Many insect pests attack the vegetable garden every season. But some of them are so clearly parasitic in the beds that it is impossible not to notice them. These pests include the Colorado potato beetles. For every summer resident, the Colorado potato beetle and the fight against it are associated with certain difficulties. The main reason for the hatred of the owners of the garden for this small bug is its gluttony and quantity. The spread of the species occurs quickly, it is very difficult to prevent its dispersal over all the plants it prefers. It is possible to remove this evil from the garden only with the use of effective means at an early stage of infection.
Description of the Colorado potato beetle
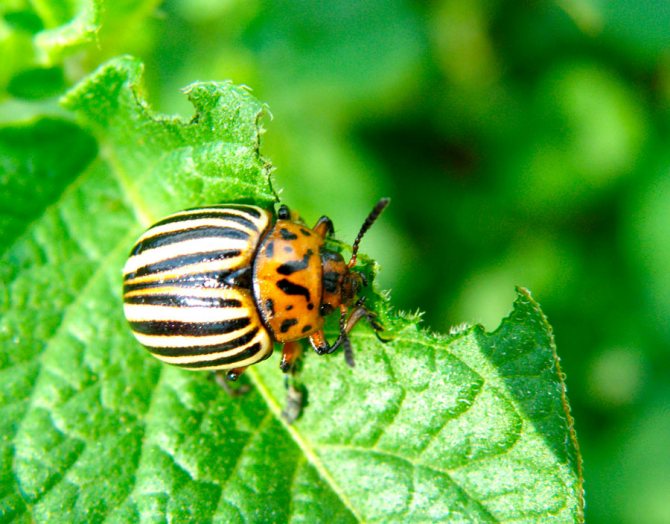

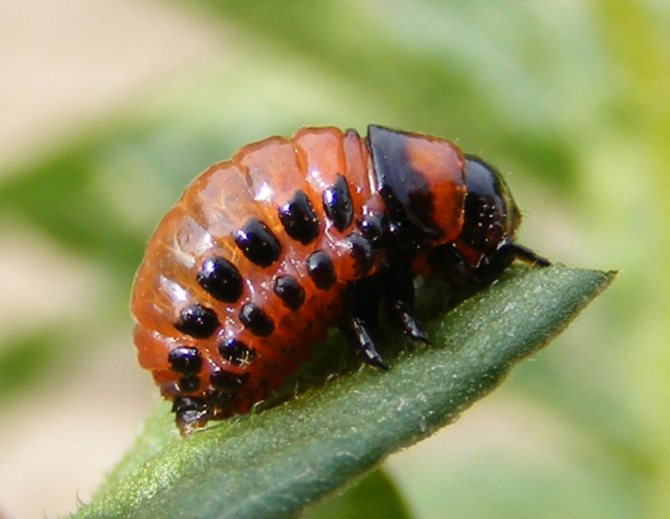
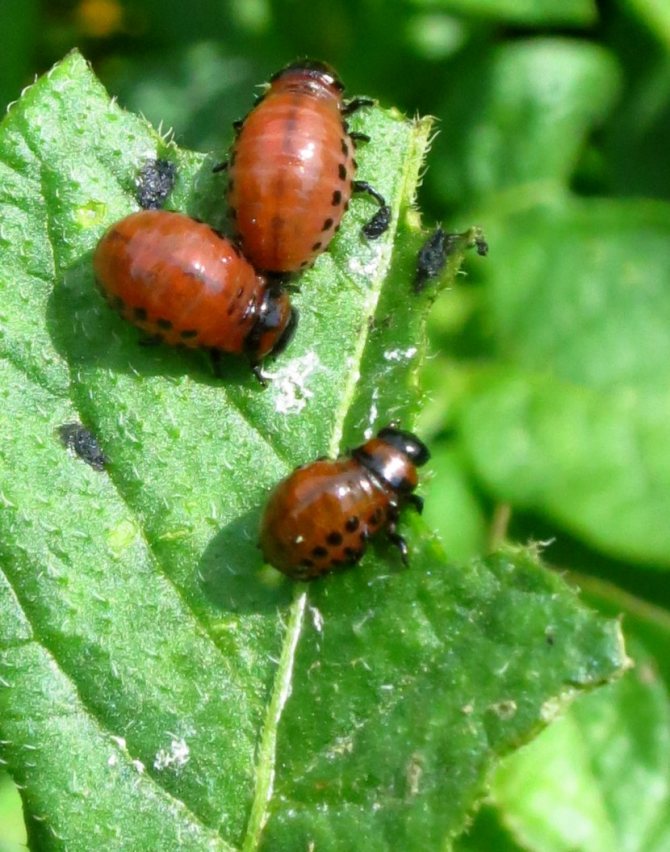
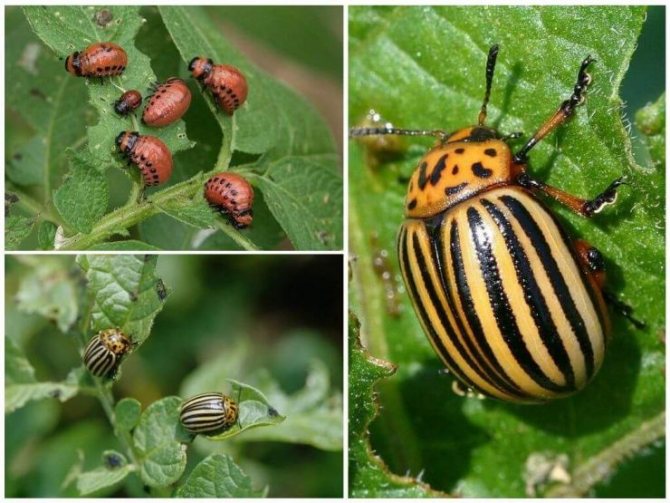
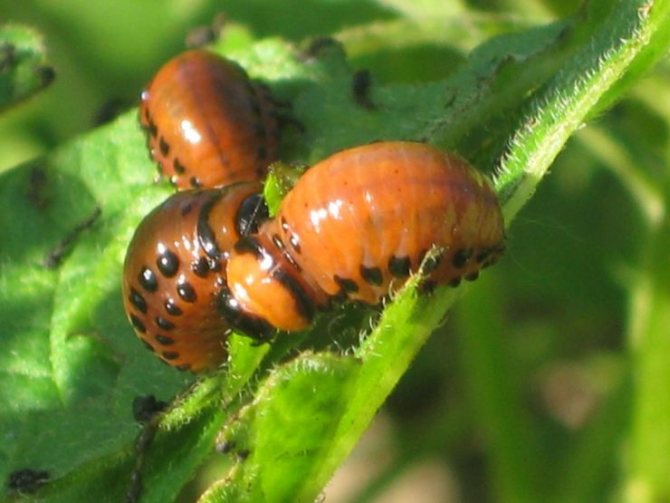
Almost everyone who has come across the Colorado potato beetle knows how dangerous this pest is for the potato crop. Particularly dangerous are the larvae of the beetle, which are distinguished by a bright red color, with a burgundy tint. The fight against this pest has been going on for many decades, but it has not been possible to get rid of it. Every time a new crop of potatoes emerges from the ground, you can see these pests on it, which are busy laying eggs.
What is characteristic of the Colorado potato beetle:
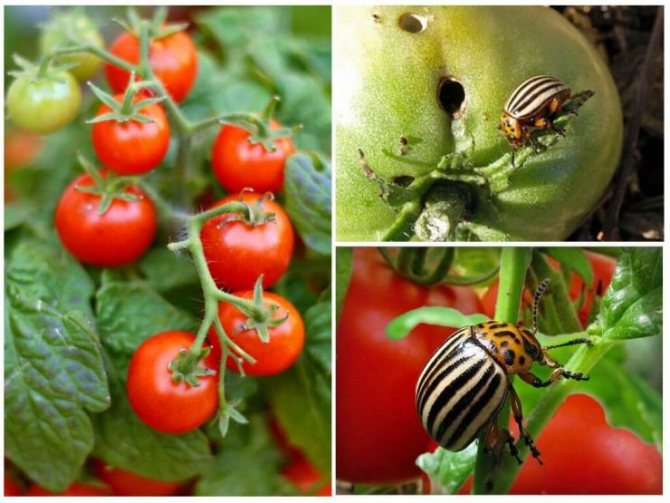
- This pest prefers to feed on crops of the nightshade family. Therefore, the beetle can be found not only on potatoes, but also on tomatoes, eggplants, and salad peppers. In addition, adults and larvae can feed on some plants of this family, such as dope, henbane, petunia, fragrant tobacco, wolfberry and others.
- Beetles appear on the surface of the earth already at an air temperature of +11 degrees and a ground temperature of +4 degrees.
- Potatoes are just beginning to appear, and adults are already sitting on green, young shoots. They not only begin to eat green shoots, but also lay eggs.
- The larvae are so voracious and there are so many of them that they are easily capable of destroying potato plantings if appropriate measures are not taken. The sooner you start fighting with them, the greater the guarantee of preserving the harvest.
- From late August to mid-September, the beetle, if the air temperature rises to +30 degrees or more, switches to sleep mode. This period can last up to 10 days. During this period, he does not eat potatoes, especially since there is practically no potato, since the stems of the potatoes are already dry, not to mention the leaves.
- The Colorado potato beetle, in search of potato beds, is capable of flying long distances.
- The pest has already managed to develop immunity to some types of chemical control agents, as well as various folk remedies. Therefore, gardeners desperately, every year, are fighting this pest, using more and more new means of struggle.
where did it come from?
