Why do rabbits die?
Mass death of all or the sudden death of one rabbit - sooner or later every rabbit breeder faces this. The main reasons are lack of proper care, unsanitary conditions, poor quality feed and dirty water. This content of eared rodents increases the risks of contracting infectious diseases, as well as diseases that are not transmitted from individual to individual.
To prevent death or at least reduce the number of affected animals, you need to know the rules and conditions for keeping rabbits, what diseases they are susceptible to and their symptoms, as well as what preventive actions will save the livestock from death.
What rabbits are sick with and how to treat
All diseases of eared pets can be divided into infectious and non-infectious. The former are much more dangerous, because if one individual becomes ill, there is a risk that all livestock may die.

Why do rabbits die?
Why do chickens die?
Major infectious diseases:
- hemorrhagic disease;
- coccidiosis;
- myxomatosis;
- pasteurellosis;
- stomatitis;
- cysticercosis;
- tularemia;
- listeriosis.
About some of them in more detail:
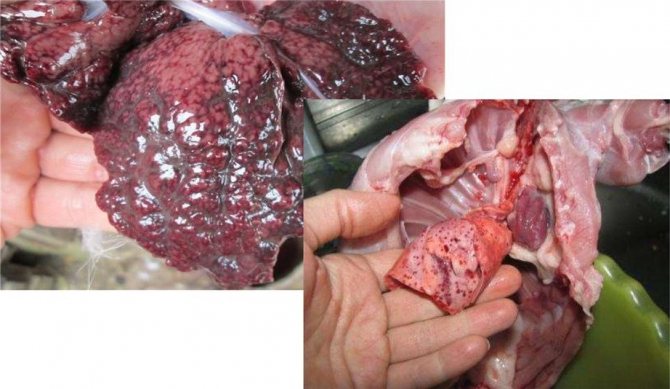
Hemorrhagic disease (HBV)
One of the most common diseases. Its other name is fever. It is transmitted by airborne droplets (VKP), through feces, contaminated food. The disease can be acute or asymptomatic at all. Most often, infection occurs in the summer. The rabbit dies one day after infection. There are no effective treatments. As a preventive measure, animals need to be vaccinated: the first time in 1.5 years, then every six months.
Important! An unexpectedly dead animal must be taken to an autopsy. If you don't know what the rabbit died from, you can lose all the livestock!
Coccidiosis
The causative agent is coccidia, which affects the intestines and liver. Infection of animals occurs through poor-quality feed, dirty water and feces. The carrier can be humans or other pets. A sick rabbit loses appetite, weight is lost, the stomach begins to swell, and diarrhea opens. For treatment, animals need to be drunk with antibacterial drugs. As a preventive measure, it is required to comply with hygiene standards in the rabbitry, disinfect equipment and cages. Dead rabbits must be burned.


