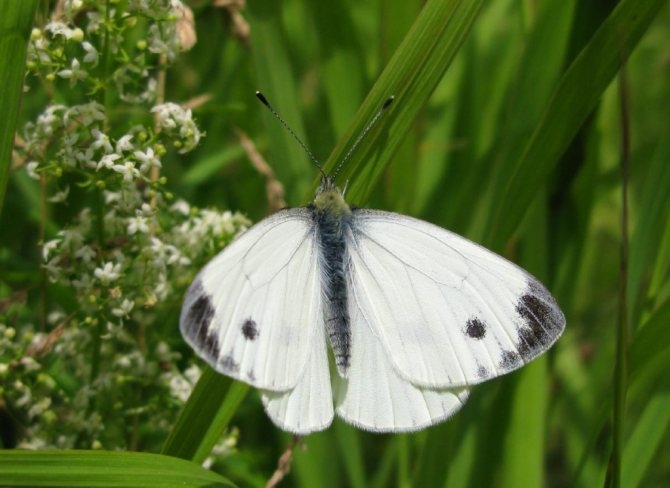
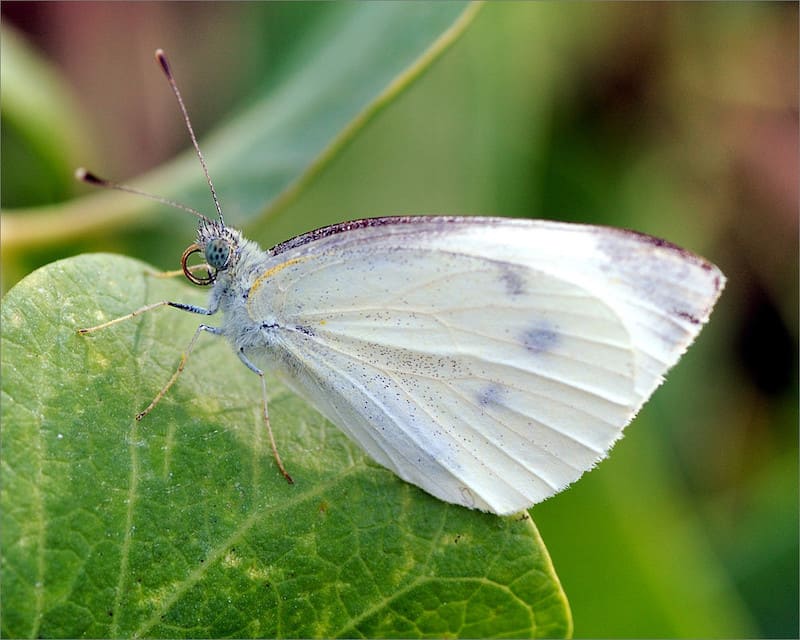
Botanical description and characteristics of the wings
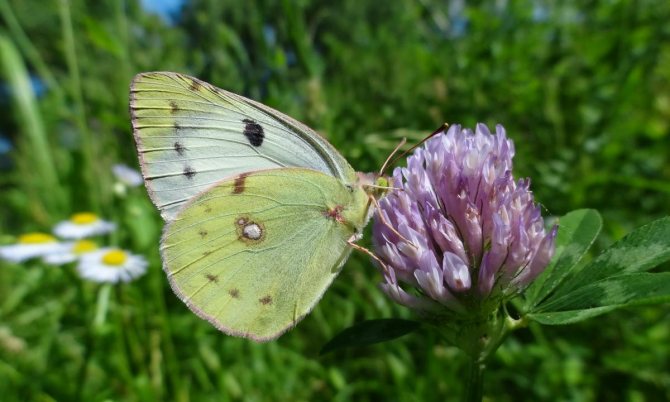
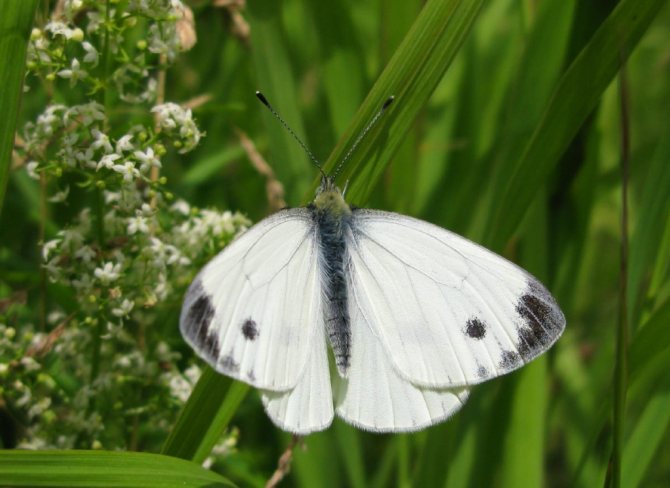
Cabbage is a diurnal representative of the white family. The front wings are 25 to 33 mm long. The span - from 4.9 to 6.2 cm in males, in females - up to 6.3 cm.
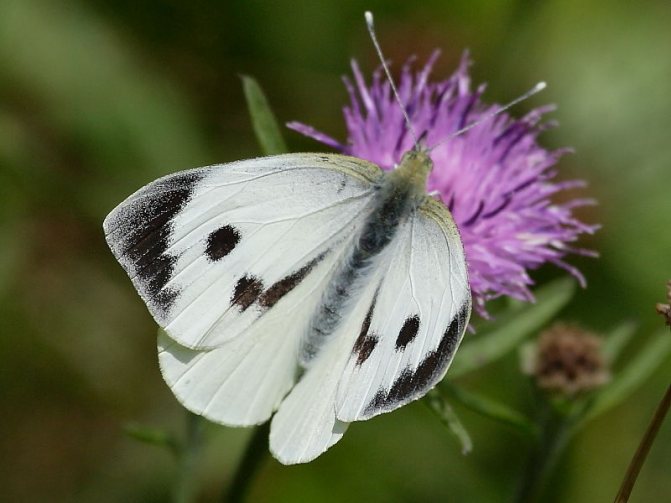
The color of the wings of a cabbage butterfly is yellowish-white, with small blotches of black, on the front wings there are spots on the outer upper corner and in the middle. On the hind wings there are blotches in the middle, there are yellow blotches below.
When you touch the wings, pollen falls off them, and they lose their color. The very same wing pollen is represented by the smallest scales that lie tightly on the wing and overlap each other, like a tile masonry. For this reason, butterflies are classified as a lepidoptera species.
The insect has very well developed eyesight and smell, which allows it to accurately identify an edible plant. On the head, almost all the space is occupied by the eyes. The insect's whiskers are long and have thickening at the tips, which are also involved in the process of recognizing edible plants.
The butterfly spreads its pollen on its wings, pollinating the plants. Therefore, the insect is not only harmful, but also beneficial.
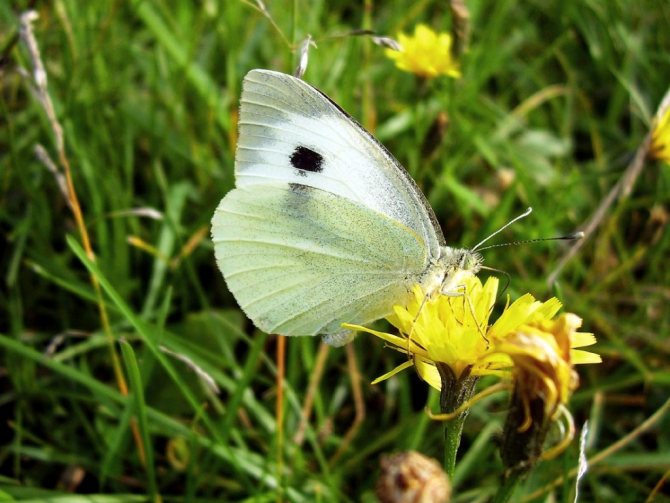
Females are larger than males. In the female, the bottom of the winglet is always more yellow, which is especially pronounced in the second generation.

