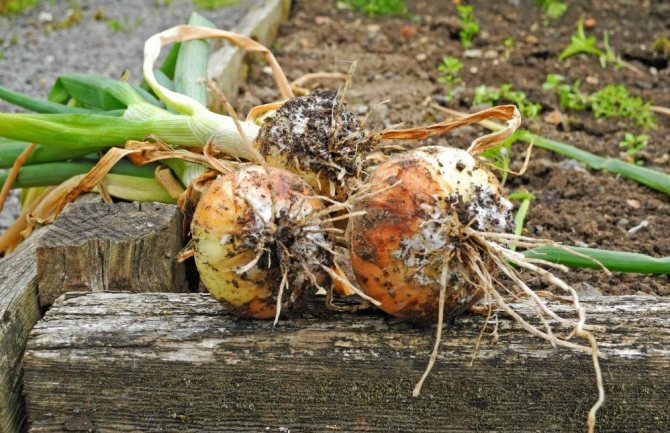
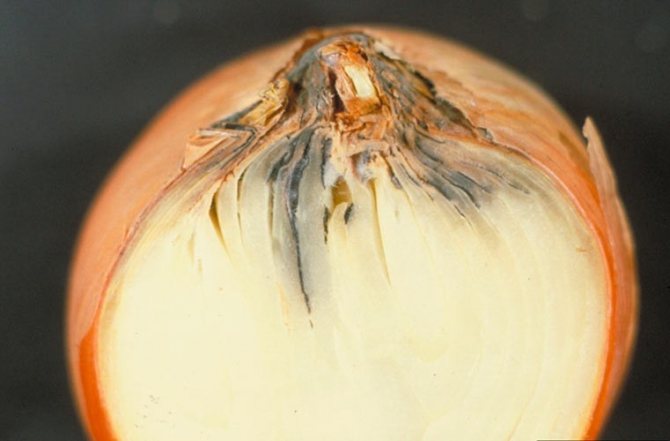
Onions are a healthy vegetable, without which it is difficult to imagine most of the first and second courses.
They need to be stocked up in the fall, since it is perfectly stored until next spring, but only on condition that suitable conditions have been created for it.
Read about why onions rot when stored inside and out, what to do and how to prevent damage to the crop, read the article.
What is rot
Rotting is the process of decomposition of a vegetable, affecting both the bulb and the feathers. Many vegetables are susceptible to this phenomenon. When the onion rot is damaged, the green part dies off, the leaves turn brown, and an unpleasant odor appears.
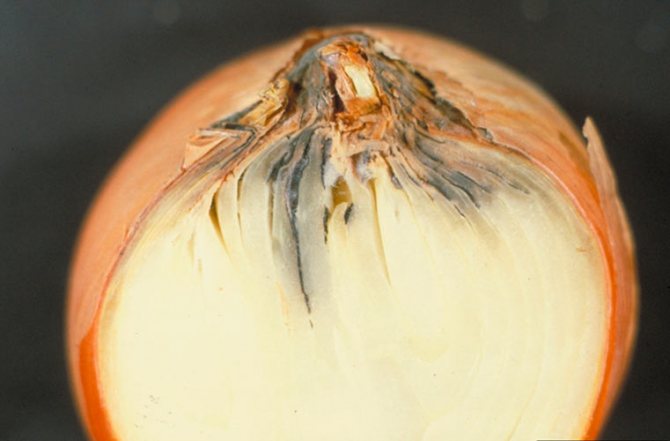
Often, a bulb that is healthy on the outside can be rotten on the inside. The fruit becomes soft, the bottom also looks watery. Not all gardeners know what to do if onions spoil during storage.
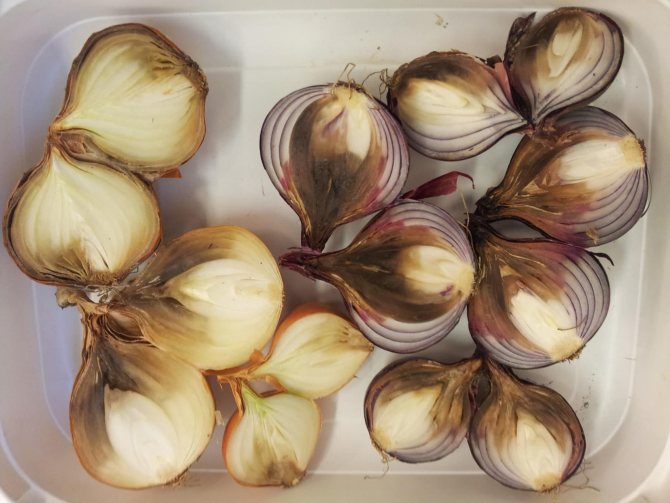

Onions can rot on the inside for several reasons.
Attention! Rotten onions should not be eaten.
Spoilage of onions during growth in the garden