For the first time, the Colorado potato beetle was noticed on the territory of Mexico - it was a wild species parasitizing on the seedlings of nightshade crops. Gradually, with the spread of fields in America, the beetles began to multiply rapidly. At that time, there were no effective methods of pest control, so a large number of crops died in a matter of days. The first focus of damage was the potato fields in Colorado.


Then the beetle continued its journey across North America, damaging the harvest and devastating all agricultural land in its path.In the 1870s, the Colorado potato beetle first entered the territory of Europe, it was brought with a large batch of potatoes across the Atlantic Ocean to Leipzig. It is worth noting that enterprising Europeans successfully eradicated a petty enemy until the First World War, when insects began to multiply at the speed of light in the fields of France.
In the 1940s, parasitic individuals were seen in the territory of the former USSR, from where they began to spread throughout its vast area. The region of Transcarpathia received particular harm in the initial months, where colonies of pests appeared at the same time from Poland, Hungary and Czechoslovakia. Gradually, parasites occupied all the fertile lands of the Russian land and every season they are found in our gardens and fields.
How to tell if it's a Colorado potato beetle?

The Colorado potato beetle is difficult to confuse with any other pest on potatoes. It is recognized by its characteristic color:
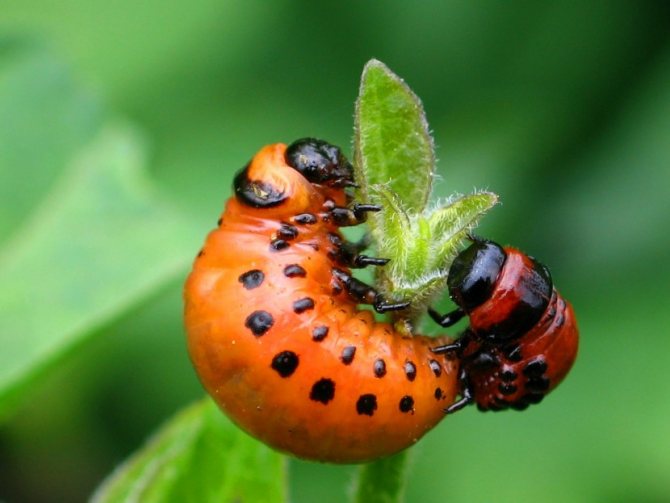
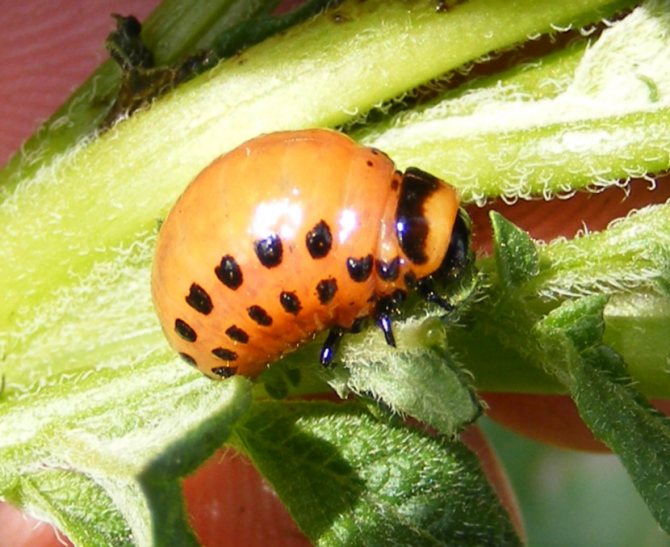
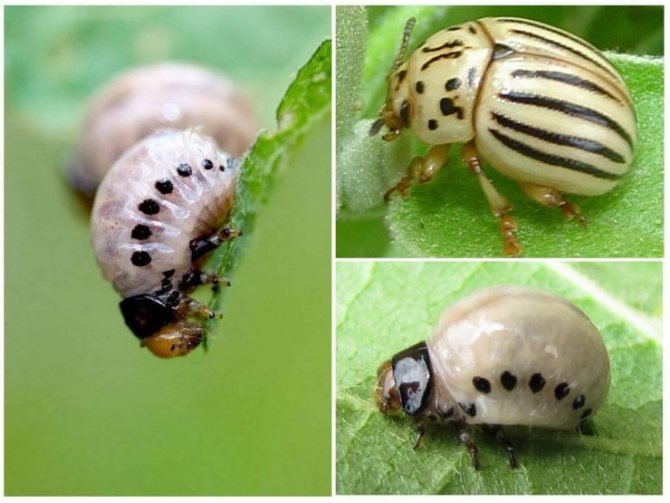
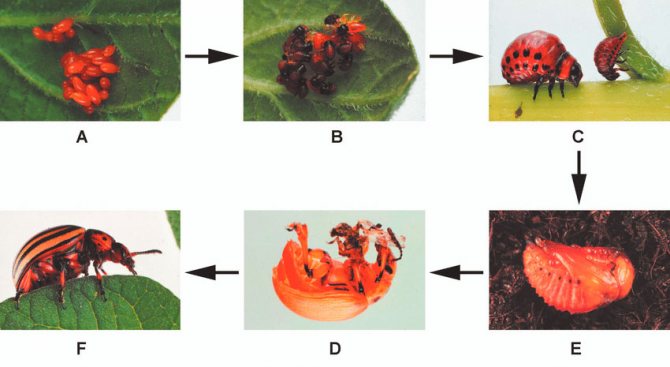
- The larvae, just born, first have a gray, and then acquire a bright reddish-orange hue.
