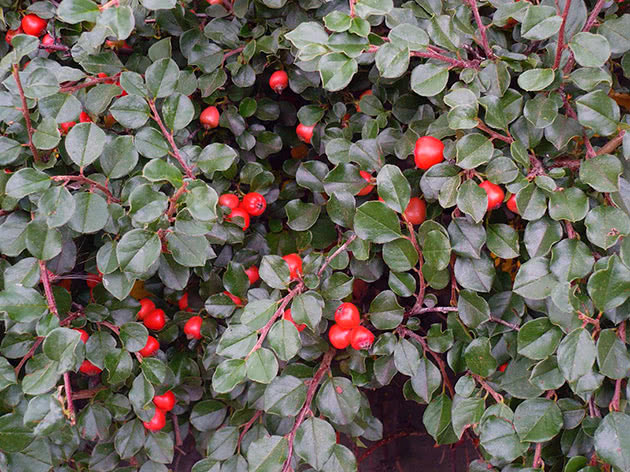


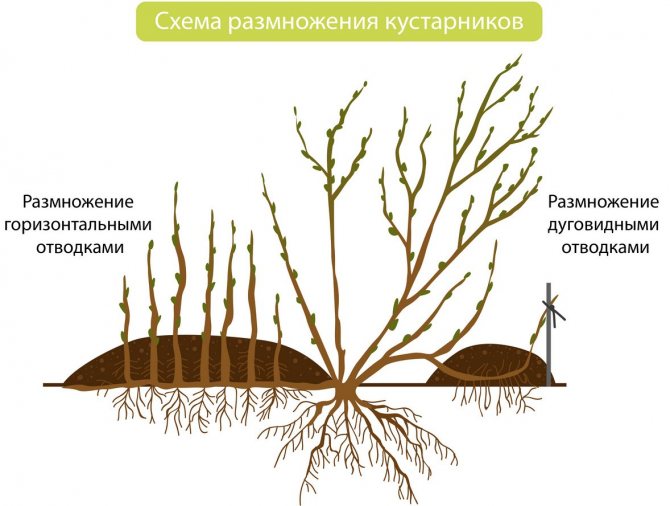
Reproduction of cotoneaster by layering
In this way, mainly ground cover species of cotoneaster reproduce, for example, creeping and horizontal, since their shoots are located close to the soil or in contact with it. Select young shoots, pin them to the soil with metal staples or hooks, and sprinkle the attachment with humus. Next spring, chop this branch off with a shovel at the base of the mother bush and transplant the layers to the place that you have assigned to it. Reproduction by layering is the easiest and most reliable way to propagate a cotoneaster.


Reproduction of the cotoneaster by dividing the bush
Mature bushes, which have grown a lot, can be divided into parts, followed by rooting of the divisions. This is a fast and efficient way. It is possible to divide the bush both in the spring and in the fall, immediately transplanting the parts obtained during the division into new places.
How to propagate a cotoneaster by layering
For a cotoneaster ground cover type, propagation by layering is ideal. In such plants, shoots spreading above the ground can reproduce independently. To streamline and speed up the process, select the shoots of the current year and use metal staples to attach to the surface. Sprinkle humus on top. In the spring, the rooting site is carefully dug out, the branch is separated from the donor bush and transplanted to a permanent place. This method is considered one of the best: the shoot, while rooting, receives the necessary nutrition from the donor thanks to an adult, well-developed root system. At the time of transplanting, you have a strong and healthy seedling.
Cotoneaster in winter
Cotoneaster in the fall (preparation for winter)
Almost all cotoneaster are cold-resistant and winter well without shelter, it is enough just to mulch the soil around the bush with peat, but if you are afraid that your cotoneaster will freeze, bend it to the ground, fix it in this position and throw dry foliage.
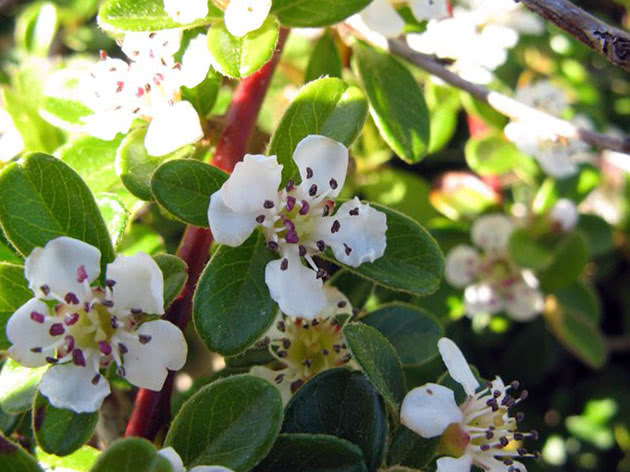