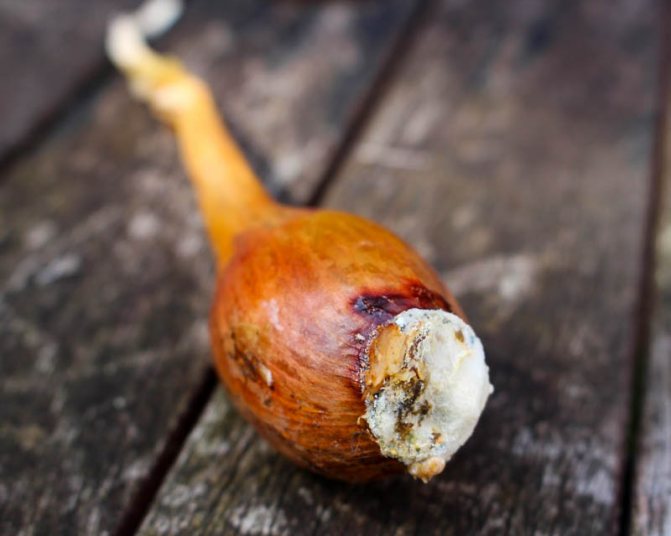
If during the next inspection you find yellowed feathers, make sure that the heads have not started to rot from the inside. If the bulb is soft, watery, and smells unpleasant, then it is rotting.
They begin to solve the problem by determining the cause of the appearance of rot.
Violation of the irrigation regime
Too frequent watering, especially in combination with rainy weather and the location of the beds in the lowlands, leads to decay.
The solution will be active watering, carried out only at the beginning of the growing season. After the formation of the bulbs, watering is reduced, and a month before harvesting, they stop altogether.
Excess nitrogen in the soil
Excessive concentration of nitrogen fertilizers provokes softening of the tissues of the bulb and the development of putrefactive infections.
The solution is to comply with the norms when applying fertilizers. If a problem arises, the soil is washed with a solution of wood ash.
Fusarium rot of the bottom
The causative agent of the infection lives in the soil. First, it strikes the feather, then provokes rotting of the bottom.
The infection can spread to neighboring plants, so the affected specimens are removed from the garden. Crop rotation helps fight the spread of the disease. Onions are planted in their original place only after 3-4 years.
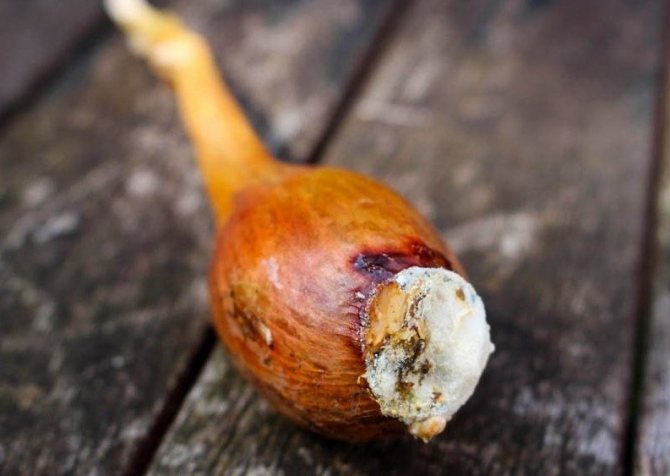
Cervical rot
A fungal disease that develops with high humidity. It manifests itself in the form of mold. The diseased plant takes on a slimy, soft appearance and gives off an unpleasant odor.
To prevent, follow the rules of prevention: planting is placed in a high, sunny place and maintain optimal soil moisture.
Onion fly
The larvae of the pest eat the tissues of the plant, causing it to rot and die.
Spraying with an infusion of ash, tobacco dust and ground pepper helps to fight the parasite. Protecting the onion beds with covering material during the fly's summer will prevent the pest from laying eggs in the beds.
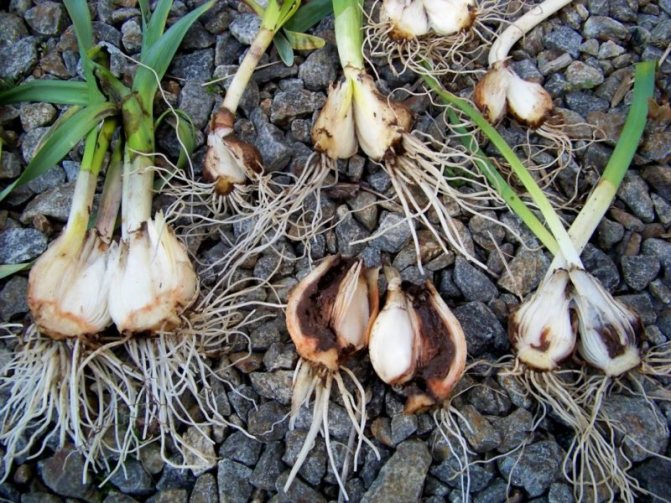
Stem nematode
Small wormeating onion juice. Propagated by laying eggs in plant tissues. Affected tissues become friable, rot and take on an unpleasant odor.
The appearance of the parasite is prevented by observing crop rotation and sowing healthy seed.Immediately before planting, the seedlings are soaked in a solution of the "Fitosporin-M" preparation for 20-30 minutes (38 g of substance per 10 l of water).
The main causes of rotting in the beds and how to deal with them
Onions rot for several reasons. In most cases, improper crop care is to blame.
Failure to comply with crop rotation
It is imperative to observe the crop rotation every year. Each plant picks up specific elements from the soil. If you constantly grow the same thing in one place, then gradually the soil becomes poorer. As a result, the culture will not receive the necessary substances in a couple of years. The bulbs will grow weak, more prone to various diseases, including rotting. Failure to comply with crop rotation leads to the fact that vegetables become more vulnerable to damage by insects and pests, which also leads to the appearance of rot in the future. Therefore, it is recommended to re-plant the onions in the same garden only after 3-4 years.
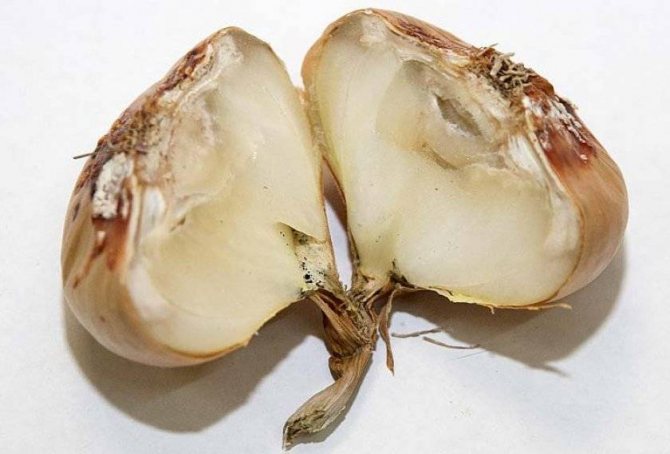


