How did you do it before?
Previously, gardeners simply gathered the fruits of wild pears, sowed seeds and grafted cuttings or buds of cultivated pear varieties onto the seedlings.
Pros: Plants cost nothing for the gardener, frost-resistant, get sick less, quickly bear fruit. But they differ in gigantic growth -6 m for them is not the limit.
Which pear stock will provide early yield and excellent frost resistance?
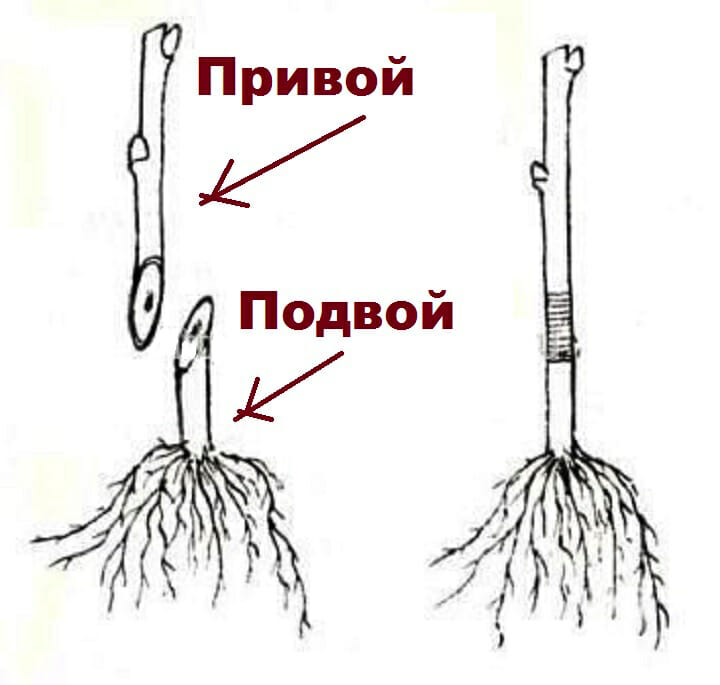
The rootstock is the base of the tree, part of the trunk, its roots. Literally it is the foundation of the tree. The quality of the stock often depends on the resistance to frost, soon-fertility, the degree of fruiting, the strength of the plant's growth. Let's talk about pear rootstocks. What should they be in order for the tree to bear its first fruits already in the third year?
When the stock is ready for vaccination and how it is done
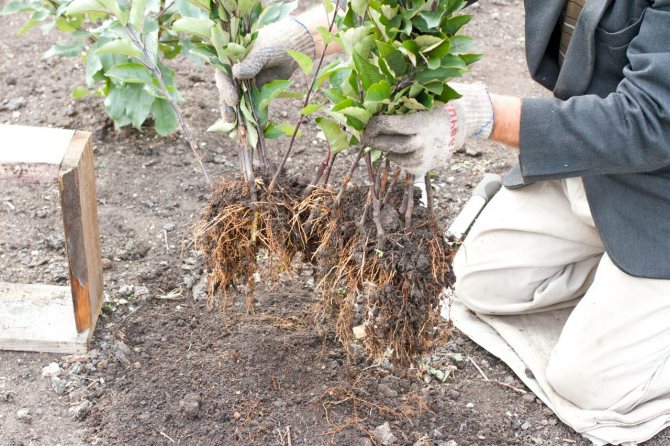
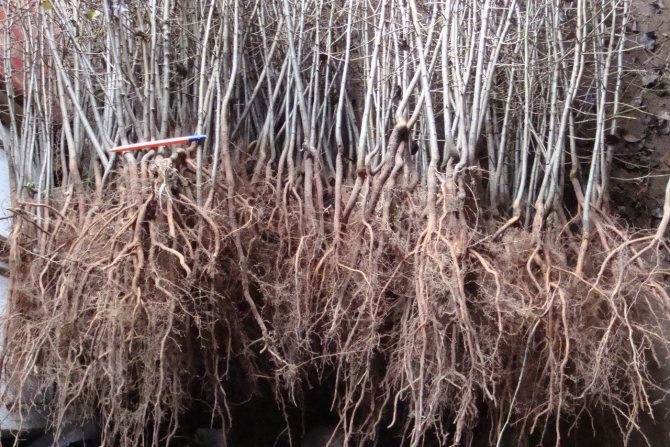
The stock is considered ready for grafting when, at the level of 5-10 centimeters from the soil level (the point of future grafting), its thickness will be no less than a pencil.
When growing seedlings, two main methods of grafting are used:
- Budding takes place in the second half of the summer. A T-shaped incision is made in the bark of the rootstock, into which a small shield of wood with an eye (bud) cut from the graft is inserted and fixed with an elastic strapping.
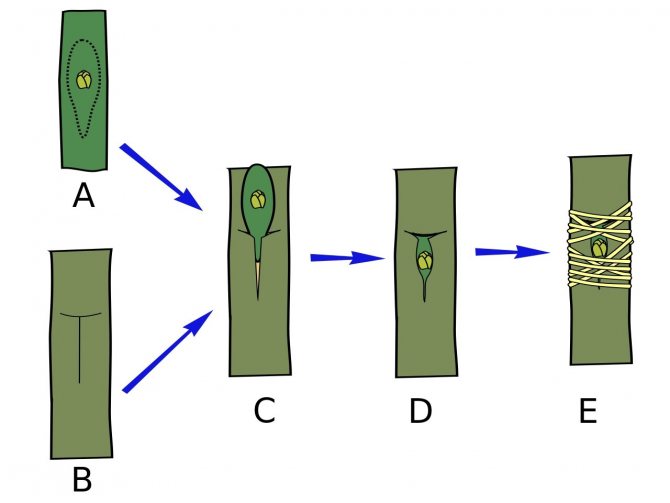
Budding - summer eye (kidney) grafting
- Copulation is carried out in the spring before bud break. On the rootstock and the scion, the same oblique cuts are made, which are tightly combined with each other and wrapped with an elastic tape.