Wintering cotoneaster
In the event that the winter is too frosty and snowless, you can additionally cover the plant with spruce branches or covering material, but if it starts snowing, remove the shelter and let your bush winter under a layer of snow. Black cotoneaster, whole-edged and shiny cotoneaster, which are most often grown in our climate, have high winter hardiness and can withstand even significant frosts without shelter.
Variety of varieties
The horizontal cotoneaster is the most popular and valuable species grown in gardens for a long time. This plant has several varieties that have their own unique characteristics. The most famous of them:
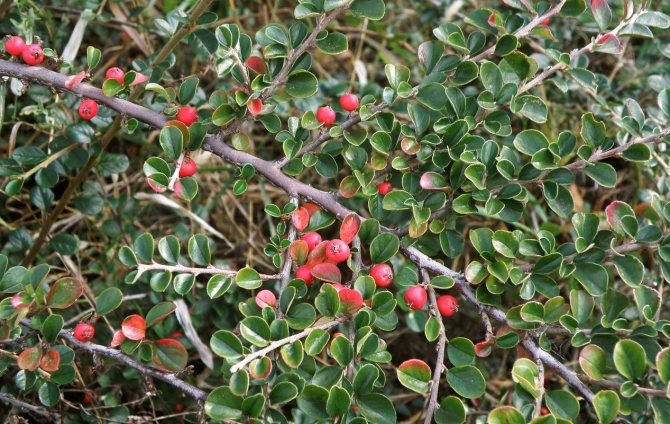