Rotten onions can cause stomach poisoning
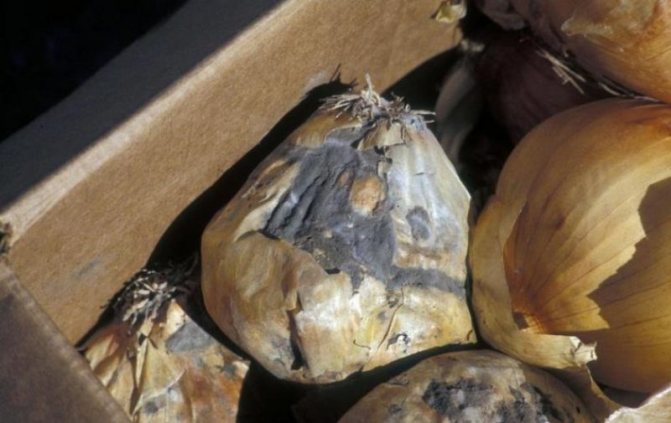
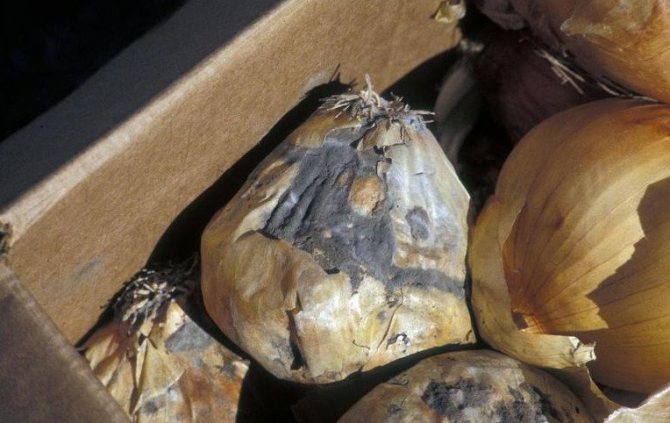
Cervical gray rot
This disease is caused by a fungal infection. Quite often, it can be found already on the collected and prepared for storage onions. Infection with the disease occurs for several reasons:
- Lack of crop rotation.
- Using seeds untreated with fungicides or onions for planting.
- Failure to comply with the harvest time.
- Over-watering and long rainy season.
Cervical rot manifests itself in several signs that should be paid attention to. These include:
- Soft bulbous neck.
- The appearance of gray spots on the fetus.
- Gradual formation of a gray coating throughout the vegetable.
- The presence of fungal spores in the plaque (visible as black specks).
Note! In this case, it will not be possible to save the entire harvest: you will need to sort out all the onions and throw away the spoiled heads that have time to rot.
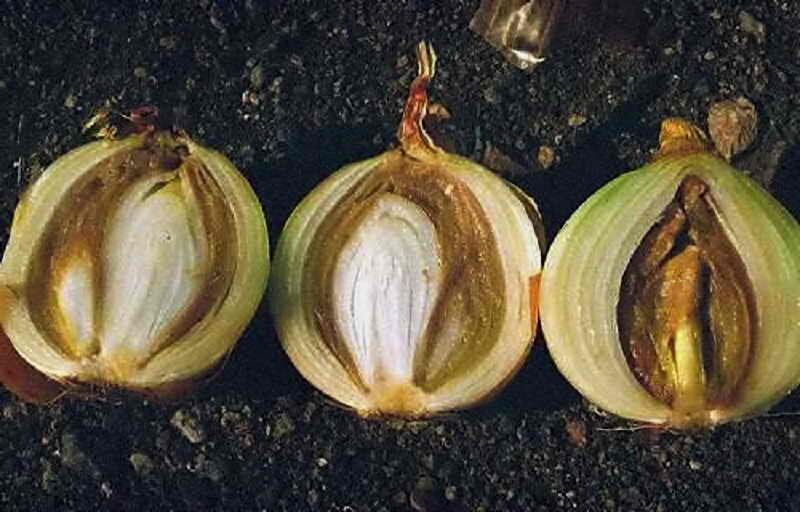


Neck rot is caused by fungi
Stem nematode
Nematodes are small white worms. You can notice that they "attacked" the plant only in the garden, and sometimes even during storage. Signs of onion nematode damage are damp scales, they become soft, the decay process gradually develops.
Diseases and pests that lead to decay
Diseases and pests are the most dangerous for growing onions. They not only spoil the harvest, but can also infect neighboring crops. To cure the planting, the gardener needs to immediately determine the disease and start solving the problem.
Read more about onion diseases and the fight against them.
Diseases
Diseases are caused by harmful infectious agents that were in the soil and planting material or found themselves in the beds during the growth of vegetables. Rotting can be caused by bacterial soft rot, bacteriosis of onions, neck rot, white rot, fusarium or powdery mildew.
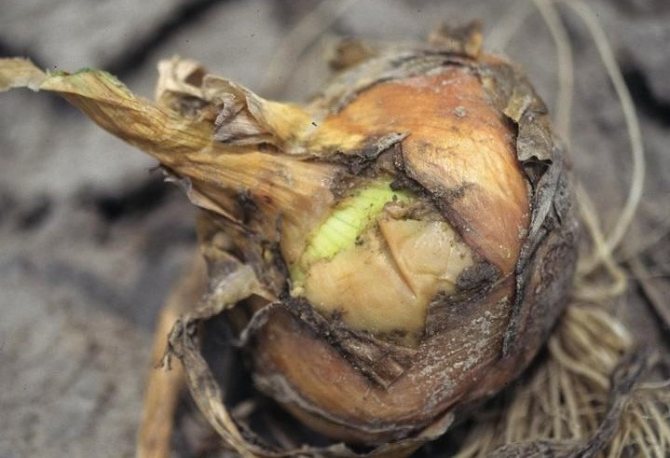
Bacterial soft rot
The causative agent of the disease is a bacterium that settles on mature onions. The disease can be determined closer to harvest.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- improper watering;
- temperature drops;
- lack of dressings or their deficiency.
Signs of the disease:
- 2-3 plates rot inside the onion;
- the affected parts turn yellow, sandy or grayish;
- there is a fetid odor;
- plates that have not been affected by rot look completely healthy.