- The larvae grow in a couple of weeks, already at an ambient temperature of +12 degrees. During this period, they are able to destroy all the leaves on the potato and leave only the stems.
- The larvae have a body that is unpleasant to the touch, although in appearance they are somehow disgusting. It is fleshy and convex on the outside and flat on the bottom. Sparse bristles can be seen on the sides. If the larva is accidentally crushed, then a bright, yellow in color and unpleasant-looking liquid is released.
- Grown individuals reach a size of 1.5 cm, while they actively eat the leaves of nightshade crops.
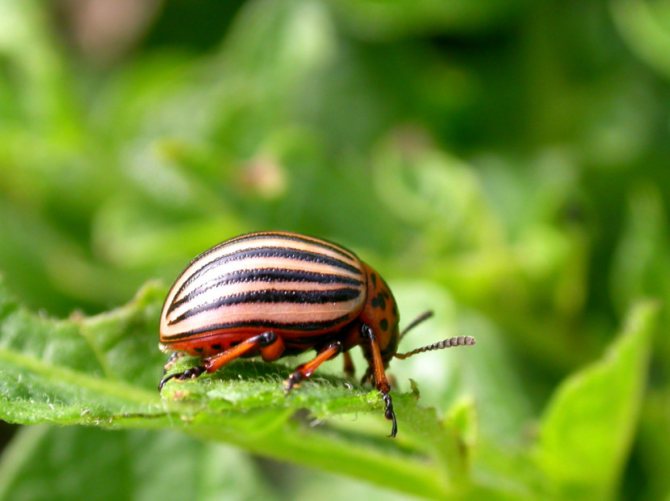
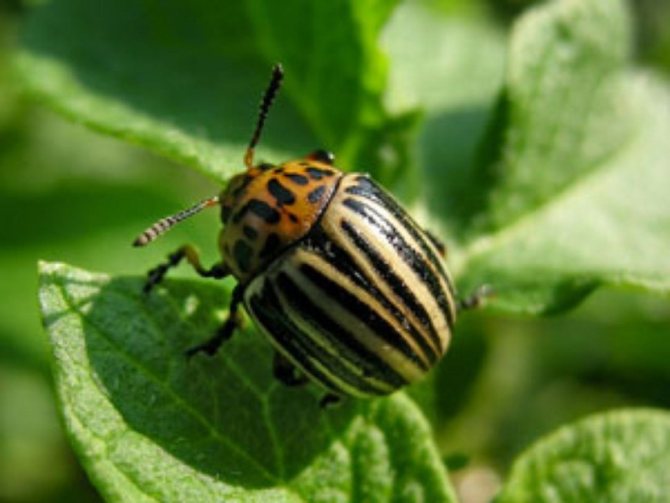
