Blooming tulips with their enchanting beauty can cause genuine delight and decorate the landscape of any garden plot or park area. In nature, the flowering plains of steppe tulips amaze the imagination and cause trembling admiration. The inhabitants of our planet have fallen in love with these flowers since ancient times. Passionate aficionados collect varieties, try to find new varieties and are willing to pay a high price for a rare variety.
Short description
Tulips are perennial bulbous plants of the lily family. For decorative purposes, they are grown in garden plots by almost all growers.
Specialized floriculture farms are engaged in the cultivation of large quantities of cut for subsequent sale.

The buds have a varied shape and color, among the hybrids there are varieties with variegated petals. During the short growing season, tulips have time to bloom, form seeds and plant new bulbs in the ground, while old bulbs die off.
During the summer dormancy, the rudiments of shoots and buds of the new season are formed in new bulbs. In the fall, the bulbs will form roots and the shoots will be completed.
Diseases and pests
- A bulb mite can infect a plant, for prevention, it is necessary to treat with a fungicide.
- Among the dangerous diseases of tulips, gray rot, which also affects bulbs, fusarium, penicillosis and trichoderma... As a preventive measure, it is necessary to provide improved drainage and good clean soil.
- Viral infections must be destroyed along with the part of the land in which the bush is planted.
to the table of contents
Reproduction in nature
Tulips are easy to care for and easy to cultivate. For successful cultivation, it is important to understand how tulips reproduce in nature. Under natural conditions, steppe tulips undergo self-renewal: every year the out-of-date bulb is replaced by a new one, in the next season the natural cycle is repeated. This can go on for a long time (up to 60 years), but not indefinitely.


Physiological signs of aging accumulate in replacement bulbs year after year. The moment will come when the plant will grow old and will not be able to recover in the next season. But other younger tulips will bloom violently around, and the steppe will be covered with a luxurious spring carpet.
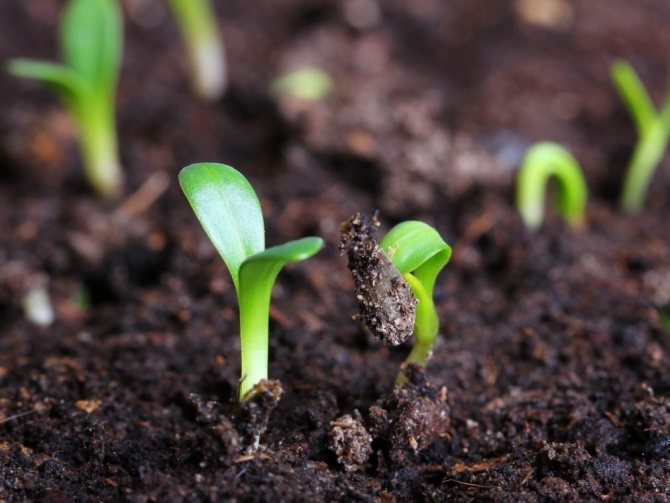
In addition to self-renewal, wild tulips sprout from seeds that fall from ripe seed bolls.