Coccidiosis
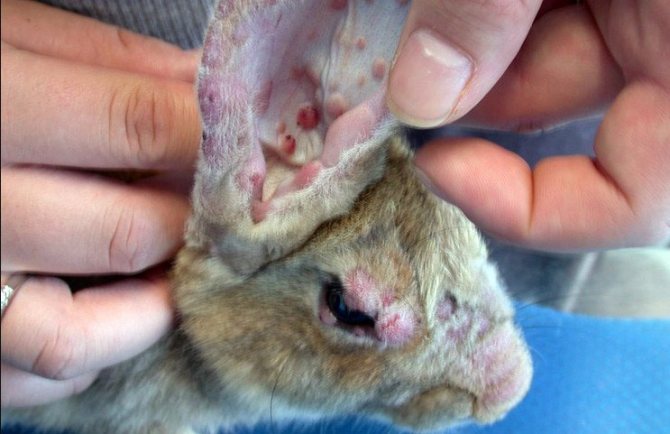
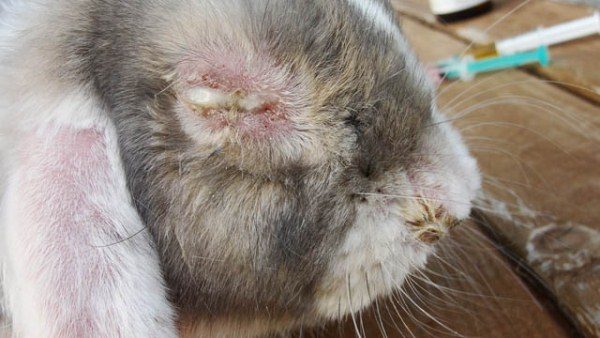
Myxomatosis
The most dangerous disease. It is transmitted by VKP, as well as through the bites of mosquitoes and other insects. A nursing rabbit infects rabbits through milk. At first, the disease is asymptomatic, then bumps form in the region of the head and ears, purulent discharge is observed from the eyes, and the animal begins to develop a fever. The duration of the disease is 1 to 2 weeks. Death occurs in 95% of cases. There is no effective treatment. You can only be safe by vaccination.
Pasteurellosis
A viral disease transmitted by air, food, water and humans. It manifests itself in the form of coughing, sneezing, shortness of breath. The rabbit loses appetite, the temperature rises, and purulent discharge from the oral cavity appears. If you do not start to treat, then the animal will die. Antibiotics and sulfonamides help well. With timely veterinary care, rabbits survive. As a preventive action - vaccination from one month of age. Adults - twice a year.

Myxomatosis in rabbits
Stomatitis
A viral disease in which there is increased salivation, swelling of the tongue, redness of the oral mucosa. Loss of appetite is accompanied by lethargy and dramatic weight loss. Treatment is performed as directed by a veterinarian. Failure to provide medical attention to the rabbit will result in its death.
Cysticercosis
The cause of the disease is the larvae of the cestode, which infect the liver and contribute to the onset of peritonitis. The disease cannot be cured, the animal dies. Diagnosed after death. The corpse is burned.

Cysticercosis
Tularemia and listeriosis
Although these diseases are not similar, they have something in common:
- Carriers are rats, fleas, bugs, ticks.
- The disease cannot be cured.
- It can only be diagnosed by autopsy.
- Carcasses must be burned.
Note! Listeriosis is dangerous for humans, so if the autopsy diagnosis was confirmed, the rest of the individuals in contact with the deceased rabbit must be destroyed!
The most common diseases of adults and young animals
- VGBK;
- myxomatosis;
- pasteurellosis;
- coccidosis;
- flatulence.
HBV (fever) - viral hemorrhagic disease of rabbits, when to get vaccinated
The abbreviation stands for - rabbit viral hemorrhagic disease... This disease is the cause of the death of rabbits. Animals are susceptible to diseases from two months. VGBK, or in simple words, fever, is very contagious, it is transmitted not only through the wool, meat and feces of infected individuals, but also by air. Mortality occurs in 90% of cases... It is not always possible to notice that the animal is infected, since HBV can pass in an asymptomatic form. In the acute form, rabbits completely refuse food, behave restlessly, very quickly lose strength and become inactive, but at the same time they convulsively twitch their paws and throw their head back.
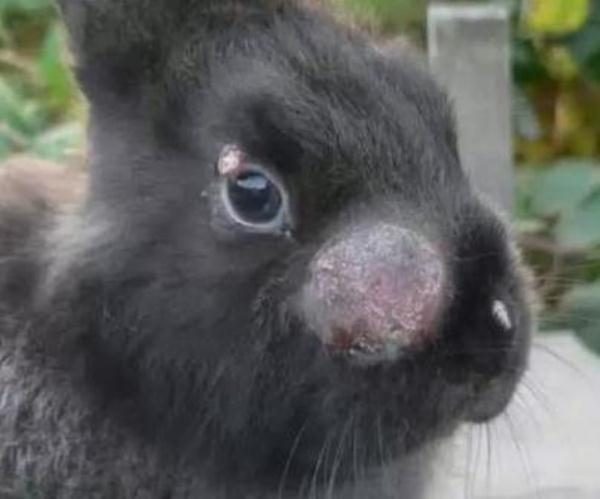