Common cotoneaster. This variety is distinguished by the shiny surface of the leaves and the black color of the fruits.- Multi-flowered is a shrub that grows up to 3 meters. Light green leaves change color to crimson in autumn. Flowers are collected in corymbose inflorescences.
- Appressed - a variety with low-lying branches. The height of the bush is about one and a half meters.
- Chokeberry. A feature of this cotoneaster is the black fruit. The bush blooms within one month, starting from the 5th year of life.
- The red-fruited variety differs little from the black-fruited one. The only difference is in the color of the fruit.
- Horizontal shiny - one of the most popular types, up to 2 meters high. The leaves of this plant are green with a shiny, silvery surface.
- Variegatus is an evergreen low shrub with creamy leaves.
- Coral extravaganza - characterized by a spreading crown. Dark green leaves turn red in autumn. Small flowers with pinkish petals. The fruits ripen in early autumn and have a shiny, smooth surface.
Planting and caring for variegated turf
Types and varieties of cotoneaster
We offer you an acquaintance with the most popular types of cotoneaster grown in culture.
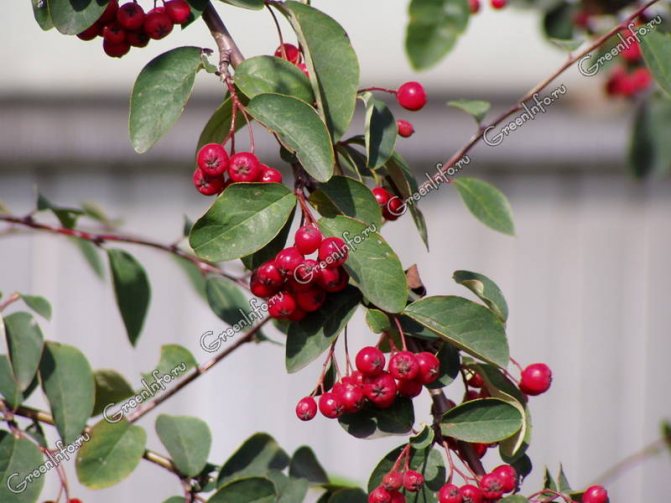
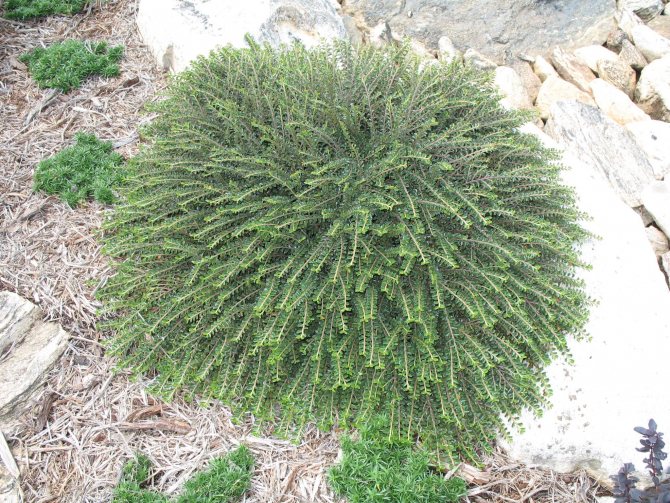
Brilliant cotoneaster (Cotoneaster lucidus)
native to Eastern Siberia, where it grows singly or in groups. It is an upright, densely leafy deciduous shrub.The height of the brilliant cotoneaster reaches two meters. Its young shoots are densely pubescent, elliptical, shiny dark green leaves up to 5 cm long are pointed towards the top. Pink flowers in loose corymbose inflorescences open in May or June and bloom for 30 days. Decorative shiny spherical black fruits that remain on the bushes until winter. Fruiting occurs at four years of age.
It is most often used to create hedges, group plantings on forest edges and lawns. In culture since the beginning of the XIX century.
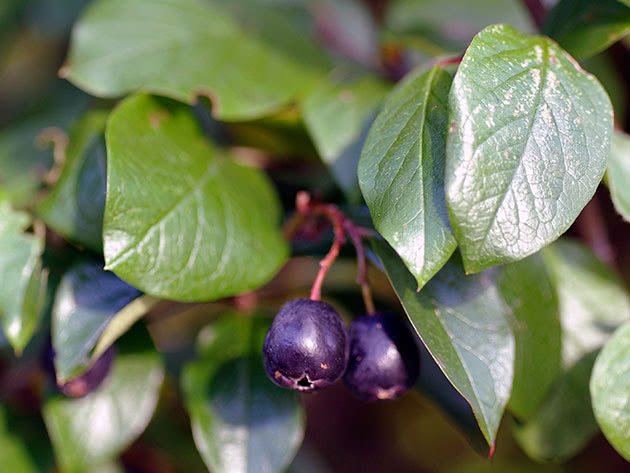


Black cotoneaster (Cotoneaster melanocarpus)
Also winter-hardy enough for our latitudes. This cotoneaster is edible, unlike many other plant species. In the wild, it can be found in the Caucasus, Central Asia, Northern China and Central Europe. The shrub reaches a height of 2 meters, its shoots are red-brown in color, the fruits are black. Leaves are ovate, up to 4.5 cm long, the upper side of the plate is dark green, the lower side is white-tomentose, the apex is obtuse or notched. Annual fruiting begins at the age of five. Pink flowers in loose clusters of 5-12 pieces bloom for about 25 days.
The species is frost-hardy and not picky about moisture, in addition, plants of this species are excellent honey plants, canes, pipes and other crafts are made from their wood. The species has a decorative laxiflora shape with loose drooping inflorescences and larger fruits than the original species. The black cotoneaster has been cultivated since 1829.
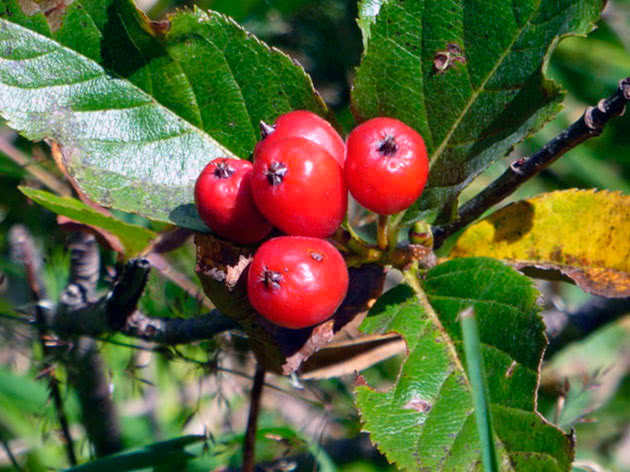