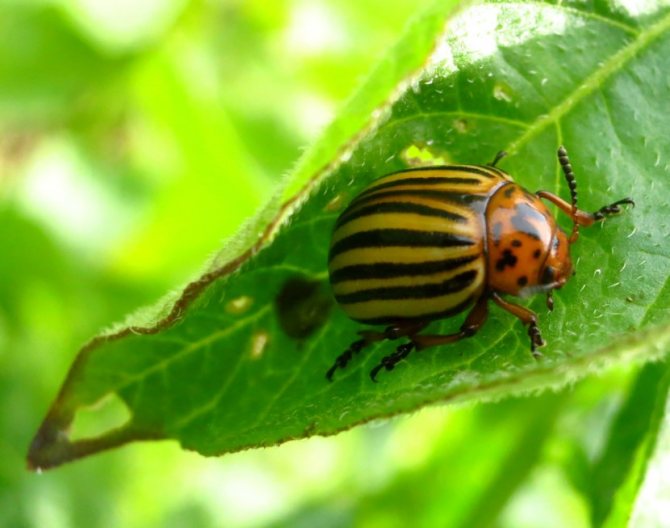
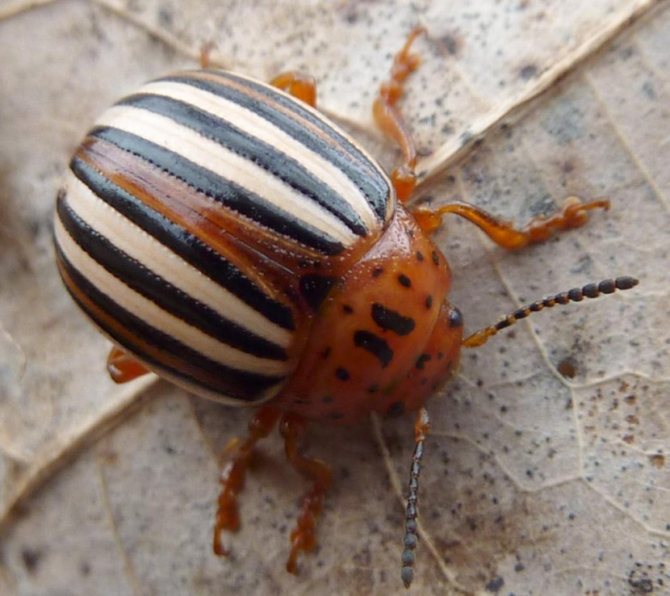
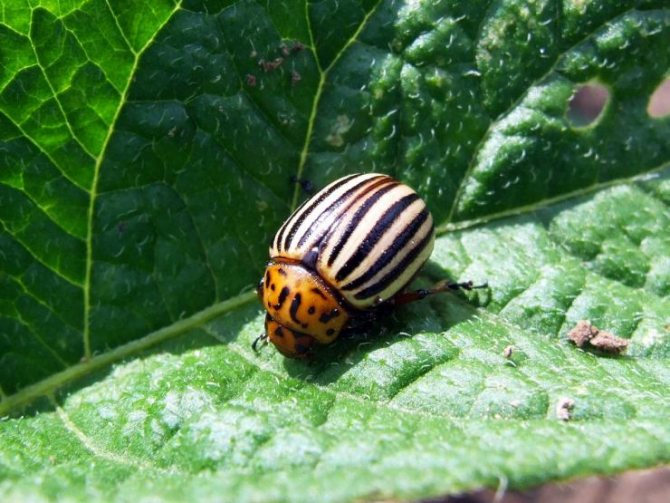
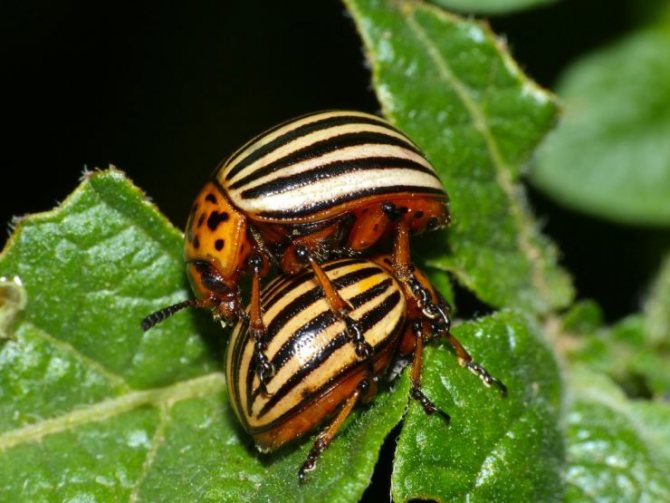
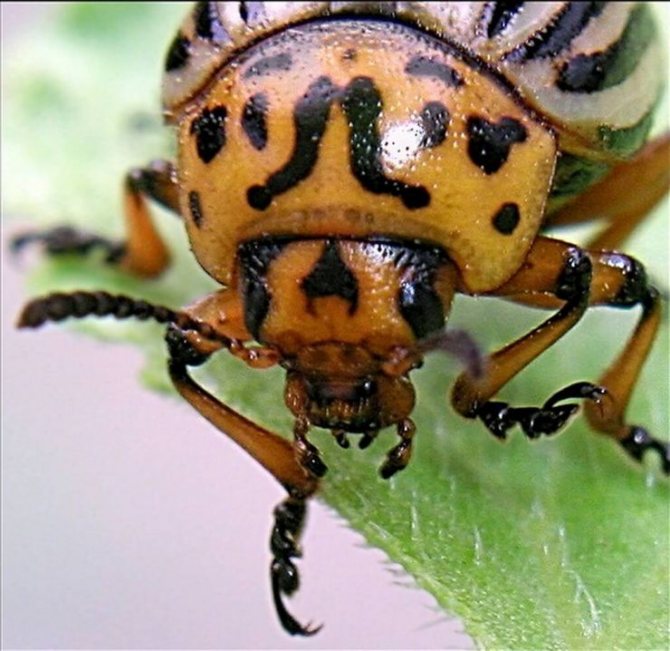
- Adult beetles are distinguished by dense elytra with black stripes along them. The beetle is yellow-red or reddish-orange in color. The legs of the beetle are black.
- Thanks to the tenacious claws placed on the paws, the pest moves without problems over plants and other surfaces.
- An adult beetle grows up to 1.2 cm in length and has an oval body, up to 7 mm wide. Although the beetle itself is not large in size, the harm from it is simply enormous.