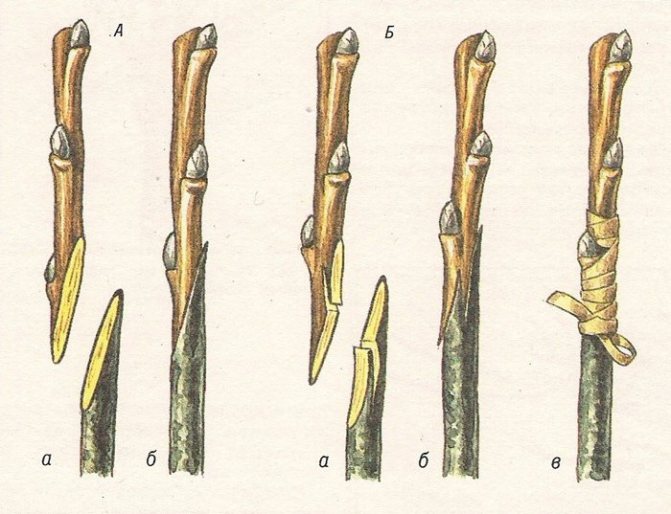

Copulation - spring grafting by cutting
PG-12
Pears grafted on such a rootstock actively begin to branch. If you are a grower of planting material, then this is the perfect choice: the seedlings will look very attractive.
Grafting a pear on this rootstock will bring the period of entry into fruiting (3 years) closer, will increase winter hardiness, drought resistance and resistance of plants to pests and diseases.
Clonal pear rootstocks
We also advise you to read: Rootstock for peach - which is better?
Summer pear varieties on quince rootstock
Unfortunately, at present, most fruit nurseries offer pear seedlings on a seed stock of a wild pear, or on a clonal stock, also grown from pear cuttings. In our city, there was only one garden center selling pears grafted onto a dwarf quince stock "IS 2-10".
Due to the fact that not every one of the many varieties is able to take root well on quince, the range of cultivars on the rootstock "IS 2-10" is significantly limited. Nevertheless, on the quince rootstock, you can find very popular and worthy varieties.
Pear on quince rootstock "Allegro"
You can harvest fruits in mid-August. Elongated pears with an elegant yellow-green color and pink blush, the average weight is 140 grams. The white, sour-sweet pulp has a delicate texture and a pleasant taste. Medium-sized, high-yielding trees with drooping crown. The variety is characterized by high winter hardiness and increased resistance to fungal diseases.
Pear on quince rootstock "Lada"
One of the earliest summer varieties - the first pears can be harvested in late July-early August, and at the same time, the fruits of this variety are quite mature and can be stored for about 60 days at a temperature of 0 degrees. The crumbling rate of ripe pears is low."Lada" regularly bears fruit with juicy, slightly aromatic pears of sour-sweet taste with fine-grained pulp, 100-110 grams in size. The shape of the crown is standard, the tree is medium-sized, highly winter-resistant and resistant to diseases and extreme living conditions.
PEAR Dwarf
This rootstock is obtained in Germany from crossing of pears resistant to pest - blight - cultivars: Old Home and Louise Bonne. Unfortunately, it was not possible to achieve complete resistance, but this rootstock and the varieties grafted on it have an average resistance to diseases.
Trees grafted on the Pear Dwarf can reach a height of 4-5 m. The grafted pear varieties on this rootstock turn into compact trees, which begin to bear fruit as early as 3-4 years after planting.
This rootstock is completely tolerant to alkaline soils. The only negative is that in cold winters, as well as in cold regions of Russia, there may be a slight freezing of plants.
Features of planting and caring for pears grafted on quince
Plants on low-growing rootstocks require constant care and adherence to the basic rules of agricultural technology in order to obtain high yields of high quality fruits.
Important! It is imperative to add 1 bucket of humus, 500 g of ash and 300 g of superphosphate to the seedling pit.
Planting pears
The quince stock has a reduced winter hardiness, therefore, it is necessary to choose the warmest place, protected from strong winds and drafts. Usually, when planting grafted seedlings, they provide the height of the grafting site above the soil. but quince has a low winter hardiness, therefore such a plant is planted with a deepening of the trunk to the level of grafting, and in the regions of the middle lane this point is even lowered 10 cm below the ground level.


Tree care
Trees on quince rootstocks are demanding on moisture and need frequent watering. Most varieties will also need a firm support and a harness. For the winter, the trunk circle should be mulched with straw or sawdust by 10-15 cm.
PEAR ROOT COMPARISON - VIDEO
Comparison of rootstock seedling pear and quince S1
TOOL FOR MASTERS AND MASTERS, AND HOUSEHOLD GOODS VERY CHEAP. FREE SHIPPING. RECOMMENDED - CHECKED 100% THERE ARE REVIEWS.
Below are other entries on the topic "How to do it yourself - a householder!"
- Inoculation of apricot on the sprout of plum - scheme and result HOW TO IMPROVE APRICOT ON SPRED ...