Cotoneaster whole-edged, or ordinary cotoneaster (Cotoneaster integerrimus)
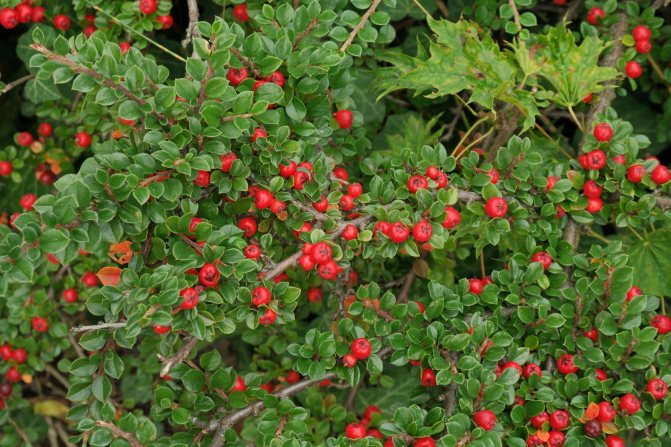
Deciduous shrub, found in nature from the Baltic to the North Caucasus on mountain slopes, in limestones and sandstones. In culture, this deciduous shrub is still a rare occurrence. An entire cotoneaster bush grows up to two meters in height, its crown is rounded, young branchy shoots are covered with woolly pubescence, but with age they become naked. Its leaves are broadly ovate, up to 5 cm long, dark green above, smooth and shiny, gray-tomentose below. Pinkish-white flowers are collected in clusters of 2-4 pieces. Fruits are bright red up to one centimeter in diameter.
Winter hardiness of this species is high, in addition, it is resistant to gas and drought. In culture since 1656.
- How to store bulbs in winter
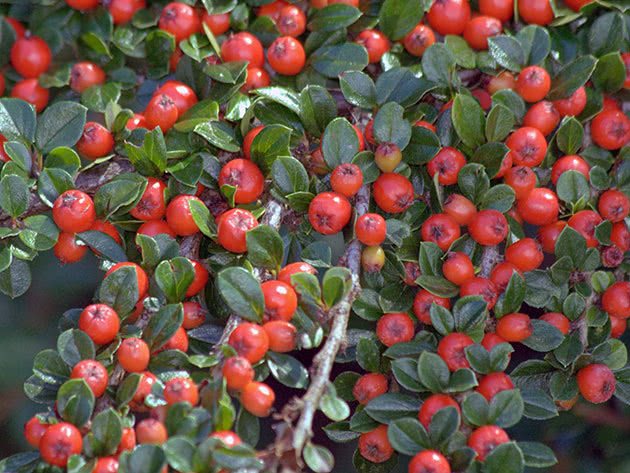