Biological features and origin
Colorado potato beetles (Leptinotarsa decemlineata) are members of the leaf beetle family. The length of the oval convex body of an adult is 10-12 mm. On the dorsum, red-yellow or brown, there are characteristic dark stripes, 5 each on two elytra. With the help of its wings, the beetle is able to travel long distances - up to 500 m per day.
The origin of the pest explains why the Colorado potato beetle has such a name: it was first discovered in 1824 in the US state of Colorado. It was there that he completely destroyed the potato crop, causing enormous damage to the inhabitants of the region. The pest spread rapidly in America, and quickly appeared off the coast of the Atlantic Ocean.
The potato imported in 1914 was responsible for the emergence of the harmful beetle in Europe. It was first discovered in France. In the Soviet Union, they started talking about him in the last century - in the early sixties. The pest turned out to be very tenacious: it is not afraid of water, it can withstand temperature changes, and is also able to remain without food for a long time.
Reasons for the appearance
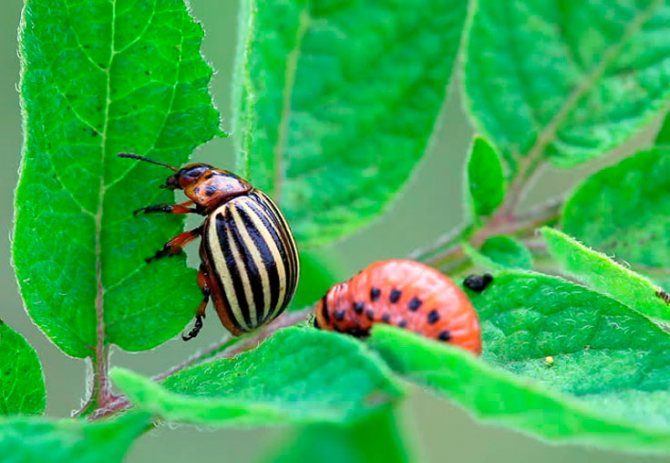


The Colorado potato beetle enters the garden in various ways. For example:
- Crawls or flies from neighboring gardens.
- As a result of natural migration of pests.
- After hibernation, the beetle gets out of the depths of the earth.
Most of all, the beetle loves potatoes, although it easily eats beds with nightshades. A lot of food is needed for its life, so adults and larvae actively eat plant leaves.
Beetle harm
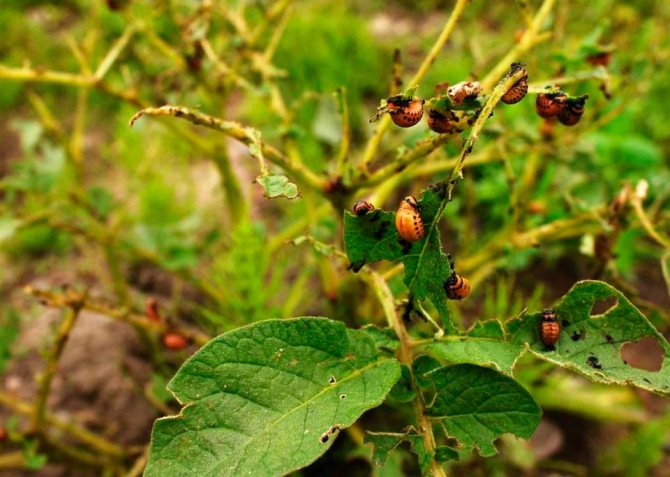


The larvae of this pest are especially gluttonous. Under favorable conditions (warm weather), they develop much faster. In such conditions, the number of larvae in the garden is in the thousands.A couple of days is enough for them to cause serious damage to the potato crop: they will eat up all the leaves and only the stems will remain. In such cases, you cannot count on a good harvest of potatoes. Therefore, one should not hesitate to destroy the beetle.
It also harms other crops of the nightshade family. These include:
- Potatoes.
- Tomatoes.
- Salad pepper.
- Eggplant.
Interesting to know! The Colorado potato beetle feeds not only on green shoots of potatoes, but also on tubers, especially in spring, when the green shoots have not yet made their way out of the ground. During this period, the beetle is easy to fight with the help of traps. Chopped potatoes are used as bait. During the winter, the beetle got hungry, so it will immediately pounce on the bait.
Life cycle of adults
On average, the duration of the period, how long the Colorado potato beetle lives and all stages of the development of the Colorado potato beetle rarely exceed 1 year. A specific feature of the insect is its ability to stay in diapause. This is a special condition, like the adult Colorado potato beetle hibernates, in which the physiological phases of metabolism are inhibited and morphogenetic processes are stopped. Some representatives, being in diapause during the cold season, live in such conditions up to 3 years of age.
The number of young generations of the potato leaf beetle directly depends on climatic conditions. In the northern regions, he breeds one generation at a time, in the southern regions their number reaches 2-3.