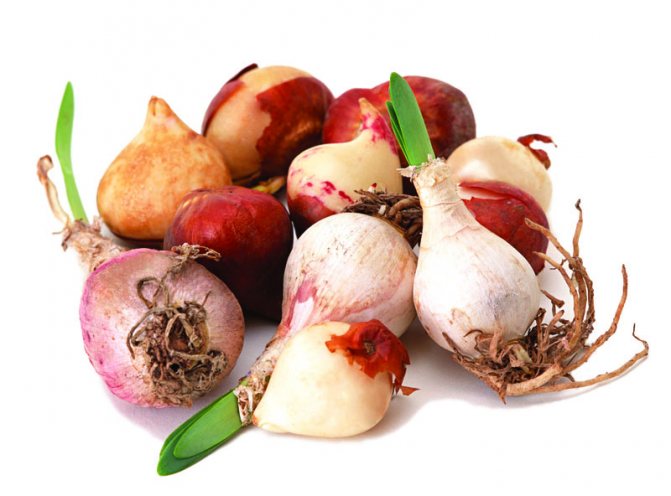
How to prepare bulbs for planting
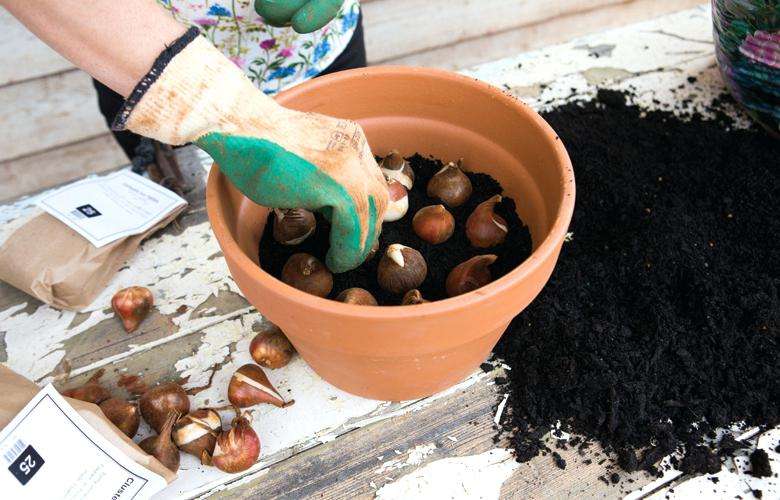
The quality of their germination in the future depends on how well and correctly stored the bulbs.
If you start planting tulips in the autumn, then around the end of July you should start digging out their bulbs and separate the mothers from the babies.
Then the bulbs must be peeled and dried, and then sent to storage. They are stored for about a month at a temperature of 20 degrees.
Then they are moved to a colder room where the temperature will be kept at about twelve degrees and there they will be there until landing.
Correct planting of tulips
For novice florists and those who are interested in how to propagate tulips, the question of proper planting is important.
It is very important to choose not only the right time for planting, but also the right place. It should be noted that tulips are light-loving plants and areas with good lighting are excellent for them. But at the same time, they do not like drafts, so protection from the wind should be provided.
Sandy loam soil is best suited for these bulbous flowers. Their development, growth and flowering are very well influenced by the preliminary application of wood ash and rotted compost as fertilizer. However, it should be noted that manure fertilizer for these flowers is not very suitable due to the presence of a large number of fungi in it, which can negatively affect it, causing fungal diseases.
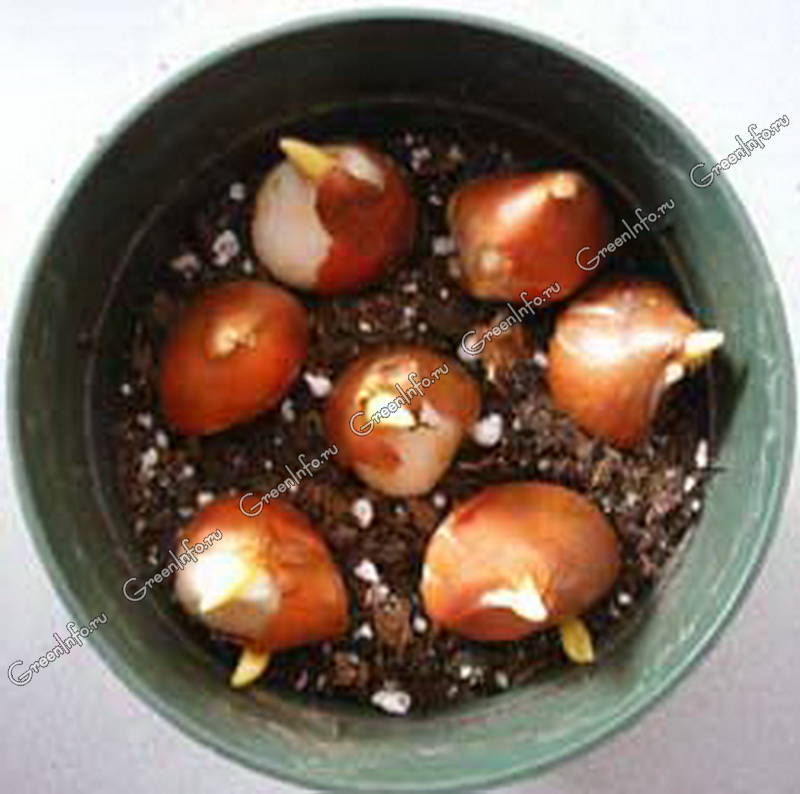
Plants are planted quite deeply. Large ones can be planted to a depth of fifteen centimeters, small ones up to ten. After planting, they are watered with hot water, with potassium permanganate diluted in it. This is necessary for the prevention of various kinds of diseases.