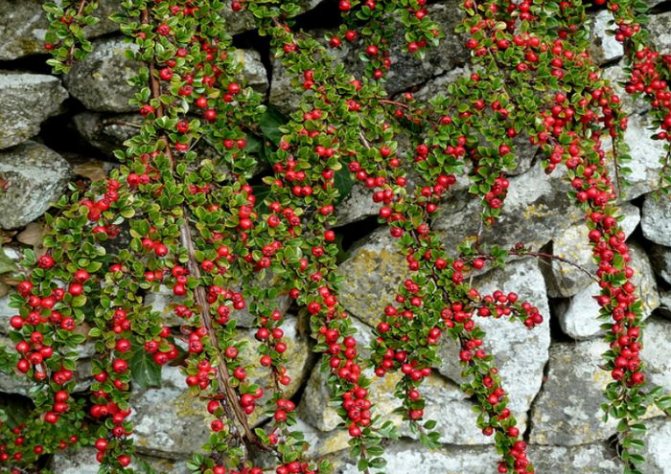
Horizontal cotoneaster (Cotoneaster horizontalis)
Refers to common types. This is an evergreen cotoneaster, up to one meter high and a crown growth up to one and a half to two meters wide. Shoots are arranged in layers, like a fish ridge. The leaves are shiny, rounded, green, in autumn they acquire a fiery red color. Small pinkish-white flowers bloom in late May and bloom for three weeks. Numerous scarlet fruits ripen in September and can remain on the bush until spring.
This type of cotoneaster, unlike others, is picky about the composition of the soil. In culture since 1880. It has two varieties:
- Variegatus - up to 30 cm in height and with a growth diameter of up to one and a half meters, on each of its leaves a white stripe along the edge;
- Perpusillis - a spreading shrub up to 20 cm high, eventually covering an area with a diameter of up to one meter. It grows slowly. It blooms in early summer with pink flowers. Scarlet berries ripen at the end of summer. The green leaves take on a burgundy color in the fall.
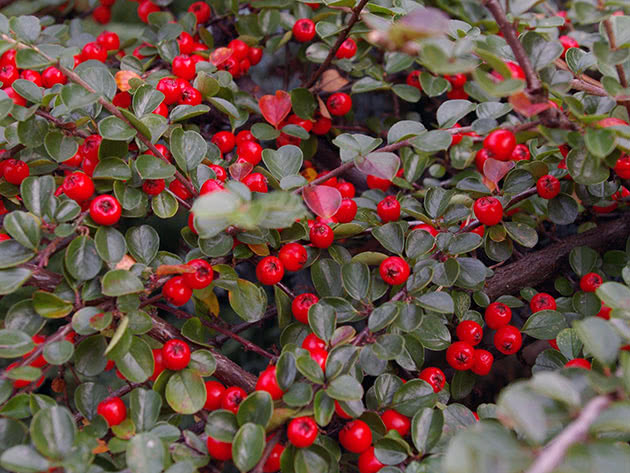


Dammer's cotoneaster (Cotoneaster dammeri)
Outwardly, it resembles a horizontal cotoneaster. In the wild, it is found in the mountains of Central China. Its shoots are creeping, they are almost pressed to the ground, therefore they often root themselves. Branching of shoots occurs in one plane, they rise no higher than 20-30 cm, growing in width up to one and a half meters. Leaves are leathery, small, elliptical, dark green in summer and purple in late autumn. Reddish flowers are sessile, coral-red fruits ripen in September and do not fall off for a very long time. This species has been cultivated since 1900. Popular varieties:
- Aichols - up to 60 cm high with red-orange fruits;
- Coral Beauty - up to 40 cm high, with large single red fruits. This variety is the most winter-hardy of this species;
- Stockholm - shrub up to one meter high with bright red fruits.
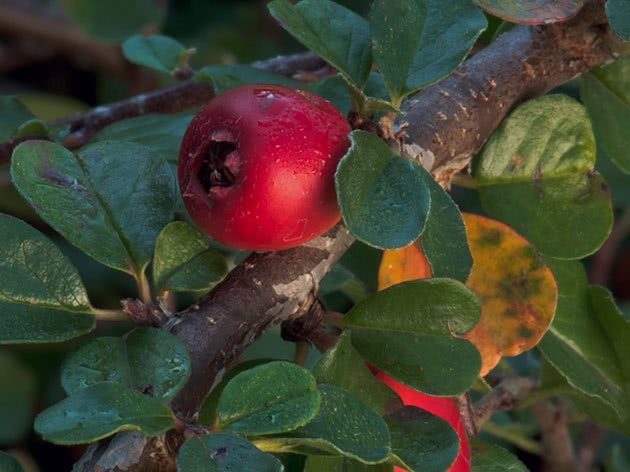


Reproduction
Among the several methods of breeding a horizontal cotoneaster among gardeners, the most popular method is cuttings.
Features of the:
- a good stalk is harvested at the end of July;
- planting nutrient mixture consists of peat and sand. Ratio 1: 1;
- cuttings root well under the film.
Seeds of cotoneaster reproduce worse. Germination rate is within 60%.
Features of the method:
- seeds are poured into a container with water, the floating ones are taken up. This planting material is unusable;
- good quality seeds can be sown, but they do not germinate well. The reason is a long period of rest;
- experts recommend stratifying them and sowing only next fall.
Privet: landing and care. Read about it here. And here it is said about caring for the lawn after winter.
There are many more informative articles about the landscape in this section.