Rabbit viral hemorrhagic disease
The animal is in pain, therefore, it periodically emits a squeak, blood discharge through the nose is possible. Death occurs from 24 to 72 hours from the moment of infection... The disease affects and destroys the animal's liver, and also causes pulmonary edema, which often becomes the cause of death, as the body picks up oxygen.
In order to protect your livestock, you need to use a special the vaccine given to rabbits at 45 days of age... Adults can be administered at any time. The vaccine is valid for one year, after which revaccination should be carried out. Treatment of the disease has not yet been developed, and the reasons for the recovery of individual individuals have not been established.
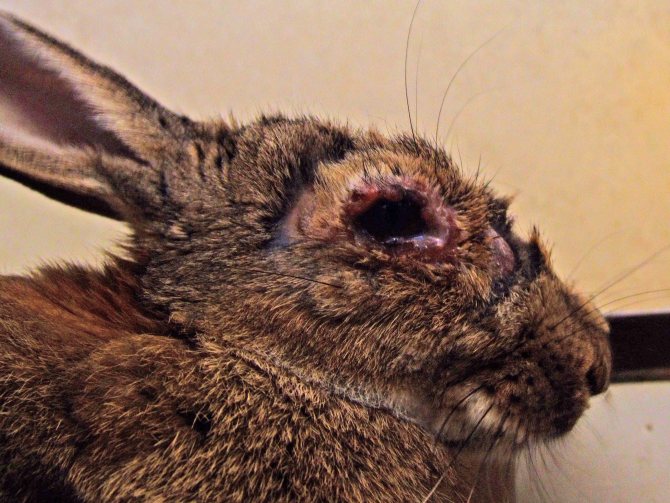
Myxomatosis (distemper), visible symptoms
Disease transmitted by insect bites and produces profuse mucus from the nose and eyes. An infected animal can live with these symptoms for a long time, while infecting its relatives. Myxomatosis, common plague, very dangerous for young livestock, in which mortality occurs much faster than in adults.

Rabbit affected by myxomatosis
In addition to secreting mucus, infected individuals have swelling or nodular swellings in the nose, ears, and eyes.
After the onset of symptoms, the disease develops rapidly and leads to the death of adult animals in about 10-14 days, and young animals in 7 days.
Myxomatosis spreads very quickly, and if one infected rabbit is found on the farm, then most likely the rest are already infected. The disease has no effective treatmenttherefore vaccination is needed to prevent it. Possible use of the associated vaccine, which has in its structure the strain of myxomatosis and VGBV, which eliminates the need to inject the animal with a syringe twice.
Pasteurellosis
Infectious a disease that can cause a massive death of livestock in just 2 days... Visible symptoms are a runny nose, sneezing, and lack of appetite. Unlike the above diseases, which appeared relatively recently, pasteurellosis has been known for a very long time.
The disease is fatal, but on a much smaller scale than the former. Death occurs in 15-75% of cases. The better the feeding and sanitary conditions, the lower the death rate.
The disease can pass in an acute form or develop into a chronic one. In an acute course, the temperature of the animal rises to 41 degrees, after which shortness of breath, runny nose and sneezing begin. After a few hours or days, such a rabbit will most likely die. In the chronic form, the animal shows all the signs of rhinitis and conjunctivitis., which complicates timely diagnosis. The patient's stool becomes liquid, the appearance of purulent abscesses under the skin is possible, which open after 1.5-2 months. Fortunately, this ailment can be cured with medication.
Coccidiosis
The disease is caused by parasitic protozoa unicellular organisms. Parasites infect the liver and intestines... Every rabbit is a carrier of coccidosis, but the clinical form is rare.
Coccidosis manifests itself vividly, which helps with its diagnosis. So a sick animal has bloated belly and emaciated body, while there is no appetite. The disease is transmitted by coccidial oocytes, which are present in food and water. Healthy animals with strong immunity can independently resist the development of coccidia to a painful clinical form.
When an infected rabbit is slaughtered, point light growths in the form of nodules are observed on the liver and in the intestines. In addition, the liver will increase 5 times. The disease is treated with antibiotics, but first of all, it is necessary to improve the conditions of detention, preventing the accumulation of dirt and overpopulation of cells.
Flatulence
Flatulence or bloating, a common cause of death. Since the intestines of a rabbit are sensitive, it is difficult to restore its work if it fails, and sometimes it is impossible. The cause of flatulence is a sharp change in the flora of the digestive system.... This can happen if the food was very moist or juicy, which was unusual for the animal.