Onion bacteriosis
Onion bacteriosis is a bacterial disease, which, like the previous one, is more often determined in the last period of ripening.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- weakening of the fit due to improper care;
- excessive watering;
- dampness of the soil.
We recommend that you learn how to properly water the onion.
Signs of the disease:
- the head rots from the middle;
- rot is gray, often closer to brown;
- the affected areas are soft and slippery to the touch;
- a putrid smell is felt;
- at the maximum degree of damage, the entire bulb rots.

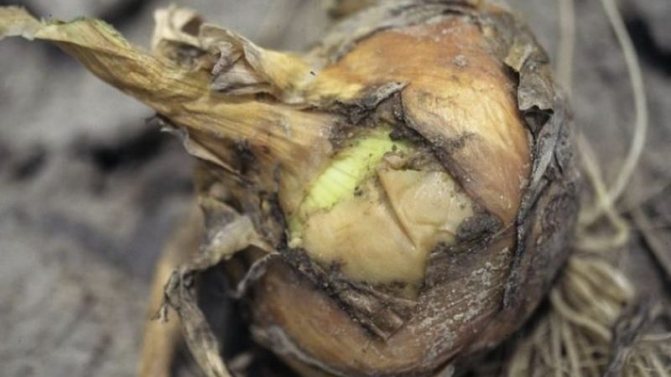
Cervical rot
Cervical rot is a fungal infection. Like the above-described diseases, it can be determined closer to the end of the growing season. Often it manifests itself already in the onion set aside for storage.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- untimely harvesting;
- incorrect crop rotation;
- lack of seed treatment or sowing with fungicides;
- frequent rains;
- excessive watering.
Signs of the disease:
- the neck of the bulb becomes soft;
- the affected areas turn gray;
- the entire head is gradually covered with a grayish coating;
- on the plaque, fungal spores are observed in the form of black blotches.


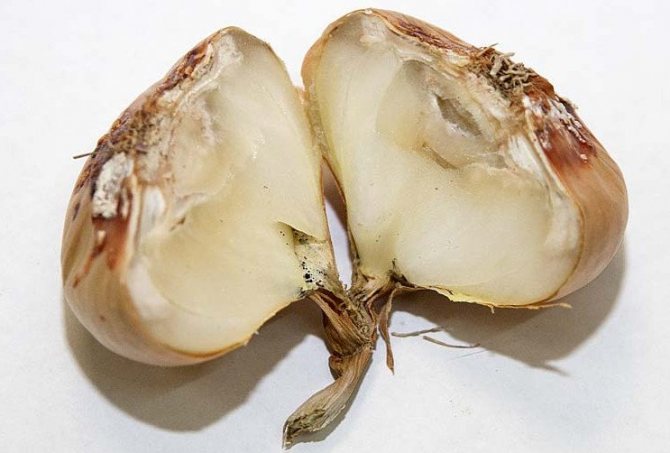
White rot
White rot is caused by fungal spores.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- excessive watering at low temperatures;
- incorrect crop rotation;
- a lot of nitrogen in top dressing;
- acidic soil.
We advise you to read how and what to process onions before planting.
Signs of the disease:
- feathers wither and turn yellow;
- white bloom appears on the bottom of the bulb;
- gradually the plaque spreads to the entire outer shell of the vegetable;
- if you start the disease, the onion begins to rot from the inside;
- the rotten fruit dries up.


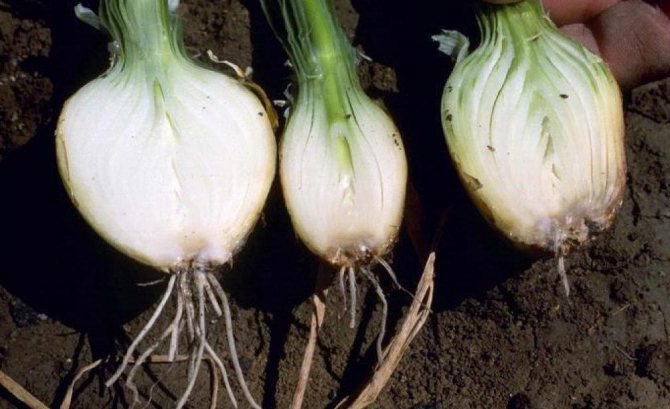
Fusarium rot
Fusarium is a dangerous fungal disease that affects many garden crops, and onions are no exception.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- high air temperature;
- abundant watering;
- frequent rains;
- onion fly attack.
It will be useful for you to learn how to prepare a bed for onions in the fall.
Signs of the disease:
- feathers turn yellow, then lose their shape and die off;
- the vegetable grows more slowly than usual;
- the roots of the bulb turn brown, begin to rot;
- the bottom is covered with a filamentous coating;
- with excessive moisture on the decaying areas, you can notice pink blotches;
- in section, the lower part is grayish and watery.


Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew is caused by a fungal infection. The disease can destroy the entire crop.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- high air humidity;
- cold weather.
Possible causes of decay when stored at home
Often a person does not understand why onions deteriorate during storage. If it starts to rot at home, it means that some mistakes were made during the collection and storage. These include:
- Use for storage of early varieties.
- Failure to comply with cleaning deadlines.
- Lack of sorting before storage.
- Poor ventilation.
- High humidity.
- Freezing of fruits.
- Damage by pests and diseases.
- Poor storage container.
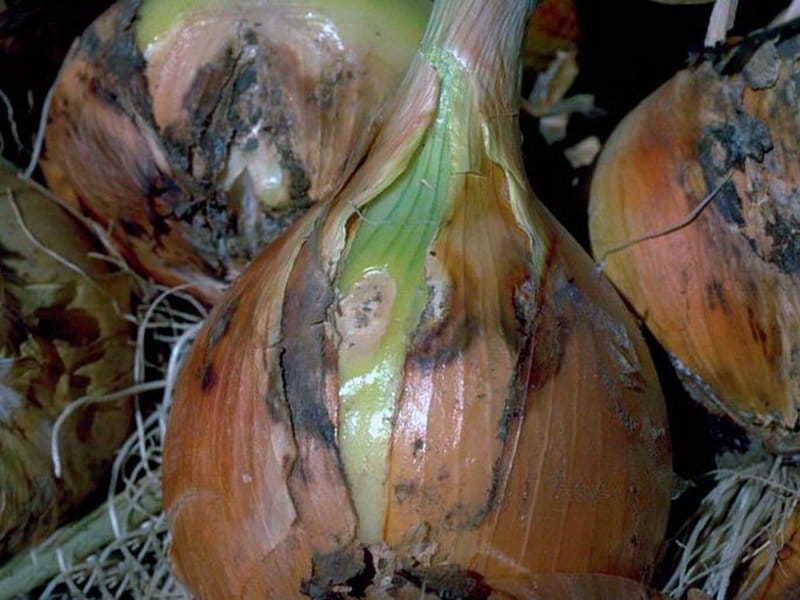


Failure to comply with storage rules often leads to the development of decay.
It is important to properly prepare and store onions in winter. Otherwise, you can lose the entire crop.
Onion diseases: how to fight
If you did everything correctly: you adjusted the temperature regime, adjusted the humidity and carried out drying - the risk of the onset of putrefactive processes still exists. There are a number of diseases that pose a threat to the crop.


Gray neck rot
This attack can hit the bow at any time. It appears both during storage and during the growing phase. Its development is triggered by a fungus - it may not manifest itself for a long time, but under certain conditions, it can become more active.
Affected bulbs can be distinguished during the growth stage. Saw a weak, stunted plant with curved leaves - remove such a copy immediately. After collection, you will no longer be able to determine the disease.
To prevent the development of gray rot, you will have to work hard:
- Inspect each head - any suspicious specimens should be discarded.
- All vegetables that will be deposited must be thoroughly dried. It is advisable to do this on the stove or in the dressing room.
- It is important to maintain a certain temperature regime - the mark of the thermometer should not go below + 3 ° C.
- Watch out for humidity. At a humidity of more than 70%, the bulbs will come out of dormancy - they will begin to germinate.
Fusarium
Fungal disease manifests itself even at the stage of cultivation - feathers begin to rot, and then the process penetrates into the bulb itself. It can also develop later, during storage - the reason for this is the areas of the head damaged during cleaning and high humidity in the room. If you notice damaged bulbs - remove the damaged ones, check the microclimate of the store.
Bacterial rot
It is difficult to determine the diseased plant - the symptoms are detected after the onion is placed in storage. Visually, the bulb looks normal, but its inner part is already rotting with might and main. It will be possible to find such a vegetable only when the rot reaches the neck and makes it soft - this can take several months. Only prevention can help - do not allow the vegetable to become a victim of an onion fly, hoverfly or spider mite during cultivation.


Fighting onion diseases during storage
To prevent their occurrence and development, it is recommended to treat the plantings with special fungicidal agents "Signum", "Protector", etc. In addition, all storage conditions should be observed - maintain the required temperature in the room from 0 to -3 ° C and humidity not higher 70-75%. Before storing vegetables in storage, they must be dried.
Pests also need to be dealt with with the help of special chemicals, such as "Fitosporin". From the nematode, an annual soil cultivation is carried out.


