Almost every farmer who grows fruit trees has at least once faced the problem of fruit rotting right on the branches. However, not everyone knows why this happens and how to deal with it. It should be noted right away that fruit units cannot rot on their own - this means that a pathological process has begun, and the problem must be urgently addressed, otherwise the infection can destroy the entire garden. In addition to the development of diseases, other factors can also become the reasons.
Causes of fruit rotting
Common causes of damage to an unripe crop are:
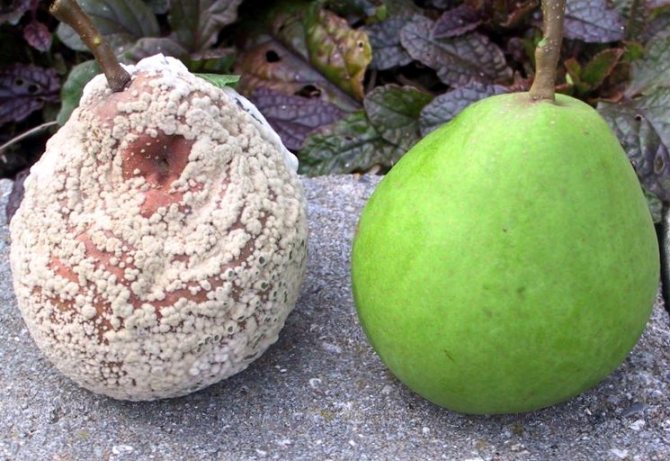
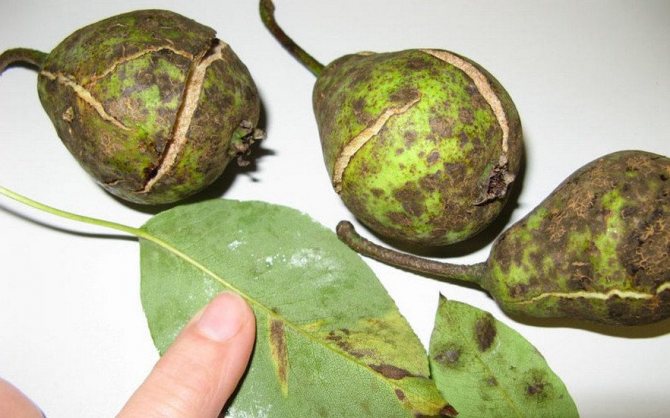
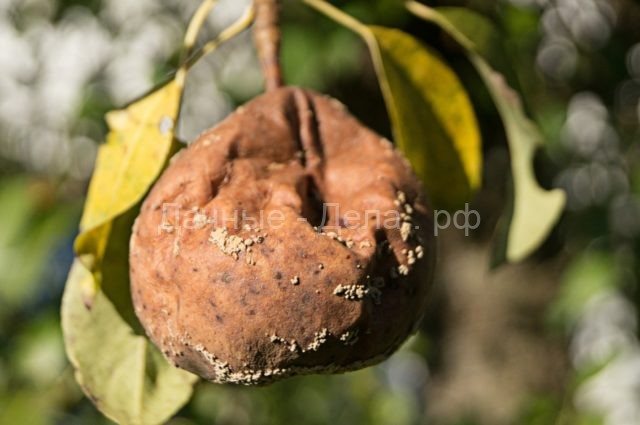
- Pear moniliosis is the most common fungal disease.Fungal pathogens develop in rotten fruits that were not removed in the fall and were left to winter on the tree. As soon as the weather conditions become optimal for development (heat and moisture), the spores of the fungus begin to actively develop, and then are spread throughout the garden by wind and insects. Disease-causing pathogens seep into fruits, the skin of which is damaged. As a rule, pears damage wasps, moths. Pear moniliosis is also transmitted by touching a sick fetus and a healthy one. The fungus is considered very insidious and can infect garden plants and vegetable gardens in a short time.That is why prevention should be carefully carried out in order to prevent pathogens from entering the garden.
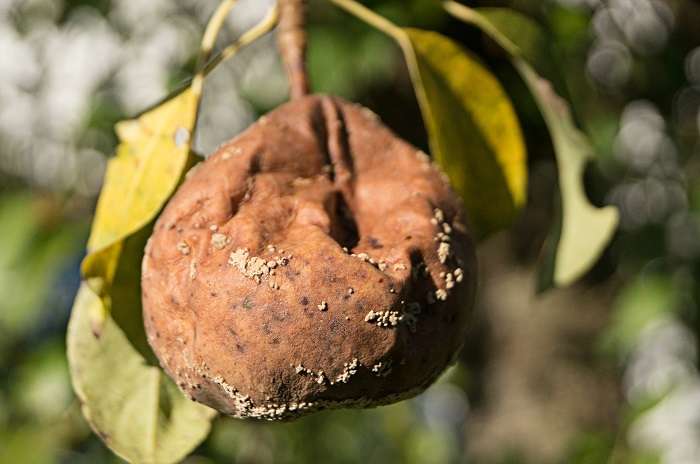

Fruit rot is a fungal disease that develops in warm and very humid weather. The disease always occurs on a plant that is affected by scab. It is very important when growing trees to give preference to varieties that are resistant to scab. Timely prevention of the disease will also help.


- Unfavorable weather conditions. Rotting trees can be observed if long dry periods are followed by heavy rains. Due to physiological cracking of the skin, harmful microorganisms enter the fruit, which can destroy the pear harvest in just a couple of weeks. Rotten fruits, with the development of the fungus, become a medium for the development of spores and pose a threat to the entire garden.
It is very difficult to treat fungal diseases of fruit crops; it is much more expedient to carry out preventive measures.
What else can cause fruit rot
Sometimes pears rot right on the tree, not because of some terrible disease, but because of poor-quality planting material, the owners' ignorance of the peculiarities of the variety, or banal non-observance of elementary care rules. Before embarking on a long and difficult treatment of a fungal disease or destroying a tree, the source of the problem should be identified.
Feature of the variety
Some old varieties have this feature - pears, not having time to ripen, soften from the inside. If the fruit is cut, the outer layer will still be hard, and in the middle there will be real porridge. By the time the pear acquires a characteristic color and aroma, there is no longer a semi-liquid mass inside, but rot.
This feature is caused by the imperfection of the variety and the culture inherited from wild ancestors. So the pear accelerates the ripening of the seeds, and they germinate very quickly. Modern cultivars usually lack this disadvantage.
Comment! This does not apply to late varieties harvested later than the due date.
Which exit? Better to re-graft the tree.You can collect pears when they have not had time to soften from the inside, put in a dark cool place for ripening. If the fruits are whole and tasty, this should be done in subsequent seasons. But since the pears are rotten inside anyway, the variety needs to be changed.
Wrong harvest time
Late varieties of pears must be picked at the stage of technical ripeness. They reach the consumer level during storage. Those gardeners who do not pay attention to this, and wait for the fruits to ripen on the tree, risk being left without a crop.
Advice! When buying a seedling, you should carefully familiarize yourself with the characteristics of the variety.
Overflow
It seems that everyone knows that a pear cannot be poured. All articles on culture write this warning. But even experienced gardeners sometimes step on the banal "rake" of watering.
Probably, at least once the issue should be given a little more attention than usual. And in order for the essence of the problem to become clear even to novice gardeners, and experienced "to see", it is better to do this with a specific example.
On a small (or very large) area, there is always not enough space. The owners are in search every season - they are trying to carve out at least a small piece of land for a new culture. They brought a wild strawberry adapted for the garden to the plot. Where to put her? And over there, under the pear, the earth "walks"! And strawberries endure partial shade well.


The culture has taken root, has grown, blossomed. Handsomely! And in the summer it began to dry up right with the berries - there is not enough water. Let's water it, we need to save the harvest. What about a pear? She's a tree, can withstand a couple of extra waterings.
So they pour water under the pear twice a week, and nothing seems to be done to her. It's time to harvest. And pears rot from the inside on the tree! No, no, this is not due to the fact that the tree was drowned in water, this is a bad variety! Let's re-graze the pear!
The next variety will be the same. So what? The gardener complains that he is unlucky with pears. Well, whatever it grafts, all one rot grows. Even from the shanks, personally taken from a neighbor, who treats all her acquaintances with beautiful sweet fruits, nothing good has come of it. Well, just some kind of mysticism!
Advice! You cannot pour the pear.
Insect prick
Often pears damage wasps - an infection gets into the injection site of an insect, the fruit rots. To prevent this from happening, the crop must be harvested on time and the fruit must not be overripe.
But not always the striped pest is attracted by the aroma of ripe fruits. A wasp can fly to the smell left by the hands of an unlucky gardener, who first picked other fruits or berries, and then for some reason decided to touch the pear. This happens quite often.
Comment! In the place where the bird pecked the pear, the infection will penetrate even faster than in the puncture left by the wasp.
Weather disasters
Strong winds swinging heavy pears can damage them in the area of the stalk. If spores of moniliosis or other infection get there, the fetus will start to rot. It is not for nothing that all recommendations for choosing a site for planting trees say: "a place protected from the wind."
Hail, which can start every few years in the summer even in the southern regions, damages not only pears, but also other crops. It is impossible to predict or protect yourself from it, but you need to treat it like a natural disaster. What hail is.