Butterfly Belyanka cabbage (Cabbage). Insect pest
04/26/2017 In total, about a hundred thousand species of various butterflies live on earth, and each is beautiful in its own way. The inhabitants of Ancient Rome, seeing the unusual beauty of these insects, believed that butterflies originated from flowers that came off plants.
Most butterflies feed on nectar, and some species benefit from pollinating flowers.
Belyanka Kapustnitsa
also carries pollen on its shaggy body, thus pollinating flowers and plants, but its harmful offspring, which are usually called caterpillars, negate all its merits.
Adult insect (imago)
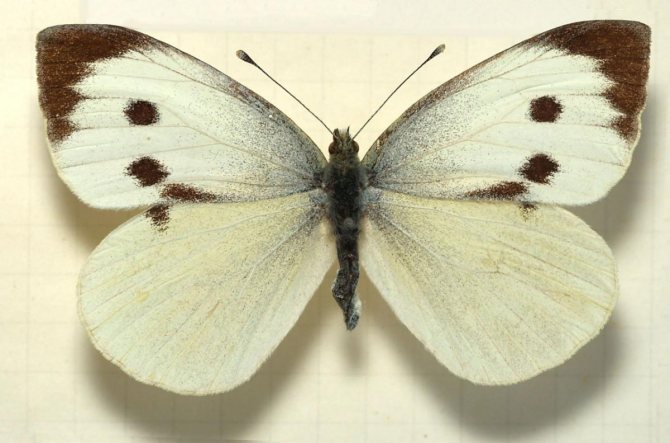
Butterfly Cabbage Belyanka
(
lat. Pieris brassicae L.
) is quite large. Males of this species of butterflies can reach a wingspan of five and a half centimeters, and the wings of a female even reach six.
The butterfly flies unevenly, spasmodically, and this manner of flight makes it a difficult prey for birds of prey. Sitting on a flower, the insect folds its wings and immediately becomes invisible, completely merging with the plant, which also complicates the hunt for them.
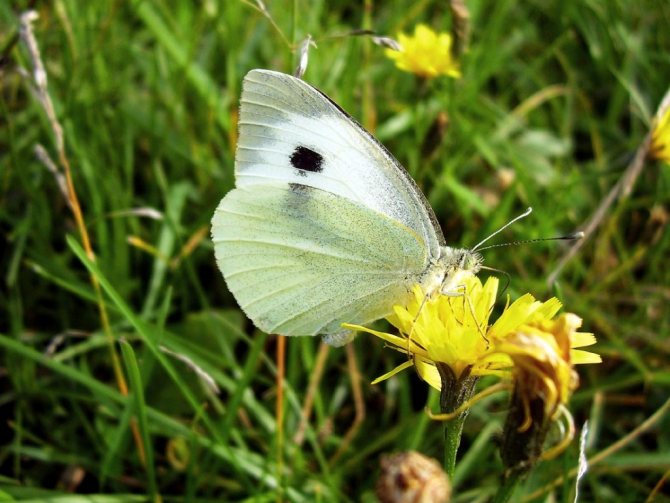


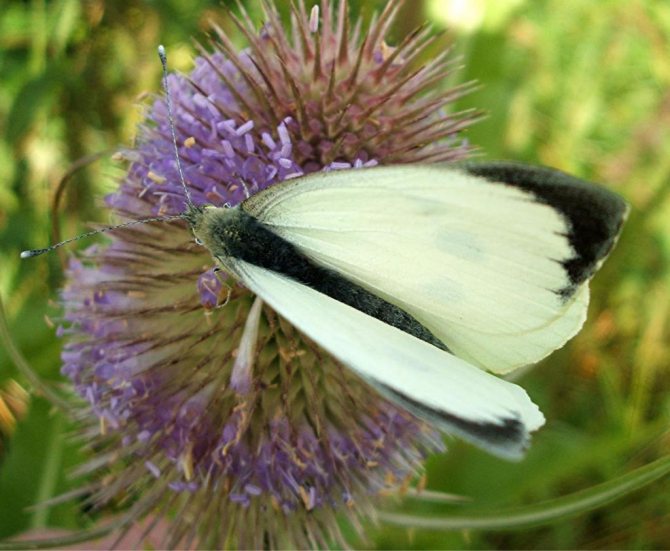
To distinguish Cabbage Belyanka
from other butterflies is easy. Males have characteristic black corners on the front and hind wings (the upper part of which is colored cream or white). The female insect also has dark corners, as well as two black round spots, which are located on the front wings. The lower part of its wing is painted in a pale greenish shade with black specks. If you touch the wings with your fingers, pollen will remain on them, and the wings will lose their original color.
The body of an insect consists of three parts: head, chest and abdomen. On the head there is a proboscis, twisted into a spiral, which the butterfly straightens in order to get the sweet juice from the flower. The proboscis indicates that this way of feeding the butterfly is predisposed only for taking liquid food (nectar).
Have Cabbage Belyanka
well-developed vision (large round eyes are located on the head) and sense of smell, which allows her to perfectly navigate in space. The organs of smell and touch are long sensitive antennae with small thickenings at the ends.
The main habitat of the insect is meadows and fields. Cabbage
can be easily found at the edges, in gardens, meadows.
Butterflies are able to rise to a height of twenty meters and develop a flight speed of about twenty kilometers per hour, thanks to which they safely migrate from one place to another, while covering considerable distances and are thus able to travel from country to country.
Mass emergence of adult butterflies usually begins in April - May. The warmer the weather, the earlier in time. They fly in the daytime and feed on the nectar of flowers, preferring plants of the cruciferous family.
They are especially active on a warm sunny day.