- We buy seedlings - types of rootstock: which is better clonal or seed? WHAT STOCK TO BUY A SEEDLING? ...
- Grafting a pear on an apple tree - advice from experienced people Grafting a pear on an apple tree - ...
- Peach stock - which is better? BEST ROOTS FOR PEACH Experienced gardeners ...
- Grafting a cutting of a fruit tree on a seedling in the spring - do-it-yourself copulation How to graft a varietal cutting on ...
- How to form a pear in a stlate shape - practice and advice PEAR in a stlate shape I believe ...
- Methods of grafting trees: pros and cons Pros and cons of different types ...
Subscribe to updates in our groups and share.
Let's be friends!
With your own hands ›Summer cottage garden and vegetable garden› Vaccinations › The best rootstocks for pears - advice from Ph.D.
Winter pear varieties on quince stock
Pear "Yakovlevskaya"
This cultivar turned out to be the only winter pear variety that can be combined with quince. Pear "Yakovlevskaya" is a medium-sized tree of medium density with a pyramidal crown. The fruits of this variety can be removed from the tree at the end of September-October. Elongated pears of medium and large size, weighing from 130 to 210 grams. The delicate juicy pulp has a creamy color and a semi-oily dense structure with a small amount of granulation. The taste of the fruit is sour-sweet. The variety has a long shelf life; at zero degrees, the fruits can last up to 180 days. Winter hardiness of trees is high.There is also a high resistance of "Yakovlevskaya" pear to entomosporia and scab.
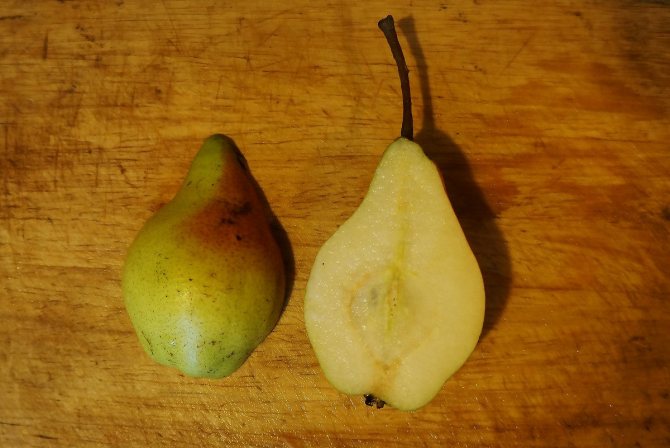


Pear of the "Yakovlevskaya" variety in the context. <людмила>
Choosing a site for planting
Columnar pear - planting and care
Unlike tall ones, the varietal feature of columnar pears is an increased demand for the type and composition of the soil. Loamy, well-moistened soils, enriched with nutrients, are well suited for them. These can be chernozems, sod-podzolic soils. Moisture deficiency negatively affects the growth and fruiting of trees. The dwarf pear is not demanding on the level of groundwater. Its root system is located close to the soil surface, requiring frequent watering.
Note! Undersized pears need a competent light regime. They require a lot of sunlight, but on hot days they can get burned. Optimal joint cultivation of dwarf and vigorous pears. Tall pears will provide the necessary shade on hot days.
Vegetative propagation
The asexual method includes the propagation of pears by cuttings, overgrown branches and air layers. Vegetative propagation is a way to obtain a quality tree with its own roots, which will bear fruit in 3 years. The breeding process is simple and effective if you follow certain rules.
Propagation by cuttings
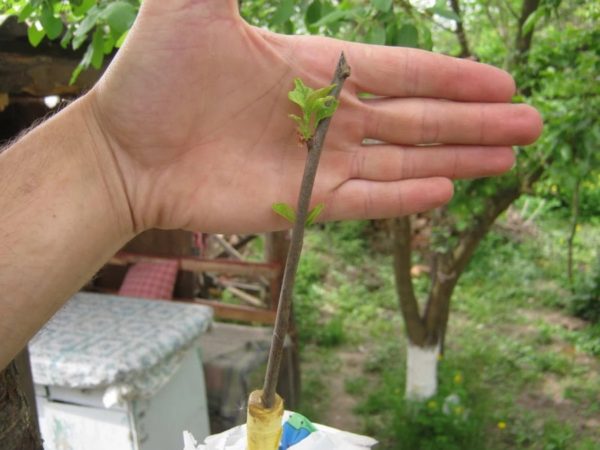


When propagating a seedling by cuttings, you can get own-rooted pears. Shoots taken from a seedling retain all varietal characteristics: taste, fruit size, resistance to diseases, climatic conditions, keeping quality. If the pear is propagated by cuttings, it will have advantages over grafted trees: the taste of the fruit is sweeter, the yield is greater, the duration of fruiting is longer.
Often, seedlings are propagated by grafting using a rootstock - the main tree and a scion - a shoot from a pear that they want to breed. If the components are incompatible, then the resulting hybrid will bring little harvest, its fruits will be small, sour, and resistance to frost and diseases will decrease. Therefore, it is better to grow self-rooted seedlings, which are distinguished by their durability, good regenerative ability, and resistance to cold.
Varieties for the Nizhny Novgorod region
The best pear varieties for the Nizhny Novgorod region:
- In memory of Yakovlev. A fast growing tree, the maximum height of which does not exceed 2 meters. The harvest is large fruits - 150-200 g, with a smooth glossy skin. The pulp is oily, juicy, without tart notes. Ripening begins in September;
- Russian beauty. Grows up to 3.5 meters. Differs in elongated fruits - 200-250 g. In weight. Ripe fruits are green, with a dull blush;
- Elena. A low-growing variety characterized by medium fruits of 150-200 g, bright yellow during ripening. The pulp is sour-sweet, tart, buttery;
- Pear Gnome. The smallest variety, the height does not exceed 40 cm. The crop consists of medium green fruits - 150 g. The flesh is white, sweet. Differs in good keeping quality, in cool conditions - until mid-January.