Bloating or flatulence in rabbits
With flatulence, the rabbit falls into apathy., he suffers from colic and refuses to eat. This leads to fermentation in the intestines of the eaten food, since it is not pushed out by new food. As a result, bacteria develop in the digestive system, which begin to destroy the intestinal walls and lead to the death of the patient.
Other reasons due to which the livestock dies
In addition to the common causes of the death of rabbits, there are several more rare, but also dangerous diseases.
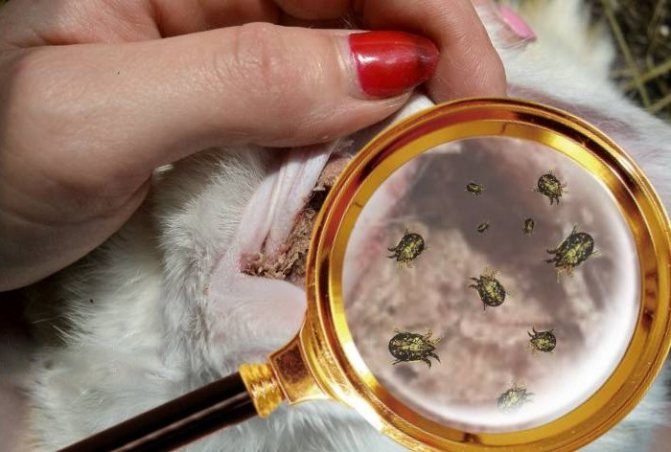
Rabbits are susceptible to scabies mites infestationthat parasitize in their ears. Ticks eat into the skin of the animal and drink its blood, causing severe itching. Scabs appear in the ears, the hair falls out on them. The exhausted animal gradually withers, it refuses food, loses strength and dies after long torment. These parasites can be killed with modern drugs, so the rabbit can be cured.
Females during lactation are prone to the appearance infectious mastitis on the nipples... The cause of the disease is the wounds received from the rabbits' sharp teeth. These bites are natural, but if poorly kept in a dirty cage, an infection begins to develop on them, which spreads throughout the body, infects the blood, which is fatal. Therefore, the cages with rabbits feeding young animals must be especially clean.
Non-communicable diseases of rabbits
Why do chickens die
In addition to viral diseases, non-communicable diseases can also threaten the life and health of rabbits.As a rule, they do not cause mass deaths, however, the death of even one head causes a lot of trouble for the breeder. The most common ailments:
- Flatulence. It occurs due to an excess of succulent feed, wet grass and the presence of mold in it. The rabbit loses appetite, mucous membranes turn blue, and rapid breathing is observed.
- Avitaminosis. Develops with an unbalanced feed, vitamin deficiency. Observed: hair loss on the back, bleeding gums, dry eyes, growth retardation.
- A rabbit can get a heat stroke if the rabbitry is not ventilated, the temperature in it is higher than the required value. The animal becomes lethargic, constantly lies and breathes heavily.
- Injury. Scratches, abrasions, bruises, and finally, limb fractures - all this is the result of overpopulation of cells, the presence of traumatic equipment in them - feeders or drinking bowls with sharp angles.
- Parasites. Most often - ear mites, which cause discomfort to the animal. Their presence is indicated by itching and redness of the auricles. The rabbit begins to lose hair, it loses weight, general weakness and exhaustion appear.
- Mastitis. If the cage containing the nursing rabbit is constantly damp and not cleaned, then microbes enter the body through microcracks on the nipples, which can lead to inflammatory processes in the body of varying severity.
These diseases cannot cause instant death, are not epidemic, and do not occur suddenly. They are manifested due to improper feeding and maintenance of rabbits, the farmer's lack of the necessary knowledge and experience base. In a neglected state, they will eventually lead to the death of the animal.
Other causes of death of animals
Female rabbits rarely suffer from mastitis, but this pathology occurs as a result of nipple injury or accumulation of milk in the ducts. In a neglected degree, an accumulation of pus occurs, the mammary gland becomes inflamed. The infection can spread throughout the body. Mastitis is treated with absorbable topical ointments.