What to do?
Professional gardeners recommend:
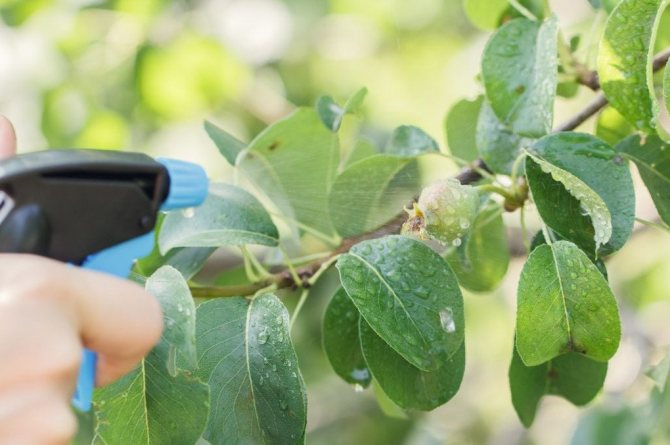
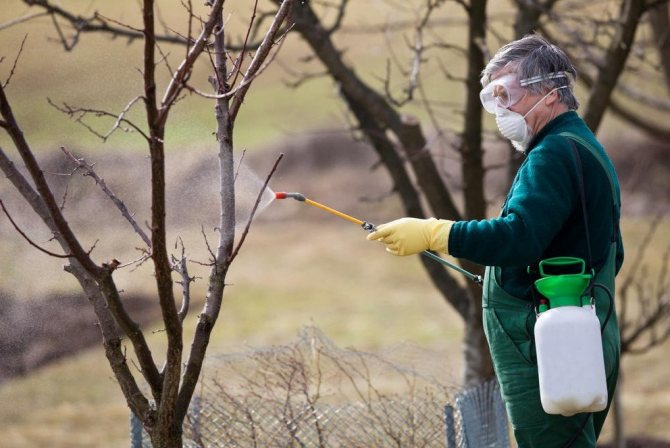
Prevention should be carried out one month before harvest.A copper-based preparation is used - Hom, Oxyhom, Bordeaux liquid. Spraying is carried out on a healthy crop.
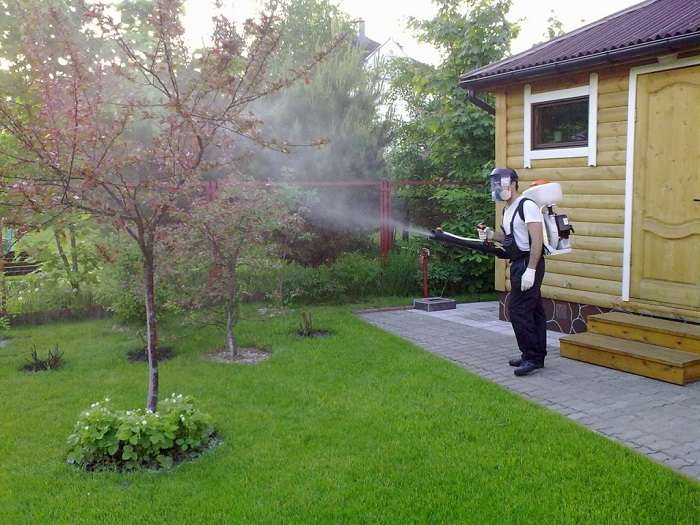


If pear fruit rot already dominates in the garden, then the effective control measures are the use of Fitosporin. The drug is used constantly with an interval of 7 days, right up to the moment of harvesting. You can also use an iodine solution (5 ml of the substance is dissolved in 5 liters of water).The plant is sprayed every 3 days.


For minor damage, Zircon is used, which will help protect healthy fruits.




Important! Using simple tips, you can achieve the disappearance of the disease from the garden and not be afraid for the harvest.
Chemical treatment
It is necessary to process fruit trees 30-45 days before the start of the harvest. There are the following methods of exposure that bring positive results in the spread of rot on fruits:
- Spraying is carried out by diluting an iodine solution: 10 drops per bucket of water, repeat the procedure after 3 days;
- Irrigation with Fitosporin is carried out as a preventive measure;
- When the first symptoms are found, you should act with Zircon;
- Affected cultures must be disinfected with Nitrafen, Iron or Copper sulfate, Oleocobrite. The procedure is carried out in March before bud break on the branches;
- During cracking and budding, spraying with Bordeaux liquid is carried out - a ratio of 10 liters is used. water 0.4 kg. funds. In the phase of advancing the flower ovary, irrigation should be performed with a 1% solution (10l: 100g of the preparation);
- After flowering, you can spray with 1% Bordeaux liquid, as well as chloroxides of cuprozan, copper, phthalan or captan.
The last irrigation is carried out 10-20 days after flowering. Apply Bordeaux liquid or copper chloroxide.
Read also: Greenery on the windowsill in winter for beginners
Tips & Tricks
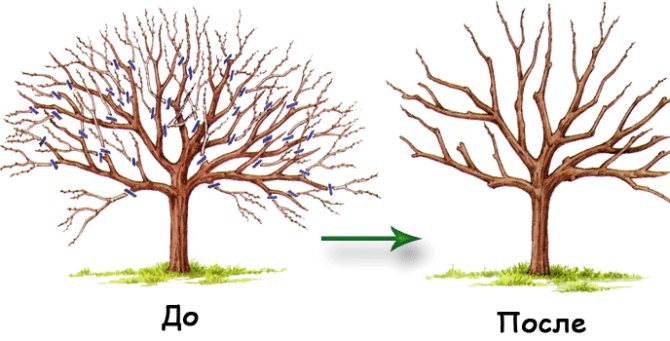
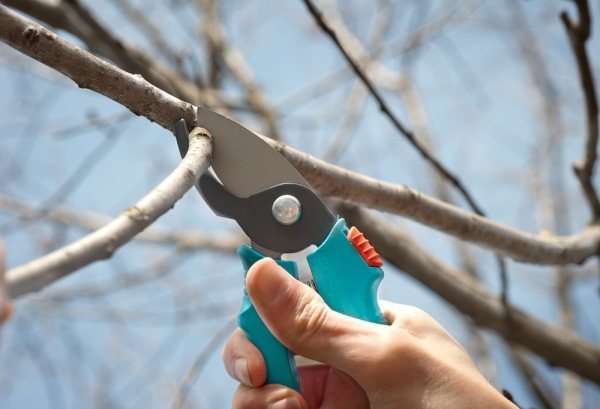
It is noteworthy that pears, like other fruit trees, rot much less if the crown of the trees is not thickened. Timely sanitary pruning will help eliminate many of the hassles associated with growing fruit in the garden.
You can prevent skin cracking if you regularly moisten the soil in the near-stem circle. When watering, the plant will not deplete, and the pulp and skin will develop evenly. The plant should be watered during the growing season, after which the soil must be mulched.


Damaged fruits should be removed from the tree, as they are the incubator for the development of spores. In the next period, fungal spores will fall from these pears and damage many plantings.
Quite often, the reason why the core of a pear rots is the cultivation of the so-called folk varieties. The fact is that genetically they come from wild animals and it is simply impossible to eliminate such a problem. A pear of incomprehensible selection is uprooted, and a varietal specimen is planted in its place.
It is equally important to fight scab in the garden. Despite the fact that the disease is not so insidious and can only reduce the appearance of the fruit, it is she who becomes the cause of many diseases. Professionals recommend spraying the garden 3 times:
- In early spring, as soon as the leaves turn green on the branches. Applies Speed or Vectra. Preparations with copper content are also considered effective.


The preparations Uniflor-micro, Florist will help to saturate the tree with microelements. You should also be careful about the iron content. Prevention - spraying with a solution of ferrous sulfate (dilute 2 tsp of the drug in a bucket of water).


Advice! Foliage and rotten fruits can be an excellent fertilizer for the garden and vegetable garden. To obtain it, you should collect all the vegetation, place it in a prepared compost pit and sprinkle it with soil.In the process of processing by soil microflora and earthworms, waste is converted into the richest humus.
Getting a healthy harvest of pears without losing fruit is a snap. To do this, you need to give a little of your attention to the plant and carry out prevention. And then the tree will thank you with sweet, tasty and, most importantly, healthy fruits.
What other problems could there be?
We arm ourselves with knowledge (just in case).
In August the pear leaves are covered with black spots... Reasons: scab or iron deficiency.
The scab itself is not so insidious. Because of it, black spots may appear on the leaves and fruits, which will slightly reduce their presentation. However, the fruit remains edible and just as tasty. Scab control begins, as a rule, in the spring. Three sprays are carried out per season:
- Young leaves are sprayed with Skor or Vectra preparations. Also, preparations containing copper are used (they have already been listed in this article). A 0.1% solution is prepared, for which 1 teaspoon of the product is diluted in 5 liters of water. The drug "Zircon" is also considered effective against scab on a pear.
- Spraying is carried out again when the ovaries have formed.
- The pears are sprayed for the last time after harvesting the fruits.
When lack of iron plants are sprayed with a 0.1 percent solution of ferrous sulfate, for which 2 teaspoons of the product are diluted in 10 liters of water. And for the purpose of prophylaxis in spring and summer, even at the stage of pear ovary formation, it is recommended to spray with the preparations "Uniflor-micro" and "Florist". They will enrich plants with microelements.
Bumps appeared on the leaves of the pear... Pests are sitting in them. In this case, you can use the preparations Iskra-Bio or Fitoverm.
Pear fruits crack and rot on the tree: 5 reasons why they turn black on the branches before they ripen
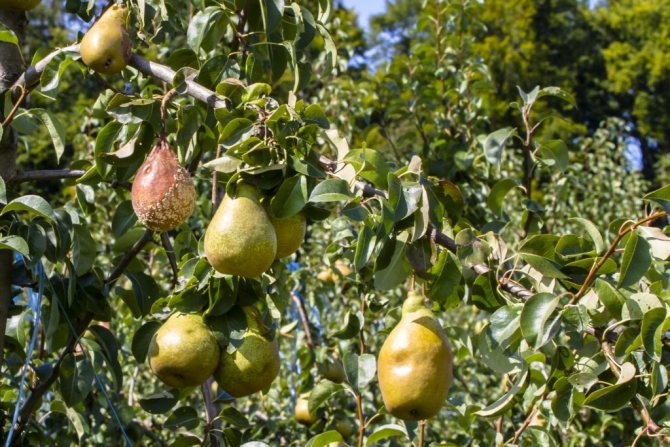
The main reasons why pear fruits begin to rot include: infection with infectious diseases, hail that injured the fruits, damage by the moth, excess or lack of moisture, improper care, scab or moniliosis. Depending on the cause, a method of treating a sick tree is chosen. This problem applies not only to pears, but also to apple and cherry trees. Therefore, it is important to know what to do in such a situation and how to prevent lower yields due to rot.
Pears from our garden: photo
These are the pears we managed to grow in 2020.