The most suitable time for pear grafting
The main nuance in the process of grafting this fruit tree is the choice of the most suitable timing. There are a number of gardeners who argue that budding time does not matter, but they are deeply mistaken.
The most suitable time for planting a tree is spring. It is during this period that active sap flow occurs in the pear, and this contributes to easier separation of the bark. But the main condition for successful budding is that pear grafting must be carried out before flowering. If you follow all these rules, then the likelihood that the scion will not take root is practically absent.


You can plant different varieties on one pear tree
It is also worth noting that it is necessary to select just such a moment when the difference between day and night temperatures will be insignificant, otherwise the death of an already grafted plant is not excluded. The day on which budding will be carried out should be sunny and calm.
Occasionally, budding is practiced in early summer and even in autumn. It is worth noting that at this time the plant can be grafted, but the likelihood that it will take root is minimal.
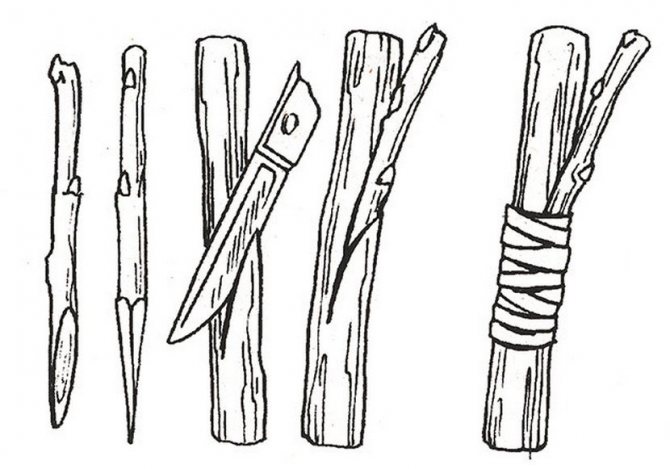
Methods for preparing rootstocks


As a scion, you need to choose those varieties and trees that you like. And which have excellent characteristics.
And also good fruiting. You also need to pay attention to the age of the mother plant. He must be at least one year old.
It is better to choose those shoots that are on the south side of the tree, from the edge. If we consider the height of the tree, it is better to take the middle level for the cutting.
It is recommended to cut a stalk for the future stock at the end of autumn. Or even at the beginning of winter.
Care should be taken to ensure that the branches are not frozen. And also strong growths are more suitable as cuttings.
About the width of a pencil. And the length is close to half a meter. It is advisable to store prepared cuttings under a snowdrift at least 50 cm thick.


If, however, in the region of cultivation for winter, a small presence of precipitation is characteristic, then before the snow falls, the stems can be shortened to about 30 cm.And put them in a plastic bag, mixing them with peat or moss.
Sand is also good. The bag is tied tightly and placed in the lower compartment of the refrigerator. The optimum storage temperature in this case is one to two degrees.
During the entire storage period, it is necessary to constantly inspect the prepared material for the presence of fungus formation in it. And also make sure that the kidneys do not swell prematurely.
If you are growing a seed stock, the seedlings should be weeded here. And also regularly feed, bringing the stem to a width of at least 7 mm. In addition, growing branches around the grafting site must be removed at all times.
How to grow pear seedlings by cuttings
The mini-greenhouse, where the pear is propagated, is only slightly opened for 2-3 hours to allow air circulation. Carefully monitor the condition of the leaf halves. At the first signs of rotting, the leaf is torn off and thrown away; later, it may be necessary to remove the stalk so that the infection does not spread to other branches. It is better to refuse watering with a trickle, since the soil is greatly eroded. Moisten the greenhouse with a spray bottle. Roots are formed in 30-35 days. After this period, airing is increased, the humidity is maintained the same. By autumn, the seedlings are taught to stay in the air, the shelter is removed.
Growing
Pure dwarf pears have not yet been bred. They are formed using a rootstock for quince or other fruit trees. The result is dwarf trees /
A new tree is formed only in the upper part, and in the lower - quince with its features. Quince cannot withstand severe frosts.
Therefore, when planting a grafted tree, it is necessary to hide its entire lower part under the ground up to the grafting site. So, the tree will survive in a frosty and little snow winter.
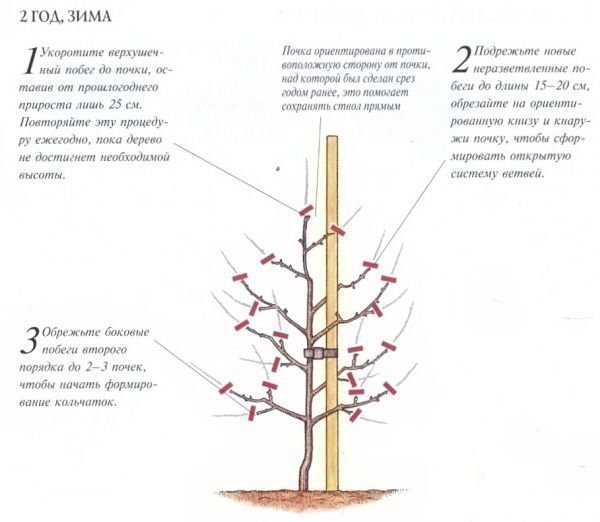

Formation of the crown of a dwarf pear
For the stock, a cotoneaster is often used, which tolerates frost well, which is very acceptable for the northern regions. The cotoneaster will be able to extend the life of a pear up to 30 years, and significantly increase its fertility. But these are rare cases.