Some rabbits suffer from various external parasites. The accumulation of scabies mites is observed on the surface of the ears. Individuals begin to scratch such places, as a result of which wounds form on the surface, through which pathogenic microorganisms penetrate. Rabbits die from a sharp loss of body weight or after infection with staphylococcus.
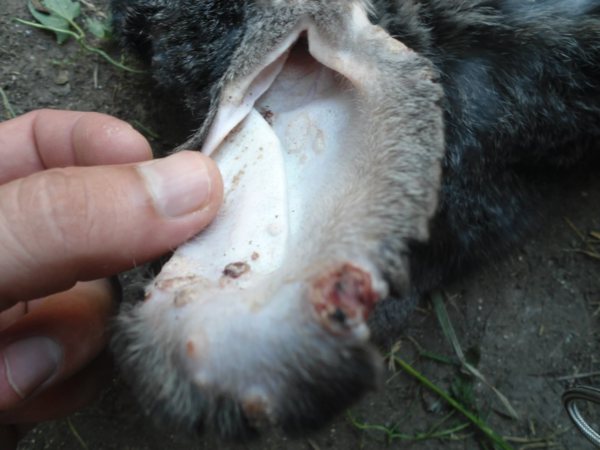


Parasites in rabbits
What to do if the pestilence begins
Why rabbits gnaw on cages and what to do
If trouble nevertheless came to the rabbitry, and young animals begin to die for no apparent reason, and the farmer does not know why young rabbits are dying, then, without wasting time, you need to act:
- Isolate fish that look suspicious. It is advisable to remove them not just to other cells, but to another room.
- Then you need to figure out why the rabbits are dying. To do this, the dead rabbit carcass must be taken to the veterinarian for autopsy.
- After receiving a conclusion on the cause of death, proceed either with treatment (if the disease is being treated) or with the destruction of infected individuals.
- The rest of the young should be quarantined under close supervision.
- Treat the cells where sick individuals were kept with a disinfectant.
Prevention measures
In order to prevent diseases and problems, do the following:
- Waste and food debris are removed in time, water is changed. A mesh floor helps to collect sewage.
- Disinfection is carried out regularly.
- Organize and maintain good ventilation.
- Rabbits are examined: small - daily, adults - at least once every half a month.
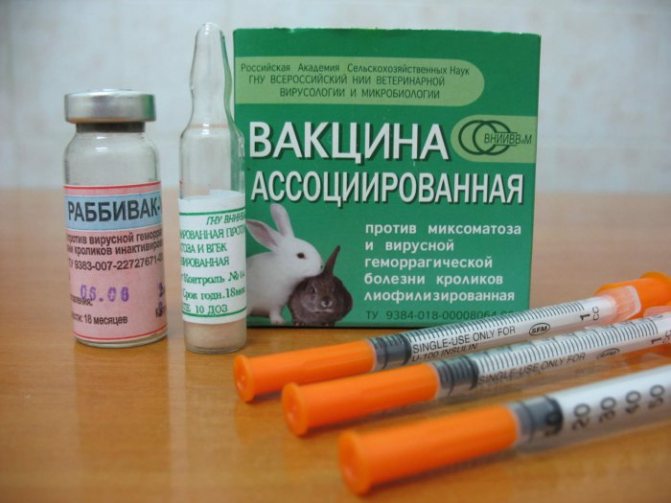
- They are vaccinated when the juveniles are about 45-60 days old. Immunity does not appear immediately. Vaccination is repeated every year. Vaccinations are a reliable, and sometimes the only way to protect, for example, with HBV.
- Make sure that there is no dampness in the rabbitry.
- They fight cold, heat in cells.
- Avoid stress or minimize it.
- Pay attention to feed. Products should be fresh, with a set of necessary substances, in a normal amount. There should always be enough water, especially in pregnant, lactating, weakened and elderly animals.
- Conduct parasites: mice, rats and insects.
- Sick individuals are isolated.
- For prevention, even healthy-looking rabbits are treated.
- The carcasses of the dead individuals are destroyed, the cells, inventory, and premises are disinfected after them.
- Keeping order. They do not allow fights, injuries.
- Protect from other animals.
- Organize spacious cages and regular walks.
- They keep the livestock in warm rabbitries, fight against drafts.
- Only suitable animals are allowed to breed. Some diseases are transmitted to offspring.
Why do little rabbits die?
All mammals at a young age very rarely die from diseases, and rabbits are no exception. The fact is that at birth, and then with mother's milk, babies receive a significant portion of immunity. The mortality rate from infectious diseases in rabbits during the suckling period is extremely low.