Pear is a fragrant fruit with delicious juicy pulp. Every garden is not complete without a pear tree.
The fruits are consumed fresh, and they also prepare compotes, preserves, confitures and make juice. The advantage of the fruit is that it has a long shelf life.
Every gardener strives to get a good harvest. But it happens that the fruits begin to rot before they have time to ripen on the tree... What are the reasons and how to save the fruits?
Reasons why pears start to rot
Consider the main causes of pear fruit rot and how to deal with them.
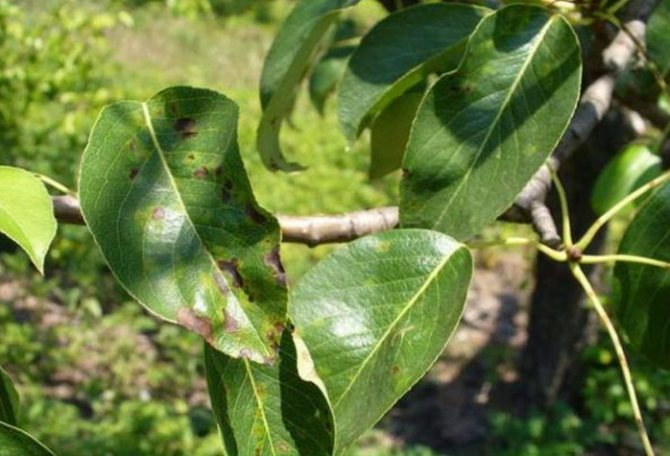
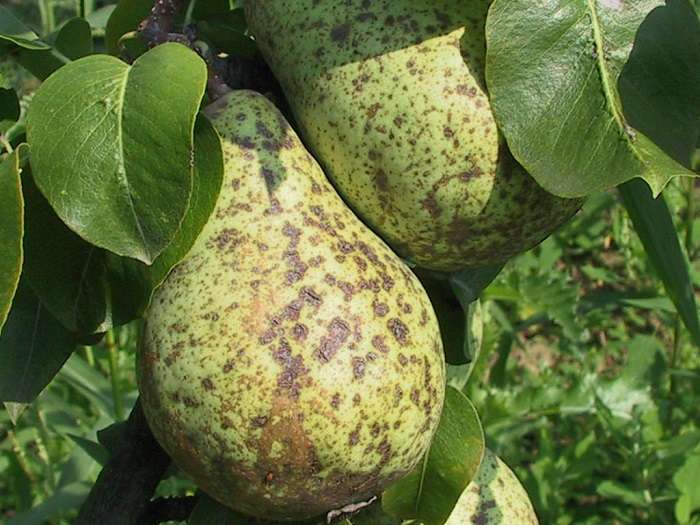
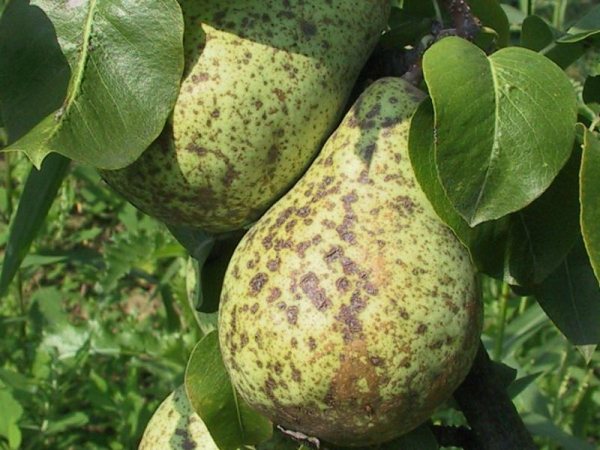
Fruit scab: brown spots on fruit
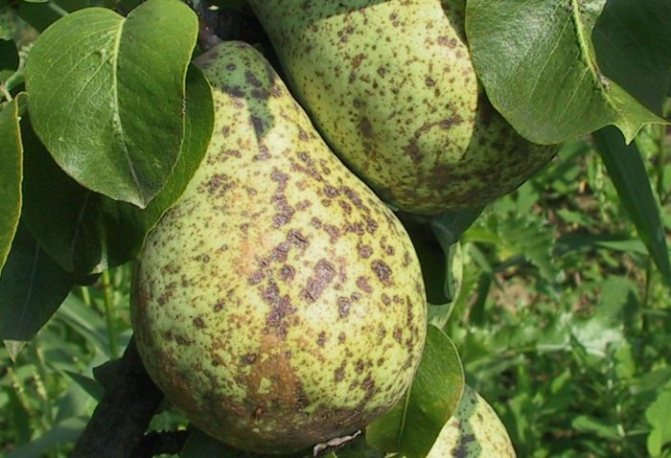
Scab is a common fungal disease of fruit trees in the temperate climatic zone. Pears cease to form ovaries, which accordingly affects the yield. If already fruiting plants have been infected, dark brown spots with a characteristic bloom are formed on the fruits, which greatly spoils the taste.
Read about red dots on pear leaves and how to deal with them in this article.
What to do: control measures
To treat pears for scab, spraying with copper sulfate and lime is used - this event will have to be repeated several times a year. Good results are obtained by treating pears with Bordeaux liquid or colloidal sulfur, copper oxychloride, copper sulfate. In advanced cases, treatments are carried out 5 times per season:
- When the kidneys formed and swollen - spraying with copper sulfate.
- When buds form - it is recommended to use the fungicide "Skor".
- After the end of flowering - you can use "Speed" again.
- In half a month.
- At the end of summer.
Alternate between the preparations you use to treat scabs on trees, as they become addictive.
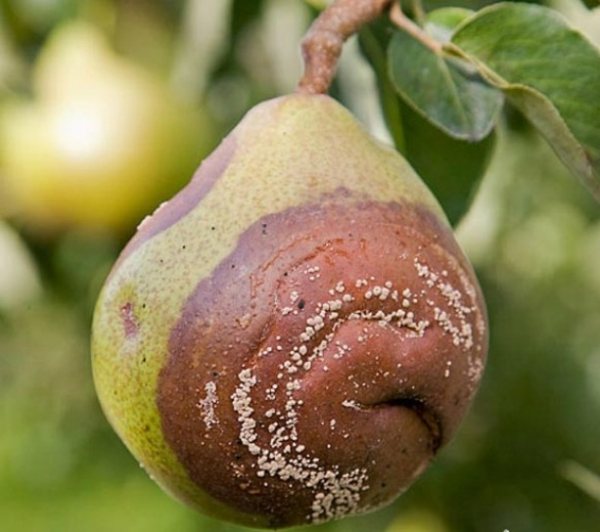
Mollinosis or fruit rot when the fruit begins to darken
Mollinosis is a fungus that enters the fetus through lesions on the skin. Also, direct contact of a healthy pear with a sick one can become the cause of infection. The pathogen normally tolerates winter cold, therefore, in the fall. Mollinosis is transferred along with spores of insects and wind. The pathogen loves warmth and high humidity, therefore it is most often found on pears with strongly thickened crowns. Infected fruits usually fall off in strong winds, but they can also reliably hold on to the stalk, drying out over time (that is, they are mummified). In appearance, pears begin to darken, and then rot appears.
Preventive measures
Correct agricultural technology is the best prevention of pear fruit rot. To what is written in the chapter "Agrotechnical techniques" should be added the early spring and late autumn processing of wood with copper-containing preparations.
Sometimes growers complain that treatments are ineffective. Some even point out the reason - a blue sediment remains at the bottom of the cylinder, therefore, copper does not dissolve well and does not fall on the tree. To make your life easier, you can buy drugs that the manufacturer produces in the form of an emulsion, for example, Cuproxat.


Prophylaxis
Pears need careful care and attention throughout the season, but special care should be taken in the spring:
- Pruning - it is necessary to remove all dried shoots at the end of winter, until the kidneys had time to swell. You can do pruning of broken, dead branches, going to the healthy part. Remove all last year's leaves, and also remove those that remain on the branches, burn them.
- Do the same with mummified fruits, as they are potentially hazardous to the new crop.
- Thin the crown - so the trees will dry out faster after rains, abundant pear irrigation and sprinkling.
- If the crops are too plentiful, you need to leave only large fruits.
- Remove pears from the tree carefully, so as not to damage either the crop or the branches themselves. Each fruit should be carefully examined before being sent for storage.
- Treat with organic fungicides in a timely manner. As the buds swell, the trees are treated with Bordeaux liquid. Also work with the near-trunk area, which can be affected by pests and fungi. Repeat the procedure several times until the fruits are ripe.
You can read about how a pear is properly pollinated in this material.
A non-thickened crown leaves practically no chance for mollinosis, so do pruning and shaping in a timely manner.
Old garden
As the tree grows, the fruit may become small, sparse, herbaceous, or begin to mend directly on the branches. In such cases, the pears become soft and tasteless on the inside, the middle rots, causing the fruit to fall off.
The only defense against this trouble is a radical rejuvenation of the garden. Old trees are cut down, giving interests to new ones. For renewal, it is recommended to choose noble varieties, and an unprofitable wild tree - they will delight you with a tasty harvest for a longer time.
That's all you can get out of the situation by removing the unripe fruits, and letting them limp on a litter in a warm, sunny place. Compotes, preserves and marmalade are made from sour greenish pears. It retains enough vitamins and pleasant juice.
It will be necessary to find out that an unkempt pear is running wild. If you do not cut off the branches in time, do not graft the plant, then to this day the tree will spend its strength on the growth of the trunk and greenery, and the fruits will become "idle".That is why it is so important to choose for new plantings cultivated selective varieties that are less prone to degeneration.
Small slender trees bear tender and ruddy fruits, almost never get sick and are well pollinated. Young trees produce more scented pollen by attracting pollinating insects. Therefore, it is important to renew the branches, allowing new shoots to break through.
Why do pears rot and crack on tree branches?
Everyone noticed rotten pear fruits on the tree, old breeding varieties are mainly susceptible to this phenomenon. Since their ancestry is directly related to the wild pear.
It so happens that there is only a small speck on the skin, and inside all the flesh is brown and very soft... This speaks of the insidiousness of the fungus, which is ready to destroy not only the appearance, but also the taste.
Fruit rot on apple and pear trees:
Sporulation of the fungus appears on the infected fruit, on which conidia are formed. They are carried by wind, rain and insects.
As a result, the remaining fruits are completely infected. Rotting of a pear begins with the tail and by full ripeness the fruit can rot completely.