Outdoor flower care
Caring for tulips is simple and can be carried out from the moment the first sprouts appear from the ground. If some bulbs have not sprouted, then this may mean that they are sick, so the first thing to do is to remove the bulbs that have not sprouted. This will help prevent the spread of the disease to healthy and emerging sprouts.
The tulip loves moisture, but the structure of its root system does not allow it to get moisture from groundwater, so you should take care of regular and timely watering. It is especially necessary to observe a regular watering regime during the period of bud ovary and flowering. Water the tulips abundantly for about two weeks after the flowers have faded.
Water must penetrate to the full depth of the roots. It follows from this that on average it is necessary to pour from 10 to 40 liters of water per 1 m². Only in such a way that water does not fall on the leaves, otherwise burns may form on them.
The tulip needs weeding and loosening on a regular basis, so do not forget about loosening this area even when the flowers fade. This is best done after a heavy watering, when the soil is moist and soft. This makes the weeds easier to remove.
Weeds negatively affect the plant. They take nutrients from the soil, thereby depleting it and tulips begin to grow worse. But loosening helps to get rid of them.
So that weeds do not appear and they do not have to be weeded out, you can mulch the soil. In addition, you should remove those flowers that have already wilted so that the plant does not waste energy on their growth.
What to do when tulips are blooming
After these wonderful flowers have bloomed, it is necessary to remove the wilted flowers. Abundant watering should be continued for about two more weeks. Also during this period they can be fed, because at this time their bulbs begin to accumulate nutrients. Top dressing can be done with:
- phosphorus-potassium fertilizers with the calculation of 30-40g per 1 m2, for example, aquarine, solution, crystallin;
- fertilizers with chlorine and nitrogen should not be used.
When the tulip foliage turns yellow, you can cut it off. you shouldn't do this before. If the foliage is cut before it turns yellow, the bulbs may stop developing and tulips will not be able to propagate later.
When the foliage of the tulips turns yellow completely, they can be dug up. Usually, by this time, the bulbs are already mature enough and ready for the subsequent propagation of tulips. In addition, the babies have not yet disappeared, which means it will be easy to separate them on their own.
Of course, it is difficult to name the exact date of digging the bulbs of these flowers. This time may differ for different varieties. But the main and main landmark in this is the yellowed color of the foliage. This is what you should pay special attention to when preparing bulbs for propagation.
Thus, propagating tulips is not difficult at all.The main thing is to dig them up and plant on time, as well as follow some simple rules for caring for them, and then they will certainly delight the grower with their splendor.
Reproduction of cultivated species
There are 2 ways: vegetative (asexual) and seed. The choice of method depends on the goal. If it is planned to select a new variety with a change in decorative properties, then the seed method is chosen. When growing flowers while maintaining varietal characteristics, a vegetative method is used.