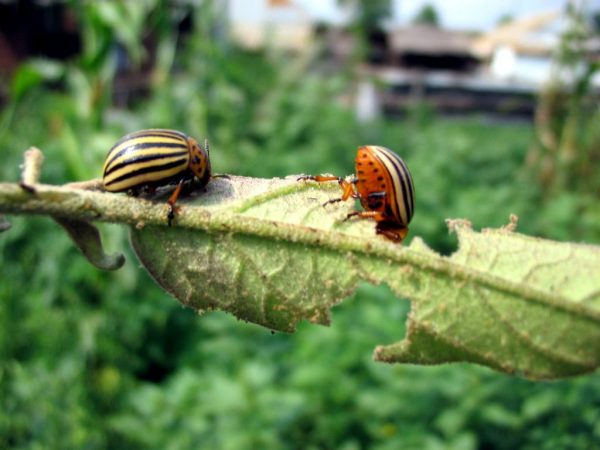


The beetle feeds on the vegetable part of the potato
The imago of the potato leaf beetle hibernates in the soil, climbing to the depths. The distance from the surface to the place where the Colorado potato beetle hibernates can be up to half a meter. At the onset of spring heat, it gets out to the surface and starts feeding on plant shoots, while simultaneously starting the mating process.
In the period from the beginning of the spring season until the arrival of autumn, adult females lay oblong eggs of light orange color on the underside of the leaf blades. For one day, each of them can postpone from 5 to 80 pieces. In total, for the entire summer period, a female Colorado potato beetle is able to lay about a thousand eggs.
How to get rid of the Colorado potato beetle


There are two ways to deal with this gluttonous pest: the use of chemicals and collection by mechanical means. The latter method, although laborious and suitable only for small areas of potato planting, is effective. In addition, toxic substances are not used in the garden, which is important, since one treatment with chemicals is unlikely to be enough. The use of chemicals is a quick way to get rid of the beetle in the garden, although there is a risk of poisoning. This is the only way to kill the beetle in large areas of potato plantings.
In any case, an integrated approach is needed, with the use of agrotechnical measures, although everything is not so simple with the Colorado potato beetle: it burrows into the ground to a great depth and waits out the winter. Therefore, having dug up a vegetable garden in the fall, it will not be possible to get rid of the beetle.
Chemical control agents


For those who want to quickly get rid of such a pest, there is a large selection on the market for insecticidal-acaricidal chemicals. It is better to take a couple of drugs to determine which one is more effective, but you should not get carried away with chemistry and conduct experiments in your garden. The fact is, the beetle has already managed to adapt to some of them, so the fight may turn out to be ineffective, and the person may suffer.
Need to know! The greatest effect can be obtained if systemic drugs are used. Eating a plant, the poisonous substance enters the gastrointestinal tract of the pest, after which the insect dies.
In the fight against the Colorado potato beetle, they are used:
- Prestige.
- Decis.
- Karate.
- Fitoverm.
- Aktar.
- Inta-Vir.
- Bushido.
- Colorado.
- Regent.
- Sonnet.
Mode of application:
- Processing plantings of potatoes, tomatoes, peppers and eggplants should be carried out early in the morning or late in the evening, when the effect of the sun is minimal. In the heat, it is forbidden to process the site, as you can get poisoned by the vapors of the drug.
- The use of toxic drugs is limited to a specific term - 2 months before the start of the harvest. Failure to do so may result in family members being poisoned.
- It is better to use a knapsack sprayer. The sprayer is selected depending on the area of potato planting.
- Before using a chemical, a solution is prepared on its basis in a certain proportion indicated in the instructions. It is not recommended to violate the proportions in either direction.
- Site processing is carried out only in protective clothing. As a rule, glasses, rubber gloves, a respirator or gauze bandage, long-sleeved clothes (preferably old and unnecessary), shoes are used.
- Do not eat while spraying, and after work wash your hands thoroughly, rinse your mouth and wash yourself. Clothes need to be washed to be reused, or better yet thrown away.
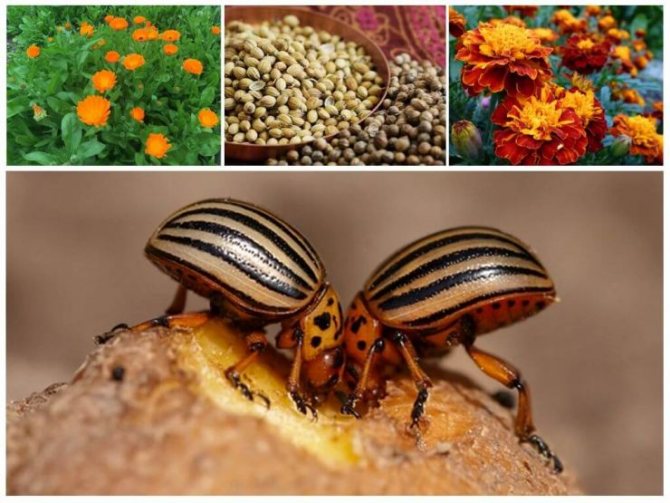
Folk remedies


As a rule, infusions and decoctions are used, which negatively affect the vital activity of this gluttonous pest: they either destroy the beetle, or give the potato greens an unpleasant taste for the beetle. As a result, the beetle refuses to eat potatoes. In this case, you need to use folk remedies on a regular basis.