The soil where such pears will grow must be fertile. Chernozem, chestnut loamy, sod-podzolic lands are suitable. Trees will not grow on salty soils. Since the roots of the dwarf pear are located in the top layer of the soil, frequent watering is required. But the accumulation of groundwater will not destroy the tree.
Pears on quince rootstock that grow in our garden
In terms of the totality of positive characteristics, we settled on the variety “Pamyati Yakovlev”, for which the “Yakovlevskaya” pear was also purchased as a pollinator. Our two-year-old seedlings a little more than a meter in height have bloomed already in the year of planting. But, in order not to waste the power of the plants, the first flowers were removed.
But the next year, the pears bloomed really profusely, and about 10 cute fruit trees were set on each tree. We took off the harvest quite late - at the beginning of October, but the pears were not quite ripe, and finally ripened indoors a month later. Everyone was pleased with the taste of the charming ruddy pears.
All the time, while pears grow in our garden, the site was flooded every year during floods, and in August a period of prolonged drought began. But, despite such difficult conditions, the trees continue to grow and develop actively. The maximum height reached by pears grafted on a quince stock "IS 2-10" is about 3 meters, and the life expectancy in the most favorable scenario will be 17-20 years. Nevertheless, during this relatively short time, the trees will delight with a bountiful harvest, which is easy to harvest without even resorting to using a ladder.
Rootstocks for different crops


Many factors must be taken into account for the successful fusion of rootstock and scion.
One of them is the botanical relationship. The best results can be achieved by carrying out intraspecific inoculations (for example, wild cherry is used as a rootstock, and varietal cherry as a scion).
Many gardeners also practice grafting between species (for example, the stock is cherry plum, and the scion is plum) and even intergeneric vaccinations (the stock is plum, and the scion is peach).
In the table below you can find the most common rootstocks and the most suitable scions:
| Rootstock | Graft |
| Quince | Quince, pear |
| Cherry plum | Cherry plum, plum, apricot, peach |
| Aronia | Aronia, pear, mountain ash |
| Hawthorn | Hawthorn, pear, apple, quince, cotoneaster |
| Cherry | Cherry, plum, apricot, sweet cherry, peach |
| Wild cherry | Cherry |
| Pear | Pear, apple tree |
| Cerapadus | Cherry |
| Apple tree | Apple tree, pear, chokeberry, cotoneaster |
| Plum | Plum, apricot, cherry plum |
| Peach | Wild peach and bitter almond |
| Cotoneaster | Pear |
| Irga | Irga, pear, mountain ash |
Remember that this list is quite relative, and a lot depends on the specific plant varieties, climatic conditions, soil, etc.
In any case, you can experiment in the process of choosing a rootstock and, of course, try to plant several varieties on one rootstock - something will definitely take root.
Pear rootstock compatibility
You might think that with the beginning of the era of dwarf trees, any sort of pear can be grafted onto a quince and get a low tree. But it is not so. Some varieties are not compatible with quince. Dwarf pears are widespread - varieties Chizhovskaya, Sverdlovchanka.
Pear compatibility with irga is much better than with cotoneaster. Many well-known varieties do not take root on it. Therefore, experienced gardeners advise using an intermediate rootstock compatible with it to grow pears of these varieties on a cotoneaster.
What you need to know about rootstocks
Autumn has come - the time for planting apple trees. When purchasing this or that seedling, it is not out of place to ask on which rootstock it is grafted. Knowing this, you can guess what to expect from a tree planted in your garden.
The stock is the foundation of a fruit tree. A stalk or bud of a grafted plant or variety is grown to it. Under its influence, the growth force of the fruit tree, the time of its entry into fruiting, endurance, durability, yield, frost resistance, drought resistance, adaptive ability to soil, resistance to diseases and pests change. The influence of the rootstock on the scion is somewhat stronger than that of the scion on the rootstock.The stock provides the scion with nutrients and water, and the scion (later - the crown) supplies the stock with assimilation products - carbohydrates, proteins, etc. If you choose the right stock, thoughtfully, you can get a seedling that fully meets your desires.