Why do little rabbits die?
Such a misfortune can happen if the rabbit herself is already infected with the virus and is its carrier. It can become infected both during pregnancy and after birth. An example is the coccidiosis virus. A rabbit can get sick by receiving contaminated food, then transmit the infection to the rabbits with milk.
Note! But not only mother's milk can lead to the death of newborn animals. The reason why the rabbits died was often dampness in the nest (in autumn) or cold (in winter). If the mother liquor is kept in unsanitary conditions, then various cocci may appear there, for example, staphylococcus. Such an infection is fatal for young rabbits.
Another cause of death of rabbits is rats. These omnivores are not averse to feasting on a helpless rabbit. And very often it happens that all the cubs go to be eaten by these rodents. Therefore, it is very important to carry out regular disinfection and other measures to combat rats in the rabbitry. Some farmers even breed burrowing dogs to combat them.
Every rabbit breeder should clearly know what to do if the rabbits are dying. Measures must be taken instantly, otherwise you can be left without offspring altogether.
The most common diseases of adults and young animals
Diseases that most commonly attack rabbits:
- VGBK - viral hemorrhagic disease of rabbits;
- pasteurellosis;
- coccidiosis;
- myxomatosis.
VGBK (fever) - viral hemorrhagic disease of rabbits
The high mortality rate of rabbits was established precisely from VGBK - 95%.
Individuals are sick at the age of two or more months. Infection occurs through the air, through animal feces, wool and meat.


The high mortality rate of rabbits was established precisely from VGBK - 95%
The disease may be asymptomatic.
If there is an acute phase, then the sick crawl is observed:
- anxiety;
- loss of appetite;
- losing weight;
- impotence;
- inactivity;
- the occurrence of seizures;
- throwing the head back;
- nosebleed;
- squeak due to constant pain.
The virus kills the animal in a short period (1-3 days). The liver is being destroyed, the lungs are swollen. The disease cannot be treated.
You can only vaccinate for prevention. Initially, the vaccine is given at 1.5 months. An adult crawl should be repeated at any time, at least twice in 12 months.
Myxomatosis (distemper)
If the breeder noticed mucus from the eyes or nose in his pet, as well as neoplasms in the body in the form of bumps, this indicates infection with myxomatosis, or plague.
The incubation period is one to two weeks. Throughout this time, there are no symptoms, but the animal is already spreading the infection and infecting others.