To prevent rotting, plants are treated with special agents.
How to store it correctly?
To prevent the onion from rotting, you need to properly harvest and store it.
Key recommendations:
- store only onions that have been thoroughly dried;
- sort vegetables before storing them for the winter;
- any instances that are in doubt should be removed;
- the neck of each vegetable must be cut at a height of 5 cm;
- place the crop in a cellar, in which optimal conditions have been created for it: air humidity - up to 70%, temperature - from -1 to +1 degrees;
- onions can be stored in boxes, in nets and in bundles suspended from the ceiling, on pallets made of boards.
The room must have good quality ventilation, which will ensure a normal level of humidity. If the cellar is damp, the onions will begin to sprout.
It is not recommended to keep onions in the refrigerator. Even in the vegetable shelf, it quickly loses its freshness, begins to grow and deteriorate. In the best case, it will last 30 days.
Vegetables are spoiled by the starch in the fruit being converted into sugar in the refrigerator.... The heads become damp, start to smell unpleasant, become moldy and rot.
The bow must breathe. It cannot be kept in plastic or paper bags. You can find all the most important things about onion storage here.
Preventive measures
So that the crop can be stored for a long time and it does not deteriorate for a long time, it is recommended to follow simple preventive rules:
- Crop rotation.
- Selection of varieties resistant to diseases and pests.
- Seed treatment before planting.
- Compliance with the rules of care.
- Weed removal.
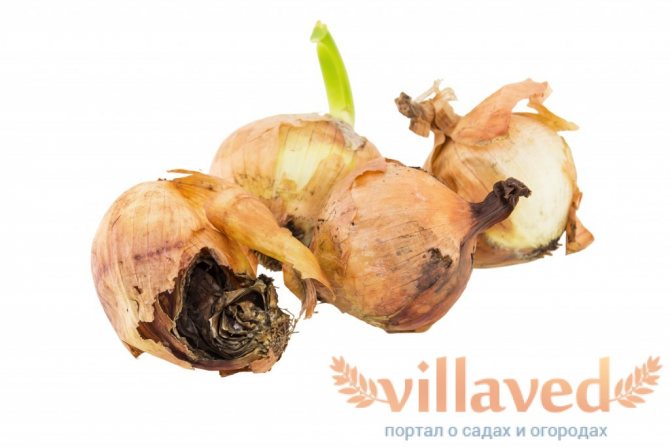
Rotting onions from the inside is possible for several reasons. If you find spoiled bulbs, you need to sort out the entire crop, get rid of the bad ones and try to find and eliminate the cause of rotting. Compliance with all the rules will exclude the possibility of rot and crop death both during ripening and during storage.
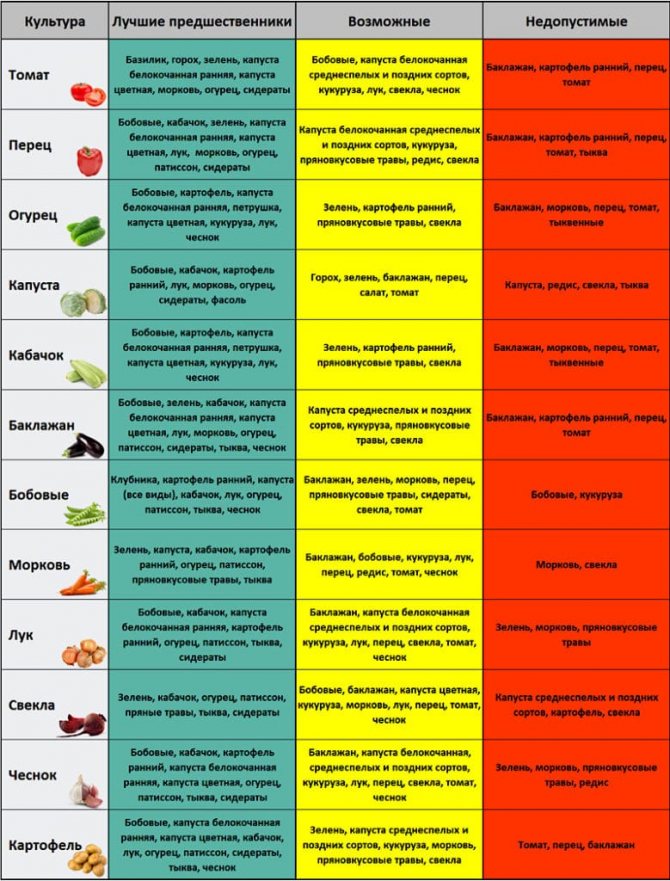
Table: prevention of onion rotting in the garden
| Causes of onion decay | Prevention measures |
| Infected planting material |
|
| Violations of agricultural technology |
|
| Excess moisture |
|
| Onion diseases |
|
| Onion fly defeat |
|
As you can see, bulb decay occurs for various reasons. Take preventive measures, use folk remedies, if necessary, chemical preparations, and you will reduce the damage to onions by rot to a minimum and get a healthy harvest.
What to do with spoiled onions
If you find a spoiled onion in your net, do not rush to throw it away. There are several ways to save onions from the trash can:
- Peel the onion, cut and discard the rotten parts, and cut the remainder in half. Juice it with a juicer. Onion juice is an excellent antimicrobial and antiseptic agent. Spray them on healthy bulbs and dry them. This will help get rid of the rot on the rest of the onion.
- Finely chop the whole parts of the onion and fry in sunflower oil. Place in a glass container and store in the freezer.
- Onion juice washes well windows and mirrors. Mix part of the onion juice with part of the water and pour into a spray bottle. Apply the solution to the window and wipe with a dry cloth or newspaper. You can also rub lacquered furniture with this solution.
Watering
To avoid onion rot, it is important to choose the right irrigation regime. Excess moisture in the ground negatively affects the later stages of development. The root system cannot cope with the incoming liquid, therefore, the decomposition process begins.
Abundant watering is needed in the first weeks after planting. After the feather has appeared above the ground, it is necessary to switch to less intensive irrigation. The procedure is recommended to be done as the soil dries out.
The cause of rotting onions can be a lack of oxygen. After watering, a dense crust forms on the ground, which does not allow air to pass through. In such conditions, the area is unevenly dried and irreversible processes begin. To prevent the entire crop from beginning to disappear, you need to regularly loosen the beds. Mulching will help to simplify work.
Before you start digging, stop watering the culture. The plant does not accumulate moisture in the tissues. This trick protects against the onset of decay and prolongs the shelf life of the product.
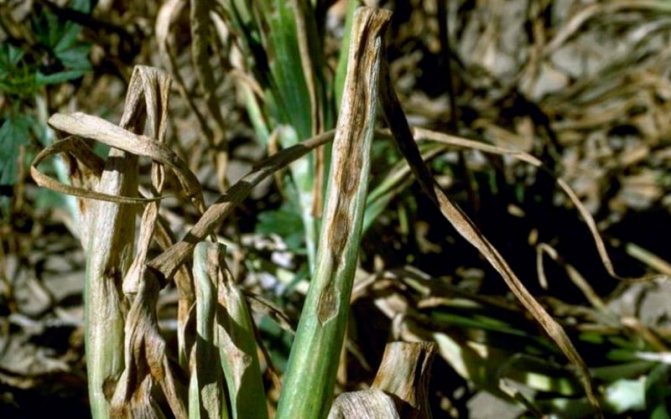
Viral mosaic
This disease is transmitted by small insects when the onion grows in the garden. Therefore, it can be determined during the period of growing onions in the garden. To do this, you need to pay attention to the feathers. If they contain light green spots or stripes, this is a sure sign that the onion is infected with a viral mosaic.
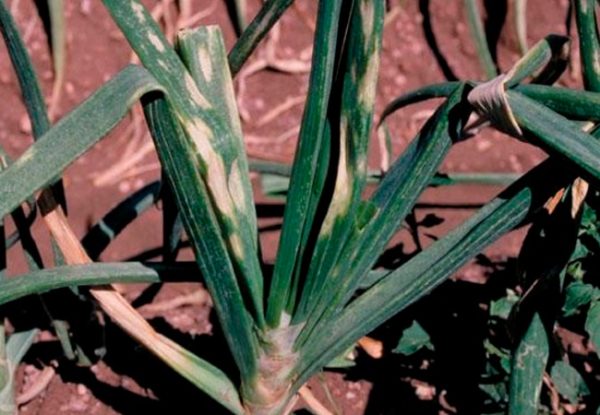