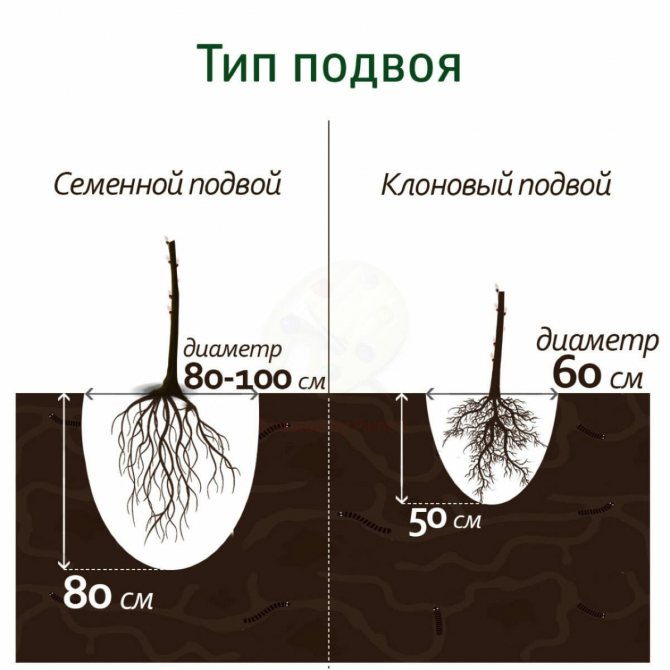
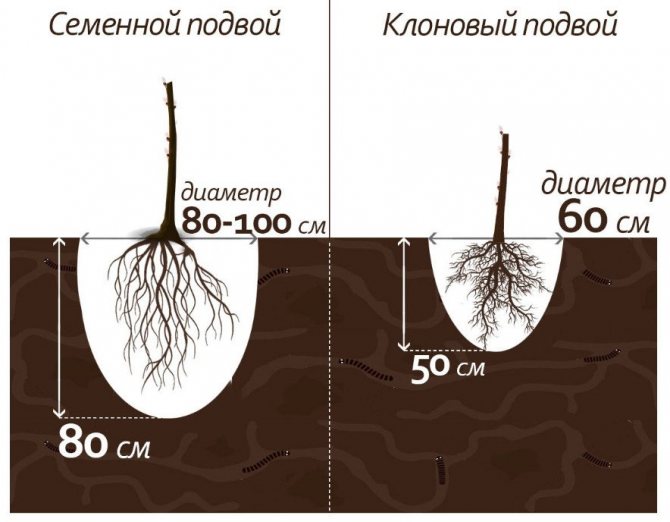
What are they like?
Rootstocks are divided into clonal (obtained by vegetative propagation) and seed (grown from seeds). It is customary to divide clonal rootstocks into dwarf (obtained from Paradizka) and semi-dwarf (obtained from the Dusen variety). I adhere to the European classification of clonal rootstocks: superdwarfs, dwarfs, semi-dwarfs, medium-sized and vigorous.
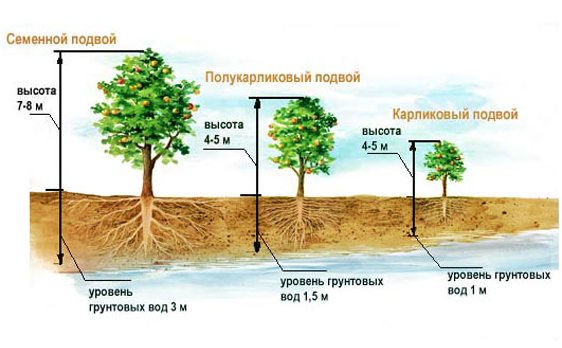

In recent decades, clonal rootstocks have been used as a rule for home and industrial gardening. The main advantages of apple and pear on clonal rootstocks include: early entry of trees into the fruiting period, rapid growth of yield, good fruit quality. Their size is larger, they are brighter in color, have an increased content of nutrients and biologically active substances. The yield of marketable fruits of the first grade can reach 90–95% (while trees on seed stocks give 70–80%). At the same time, marketable yields begin to be obtained 2–4 years after planting. Often gardeners have to pick flowers from planted annual seedlings grafted onto some super-dwarf rootstocks - PB-4, M-27, R-22. This must be done so that young trees develop normally without being depleted of fruits. In such a garden, a person is able, standing on the ground, without ladders and other devices, to carry out the basic work of caring for the crown and harvesting. Small trees make it easier to control pests and diseases, especially for the elderly. Trees on such rootstocks reach a height of 1.4 to 2.8 m. The yield on clonal rootstocks is 1.5–2 times higher than in the garden on seed. Professional gardeners have such a concept as “fruiting in kilograms per 1 m3 of crown”. Trees on dwarf and semi-dwarf rootstocks yield 8-9 kg / m3 of crown, and on seed - 5 kg / m3. With proper care, you can get a harvest of 500–1000 kg of apples from one hundred square meters of your garden plot.
The disadvantages of apple trees and pears on clonal rootstocks include: fragility (15-30 years), superdwarfs and some dwarfs need support, they require high agricultural technology, constant fight against diseases and pests.
Let me introduce you to the tried and true clone rootstocks that I have worked with.
Clonal rootstocks
Super dwarf
PB-4... Trees grafted on this early-growing rootstock begin to bear fruit in the second year after planting, many varieties bloom in the first year. The height of trees on PB-4 is usually in the range of 140–160 cm when the variety is grafted at a height of 10 cm. If grafted at a height of 5 cm, the tree will be lower; when grafted at 15–20 cm, it can reach 2 m. the grafted trees are quite developed, but requires compulsory support or trellis. On this rootstock, the apple variety Alesya gives good yields, and varieties such as Verbnoe and Topaz are capable of producing yields higher than 62-396.
P-22... The stock was obtained at the Institute of Horticulture in the Polish town of Skierniewice. Bred by crossing the stock M-9 and Antonovka ordinary. It has a great influence on the grafted variety. Very early, fruit buds are already laid in the nursery. High resistance to frost. In spring, varieties on this rootstock later enter the growing season, which avoids damage to flowers by spring frosts. The stock is highly resistant to diseases, including fruiting cancer. The root system of trees grafted onto this stock is well developed, but it lies in the soil in the upper layer and requires watering and support. Apple varieties of Western breeders - Gloucester, Jonagold, Elstar, Cortland, Ligol, Lobo, Melrose, etc. - have proven themselves positively on this rootstock. The grafting must be carried out at a height of 5–10 cm from the root collar.