Trusted remedies include:
- Infusion based on tomato tops... To prepare the active composition, you will need tomato greens (leaves and stepsons) and a bucket of boiling water. Tomato greens are poured with this boiling water and infused for about 5 hours. After that, the agent is filtered, after which it is sprayed with plantings of garden crops, which the beetle prefers to feast on. For greater efficiency, 50 g of soap (liquid soap can be added) to the solution.
- A decoction based on soap and bitter pepper... Take 10 liters of water, put on fire and bring to a boil, after which 100 g of dried hot pepper is added to the water and cooked for 2 hours. As the solution cools down, add 40 grams of soap shavings to it and mix well. After that, you can start processing plantings of potatoes and other plants.
- Walnut-based decoction... To prepare the solution, you need to take young leaves and fruits, and then pour them with 10 liters of boiling water. The remedy is infused for a week. After that, the product is filtered and sprayed with a vegetable garden.
- Celandine decoction... Take half a bucket of raw materials and fill it with hot water, boil it a little and filter it. The spray agent is prepared in the following proportion: for 10 liters of water, half a liter of broth is taken.
- Infusion of onion peel... Take 300 g of onion husks and boiling water, but enough so that it covers the husk. The remedy is infused during the day, filtered and used to combat this gluttonous pest.
The use of dry products to combat the Colorado potato beetle:
- The use of birch or pine sawdust, which are located in the aisle, perfectly repels the pest.
- The use of cornmeal is not to the liking of the Colorado potato beetle. When a beetle eats grains of this product, they swell in its stomach and lead to death. It is better to cultivate the garden early in the morning when dew is on the plants.
- If you sprinkle the soil and potatoes with ash, it will also save the crop from the pest. Better to take ash after burning birch firewood.
Partially you can destroy the pest, especially its eggs, if you carry out high hilling of potato plantings.With high hilling, the lower leaves end up in the ground. It is on the lower leaves that Colorado beetles like to lay their eggs.
DIY traps
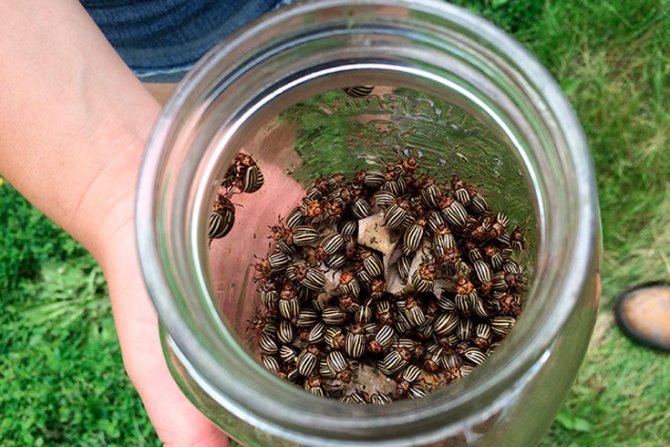


Traps are fairly simple but effective devices for dealing with pest infestations. For their manufacture, it is better to take plastic bottles. It's not a problem to find them. One trap is enough for 5 square meters of garden. In short, the more traps there are, the more noticeable the effect is.
Trap manufacturing technology:
- A plastic bottle is taken and cut off at the expansion site.
- You need to put the bait in the form of sliced potatoes in the trap.
- The container is placed in the ground, at the soil level. When the trap is full of beetles, they need to be emptied and destroyed, after which a new bait is placed in the trap.
The fight against the Colorado potato beetle is carried out annually. Unfortunately, a person cannot cope with this pest, and here, oddly enough, the person himself is to blame. Unfortunately, each owner fights the beetle in his own way, and some refuse it altogether or collect it by hand. Of course, no one wants toxic substances to penetrate the ground every year. But to cope with the beetle mechanically is generally unrealistic. Of course, the beetle will not eat the potatoes, but as a result, many adults will appear, which will again appear in the garden next year.
Wintering method, causes of plant damage
The larva of the Colorado potato beetle, which is distinguished by a fairly high appetite, actively feeds until the pupation period, destroying the bushes of vegetables.


Due to the increased adaptability to external conditions and the seasonality of changing weather conditions, the beetle tolerates frost perfectly, being underground at this time.


The first rays of the sun, heating the soil, awaken the insect, ready to reproduce and lay eggs, which will then turn into larvae.


You can get rid of the beetle and its offspring using chemicals and folk remedies, by manually collecting all types of pests.