Butterflies of Cabbage Belyanka
usually so numerous that males do not need to go on a long journey in search of a mate to find females. The male emits a strong smell, reminiscent of the smell of geranium, by which an adult female butterfly finds him.
Before the mating process takes place, the couple flies together some distance (more than one hundred meters), which is very similar to the scene of dating and courtship.
Soon after the female leaves Belyanki
begin to lay eggs, laying them on the underside of a cabbage leaf or on other cultivated cruciferous families (rutabagas, radishes, turnips, radishes, rapeseed, horseradish, as well as nasturtium and garlic).
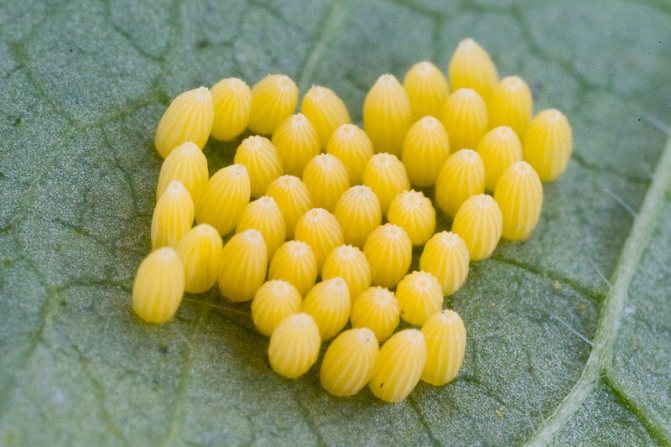


Located at the bottom of the leaf, the eggs are well protected from the sun, rain and are invisible to predators.
The butterfly finds the right plant for laying by smell. This was proved in the course of the experiment: if you generously spread the fence with fresh cabbage juice, the stupid cabbage will immediately lay eggs even on it.
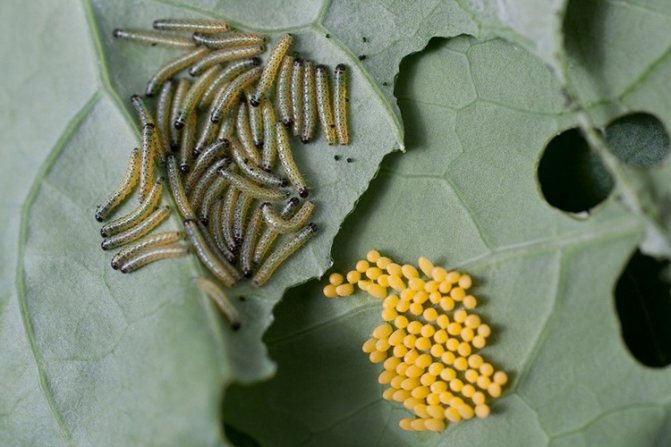
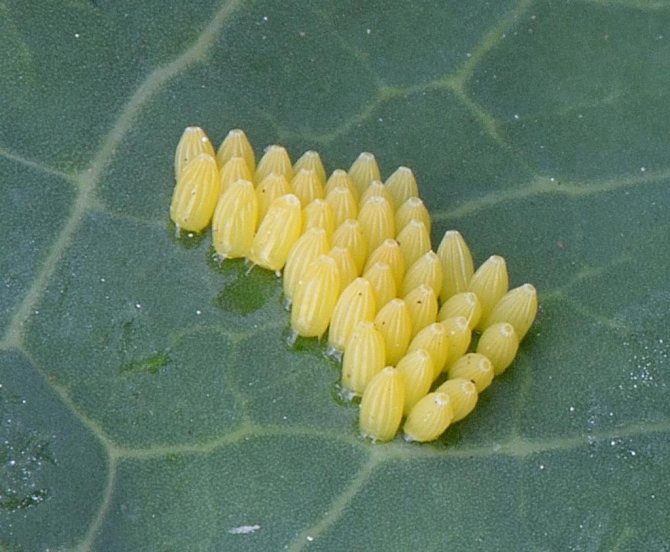
Egg
Eggs are located on a leaf in groups of fifteen to one hundred pieces (under favorable conditions, the number can reach up to two hundred pieces in each clutch).
The eggs are cone-shaped with longitudinal ribs. The color is rich, yellow and outwardly the embryos resemble small squat barrels, a little more than a millimeter in height.
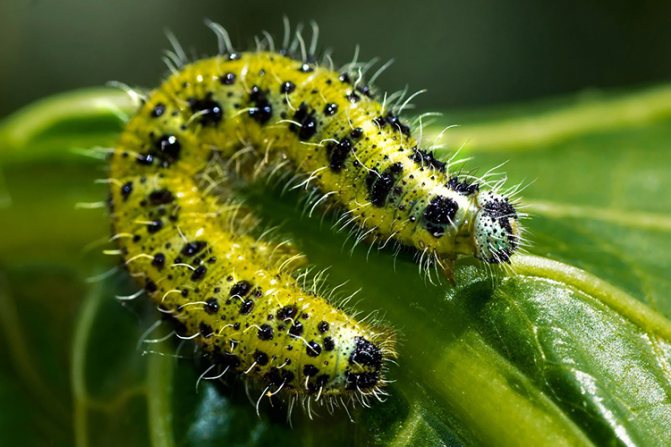
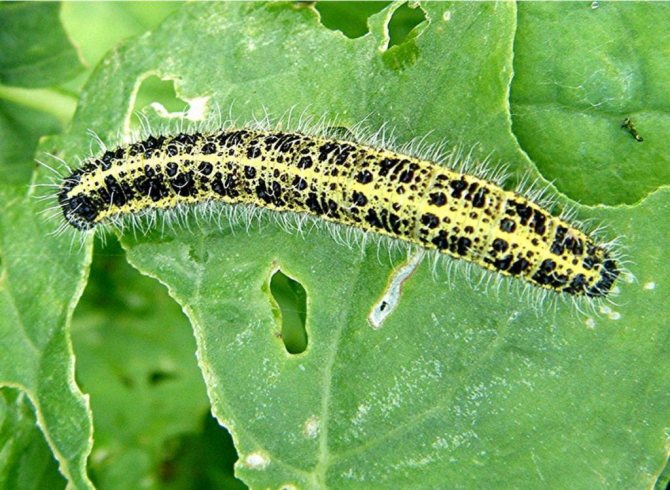
Caterpillar
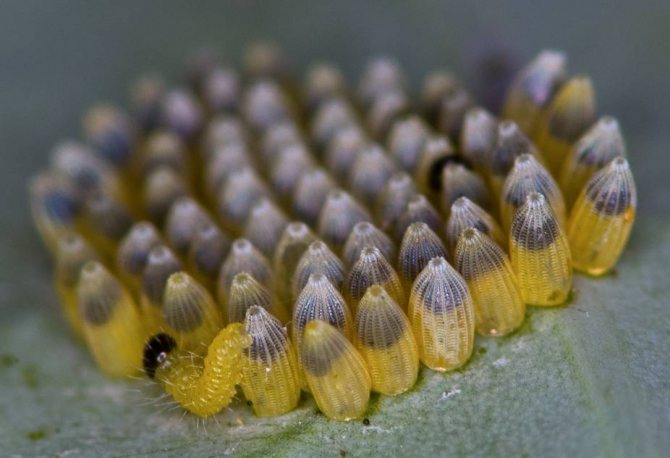
Soon (after about a week), larvae hatch from the egg. Their main function is to accumulate the necessary resources to ensure their next winged incarnation, therefore the caterpillars are extremely voracious. For their insatiability, the people call them "cabbage worm
" or "
cabbage caterpillar
».
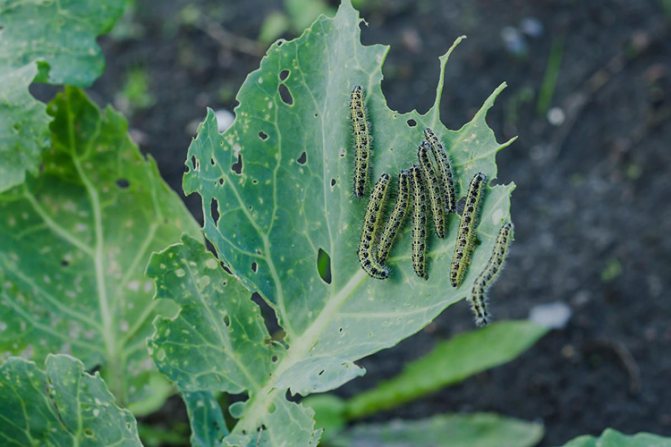
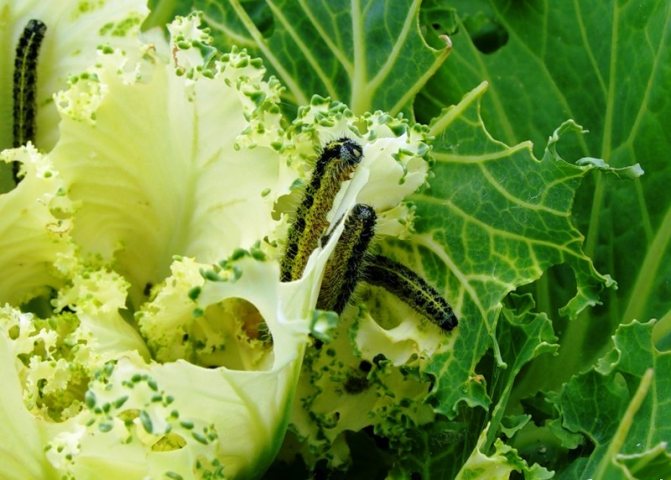
The hatched larvae live in a colony and immediately begin to feed, scraping the delicate skin and pulp from the underside of the leaf.