Also, during the illness, there is swelling of the eyes, nodular formations in the nose and near the ears.
After the onset of symptoms, the end is near. Rabbits die in a week, adults - in two weeks. The spread of the disease is lightning fast. If you find one sick individual, then 95% of 100% that the entire brood is already infected.
You can fight distemper with antibiotic therapy and immunostimulants. Recovery occurs in 40-50% of cases. Prevention of myxomatosis - vaccination.
Important! The meat of a rabbit that died of plague is not suitable for food.
Pasteurellosis
The disease kills the body in two days.
Visible symptoms include:
- discharge from the nose;
- loss of appetite;
- sneezing.
The better the maintenance of rabbits, their nutrition, the less mortality from this disease. Both the fourth part of the brood and most of it perish.
Pasteurellosis is acute and can be chronic.
The acute phase is characterized by:
- high temperature (39-41 degrees);
- shortness of breath;
- runny nose;
- the appearance of sneezing.
If the form is acute, the rabbit can die in a matter of days, sometimes even hours.
Symptoms for the chronic form:
- conjunctivitis;
- rhinitis;
- loose stools;
- subcutaneous abscesses (rare).
It is not difficult to cure this pathology. Early therapy does not last long.
The main thing is to normalize nutrition so that the animal receives all the necessary vitamins.
For 3-4 days, in the morning and in the evening, the antibiotic biomycin, tetracycline, sulfanilamide are injected. The veterinarian picks him up.
If the disease has become chronic, then the duration of treatment is extended to two weeks. The infected are shielded from the rest. For preventive purposes, the drug is administered to the entire livestock.
Coccidiosis
A disease in which the liver and intestines are affected. Each individual is a carrier of coccidiosis, while clinical manifestations are observed in units.
Why do decorative rabbits die?
Recently, it has become very popular to have decorative rabbits as pets. And not everyone knows how to keep them, how to feed them and how to take care of their health.
For the first time, attention was paid to these pussies at the end of the 19th century. Then they began to breed because of their wool. At the end of the 30s. of the last century, the first breed standards appeared. They began to be imported to Russia en masse after 1995.
For your information! Now there is a huge variety of breeds of decorative rabbits. Among them there are giants weighing up to 8 kg, and very miniature, whose weight does not exceed 1 kg. There are real shaggy and very smooth-haired. Some have long ears and hang to the sides, while others have very short, erect erect ears.
Decorative rabbits, like ordinary rabbits and their wild cousins, have nothing to do with hamsters, guinea pigs and other rodents. And their requirements for the content are different. They are very attached to a person, love to be given attention and very badly tolerate loneliness. On this basis, they can even get sick and die. The first signs that something is amiss is evident in their behavior:
- the rabbit refuses to eat;
- reluctantly leaves the cage;
- his movements become sluggish and heavy.
When breeding breeds of decorative rabbits, attention was paid to appearance. No one was involved in the selection of manufacturers by character. Therefore, today's descendants of old breeds have individuals with completely different types of nervous systems: from cute affectionate creatures to grumpy, pugnacious and even aggressive types.


Why do decorative rabbits die?
Pets can get sick with the same infectious diseases as their fellow tribesmen living on rabbit farms. The same symptoms, the same terms of the disease, unfortunately, the same outcome. But, in order to avoid infection, the same prevention is carried out.
Important! Decorative rabbits simply need to be vaccinated! An unvaccinated animal can pose a direct threat to the health of the people around it!
There is another reason why rabbits of decorative breeds die, this is a natural death from old age. Rabbit life lasts 8-10 years. On farms, animals are not kept up to this age, but a pet may well live to a ripe old age. Signs of his veteran age:
- refuses to play;
- a saggy belly appears;
- the lenses of the eyes become cloudy;
- wool falls out.
A rabbit in old age needs increased attention and increased care. The diet must also correspond to his "status".