Disease control methods:
- Carry out measures to protect onions from small pests.
- If infected plants are found in the garden, they must be removed immediately in order to prevent infection of healthy bulbs.
- Compliance with crop rotation. This is one of the most important factors that amateur gardeners for some reason do not want to observe. Long-term cultivation of the same plant species in a certain area leads to the constant presence of diseases and pests in the soil, characteristic of such crops. The most suitable precursors for onions are nightshade crops, as well as carrots and parsley.


Why does the onion rot
First you need to determine the factors that caused this process. The most common cause of problems is irrigation violations. Waterlogging of the soil creates a favorable environment for the development of bacteria, this provokes the appearance of onion rot. However, the problem arises not only due to excess moisture: so that the onion does not rot in the ground, it is necessary to provide it with good conditions for growth.


The soil
A common reason why onions rot in the garden is too heavy soil, in which a large proportion of clay particles are present. Clay does not allow water to pass through, which leads to its stagnation. Pests are actively developing in excessively moistened soil. If the soil is clay, you can plant the bulbs in grooves, on the bottom of which a layer of sand has been previously poured, and then covered with a layer of soil. The sand will act as a drainage layer: it will remove excess moisture and protect the plant roots.
Another reason that the bulb has rotted is the presence of bacteria in the soil. Two days before planting onions, experienced gardeners recommend pouring boiling water over the beds. Before planting, you can shed the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate of a pale pink hue. These measures will disinfect it and make it safe for planting.
An important risk factor is non-compliance with crop rotation rules. When onions are planted in the same place, potassium is extracted from the ground for several years, and pathogenic bacteria and fungal spores accumulate.
To fight them and prevent soil contamination, you need to move the garden to a new place every year. Ideally, potatoes or legumes grow on the site of the future onion ridge.
Onion storage rules
To keep onions in good condition for a long time, you need to adhere to simple rules:
- When digging up the onion, be careful not to damage the bottom and roots of the onion.
- Air dry the onions well in warm weather. But not in direct sunlight.
- Cut the roots and neck of the onion 5 cm before storing.
- During storage, sort the onions, selecting diseased and damaged bulbs. One rotten onion can ruin an entire crate.
- Store onions at a temperature of -2 to + 3 ° C in a dark, dry place.
- Store your onions in braids or knits at home. To make a bundle, sort the bow and tie in pairs with necks. Fold the rope in half and tie the ends together. Hook the ends onto a nail in your barn or balcony. String the paired bulbs, inverting the rope after each pair. This will create a uniform knit.
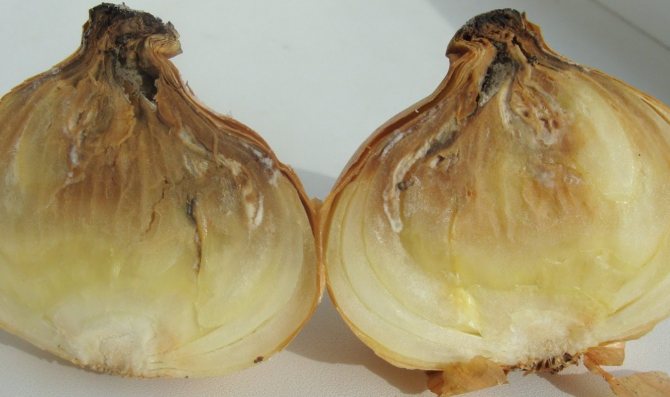
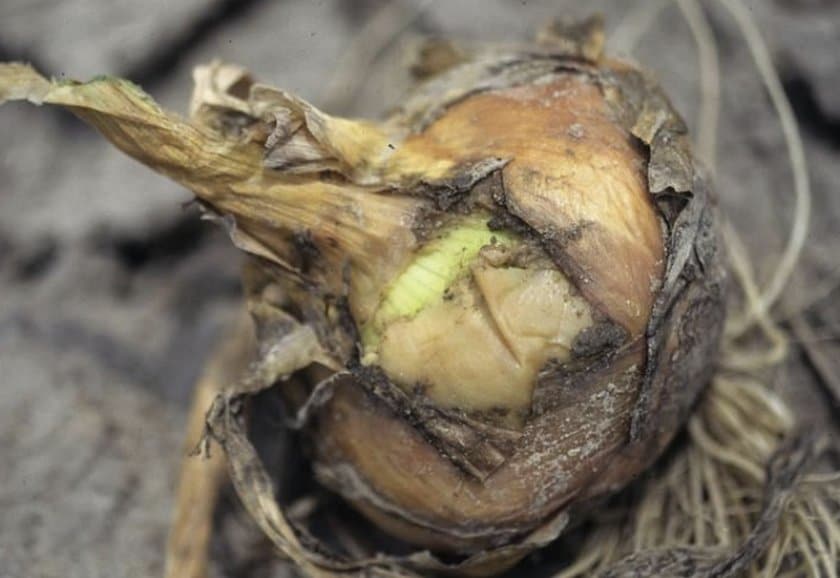
Bacterial rot
Another harsh attack relates to bacterial diseases. Even if you are the most attentive person in the world, you still run the risk of looking at a diseased bulb during harvest. And all because it is very difficult to recognize bacterial rot. The infection manifests itself only after a while.
The bulb may look healthy and beautiful, but the inside may be rotten. Rot spreads from the center to the edge, infecting the entire bulb. Only after a couple of months can you notice a softened neck and understand that the bulb has become a victim of an insidious disease. If you are not too observant, an unpleasant smell will tell you that the onion is spoiled.
With bacterial rot, the onion begins to deteriorate from the center
How to fight?
1. Only preventive measures will help to cope with bacterial rot. In particular, the fight against vectors of this disease: onion fly, onion hoverfly, spider mite.
A source
If an alternation of healthy juicy and soft, smelly scales is found on the cut of the bulb, these are signs of a common fungal disease. When harvesting, such root crops practically do not differ from unaffected ones, but after 2-3 months the turnips will begin to disappear.