The cause of pear rotting right on the tree is a fungal disease - fruit rot
The problem must be solved radically, that is have to remove the old tree.
There is another option save the harvest. Harvest unripe pears. Large and firm green pears are laid out in the shade, and after a few days you can enjoy the aromatic, sweet fruits.
As for the varieties of the new selection, they ripen on the tree. They are stored for a long time in a cool place. Fungus becomes the cause of rotting.
The fight against the disease is necessary instantaneous. Harvest infested pears away from healthy people. Fruit infected with moniliosis should not be buried in the ground or stored in a compost pit.
Why? This is due to the fact that fungal spores tolerate cold well, so they can fall on other trees in the spring. And a massive defeat threatens with a lack of harvest.
Moniliosis on fruit trees:
Why are insect pests dangerous for an orchard
The moth is a garden moth that attacks pears, apple trees, peaches and other fruit trees throughout the summer. It is she who is one of the most frequent threats. This moth spoils the wholeness of the fruit, leaving inside its caterpillars, which develop in the garden, and boldly migrate from tree to tree. The weevil beetle hunts in the spring and summer, spoiling not only the fruits, but also the buds, flowers and young foliage. This parasite pierces the fruits, making a hole in them, and leaves its faces to develop in the sweet environment, after which it attacks the following trees.
The danger of these pests is not only in their high numbers, but also in the fact that such an infection is potentially harmful to the entire garden. When the spoiled fruits fall off, the caterpillars leave them and move to a new juicy "house".
To protect the garden from an insect raid, several methods are used:
- Fallen fruits are carefully collected from the ground throughout the summer and autumn to avoid pest migration.
- Illuminated traps are placed around the garden, because, as you know, butterflies fly to bright lanterns. Containers with kerosene or soapy water are placed next to the lamps. Also, the moth is attracted with apple syrup or whey, hanging traps directly on the branches.
- Sticky tree wraps also help: the trunk is wrapped with rags or thick paper and impregnated with solid oil, non-hardening glue. Caterpillar, larvae and beetle are collected on such barriers.
- A gentle and simple solution of field chamomile will help from the weevil. Make a mixture at the rate of 150 g of dry raw materials per bucket of water, leave for a day, strain, mix with a little soap and spray the foliage of the trees. The use of such a drug must be alternated with coniferous, onion or garlic broth so that the tree does not have time to get used to processing.But such "fragrant" infusions are allowed to wander for 2 weeks before use in order to achieve the effectiveness of the care.
- Spraying with infusion of tomato tops or wormwood will also help. 400 g of dry raw materials are taken in a bucket of water and the solution is boiled for an hour, after which it is used in the usual way.
Read also: Potato tops turn yellow: what to do, causes and treatment measures with photos and videos
Interesting to know!
Some gardeners set up birdhouses and bird feeders on the site. When wild birds settle in such a territory, woodpeckers and other species appear on it, which help to clear the trees of insects.
Where does fruit rot come from on trees?
Moniliosis fungus can enter the fetus through lesions in the skin. It is easy to damage the fetus. This can be done by insects, hail, rain, wind.
Infection is also possible due to close contact with a fetus infected with a fungus. From last year, infected fruits may remain hanging, which spread the infection to the new crop.
The crown of a tree can also spread the disease., therefore, all affected leaves, branches, fruits must be removed during sanitary pruning.
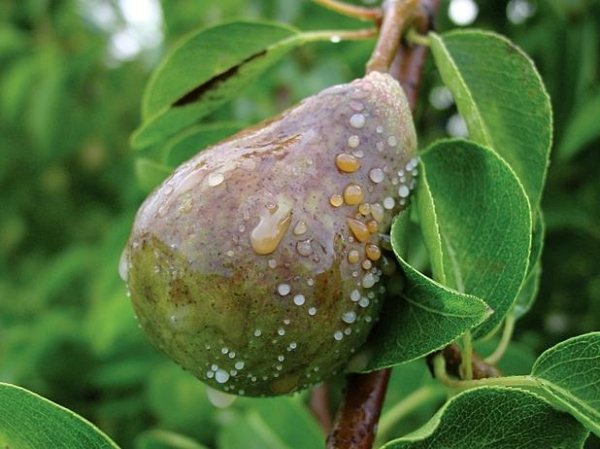


The fungus can get on the pear through insects, hail, rain and wind.
Prevention of the garden from pests throughout the year
To get the enemy out of your territory, you need to carefully monitor the health of the trees and maintain the hygiene of the garden. Most infections and larvae persist in frost, therefore, the preventive cleaning process begins in early spring after the snow melts:
- Collect all dry leaves, branches, rotten fruits, both from the ground and from trees, and burn such potentially dangerous debris in which infection could remain.
- Pruning is carried out, and not only dry and frozen branches, but also shoots that were in the affected area. It is important to carry out this procedure even before the first buds appear, in order to deprive the pest of the opportunity to develop.
- They dig rows between plantings and around the trunks, loosen the soil, destroying all remnants of infections. First, such a procedure is best done in the fall, immediately after the harvest, and then - in the spring, "revitalizing" the earth.
- 3-5 times the orchard is treated with copper.
- Ripe foliage is thinned so that the garden dries up faster after rains, and the fruits receive more sun. The overwhelming majority of pests love shade and stagnant moisture.
- If the harvest is very plentiful, the weak fruits are taken away, giving strength to the largest.
- Remove the fruits from the branches carefully so as not to damage the integrity of the tree.
Take care of your trees - and they will generously reward you with their fruits.
What to do if the fetus is rotting, how to deal with moniliosis?
Caring for future harvests starts in spring... As soon as the snow melts, you need to inspect the tree and the area around it. Collect all last year's foliage and branches, and most importantly, fallen fruits.
If last year's fruits are hanging on the tree, they must be removedb, as they can be infected with fungal spores. He loves a dense crown and dried branches that do not give a crop.
Therefore, in order to prevent moniliosis from multiplying, it is necessary to thin out the crown, cut off dried and weak branches.
You may be interested in the following publications:
- The benefits and harms of pears for the health of men and women.
- Scheme and features of pruning pears in autumn, spring and summer.
- Pear care in autumn and preparation for winter.
If the pear variety is prone to rot formation, be sure to treat the tree with drugs as a prophylaxis:
- First processing must be done during the period of swelling of the kidneys. To do this, use products containing copper. They will help protect the tree from moniliosis. You can use Bordeaux liquid as a chemical.
- Second processing preparations after pear flowering.
- During fruiting carry out the procedure several times.
- Last treatment fungicidal to be carried out after harvest. To do this, use copper sulphate, which needs to be well treated with the crown, the trunk of the pear and the trunk circle.


Be sure to treat the tree as a prophylaxis with Bordeaux liquid and copper sulfate
At high air humidity all varieties of pears must be treated with preparations to prevent the spread of the fungus.
It is advisable to use organic fungicides such as bordeaux liquid, copper oxychloride... Processing can be carried out during and after flowering.
Moniliosis affects only the fetus, but spores of the fungus can be stored on foliage, crown, ground. As soon as you notice rotten pears on the tree, immediately remove them from the branches so that the infection does not spread further.
Collect fallen rotten fruits, as they are also a carrier of the fungus.
Experienced gardening tips
In order to safely grow the harvest of plums, pears, apples, quince, farmers should avoid punctures that many farmers sin with, especially beginners:
- do not neglect regular tree inspections;
- promptly treat detected infections;
- not to violate the agrotechnical rules for caring for fruit trees;
- regularly carry out preventive treatments of plants;
- do not leave garbage in the garden in the fall, be sure to dig up the soil in the zones of the near-trunk circles;
- feed the trees correctly, on a schedule.