Dwarf rootstocks
P-59... Bred in Poland by crossing A-2 and B-9. Many experts classify it as a superdwarf, but, having worked a lot with this stock, I believe that it still needs to be classified as a dwarf. The trees reach 2–2.2 m. The apple varieties grafted on this rootstock give a good harvest, the fruits are marketable and bear all the characteristics of the variety. Possesses sufficient frost resistance for our region. However, the stock is susceptible to powdery mildew and scab and is very fond of mice. Requires support. It has proven itself better on fertile soils. Vaccination should be carried out at a height of 5-10 cm.
P-60... The dwarf Polish stock was also obtained by crossing A-2 and B-9. In terms of growth strength, it is close to the stock of M-9, sometimes higher, in some varieties it approaches M-26. Possesses high drought resistance and winter hardiness. Combines well with most varieties. Trees can be planted on light soils. It is best to vaccinate at a height of 7-10 cm.
M-9... The main most common clonal dwarf apple stock in Europe. He was selected in 1914 at the East Mulling Experiment Station in England. Compatible with almost all apple varieties. On the seedlings at the grafting site, small nodules usually form, but they are not a sign of incompatibility. Trees on M-9 are very fast-growing, most varieties begin to bear fruit in the 2-3rd year after planting, late-fruited - in the 3-4th year. The yield is very high, usually higher than on other low-growing rootstocks. The longevity of trees is about 20 years. The stock promotes earlier ripening of fruits (by 3-5 days), an increase in their size, keeping quality is satisfactory. Young and fruiting trees on M-9 tend to form axillary flower buds on long growth shoots and fruit twigs. The height of trees, as a rule, does not exceed 2.5 m, although I have seen specimens of 4 m or more, which are grafted at a height of 20-25 cm, with a deep planting. Skeletal roots are poorly developed, brittle, therefore the anchoring of trees on M-9 is low, for them it is necessary to install an individual support or trellis. Medium and vigorous apple varieties, such as Gloucester, should be grown on M-9. The ribbing of Anthea fruits on M-9 disappears, which improves their presentation. The rootstock is most often damaged by aphids and rodents.
Semi-dwarf rootstocks
M 26 - semi-dwarf stock, somewhat taller than M-9. Bred in England by crossing M-16 and M-9 rootstocks. Good compatibility with all varieties. Trees on the M-26 reach a height of 3.5 m, are early-growing, and surpass all other rootstocks in terms of yield, except for M-9. The root system is better developed and takes up a larger volume of soil than that of M-9, the anchoring is higher, but support, especially during irrigation, is necessary. The quality of the fruits on this rootstock is high, but they are worse stored due to less calcium accumulation. In terms of resistance to lack of moisture and other unfavorable factors, M-26 surpasses other rootstocks. The roots can withstand a drop in soil temperature down to –12 ° C at a depth of 20 cm. It can grow on light and heavy soils, it tolerates waterlogging well. In the nursery, it is affected by scab and blood aphids, resistant to powdery mildew. Many varieties on this rootstock do not work well, for example Gloucester, Gala. The compatibility with the varieties is satisfactory. According to my observations, the trees on this rootstock are inferior in many respects to the seedlings on the 62-396 and M-9 rootstocks.
Rootstock 62-396... One of the best and most promising dwarf rootstocks for Belarus. In Europe, it is referred to as semi-dwarf. The strength of growth resembles the M-26. The early maturity and productivity of trees is 62-396 the same as on M-9, or slightly inferior to it. Apple trees on stock 62-396 are distinguished by vigorous growth in the garden, reaching a height of 2.8-3.2 m. The roots can withstand a drop in soil temperature to -16 ° C. Trees require temporary support. The stock 62-396 is resistant to disease and drought. The optimal planting scheme, at which the highest gross collection is achieved, is 4x1.5 m.
Medium-sized rootstocks
54-118... The Russian stock has a high frost resistance of the root system - up to –16 ° С. It is well compatible with various varieties, it is distinguished by its early maturity and high yield of the varieties grafted on it. Trees grafted onto rootstock 54-118 do not require support. Their dwarfism is poorly expressed. The beginning of fruiting is the 3-4th year. Planting patterns: 5x3 or 4.5x2.5 m. The height of the trees reaches 5 meters or more. The yield is up to two times higher than that of similar varieties grown on seed stock. Apple varieties on this rootstock are slightly affected by scab. I consider this rootstock to be the best among medium-sized and semi-dwarf ones.
57-545... According to its characteristics, it hardly differs from the stock 54-118.
Seed stock
Apple seed stock is basically a vigorous seed stock grown from the seeds of a wild forest apple, Antonovka apple and some others. They are well compatible with all apple varieties. Perhaps, after a while, gardening will return to seed stocks. They are more adapted to the environment, practically not affected by viral diseases, and are more resistant to fungal diseases. The seed stock has strong deep roots, so the trees suffer less from drought and, with good care, bear fruit up to 70-100 years.
The disadvantages include the large size of trees, which are inconvenient to maintain during pruning, pest and disease control, and harvesting. Begin to bear fruit in 7-10 years. The scheme for planting apple and pear trees on such rootstocks is 6 × 4 m or more.