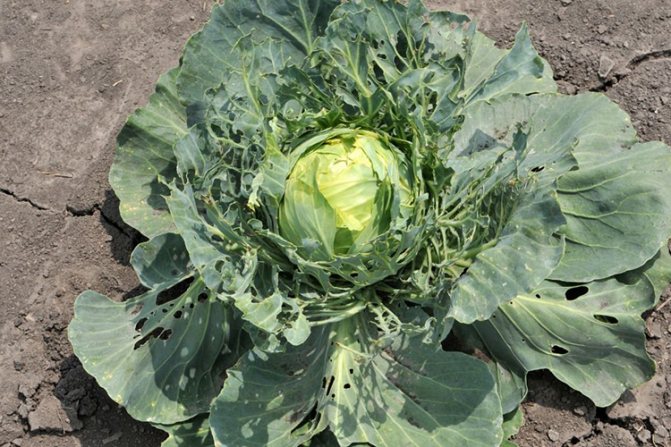
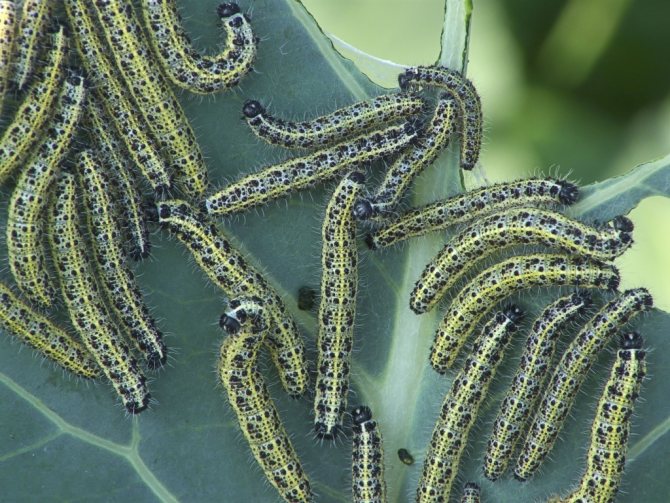
Soon, pests spread throughout the plant, nibbling the leaves from the edges, and growing up, they can severely damage them, leaving only coarse veins.
If there are a lot of larvae, they are able to completely destroy a whole head of cabbage in just a couple of days.
During development, caterpillars molt three to four times.
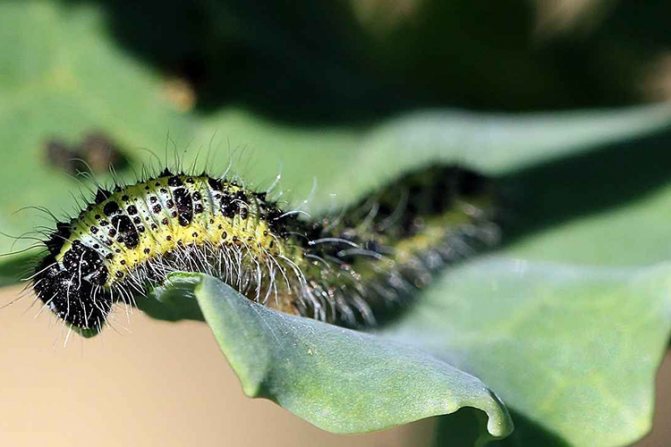
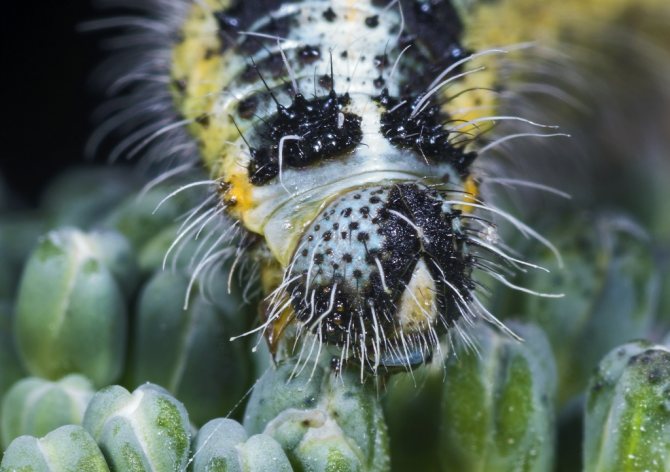
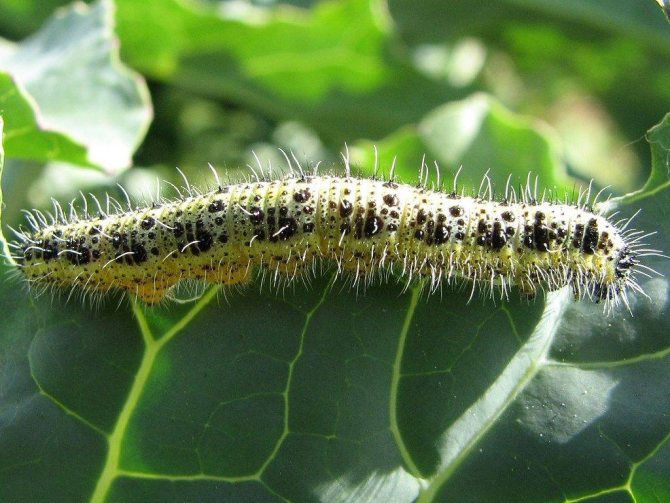
Caterpillar Cabbage
has a greenish-gray color, which also has yellow stripes with dark spots. They have a yellowish stripe on the sides, a lighter stripe runs along the back, and the whole body is covered with small bristles.
As they grow up, they change color, acquiring a blue-green hue with narrow yellow stripes and black dots on the sides and back. Such protective coloring on the cabbage bed makes the caterpillar secretive.