Vegetative propagation
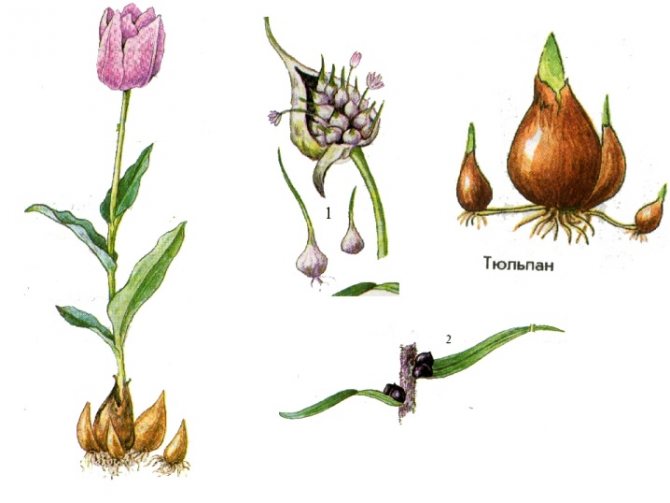
In this most convenient way, tulips reproduce most often. Flowering occurs quickly, the decorative properties of the mother plants are steadily preserved. During active vegetation, small nodules (babies) of different sizes grow around the mother bulb, and a replacement bulb is formed - the largest of the daughter ones. In it leaves and flower buds are laid for the next season.
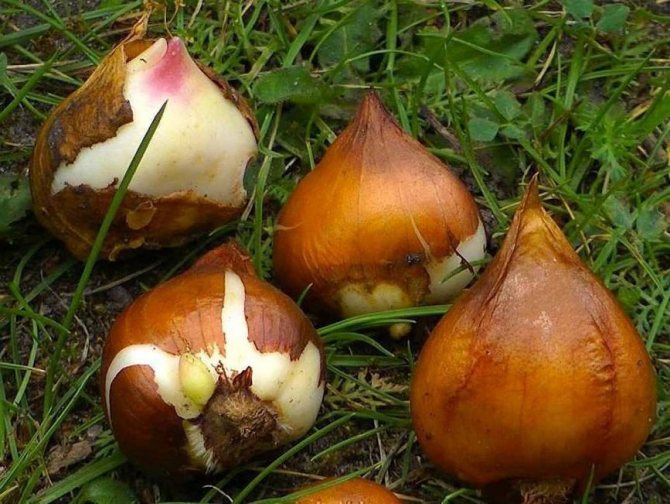
To obtain high-quality planting material it is necessary to timely and correctly dig up the bulbs after flowering, process, sort and store them until autumn planting.

Digging
The timing depends on the variety of tulips, usually the end of June - the first half of July. Tulips are ready for digging if the leaves have become lethargic, turned yellow, have lost their turgor, but have not yet dried up. If the leaves rustle and collapse, then they were a little late with the digging.
Bulbs should not be dug out too early - they still have white covering scales, the accumulation of nutrient resources has not ended. If the digging is delayed, the nest of bulbs will collapse in the soil, some of the children will not be able to collect.
An important point: the shovel should be inserted into the soil not at an angle to the stem, but vertically, as deeply as possible, swinging it with your foot in order to eliminate the risk of damage to the bulbs as much as possible.


Treatment
The dug out bulbs are cleared of the ground, examined and discarded suspicious specimens: damaged, with signs of diseases, of irregular shape. All planting material is soaked for half an hour in a weak solution of potassium permanganate, then dried in the shade for two days, and carefully examined again.
Gardening Tips
In order for the appearance of the garden to please, you need to make a little effort and follow a number of rules:
- when tulips are propagated by the vegetative method, it is required to properly dig, sort and store the bulbs;
- after digging, the bulbs must be cleaned of soil and roots, dried well and determined for storage;
- correctly carried out sorting will create a beautiful garden;
- the seed method takes time, but the result exceeds all expectations;
- do not leave the bulbs until spring - the quality characteristics may decrease, which will affect flowering;
- you need to correctly calculate the planting depth - this guarantees germination and flowering in due time.
Proper flower care and propagation will help preserve tulip varieties or add new luxurious species that will delight you for a long period of time.
Propagation of tulips
Reproduction occurs in the following ways:
- separation of daughter bulbs from mothers;
- by the seed method.