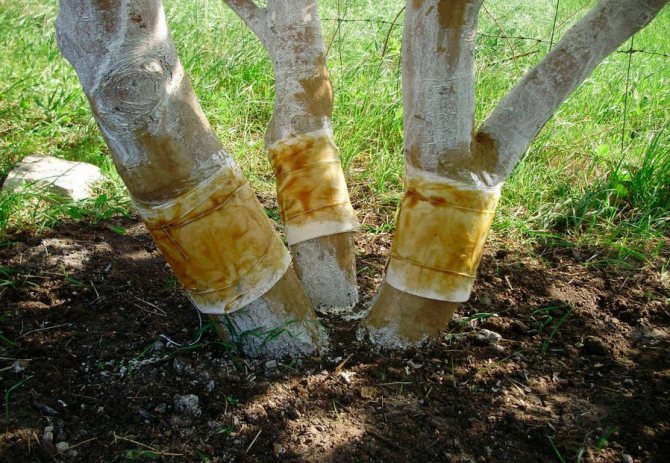
Preventive measures against garden rot include: correct selection of seedlings, routine and pre-treatment of trees and soil, control of insect pests, immediate removal of affected fruits and branches from trees. Spring preparation of the garden for the next season is extremely important: clearing of debris, whitewashing of trunks, digging up the soil.
Growing a bountiful harvest of plums is not easy. To do this, the gardener needs to know and correctly apply the means of protecting fruit trees from pests, fungal infections, and correctly build agrotechnical plant care. To avoid the need to treat the affected trees, it is necessary to carry out their preventive treatment in time, fertilize correctly, and take care of the safety of ripening fruits.
Fruit trees need full sun spectrum for better fruit production. Insufficient sunlight delays the onset of flowering and can reduce the number and size of fruit, as well as weaken the tree, which can later cause rotting due to disease or pest attacks.
Avoid planting fruit trees in places where they will be shaded by buildings or other trees. Plant residues collected under trees infected with fungal or viral diseases cannot be used for composting. When composting, mushroom spores will not die, but will develop further.
The gardener needs to remember:
- the fungus hibernates on leaves that have fallen from a tree affected by diseases;
- in the spring, spores of pathogenic fungi enter the air with the help of the wind and are carried around the garden;
- in rainy weather, a suitable environment for the development of fungal spores appears, and you need to carefully monitor the trees so as not to miss the onset of the disease;
- It is very important to collect and burn all the leaves around the diseased trees in the garden in the fall.
So that, according to the results of cultivation, the gardener is not disappointed with the harvest of pears damaged by rot, the owner of a pear tree must adhere to the rules for caring for this crop. It is also important to take all preventive measures to ensure the health of the fruit tree.
Prevention of fruit rotting
It is necessary to take care of the tree throughout the year, but special attention should be paid to early spring:
- Pruning dried shoots at the end of winter, before the buds swell... Prune dead and broken branches with an approach to the healthy part. At this time, it is necessary to collect and destroy all last year's fallen leaves remaining on the branches.
- Collect all mummified fruits, they pose a danger to the new crop.
- Thinning of the crown is necessary so that the trees dry out faster after rain. Due to this, the chances of getting sick with moniliosis in a tree is reduced several times.
- Thinning of fruits... For a good harvest, leave only large fruits.
- Remove fruits carefully during harvest, don't damage the branches. Inspect each fruit before storing the pear. Infected pears should not remain on the tree and the ground, they must be destroyed.
- Wood treatment with organic fungicides... When the buds begin to swell, it is advisable to treat the tree with Bordeaux liquid. It is necessary to process not only the tree, but also the near-trunk territory. Treatment should be carried out after flowering with fungicidal preparations that will protect the fruits. The procedure is repeated several times, before fruit ripening and after harvesting.


Thinning the crown and fruits on a pear tree, treating with fungicides will help protect the crop
Remember that timely fight against fungus will save the harvest... Moniliosis affects fruits with seeds and seeds, therefore, at the first signs of the disease, it is worth starting an active fight against the problem.
Take care of the tree in time, and it will surely thank you with a rich harvest.
Recording Why do pears rot on a tree and what to do about it? first appeared About the farm.
Gardening mistakes and prevention of garden rot
Common mistakes:
- The fallen carrion is not removed. Fallen and infected fruits must be collected and destroyed daily. They are the source of a disease that is easily transmitted by pests.
- The whole crop is not harvested. Overripe fruits remaining on the branches are easily infected with a fungus and are the source of the disease, which will move to a new crop next year. Therefore, it is necessary to remove ripe fruits in time.
For prevention, it is required to protect the plant from pests and monitor the condition of the crown, preventing its thickening.


In August, we all look forward to the pear harvest. Self-grown fruits are juicier, softer and sweeter than purchased ones. But already at the stage of maturation pears may suddenly start rot right on the tree. What to do and how to save the harvest? We find the answer in one of the directories of our summer cottage library (
The reason why pears rot on the tree
The fruits are affected by the fruit rot caused by the fungus.
Fruit rot - photo, description and control measures
Adding an article to a new collection
Fruit rot (moniliosis) is a gardener's nightmare. The fungal infection quickly spreads through the garden, destroying apple trees, pears, plums, cherries, sweet cherries and cherry plums. In warm and humid years, you can miss up to 80% of the harvest. Is it possible to defeat this attack?
The causative agents of fruit rot of trees are a group of fungi that infect leaves and fruits and cause decay of most of the crop. Both pome crops (apple, pear, mountain ash, quince) and stone fruits (cherry, sweet cherry, plum, apricot, peach) are under threat. The infection is carried by the wind, spread by raindrops, and transmitted by insects. First of all, it affects fruits with wounds and cracks, damage and wormholes, which are caused by birds, wasps, hail or diseases.
Pear scab
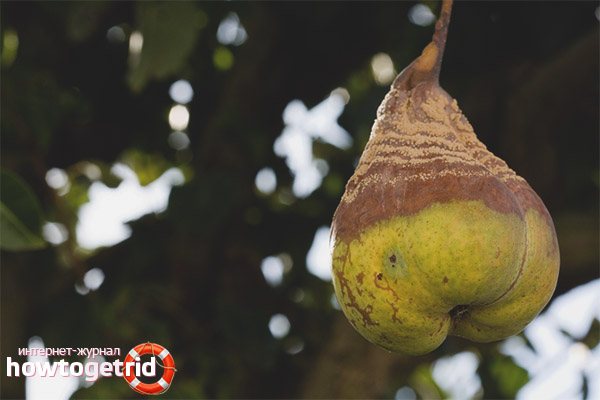
Scab is a dangerous disease. Pear fruit affected by this disease.
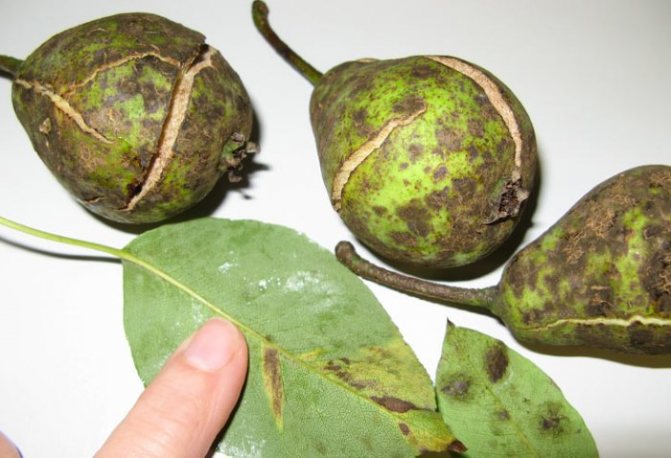
Scab can lead to the formation of deep cracks in pear fruits. As a rule, it is this fungal disease that is the most common cause of cracks.
The places of the pear, affected by scab, turn cork and burst, the fruits stop growing, the peel dies off.
Scab control measures - fungicide treatment:
- Azophos - during the beginning of budding (100 ml per 10 liters of water);
- Pennkoceb (Tridex) - during bud break (20 g per 10 liters of water);
- Speed - before flowering (1.5-2 ml per 10 liters of water);
- Strobi - during the growth of fruits (1.5-2 g per 10 liters of water).


The causative agent - the fungus Fusicladium pirinum - affects many garden and vegetable garden crops. This is the most common pear disease, but the leaves of the tree are also often affected.
At the initial stage of the disease, spots of olive and yellowish colors with a velvety bloom appear on the underside of the leaf plate (this is an accumulation of fungal spores). After that, the disease passes to the fruits: they are covered with dark putrefactive spots, and the peel cracks in these places. The fruits become deformed and tasteless.
To prevent scab, trees are sprayed with 1% Bordeaux liquid 3 times per season: in spring, when the leaves are blooming, on the buds and after flowering. In addition, the crown of trees is thinned out in a timely manner so that the plants are well ventilated. The carrion is regularly removed, and the fallen leaves are burned. If the trees are heavily infested, they are sprayed with the fungicide Skor (according to the instructions).
- Scab - signs of the disease and methods of treatment
Why is scab, although it does not destroy plants and fruits entirely, is considered one of the most unpleasant diseases of horticultural crops?
Such pear varieties as Muratovskaya, Rusanovskaya, Yanvarskaya are relatively resistant to scab.
Common signs of fruit rot
Sources of infection are usually affected fruits that were left hanging on trees after harvest, as well as dry branches affected by moniliosis that were not removed during sanitary pruning. The first signs appear with carrion, with which the spores are transferred to healthy fruits. Rotten fruits that remain hanging on trees are mummified and remain carriers of the infection for two years. Through the peduncle, the fungus penetrates into the fruit twig (fruit) and nearby branches and hibernates there. In spring, it passes into a young ovary, causing wilting and death of overgrown branches.
With the onset of warm (24-26 ° C) and damp weather (humidity over 75%), fungal spores begin to actively transfer from plant to plant. Once on young flowers, they penetrate, causing the petals and leaves to wilt.
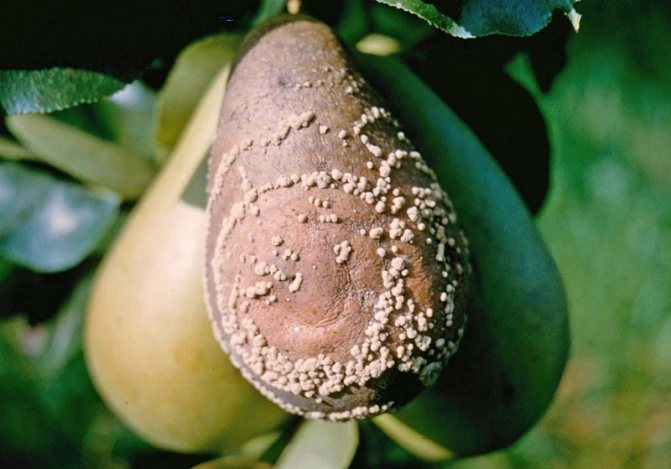
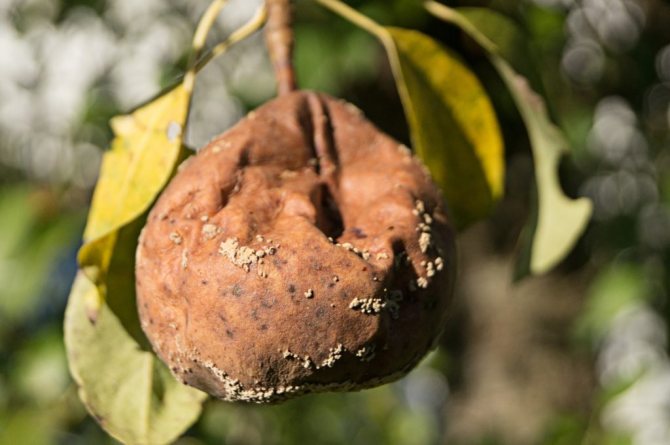
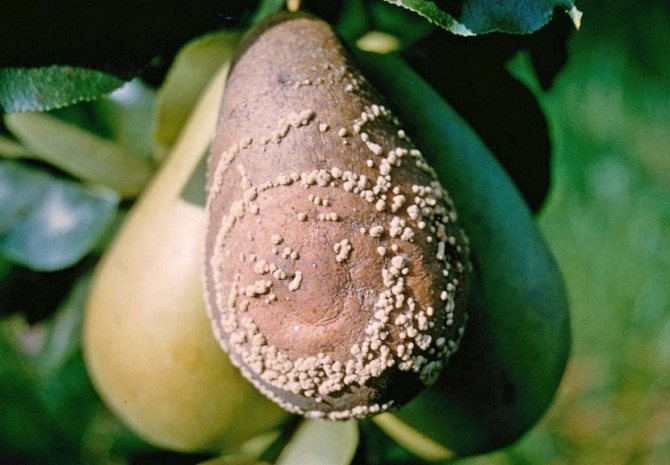
Subsequently, spores affect both green and young, and ripe fruits. Large white growths (carriers of fungal spores) appear on them, arranged in neat circles. Brownish spots also appear, which increase as the disease develops and cover the entire fetus in just a week. The pulp becomes loose and loses its flavor.
In the second half of summer, the second wave of the spread of the fungus begins. First of all, apples and pears are "hit", less often - plums and cherries. During storage, the fungus causes black rot of the fruit, which becomes glossy black with brown flesh.
Fungal infections on the pear
You can often find a fruit fungus in the form of growths on the fruits and leaves of a pear, which seems harmless. A dense crusty coating covers the fruit, due to which their taste and aroma properties are significantly deteriorated, and the pulp coarsens. So that your pear does not lose value, you need to fight with such a fungus by spraying:


- In the spring, when the kidneys appear - copper sulfate.
- During the ovary of flowers and after flowering - with the preparation Speed.
- During the summer, repeat the procedure after another half month and at the end of the season after harvest.
- Alternate preparations of colloidal sulfur, Bordeaux liquid, copper sulfate and copper oxychloride so that the parasite does not develop immunity to the remedy.
Another ailment is mollinosis. This fungus penetrates deep into the fruit and makes it ferment. Such pears deteriorate right on the branches, softening and becoming covered with characteristic white growths that look like mold. In the presence of wind, such fruits fall off, but sometimes they remain on the branches and dry out. Mollinosis is spread from spoiled fruits to fresh ones by the wind or by close contact.
Note!
A source of infection such as mollinosis is potentially dangerous for the entire garden, therefore it is very important to destroy infected fruits in time. The contaminated material must be burned and in no case left to lie under the trees.
In the spring, the garden must be cleaned of dry debris. If signs of fungus were observed on the crop, all potential carriers are burned and the crown is treated during the swelling of the buds. The second treatment is done during flowering, and after that - 2-3 times during the ripening of the fruit and after harvesting. For care, organic and copper-containing fungicides are used. It is necessary to pay attention not only to the branches and crown, but also to the bark and the near-stem area.
Pome fruit rot (apple, pear, quince)
Moniliosis, or pome fruit rot, is one of the most dangerous and common diseases. The fungi that cause the disease are absolutely resistant to the most severe frosts, many traditional methods of treatment and prevention. How does fruit rot manifest itself on plants?
Signs of moniliosis pome fruit
Initially, a small reddish spot is formed on the surface of the fruit, which increases in size every day and gradually covers the entire fruit. It becomes completely brown, softens and is no longer suitable for food. In parallel with the browning, light yellow sporulation pads appear on the surface of the fruit, which form continuous rings of regular shape. The diameter of the pads is 2-3 mm, and they are all filled with new spores of the fungus.
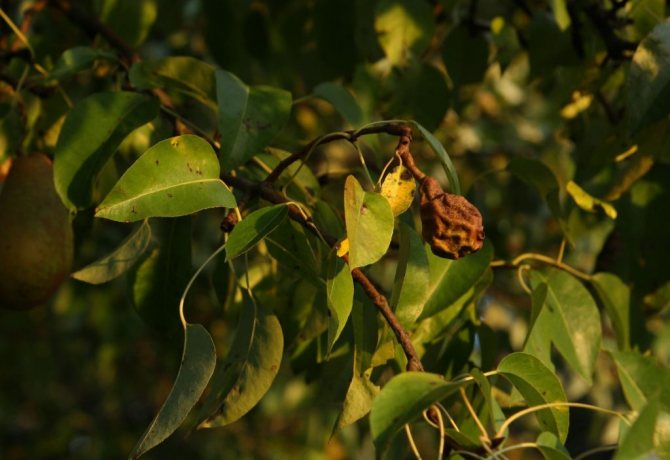
The fruits of apple and pear trees completely rot in just 3-5 days after infection, and sporulation begins in 8-10 days. If the fruit is not removed, it will mummify and cause further spread of the fungus. The color of apples, pears and quince changes to bluish or blue-black with a glossy shade.
The overwintered fungus begins a destructive effect in early spring, penetrating the ovaries and flowers, as a result of which they begin to turn brown and dry, ringlets and fruit twigs die off. Depending on the type of fungus, ash-gray spore-bearing pads or ocher-colored formations are formed on the flowers.
The harmfulness of fruit moniliosis lies in the defeat of inflorescences, flowers, fruit twigs and, finally, the fruits themselves at any stage of development. Crop losses are at least 30%, and sometimes reach 80%. Moreover, not only the harvest on the trees perishes, but also the one in storage.
There are no varieties of apple, pear or quince with absolute resistance to fruit rot. All of them are more or less susceptible to infection with moniliosis.
Measures to combat pome fruit moniliosis
- Avoid damage to fruit by pests, birds, hail and garden tools. Remove damaged fruits immediately and never store them. Harvest carefully so as not to damage the fruit.
- Perform preventive spraying of the garden one month before harvest. Use Fitosporin-M or iodine solution (dilute 10 ml of substance in 10 liters of water and spray trees evenly). Repeat spraying after 3 days.
- Collect and burn fallen leaves, diseased flowers, and carrion that shows signs of damage. Remove damaged twigs and shoots in a timely manner. Perform the whole range of agrotechnical measures for tree care - carry out timely pruning (in the fall after leaf fall, when the crown opens, and in summer, when damaged fruits and branches are visible), do not allow the appearance of pests and signs of other diseases.
- It is especially important to protect trees from the development of scab, which provokes moniliosis. To do this, spray pears and apples with 3% Bordeaux liquid (300 g of copper sulphate and 450 g of quicklime per 10 liters of water) in the green cone phase, that is, at the very beginning of bud break.If spraying was in the bud extension phase, use a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid (100 g of copper sulfate and 150 g of quicklime per 10 liters of water). The second spraying is carried out immediately after flowering (with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid or fungicides (Abiga-Peak, HOM, according to the instructions). The third spraying is carried out 15-20 days after flowering (with copper chloride 40 g per 10 l of water or 1% - no less Bordeaux liquid) .At one tree during each treatment, you need to consume at least 2 liters of solution.
- Plant apple varieties that are relatively resistant to moniliosis (Idared, Babushkino, Kandil Sinap, Slavyanka, Uralets) and pears (Aurora, Bere Zimnyaya Michurina, Conference, Oktyabrskaya, Saint-Germain).
Harvest conservation measures
Control measures can be different, everyone can choose the most suitable option for themselves.
Chemical treatment
The plant is processed one month before technical maturity. When the fruits are ripe and begin to rot, processing is prohibited. Suitable preparations:
If time is missed and rot is noticed during ripening, then you can treat it with the drug "Fitosporin". They are processed weekly until harvest is complete.
At the first signs of illness, Zircon will help. Processing begins as soon as the first rotten specimen was found. This will help save healthy fetuses from damage.
Folk remedies
At an early age, the plant will help the plant to cope with rot with simple tools that do not harm the environment:
- If the fruits begin to dry and rot from the inside, then citric acid (40 g) and ferrous sulfate (25 g) diluted in water (10 l) will help. The prepared solution is stored for no more than 2 weeks. Spray the pear if rot is detected.
- A solution of soap (50 g), water (9 l) and ash (500 g) will help to cope with pests.
- A good anti-rot agent is colloidal sulfur.
If the disease has become widespread, then it is better to use chemicals.
Correct care
If the fruits dry out and rot, then the main reason lies in illiterate care and non-observance of the basic rules. If the tree is old and the cause of rot is only this, then the harvest is unripe. Then spread in the basement on a layer of newspaper. This event will help the fruit ripen and not be affected by rot.
If moniliosis develops on the plant, then it is necessary to carry out in the autumn:
- Sanitary pruning. Remove all branches, fruits, leaves affected by the disease.
- The carrion is collected and buried in the ground. The minimum depth is 1.5 meters.
- Rotten specimens should not be thrown into the compost pit. The bacteria have a good survival rate and will pass back to the plant at the first feeding.
Diseases are spread by parasites-pests. They spread spores and infect the fruit from the inside. To eliminate the disease, the plantings are regularly treated with the necessary preparations on a regular basis. A healthy tree resists infections more easily, so proper and timely feeding will help the tree to be strong. Weeds should be removed regularly. To reduce the number of weeding, the area around the trunk is mulched.
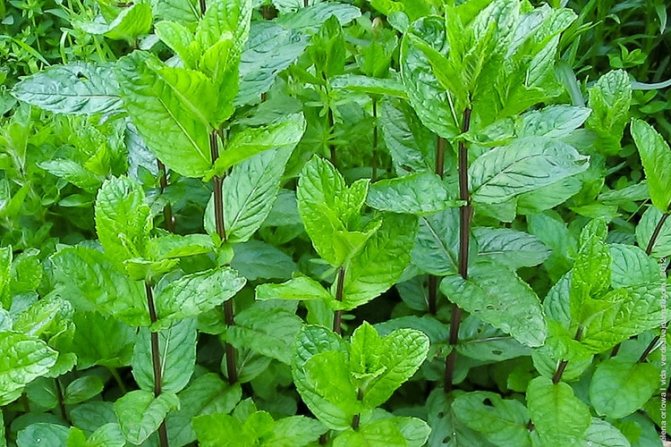
Helper plants
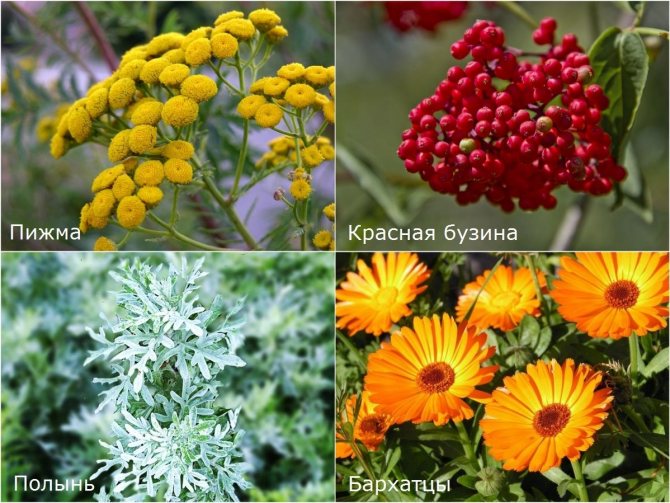
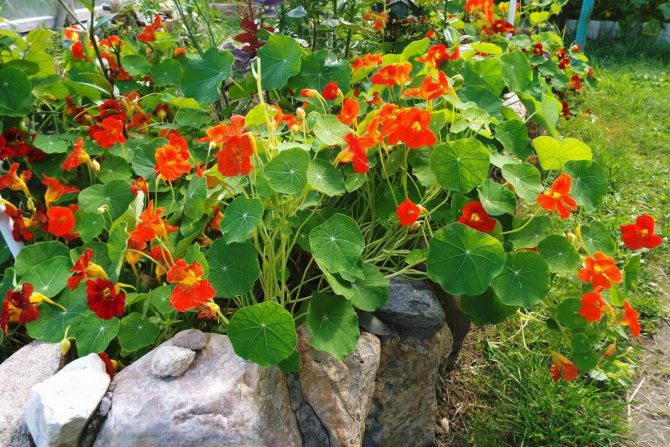
To protect against pests, it is recommended to plant around the pear:
- Marigold. They repel many pests with their smell. Also, decoctions and infusions are prepared from flowers, with the help of which the plant is treated from rot.
- Moth moths bypass the trees, next to which grow bitter wormwood and elderberry.
- Mint.
- Sagebrush.
- Thyme.
Well-distributed repellent plants will help to heal the plantings. Using them on your site in combination with preventive measures, it will be possible to achieve a high yield of healthy fruits.
Fruit rot of stone fruits (cherry, sweet cherry, plum, cherry plum, apricot)
The fungus that causes stone fruit moniliosis is slightly less common than the fungus that infects pome crops, but under favorable weather conditions it can also destroy almost the entire crop.
Signs of stone fruit moniliosis
The fungus hibernates in mummified fruits, infected branches and shoots, and in spring it begins to spread throughout the site. The disease is most pronounced in seasons with high temperatures (up to 28 ° C) and humidity over 75%.
External signs of infection are manifested in the fact that at first the shoots and branches of trees turn brown, wither and become like burnt ones. Old branches are covered with cracks, gum protrudes on them, and influxes are formed, they gradually die off. Small gray growths appear on the bark of the tree. The affected flowers also dry up, turn pale, but at the same time they remain hanging on the tree without dropping their petals.
Ash-gray pads with spores appear on the affected inflorescences. At the same time, the first wave of mass infection of plants begins. Spores enter the flower, germinate, develop into a vast mycelium, which penetrate into the ovaries and pedicels. From there, it spreads along the branches, which eventually dry out and die off.
In summer, the disease progresses and begins to affect the fruit. It all starts with a small dark speck, which absorbs the entire fruit in a few days. First of all, cherry, sweet cherry, plum or cherry plum, already damaged by insects or birds, are at risk. The color of the spot can change depending on the color of the skin of the fruit itself, but the flesh always turns brown. Over time, the surface of the fruit becomes covered with a net of small spore pads.
Unlike moniliosis of apple and pear, which appears in the form of regular circles, the pads on stone fruits are randomly located.
Gradually, the fruits acquire a bluish-dark or black color, become smooth and begin to mummify. Some of them fall off, but some remain hanging until next spring, being a source of infection.
Measures to combat stone fruit moniliosis
- Cut and burn all damaged shoots, buds and branches. Remove affected inflorescences 15-20 days after flowering, when the line between healthy and diseased tissue becomes noticeable. Remove inflorescences, capturing healthy tissue 10-20 cm. Regularly (in autumn and spring) collect and destroy all mummified fruits, and also get rid of carrion and damaged fruits throughout the season.
- Spray trees with Bordeaux liquid (100 g of copper sulfate and 150 g of lime per 10 l of water) or copper oxychloride (40 g per 10 l of water), as well as HOM preparations (40 g per 10 l of water) or Abiga-Peak (40-50 g 10 liters of water). The first spraying should be done in the spring just before the blooming of the flowers to protect them from infection. The second - immediately after the summer sanitary pruning of damaged inflorescences.
- Store only whole and healthy cherries, sweet cherries, plums, cherry plums and apricots without visible damage. So you will get rid of the further spread of the disease.
- Grow relatively resistant varieties of cherries (Aleksa, Zhukovskaya, Chosen, Kazachka, Nefris), cherries (Voskhod, June early, Large-fruited, Prestigious, Home), plums (Venus, Nagrada Nemanskaya, Perdrigon, Edinburgh), cherry plums (Asaloda, Comet, Promen , Traveler, Soneyka), apricot (Pineapple Tsyurupinsky, Melitopol early, Monastyrsky, Obolonsky, Denisyuk's Special).
Moniliosis (fruit rot) is a very dangerous disease that spreads quickly and affects the bulk of garden trees. It is easier to prevent it from occurring than to treat it. Follow the full range of preventive measures and follow agricultural techniques, and then the trees will delight you with a notable harvest.
Folk remedies
If pear fruits rot on a tree, you can use folk methods. Available means are used:
- Citric acid (40 g.), Iron vitriol (25 g), combine the preparations and dilute in 10 liters. water. Spray fruit crops with the resulting essence. Duration of storage of the consistency - 2 weeks;
- Stir iron vitriol (1.5 kg), humus (60 kg) into a single batch, pour in a bucket of water (10 l). Under the tree around the trunk, dig a small trench and pour all the contents into it, evenly distributing the mixture;
- Prepare a soapy ash solution. It will help get rid of pests;
- Spray with colloidal sulfur;
- Disinfect with a decoction of a mixture of yarrow, tobacco dust, chamomile, dandelion and garlic cloves, previously crushed.
With a strong development of the disease, it is worthwhile to carry out a complex effect against rot on fruits. The main thing is to spray on time in the form of preventive measures.
Varieties resistant to moniliosis
In places with a temperate climate, especially with a cold and damp spring, this disease is a frequent visitor to the sites. In such areas, experts recommend choosing pear varieties that are immune to fruit rot. It:
- "Aurora";
- "Take winter michurina";
- "October";
- Saint Germain;
- "the conference";
- Krasnodar Summer;
- "Trembita";
- "Ramshina";
- "Autumn dream";
- Roxolana;
- "Curé";
- "Moldavian early";
- Augustine;
- "Summer Sergeeva".
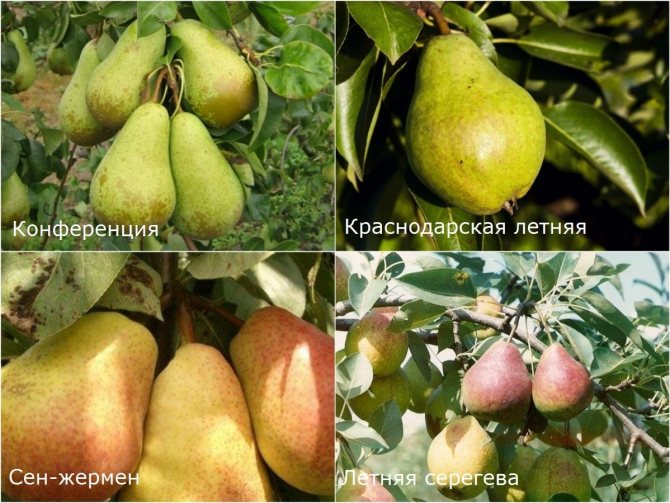