Larvae Cabbage
have a chitinous cover and tenacious abdominal legs, which allows the caterpillars to crawl freely on the surface of the leaves. The strong gnawing type jaws move constantly, allowing the caterpillar to bite off and chew on hard plant tissue.
An adult caterpillar can reach four centimeters in length.
Depending on weather conditions, insects are in the caterpillar phase for about two to three weeks. Then they leave the plantation with gnawed plants and crawl onto trees, fences, walls of buildings. Having settled in a secluded place, with the help of spider webs, the caterpillar is securely attached to a solid base to turn into a pupa.


Soon the caterpillar envelops itself with silk thread and freezes. If the cocoon is produced in August, and the weather conditions are unfavorable, the pupa survives the whole winter in this form, so that in April it will be reborn into an adult (imago).
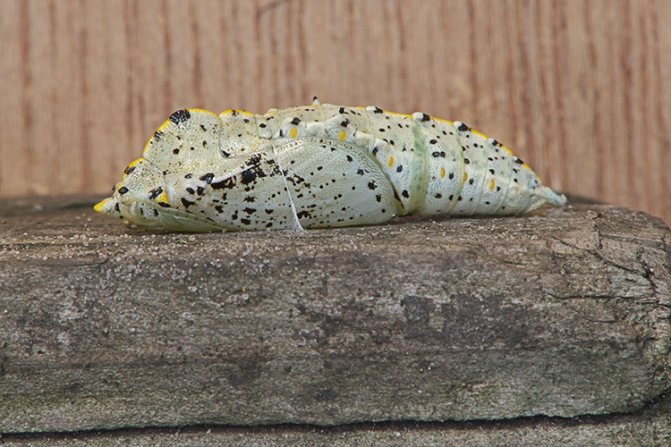
Chrysalis
The pupa of the pest has an angular shape with a yellowish-green color, on which black spots are present (on the back and sides). Inside it are soft tissues.
On average, a pupa needs about a couple of weeks to turn into an adult insect.
When the time comes, the skin bursts and an adult butterfly emerges from the pupa. Once her wings harden and unfold, she gains the ability to fly, mate, and lay eggs.
Belyanka's butterflies
the second generation produce the next offspring in July - August. The second generation of pests develops en masse, provided that the fight against the first generation was not carried out at all or the measures turned out to be ineffective, and then a new massive wave of pest infestation begins.


Usually for the season Cabbage butterfly
manages to give birth to two offspring, but under favorable weather conditions (with warm and long autumn), the pest is able to complete the third cycle of development, which lasts from September to October.
Methods of dealing with Cabbage
The simplest (and also the most time-consuming) way to control the larvae is to collect the caterpillars by hand and then destroy them. If the pest is in danger, it immediately curls up into a ring and rolls off the plant to the ground.
Preventive methods:
For the prevention of infection of cruciferous crops by larvae Cabbage
, it is necessary to periodically inspect the leaves of plants from the underside of the leaf and, if possible, destroy all found clutches with eggs.
Another preventive method of dealing with Cabbage
is the destruction of her pupae. To this end, it is necessary in the spring to carefully inspect the places of their possible wintering (tree trunks, dry branches, fences, walls of barns and other buildings).
Peeled tree trunks must be whitewashed in the spring.
Agrotechnical methods:
First of all, it is advisable to plant the cabbage as early as possible, even before the mass flight of butterflies.


To combat the pest, it is necessary to thoroughly harvest cruciferous weeds on the plantation. Plants such as "shepherd's purse", "rape", "yarutka" attract pests. And vice versa, such crops as tomato, eggplant, carrots, parsley, dill, lemon balm, valerian - cabbage repel. This factor must be taken into account when designing a site for cruciferous crops.
In the fall, it is necessary to carefully remove all plant residues from the site and carefully dig up the ground.
Biological methods:
Mass reproduction Cabbage Belyanka
prevent diseases, various types of fungi and bacterial parasites.
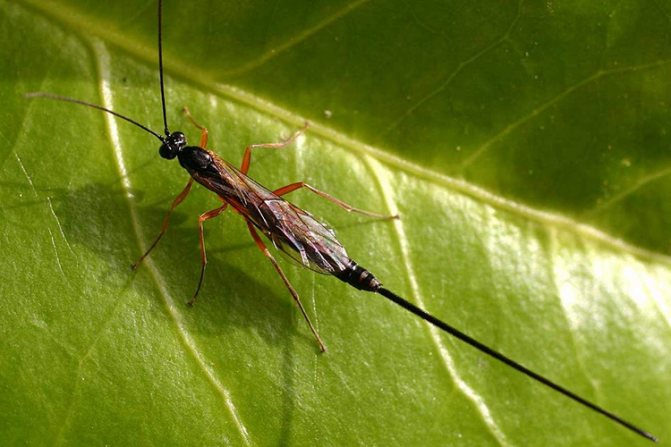
The most dangerous for caterpillars is a small parasite-parasite insect “small belly
", Laying eggs in the body of the larva. The parasite develops inside the caterpillar, feeding on its tissues, which causes the insect to die. Determined that "
small belly
"Under favorable conditions, it can infect up to ninety percent of harmful larvae.
Another, no less effective species of egg-eating wasp, which also parasitizes on caterpillars Bfir trees
, called "
Trichogramma
". The parasite infects eggs
Cabbage
.
To fight Belyanka
the bacteria of the wax moth can also be used, which infect caterpillars (the disease is called "
flasherry
"), Causing the pests to die. Infected
flasher
»The caterpillar is easy to identify as its body takes on a bright lemon hue.
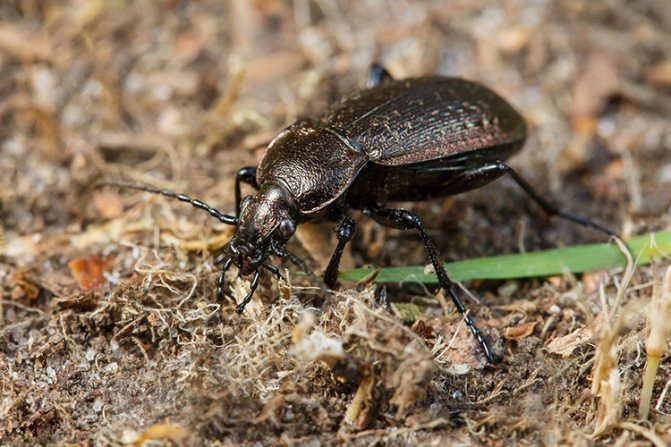
Entomophagous insects, in particular the predatory ground beetle and ticks, also cause significant damage to the pest population.
Unfortunately, the birds are not very willing to feed on the white hare caterpillars, since they release poisonous liquid.
Chemical methods:
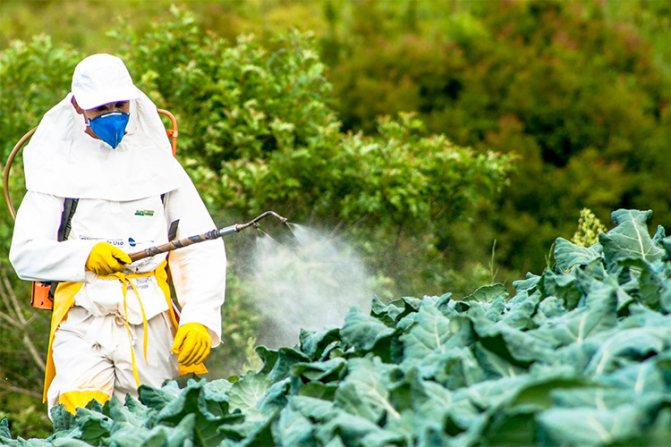
In case of mass infection with a pest, in order to save the crop, it is necessary to use specially designed pesticides (insecticides) for this.
The most effective are drugs such as "Kinmix
"And"
Fitoverm
».