Onions can rot on the vine, so it is not always possible to quickly detect signs of the disease.First, light burn spots appear on the feathers in the center, and then cover the space up to the neck. On such leaves there is no plaque characteristic of the fungus, but against the background of healthy ones, they look faded and drooping.
Excessive sprinkling or wet summer is enough to rot the product. By the time of harvest, the disease penetrates into the sinuses of the greenery and into the neck. Gradually, the onion infection moves into the juicy layers. The disease increases the temperature in root crops, as a result of which the production is completely lost.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Do-it-yourself box for storing vegetables on the balcony in winter
Rotting onions can be prevented if you remember the rules of crop rotation. You cannot plant a spicy vegetable in one place for more than 2 years in a row. There are also a number of prohibited and recommended predecessors.
To avoid onion rot, you must not leave lost plant residues in the soil: they accumulate dangerous bacteria that do not die from frost. The affected area is treated with fungicides.
When the first signs of the disease appear, the beds of root crops are watered, sprayed with preparations based on copper. It is important to choose the right product and follow all the instructions in the instructions. You cannot apply a lot of nitrogen fertilizers.
Gray rot
This fungal disease affects the onion even in the garden, but it does the most harm during storage. Pathogenic fungi are very tenacious and can exist inside the bulbs for a long time. Gray (or neck) rot is considered the most dangerous disease of onions in storage.
Most often, weakened plants suffer from this scourge. And after being damaged by gray rot, they begin to lag behind in growth at all, and their leaves - to bend. But it is difficult to detect symptoms on harvested bulbs: rot develops very slowly.
During storage, the affected seed or turnip bulbs begin to soften in the upper part, dents appear on them. In 1-2 months, such bulbs rot completely. They are soft to the touch, as if fresh from the oven.
Onion pests
Often, gardeners are interested in: why onions rot in the ground, because the irrigation regime is observed, the nitrogen content in the soil is permissible, agricultural technology is correct. Onions begin to rot due to pest infestation. To combat this, you first need to determine the type of insect.
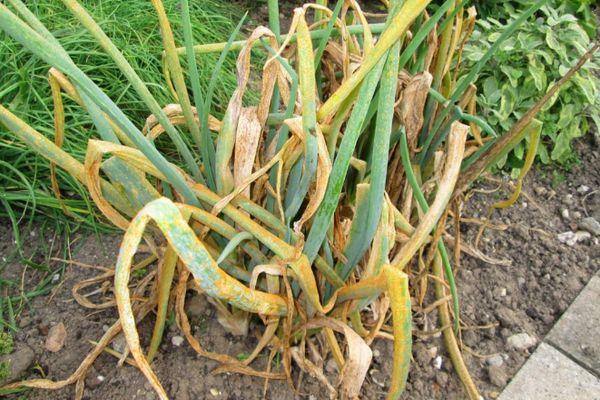


Among pests, particular harm is caused by:
- onion fly;
- root mite;
- onion lurker.
They infect plants overfed with nitrogen. The culture cannot develop normally, it starts to rot. If pests are found, it is recommended to add ash to the soil, reduce watering and apply insecticides. To prevent insect infestation, pre-sowing seed treatment methods with protective compounds should be used.
Prevention measures
It is much easier to prevent the process of crop rotting than to deal with its consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out the following preventive measures:


- compliance with crop rotation;
- processing of planting material;
- compliance with agrotechnical rules for growing crops;
- treatment with fungicides and insecticides;
- loosening and weeding;
- observance of the garden "good neighborliness" (cultivation of plants that repel pests next to onion beds).
Compliance with all norms of planting, prevention, care, processing and storage of crops will help prevent problems and preserve the harvest throughout the winter.