Photo: collage <>
Pear rust
The causative agent of rust is the pathogenic fungus Gymnosporangium sabinae. This pear leaf disease is characterized by yellow, orange and rusty-brown raised spots that appear most often in the second half of April - early May. Damaged leaves lose their ability to photosynthesize. With a strong infection, rust also spreads to the fruits of the plant.
Rust can affect all varieties of pears.
Root cancer occurs in young plants. It is caused by the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. On the roots and root collar of seedlings, hard woody outgrowths of various sizes are formed. In the case of diseased seedlings, the bacteria-causative agents of root cancer can live in the soil for several years. Treatment.
Important! The variety most resistant to root cancer is Limonka.
Black cancer affects the bark of the trunk, skeletal branches and fruits. First, small cracks or wounds form on the bark, which further increase, which provokes breaks in the bark. Bright brown spots appear around the wounds.
Treatment. To prevent the appearance of pear cancer, fallen leaves are carefully removed and burned. Infected fruits and areas of the bark are removed, fresh wounds are smeared with copper sulfate, clay with mullein, or special lubricants. They inhibit the development of black cancer and fungicides.
Important! High immunity to "Antonov fire" is observed in pear varieties Avgustovskaya dew and Samaryanka.
The cause of cytosporosis of the pear can be frost cracks and sunburn. With cytosporosis, the pear bark turns red-brown and dries up. On the diseased areas, tubercles are formed - an accumulation of the causative agent of the disease: the fungus Cytospora leucostoma. Treatment. The recipe for the treatment of pear cytosporosis is identical with the methods for treating black cancer. Owners of Moskvichka and Yanvarskaya pear should not be afraid of this disease.
Pear stem and root diseases
When rot is detected, it is necessary to take timely measures to combat pathology. It is worth identifying the reasons provoking the developing process:
- An "old" variety that has been grafted onto a wild plant. Such trees have a rotting mechanism in their heredity in advance;
- Fruit rot or moniliosis is a dangerous fungal pome disease. Compounds that stimulate the formation of rot, blackening of leaves, are not afraid of severe frosts, they are not affected by the effect of chemicals.
In the latter case, infection occurs when infection from an old fetus, from the crown or branches.The disease penetrates through minor injuries in the skin caused by insects, as well as in case of injury from rain, wind or hail.
To prevent the development of rot on fruits, it is necessary to properly care for the plant, to fulfill all the basic requirements for care. In the case of the "old" variety, there is no need to carry out special prophylaxis.
It is worth picking fruits half-green, or as soon as they are ripe, do not wait for overripening. The fruits are laid out in a cool room or wrapped in paper and stored in a dark place. In this form, they fully mature without decay.
If there is no possibility or desire to fight the heredity of the fruit tree, then you just need to change the old plant for a new one. With the development of moniliosis, it is important to carry out sanitary pruning in the fall. All damaged and diseased branches, foliage, crown, rotten fruits are removed. It is worthwhile to collect the carrion and bury it in the ground to a depth of 1.5 m.
During the growing season, it is necessary to actively fight against parasitic insects that spread the disease. Pests include: aphids, bedbugs, honeydew, moth. Thanks to them, the fruits of the pear rot from the inside, become infected with an infection transmitted by parasites. To eliminate the disease, it is necessary to periodically fight with the help of chemicals and folk exposure.
There are signs of some diseases on the fruits of the pear tree. Then you can be left without a crop, if you do not neutralize the pathogenic fungus in time.
One of the most dangerous pear diseases is associated with the appearance of olive-colored spots on the leaves. And then they move on to fruits. The description of the infection includes the fact that the flesh of the pears begins to harden and crack. If the fungus acts on the pear at the beginning of fruit setting, then their shape is bent.
Prevent the development of pathology by spraying with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid in the spring and 1% after flowering. Trimming the crown will help to improve ventilation and its illumination. In the treatment use drugs "Skor", "Nitrofen".
When pears are damaged by the moth, spores of the pathogenic fungus are introduced into them. From infected fruits, the disease spreads to neighboring ones. You can identify moniliosis by brown skin, concentric circles of grayish rot on the surface. If the damaged fruits are not removed, then the next year you can be left without a crop. Pears are treated with a solution of Bordeaux liquid before and after flowering. Do not forget to collect and destroy rotten fruits.
Sooty fungus
When the leaves and fruits of a pear turn black, the plant is affected by a sooty fungus. Crops that are weakened or damaged by aphids are affected by the infection. By releasing a sweet and sticky substance, aphids create the soil for the development of a sooty fungus. It is possible to suppress the reproduction of spores of a pathogenic organism by spraying with "Fitosporin".