Such insecticides as “Actellic
», «
Lepidocide
". These drugs will simultaneously help get rid of other pests of cruciferous crops.
Of the biological means of fighting cabbage larvae, bacterial preparations are recognized as the most effective - “Bitoxibacillin
», «
Entobacterin
», «
Gomelin
"And"
Dipel
».
Traditional methods:
Long since caterpillars Cabbage
dared from cabbage with the help of various infusions and decoctions. One of the simplest ways is as follows: you need to mix valerian tincture (half a liter) with three liters of water and spray the cabbage crop with this mixture.
Another method: it is necessary to collect wormwood (preferably at the time of its flowering), finely chop the inflorescences (about a kilogram of flower mass), then add one hundred grams of dry mustard and insist in ten liters of hot water. Some gardeners recommend boiling the solution for ten minutes beforehand. Insist for several days, then dilute the resulting solution with cold water (in a ratio of one to one) and can be used. It is advisable to spray cruciferous crops every seven days.
Field chamomile flowers are also used for pest control (available at the pharmacy). It is necessary to take one kilogram of grass, dilute it in ten liters of water and insist during the day. Then strain the solution and add one hundred grams of laundry soap to it. Bring the volume to twenty liters.
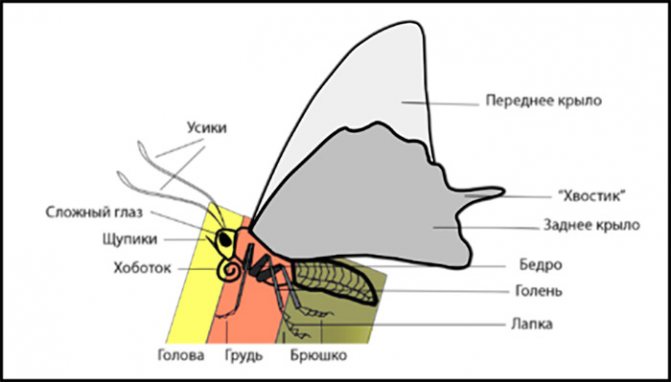
Structure
The cabbage butterfly has a shaggy body, very similar to that of the May beetle. Consists of three departments:
- abdomen;
- head;
- breast with fused segments.
The butterfly has three pairs of legs, at the end of each of which there are very sharp claws that allow it to stay on trees and plants.
Like other butterflies, the cabbage has a developed only a pair of lower chitinous jaws, which can even gnaw through a cabbage leaf.

Varieties and characteristics of cabbage whites
Stereotypically, all white butterflies are immediately perceived as pests, and gardeners immediately call them cabbage. In reality, in addition to the cabbage white, there are also its counterparts, which belong to the same genus.


Repnitsa. A butterfly similar to the cabbage from the same family. She also has black dots on the wings (2 in the female, 1 in the male) and a black border on their upper corners. This insect differs from the cabbage in size - the turnip is smaller and its wingspan almost never exceeds 4 cm.
Bruckenny. The males of these butterflies are especially strongly similar to the cabbage whites, since the upper angles of their wings, like those of the cabbage, are black. The difference is that this border is less bright and can be gray or brown-gray. The lower wing of the twin is yellowish. The sizes are smaller.
See also Secrets of Growing Cauliflower Outdoors and Greenhouses
Hawthorn. This butterfly also bears a resemblance to the cabbage pest. It is the same in size, but the color of its wings is somewhat different. They are white, but not with spots, but black veins.
Pea whites. A distinctive feature of this butterfly is that it always has bright corners on its wings. Such a butterfly hardly ever visits vegetable gardens.The species is recognized as one of the rarest among whitebirds and is more common in open meadows and glades.
None of the doppelgangers attacks cabbage beds, but also affects plants that provide food for their larvae, which is reflected in the name of each of the butterflies.
Habitat
Belyanka is widely represented in Eastern Europe and North Africa. It is present in Asia and in the east of Japan, where the climate is temperate. In the 90s of the last century, it was seen in South Primorye. Found even north of the Arctic Circle. It is clearly established that these are migratory individuals.
In Chile, South America and Panama, it appeared exclusively due to globalization, that is, it was introduced. But still, the butterfly is more common in the north, where it is not so hot.
The cabbage butterfly prefers meadows and forest edges, parks and gardens. It takes root well in forest belts and where people live, but subject to the presence of crucifers.