Pear rootstocks
Vigorous pear rootstocks: wild forest pear and seedlings of some cultivated varieties. Cultivar compatibility is good. The grafted trees begin to bear fruit in the 7-8th year after planting, and slowly increase the yield. In the period of full fruiting, the yield is high. The longevity of individual varieties on seed stocks is up to 80 years or more. The root system is powerful, weakly branching, penetrates deeply into the soil. It does not tolerate even temporary waterlogging and the close standing of groundwater. Drought resistance is average. Seedlings of local pear varieties are the best vigorous stock for this crop. Seeds are harvested from the fruits of Limonka, Ilyinka, etc. The roots of seedlings of cultivated varieties branch better than those of forest pears, and regenerate well after transplantation. The stock is relatively drought-resistant, but also does not tolerate the proximity of groundwater.
Weak rootstocks: irga, hawthorn, northern Michurin quince, chokeberry, cotoneaster, etc.
Clonal pear rootstocks
Two forms of quince were tested in Belarus: A-semi-dwarf and C-dwarf. Both have reduced winter hardiness. It makes sense to use these rootstocks in the southern and southwestern regions of the republic. Most pear varieties are incompatible or poorly compatible with quince rootstocks. I do not recommend working with “quince S” stock - a waste of time and money.
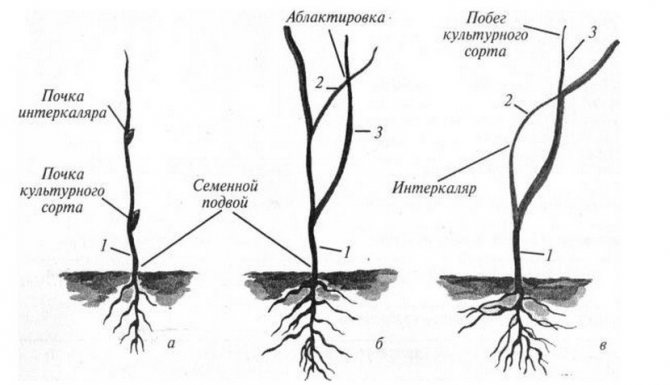
On the “quince A” rootstock, the varieties Almaatinka, Aleksandrovka, Bere Kievskaya, Belorusskaya late, Bere Gardi, Bere Ardagon, Kure, Conference, Noyabrskaya, Sladkaya iz Mliyeva, Smerichka, Jurate and many others work well. Incompatible - Williams, Lyubimitsa Klappa, Decanka winter, etc. If pear varieties are incompatible with the stock, it is necessary to use an insert (intercalator) from compatible varieties - Aleksandrovka, Kure, Jurate, Bere Gardi. When growing such seedlings, we lose a year.
Quince VA-29... Vigorous, strong quince stock, obtained in France from Provencal quince. The trees on this rootstock are winter-hardy, good compatibility with most varieties of scion and anchoring. I recommend this stock for both industrial gardening and home gardens. The varieties Almaatinka, Belorusskaya late, Bere Loshitskaya, Bere Luka, Zabava, Conference, Lukasovka, etc. work well on it.
There is no doubt that the fruits of pears on clonal rootstocks in all parameters, including taste, are significantly superior to those grown on tall ones.
I would like to highlight hawthorn and mountain ash from low-growing seed rootstocks for pears. Good compatibility with most varieties, early maturity, high winter hardiness and disease resistance.
In my garden there are pears grown on rowan and hawthorn. These are very frost-resistant trees, the height at the age of 6-7 years is no more than 3.5 m, they are undemanding to the soil, they are not afraid of the close standing of groundwater, they began to bear fruit in the 3-4th year, the fruits of good taste. However, not all varieties are compatible with these rootstocks. In such cases, you can use the inserts, as well as on the quince. If you come across pear seedlings on hawthorn or mountain ash on sale - buy without hesitation.
Anatoly KRAVCHUK,
agronomist,
Kobrin district
Tweet
Pear grafting
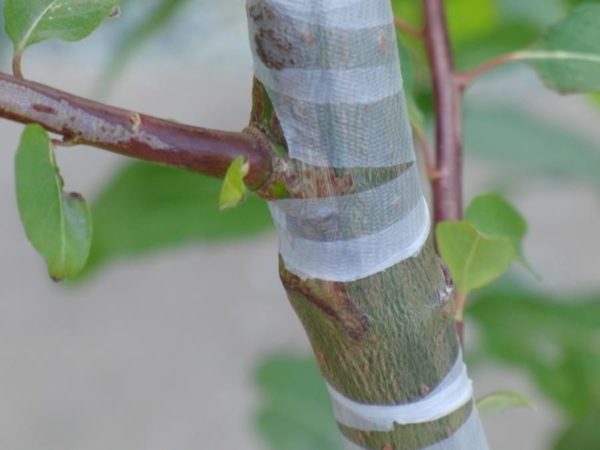


With the help of grafting, you can update an old tree by adding a couple of branches to it at the expense of cuttings. If the crown of the tree has died, but the trunk is viable, you can grow a pear by grafting using the technique into the split or behind the bark. In the first method, the tree is cut down, leaving a stump in which small crevices are made. At the handle, one edge is sharpened, with which the handle is inserted into the crevice. The vaccination site is treated with garden varnish, fixed with electrical tape.
In the second method, the main tree is also cut down, only to graft a stalk by the bark you need not an old, but a young tree with an elastic, easily detachable bark, more often it is wild. A small incision is made on the bark from top to bottom, slightly unbending it. The stalk is inserted with an oblique cut into the prepared incision, pushed inward so that it is in close contact with the cambium of the trunk. The incision site is treated with garden varnish, fixed with electrical tape.
Important!
By grafting, you can not only multiply pears, but also improve the taste of fruits, increase productivity, and resistance to diseases.