There are diseases that affect the stems, shoots of the fruit tree. Most often these are viral infections that are especially dangerous for the life of the culture. They lead to deformation of the trunk, the appearance of growths, cones, and depressions on the bark.
Black Pear Cancer
How Antonov fire burns a tree disease. The trunk and branches look burnt. The bark bursts, becomes covered with cracks, the edges of which are constantly wet. They are penetrated by pathogenic microorganisms, fungal spores.
The treatment for pear cancer is to cut the bark into healthy tissue. At the same time, the sections are treated with a solution of copper sulfate, covered with garden var. In the initial stages of the disease, you can save the pear.
Cytosporosis
The fungus of cytosporosis affects the bark of horticultural crops. Most often, it penetrates into the tissues of a tree in places of burns, frost damage. On the affected area, it begins to flake off, dry out, and become a red-brown bark. To combat the disease, the damaged bark is cleaned by coating the cut sites with clay or pitch.It is necessary to protect the pears from damage by whitening the trunks in the fall and spring.
Root cancer
The disease manifests itself on the roots, more often the root collar. Its signs include growths of various sizes and shapes. Small, gray-white, pea-like tumors. But, as they develop, they increase in size, turn brown, lignify.
Seedlings affected by cancer die, although at first they develop rapidly. Before planting pear seedlings, you need to carefully examine the root system, removing growths. After trimming, it is necessary to process the roots with a solution of copper sulfate, and then rinse with water. A solution of boric acid, 10 grams per 10 liters of water, is suitable as a disinfectant.
Bacterial burn
Symptoms of a fire blight include:
- blackening of the kidneys, their drying out;
- drying of inflorescences;
- rolling leaves;
- darkening of the trunk.
It is difficult to detect the disease immediately. When a tree is completely black, it cannot be saved. With a small infection, diseased branches can be cut off and burned. The cut site must be treated with copper sulfate.
Preventing disease and pest attacks on horticultural crops is easier than treating them later. After all, you will have to use chemicals, which bears some harm to the pear fruits. Preventive measures must be carried out on time:
- A place for planting pears is chosen where the soil does not swamp due to the close location of groundwater.
- The trunk circle is dug up in the fall, after harvesting and in the spring.
- Loosening and weeding are important in disease prevention and pest control.
- Pruning dry, damaged branches will provide an opportunity to increase lighting and fresh air flow into the crown.
- The burning of plant residues is carried out without fail, thereby destroying hibernating pests and pathogenic microorganisms.
- They take care of the bark, patching up cracks, damage with pitch, whitening.
- The garden is sprayed with Bordeaux liquid in spring and autumn.
These are the main measures for the prevention of disease. But you need to apply your own treatment for each type of pathology.
Chemicals, insecticides, acaricides, pesticides, fungicides are used when it is impossible to cope with neglected pathology. At the initial stages, folk remedies that have been tested by gardeners in practice are suitable. Infused tobacco is used to treat pears affected by aphids and mites. It is prepared from a kilogram of makhorka waste for 5 liters of water.
The infusion of onion husks is prepared as follows: 20 grams of husks are insisted in 1 liter of water. Spray trees affected by aphids, ticks, 3 times a month with a break of 10 days. The sawfly is afraid of sulfur fumigation. Half of the matchbox is placed in the smoker, blowing smoke on the pears.
Infusion of soda and soap helps with powdery mildew. Processed after blooming leaves every 7 days. You cannot carry out the procedure during flowering. You can replace the agent with an infusion of manure, which is prepared from 1 part of a mullein and 3-4 parts of water. Before processing, the solution is diluted with water 1: 3. Used for spraying against pests infusion of red pepper, dandelion, chamomile, celandine.
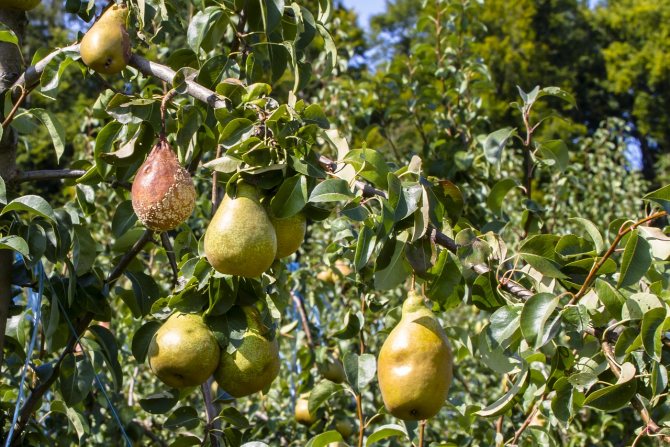
Dangerous diseases are carried by insects, and spores are also formed on overripe fruits. As a result, pears crack and rot on the branches. If they are not removed in time, the wind will carry these spores, infecting neighboring trees.


At first, few people pay attention to it. Small black specks appear on the fruits, but their taste does not change from this. Another symptom is that the leaf plates acquire an olive tint, which eventually turns brown. In spring, fungal spores develop mainly on the leaves. In this case, the fruits rot at the stage of the ovary.
If the scab appears in the middle of summer, it hardly affects the leaves. The disease affects only pears. They begin to deform, the skin becomes covered with dark spots and bursts. Infection gets into the pulp, pears rot on the branches.Particularly dangerous are periods with hot, humid weather. For the winter, spores attach to the bark.
Complex treatments with special preparations will help get rid of the scab. The most effective are "Skor" (used in the formation of buds, as well as after flowering), as well as copper sulfate (they treat swollen buds) and colloidal sulfur. The use of these funds must be alternated so as not to provoke addiction.
Moniliosis
This disease is also fungal in nature. In the summer, the fruits begin to rot, and in the spring, young leaves, shoots and ovaries are affected. Gradually, the entire surface is covered with small brown spots. With increased humidity, bubbles of gray or yellow color appear on the skin. Further, a process starts, affecting not only the peel, but also the pulp, pears rot right on the tree.
At the slightest suspicion of moniliosis, you need to immediately process the tree. The first time this is done at the stage of the kidneys. For this, drugs with a high copper content are used. The next processing is carried out when the pear has bloomed. It is permissible to spray the formed fruits (at least about 2 weeks before harvest).
Attention! When the entire crop is harvested, you need to carefully process the trunk circle, crown, and also the trunk.
The most commonly used chemicals are Horus, Rovral, as well as Bordeaux liquid and copper sulfate. When preparing the solution, the dosage indicated by the manufacturer must be strictly observed. In the initial stages, biological products will help. Gardeners often use Mikosan, Fitosporin-M and Alirin.