Cabbage lifestyle
Whitefish is a very active insect, it migrates a lot. Cabbage is most active from April to mid-October. If the insect's region is warm enough, then it can give up to three offspring per season.
The butterfly does not fly at night, it is completely a day resident. The peak of activity occurs on warmer days, when there is no rain. The insect does not like windy weather.
It is believed that the white woman is very harmful to gardeners. In fact, adults do more good than harm by pollinating plants.
Features of character and lifestyle


Photo: Cabbage insect
Cabbage whites are one of the first to appear as soon as it gets warmer. Even on cloudy days, when there are still few other insects, they can be seen hovering over green spaces. They have a rather powerful, undulating flight, and over obstacles such as bushes, trees, buildings, they easily fly overhead or maneuver between them.
As soon as cabbage whites reach the place where there are flowers, they stay there for several days. In sunny weather, they make short but regular flights, stopping briefly every few seconds to drink nectar on the undersized flowers.
Two generations of butterflies grow during the season. In the southern regions, the first generation is in April-May, in the north - a month later. In the second period, more individuals appear, it falls on the second half of summer. Another generation is possible in the south.
Despite the fact that caterpillar larvae live on the plant they feed on, pupae of these insects can be found on tree trunks, fences, walls, at some distance from the host plant. Sometimes pupation occurs on the trunk or leaf of the plant. Most often, the pupa is attached with a thread in an upright position.
Fun Fact: Those pupae that form on the trunk or leaf of the host plant are monochrome dull green, while those that form on artificial bases are pale yellow, mottled with tiny black and yellow spots.
Development stages: description
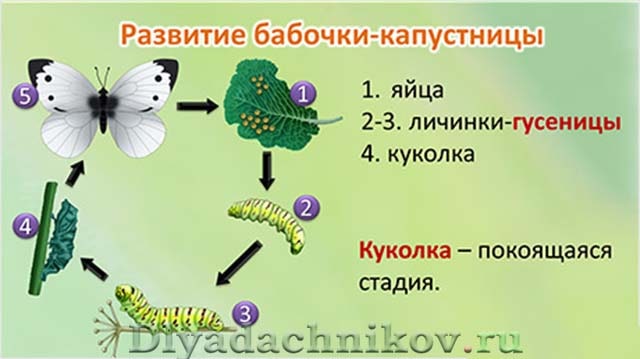
The cabbage butterfly develops in the same way as all insects with a full cycle of transformation, which occurs in 4 stages:
- egg;
- larva or caterpillar;
- chrysalis;
- an adult or an imago.
Scientists in the last century noticed one interesting feature of the insect - the butterfly is very careful about its offspring. The female never makes a clutch on the leaves, where another individual has already laid eggs. It is assumed that the butterfly determines by smell that the leaf is already occupied.
General information:
0
A source:
Cabbage, like some other types of whites, is harmful to agriculture. Cabbage, being a massive, widespread and migratory species, has no races. Previously, cabbage was not found so often, because the food she needed was not so abundant.Mass reproduction took place only after humans began to cultivate cabbage in large areas - this created a real fairyland of abundance for caterpillars. Monocultures always lead to mass reproduction and thus "create" pests. There are practically no two years in a row in which the cabbage can multiply intensively. The spread of the pest is also limited by combinations of high summer temperatures (above 26 ° C) and low air humidity (up to 60%), unfavorable for the development of a butterfly, as well as low winter temperatures (below -20 ° C).
Egg stage
The breeding frequency of a butterfly depends on temperature conditions. The warmer it is, the more often it reproduces, generally two to three times. In light of this, egg-laying can occur from April to September.
After mating, the female lays about 200 or more eggs. The first clutch is made on wild plants. But already 2 and 3 clutches can be produced on cultivated plants in the gardens of summer residents.


Reproduction and development
Reproduction in this species is bisexual and the female needs a male to fertilize the eggs. Before mating, the male and female fly together up to 100 meters. The development of the cabbage butterfly has four stages:
- egg;
- larva (caterpillar);
- chrysalis;
- adult butterfly.
The eggs laid by the female have a pronounced ribbing and the shape of an elongated barrel. Each egg is 1.25 mm long. Already after 7-10 days from the moment of laying, movement is visible in them and small larvae begin to hatch. The body length of the larva is only 1.75 mm and their first food is the shell of the egg. The cabbage butterfly larva has a green (ocher) color, a black head and is highly viable.

Compared to the rest of the body, the head of the larva is very hard with serrated jaws. Immediately after birth, the caterpillars keep in groups, eating the shell and pulp of the cabbage leaf from the back side. During this period, cabbage butterfly caterpillars eat little. However, as soon as they get stronger, they creep to the sides. Their appetite becomes insatiable, and they make whole holes in the leaf.
Adult caterpillars prefer to live separately.
Cabbage larvae are gluttonous and become a real disaster for gardeners if you do not fight them. With their powerful jaws, they eat the cabbage leaf, leaving only hard veins from it. The caterpillar's life span is several weeks, but during this time they are able to completely destroy the crop. Unlike an adult, the larvae have very poor eyesight and see no more than one centimeter, therefore, in search of food, they rely only on their sense of smell. Their eyes are very small and do not have the complex structure of an adult butterfly.
You can only see them with a magnifying glass.
During the caterpillar's life span, it undergoes 4 molts. Usually the first three times this process lasts about a day, but the last, fourth molt, can take up to 40 hours. From 3 to 7 days pass between molts. In warm and dry seasons, caterpillars develop faster than in the rainy season. Before molting, the caterpillar stops eating and moving, remaining motionless for some time after its completion.
Expert opinion
Nina Lukina
In caterpillars, the integument of the body does not grow with them, therefore molting is a very important process. The peculiarity of caterpillars is that they do not grow continuously. They can grow only after molting, while the body cover is relatively soft and able to stretch. By the time of the first molt, the body length already reaches 1.7 cm. In the period from the first to the second molt, the caterpillar is actively growing. By the fourth molt, it grows up to 3.5-4 cm. Having reached this size and having eaten well with cabbage leaves, adult caterpillars move to trees and fences.
In total, the cabbage butterfly spends 17 to 30 days in the caterpillar stage.After the completion of the fourth molt on the 7-10th day, the caterpillar pupates. It allocates a cobweb, with the help of which it attaches to the surface of a tree trunk, while climbing to a height of up to six meters. Belted with a webbing belt, it hangs freely in an upright position with its head to the top. You can meet them everywhere:
- on the trees;
- fences;
- shrubs;
- the walls of the sheds.
Black and orange specks are scattered all over the greenish-yellow body of the pupa. The pupa tends to acquire the color of the surface on which it is fixed. On a light fence or wall of a building, it will be light, on a dark tree bark - dark. In this stage, the cabbage is from 8 to 17 days, depending on the ambient temperature. The warmer, the shorter the transformation process takes. Spring and summer pupae differ from autumn ones.
They are slender and have pronounced spines on the dorsal side.
The most optimal temperature for the development of cabbage is the range from 20 to 26 degrees. In addition, whites do not like high humidity. Under favorable conditions, a young butterfly appears already two weeks after pupation. It differs from adults in slightly smaller size. Butterflies, which appeared in summer, have black markings and spots on their wings brighter than those of spring representatives of the species.