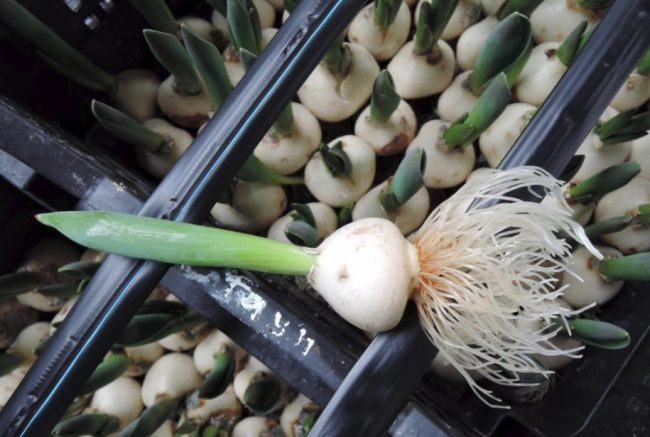


Summer residents often use the first option, as it has many advantages.
It is not recommended to propagate tulips in two ways at once, as this will stop reproduction and take away strength.
If the tulips are dug up earlier, it will contribute to the wrong bloom size or there will be no protective husk for long storage.
Comments (4)
Valeria
04.01.2019 at 05:19 |
Tulips are very beautiful flowers, I have never had to pollinate them on my own, I mainly germinated bulbs with children, these plants require special attention and care.Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
04.01.2019 at 21:15 |
Hello Valeria! From what has been described, it becomes clear that you are using a vegetative way for reproduction. It is good in that it is possible to completely preserve all varietal characteristics, that is, the shape and color will be exactly like that of the mother plant. With this method of cultivation, it is imperative to cut the flowers when they have faded, so that the plant does not spend energy on ripening the seeds. But, it is necessary to leave the leaves in order to receive nutrients through them.
If you want to experiment with the appearance of your tulips, then you should try seed propagation. Then they just carry out pollination with pollen of another species of this flower. No special effort is required for this, but tulips will delight you with flowering in about five years. To get the effect, it is worth planting next to the bulbs of those varieties that it was decided to cross. If they do not bloom at the same time, then the pollen can be collected and put in a cool and dark place.
It is better to pollinate several times within three days, and then cover the bud with loose paper so that insects do not pollinate it and interfere with your breeding experiments.
Reply
Alexander
20.04.2019 at 21:02 |
Hello Julia! I would like to ask you for advice on the cultivation of tulips, namely wild ones! In short: I accidentally met in the forest a clearing (literally several dozen) white tulips with a purple streak !!!
Reply
Julia Expert Plodogorod
20.04.2019 at 22:33 |
Hello, Alexander! As a rule, flowering tulips, like any other plants in this phase, are not recommended to be repotted. But, if there is an urgent need, then we will consider two options.
If the plant, together with the bulb, has already been removed from the soil, then it is not worth removing the peduncle. Rinse the onion carefully and place it in a container with water together with the bud. Next, you should wait until the flowering ends. After that, the onion should be dried and put in storage in order to plant it next season on its own site.
If you have not yet taken any action, then the algorithm is as follows. Cut off the peduncle, leaving only part of the stem and the two lower leaves. Next, dig up the plant using a shovel. If possible, grab as large an earthen ball as possible to avoid injury to the rhizome.
Then you need to dig a hole of the appropriate size on the site and immerse the earthen lump brought from the forest there. After that, watering is required, preferably with settled and not too cold water. You should not feed such a plant after transplanting, this will only be an additional load on it.
If the tulips take root successfully, further care is no different from caring for your family. It is important to carefully examine the selected plant so that there are no spots, damage or incomprehensible growths on it. If something like this exists, then there is a high probability of contamination of other plants in the garden.
Alternatively, you can mark the spot where you found the flowers and dig up the bulbs in June or July. This is of course a more complicated and time-consuming method, since you will have to monitor the natural cycle of wild flowers, but the likelihood that the bulbs will successfully take root in the future will be higher. You can try both.
Reply