If the climatic conditions in summer are not favorable (cold, rain), the cabbage caterpillar turns into a chrysalis. The butterfly will fly out of it only next spring, when the air warms up to a temperature of at least 20 degrees. If pupation occurs at the beginning or middle of the season, a new butterfly emerges from the cocoon and gives birth to another generation. In the case of pupation in September, the cabbage goes into hibernation and waits out the winter in a cocoon, waking up only in the spring.
Caterpillar
The cabbage butterfly caterpillar appears at about the end of the first or second week, the period depends on the atmospheric temperature.
Butterflies start laying eggs on the 5-7th day from the first day of summer. She lays yellow eggs in large groups. So that they do not suffer, the butterfly puts them on the lower part of the sheet. There can be up to 300 eggs on one sheet.
The larvae from the eggs appear quite quickly, at about 16 days. Babies are very similar in appearance to worms.
The caterpillar has a yellowish-greenish color with black spots. She has three pigments: green, black and white. Depending on where she lives, the color changes somewhat. For example, if it lives on light leaves, then the pigment brightens, darkens in the dark. The largest individuals reach 3.5 centimeters.
At first, as soon as the small caterpillars hatch, they keep in the same group as they were during laying, until they get stronger, and only then crawl away. Most often they settle on the lower part of the leaves and are actively eaten by them.
Larvae that hatch late settle on the top of the leaf and can climb inside the head or stalk of cabbage.
In the pupal stage, the butterfly lasts from 14 to 40 days.
For normal growth and development, the caterpillar requires a temperature from +20 to +25 degrees. If it is very hot, and even a lot of rain, then the larvae will die en masse.


Control methods
Among the effective methods of controlling insects and preventing their appearance, there are:
- Hand picking eggs from cabbage leaves. The method allows you to effectively destroy the population of butterflies in the embryo. The disadvantages include the cost in terms of time and effort, since it is extremely difficult to check each leaf on the garden bed.
- Destruction of pupae. If your planting is not the first time attacked by cabbage, carefully examine the trunks of nearby trees and other places where pupae may appear.
- Experienced farmers, when a white butterfly appears, try to plant cabbage seedlings as early as possible. This helps the crop grow stronger and suffer less damage from pests.
- Try to remove all cruciferous weeds near the planting. They become the first target of whitefly butterflies, after which their offspring will move to the grown heads of cabbage.
- Plant the following crops next to cabbage: parsley, lemon balm, dill, carrots and eggplant. They scare away butterflies, reducing the risk of losing the entire crop.
- There are a number of parasites that do not harm the plantings, choosing the cabbage larvae as their habitat. These include small belly, trichogramma and flasherry.
- In neglected situations, when the plantings and the surrounding environs are heavily infested with the whitewash butterfly, chemical means of control are used. They are sold in specialized stores, and it will not be difficult to acquire them.
Chrysalis
What does a cabbage butterfly look like in the pupal stage? The color is almost the same as that of the butterfly - yellowish-green with black splashes.
During the transition to the pupal stage, the larva is wrapped in threads that are somewhat reminiscent of silk, and with them it clings to plants.
If folding into a pupa did not happen too late, then a butterfly soon appears. If the atmospheric temperature does not allow transformation, then the insect enters the diapause stage and hibernates like that. With the onset of spring, such insects begin years from the first generation.
For your information, diapause is the process of inhibition of physiological processes in an insect with the transition to the stage of suspended animation.
The insect is in this stage for several weeks. During this period, the pupa molts several times, and this process is called complete transformation.
Population and status of the species


Photo: Cabbage butterfly
These Lepidoptera have a large distribution area and are quite aggressive cruciferous pests. If you do not fight them, then cabbage can lead to a 100% loss of yield of different types of cabbage, they can eat radishes, turnips, rutabagas, rapeseed. The fact that adults are prone to migration poses a threat to areas where they were previously few in number or not previously encountered.
Damage from a whitewash can lead to a significant decrease in the value of the crop. On the outside, cabbage heads will look pretty decent, but on the inside they are often damaged by larvae. Caterpillars often hide inside cauliflower, which reduces its value. The high localization of the larvae leads to the fact that one clutch devours the plant to the skeleton, and passes to another.
This pest is exposed to chemical methods of destruction. In small areas, insect caterpillars and eggs are harvested by hand. Although the population is constantly monitored and regulated by humans, the insect is considered a pest in many European countries, in China, Turkey, India, Nepal and Russia, where there is a noticeable annual yield loss on various vegetables.
In 2010, the butterfly was first discovered in New Zealand. Over the course of three years, it has multiplied and has come to be rated as a serious and unwanted invasive pest.
Fun Fact: To encourage children to join efforts to eradicate cabbage, the New Zealand Department of Conservation has offered schoolchildren a reward of NZ $ 10 for each butterfly caught during school holidays. 134 copies were handed over in two weeks. The department staff caught 3,000 adults, pupae, caterpillars and egg clusters.
To combat cabbage whitewash, in addition to chemical and mechanical methods, biological methods were also used there. Special predatory wasps were released into the fields. This pest control campaign has been completed successfully. This success was due to the fact that the alarm was raised immediately and measures to combat cabbage were taken in the early stages. But in Australia and the United States, these Lepidoptera continue to reproduce and spread.
Interesting fact: White women avoid laying eggs where they see other relatives.To deceive them, white "flags" made of light fabric can be placed among the plantings on pegs or wire, which will imitate the competitors of the pest.
Butterfly cabbage can fill your site very quickly. To prevent the reproduction of cabbage, you need to fight cruciferous weeds, in the fall and spring, sweep or whitewash tree trunks, fences to remove pupae. During the season, it is necessary to carefully inspect the plants and collect caterpillars, egg-laying. It is undesirable to use chemical protection methods that can kill beneficial insects. The use of folk remedies is more justified: infusions of wormwood, tobacco, chamomile, etc.
The cabbage butterfly, which belongs to the white family, is found in household plots in spring and summer.
The butterfly feeds on nectar, and its caterpillars eat only cabbage leaves, after which the insect got its name.
Food
Considering a photo of a cabbage butterfly, it is hard to understand how this insect eats and, most importantly, what.
Gardeners will definitely say that the white woman is very fond of cabbage and causes great damage to the heads of the plant. However, not only cabbage is present in the insect's diet. The butterfly loves rutabagas, capers, canola, horseradish, radishes and radishes. Can consume mustard, nasturtium, and even garlic.
Naturally, for those who cultivate the land, the white woman is a real disaster. Insects penetrate the head of cabbage and continually eat the leaves. The butterfly is so gluttonous that it can completely destroy the entire crop.
In the wild, the butterfly feeds on chamomile, coltsfoot, dandelion, and alfalfa.


What harm does an insect do to agriculture?
In agriculture, the insect is considered a dangerous pest of cabbage and, to a lesser extent, other cruciferous crops. The main damage from the attacks of the whites is due to the fact that their caterpillars are very numerous and eat up the plant in a short time, completely depriving the crop.
See also Top dressing of cabbage and its treatment of pests with ammonia


Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
It is interesting! Also, poultry can die from eating cabbage caterpillars. This is due to the fact that the insect secretes a special caustic substance.

































